DNA Translation
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/9
Study Analytics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
10 Terms
1
New cards
Describe the process of translation.
The process has 3 steps. The first step is initiation. A ribosomal subunit will find the mRNA and will bond to a codon called AUG. Once it finds that codon the large subunit will come on and connect to the mRNA. The ribosomal subunits will move in the 5' to 3' direction. The next step is elongation. The large ribosomal subunit has 3 sites: Exit Site, Polypeptide Site, and Amino Acid Site. Once the subunit reaches a new codon, a tRNA matching with the correct anticodon will bind to the active site. As the unit moves, the tRNA moves places. When 2 amino acids reach the polypeptide site, they bond w/ dehydration synthesis. When the tRNA reaches the exit site, they fall off. The last step is termination. When the unit reaches the end of the mRNA, it reads the stop codon will cause hydrolysis of the chain from the unit and the tRNA's fall off.
2
New cards
Why can there be 64 codons and 20 amino acids?
Multiple codons code for the same amino acid.
3
New cards
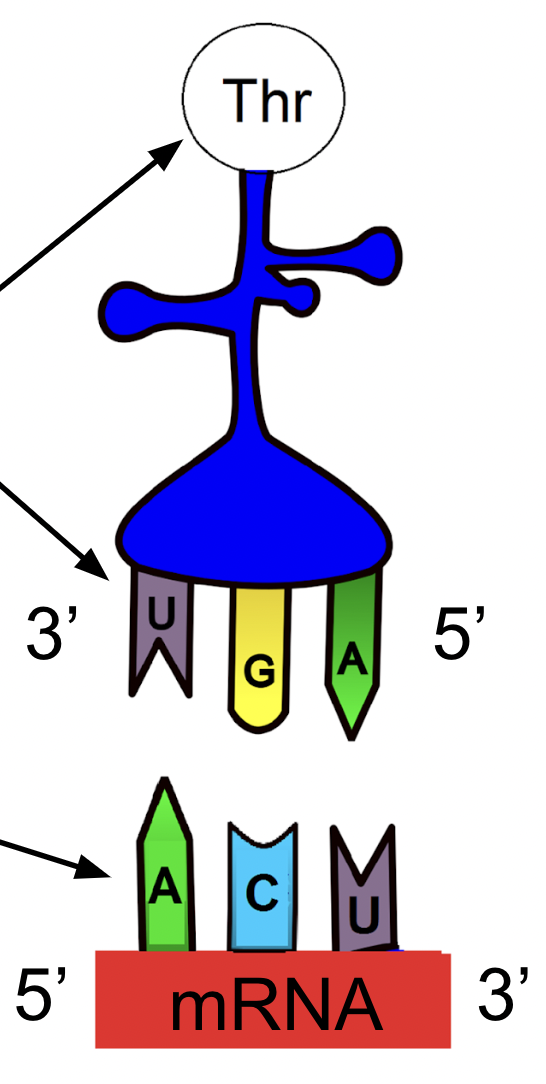
What does a tRNA molecule have?
It carries the anticodon and the amino acid for that molecule.
4
New cards
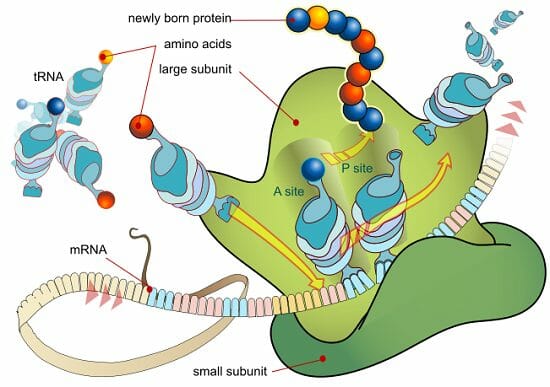
Where exactly does translation occur?
In ribosomal RNA
5
New cards
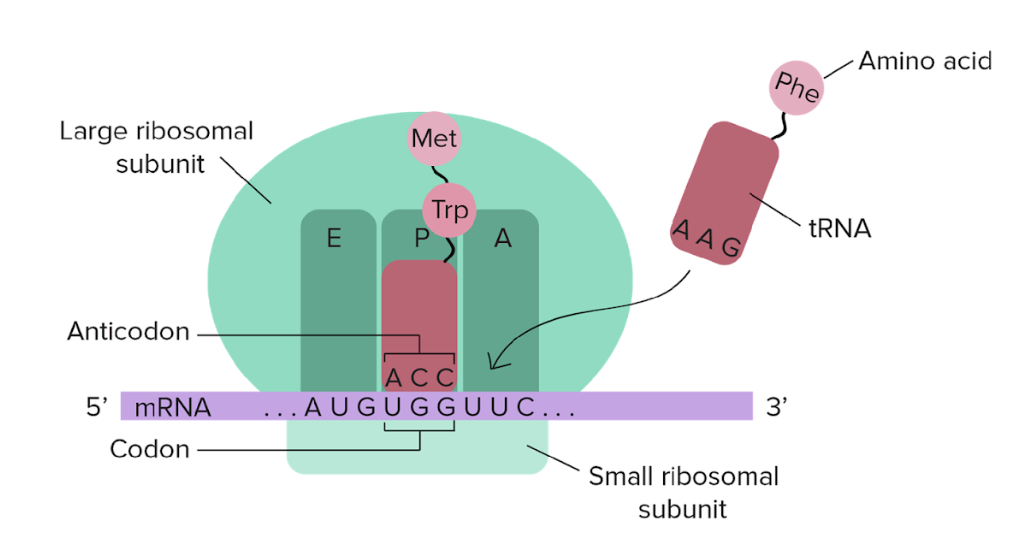
Name the two subunits of ribosomal RNA and their functions
The small ribosomal subunit is for decoding RNA and the large ribosomal subunits holds the sites for tRNA to come in and make the protein.
