MT 1OC disease Lens Pigmentations and Cataracts
1/81
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
82 Terms
- epicapsular stars
- Vossius rung
- Capsular pigment dusting
- Mittendorf's Dot
examples of lens pigmentations
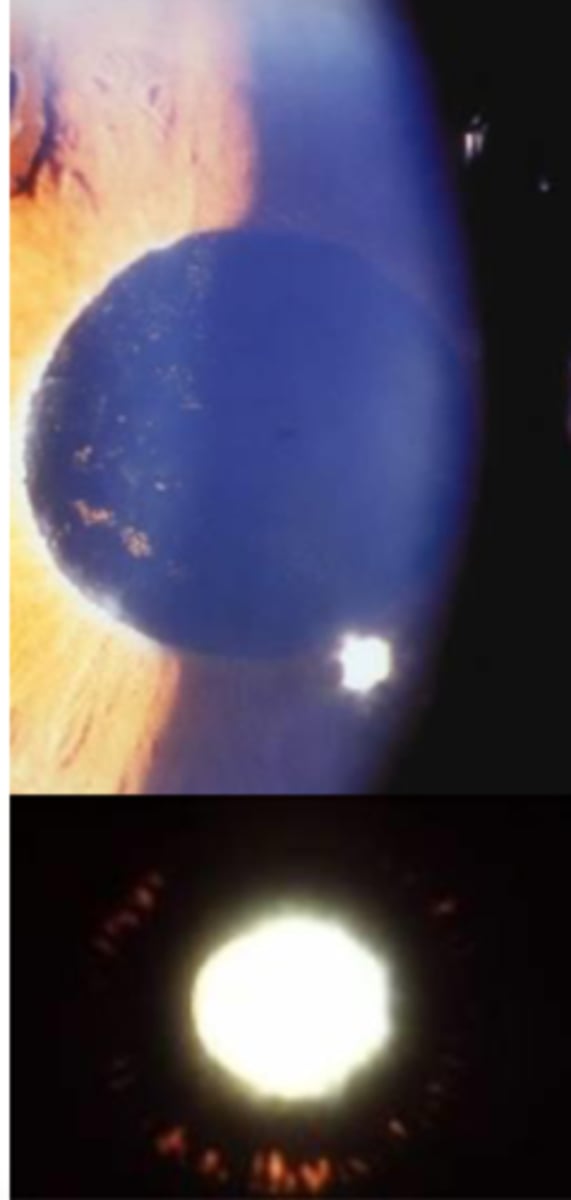
Epicapsular stars
Remnants of tunica vasculosa lentis -> small light brown or tan dots/ stars deposited on anterior lens capsule. usually unilateral, does not affect vision.
Remnants of tunica vasculosa lentis -> small light brown or tan dots/ stars deposited on anterior lens capsule. usually unilateral, does not affect vision.
describe Epicapsular stars
epicapsular stars

Vossius Ring
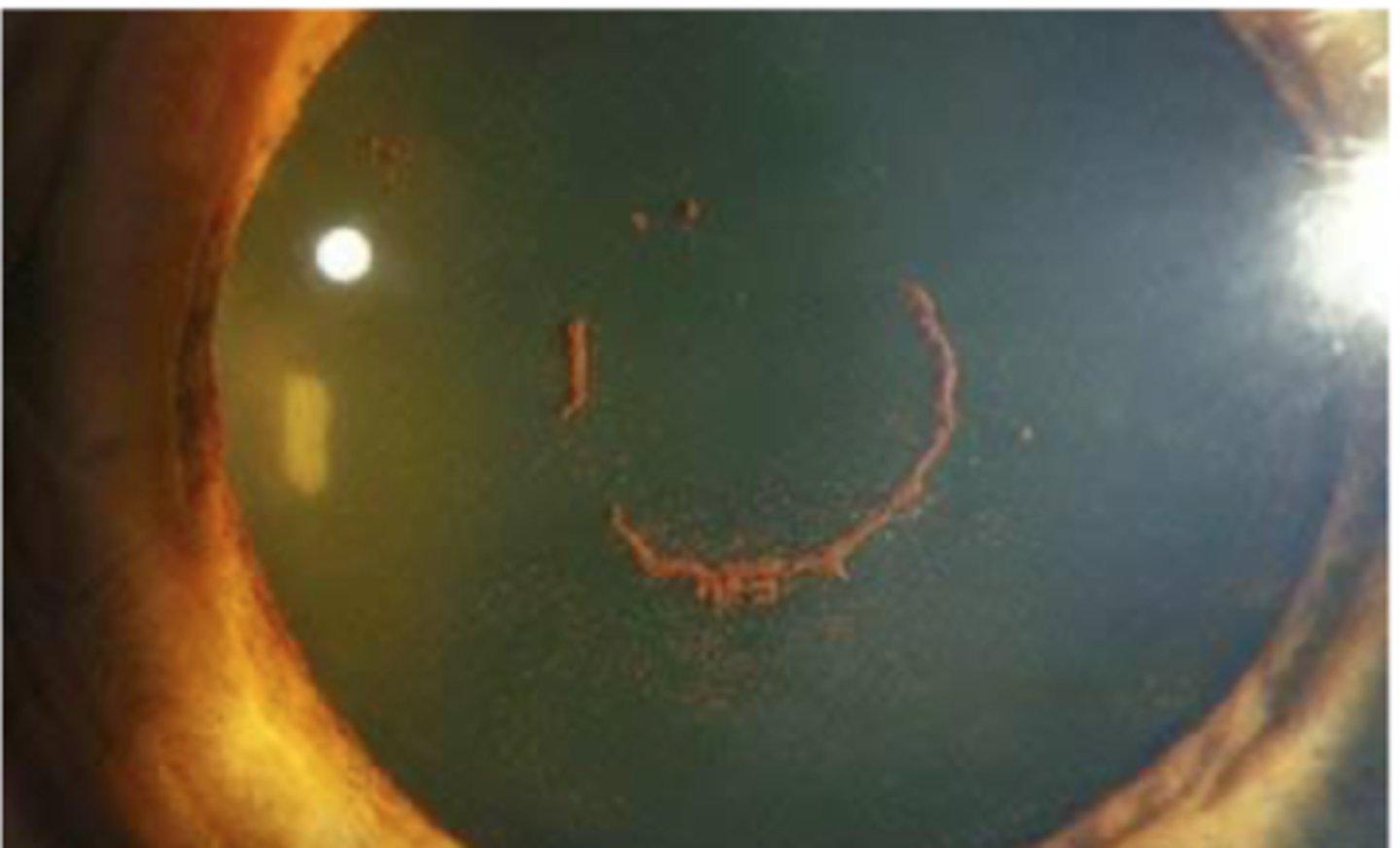
Vossius ring
related to some disease processes as well as trauma and uveitis. Is an imprint deposition of melanocytes from pupillary border of the iris due to contusion
Is an imprint deposition of melanocytes from pupillary border of the iris due to contusion. May mimic other lens pigmentary deposits.
