Biochemistry I Lesson 9: Genetic Recombination
1/37
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
38 Terms
When a cell undergoes mitosis, can you expect the daughter cells to have the same amount of organelles? Why or why not?
When a cell undergoes mitosis, the daughter cells are not expected to have the same amount of organelles because it is not genetic material thus if a cell did not get enough ribosomes or mitochondria then it can make more. Only DNA is organized into being split equally between the daughter cells.
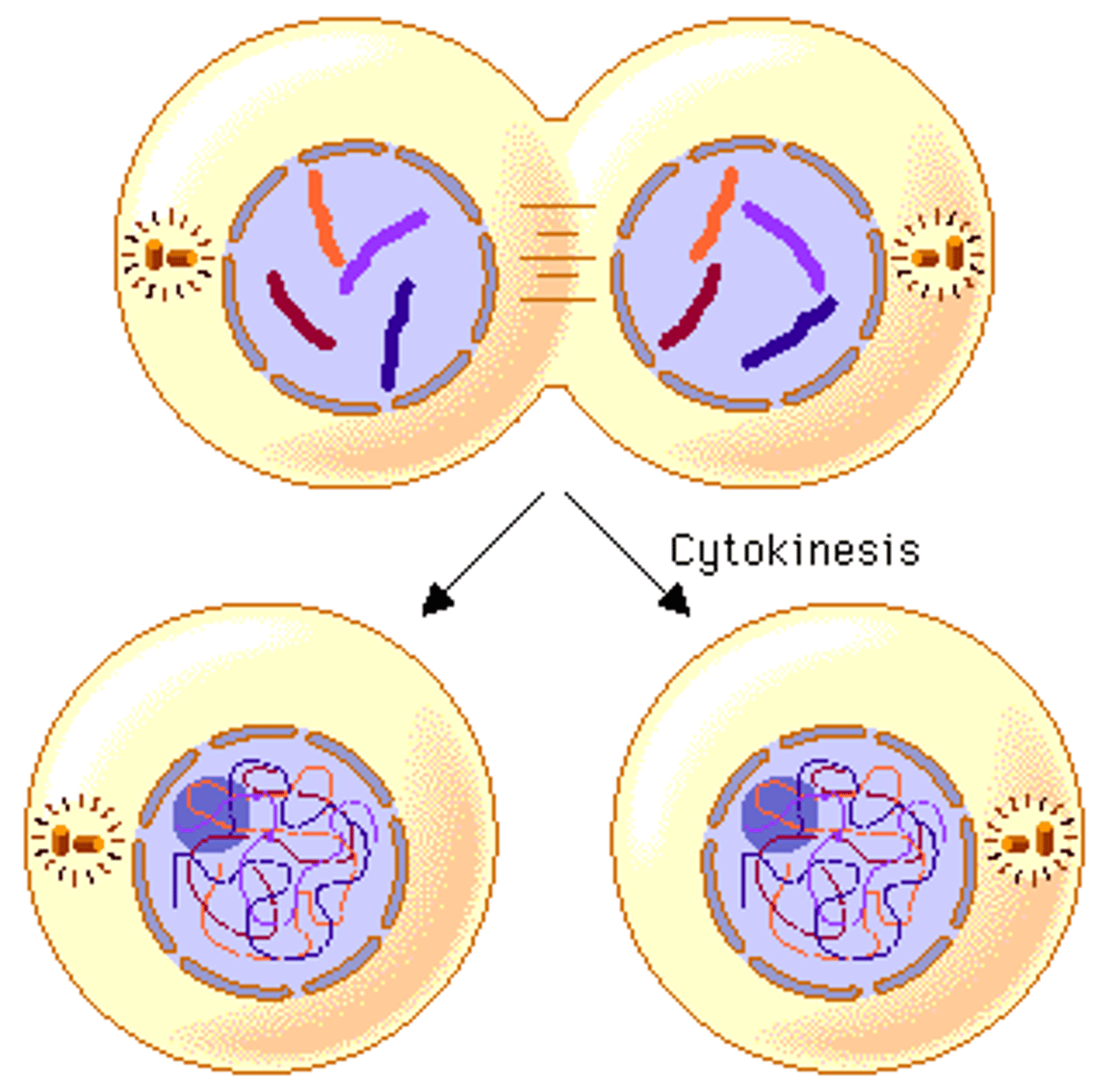
What was the conclusion of Friedrich Miescher's experiment?
Miescher's experiment helped isolate the nucleus and identified the two main components of the nucleus: protein and nucleic acids.
