unit one review for a and p 1
1/42
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
43 Terms
plasma membrane
A selectively permeable barrier that surrounds the cell, controlling the movement of substances in and out of the cell and maintaining homeostasis.
the head of a phospholipid is
hydrophilic and attracts water and polar (charged)
the tail of a phospholipid is
hydrophobic and repels water and nonpolar
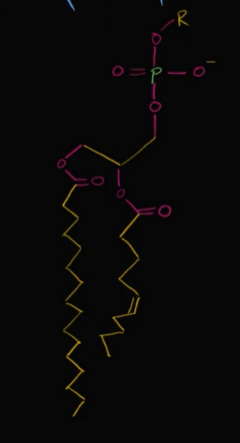
phospholipid
phospholipid tails are made of
hydrocarbons that come from fatty acids (nonpolar)
what kind of things can pass through the plasma membrane
Small nonpolar molecules and water
peripheral proteins
Proteins that are attached to the exterior or interior surfaces of the plasma membrane, playing roles in signaling and maintaining the cell's structure
example: hormones
integral protein
membrane protein that is involved in transporting substances across the membrane
lipid bound proteins
stuck on the interior surface of the membrane
channel proteins - have a hole in them and allow ions to pass through the channel membrane and allow things to exit the cell, don”t require atp
channel proteins
embedded within the phospholipid bilayer and allow ions such as Na+ to enter and exit the cell as needed, does not require ATP, as the ions are moving DOWN the concentration gradient and can be gated or non-gated for selective permeability.
carrier proteins
integral protein that attaches to the ion like a glove and transports it across the membrane. can goes against the concentration gradient which requires ATP
glycoprotein
chain of sugars attached to a protein and is used in signaling between proteins and cells, playing a crucial role in cell recognition and immune response.
endocytosis
The process by which cells internalize substances by engulfing them in a membrane-bound vesicle, allowing for the uptake of large molecules or particles.
phagocytosis - bacterial cells and organic
pinocytosis - liquids
receptor mediated - bind to receptors in membrane which initiates endocytosis, allowing specific substances to enter the cell as a coated vesicle
exocytosis
discharge of materials from membrane bound vesicles to the outer surface of the cell, allowing the release of substances like hormones or waste products.
sodium potassium pump
atp required
helps maintain resting membrane potential (more neg inside than outside the cell) as sodium and potassium are charged and need a protein to allow them to pass through the membrane
open on the intracellular side of cell with binding room for three Na+ ions which bind to the channel and phosphorylates the protein - atp transfers phosphate to the protein changing it’s shape which causes the protein to open on the extracellular side and pushes the Na+ out. 2 potassium ions can then bind to the protein and the phosphate is released, reverting the protein back to it’s original shape
low concentration to high (active transport)
more potassium in a cell and sodium outside the cell
sodium potassium concentration inside and outside the cell
The difference in concentration of sodium (Na+) and potassium (K+) ions across the cell membrane, with higher potassium concentrations inside the cell and higher sodium concentrations outside, which is crucial for maintaining resting membrane potential.
remember: 3 sodium ions outside, 2 potassium ions inside
covalent bonds
sharing of electrons between nonmetals
ionic bonds
transferring electrons from a metal to a nonmetal
metals and nonmetals
metals often transfer the electrons to the nonmetals
cations
positive charge and loose ions (usually metals)
anions
negative charge and gain electrons (usually nonmetals)
pH
measure of acidity is based on the amount of H+ ions are are present in a solution
what is the scale of pH
1 (acidic) - 14 (basic)
ph of water
7
ph of human blood
7.35-7.45
acidosis
low blood ph - can cause coma
alkalosis
high blood ph - causes contractions
monomers
small building blocks of polymers
monomer plus monomer
dimer
monomer plus dimer
trimer
monomer plus trimer
tetramer
tatramer plus monomer
polymer (macromolecules or complex molecules)
types of monomers
amino acids, nucleotides, sugars
types of polymers
proteins, carbohydrates, nucleic acids
carbohydrates
made up of sugars - monosaccharides and 3 to 7 carbons that serve as a primary energy source in living organisms.
allows glucose to dissolve
Glucose, fructose, and galactose are monosaccharides
functional group: aldehydes and ketose (carbonyl group)
monosaccharides
galactose, glucose, fructose
disaccharides
2 monosaccharides joined via glycosidic links
sucrose, lactose, maltose, cellulase (cell wall)
polysaccharides
long chains of monosaccharides
proteins
monomeric - macromolecules made of amino acids
polymeric - amino acids strung together to form protein chains, which make up specific proteins
nucleic acids
macromolecules that store and transmit genetic information :
monomeric - nucleotide (made of sugar and phosphate)
polymeric - DNA and rna
Nucleic acids are essential for encoding, transmitting, and expressing genetic information within living organisms.
lipids
macromolecules
made of glycerol (simple sugar) and fatty acids (hydrocarbons with a carboxyl at the end)
C.H.O (1:2:very little)
fats and oils
hydrophobic
ENERGY STORAGE
saturates = no double bonds
unsaturated = double bonds
ketoacidosis
ph drop due to too many ketone bodies which are produced from burning too much fat
beta oxidation
burning fat produces ketone bodies through a process where fatty acids are broken down in the mitochondria.