CFB 10: Pentose Phosphates
1/78
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
79 Terms
What is the pentose phosphate shunt?
Alternate pathway of glucose catabolism that also
is involved in the biosynthesis of pentose sugars (especially ribose) and NADPH2 through
the production of ribulose 5-P.
Ribulose 5-P is converted to ribose 5-P and other phosphorylated carbohydrates
What are the aliases of the pentose phosphate shunt?
Hexose monophosphate shunt
Phosphogluconate pathway
Why is it a shunt?
Because it starts with a glycolytic intermediate and can end with the production of other glycolytic intermediates
2 important products of the pentose phosphate pathway
Ribose-5-phosphate
NADPH
What is needed for nucleotide synthesis?
Ribose-5-phosphate
What is needed to reduce glutathione to synthesize fatty acids, NO, and steroids/sterols, to detoxify drugs, and is part of the respiratory burst?
NADPH
Pentose phosphate pathway accounts for what % of liver glucose metabolism?
5-10%
More in adipocytes
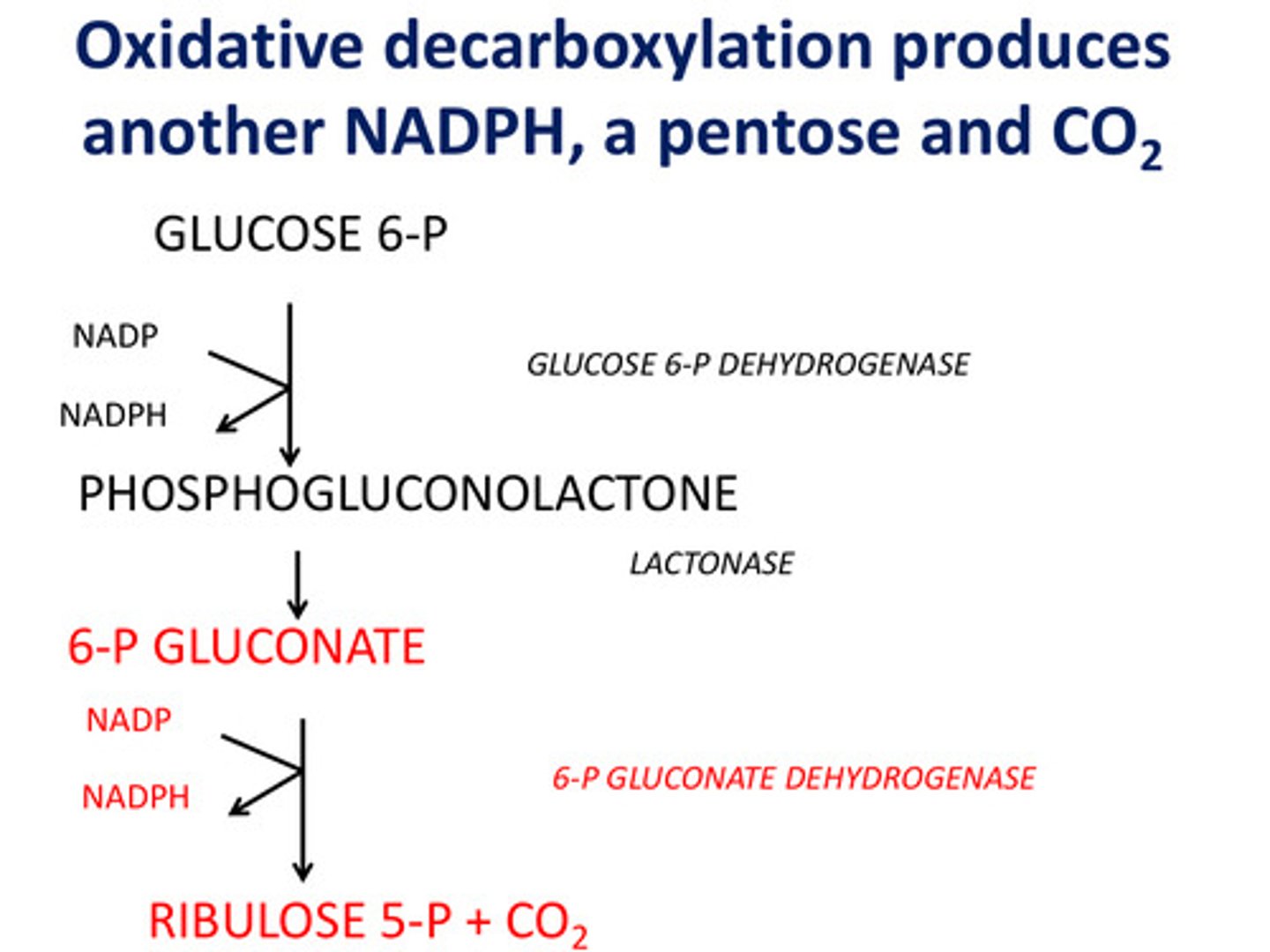
What does the first oxidative portion of the shunt produce? While converting what?
2 NADPHs while converting G6P to the pentose ribulose-5-phosphate and CO2
What is the first enzyme of the pentose phosphate pathway?
Glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase
What is the key regulated step of the pentose phosphate pathway?
Glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase
What does oxidative decarboxylation produce?
Another NADPH, a pentose, and CO2
NADP/NAPDH uses the same chemistry as NAD+/NADPH, but in the opposite ________.
Opposite polarity (i.e. reduction reactions)
Is there more NADPH or NADP?
NADPH
Is there more NADH or NAD+?
NAD+
T/F: The phosphate provides a "handle" to allow enzymes to select the coenzyme and functions in the chemistry.