describe Vossius ring
fades with time but some pigment may remain permanently. watch for associated traumatic cataract
A Vossius ring usually __________
Vossius ring
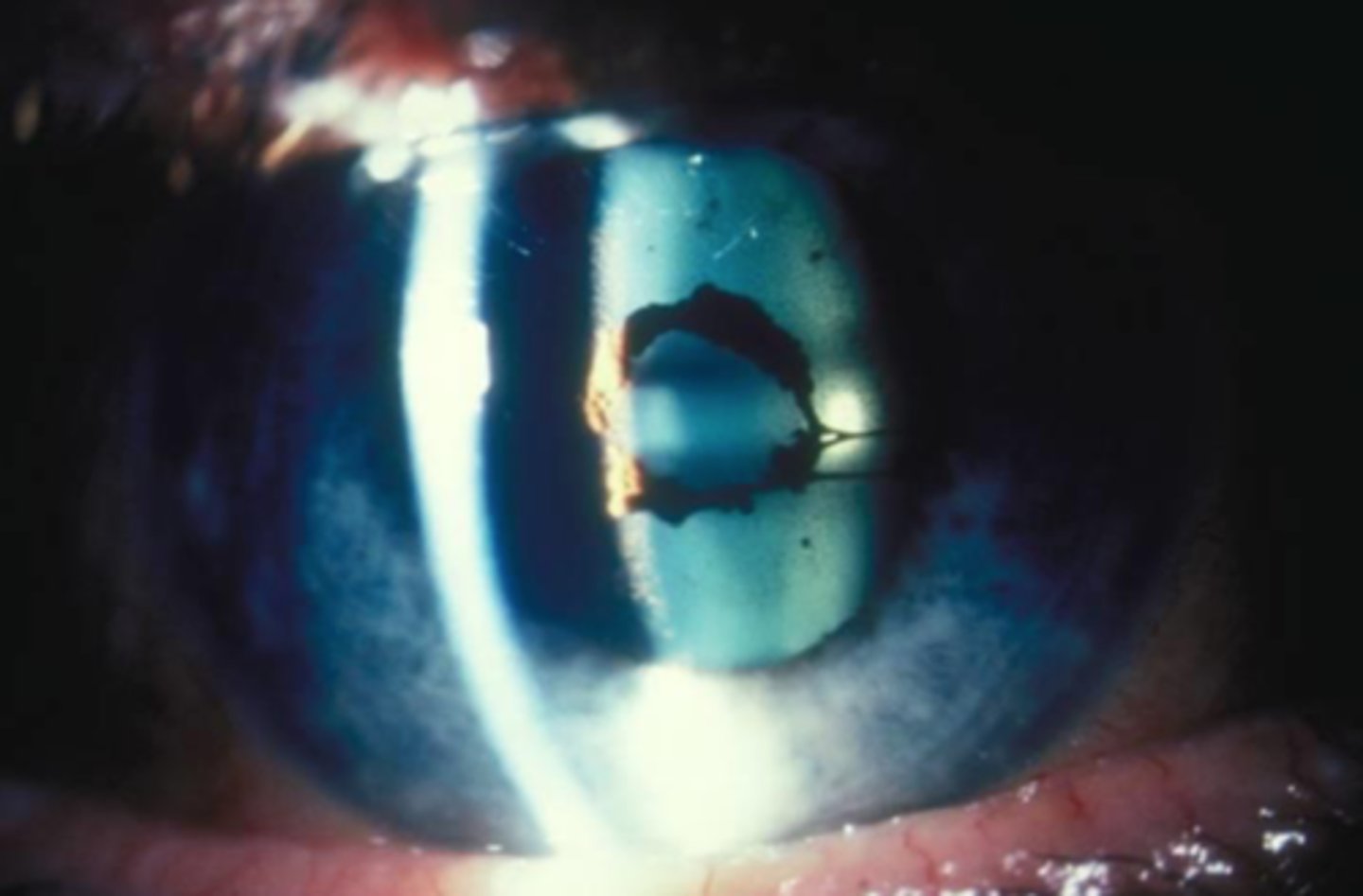
capsular pigment dusting resulting in TIDs
Capsular pigment dusting
_________ may be due to Pigment dispersion syndrome, pseudoexfoliation or trauma
retroillumination of iris showing transillumination defects
common associated finding of capsular pigment dusting
corneal endothelial pigment and pigment dusting in angle.
transillumination defects
associated finding of capsular pigment dusting
mittendorf's dot
_________ is usually unilateral
mittendorf's dot
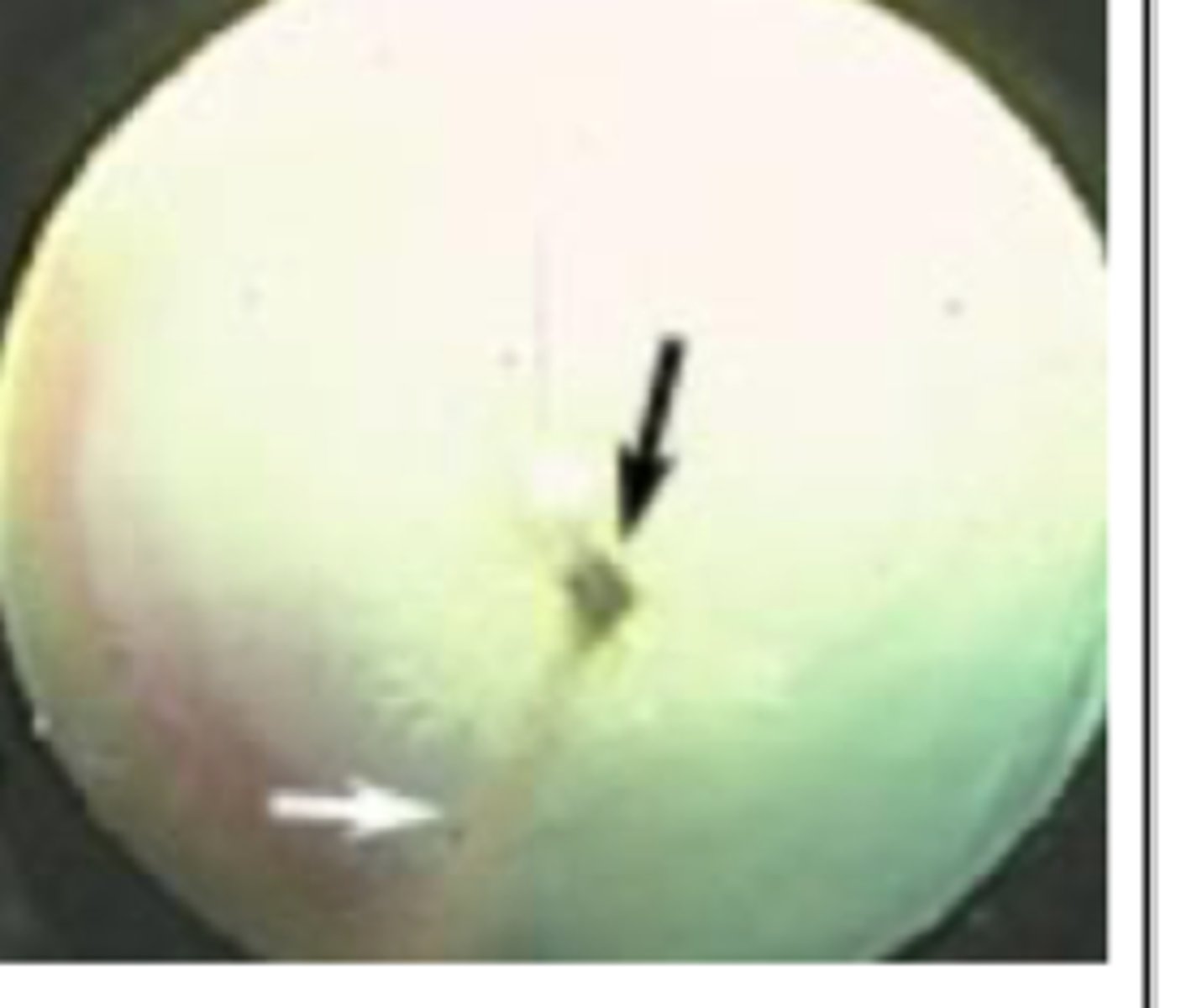
mittendorf's dot
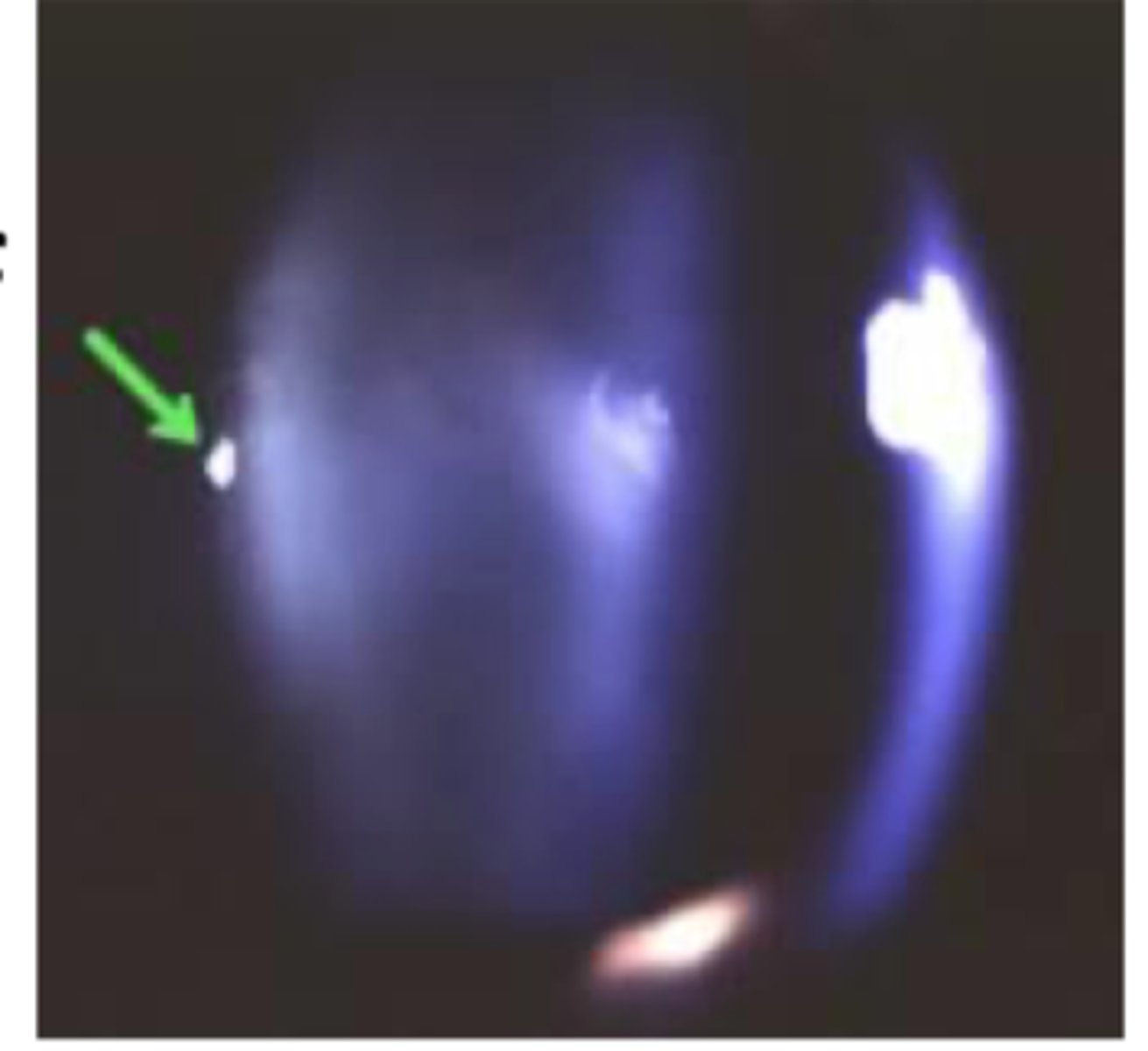
