Ch.6 Microbial Nutrition and growth
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/73
Earn XP
Description and Tags
McGraw -Hill Assignment
Last updated 8:03 AM on 11/22/22
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
74 Terms
1
New cards
Carbon, nitrogen, oxygen, and hydrogen are considered ________ nutrients because they are required in relatively large quantities and cannot be manufactured by microbes themselves.
Essential
2
New cards
Uses sunlight as an energy source and carbon dioxide as a carbon source (example: cyanobacteria)
Photoautotroph
3
New cards
Uses simple inorganic compounds for energy and carbon dioxide for a carbon source (example: methanogens)
Chemoautotroph
4
New cards
Uses sunlight as an energy source and an organic carbon source (example: purple photosynthetic bacteria)
Photoheterotroph
5
New cards
Converts nutrients from other organisms into energy and uses an organic carbon source (example: protozoa)
chemoheterotroph
6
New cards
Metabolizes organic matter of dead organisms for energy and uses an organic carbon source (example: fungi)
saprobe
7
New cards
Utilizes the tissues of a live host and an organic carbon source (example: pathogens)
parasite
8
New cards
Move the terms to their correct category to test your understanding of transport processes in cells.
passive transport: simple diffusion, facilitated diffusion, osmosis
Active transport: carrier- mediated transport, phagocytosis, pinocytosis
Active transport: carrier- mediated transport, phagocytosis, pinocytosis
9
New cards
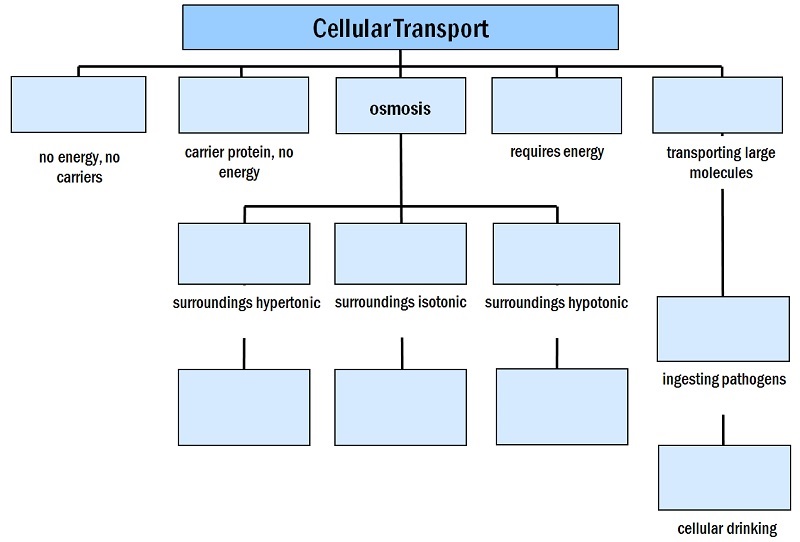
Move the terms into the correct empty boxes to complete this concept map describing cellular transport.
Left --> right line 1
simple diffusion, facilitated diffusion, OSMOSIS, active transport, bulk transport
Line 2
cell in 20% NaCl, Cell in saline, Cell in pure H2O
Line 3: Phagocytosis
Line 4:
net flow of water out of cell, no net flow of water in or out, net flow of water into cell
Line 5: pinocytosis
simple diffusion, facilitated diffusion, OSMOSIS, active transport, bulk transport
Line 2
cell in 20% NaCl, Cell in saline, Cell in pure H2O
Line 3: Phagocytosis
Line 4:
net flow of water out of cell, no net flow of water in or out, net flow of water into cell
Line 5: pinocytosis
10
New cards
Describes an organism that requires oxygen for growth and has the enzymes to remove toxic by-products of oxygen metabolism
obligate aerobe
11
New cards
Describes an organism that can grow in the presence of oxygen and can detoxify it, but can also grow in the absence of oxygen
facultative anaerobe
12
New cards
Describes an organism that cannot grow at normal atmospheric oxygen concentrations, but does require a small amount of oxygen for growth
Microaerophile
13
New cards
Describes an organism that is unable to use oxygen and lacks the enzymes to detoxify oxygen, thus requiring the absence of oxygen for growth
Obligate anaerobe
14
New cards
Describes an organism that does not use oxygen, but can grow to a limited extent in the presence of oxygen
Aerotolerant Anaerobe
15
New cards
With respect to oxygen requirements, an _________ can use gaseous oxygen and possesses enzymes to process toxic oxygen products. (1)
aerobe
16
New cards
Expanding on this classification, an ______ aerobe cannot grow without oxygen. (2)
obligate
17
New cards
______________ do not grow at normal atmospheric oxygen concentrations, but they do require very minute concentrations of oxygen for metabolism. (3)
Microaerophiles
18
New cards
Still other organisms, called__________, can grow with or without oxygen, but grow faster when oxygen is present. (4)
facultative anaerobes
19
New cards
_______ represent a final group of organisms, whose members lack the required enzymes needed for using oxygen in respiration and may not be able to tolerate any free oxygen in their environment ___________.