False; does NOT function in the chemistry
What is the NADPH-mediated reaction in fatty acid synthesis?
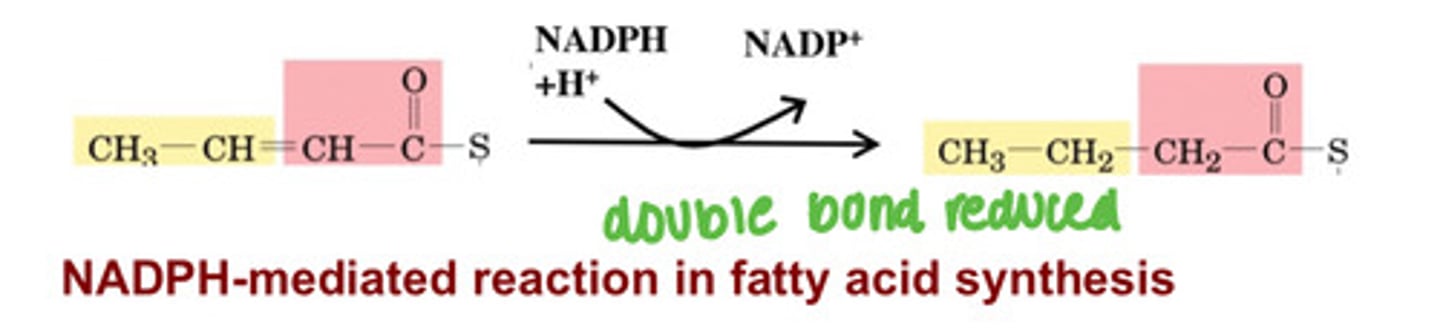
Uses for NADPH: synthesis
Fatty acid synthesis
Cholesterol synthesis
Neurotransmitter synthesis
Nucleotide synthesis
Uses for NADPH: detoxification
Reduction of oxidized glutathione
Cytochrome P450 monooxygenases
What happens to pentoses in the second, non-oxidative phase?
Pentoses are interconverted
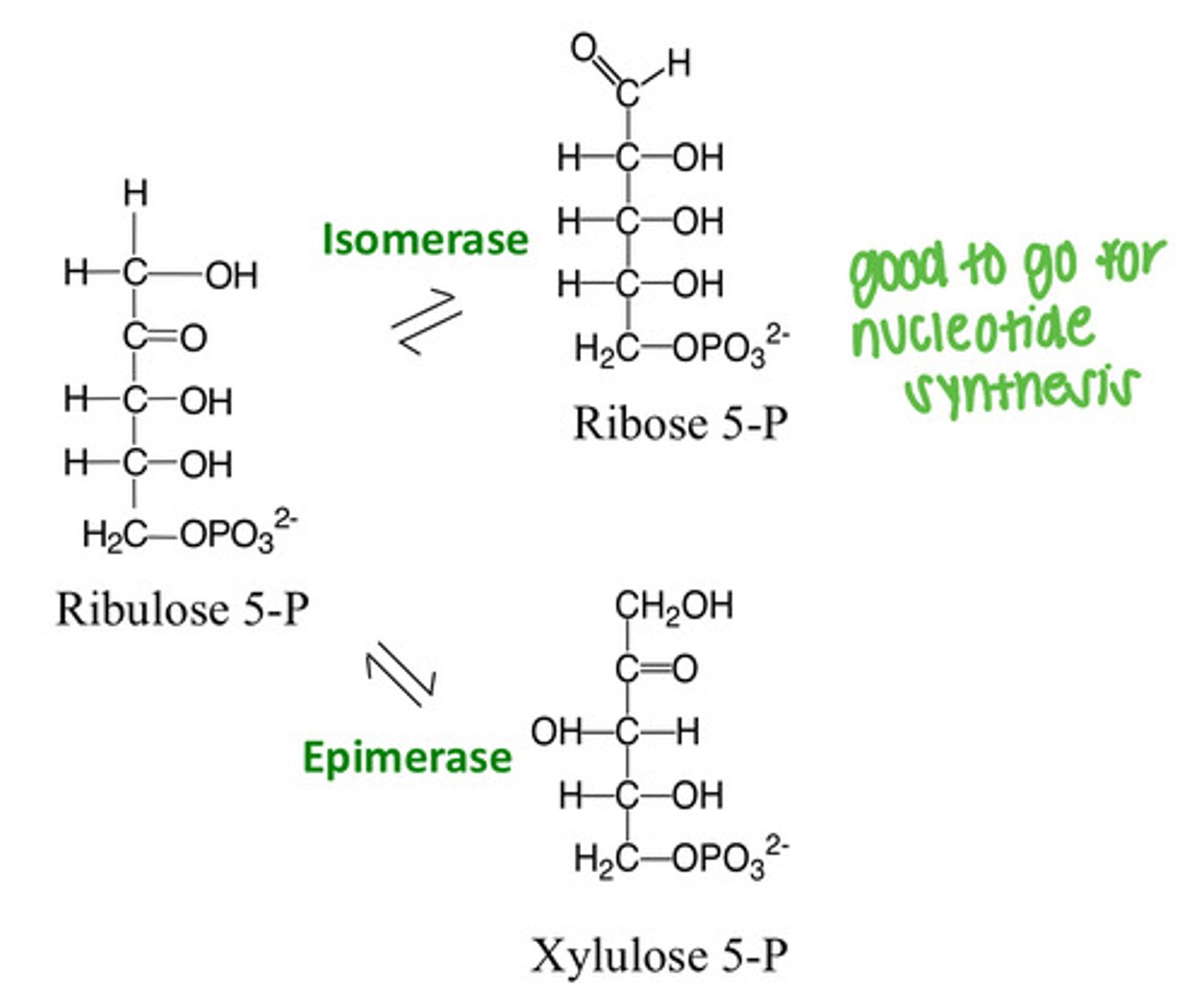
What happens to carbon skeletons in the second, non-oxidative phase?
