Topic 3 - The Voice of the Genome
1/33
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
34 Terms
Structure of eukaryotic cell
have nucleus (contains DNA), mitochondria and chloroplasts (which are all membrane bound organelles)
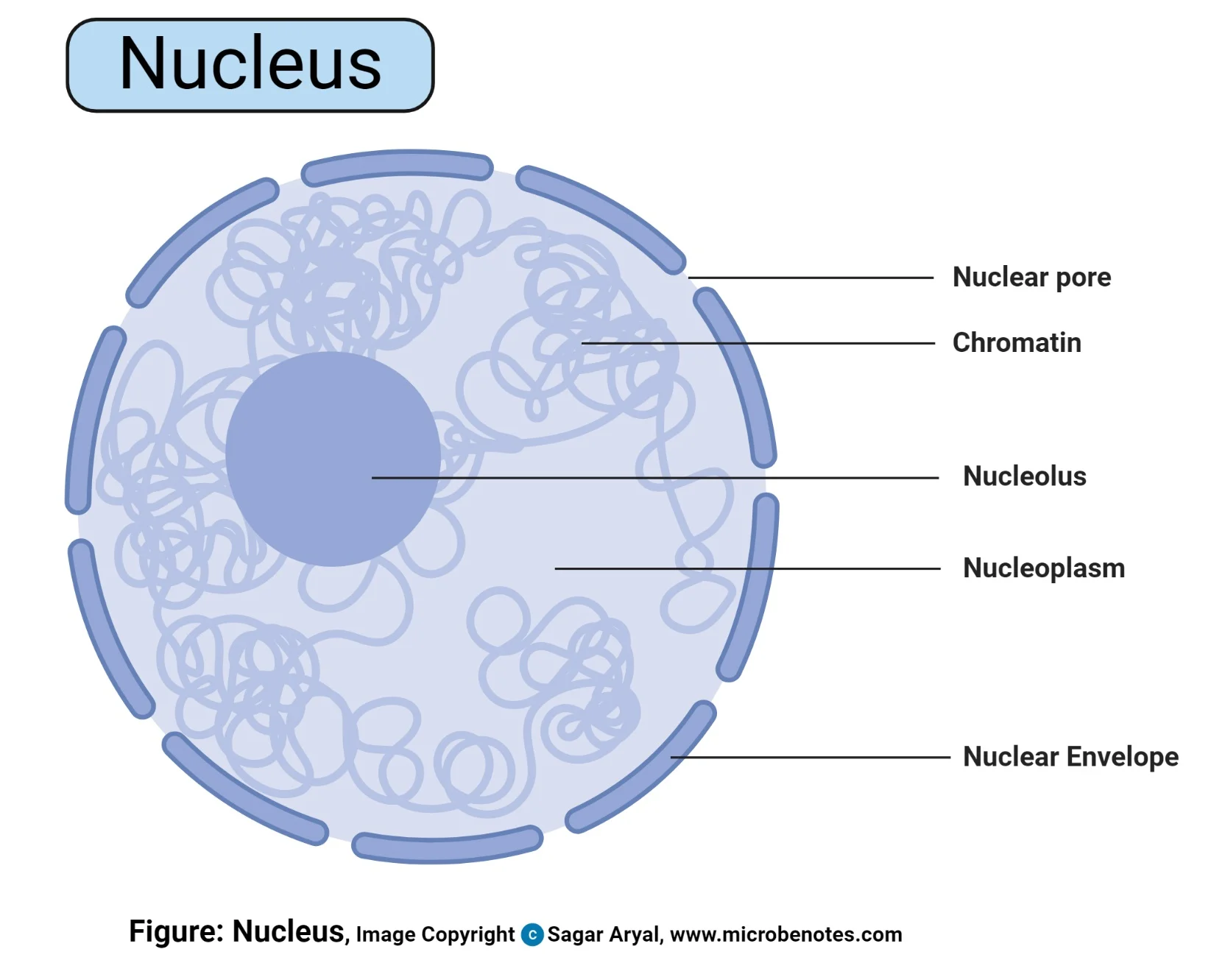
Nucleus
Structure:
surrounded by a double membrane called the envelope. which contains pores enabling molecules to enter and leave the nucleus
Function:
stores the nucleolus and the DNA
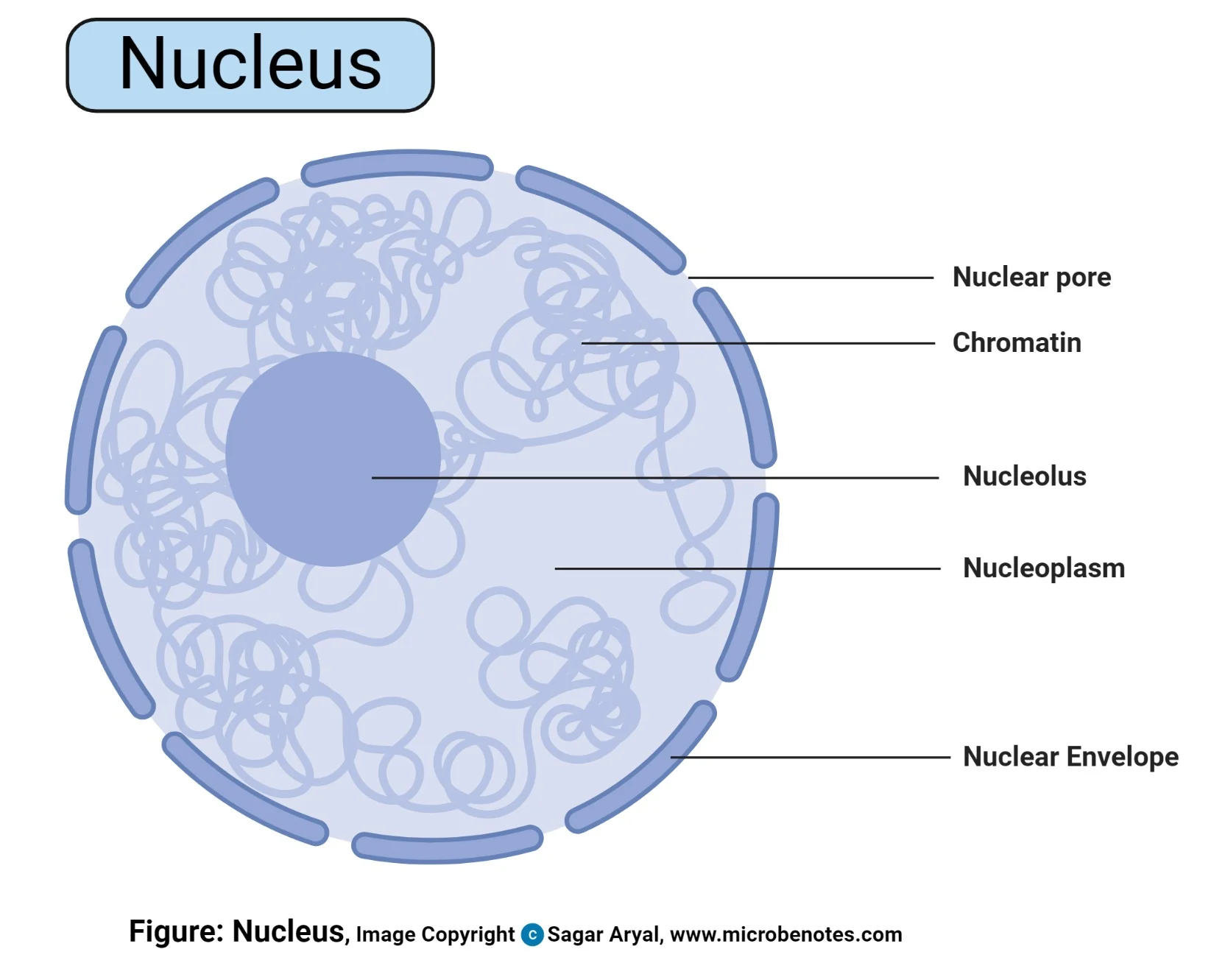