-Anaerobes
- Obligate anaerobes
- Obligate anaerobes
20
New cards
hypotonic condition
net diffusion of water into cell
21
New cards
isotonic condition
rates of diffusion are equal in both directions
22
New cards
hypertonic condition
net diffusion of water is OUT of the cell
23
New cards
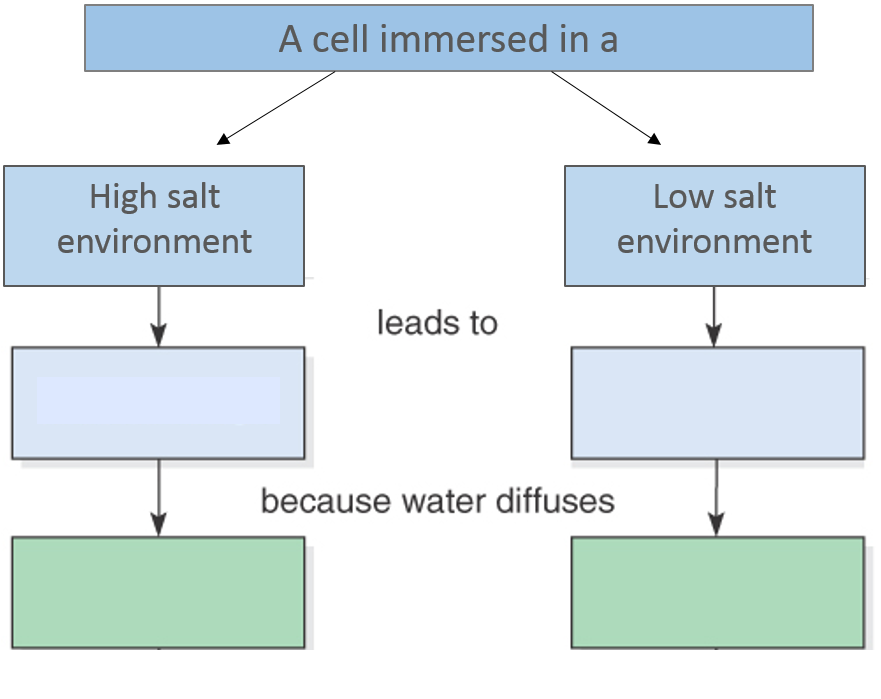
Move the terms into the correct empty boxes to complete the concept map.
Left
- plasmolysis --> out of the cell
Right
- swelling --> into the cell
- plasmolysis --> out of the cell
Right
- swelling --> into the cell
24
New cards
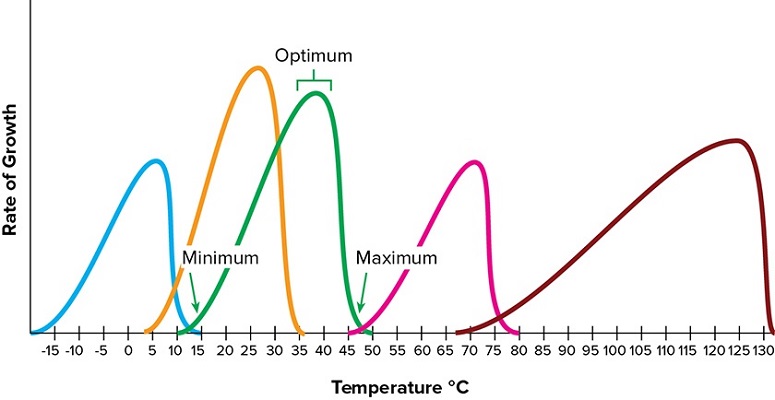
Label the image to test your understanding of temperature adaptations exhibited by various bacteria.
left --> right
- psychrophile (-15-15)
- psychrotolerant (5-35)
- Mesophile (10-50)
- Thermophile (45-80)
- Extreme Thermophile (65.5- >130)
- psychrophile (-15-15)
- psychrotolerant (5-35)
- Mesophile (10-50)
- Thermophile (45-80)
- Extreme Thermophile (65.5- >130)
25
New cards
Most of the microbiota in the human body are classified as ______.
mesophiles
26
New cards
Refrigeration will _____ the doubling time of most pathogens.
increase
27
New cards
What type of bacteria will grow in the refrigerator, and why is this usually not a concern?