embryonic remnant of hyaloid membrane attached to posterior lens surfance. usually unilateral, and typically infero-nasal. Appears as small, punctate opacity on back of lens (may look like posterior subcapsular cataract)
describe a mittendorf's dot
1. nuclear
2. cortical
3. subcapsular
3 types of age related catarcts
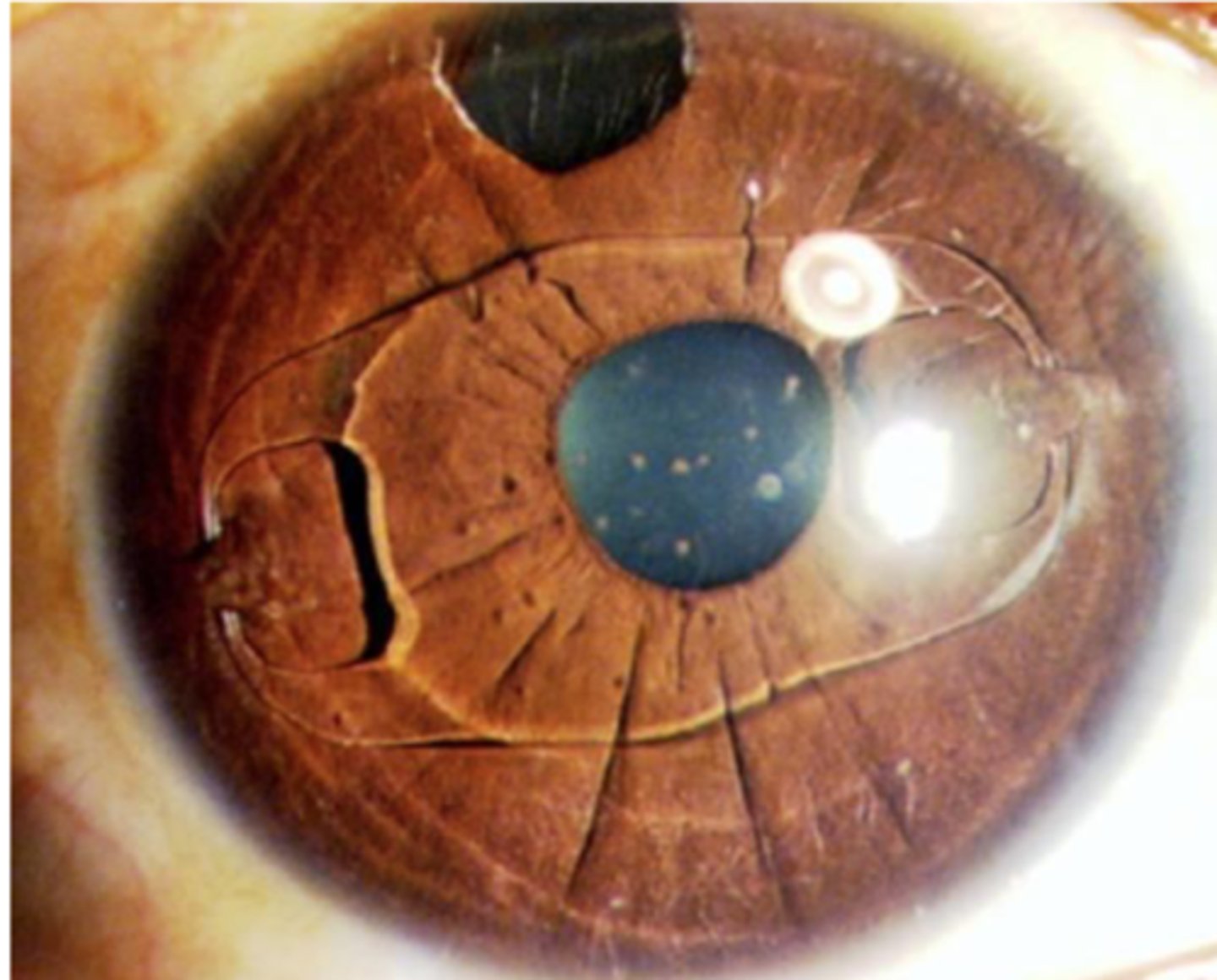
Nuclear cataract: cortex is white while nucleus is brunescent.
describe this image
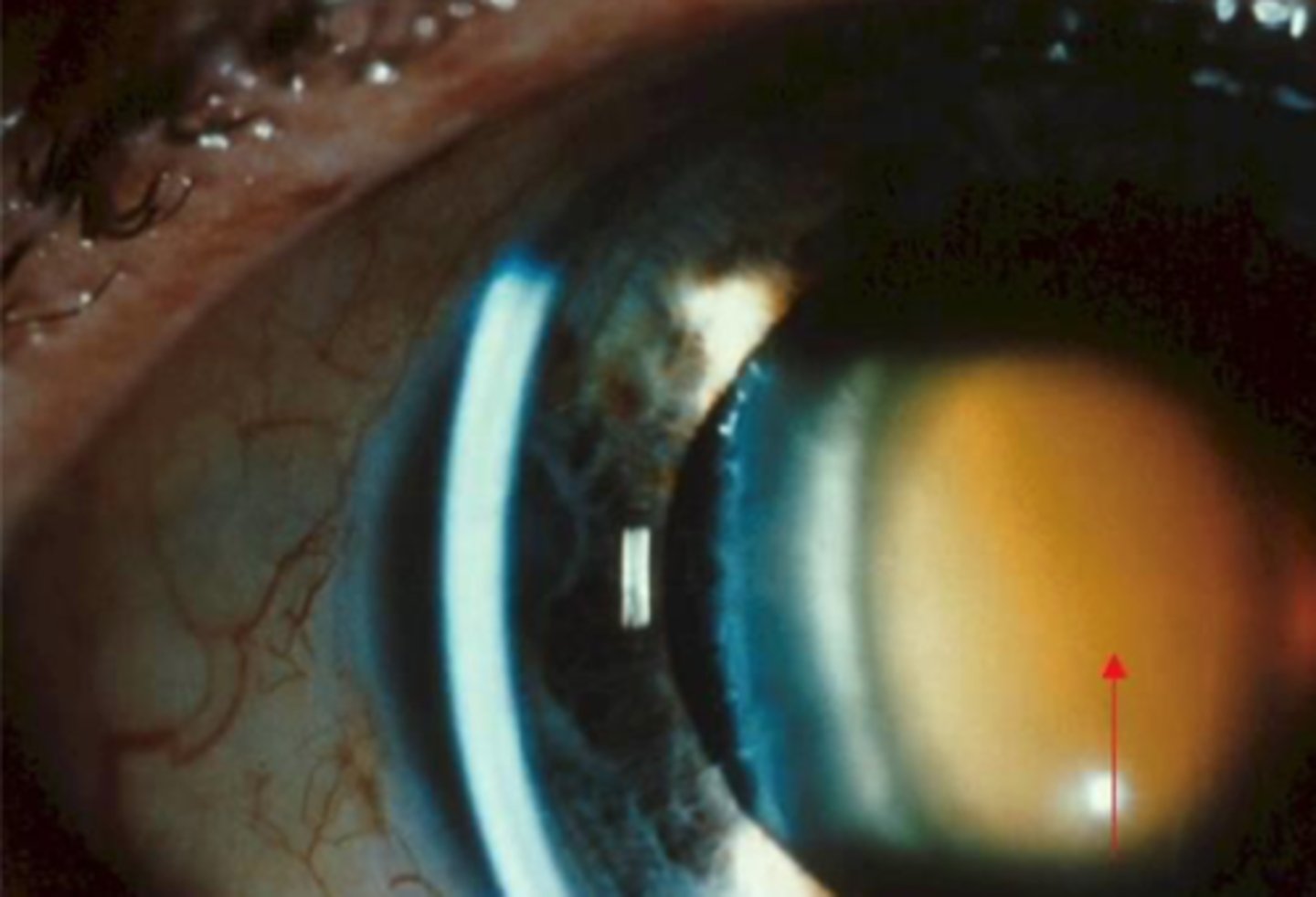
nuclear cataract
most common type of age related cataracts
yellowing of nuclear are. reduces blue light (blue blocker) will then turn brown in mature form, red in advanced form and milky white in very advanced form (VA's will be severely reduced)
describe the appearance of nuclear cataract