Nucleolus
Structure:
located in the middle of the nucleus
Function:
site of ribosome production
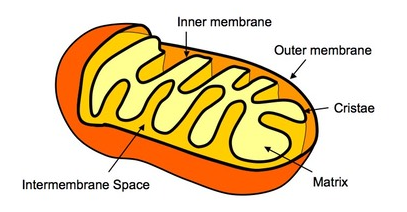
Mitochondrion
Structure:
oval shaped membrane bound by a double membrane (envelope)
The inner membrane is folded to form projections called cristae with a fluid matric on the inside containing enzymes for cellular respiration
Function:
site for aerobic respiration
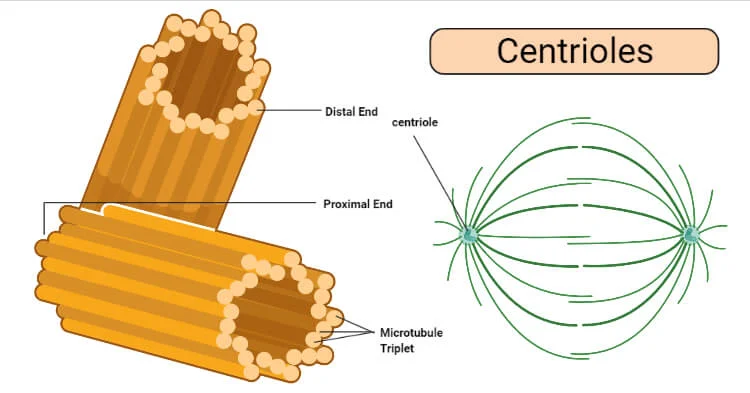
Centrioles
Structure:
hollow tubes made up of 9 proteins, 9 protein microtubes
globular protein chains
always come in a pair
Function:
spindle
help transport in cytoplasm
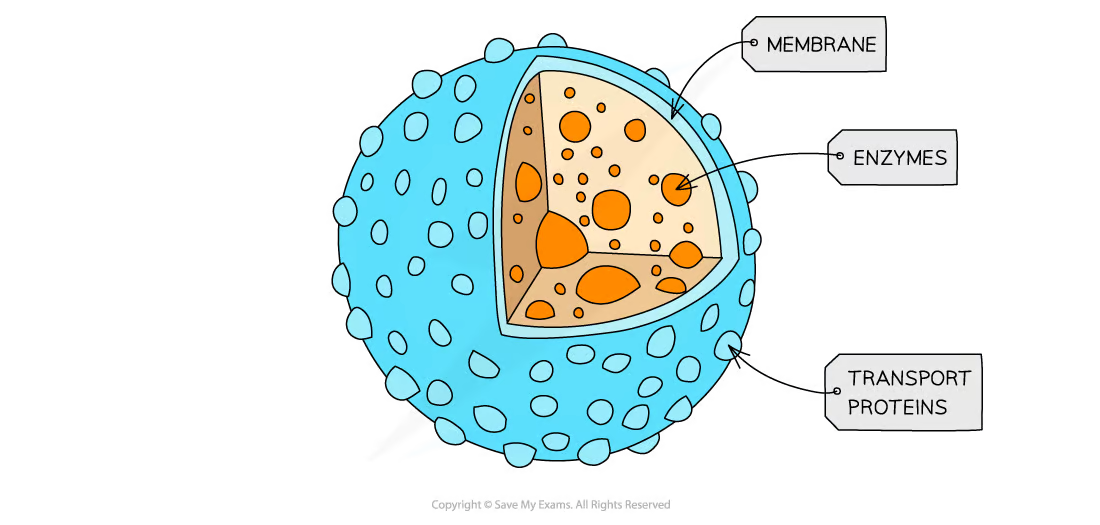
Lysosome
Structure:
vesicles containing digestive enzymes, bound by a single membrane.
protein
Function:
intracellular digestion
Autolytic function (killing of cells)
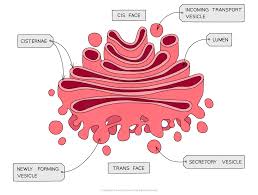
Gogli apparatus
Structure:
a series of fluid-filled, flattened and curved sacs with vesicles surrounding the edges.