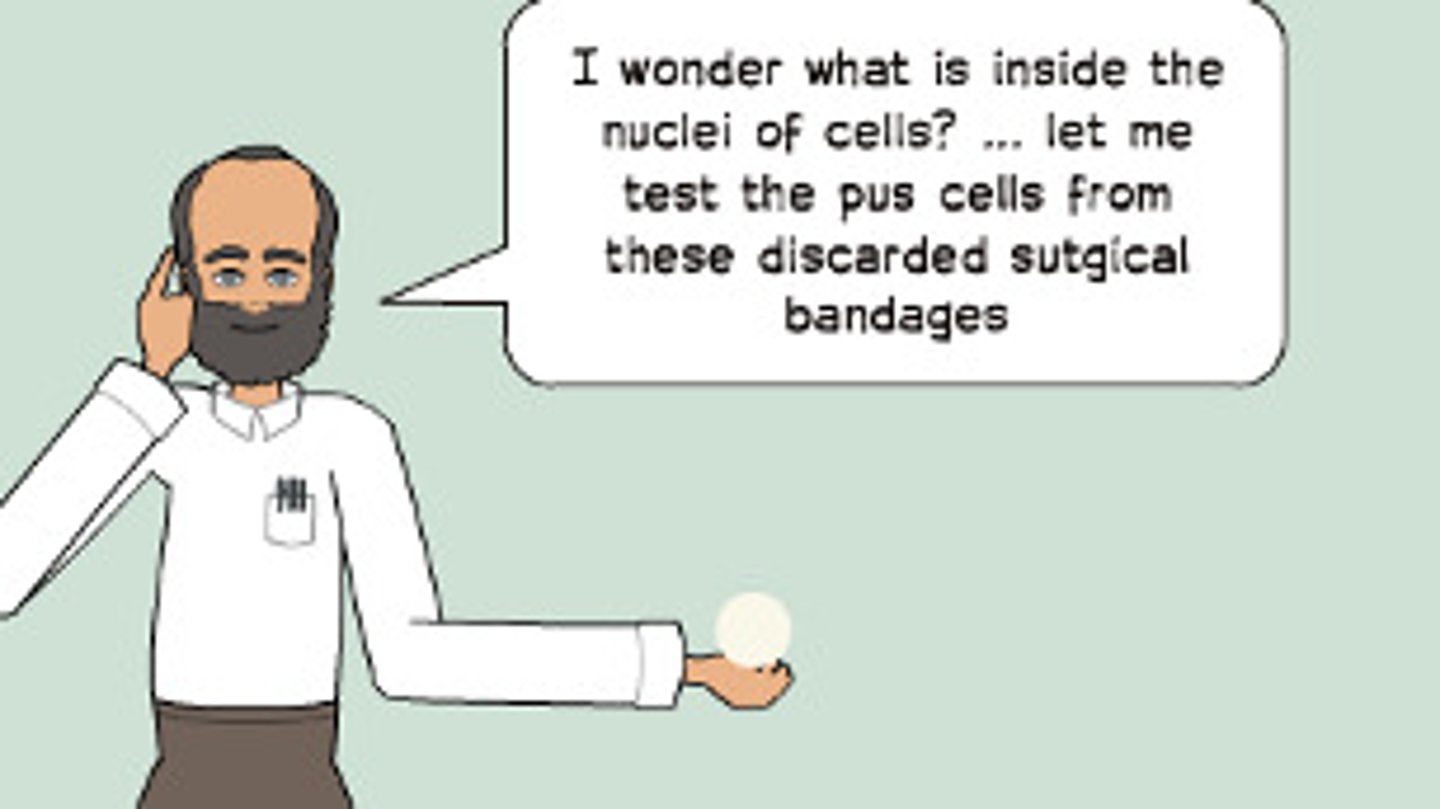
What was the conclusion of Wilhelm Roux's experiment?
Roux's experiment analyzed cells as they underwent mitosis and concluded that genetic material must be stored in the nucleus because it divided in an ordered and even fashion between the daughter cells.
CRB What was the conclusion of the Avery-MacLeod-McCarty experiment?
The Avery-MacLeod-McCarty experiment determined that DNA is the molecule of heritability, because DNA (and not proteins or RNA) transmitted viruses to bacteria
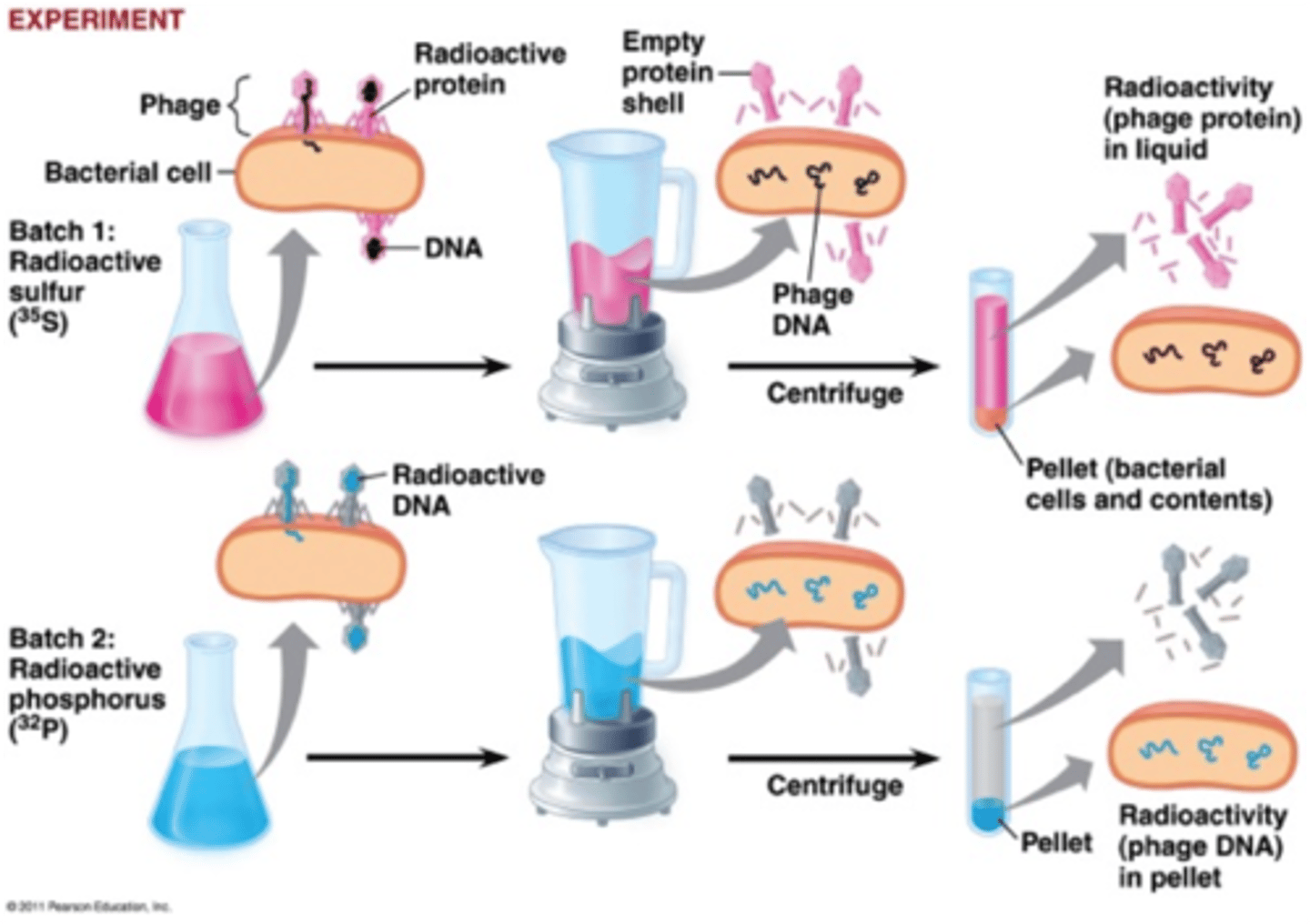
What was the conclusion of Hershey-Chase experiment?
