Chapter 6: Thermochemistry
1/72
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
73 Terms
Thermochemistry
Study of energy absorbed of released in chemical reactions
Energy
the capacity to do work or transfer heat
Mechanical energy
energy that is due to an object’s motion, position, or both
Kinetic energy
energy of motion
KE = 1/2mv²
dont have to memorize equation
m = mass (kg)
v = velocity (x/s)
Potential Energy
energy related to position
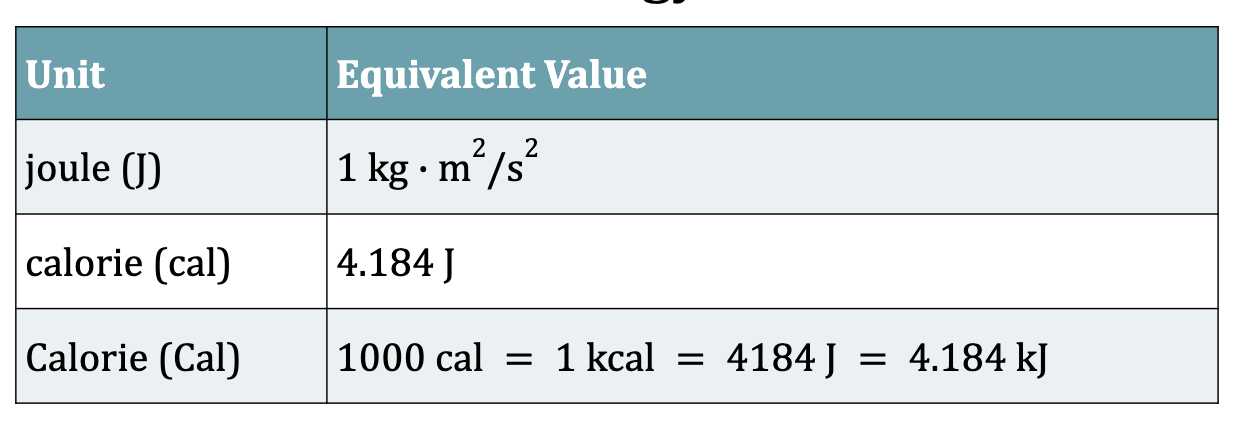
Table 6.1: Common Units of Energy
memorize: 1 calorie (cal) = 4.184 J
The System and the Surroundings
It is important to be able to define where this energy is coming from and where it is going
System: the source of the energy, such as a container with chemical reactants and products
Surroundings: the rest of the universe
universe = system + surroundings
Energy can move between a system and its surroundings
Open System
both matter and energy can move between the system and the surroundings (i.e. fireplace burning wood)
Closed System
Energy but not matter can move between the system and the surroundings (i.e. Pressure cooker)
Isolated System
Neither matter nor energy can leave or enter the system
First Law of Thermodynamics
Energy can move between a system and its surroundings
states that energy cannot be created or destroyed, just transferred from one form to another and that the energy of the universe is constant
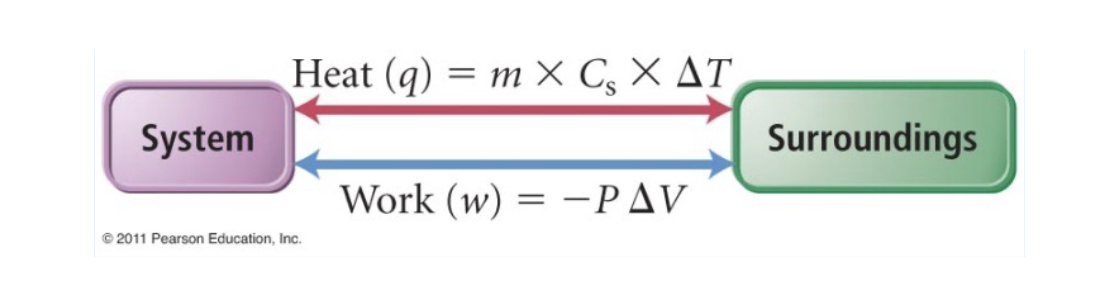
Work and Heat Flow
work, w, is the energy resulting froma force acting on an objec over a distance
The flow of energy that causes a temperature change in an object or its surroundings is known as heat, q
Both work and heat can be exchanged between the system and surroundings
Work Done on the System
w is positive (w > 0)
If the system is a car, an example is a person pushing the car
Work done by the system
w is negative (w < 0)
If the system is a car, an example is a moving car hitting a person
Heat Can be absorbed or released by the system: Heat added to the system
q is positive (q > 0)
An example is heat transferred from a person’s hand to an ice cube (the system)
Heat Can be absorbed or released by the system: Heat released by the system
q is negative (q < 0)
An examle is a bowl of cold water (the system) left in the freezer. Heat is transferred from the bowl into the freezer as the water cools and then freezes

Example 6.2.

