Syntactic structures
1/52
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
53 Terms
generative grammar/syntax
theory that there is a set of principles that allow you to produce the set of all (and only) grammatical sentences
universal grammar
often conflated w/ generative grammr but is a specific theory of generative grammar that argues that there is a set of principls and constraints that govern all natural language
grammar can refer to which 2 things?
a speakers tacit knowledge of a language
a linguist's explicit theory of a speaker's tacit knowledge of a language
derivational morphology
a process of creating new words - usually involves a change of category
inflectional morphology
the change of a word-form in relation to some grammatical relation
what is Merge?
taking two elements and combining them to form a bigger element - this bigger element can then be fed as input for further Merge - using the output as the input of the same process is known as recursion
possible word orders (most to least common)
a. SOV (Hindi, Japanese, Korean)
b. SVO (English, Mandarin)
c. VSO (Irish, Welsh, Tagalog)
d. VOS (Malagasy)
e. OVS (Urarina [Peru])
f. OSV (Xavante [Brazil])
what structure do sentences have?
hierarchical
what is constituency?
how words group together to form coherent units
what is one of the most general forms of substitution?
the use of pronouns
Substitution (or Replacement)
if a string of words can be replaced by a suitable pronoun or pro-form, that string is a constituent
example of constituency tests demonstrating idosyncratic behaviour?
there works to substitute for PP's that express location, but they can sometimes substitute for the DP inside the PP
e.g. John read a book in the lib // John read a book there (=in the lib) // John read a book in there (=the lib)
what is the rule for substitution of PP's and DPs?
use there-substitution for PP, pronominal substitution for DP
which substitution test would be used to show a DP contains an NP
the one-substitution test, e.g. a red [book] and a green [one] - sometimes this method doesn't work unless the NP is modified and contrasted with another
which substitution test identifies a VP?
did so test - John [read a book] John [did so]
issues w/ did so test - asymetrical structure of sentences
the verb and object form a VP constituent, but the subject and verb do not - telling us that a sentence has the structure S + (VO) not (SV) + O
what does recursion allow for with VPs?
bc recursion allows the use of output as input of a process, each VP that is modified becomes a bigger VP, so recursion allows us to potentiallygenerate an infinite number of VP's
trying to target non-constituents with substitution
ungrammaticality will occur
successful subs. (or any constituency test) should always allow us to recover the original meaning
how do you form a pseudocleft?
starting w/ a h- word with the string to be tested at end of sentence
Wh-word REST OF SENTENCE is/was STRING
what is movement?
refers to material that starts in one location but is pronounced in another
what is a property of movement?
only constituents can be moved
what are the most common types of movement in English and what do they involve?
topicalisation
wh- movement
both cases involve moving a string to the front of the sentence where the moved string is a constituent
explain topicalisation w/ examples
a. John ate an apple in the living room
b. [an apple], John ate in the living room
c. *[the living], John ate an apple in room
the moved string an apple is a constituent
important note about constituency tests
they only work positively
a successful test tells u a string is a constituent, a single failed test DOES NOT ALLOW U to conclude that the string isn't a constituent
explain wh- movement w/ examples
combo of substitution and movement
relevant string = replaced by a question word (wh-) and moved to the frontof the sentence
the string that undergoes wh-movement is a constituent
John ate [an apple] in the room
John ate [what] in the room
what did John eat in the room
now we kno that an apple = constituent
what does ellipsis do?
targets a string by deleting it - the deleted string is a constituent, though the test doesn't tell u what category
key notes for ellipsis
for a construction involving ellipsis to be valid, the meaning of the elided material must be recoverable
it is ungrammatical to elide the verb phrase along w/ the modal auxiliary
what is coordination, give 1 key characteristic?
a simple way of showing constituency
1 key characteristic is that only two strings of the same category can be coordinated
important notes on co-ordination
syntactic categories have nothing to do w/ the size of the constituent
doesn't tell u what category, only that the co-ordinated strings are of the same category
what are morphosyntactic features?
a smaller subunit of a morpheme you get when you break it down
a property of syntactic items/objects that syntax is sensitive to, and may determine the morphological form the word has
what is a privative feature?
a feature that is either present or absent
what do valued features allow for?
subtypes of a feature that form a natural class e.g. numbered features
how can something be considered a feature?
whether there are systematic or morphological changes associated w/ a syntactic or semantic property
examples of category features
D
N
V
Adj
P
Adv
what are Phi-features
a set of features that typically bundle together on a DP
refers to the collection of person number and gender
common cases
[nom]inative
[acc]usative
[dat]ive
[gen]itive
what is a theta-role?
describes the role an argument plays with respect to the verb
three most common are agent, theme, and goal
what are interpretable vs uninterpretable features?
interp - is interpretable to the semantics because it carries some semantic info
uninterp - is uninterpretable to the semantics bc it doesn’t carry semantic info
what are languages sensitive to?
not only whether one element is higher than another, but about their relative positions
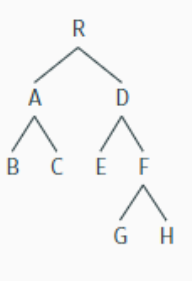
explain the structural terminology - this is a long one good luck
R is the root node
R dominates all other nodes
R is the mother of A and D
A and D are the daughters of R
A and D are sisters, as are B and C, E and F, and G and H
A dominates B and C
D dominates E, F, G, and H
R immediately dominates A and D
A immediately dominates B and C
C-command
C = constituent
a node X c-commands a node Y if either:
a. X and Y are sisters OR
b. X’s sister dominates Y
AKA a node C commands its sister and all her descendants
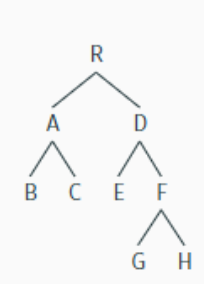
explain this with c-command
R c-commands nothing
A c-commands D, E, F ,G and H
D c-commands A, B, and C
B c-commands C
C c-commands B
E c-commands F, G, and H
F c-commands E
G c-commands H
H c-commands G
What is an anaphor?
it is a class of DP
it is usually a reflexive pronoun like ‘himself’
What do you call it when two DP’s refer to the same individual?
coreferential
what is the DP that a pronoun corefers with called?
antecedent
What is the anaphor class made of and what do they depend on?
reflexives and reciprocal
they depend on other elements in order to have their reference fixed
what do we say when an environment is one where some construction is grammatical?
we say that environment licenses that construction
what does a reflexive require in a sentence that they co refer with
another DP
summarise the relevant generalisations regarding reflexives
a reflexive must
be in the same sentence as its antecedent
appears after its antecedent
match with its antecedent in phi features (gender, number, person)