Hershey-Chase experiment dealt with bacteriophages and running multiple trials: one with radio-labeling protein coats and other trials radio-labeling DNA. Their experiment concluded and confirmed that DNA is the genetic material.
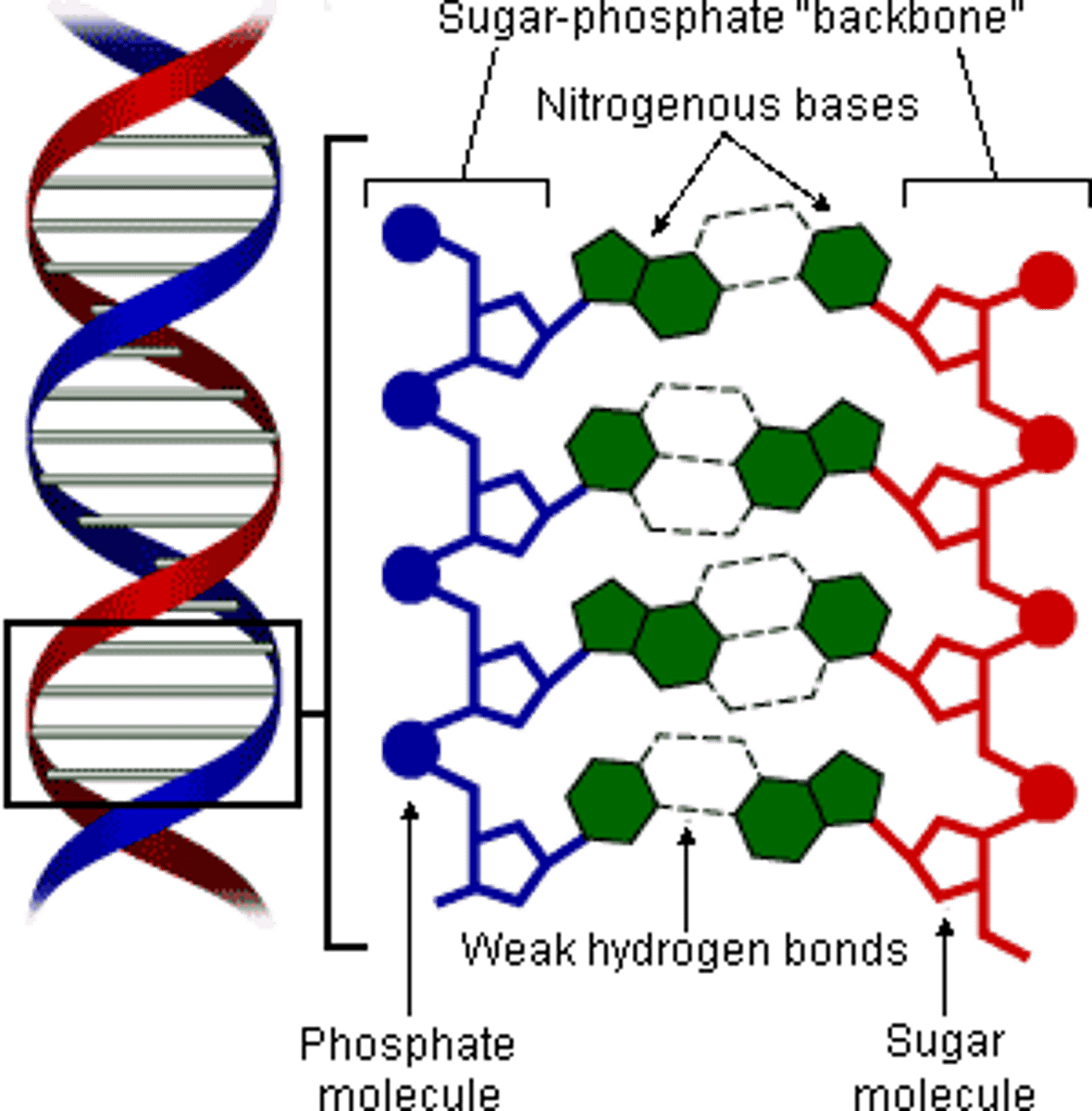
What was the conclusion of Watson-Crick's experiment?
Watson-Crick's experiment identified the double helix structure of DNA
What are autosomal chromosomes?
Autosomal chromosomes are the 22 pairs of homologous chromosomes found similarly in both males and females.
