Cardiac Axis & Deviation
1/7
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
8 Terms
Cardiac axis represents the sum of?
depolarisation vectors generated by individual cardiac myocytes
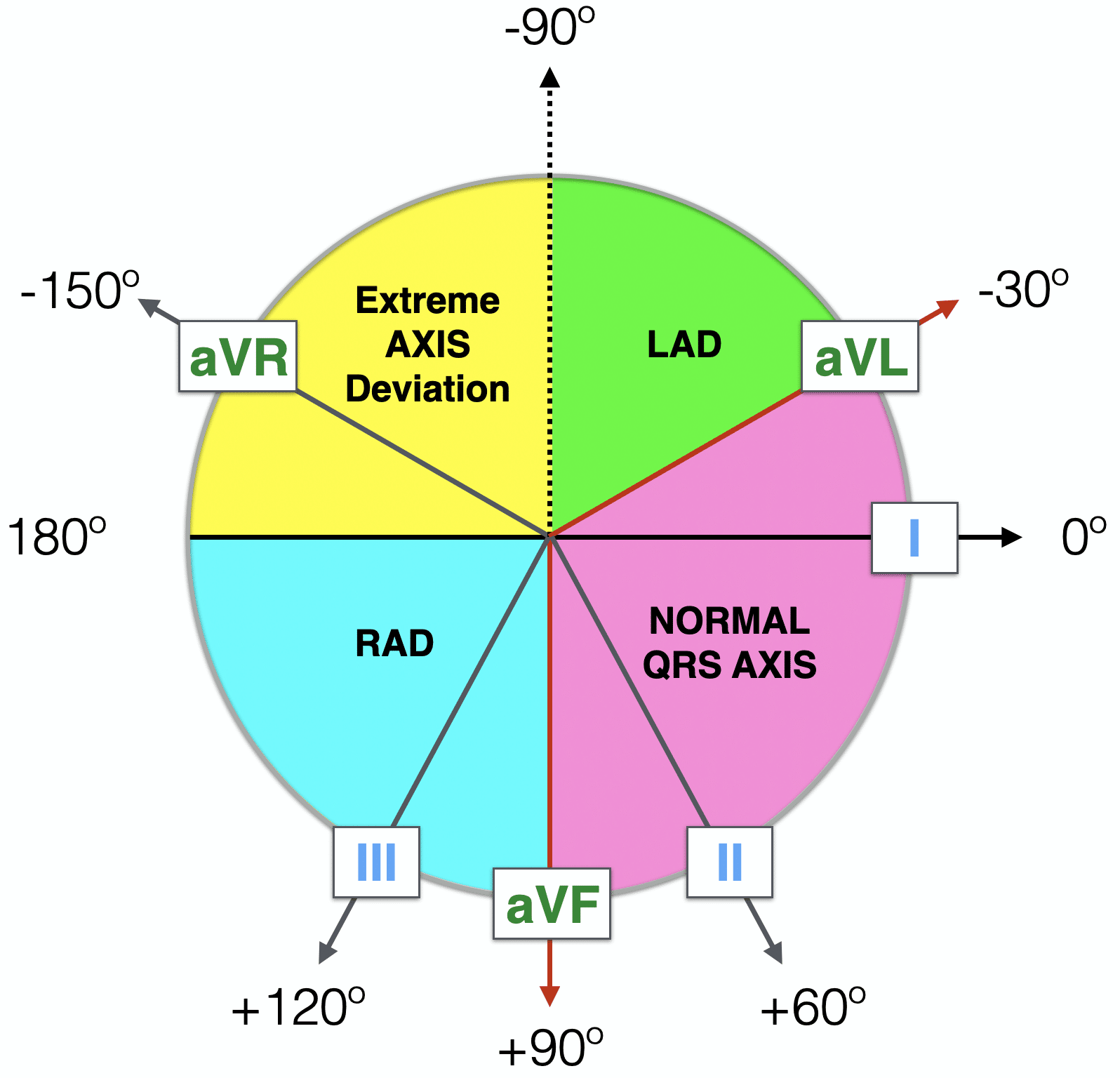
Normal Axis = QRS axis between?
