Geologic History
1/49
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
50 Terms
Uniformitarianism
A principle that geologic processes that occurred in the past can be explained by current geologic processes.
Relative Dating
Dating a rock's age by using its position relative to other rocks.
Superposition
The law of ______ states that younger rocks lie above older rocks if the layers have not been disturbed.
Original Horizontality
The principle of ______ ______ states that sedimentary rocks are deposited in horizontal or nearly horizontal layers.
Cross-Cutting Relationships
The principle of ______-______ ______ states that when fault cuts or magma intrudes through rocks, magma or fault is younger.
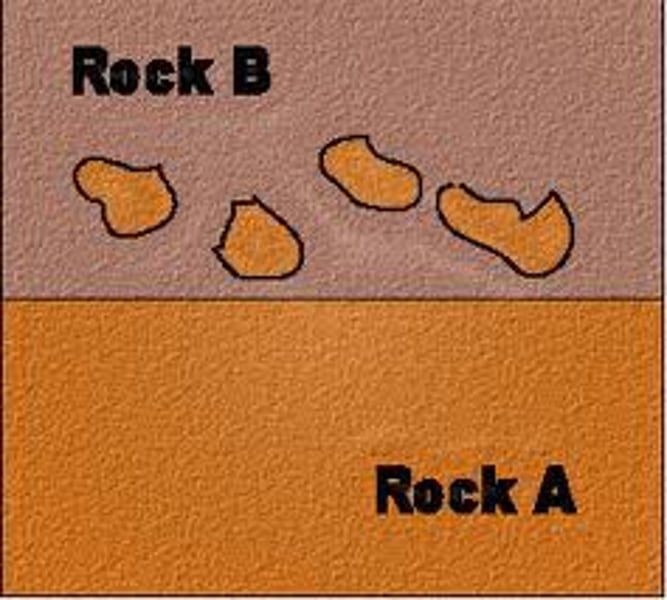
Inclusion
Rock B includes several examples of an ______, a rock within a rock.
Unconformity
A break in the geologic record created when rock layers are eroded or when sediment is not deposited for a long period of time.
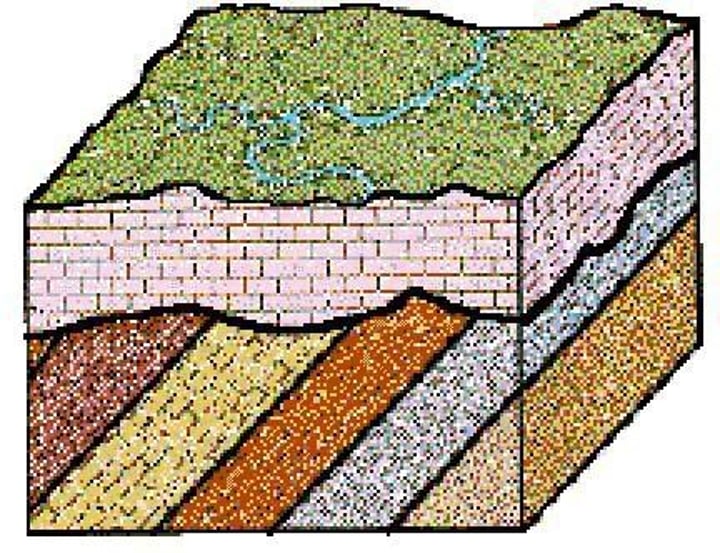
Angular Unconformity
What kind of unconformity is this?
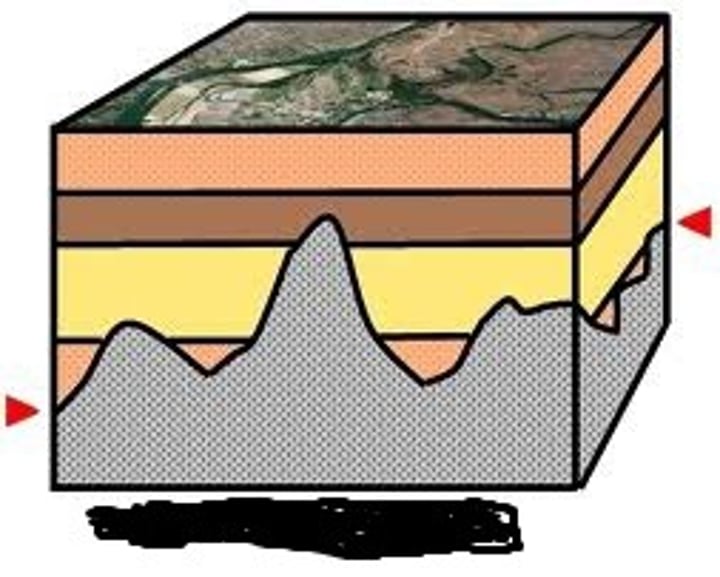
Nonconformity
This is an example of what kind of unconformity (the grey is igneous/metamorphic rock)?