What are the sex-determining chromosomes (allosome chromosomes)?
Sex-determining chromosomes are the 23rd pair of heterotypic chromosomes. These will determine the sex of the individual.
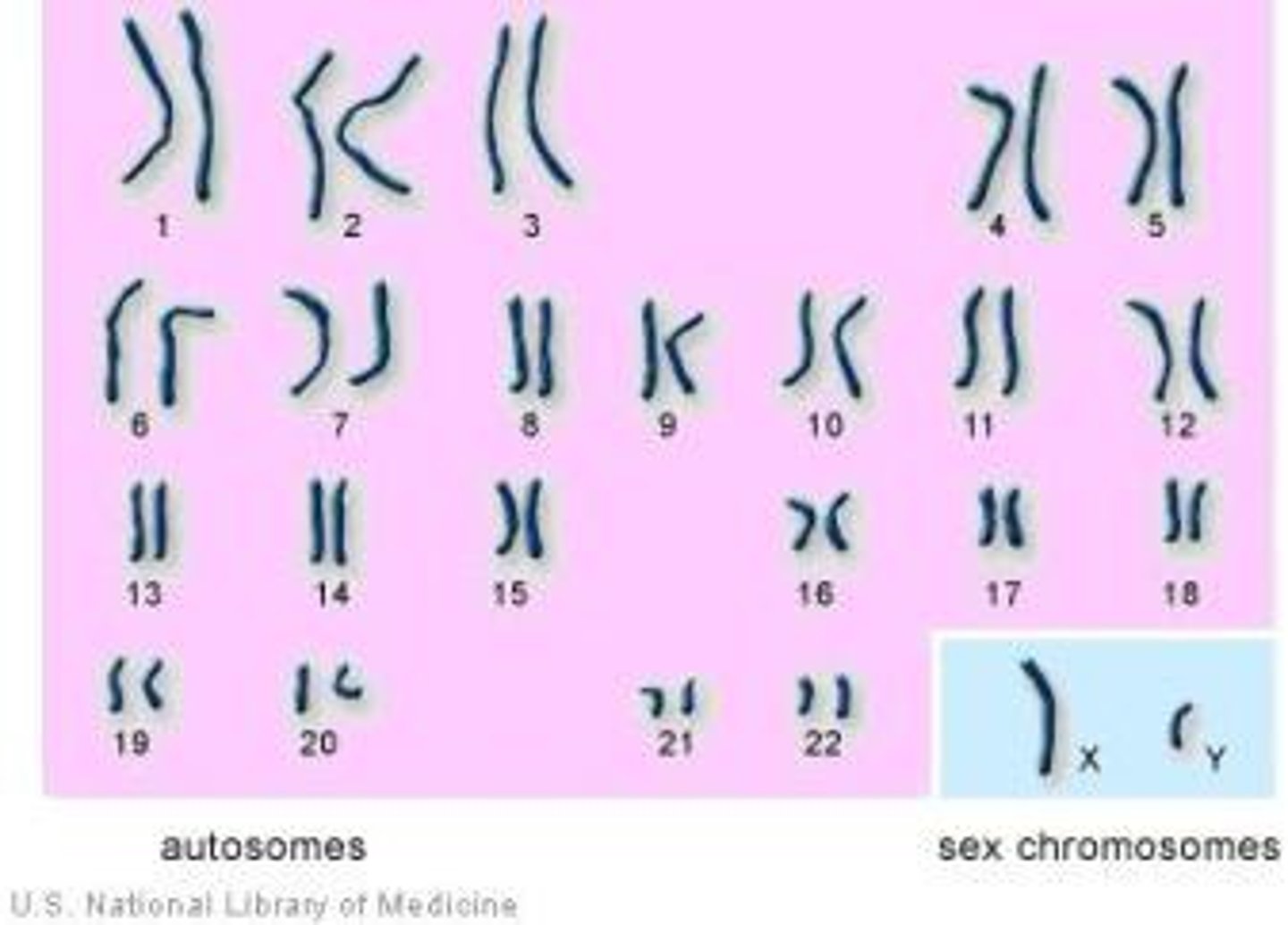
How do the sex-determining chromosomes differ between males and females?
Females have two copies of the X chromosome (XX)
Males have one X and one Y chromosome (XY)
True or False: The X and Y chromosomes in humans still must encode the same number of genes because they are both forms of the 23rd chromosome.
False. The X and Y chromosomes have nearly a 20-fold difference between the number of genes on each. The Y-chromosome only encodes 78 genes, many of them based on proper sexual development.