Carbon skeletons rearranged
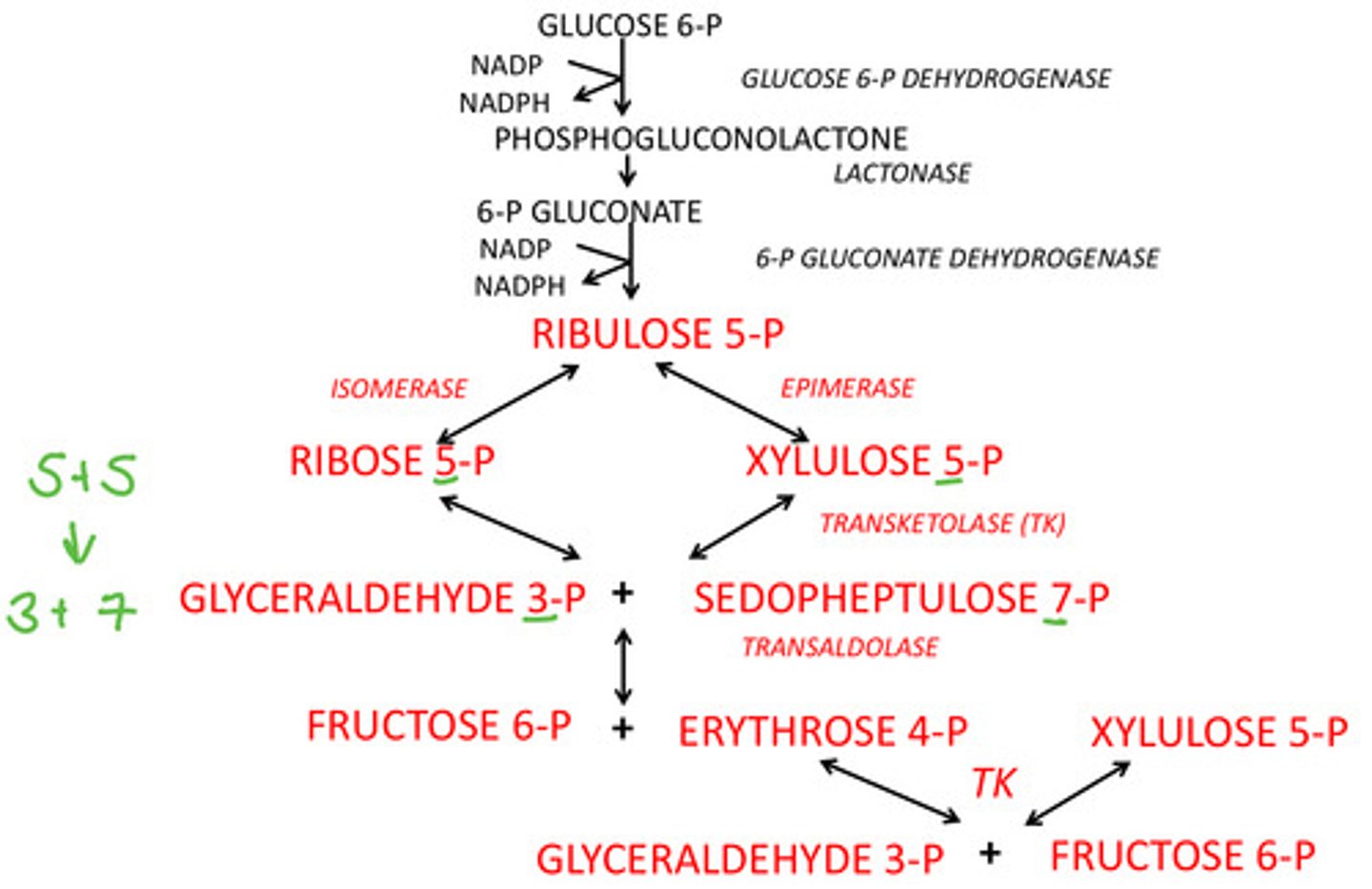
What transfers 2 carbon units using thiamine?
Transketolase
What is the disease associated with a thiamine deficiency?