Psychrophiles; very few are pathogenic to humans
28
New cards
You leave your potato salad out on the table at the company picnic. When you made it, you unknowingly introduced 100 cells of Salmonella. How much time will it take for the population of Salmonella to reach at least one million if its doubling time is 20 minutes at picnic conditions?
over 4 hr
explanation: It would take 14 generations for the numbers to rise above one million. At twenty minutes per generation, this would take about 4 hours and 40 minutes. You can calculate this using the equation: Nf = (Ni)2^n and then multiply the number you get for n by 20 minutes.
explanation: It would take 14 generations for the numbers to rise above one million. At twenty minutes per generation, this would take about 4 hours and 40 minutes. You can calculate this using the equation: Nf = (Ni)2^n and then multiply the number you get for n by 20 minutes.
29
New cards
Most bacteria increase their numbers by _______.
binary fission
30
New cards
During binary fission, one bacterial cell becomes _______ cells.
two genetically identical
31
New cards
What factors can affect the doubling time of a bacterial cell?
All of these factors can affect growth rates.
( temp, moisture, pH, Oxygen lvl)
( temp, moisture, pH, Oxygen lvl)
32
New cards
Pathogens usually have _____ doubling times.
short
33
New cards
You ingest 20 cells of Salmonella. This bacterium has a doubling time of 30 minutes. After 4 hours, how many of these bacteria would be present in the body (assuming no immune system responses or other biological activities affect its growth)?
5,120
34
New cards
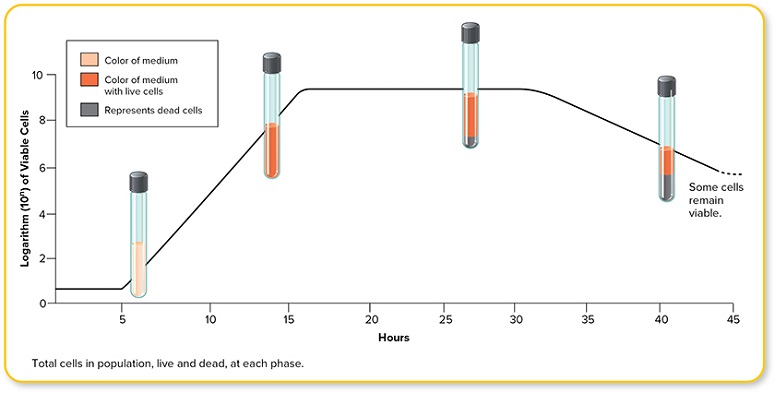
Label the image to test your understanding of bacterial growth curves.
lag phase, exponential growth phase, stationary phase, death phase
35
New cards
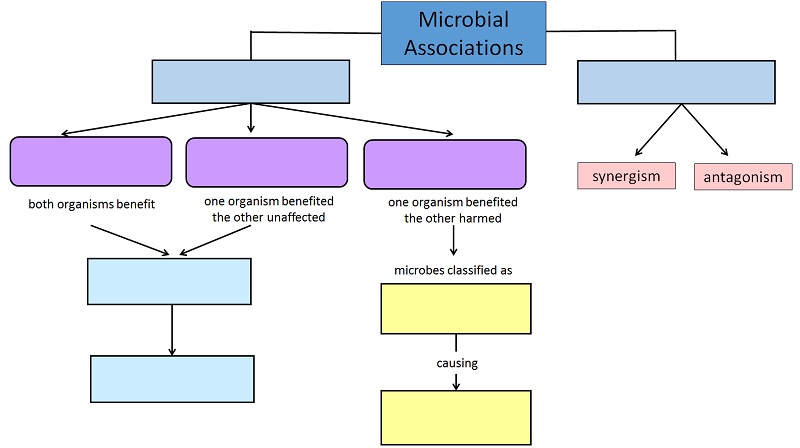
Drag and drop the labels into the correct empty boxes to complete the concept map.
