Anatomy Proficiency Exam
1/1210
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
1211 Terms
The top surface of the foot is anatomically ___, and is known as the ___ surface
anterior; dorsal
The bottom surface of the foot is anatomically ___, and is known as the ___ surface
posterior; plantar
A PA projection of the foot could also be called a ___
plantodorsal projection
An AP projection of the foot could also be called a ___
dorsoplantar projection
What is the anatomical/Latin term for foot?
pes
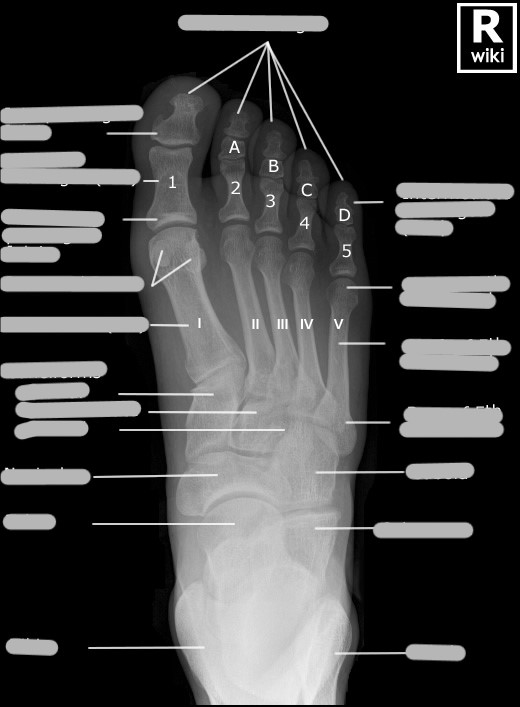
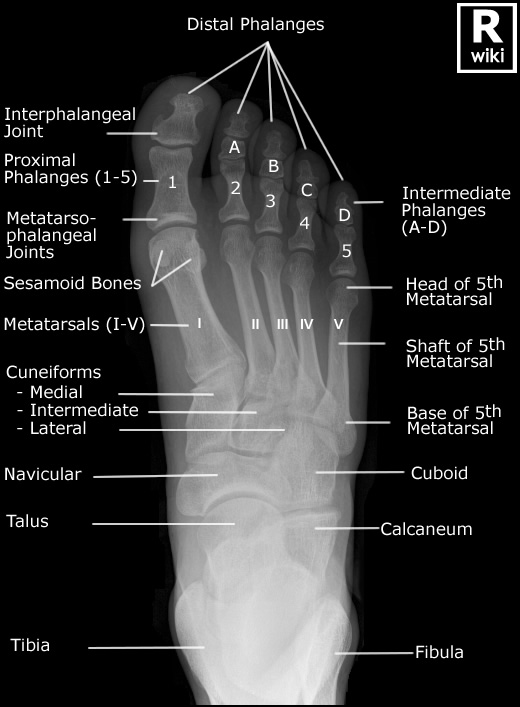
How many phalanges, metatarsals, and tarsals are in 1 foot?
phalanges: 14
metatarsals: 5
tarsals: 7
Does numbering of the foot digits start medially or laterally?
medially
What is another name for the first digit of the foot?
hallux
Is the head or base of the metatarsals distal?