Wernicke-Korsakoff (alcohol abuse)
Wet or dry beriberi (neurological or bodily)
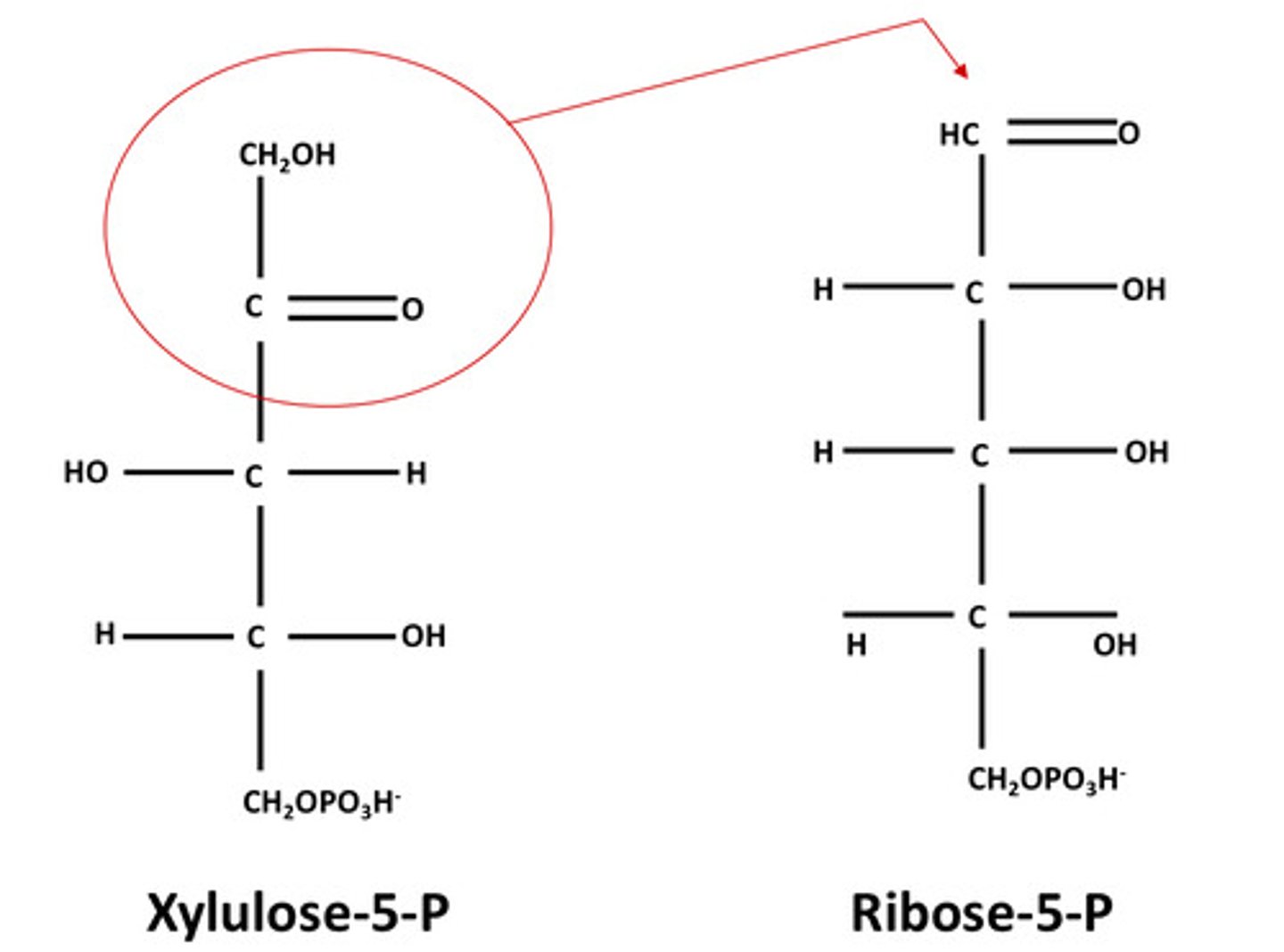
What transfers 3 carbon units?
Transaldolase
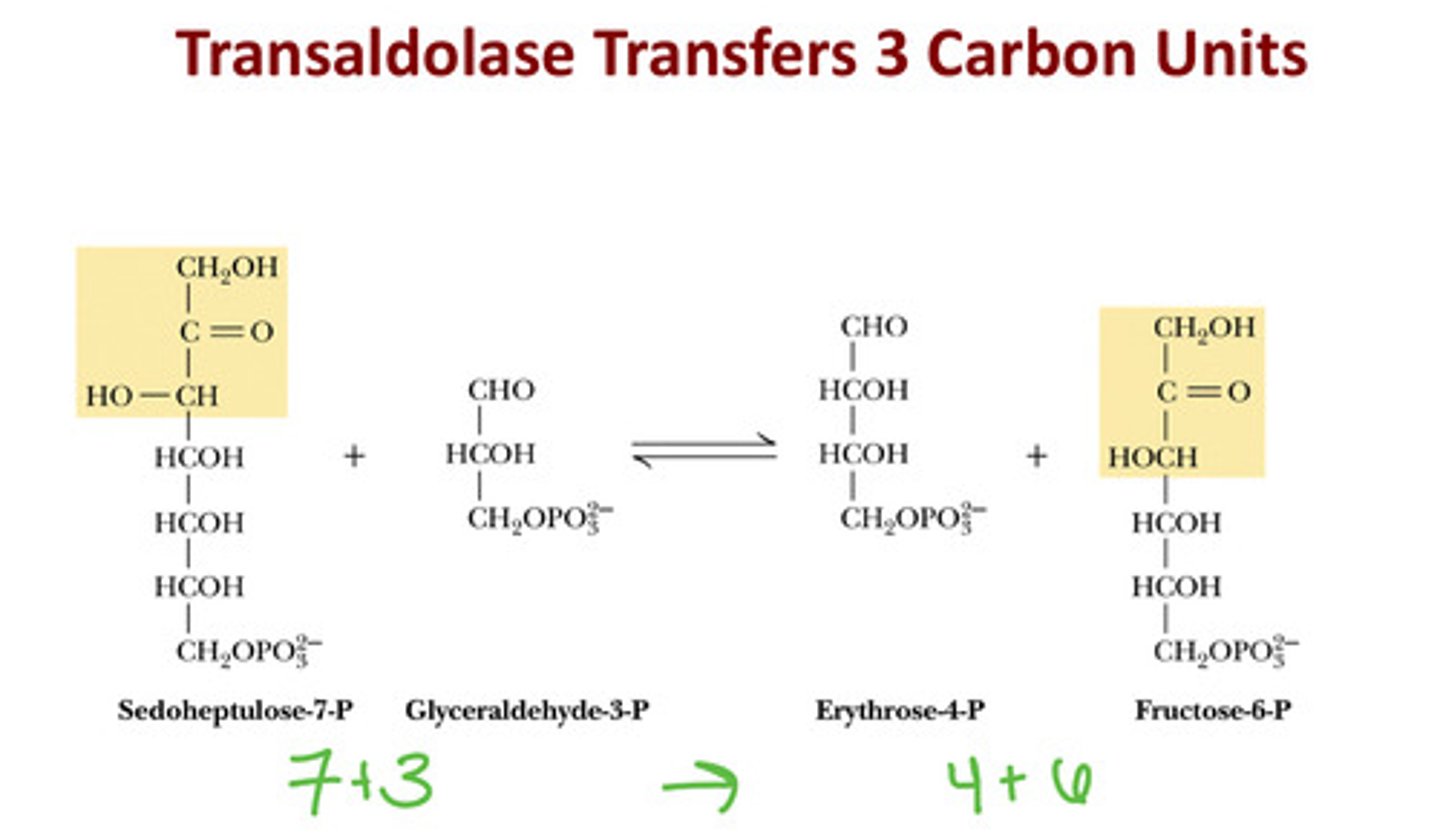
What reaction does transketolase do first?