Internal Energy, U or E
The internal energy of a system is defined as the sum of all kinetic and potential energies of the particles within a system
This includes the motions of fthe molecules inside the system
Absolute values of U or E are difficut to determine and usually we determine delta U (delta E)
Changes in Internal Energy, DeltaE
Changes in internal energy, deltaU, are more commonly measured
deltaE = Efinal - Einitial
deltaE = q + w

Ex. 6.3

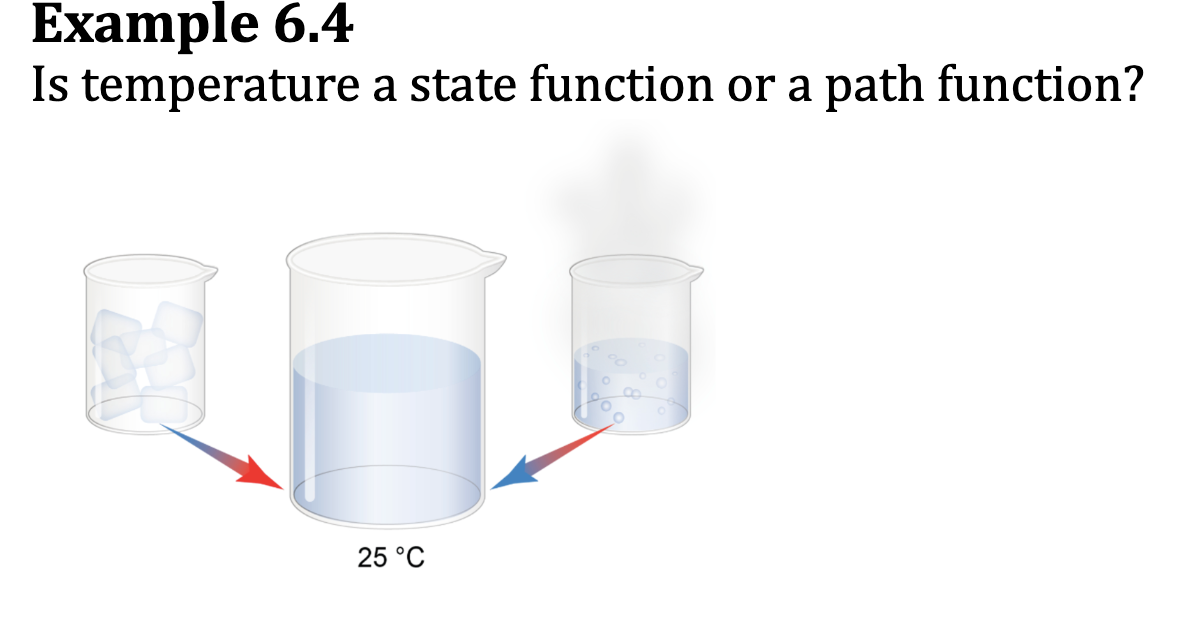
State Function
describes the current state of a system and is independent of the path taken to achieve its value
Internal energy is a state function; delta H

Path Functions
The value of path functions depends on the path taken
They depend on the sequence of steps taken between initial and final states
Work and heat are path functions
E.x. 6.4

Pressure-Volume Work
work done when there is a volume change as measured against an external pressure
Work; pressure, P; and the change in volume, deltaV are related
w = -PdeltaV
Where DeltaV = Vfinal - Vinitial
and 1 L atm = 101.325J
Example: Work, heat and internal energy: work has sign


Example2: Work, heat and internal energy


Example3: Work, heat and internal energy
Is heat positive or negative? (absorb or release)
Is system or surrounding doing the work? (on or by)x

Enthalpy (Heat at constant P)
Most chemical reactions are perofmed in open systems with exchange of both heat and work between system and surroundings
A state function that relates internal energy, pressure, and volume
H = U + PV
delta h = q subscript p
a change in enthalpy is equal to the flow of heat at constant pressure
When you heat water at a stove, you do not seal the container, means you are heating water at a constant pressure
Most reactions that you do inside chemistry lab (in test tube, spot plate and beaker, are done at constant pressure)
Endothermic Process
reactions that absorb heat from surroundings
deltaH > 0 (positive) for endothermic reactions
Exothermic Process
reactions that transfer heat to the surroundings
DeltaH < 0 (negative) for exothermic reactions