cortical cataract
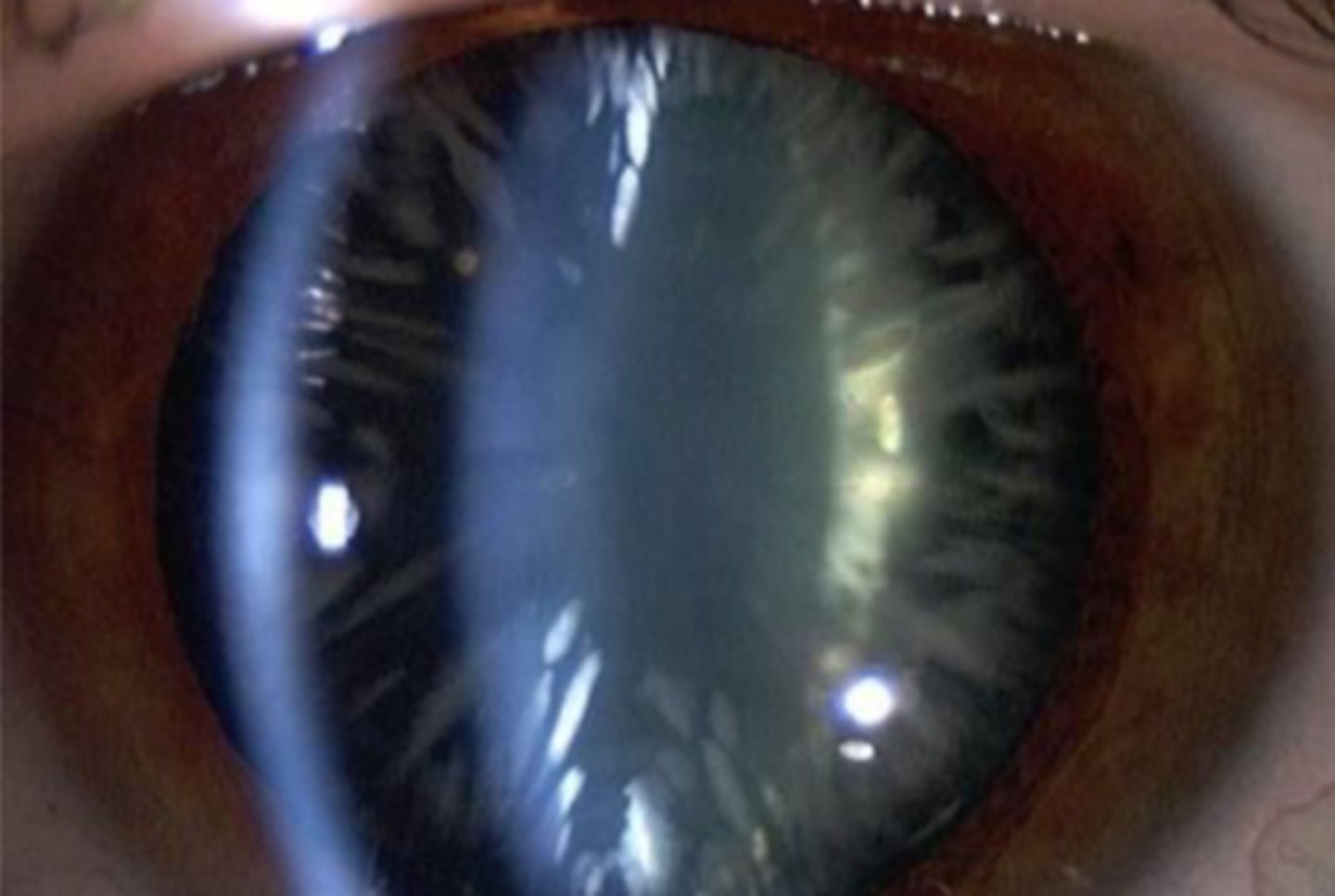
easiest to see after dilation as most of it often hidden behind iris. inferior nasal portion of lens often worst area for cortical cataracts to develop due to UV
describe a cortical cataract
aging and UV
most common causes of cortical cataract
spoke like radiations
made of anterior and/or posterior linear opacities.
get reduced VA if spokes cross visual axis
what is the appearance of a cortical cataract?
subcapsular cataract
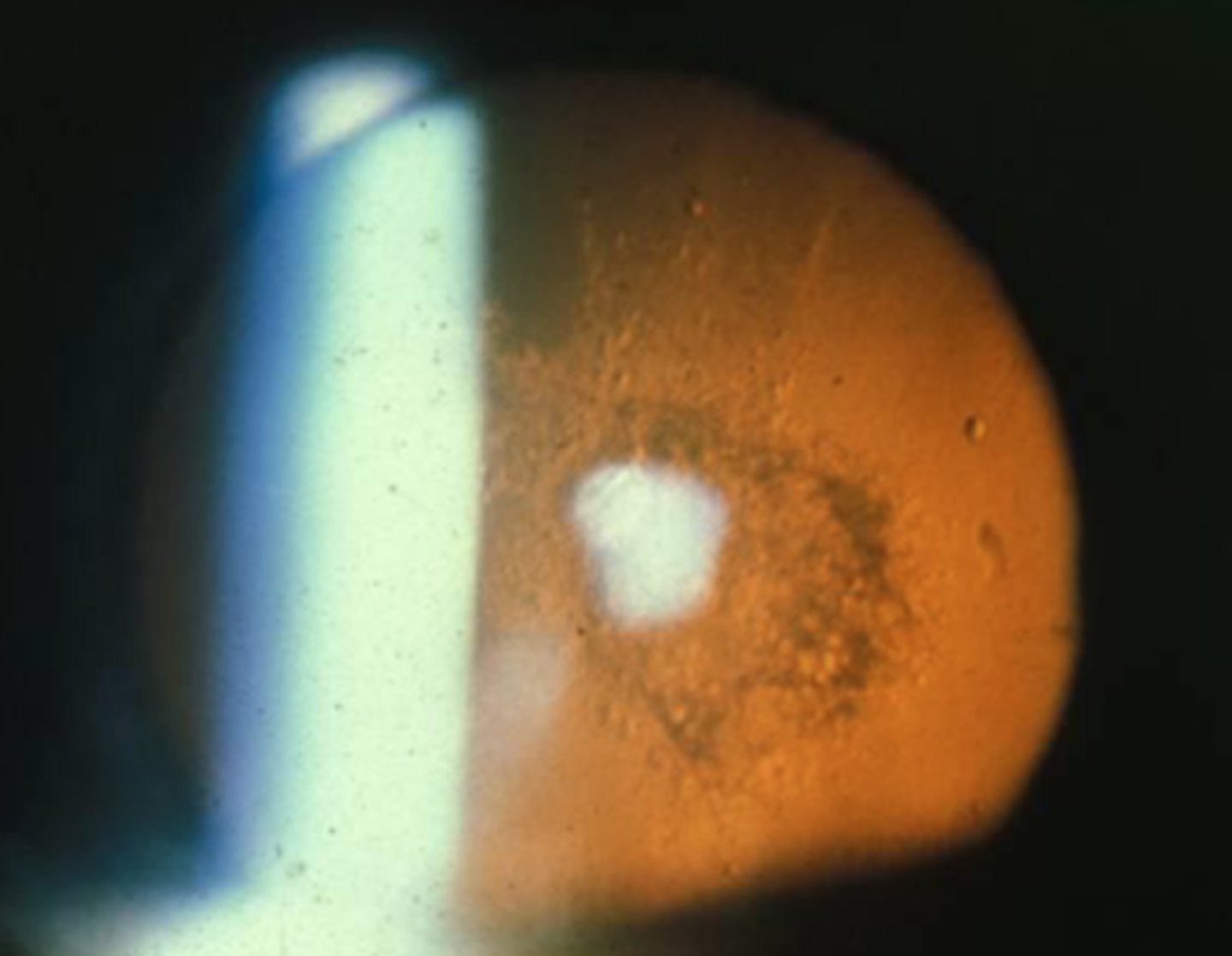
subcapsular
most devastating type of age related cataracts to VA?
most: nuclear
least: subcapsular
most and least common types of age related cataracts?
focal, usually round like opacity. posterior subcapsular most common.