Function:
transport of proteins and lipids
produces lysosomes
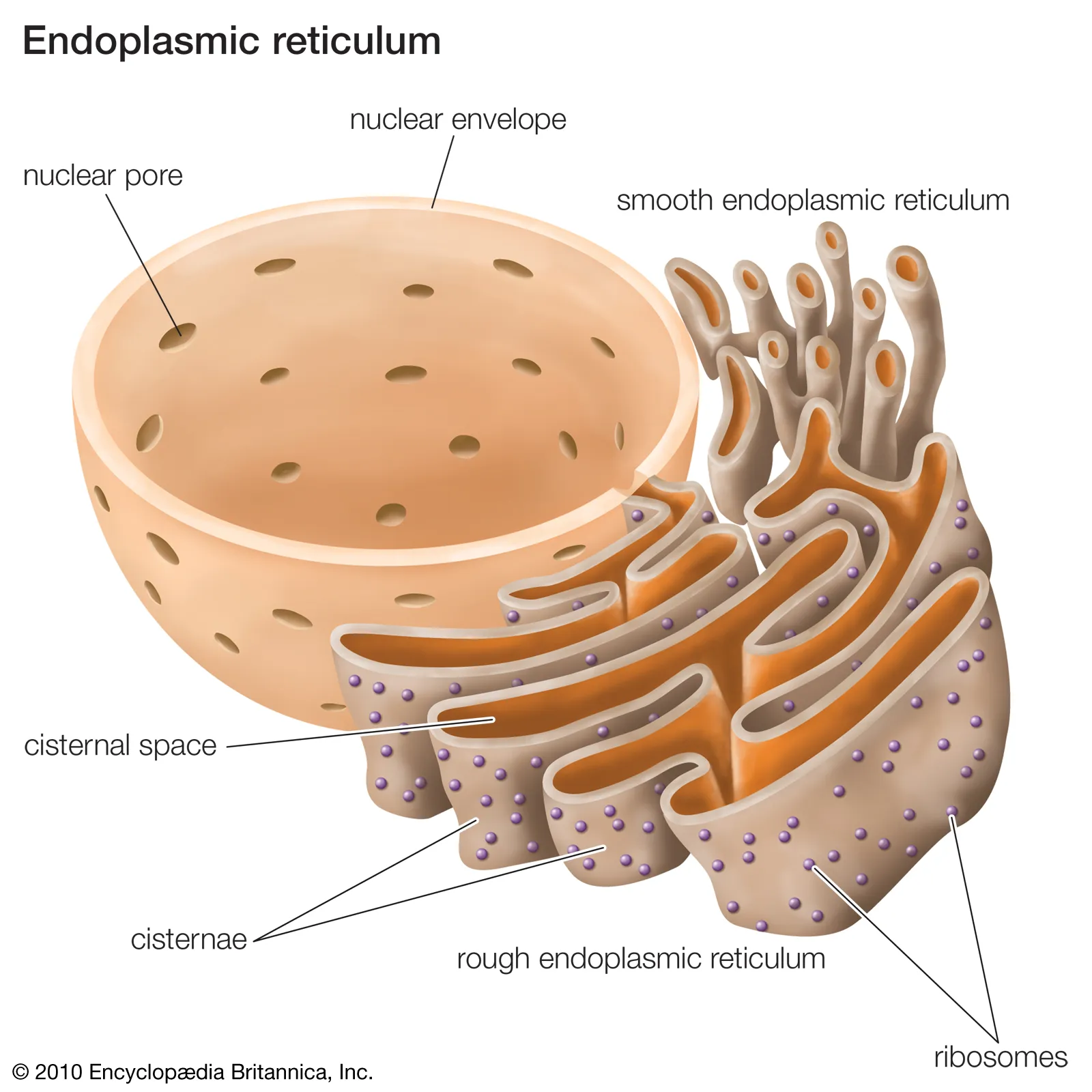
Smooth endoplasmic reticulum (SER)
Structure:
system of interconnected membrane bound flattened sacs
Function:
produces and processes lipids +steroids
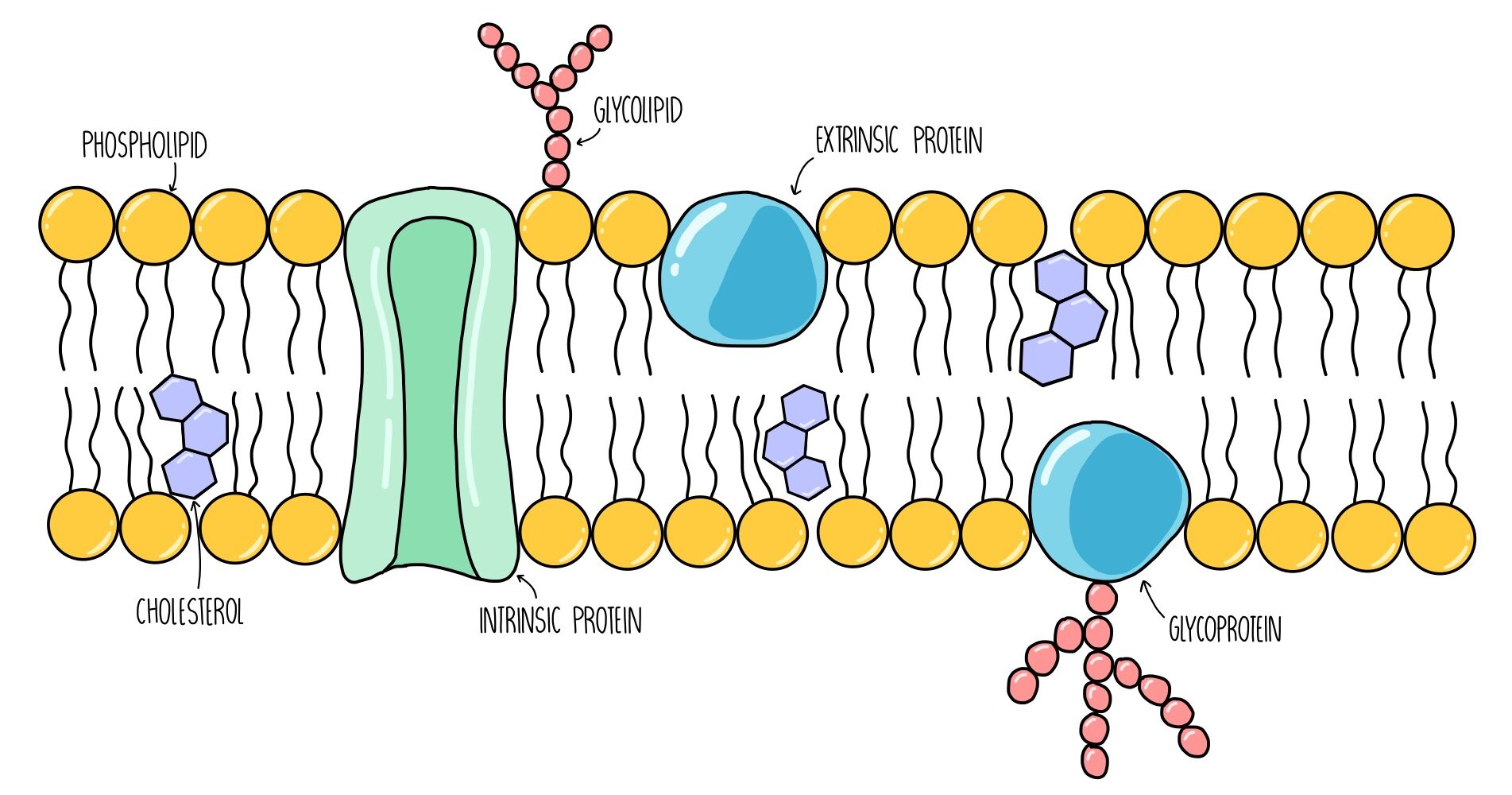
Cell surface membrane
Structure:
found on the outside of the cytoplasm