E.x. 6.6
Soln a: Heat is transferred from the system to the surroundings, so the reaction is exothermic and deltaH < 0
Soln b: Since this is an open system, the pressure is constant; deltaH = q = -250kJ
Soln c: deltaU = q + w = (-250kJ) + (-15 kJ) = -265 kJ
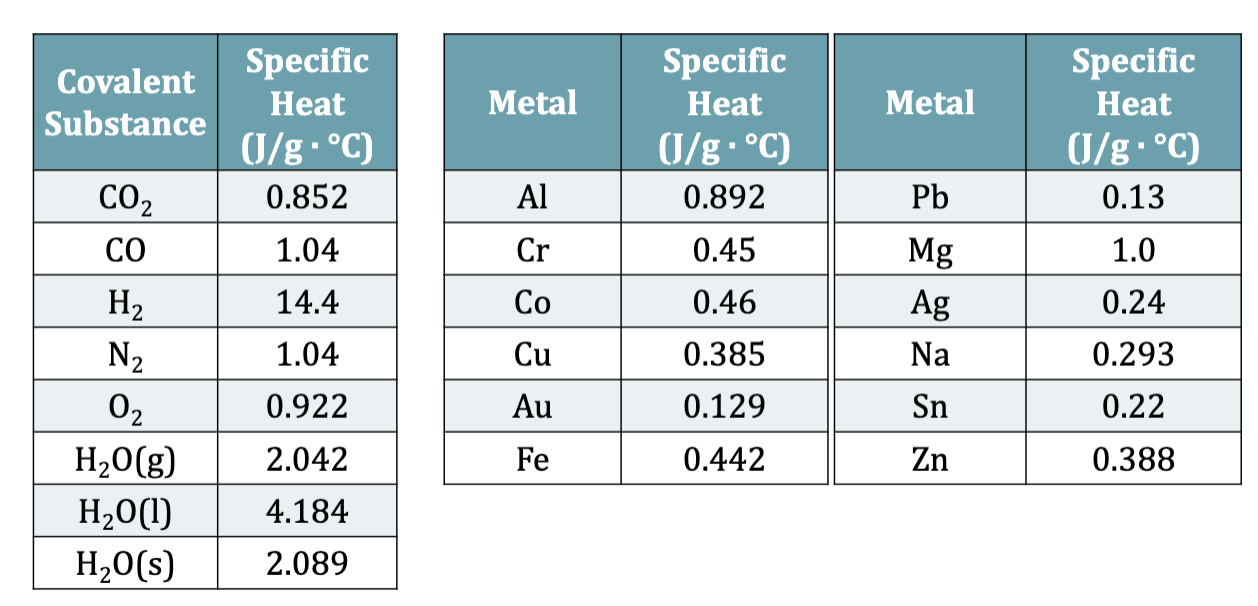
Specific Heat
the number of calories required to raise exactly 1g of the substance by exactly 1ºC Typical units are J/(g x ºC)
In the absence of a phase change, the amount of heat required to change the temperature of a substance is given by q = mcdeltaT
m is the mass of the substance, c is the specific heat of the substance, and deltaT is the change in temperature in either degrees Celsius or Kelvins
Table 6.3: Specific Heats of Selected Substances
memorize specific heat of water
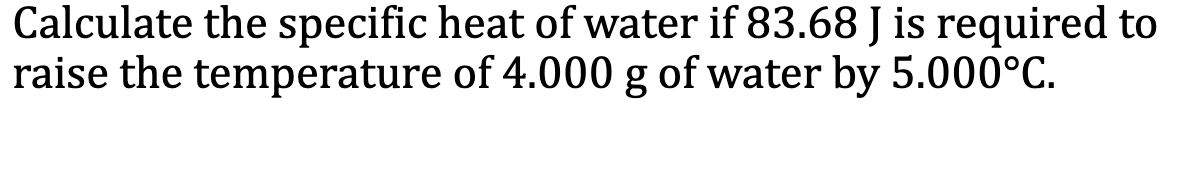
E.x. 6.7
q = mcdeltaT
q/m x deltaT = c
cant cancel anything, so all units will be part of the answer