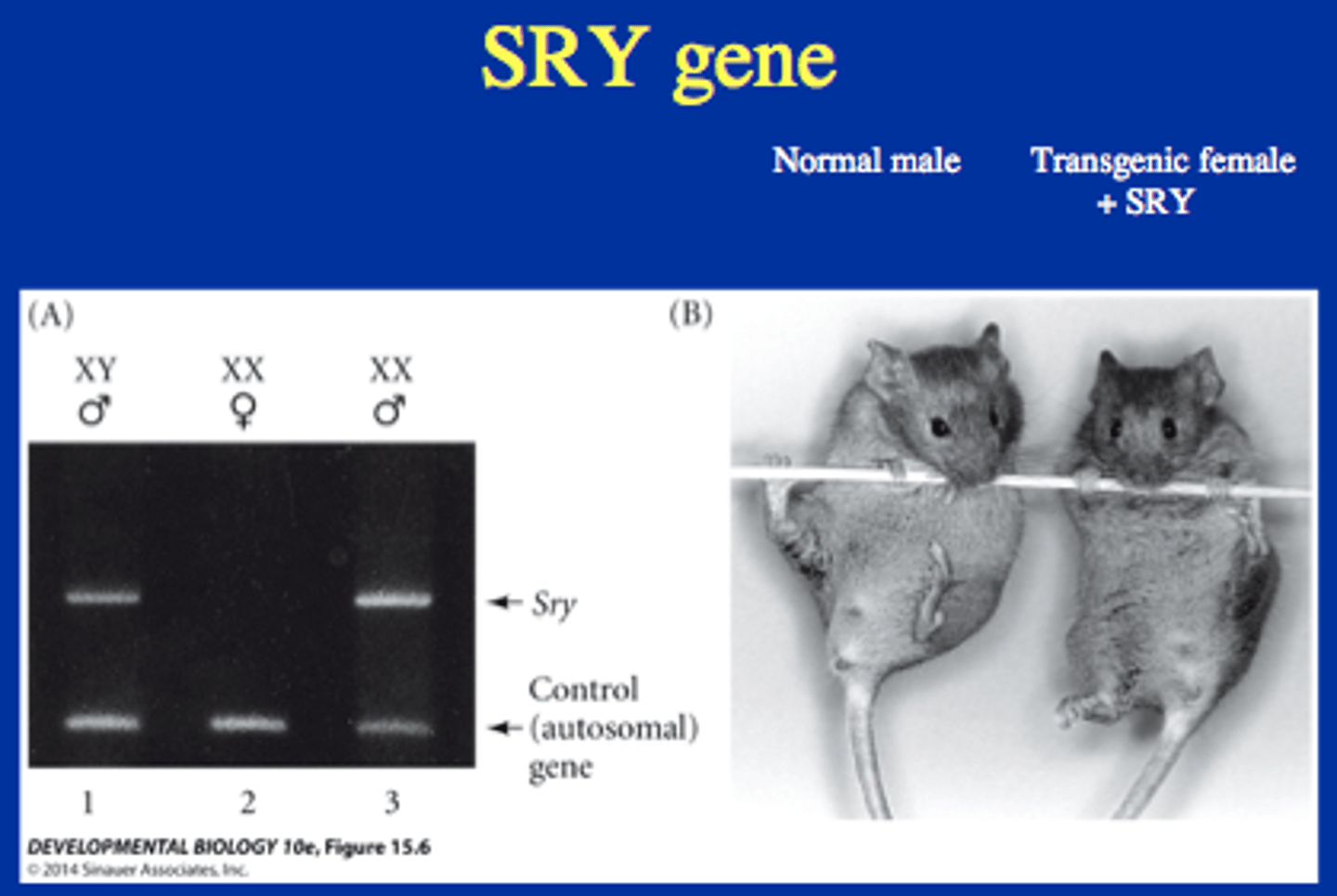
Which of the following genes is considered the "on-off switch" that, when activated, will trigger testis development in the embryo?
(A) SRY
(B) Sox-9
(C) Ghrelin
(D) Sox-11
(A) SRY
The SRY gene is considered the "on-off switch" that, when activated, will trigger testis development in the embryo
What kind of mutations (recessive or dominant) are color-blindless and hemophilia? Which chromosome mutation results in these defects?
Both color-blindless and hemophilia are recessive mutations on the X chromosome.
CRB If there are two genes that are on the same chromosome, then they may not follow independent assortment. What would this non-independent assortment be called?
(A) Non-Independent Assortment
(B) Linkage
(C) Non-Mendelian Assortment
(D) Codominant Assortment
(B) Linkage
Linkage is when genes do not show Independent Assortment.
CRB Write out the equation for Recombination Frequency, an important measure of linkage.
RF = # of Recombinants / # of total offspring
RF = Recombination Frequency
CRB If a gene shows no Linkage (follows the Law of Independent Assortment), what is the expected Recombination Frequency?
(A) 25%
(B) 0%
(C) 50%
(D) 100%
(C) 50%
CRB True or false? There should never be a Recombination Frequency significantly above 50%, given a large enough sample.
True. There should never be a Recombination Frequency significantly above 50%, given a large enough sample. The most separated they can be is a pure 50-50 chance of Recombining or not!
CRB Which of the following statements about the units for RF is FALSE?
(A) The units can simply be called "map units" or "units".
(B) The units can be called "centimorgans"
(C) 1 of the appropriate unit is equal to 1%. That means that if the RF is 25%, the genes are 25 (units) apart.
(D) None of the above statements are false.
(D) None of the above statements are false.
CRB Let's say that the length of a hummingbird's wing is either Long or Short, its color is either Blue or White, and that both of these are on the same chromosome. If the father and mother have 8 children and 3 have Recombinant phenotype what is the Recombination Frequency of these genes?
(A) 62.5%
(B) 50%
(C) 37.5%
(D) 0%
(C) 37.5%
RF = # of Recombinants / # of total offspring
RF = 3/8
RF = 37.5%
CRB If two genes moved closer together on the chromosome, how should their Recombination Frequency change?
(A) It should increase.
(B) It should stay the same
(C) It should decrease.
(D) I will go look at the formula and come back.
(C) It should decrease.
CRB Let's say that there are 4 genes, A, B, C, and D, all on the same chromosome. Between B and D, there is a 30% Recombination Frequency (RF). Between A and D, there is a 40% RF, and between B and C there is 50% RF. Between B and A there is 10% RF, and between D and C there is 30% RF. What is the RF between A and C?
(A) 40%
(B) 50%
(C) 60%
(D) 30%
(B) 50%
The easiest way to solve this type of problem is to draw it out. Increased RF means a greater chromosomal distance between the genes.
B and D are fairly far apart, and it is clear A is further from D than B was and A is close to B.