two rows of phospholipids
in the phospholipid bilayer you find channel and carrier proteins
glycolipids and glycoproteins
cholesterol
Function:
control what exits and enters the cell
Phospholipid - hydrophilic head, hydrophobic tails for small and non-polar molecules to go through
Channel & carrier proteins - facilitated diffusion of large and charged molecules
Glycoproteins & glycolipids - cell adhesion
Cholesterol - controls fluidity
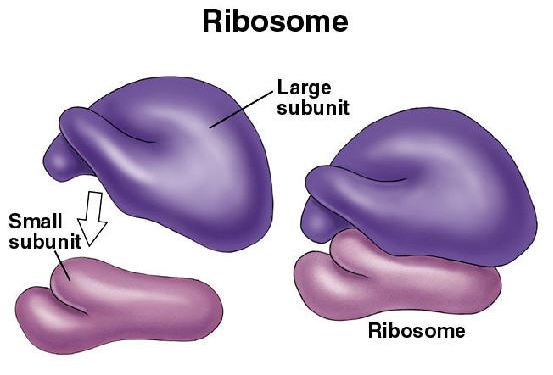
Ribosomes
Structure:
made up of RNA & proteins
Function:
site of protein synthesis
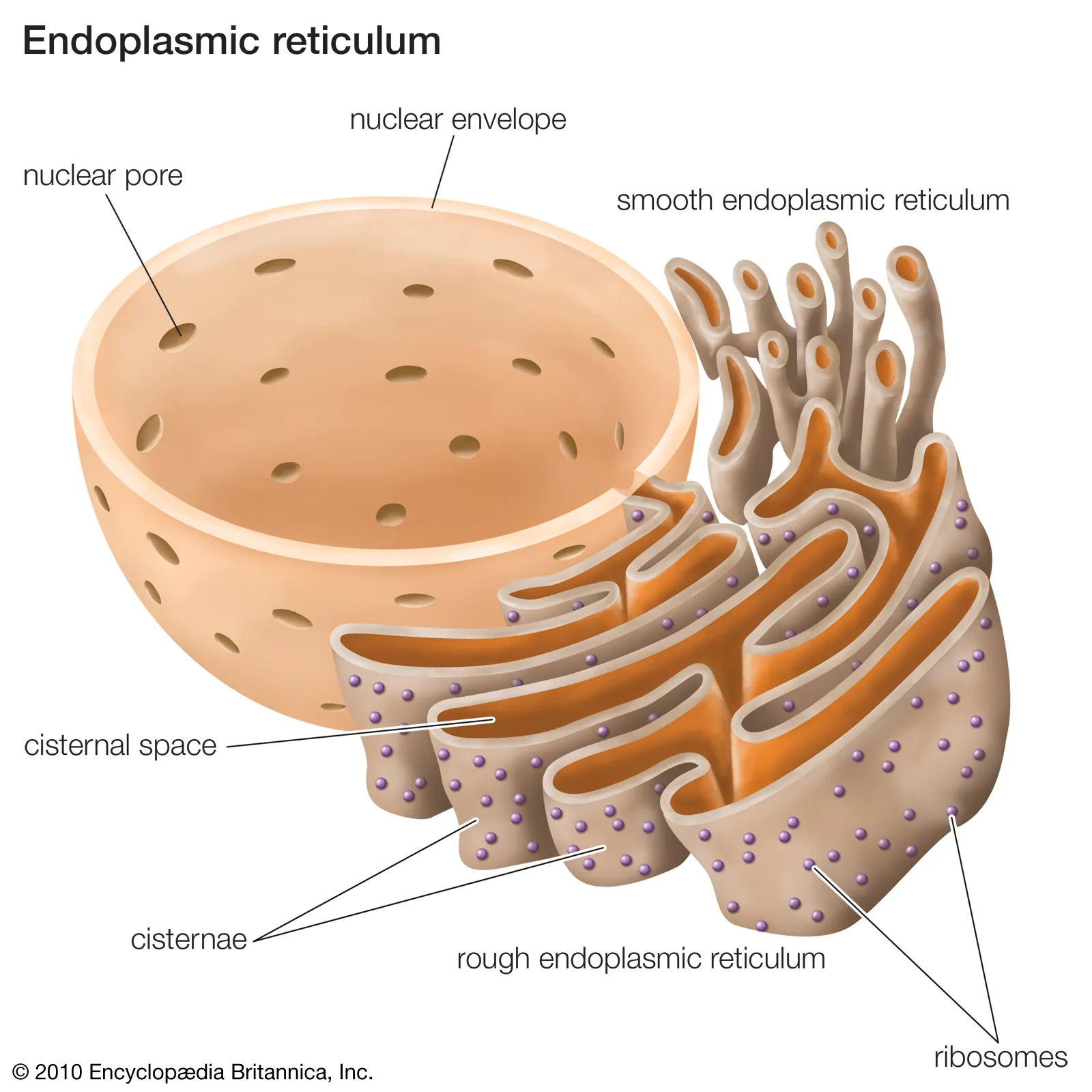
Rough endoplasmic reticulum (RER)
Structure:
system of interconnected membrane bound flattened sacs that have ribosomes attatched to them on the surface.