head
The 1st metatarsal sometimes has sesamoid bones that are usually located ___
posteriorly
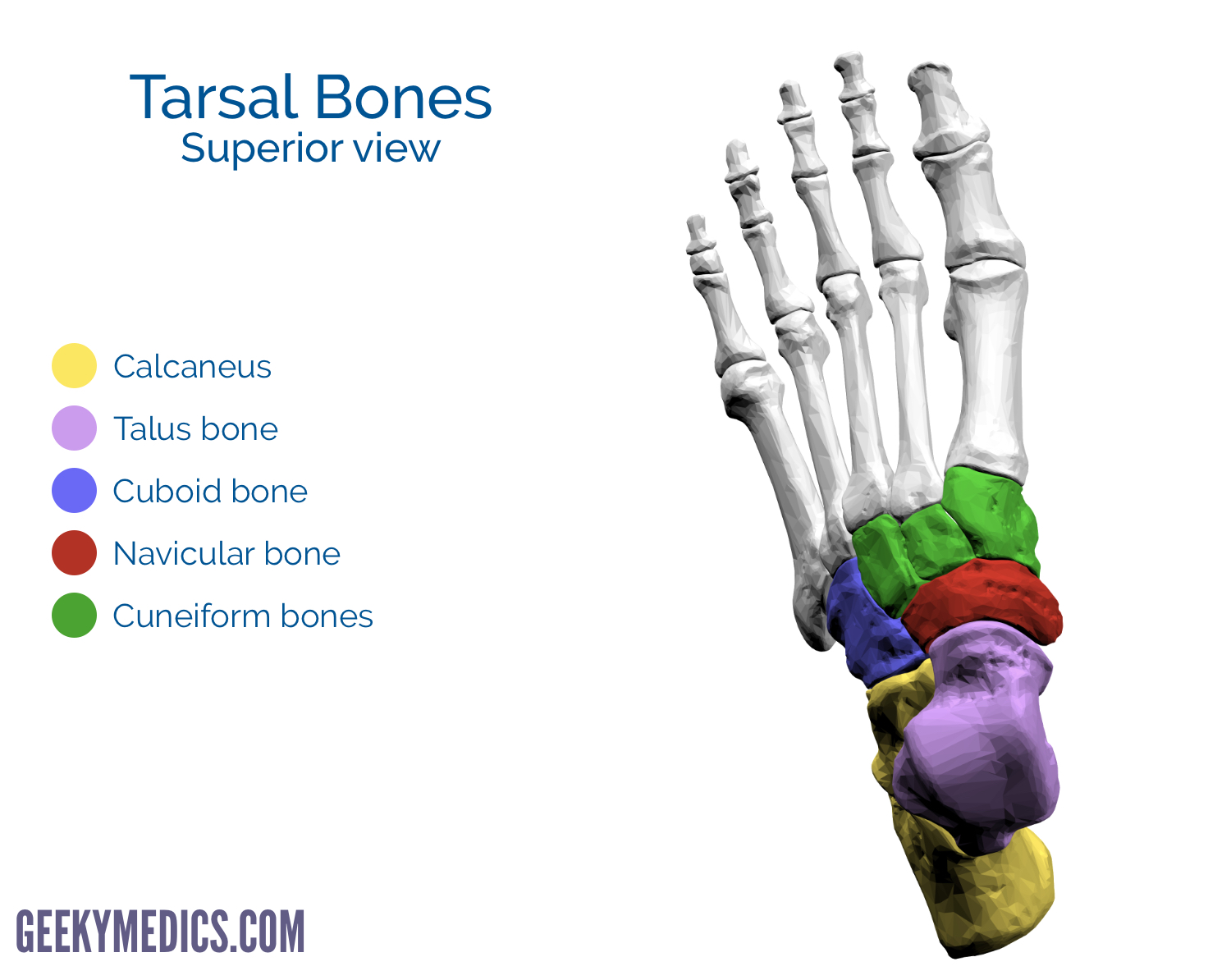
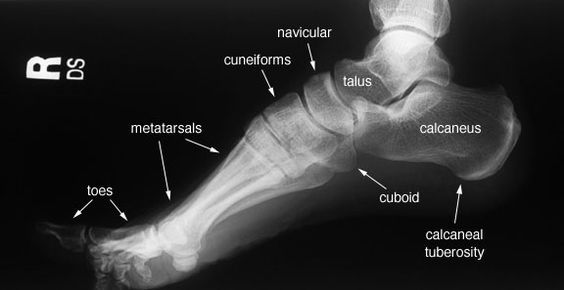
Explain the size and location of the 3 cuneiforms
1st: medial (largest)
2nd: intermediate (smallest)
3rd: lateral
What is the secondary name for the navicular?
scaphoid
The navicular is located on the ___ side of the foot and articulates distally with ___
medial; the cuneiforms
The cuboid is located on the ___ side of the foot and articulates distally with ___
lateral; MT 4 and 5
What is the secondary name for the talus?
astragalus
Explain the location of the head of the talus
rounded anterior surface
What tarsal(s) does the talus articulate with?
navicular (articulates at the head of the talus)
The trochlear surface of the talus articulates ___, ___, and ___
superiorly with the tibia
laterally with the fibula
inferiorly with the calcaneus
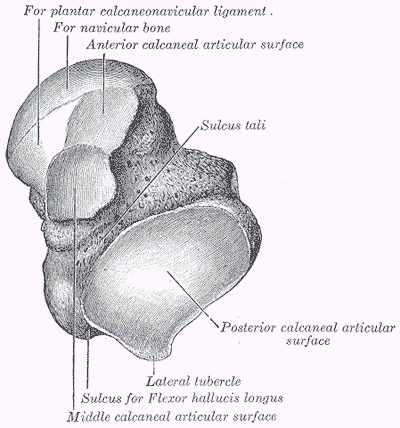
How many articular surfaces does the talus have inferiorly to articulate with the calcaneus?