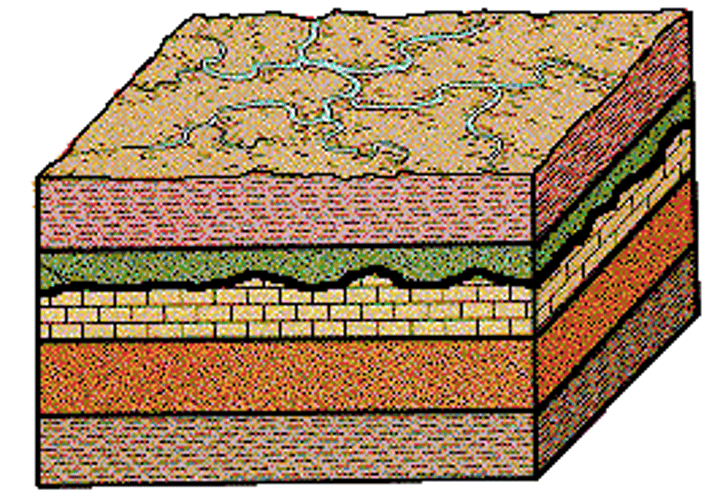
Disconformity
What kind of unconformity is this?
Correlation
What is it called when comparing rocks from different locations give you a fuller picture of the geologic record?
Fossil
The remains or traces of an organism preserved from geologic past.
Rapid Burial, Possession of Hard Parts
Conditions usually required for fossilization are a ______ ______ and the ______ __ ______ ______.
Fossil Succession
States that fossil organisms succeed one another in a definite order.
Evolution
Theory that states that life forms change over time.
Natural Selection
States that individuals better suited to their environment will survive better.
Index Fossil
A fossil known to have lived in a particular geologic age that can be used to date the rock layer in which it is found.
Marine Fossil
______ ______s (don't include "s" in answer) can be used to determine if a region was once underwater.
4.52
The Earth formed __.__ billion years ago.
88
__% of Earth's history was during Precambrian time.
Oxygen
What element did not exist in early Earth's atmosphere?
Photosynthesis
Cyanobacteria produced food using sunlight through what biological process?
Rust
Evidence of photosynthesis in the rock record includes ______.
Stromatolites
Layered mound fossils left by ancient bacteria.
Wave Erosion
Stromatolites are relatively rare and found only on sheltered coastlines due to ______ ______.
Cambrian
First period in the Paleozoic era.
Multi-Celled
The Cambrian period is known for many new ______-______ organisms.
Warming, Shallow
The ______ of the planet and ______ seas may have contributed to the explosion of life during the Cambrian period.
South, Africa, Asia
Continents included in Gondwana were ______ America, A______, Australia, Antarctica, and parts of A______.
Carboniferous
In what period did Pangea form?
Decomposers
Large organic deposits built up during the Carboniferous period due to a lack of ______.
Triassic
During what period did Pangea begin to break up?
Jurassic
During which Period did birds evolve?
Warn Blooded
Being ______ ______ allowed mammals to better survive in volatile or extreme climates.
Petrified
Fossil that forms when mineral rich water soaks into small cavities and replaces it with minerals.
Molds and Casts
Fossil created when a structure is buried in sediment and then dissolved.
Preserved Remains
Fossil in which organisms are preserved with little change such as freezing or amber.
Trace
Fossil which provides indirect evidence of prehistoric life.
Radioactive Decay
A spontaneous process in which unstable nuclei break down.
Half Life
Length of time required for half of the radioactive atoms in a sample to decay.
5700
Suppose you found a bone that has a half life of 5700. The bone has 50% of its carbon. How old is the bone (just give number)?
20,000
Suppose you found something with a half life of 10,000 years. It has 25% of its carbon. How old is the object (just give the number)?
Eon
Largest span of geologic time.
Meteorite
What caused the mass extinction at the end of the Mesozoic?
Recent
"Cenozoic" means "______ life".
Cenozoic
What era are we currently in?
Hadean
What was the first period?
False
True or False; the first humans appeared in the Triassic period.
False
True or False; the first humans appeared in the Jurassic.
True
True or False; the first humans appeared in the Cenozoic.