describe the appearance of subcapsular cataract
rarely in senile form
usually secondary to external or systemic etiology
eg. Glaukomflecken, Wilson's disease, mitotic therapy, amiodarone
can be congenital due to alport syndrome
describe who gets an anterior subcapsular cataract
anterior subcapsular cataract
Glaukomflecken, wilson's disease, mitotic therapy and amiodarone can all cause ____________
congenital anterior subcapsular cataract
alport syndrome can cause __________
usually nuclear sclerosis (NS) appears before PSC formation.
most commonly due to steroids if pre-senile.
describe posterior subcapsular cataract
Myotonic dystrophy
Retinitis pigmentosa
mittendorf's dot
besides steroids what are other causes of PSC before old age?
direct ophthalmoscopy about arms length away, rather than slit lamp
best way to view posterior subcapsular cataract
left: PSC viewed with DO
right: PSC viewed with slit lamp (harder)
left vs right

Lamellar cataract
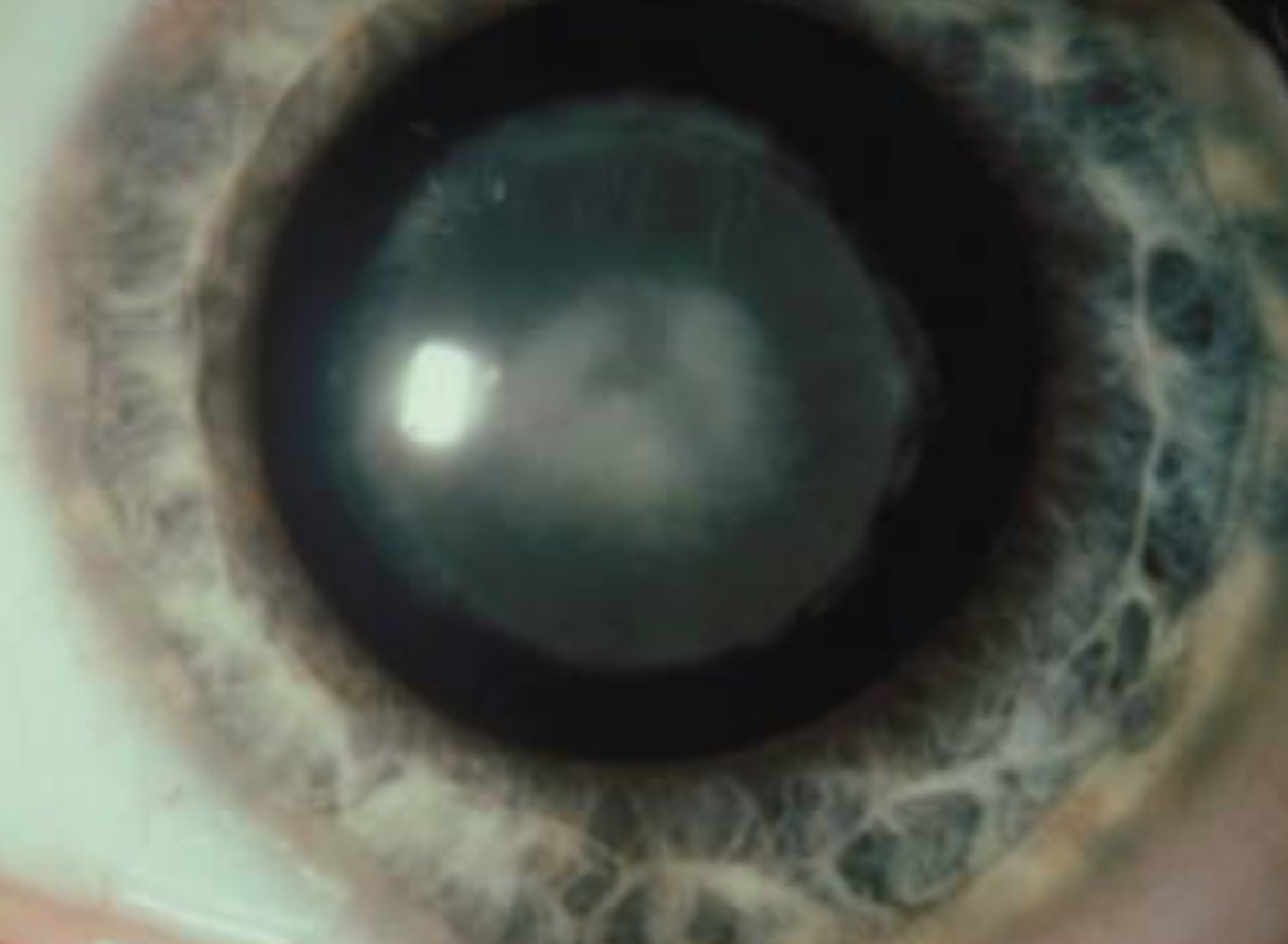
Always congenital
involve lamella of fetal or nuclear zones.
radial spoke like opacities
describe a lamellar cataract
sutural cataract
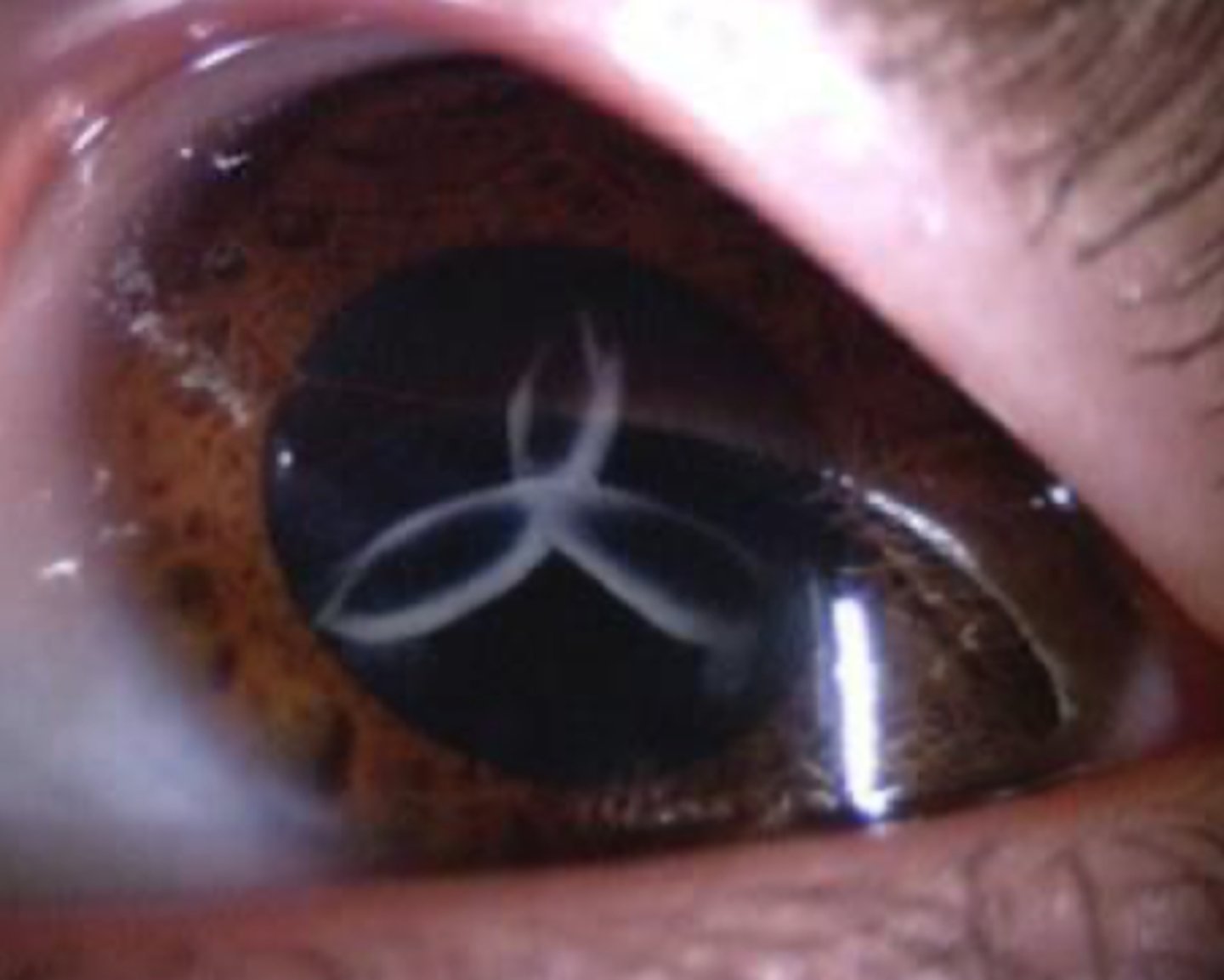
lamellar cataract
Always congenital
involve lamella of fetal or nuclear zones.
radial spoke like opacities
sutural cataract
congenital; a type of lamellar cataract
more common
Y shaped opacities within the lens nucleus
patient will have no symptoms (20/20 vision)
congenital; a type of lamellar cataract
more common
Y shaped opacities within the lens nucleus
patient will have no symptoms (20/20 vision)
Sutural cataract
quantification should correlate with VA reduction, however, this doesn't always happen clinically.