left to right Line 1:
symbiosis, nonsymbiosis
line 2(purple boxes)
mutualism, commensalism, parasitism
line 3:
normal biota(blue), pathogens (yellow)
Line 4:
protection (blue), disease(yellow)
symbiosis, nonsymbiosis
line 2(purple boxes)
mutualism, commensalism, parasitism
line 3:
normal biota(blue), pathogens (yellow)
Line 4:
protection (blue), disease(yellow)
36
New cards
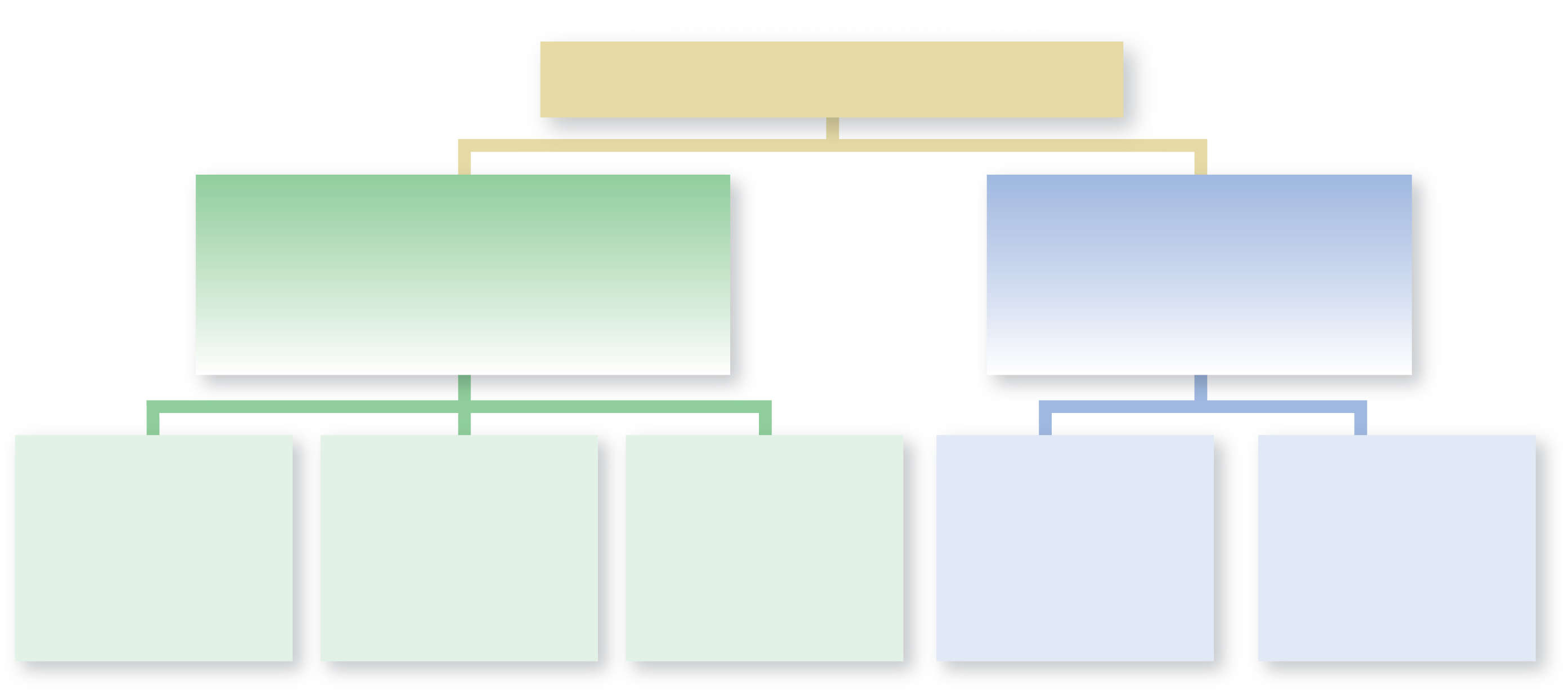
Label the chart to review the major types of microbial associations.
Green boxes
- symbiotic
- mutualism, Commensalism, Parasitism
Blue boxes
- Nonsymbiotic
- synergism, Antagonism
- symbiotic
- mutualism, Commensalism, Parasitism
Blue boxes
- Nonsymbiotic
- synergism, Antagonism
37
New cards
In a viable count, each _______ represents a _______ from the sample population.
colony; CFU
38
New cards
A _________ derives its nutrients and energy from the organic matter of dead organisms, whereas a _________ lives in or on another living organism and derives its nutrients and energy from that living organism.
saprobe; parasite
39
New cards
Diffusion of water through a selectively permeable membrane is _________.
osmosis
40
New cards
Diffusion is a general term referring to the net movement of atoms and molecules along a concentration gradient, from an area of ________ concentration to an area of _______ concentration.
high; low
41
New cards
Select the physical factors below that can affect microbial growth. SATA
- temperature
- radiation( visible light, UV, gamma)
- Barometric Pressure
- radiation( visible light, UV, gamma)
- Barometric Pressure
42
New cards
Two organisms living together in which both partners benefit from the relationship
Mutualism
43
New cards
Two organisms living together in which one organism benefits and the other is neither benefited nor harmed
commensalism
44
New cards
Two organisms living together in which one organism benefits and the other (the host) is harmed
parasitism
45
New cards
A relationship in which free-living organisms cooperate and share nutrients
Synergism
46
New cards
A competitive relationship between free-living organisms in which one organism secretes substances that are toxic to the other, in order to acquire more space or nutrients for itself
Antagonism
47
New cards
The Hawaiian bobtail squid and the Vibrio fischeri bacteria have established a symbiosis.