3 (anterior, middle, posterior)
Label the 3 surfaces of the talus that articulate with the calcaneus
What is the secondary name of the calcaneus?
os calsis
What is the largest and strongest bone of the foot?
calcaneus
What is the most posterior bone of the foot?
calcaneus
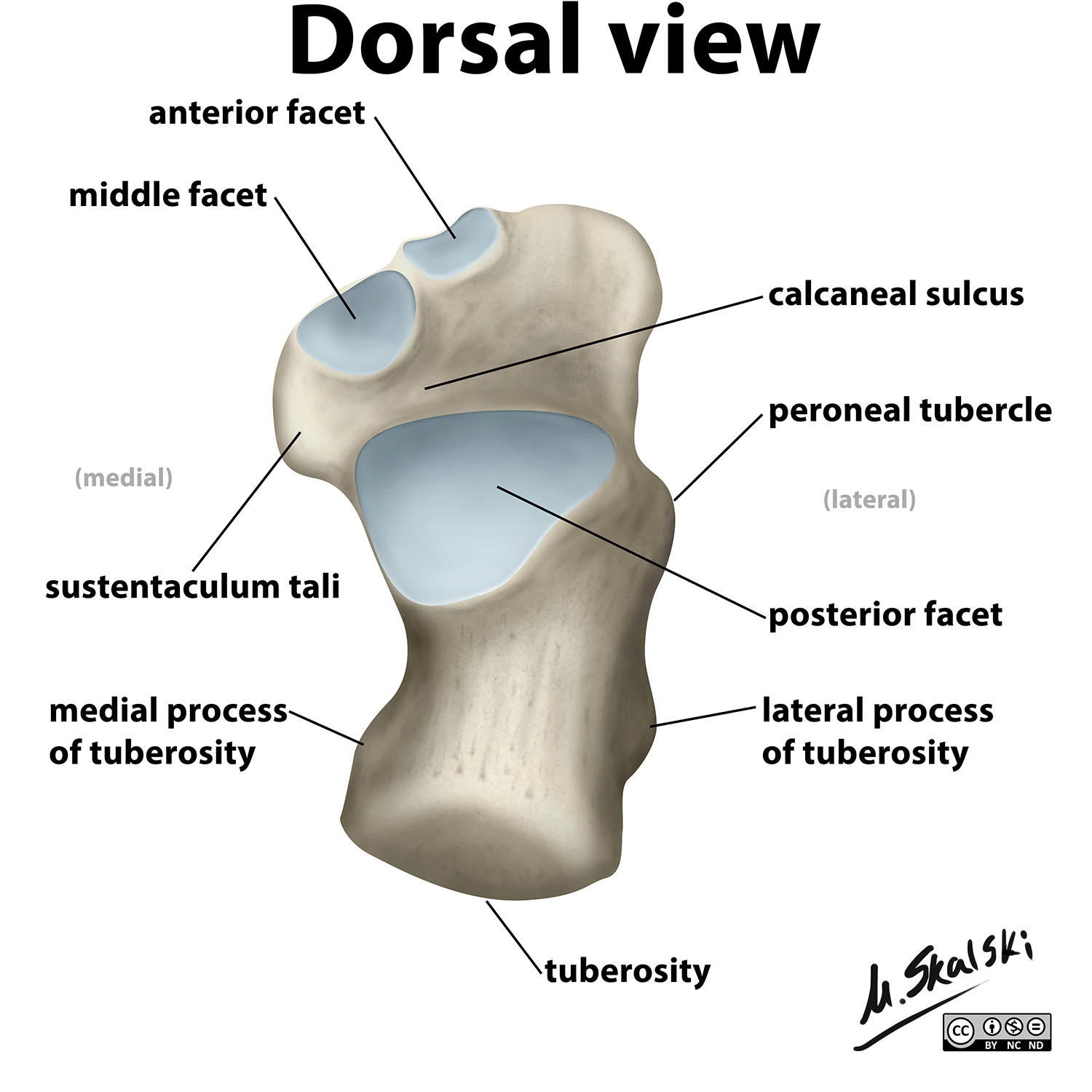
The calcaneal tuberosity serves as an attachment for ___
the Achilles tendon
What is another name for the talocalcaneal joint?