cataract density grading
0-4 scale. with 4 being the worst
describe the LOCS grading intervals for cataracts
a nuclear sclerotic lens will absorb blue light. using a 45 degree optic section and max illumination with cobalt filter, estimate the depth of beam penetration in %
what is the blue light test for cataract density grading?
more sensitive than snellen test, especially for PSCs
pelli- robson chart most clinically applicable technique
describe contrast testing for cataract density grading
immature (mild)
moderate
mature
hypermature
cataracts can be be classified upon maturity
lens retroillumination may appear clear
describe an immature (mild) cataract
may be 'presurgical' or 'surgical'
some opacification seen on retroillumination
describe a moderate cataract
cortex is totally opaque; surgery needed. posterior pole views are difficult
describe a mature cataract
water leaks out of lens, surgery needed
lens is slightly smaller with wrinkled capsule
describe a hypermature cataract
hypermature cataract
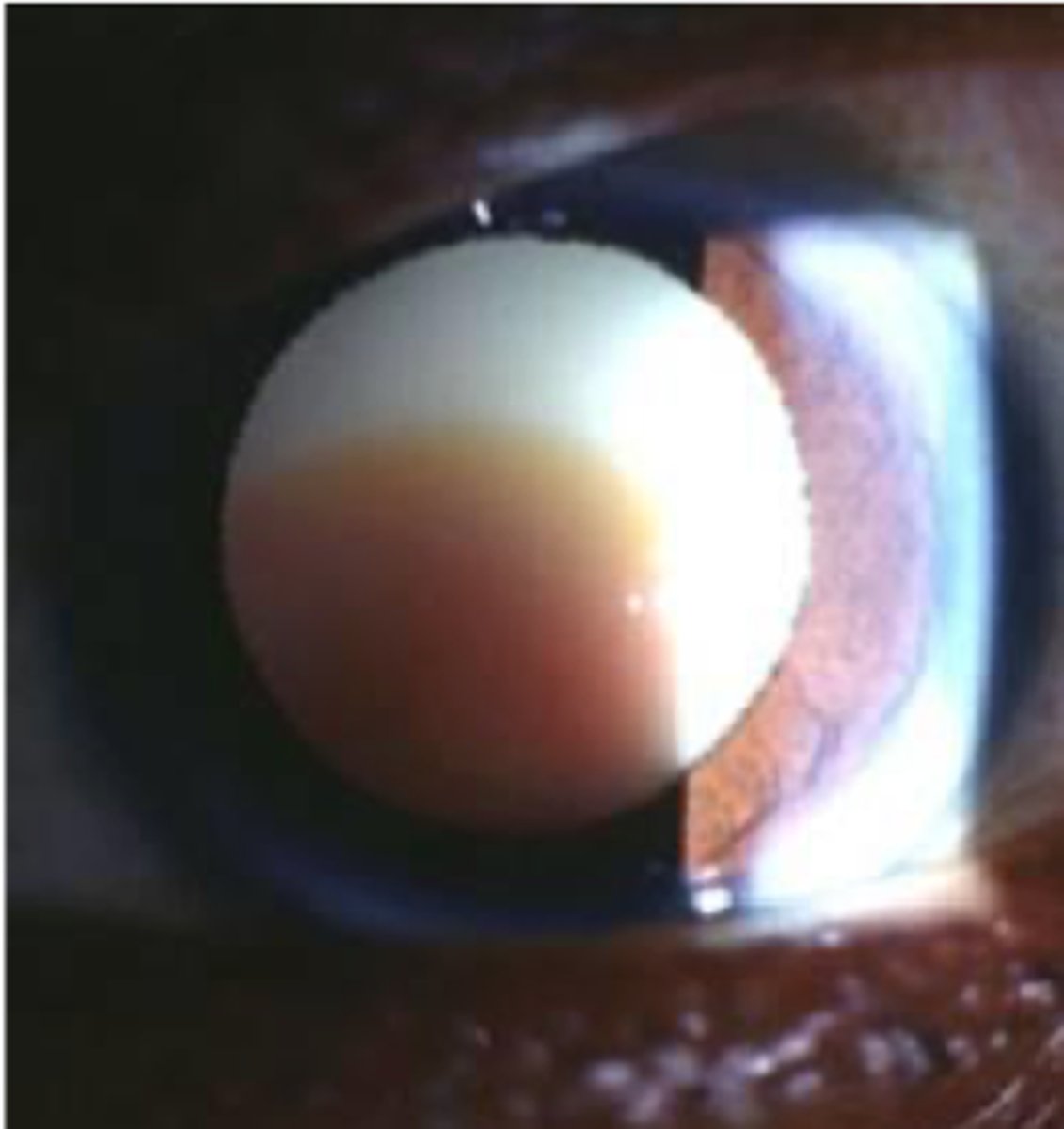
total liquidifaction of cortex, can lead to phacolytic glaucoma.
describe a hypermature cataract
most common: senile
second most common: congenital
most common age of onset for a cataract? second most common?
congenital, infantile, juvenile, adult, senile
age of onset of cataracts
use direct scope for advanced cataracts, hand help slit lamp for milder cataracts, anesthesia may be required. look for any associated ocular findings, note morphology as may give hint to etiology
how to view congenital/ infantile cataracts
OS cataract
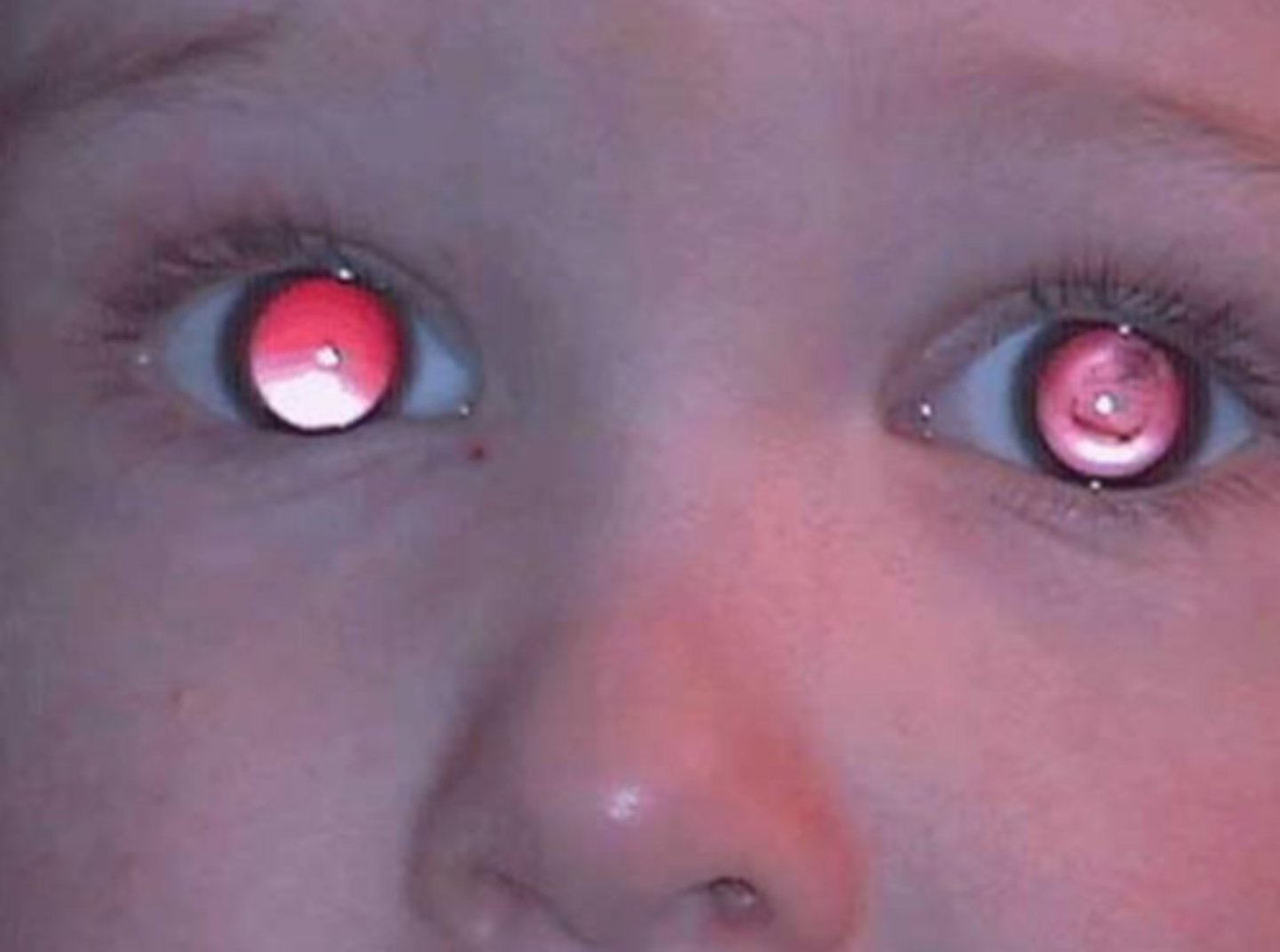
1. inspect presence or absence of central fixation, nystagmus, strabismus (bruckner, hirshberg)