Xylulose 5-P + Ribose 5-P →Sedoheptulose 7-P + Glyceraldehyde 3-P
What reaction does transaldolase do?
Sedoheptulose 7-P + Glyceraldehyde 3-P → Erythrose 4-P + Fructose 6-P
What reaction does transketolase do second?
Xylulose 5-P + Erythrose 4-P → Glyceraldehyde 3-P + Fructose 6-P
Reversible interconversion of Pentose-P and glycolytic intermediates:
3 Pentose-P → 1 Triose-P + 2 Hexose-P
What are the different modes of the pentose phosphate pathway?
NADPH ~ Ribose
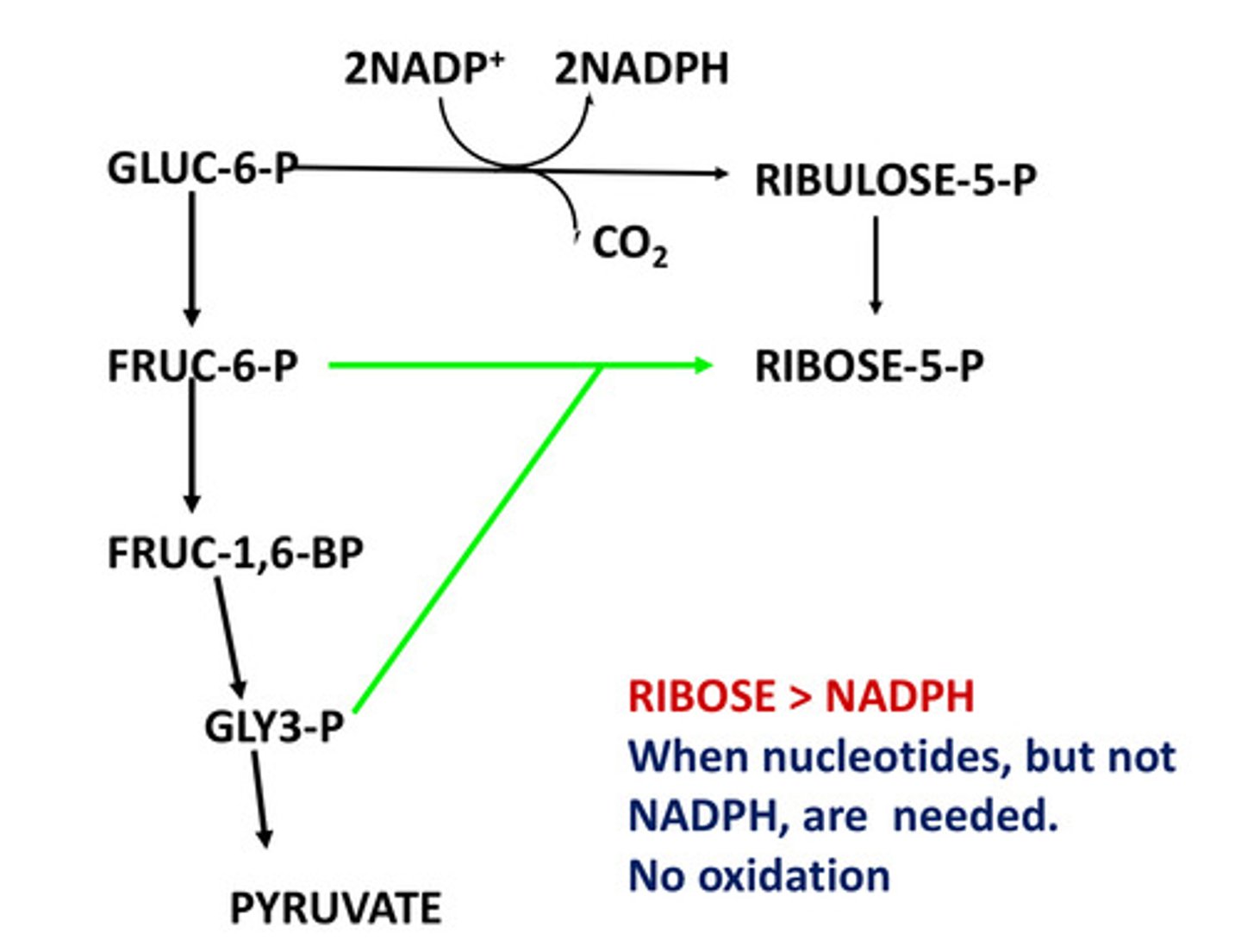
Ribose > NADPH
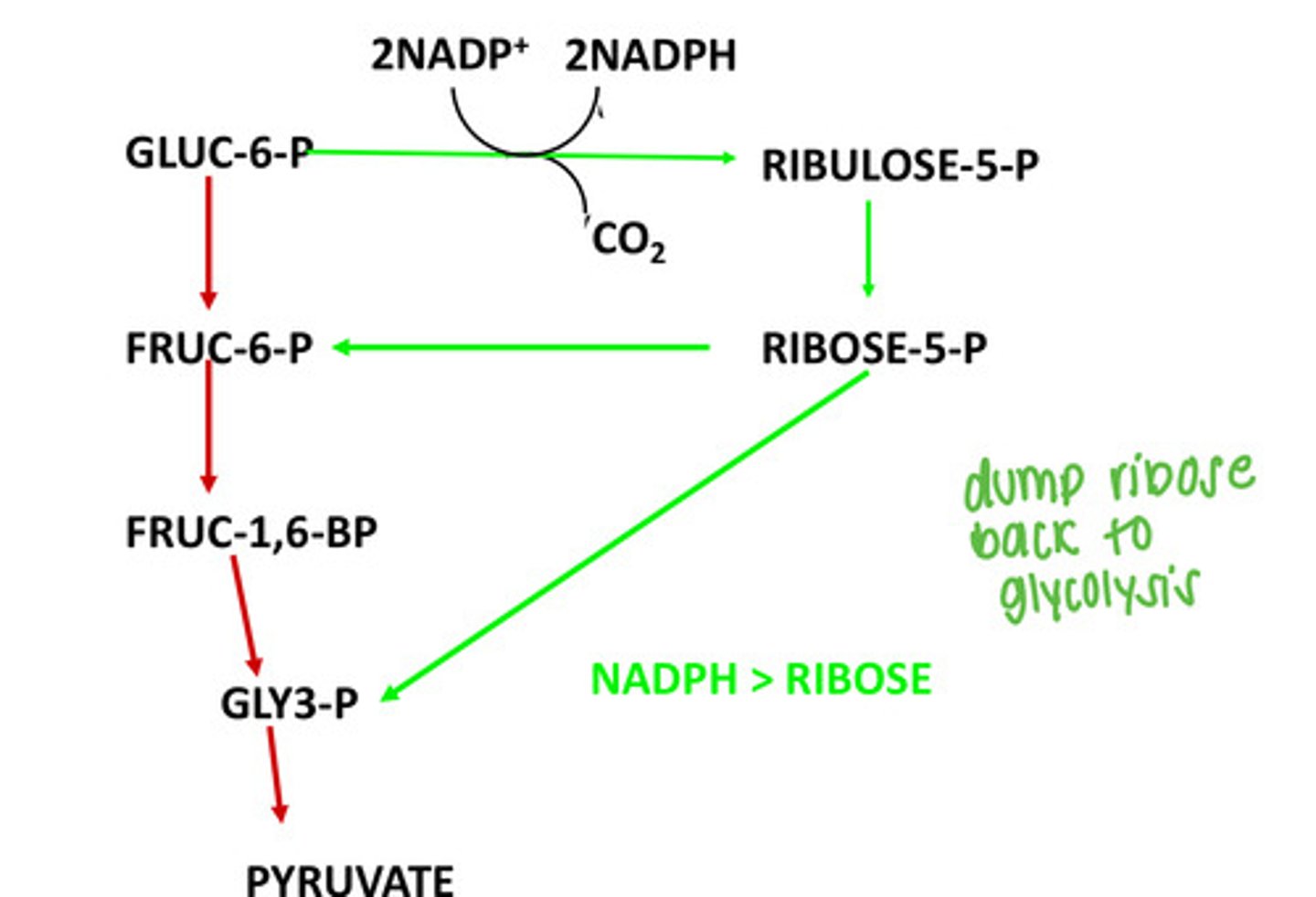
NADPH > Ribose
When is the ribose > NADPH mode used?
When nucleotides, but not NADPH are needed
No oxidation
When is NADPH > ribose mode used?
Dump ribose back to glycolysis
The non-oxidate portion of the pentose phosphate shunt:
Can lead to synthesis of pentose phosphates from glycolytic intermediates
3 multiple choice options
What is the rate-limiting step of the pentose phosphate shunt?
Glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase
What does G6P Dehydrogenase catalyze?
G6P → Phosphogluconolactone
G6P dehydrogenase is inducible by _______.
Insulin
Allosteric feedback of G6P Dehydrogenase is inhibited by _____.
NADPH
What is the coenzyme of G6P Dehydrogenase reaction?
NADP+
What inhibits the G6P Dehydrogenase reaction?
NADPH
How does the actual V compare with the potential Vmax?
1% of actual activity
Highly restricted
What reaction does 6-P Gluconate Dehydrogenase do?
6-P Gluconate → Ribulose 5-P + CO2
What enzyme is active in many cancers and may be important for some T cells?
6-P Gluconate Dehydrogenase
When is oxygen bad for you?
Hydroxyl radical is very active; can damage DNA and RNA
The _________ of oxygen yields highly reactive speies.
Reduction
What can O2- produce?
H2O2
What can O2- and H2O2 produce?
Hydroxyl radicals
What is the Haber-Weiss Reaction?
Production of hydroxyl radical, water, and oxygen from hydrogen peroxide and superoxide
What is the Fenton Reaction?
Production of hydroxyl radical and hydroxyl ion from hydrogen peroxide with the oxidation of ferrous (II) ion
Iron of hemoglobin and O2 react to give...