The bacteria live in a special organ of the squid and the squid uses the bacteria bioluminescence to camouflage itself.
The bacteria live in a special organ of the squid and the squid uses the bacteria bioluminescence to camouflage itself.
V. fischeri produces light only when quorum sensing indicates that the bacteria have reached a threshold concentration in the squid
48
New cards
Chose all correct statments about quorum sensing
- Is a chemical system of communication used by bacteria
- can only be intraspecific
- Requires bacteria to be connected via a pilus
- can only be intraspecific
- Requires bacteria to be connected via a pilus
49
New cards
For a physician, treating a biofilm infection in a patient poses a significant challenge compared to treating an infection with planktonic bacteria. This is due to the fact that ________.
the biofilm likely contains several different species of bacteria living in a thick, extracellular matrix that cannot be treated by routine antibiotic therapy
50
New cards
The time required for one complete cycle of binary fission is known as the ________ time or generation time.
doubling
51
New cards
Consider the following hypothetical conditions: A population of 10,000 bacteria has a doubling time of 20 minutes, under a given set of growth conditions. The culture is allowed to grow for 2 hours. Select the number of bacteria that best predicts the population size at the end of the 2 hours incubation. Assume there is no lag phase.
640,000
52
New cards
Stationary growth phase
Phase during which nutrient depletion and accumulation of wastes begin to slow cell growth such that the rate of cell increase equals the rate of cell death
53
New cards
Phase during which cells are growing very quickly, at their maximum rate of cell division
Exponential growth phase
54
New cards
Adjustment period during which cells are dividing slowly while they adjust to growth conditions
Lag phase
55
New cards
Death phase
Nutrient depletion and waste accumulation prevent cell growth and cells die exponentially
56
New cards
Choose the phase of the bacterial growth curve during which a bacterial population has the briefest doubling time.
Exponential growth phase
57
New cards
Most bacteria reproduce by ________.
binary fission
58
New cards
After six generations, how many bacteria would have formed from the reproduction of one bacterium?
64
59
New cards
Bacteria that grow in oxygenated environments are referred to as ________.
aerobes
60
New cards
Bacteria that grow in oxygenated environments are referred to as ________.
alkainophiles
61
New cards
What is the effect of heat on a population of bacteria?
Cells begin to die at a temperature slightly above the maximum.
62
New cards
What is the effect of cold on a population of bacteria?
Cells survive but do not divide at temperatures below the minimum.
63
New cards
What food product is least likely to contain viable vegetative pathogens?
Chicken cooked to 170°F
64
New cards
The patient asks the RN to describe the disease process of a urinary tract infection. The RN describes bacterial urea digestion and ammonium release. How does the RN most accurately describe the resultant pH following bacterial urine decomposition, facilitating pathogen growth?
Alkaline pH
65
New cards
The RN may anticipate all of the following to be ordered for treatment of the urinary tract infection, except ________.
vaccination
66
New cards
The RN educates the patient about managing the urinary tract infection at home. She recommends increasing fluid intake and consuming cranberry juice. Which of the following is the rationale for the consumption of cranberry juice?
Cranberry juice increases urine acidity.
67
New cards
his patient's wound was likely caused by ________.
poor circulation from diabetes
68
New cards
Clostridium perfringens is the causative agent of ________.
gas gangrene
69
New cards
Which of the following statements describes Clostridium perfringens?
It's a gram-positive organism
70
New cards
C. perfringens causes tissue damage by release of ________.
alpha toxin
71
New cards
Clinical findings not associated with clostridial gas gangrene
- gram staining of cultures reveals gram-negative cocci
- optimal culture growth occurs under aerobic conditions
- endotoxins from organism causes direct muscle tissue damage
- optimal culture growth occurs under aerobic conditions
- endotoxins from organism causes direct muscle tissue damage
72
New cards
Why was hyperbaric oxygen therapy an effective treatment in this case?
The causative agent is an anaerobe
73
New cards
What does it mean to say that C. perfringens can be found as normal biota in the intestine?
It can live in a commensal/mutualistic relationship with the human host
74
New cards
Why were antibiotics prescribed for Mr. Jones?
The causative agent was a bacterium