2. general observation of facial symmetry
3. assess parents conditions
4. visual acuity testing using preferential looking (normal at birth 20/400 but should be 20/40 by 1 year old)
describe management for congenital/ infantile cataracts
1. bilateral advanced cataracts
2. unilateral cataract
-> key is to prevent deprivational amblyopia
surgical indications for congenital/ infantile cataracts
1. spectacles if aphakic (+15 to +20 needed)
2. CLs if aphakic
3. laser keratoplasty (KP)
4. intraocular lens (IOL)
correction options for a child with congenital/ infantile cataracts
20/40 Visual acuity is typical referral criteria for surgery. IOL power calculated using Ks and axial length nomogram -> posterior chamber IOL most common (anterior chamber less common)
describe management for juvenile, adult and senile cataracts
extracapsular cataract extraction and phacoemulsification
current procedure for removal for juvenile, adult and senile cataracts
PCIOL (posterior chamber IOL)
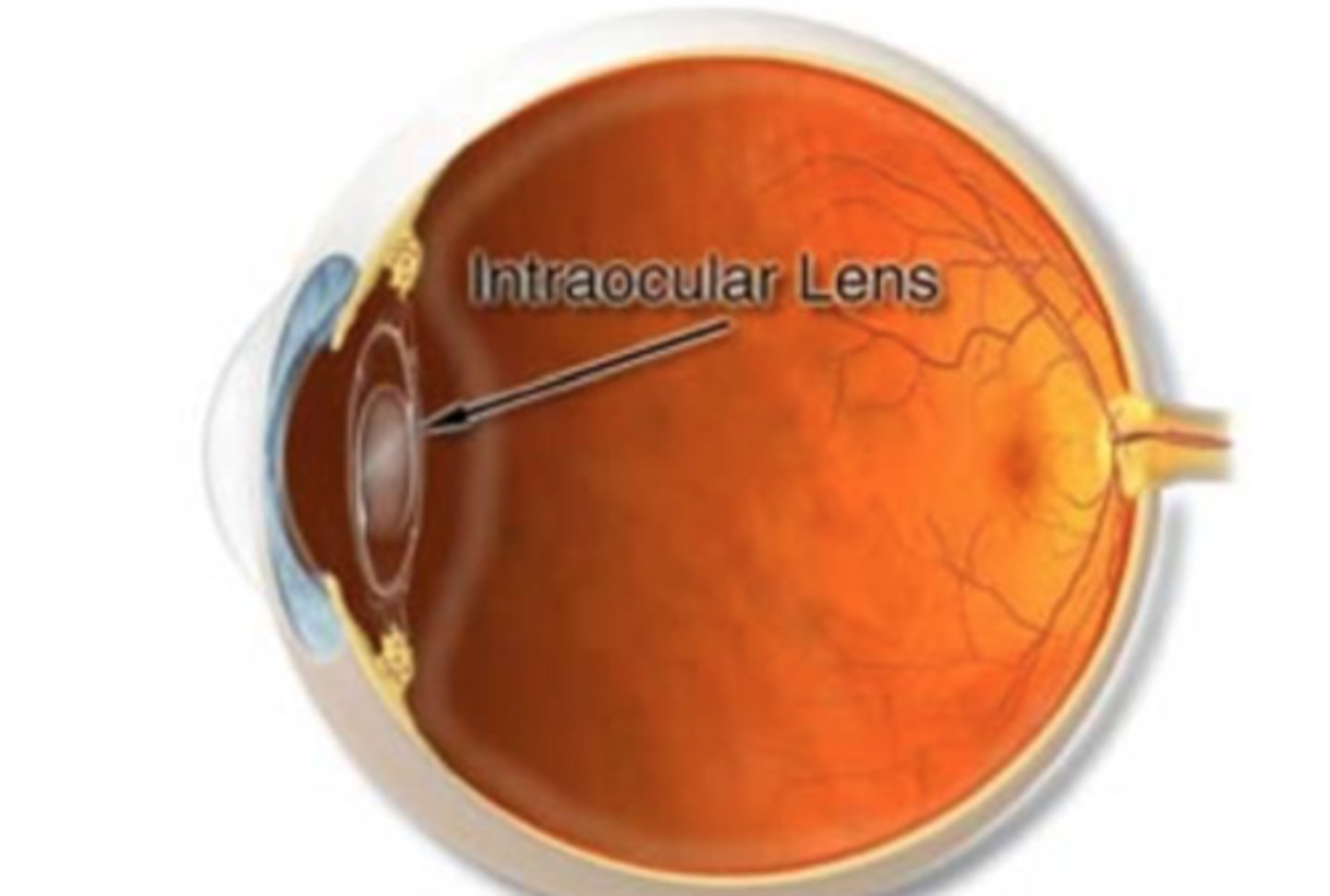
ACIOL (anterior chamber IOL) -> need chunk of iris taken out so aqueous can escape, more likely to get uveitis
accommodative amplitude after cataract extraction is zero!!! Not as critical with older patients but VERY critical for younger patients. may need asymmetrical add power in glasses if unilateral.
what do you need to remember to talk to your patients about if they want cataract removal
1. potential acuity meter
2. super pinhole
3. laser interferometry
ALL best if pupil is dilated
types of potential acuity testing
Potential Acuity Meter (PAM)
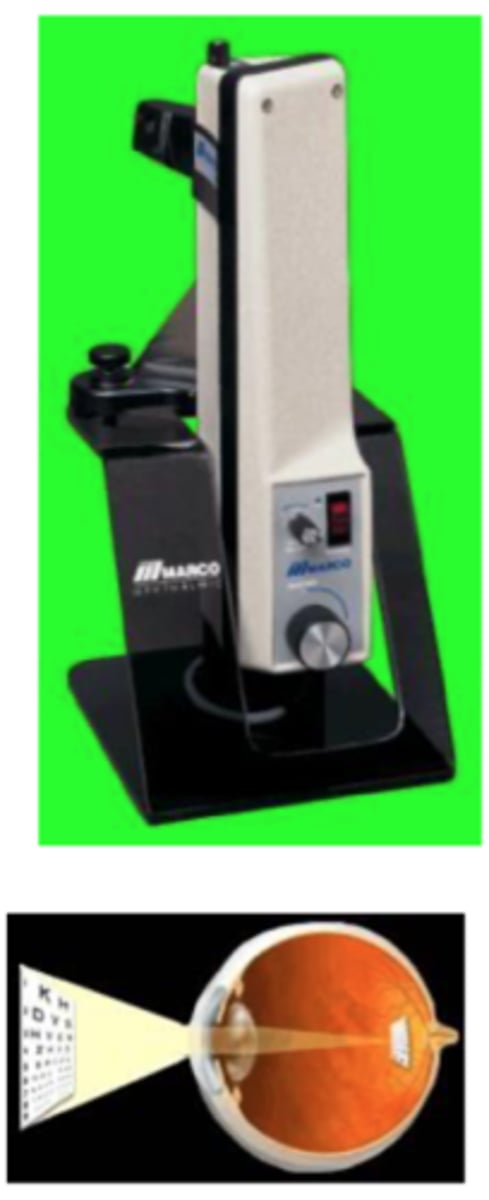

projects around cataract and helps determine actual retinal visual acuity potential. -> similar to super pinhole in that regard.