C is even further from B than D was and C is closer to D than B, so it must be on the other side of D. This tells me the order is ABDC (or CDBA, depending on how you orient it). It is clear C and A are the furthest from each other, closer genes already have no linkage (they have an RF of 50%), and no RF can be greater than 50%, so that is the answer.
What is the difference between recessive mutations and dominant mutations?
Recessive mutations require both alleles to carry the mutations in order to lead to the mutant phenotype. While dominant mutations only require one allele in order to show the mutant phenotype.
A mom is a carrier for an X chromosome mutation but does not have the mutant phenotype and a dad has an X chromosome mutation. What is the probability that their offspring will contain the mutant phenotype?
Since the mom does not have the phenotype mutation she only has one of her allele carrying the mutation. After doing a Punnett square the offspring genotype should look like: XX^, XY, X^X^, X^Y
Thus there is a 50% chance probability that their offspring will have the mutant phenotype.
Who is more likely to show the mutant phenotype from an X chromosome recessive mutation: male or female?
A male is more likely to show the mutant phenotype because males only have one X chromosome. So, if that X chromosome becomes mutated, then the male will show the mutant phenotype. A female must have both of her X chromosomes mutated to have the mutated phenotype.
CRB True or false? Autosomal Dominant or Autosomal Recessive genes should have no preference for either sex.
True. Autosomal Dominant or Autosomal Recessive genes should have no preference for either sex.
A male's frequency to have hemophilia is 1/7,000 (1 in every 7,000). What is the female's frequency for this X chromosome recessive mutation?
(A) 1/3,500
(B) 1/7,000
(C) 1/49,000
(D) 1/49,000,000
(D) 1/49,000,000
Women's frequency in showing a mutant phenotype from an X chromosome recessive mutation is squared from the male's frequency. For example, if the male's frequency to have hemophilia is 1/7,000 (1 in every 7,000) the female's frequency is 1/49,000,000
CRB There are also Y-linked genes and diseases. Which of the following statements about these is true about Y-linked diseases?
(A) Any affected father will have half of his sons affected.
(B) Any affected father will have all of his sons affected.
(C) Any not-affected father will have a 25% chance of having an affected son.
(D) None of the the above statements were correct.
(B) Any affected father will have all of his sons affected.
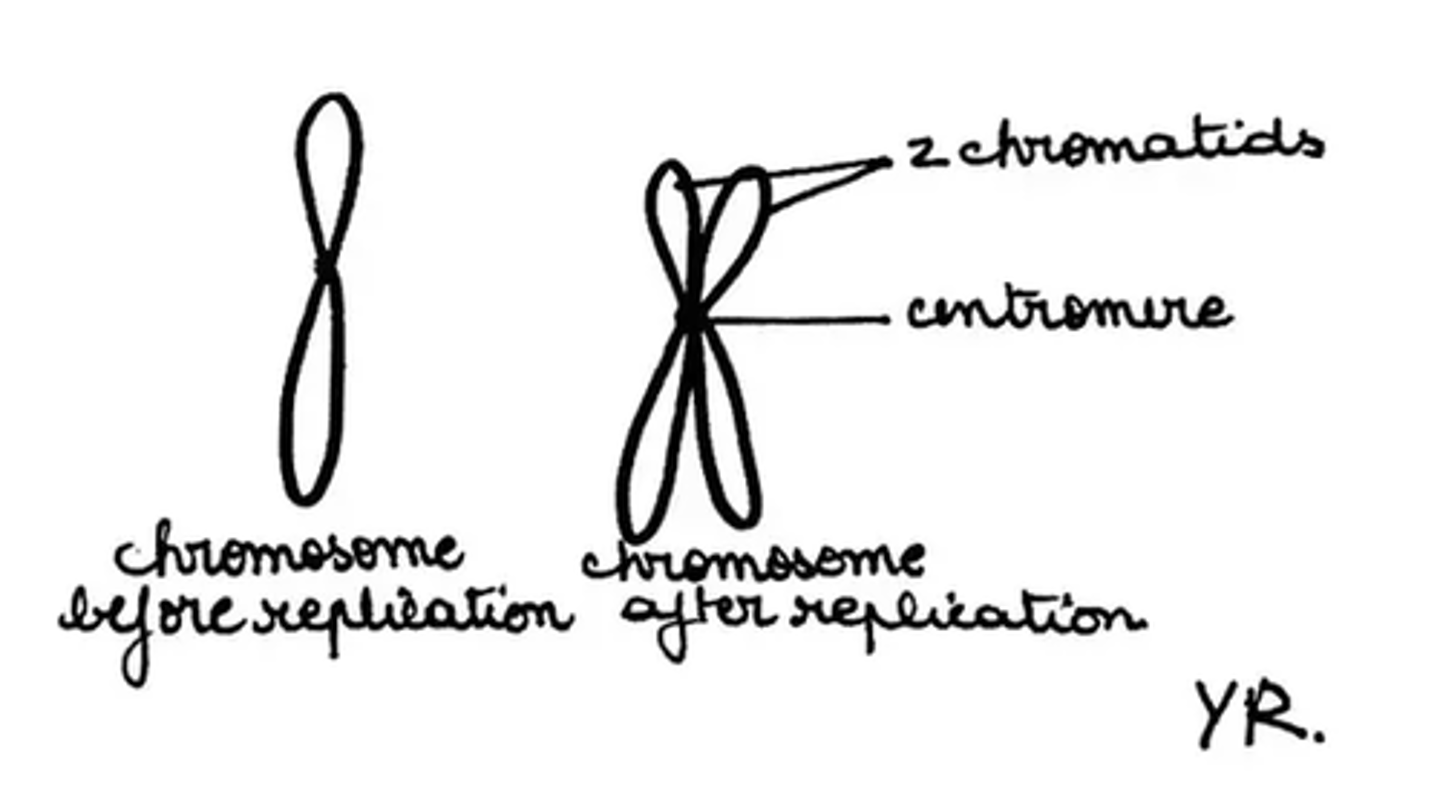
Compare the terms Chromosome and Chromatid.