-30° and +90°.
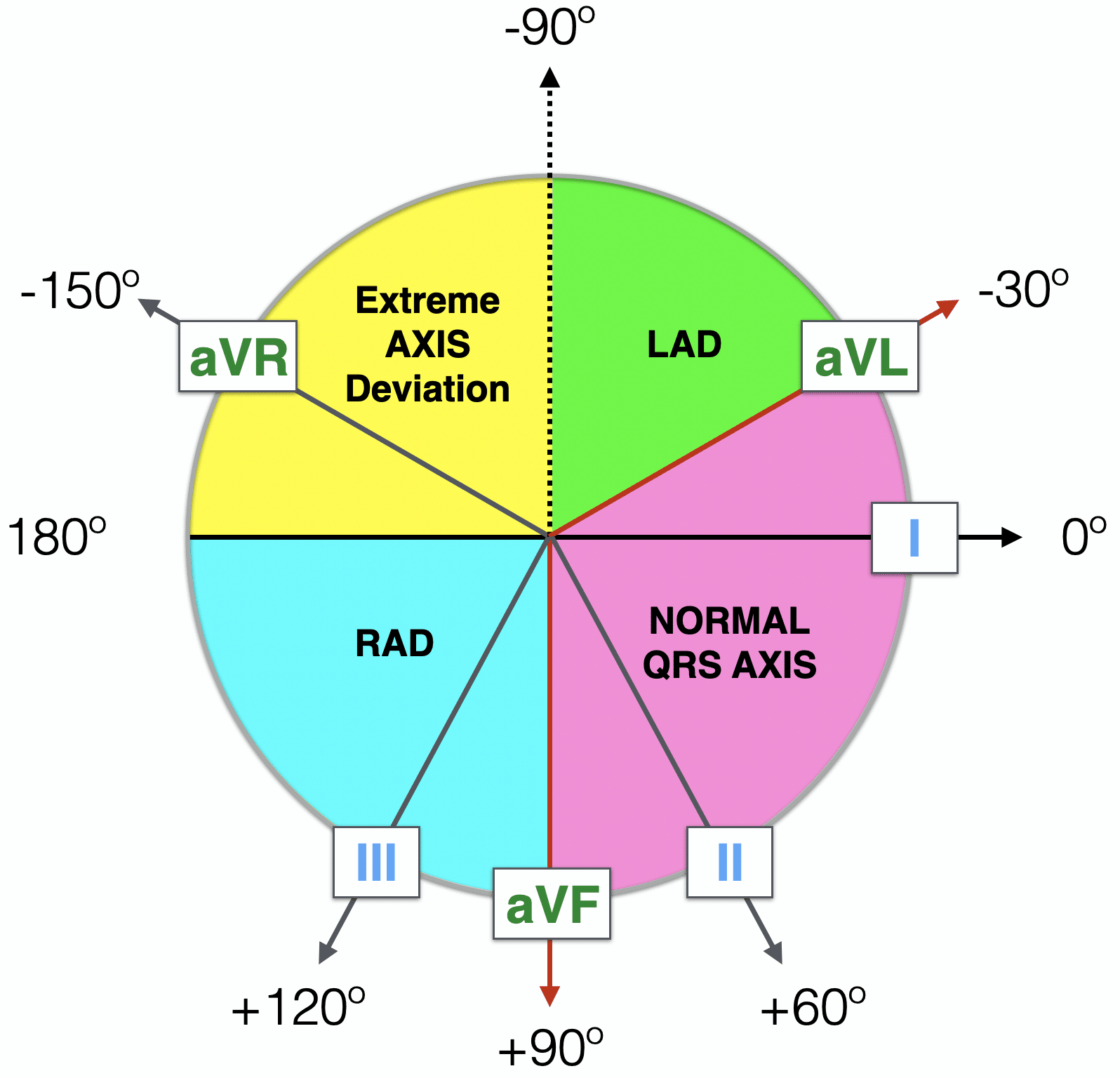
Left Axis Deviation = QRS axis..?