Function:
folds and processes proteins made on the ribosomes; often located close to the nucleus.
Explain the role of the rER and the Golgi apparatus in protein transport within cells + their role in the formation of extracellular enzymes
Rough Endoplasmic Reticulum (rER):
Protein Synthesis: Ribosomes on the rER synthesize proteins, including enzymes.
Folding and Modification: Newly synthesized proteins enter the rER lumen, where they are folded and undergo initial modifications (e.g., glycosylation).
Golgi Apparatus:
Further Modification: Proteins from the rER are transported to the Golgi apparatus in vesicles. Here, they undergo further modifications, such as additional glycosylation and sulfation.
Sorting and Packaging: The Golgi apparatus sorts and packages proteins into vesicles based on their final destinations. Extracellular enzymes are packaged into secretory vesicles.
Formation of Extracellular Enzymes:
Transport to Cell Membrane: Secretory vesicles containing extracellular enzymes move to the cell membrane.
Exocytosis: Vesicles fuse with the cell membrane, releasing the enzymes outside the cell to perform their functions.
Structure of a prokaryotic cell
nucleoid, cell wall, cell membrane, plasmids, flagella, pili, capsule, ribosomes, cytoplasm
Cell wall
Structure:
The cells rigid outer layer made out of peptidoglycan
Function:
provides strength and support
Capsule
Structure:
Protective slimy layer
Function:
Helps the cell to retain moisture and adhere to surfaces
Plasmid
Structure:
Circular
Function:
DNA
flagellum
Structure:
A tail-like structure
Function:
rotates to move the cell
pili
Structure:
hair-like structures
Function:
attach to other bacterial cells to allow the exchange of plasmids
ribosomes
Structure:
Composed of 2 subunits
Function:
site of protein synthesis
mesosomes
Structure:
infoldings of the inner membrane
Function:
May contain enzymes required for respiration
May just be artefacts from the preparation process for microscopy
Ovum structure
Nucleus, cytoplasm, cortical granules, zona pellucida. follicle cells, lipid droplets
Nucleus function
Contains the genetic material (haploid no. Of chromosomes)
Cytoplasm function
Contains nutrients and organelles needed for embryo development
cortical granules function
Releases enzymes after fertilisation to harden the zona pellucida and prevent polyspermy
zona pellucida function
A jelly-like layer that protects the ovum and regulates interactions with sperm during fertilisation
follicle cells function
Form a protective coating around the egg
lipid droplets function
Store energy for early development stages
Sperm structure
nucleus, acrosome, head, mid-section, flagellum
Nucleus function
Contains the genetic material (haploid no. Of chromosomes)
Acrosome function
Contains digestive enzymes which break down the zona pellucida an allow sperm to penetrate the egg
Head function
Contains the nucleus and acrosome
Mid-section function
Contains mitochondrion which provides energy for the rotation of the flagellum which allows the cell to move
flagellum function
For movement to swim to the egg
Describe the process of fertilisation
The sperm head meets the zona pellucida and the acrosome reaction occurs - enzymes digest the zona pellucida.
The sperm head fuses with the cell membrane of the egg allowing the sperm nucleus to enter the egg cell.
The cortical reaction occurs which causes the zona pellucida to harden and prevents polyspermy.
The nuclei fuse and a full set of chromosomes is restored, forming a diploid zygote.