E.x. 6.9
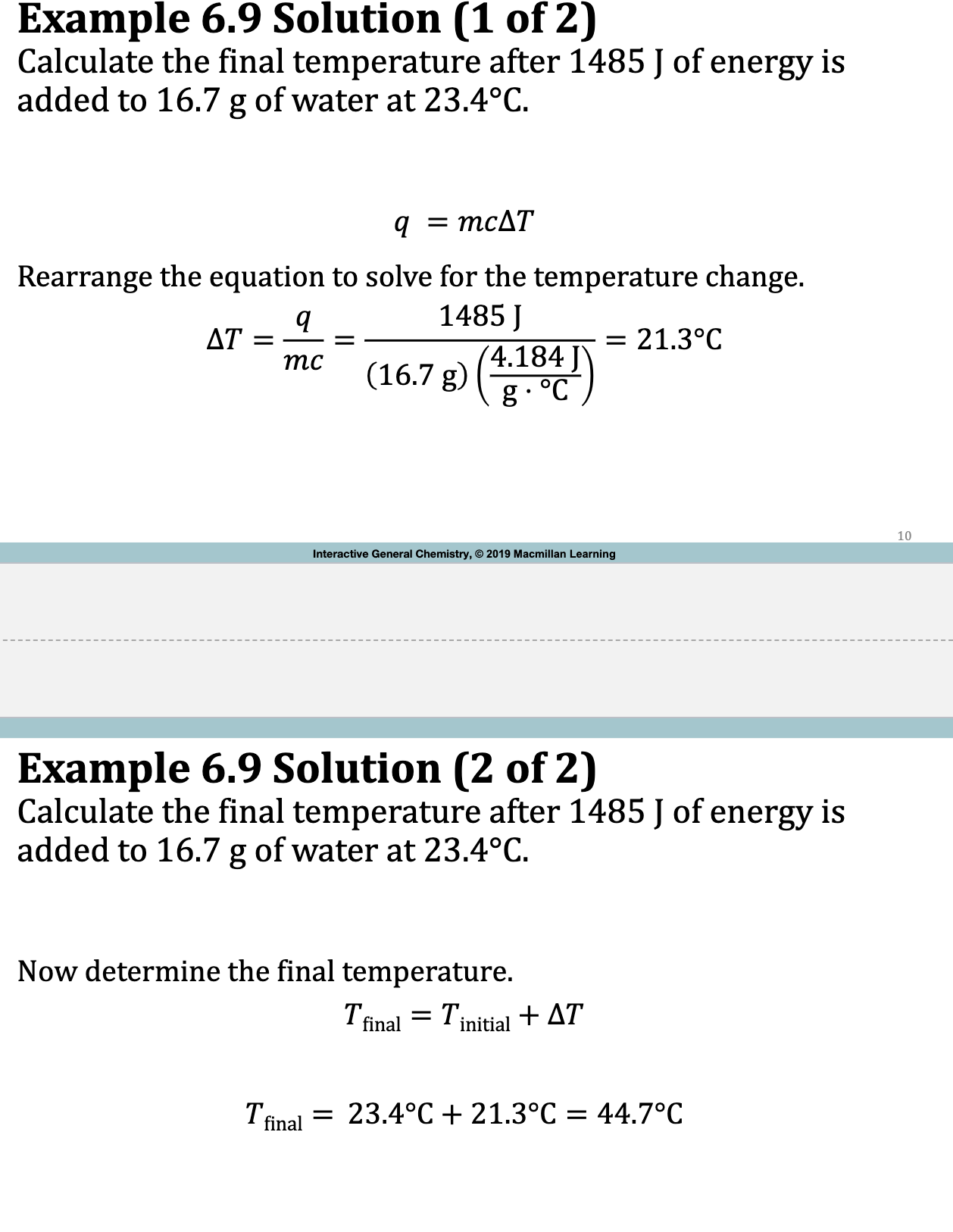
DeltaT is the ____ in temperature; what is its formula?
change
delta T (tfinal - tinitial)
OR
delta T = q / m x c
What is the enthalpy of the solution
the amount of heat absorbed or given off during the process
Calorimetry
the amount of heat lost by the metal is equal to the heat gained by the water
-qmetal = qwater OR 0 = qwater + qmetal
qmetal = (mmetal)(cmetal)(deltaTmetal)
qwater= (mwater)(cwater)(deltaTwater)

Ex. 6.10


E.x. 6.11

Constant-Pressure Calorimetry
The system is not sealed, so the calorimeter pressure is the atmospheric pressure
qp - deltaH, the enthalpy change for the reaction
Heat of Solution
For processes happening in solution, qsoln = -qp
Heat of soln / enthalpy soln (DeltaH soln): the release or absorption of heat that occurs when a solid compound dissolves in a solvent at a constant pressure to infinite dilution