describe the potential acuity meter (PAM)
super pinhole
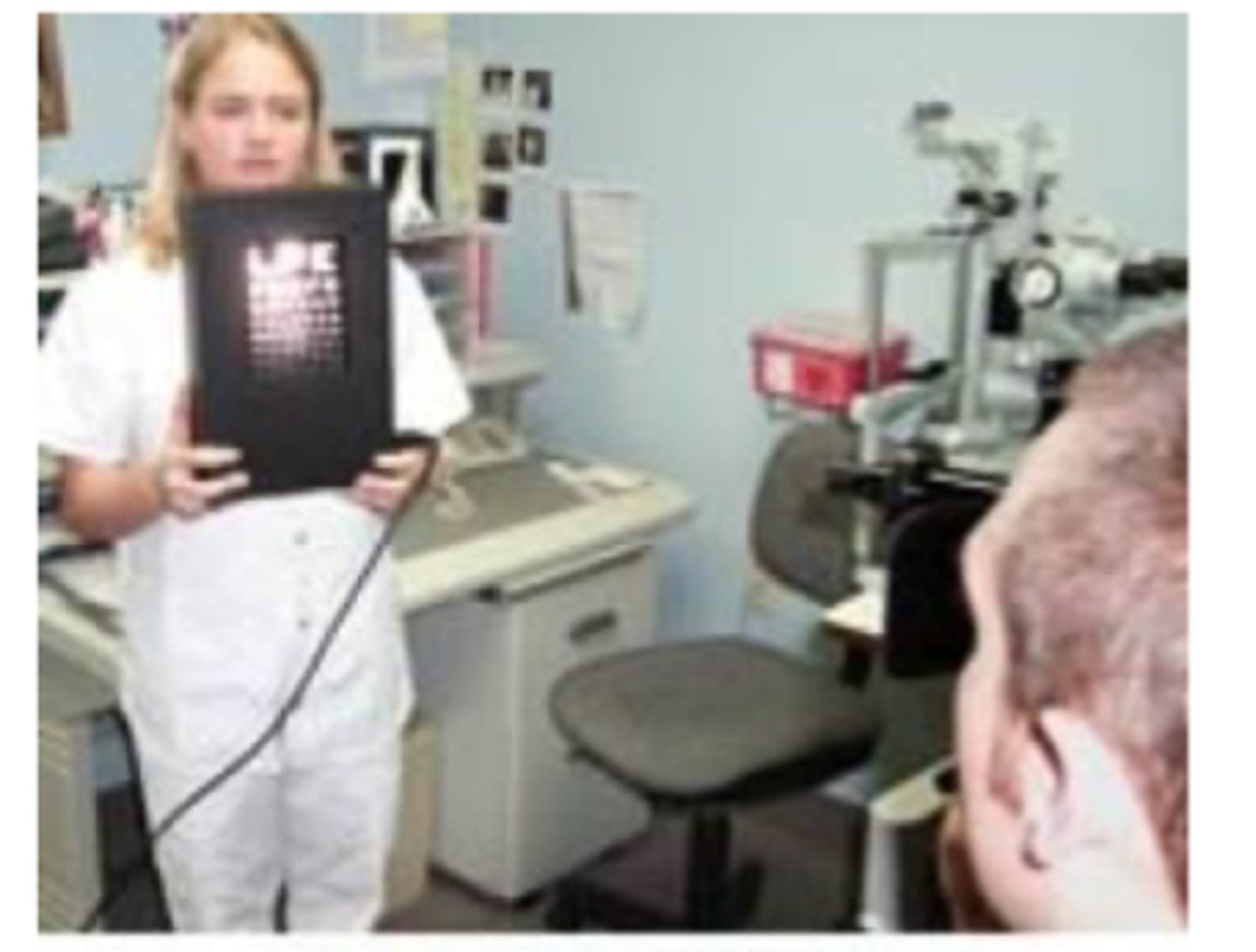
assesses the potential acuity through the cataract
The pinhole occluder also helps reduce glare, if VAs are not better with this method something else might be causing reduced vision
describe the super pinhole
bright overhead light shone on nearpoint card, patient views nearpoint card through mutliple pinhole
describe modified super pinhole
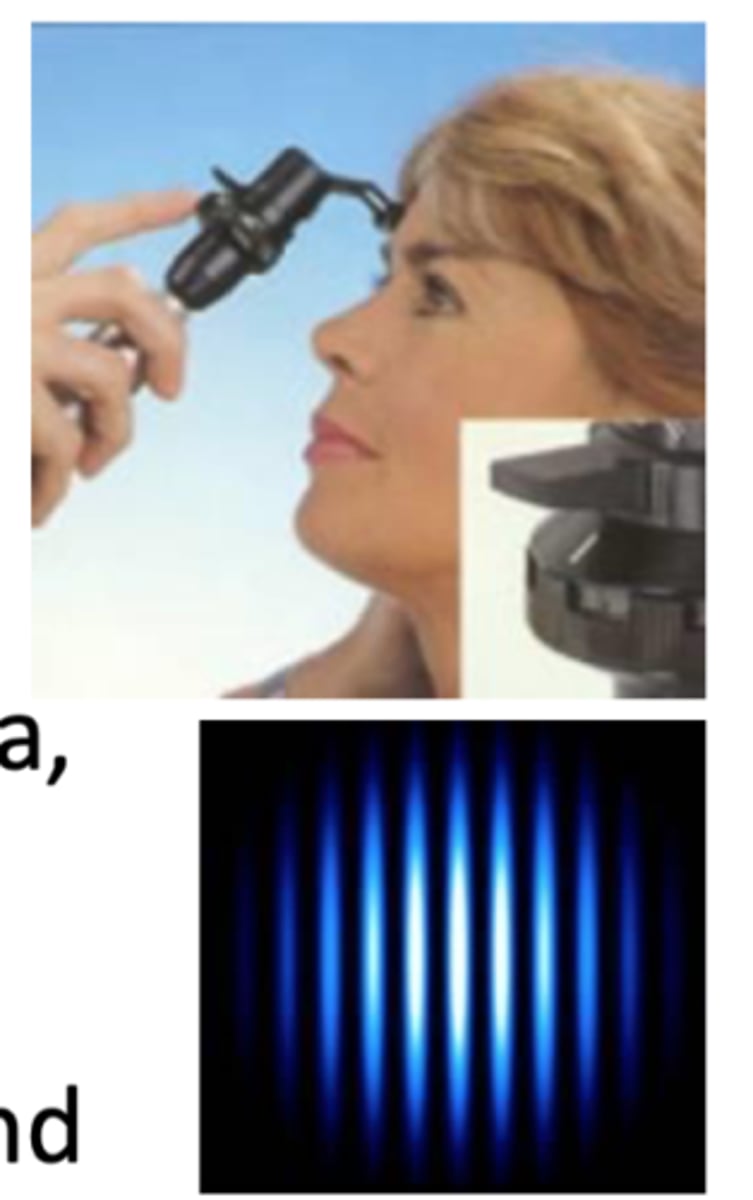
laser interferometry
what potential acuity testing is best if the patient has VERY DENSE cataracts
laser light waves pass through opacities to superimpose on retina, patient says which direction bars of light are. Can therefor determine potential retinal acuity, may be more effective than PAM or super pinhole with DENSER cataracts
describe the laser interferometry
Laser Interferometry

BAT (glare/brightness acuity test)
__________ is NOT a potential acuity test!!!!
BAT (not a potential acuity test)
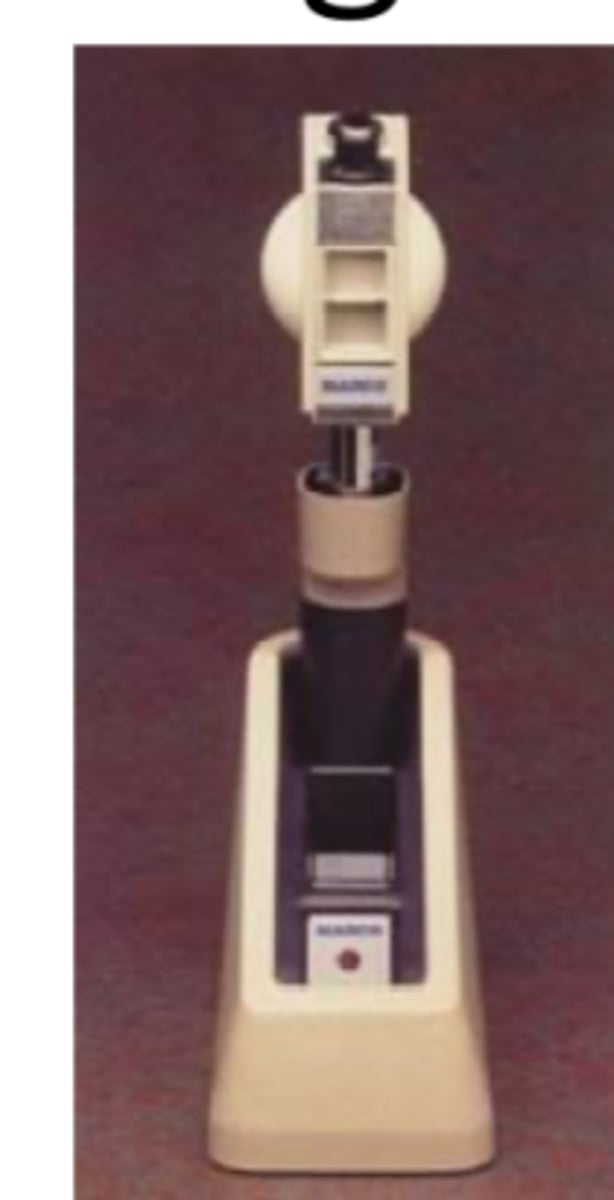

converts visual acuity test or contrast sensitivity test to a test for disability glare (distinguished from discomfort glare)
-> check acuities without light and then on the three light setting. if patients VAs are worse with BAT then they would benefit from cataract surgery. If VA's improve glare not causing the VA issue
describe BAT
glare- recovery time measured
tests of macular photostress than cataract testing
- keratometry (Ks, Topography), necessary to determine astigmatic amount
- A scan: determine IOL power
_________ required prior to cataract surgery
to determine IOL power
what is the A scan for prior to cataract surgery?
Optical Biometry
current standard for IOL calculation
cataract surgery referral criteria