Superoxide
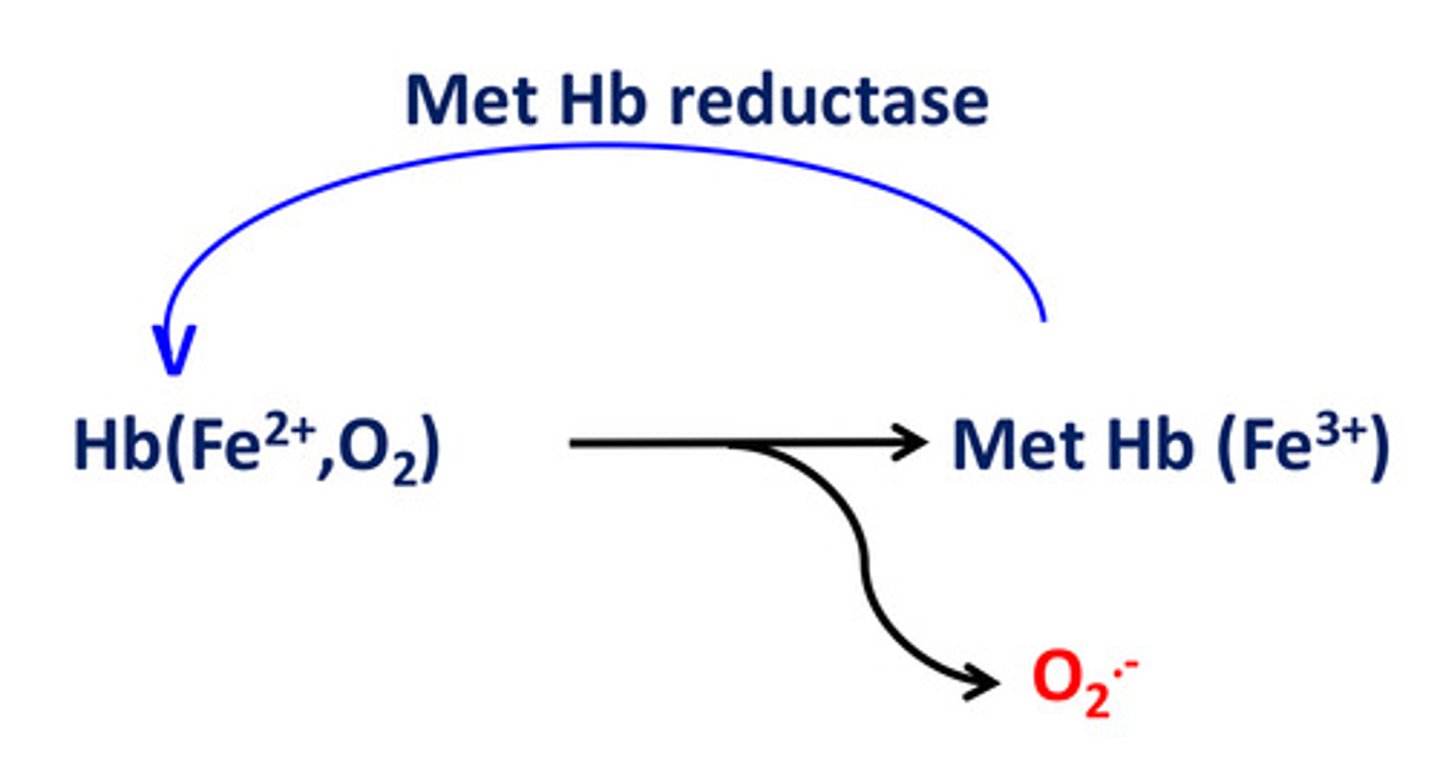
When is generation of radicals good?
"Respiratory burst" in neutrophils
What is defective in Chronic Granulomatous Disease (CGD)?
Respiratory burst
Injury of what is thought to be important in many disease states?
Atherogenesis (oxidation of LDL)
Ischemia/reperfusion injury
Alcoholism
Neurodegenerative disease (ALS)
Acute renal failure
Emphysema
Free radical injury
What can inactivate radicals?
Antioxidants
Vitamins A, C, and E
What converts superoxide to hydrogen peroxide for protection from radicals?
Superoxide dismutase (SOD)
What is required for the reduction of peroxides by peroxidase?
Glutathione (GSH)
What maintains the supply of reduced glutathione needed to destroy peroxide?
NADPH produced by G6P Dehydrogenase
What is responsible for maintaining the intracellular environment in a reduced state so that disulfide bonds in proteins stay reduced?
Glutathione
What is the most reactive oxygen species?
Hydroxyl radical
Which of the following enzymes used NADPH as the coenzyme?
Glutathione reductase
3 multiple choice options
What is characterized by "Heinz bodies" in RBCs when the cells are exposed to an oxidizing chemical in vitro?