The process by which Homologous Chromosomes pair with each other is called:
(A) Synapsis
(B) Tetrad Synthesis
(C) Meiosis
(D) Mitosis
(A) Synapsis
The process by which Homologous Chromosomes pair with each other is called Synapsis. Synapsis occurs at the beginning of Meiosis
Synapsis results in the formation of a Tetrad. A Tetrad is composed of four:
(A) Genes
(B) Loci
(C) Chromatids
(D) Chromosomes
(C) Chromatids
A Tetrad is composed of four Chromatids (2 Homologous Chromosomes).
Synapsis occurs during which phase of Meiosis?
(A) Prophase I
(B) Metaphase I
(C) Prophase II
(D) Metaphase II
(A) Prophase I
Synapsis occurs during Prophase I
Compare the terms Chiasma and Synaptonemal Complex?
The Chiasma is where the Homologous Chromosomes overlap and is a point of Crossing Over.
The Synaptonemal Complex is a protein complex that holds the two Homologous Chromosomes together. It also helps in the process of Crossing Over
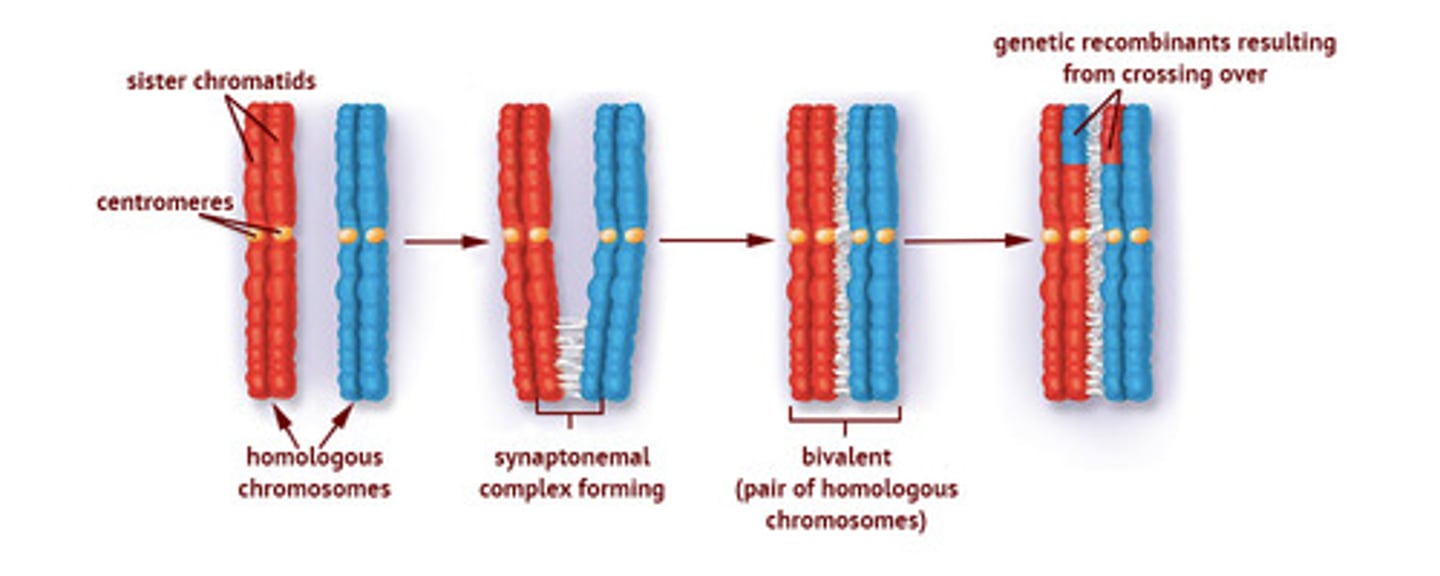
Crossing Over is the process by which:
I. Genetic Information is transferred from one Homologous Chromosome to another.
II. DNA physically moves from one Homologous Chromosome to the another.
III. Genetic Recombination occurs.
(A) I Only
(B) I and III Only
(C) II and III Only
(D) I, II, and III
(D) I, II, and III
Crossing Over (aka Genetic Recombination) is the process by which Genetic Information is transferred from one Homologous Chromosome to another as DNA physically moves from one Homologous Chromosome to the another.
If Genetic Recombination did not occur, how many possible genetically-unique Gametes would you find at the end of Meiosis?
(A) 1
(B) 2
(C) 3
(D) 4
(B) 2
Without Genetic Recombination, only 2 possible genetically-unique gametes would be found at the end of Meiosis, as opposed to the 4 that are normally seen with Genetic Recombination at the end of Meiosis.
Out of all the types of double chromosomal crossover, which one increases genetic variability the most? Why?
(A) 2 strand double crossover
(B) 3 strand double crossover
(C) 4 strand double crossover
(D) There is no difference in the genetic variability
(C) 4 strand double crossover
The 4 strand double crossover increases genetic variability the most, because it involves all of the four chromatids of a tetrad. The more strands that become involved, the more variability is introduced.
What is the pseudoautosomal region?
It is a region on sex chromosomes where crossover can occur between X and Y Chromosomes without it being problematic for sex determination in humans.