QRS axis less than -30°.
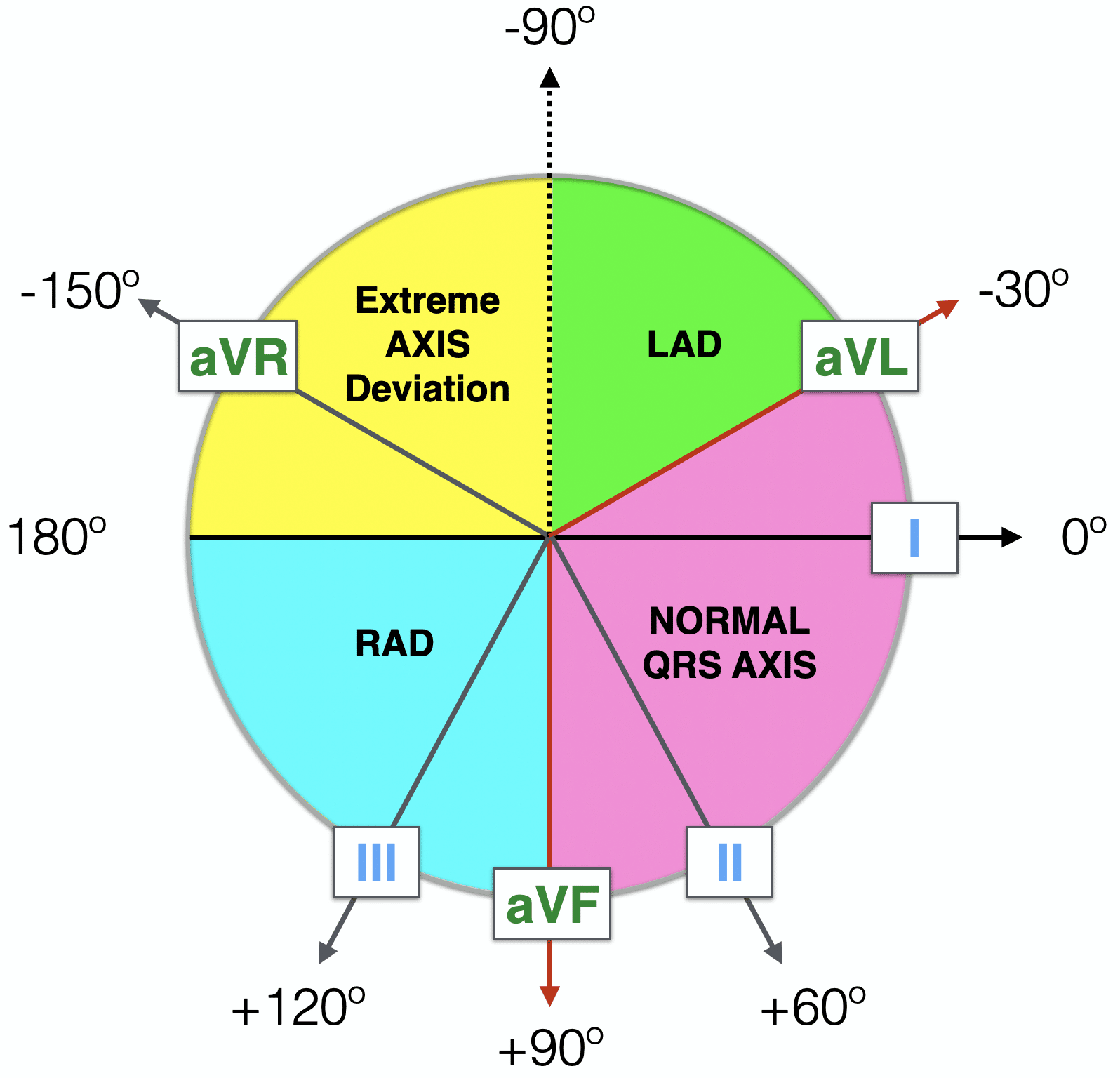
Right Axis Deviation = QRS axis?
greater than +90°.