G6PDH deficiency
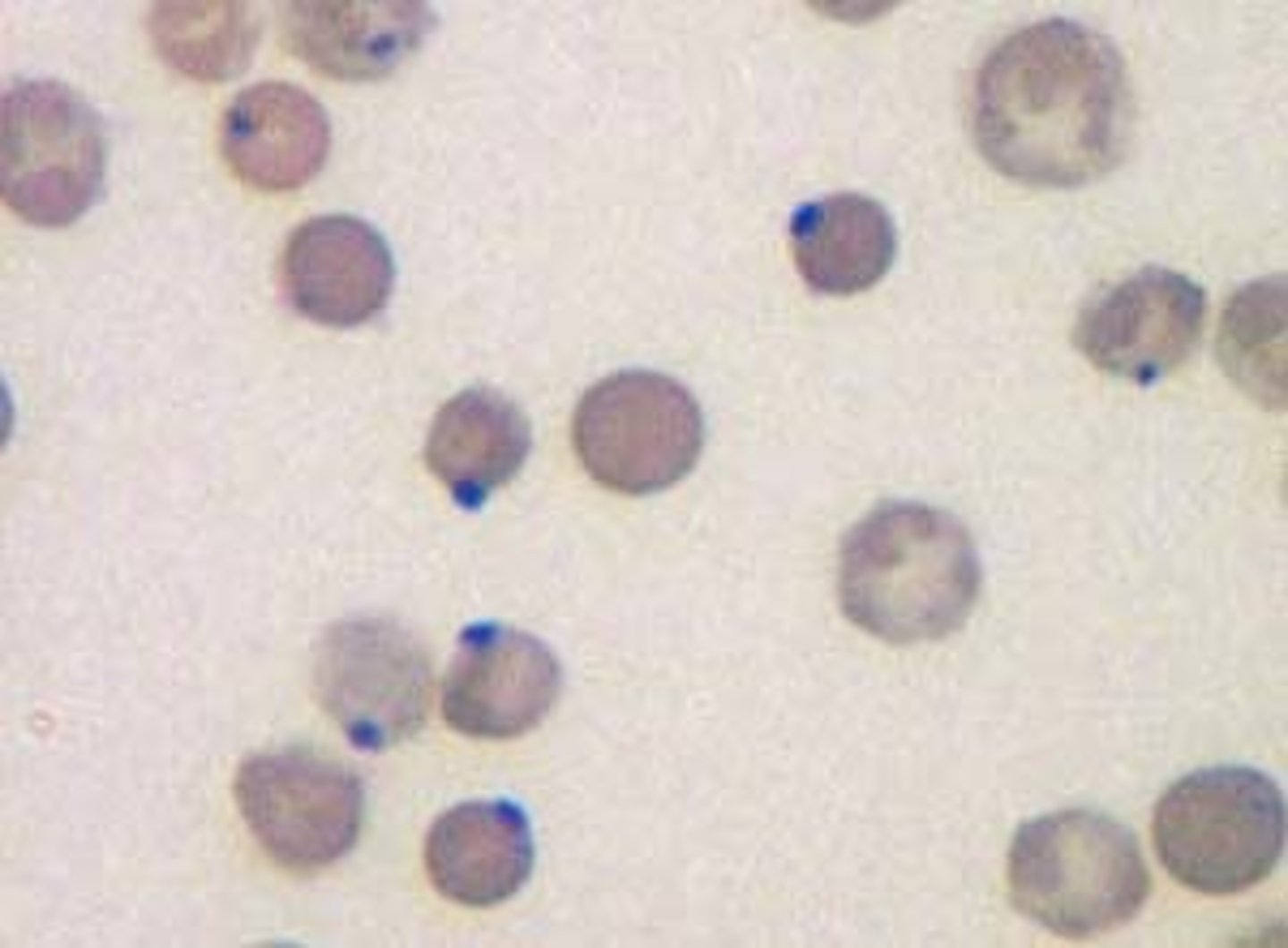
What are immature RBCs that are usually 1% of circulating RBCs?
Reticulocytes
What is an elevation of reticulocytes indicating active erythropoiesis in bone marrow?
Reticulocytosis
What does G6PD deficiency track with?
Malaria and sickle cell
What do these drugs/foods cause?
Sulfonamides
Aspirin
Quinadine and quinine
Napthylene (mothballs)
Fava beans
Hemolytic anemia
You are doing a substantial procedure on a patient. Out of concern for infection, you prescribe prophylactic antibiotics. Two days later, the patient calls complaining that his urine has turned a very dark color. What is going on?
G6P Dehydrogenase deficiency
In G6P dehydrogenase deficiency, what change from normal in red blood cells leads to hemolytic anemia?
Decreased concentrations of NADPH
Why are red cells particularly sensitive to oxidative damage?
Other cells have alternative pathways to produce NADPH, for example malic enzyme (malate dehydrogenase)
Red cells don't do this but other cells in the body do!
The pentose phosphate shunt produces _________________ used for nucleotide synthesis and _____ used in reductive biosynthesis.
Ribose-5-phosphate for nucleotide synthesis
NADPH for reductive biosynthesis
Why is NADPH>>NADP and NAD+>>NADH in oxidative reactions?
Since NADPH is mostly used for biological reduction
What does the pentose phosphate shunt start with?
Oxidative portion that generates NADPH, CO2 and pentose phosphate
What is the major regulatory point?
G6P dehydrogenase (first PPS enzyme)
Deficiencies in G6PDH are _-linked. How may unsuspected deficiency manifest?
X-linked
Anemia after oxidative challenge
What does the non-oxidative part of the shunt interconvert?
Pentoses (ribose-5-P) and converts them to glycolytic intermediates by transketolase (2 carbon transfer) and transketolase (3 carbon transfer) activity
The pentose phosphate pathway can make ribose directly from what?
Glycolytic intermediates without oxidation
What is reduced to water in single electron steps?
Molecular oxygen
What reactive intermediates are formed?
Superoxide, peroxides, and hydroxyl radicals
What can the reactive intermediates be used to do?
Inactivate pathogens
T/F: All intermediates cause tissue damage.
True
Formation of atherosclerotic plaques
What reduces superoxide to peroxide?
Superoxide dismutase (SOD)
What reduces peroxide to water and oxidizes glutathione?
Glutathione peroxidase (contains selenium)
What uses NADPH to regenerate reduced glutathione needed by glutathione peroxidase?
Glutathione reductase