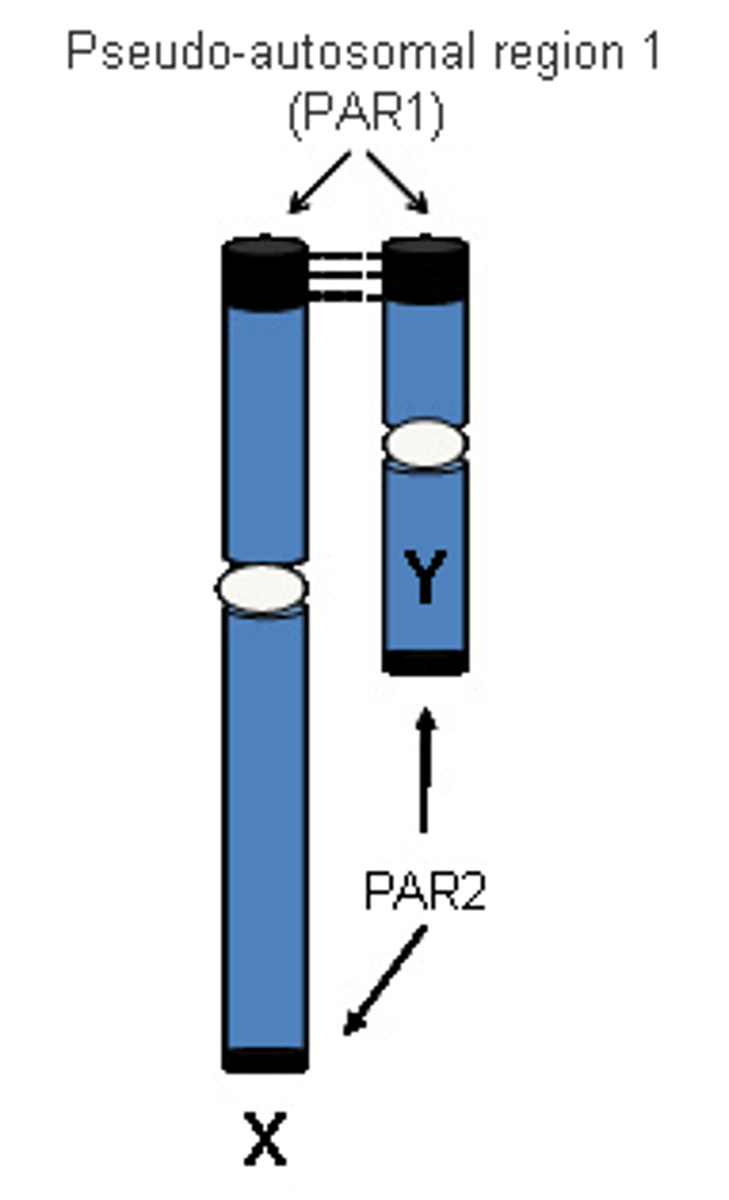
On the same chromosome, two genes QWE and RTY are close in proximity while UOP gene and KJH gene are much farther apart. Which two genes are more likely to swap genetic material and undergo genetic recombination? Why?
The UOP gene and KJH gene are more likely to swap genetic material and undergo genetic recombination with the other chromosome because they are farther apart. This increases the probability that, between the two chromosomes, there will be cross over between UOP gene and KJH gene.
What is a centimorgan (or map unit)?
A centimorgan (or map unit) is the distance between chromosome positions for which the expected number of chromosomal crossovers in meiosis is 1 out of 100.
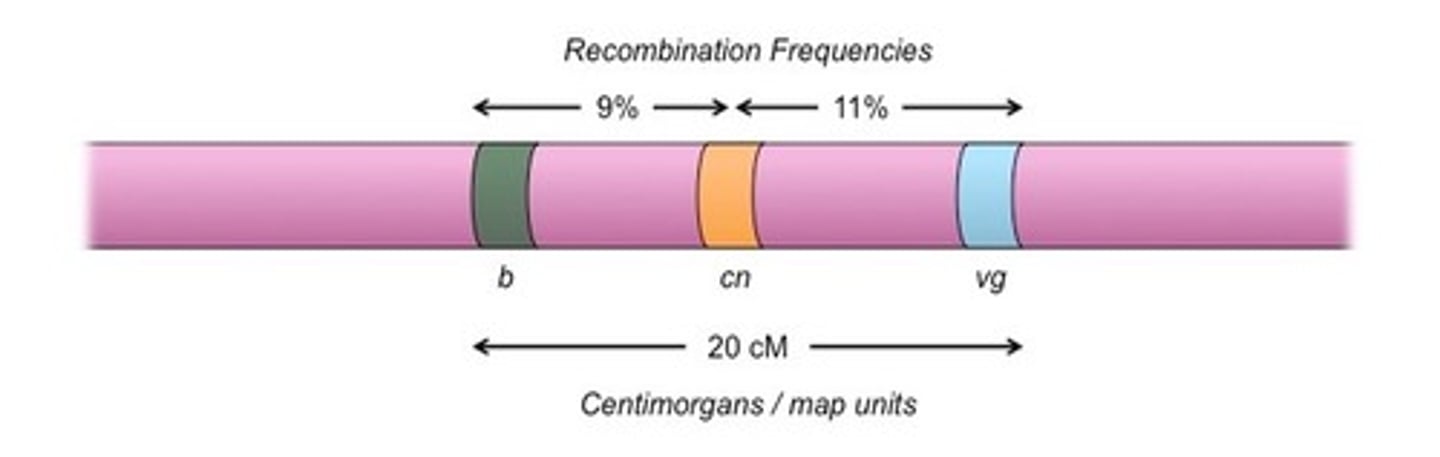
QWE and RTY are 15 centimorgans apart. What does that mean?
There is a 15% chance that a crossover will occur between them during meiosis, resulting in recombination of these genes