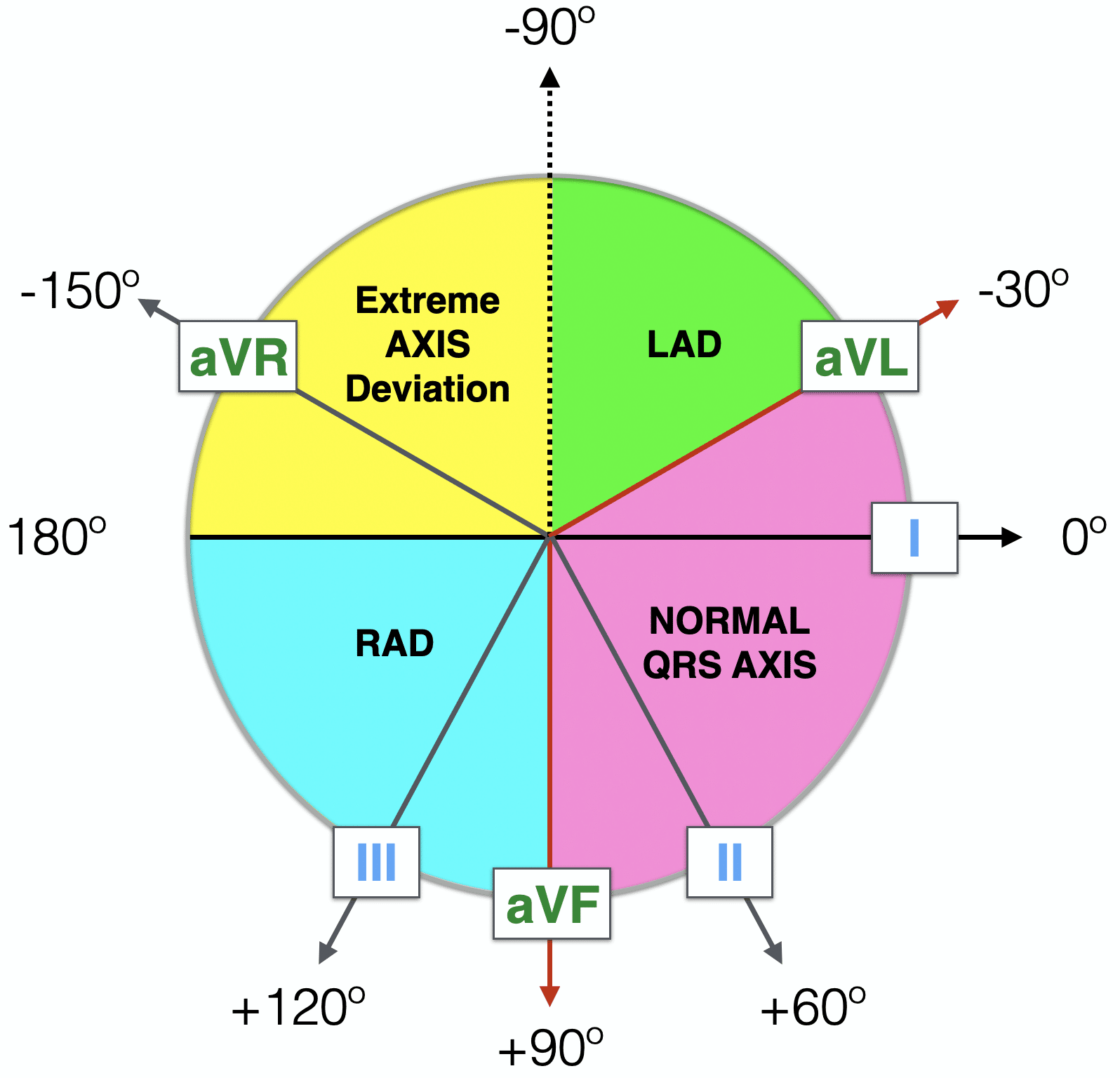
Extreme Axis Deviation = QRS axis between?
between -90° and 180°
(AKA “Northwest Axis”).