subtalar joint
Explain the location and function of the sinus tarsi
an opening on the lateral aspect of the foot between the talus and calcaneus; allows ligaments of the foot to pass through
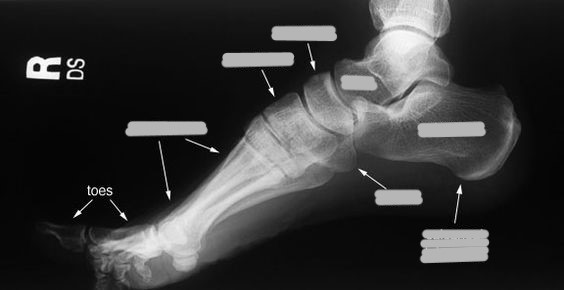
How do you obtain a frontal view of the calcaneus?
tangential view

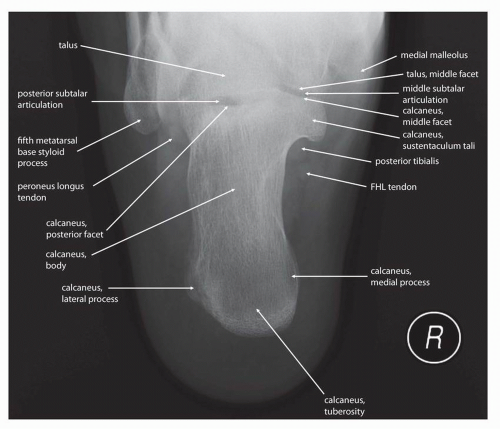
A medial oblique of the foot best demonstrates ___
the lateral part of the foot
What is the Mortise joint?
the socket formed by the 3 bones of the ankle joint
What is the Mortise view?
15-20 degree off the coronal plane to put the intermalleolar line parallel
The 45o medial ankle oblique demonstrates ___
distal tibiofibular articulation
What is an Aurora ankle routine?
AP, Mortise, lateral
How is a patient sitting for a routine ankle?
on tabletop with their leg extended
What type of joint are the DIP, IP, and PIP joints of the foot?
synovial, hinge
What type of joint are the MTP joints?
synovial, condylar
What type of joint are the intermetatarsal (IMT) joints?
synovial, gliding
What type of joint are the TMT joints?
synovial, gliding
What type of joint are the intertarsal joints?
synovial, gliding
What type of joint is the calcanocuboid joint?
synovial, gliding
What type of joint is the talocalcaneal (subtalar) joint?
synovial, gliding
What type of joint is the tibiotalar/talocrural joint?
synovial, hinge
What type of joint is the distal tibiofibular joint?
synarthrodial, syndesmosis, fibrous
Explain plantar fasciitis
the plantar fascia (thick ligament that runs from the heel to the ball of the foot) is irritated and pulls away from where it is attached at the calcaneus (calcaneus grows toward the fascia in an effort to reattach: called a bone spur)
Explain bunions
prolonged pressure put on the 1st digit toward the 2nd digit (makes the big toe unstable, affecting the 1st MTP)
caused by narrow shoes
repair is done to remove abnormal bone, realign joint, and stabilize the joint
Explain hammer toe
condition where a toe (usually 2nd or 3rd) bends downward with a deformity at the PIP joint
caused by too small shoes
Explain diabetic foot
peripheral neuropathy
can cause ulcers
decreased feeling in foot and decreased circulation
What is polydactyly?