6
New cards
Pop Quiz: Name the 4 stages of protein creation and structures.
Primary: Amino acid connection
Secondary: The polypeptide folds due to hydrogen bonding
Tertiary: side chain interaction
Quaternary: 2 or more polypeptides interacting.
Secondary: The polypeptide folds due to hydrogen bonding
Tertiary: side chain interaction
Quaternary: 2 or more polypeptides interacting.
7
New cards
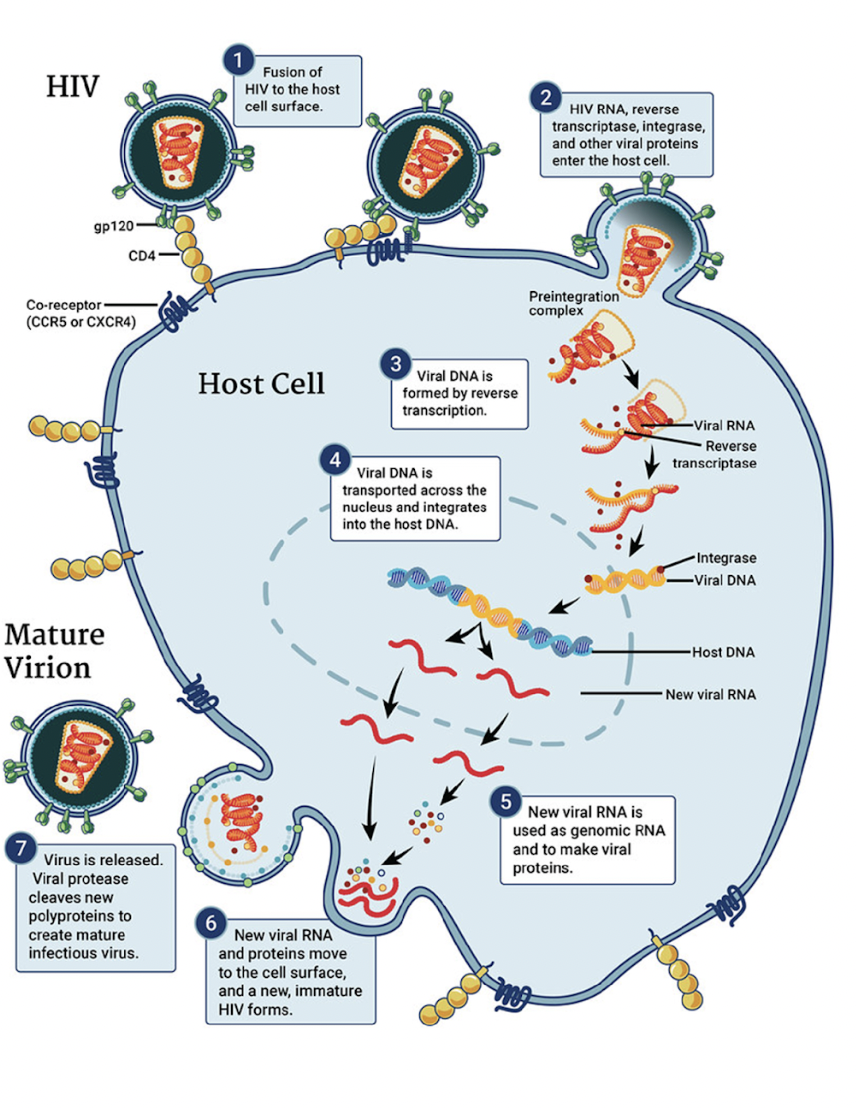
Explain what a retrovirus is and give an example
It’s a cell that contains RNA, reverse transcriptase, integrase, and several other proteins to enter a cell and convert into DNA. Once that happens it’ll change into DNA and insert itself into the host’s DNA which will code for different RNA and thus harmful proteins will be made.
\
HIV is one example
\
HIV is one example
8
New cards
9
New cards
10
New cards