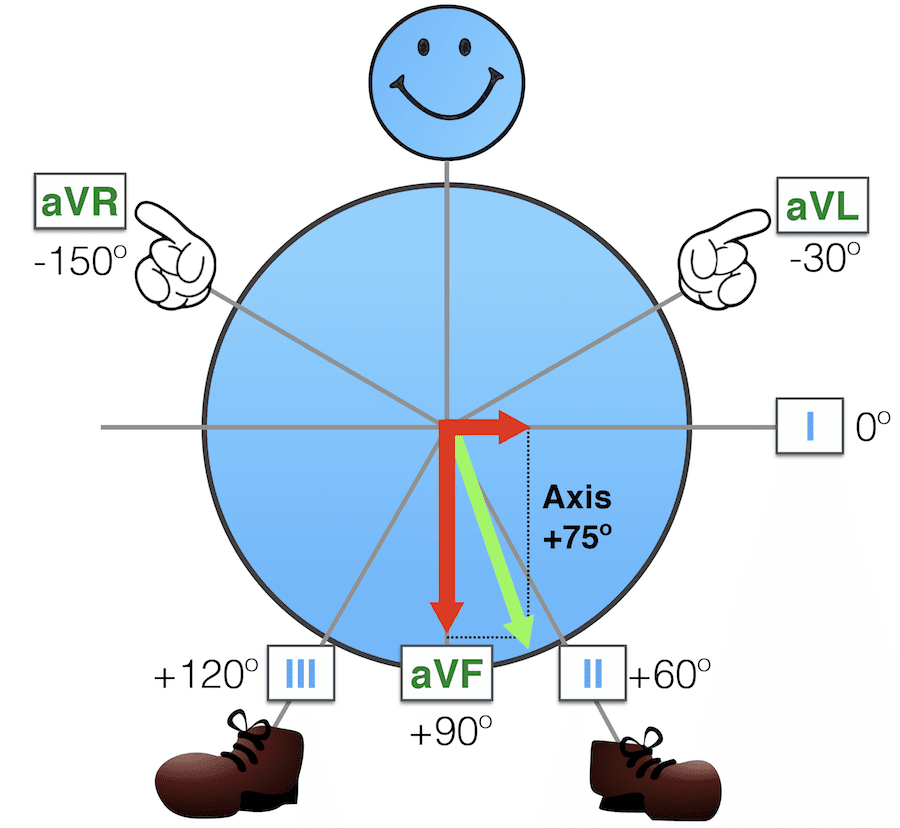
How would I determine the Specific Cardiac Axis?
Leads 1 and aVF
In Lead 1 and AVF Measure the Net Deflection of the QRS Complex
E.G
- L1 = + 4
- aVF = +15Draw it out and draw a line through the Corner. = The Axis Degree
What are Causes of LAD?
Left anterior fascicular block
Left bundle branch block
Left ventricular hypertrophy
Inferior MI
Ventricular ectopy
Paced rhythm
Wolff-Parkinson White syndrome
What are the causes of RAD?
Left posterior fascicular block
Lateral myocardial infarction
Right ventricular hypertrophy
Acute lung disease (e.g. Pulmonary Embolus)
Chronic lung disease (e.g. COPD)
Ventricular ectopy
Hyperkalaemia
Sodium-channel blocker toxicity
WPW syndrome
Normal in children or thin adults with a vertically positioned heart