having more than the normal number of digits
Explain flat foot
condition where the arch of the foot collapses
caused by genetics or repetitive stress on the tendon over the arch of the foot
Explain club foot
Congenital Talipes Equinovarus
Talipes: latin for “foot”
Equino: “like a horse”
Varus: part slants toward the midline
repaired by casting, bracing, or surgery
Explain the Jones fracture
fracture at the proximal 1/3rd of the 5th MT
Explain the dancers fracture
an avulsion fracture of the 5th tuberosity
Explain the trimalleolar fracture
fracture of the ankle that involves the medial malleoli, lateral malleoli, and the distal posterior tibia
Explain the Potts fracture
bimalleolar fracture of the medial and lateral malleoli
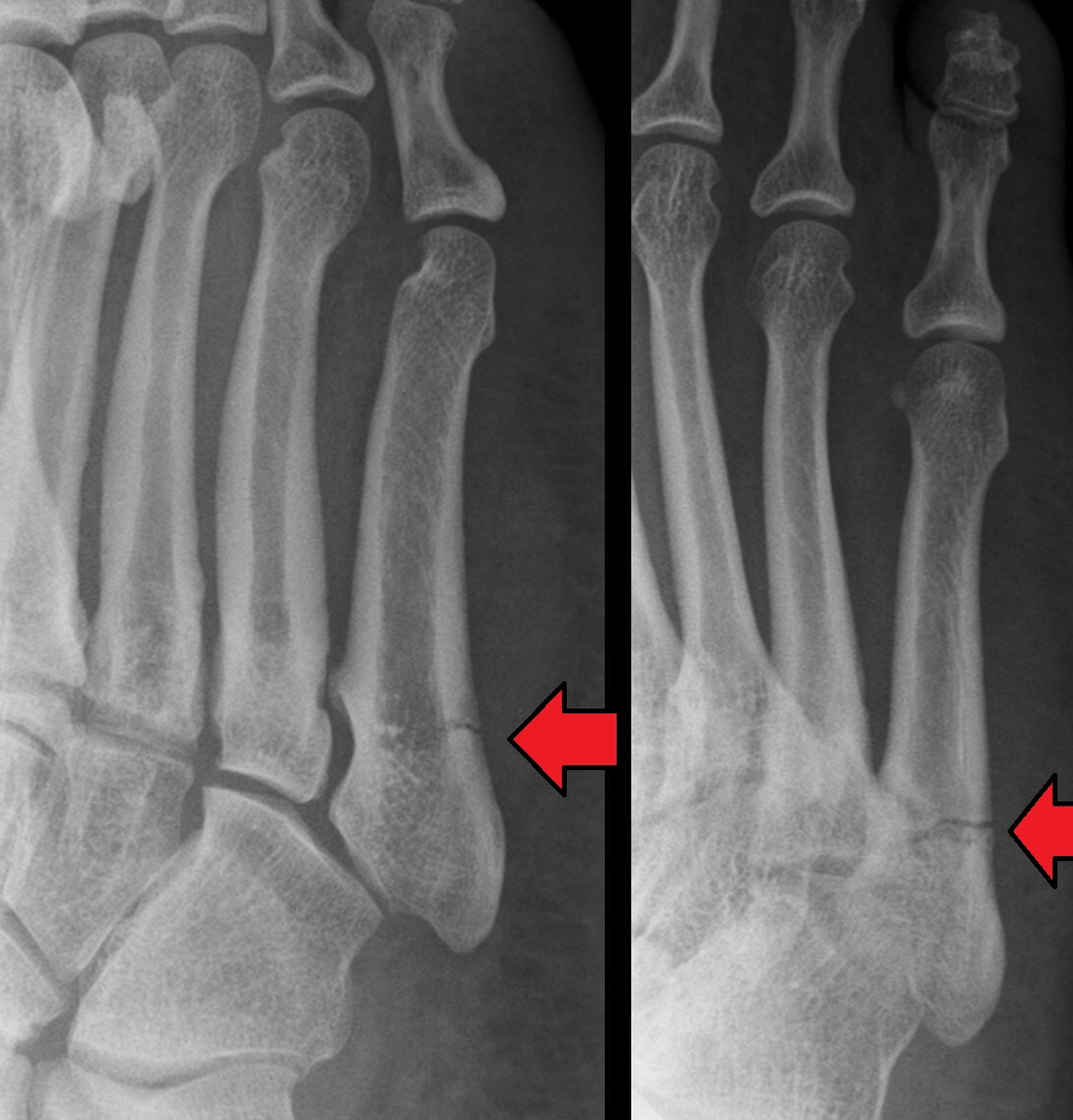
What kind of fracture is shown?
Jones
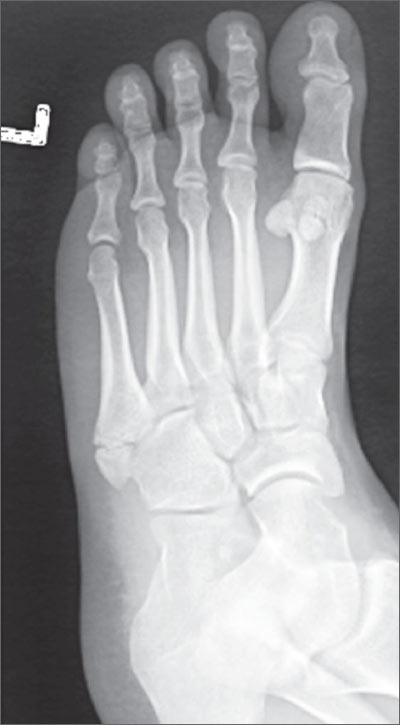
What kind of fracture is shown?
dancers
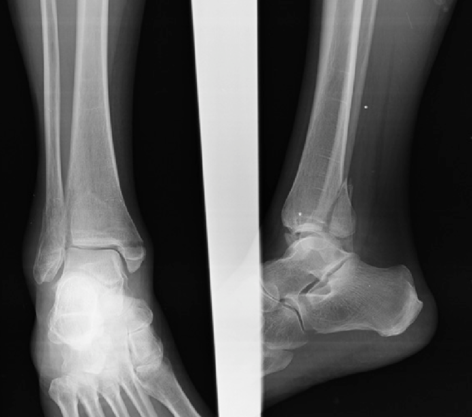
What kind of fracture is shown?
trimalleolar
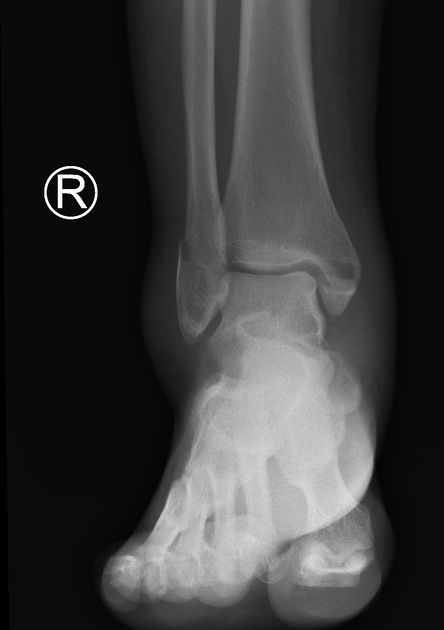
What kind of fracture is shown?
bimalleolar
What is the shoulder girdle made up of?
clavicle and scapula
What is the function of the shoulder girdle?
attach the upper extremity to the axial skeleton
What kind of bone is the scapula classified as?
flat bone
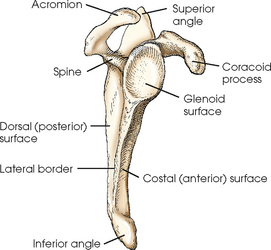
Explain the location of the scapula
lies in the superior, posterior aspect of the thorax
goes from the 2nd to the 7th rib
sits at a 30-45o angle
What is the anterior surface of the scapula called?
costal surface (comes in contact with the ribs)
What is the posterior surface of the scapula called?
dorsal surface
The scapular spine/crest divides the dorsal surface of the scapula into what 2 portions?
infraspinous/infraspinatus fossa
supraspinous/supraspinatus fossa
What is another term for the medial border of the scapula?
vertebral border
What is another term for the lateral border of the scapula?
axillary border
Which border of the scapula is thicker, medial or lateral?
lateral
What makes up the superior angle of the scapula?
junction of superior and medial borders
What makes up the inferior angle of the scapula?
junction of medial and lateral borders
What vertebrae does the inferior angle of the scapula correspond with?
T7
What is located at the lateral angle of the scapula?
head (glenoid) and neck of scapula
What is the coracoid process of the scapula?
fingerlike process extending anteriorly from the scapular notch
What is the acromion process of the scapula?
posterior flattened oval process at the lateral end of the scapular spine
What is the scapular notch?
prominent indentation along the superior border of the scapula
What is the glenoid fossa?
the head/neck of the scapula (point where humeral head articulates with scapula to form the scapulohumeral/glenohumeral joint)
What is the name of the fibrocartilage rim attached around the margin of the glenoid cavity of the scapula?
glenoid labrum
What is the rotator cuff?
group of muscles that stabilize the shoulder joint by pulling the humeral head into the glenoid fossa
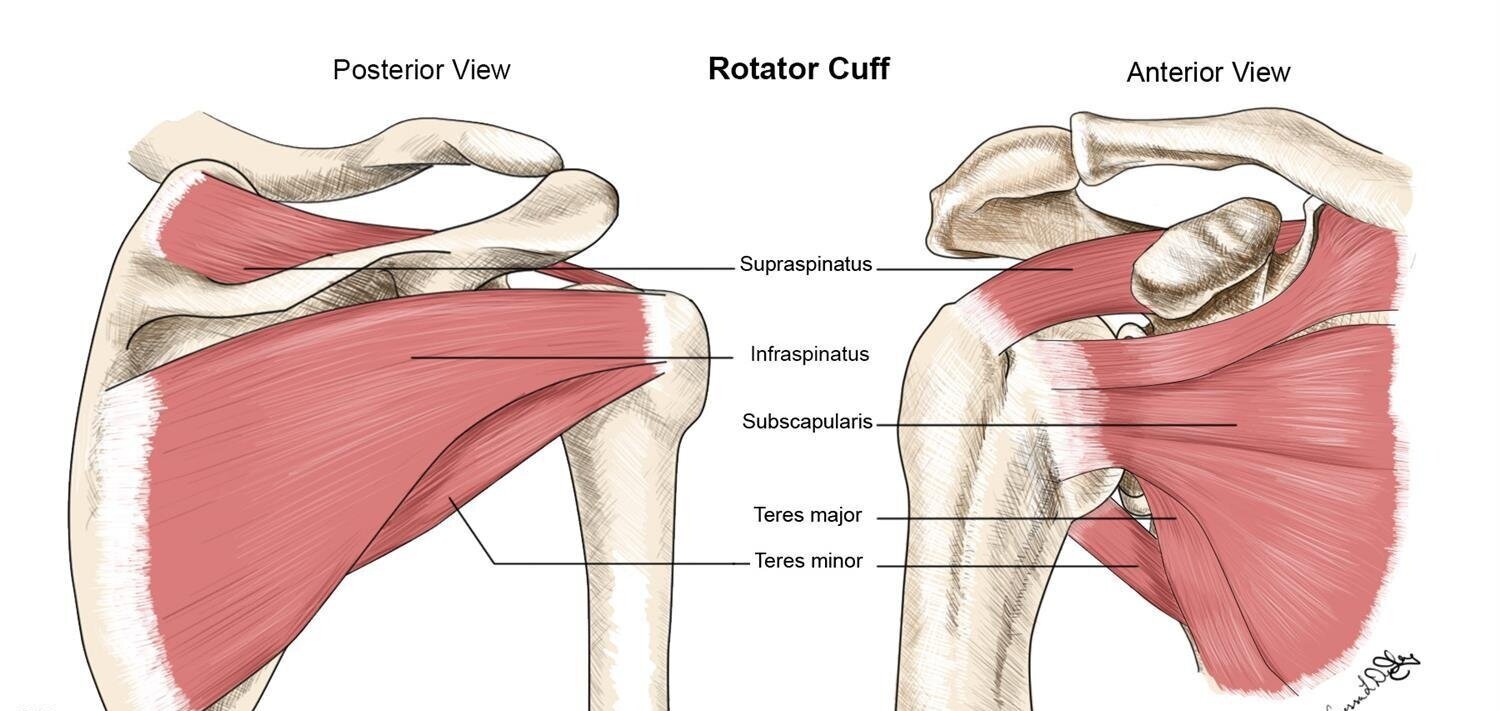
What 4 muscles make up the rotator cuff?
supraspinatus, infraspinatus, subscapularis, and teres minor
Explain the location and function of the supraspinatus muscle
originates on the upper border of the posterior scapula
allows for abduction
Explain the location and function of the subscapularis muscle
originates on the anterior surface of the scapula
allows for internal rotation
Explain the location and function of the infraspinatus muscle
originates on the posterior inferior aspect of the scapula
allows for external rotation
Explain the location and function of the teres minor muscle
originates on the posterior lateral scapular border
allows for external rotation
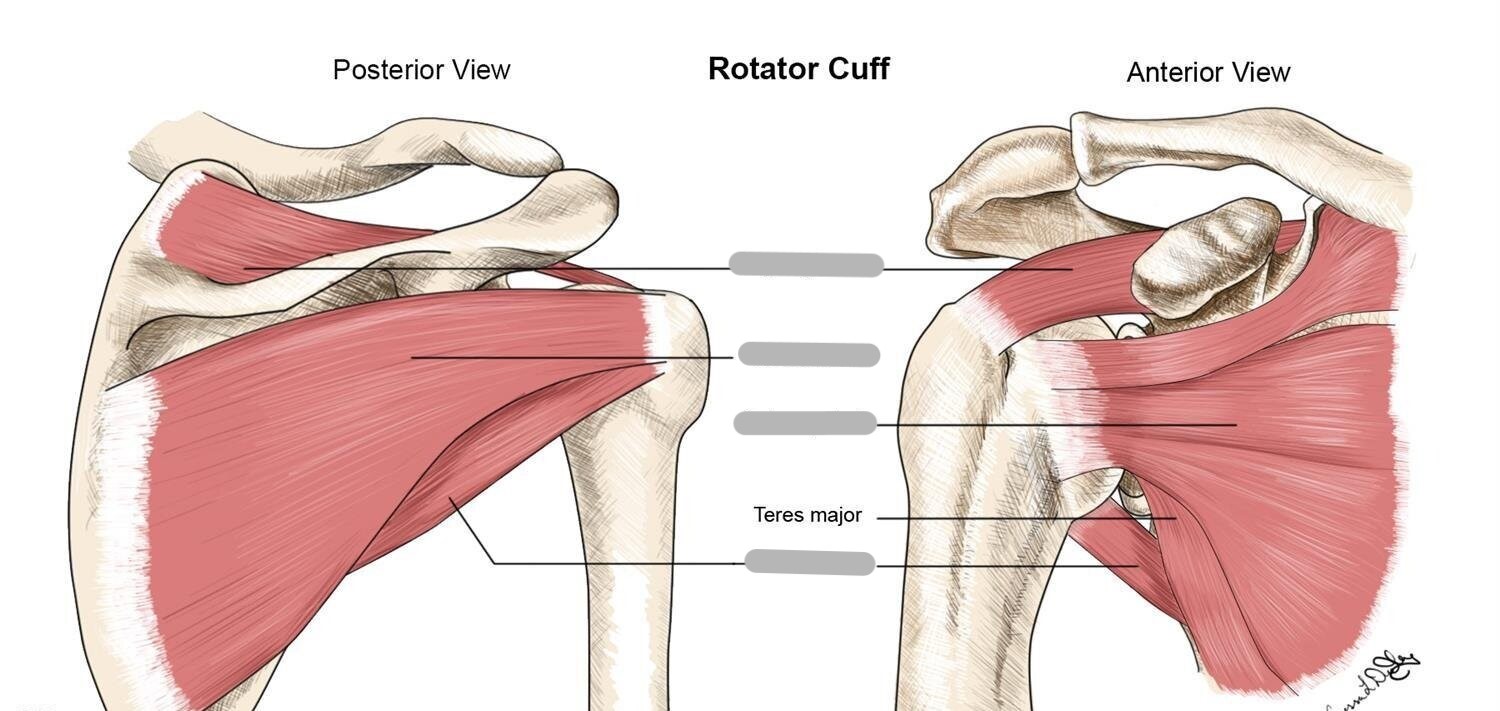
Label the muscles of the rotator cuff
What are the routine views of the scapula?
AP and lateral (Y-view)
Label the scapula (and determine whether it is a right or left)
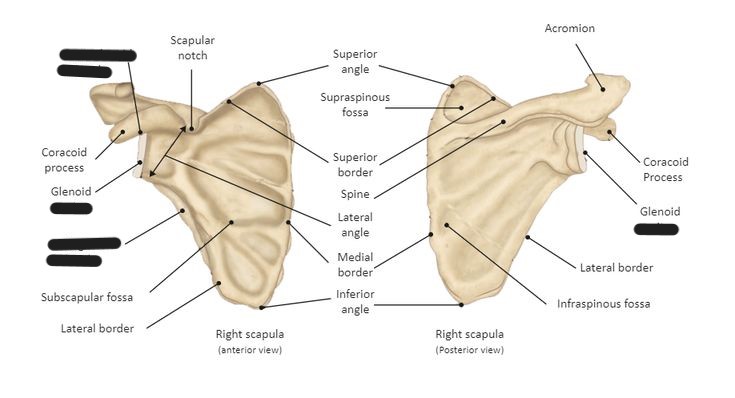
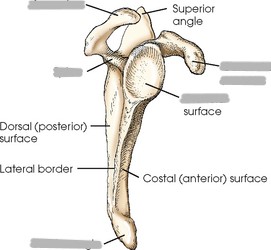
Label the scapula
What kind of bone are the clavicles classified as?
long bones
Where are the clavicles located?
they lie horizontal in the superior and anterior part of the thorax
What is the sternal extremity of the clavicle?
the medial 1/3, convex, expanded end
What is the acromial extremity of the clavicle?
the lateral 1/3, concave, flatted end
What is the body of the clavicle?
the junction of the two curves (the weakest point of the clavicle and the site of 80% of clavicle fractures)
How do male and female clavicles differ?
male clavicle are thicker, longer, and more curved
What is the articular end of the sternal extremity of the clavicle called?
sternal facet (makes up the SC joint)
What is the costal tuberosity?
the broad, roughened surface on the inferior aspect of the medial end of the clavicle (serves as a point of attachment for the ligaments)
What is the sternoclavicular (SC) joint? What are the classifications?
joint between the clavicle and sternum
diarthrodial, gliding/plane joint