E.x. 6.13
qsoln = -qrxn
Delta H = qsoln


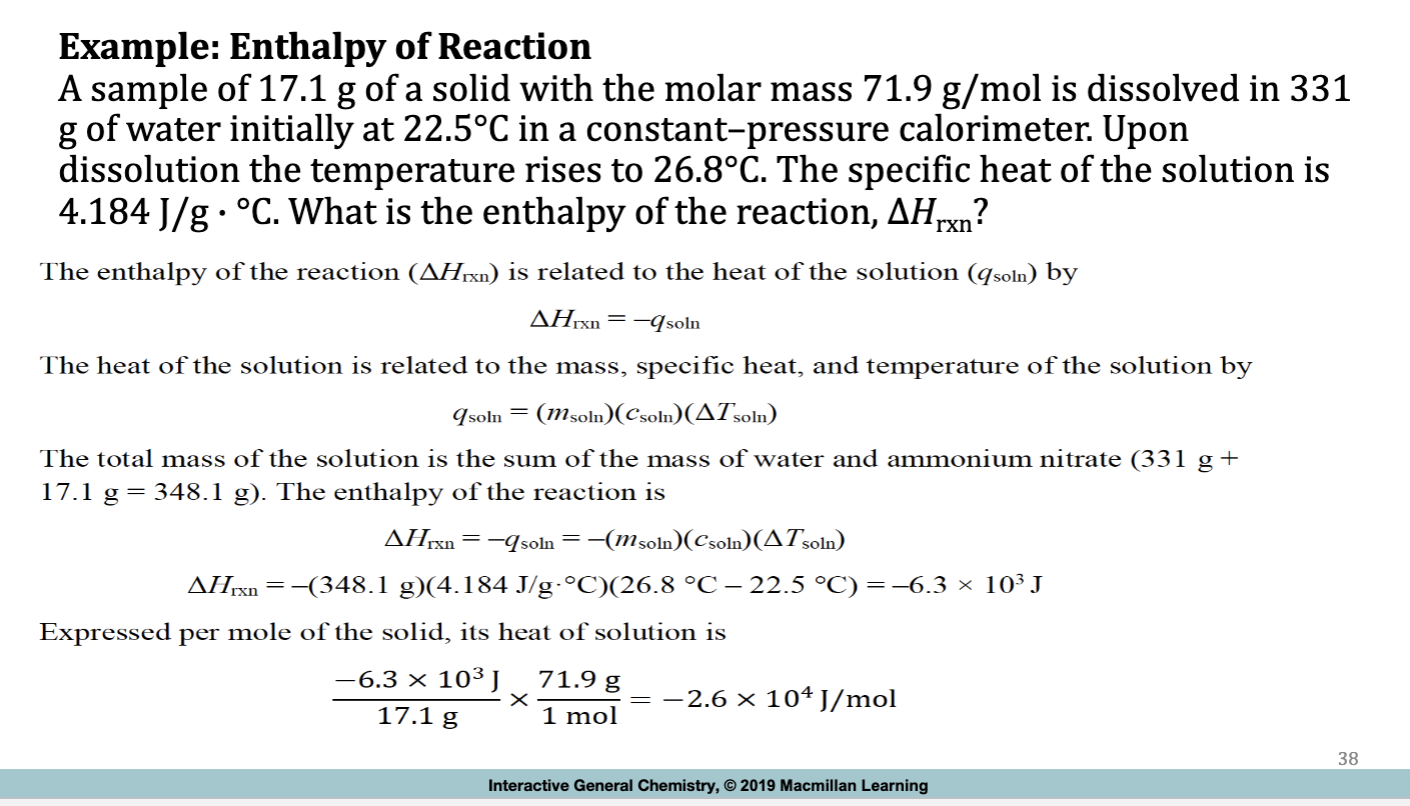
Practice Problem 6.13: Enthalpy of Reaction


Example: Enthalpy of Reaction
Constant-Volume Calorimetry
carried out in a bomb calorimeter
designed to withstand high temperature and pessure changes, and to be sealed and insulated from the surroundings
They are close to a true isolated system
Heat flow in a bomb
A measure of deltaU or deltaE
deltaU = deltaE = q + w
w = 0 inside a rigid container with a constant volume
Therefore, deltaU = qv
Bomb Calorimetry Calculations
These calculations use the total heat capacity of their calorimeter components and the water, Ccal, not just the specific heat of water, cwater
deltaUrxn = -CcaldeltaT
or (remember): qrxn = -CcaldeltaT
q=cdeltaT

E.x> 6.14

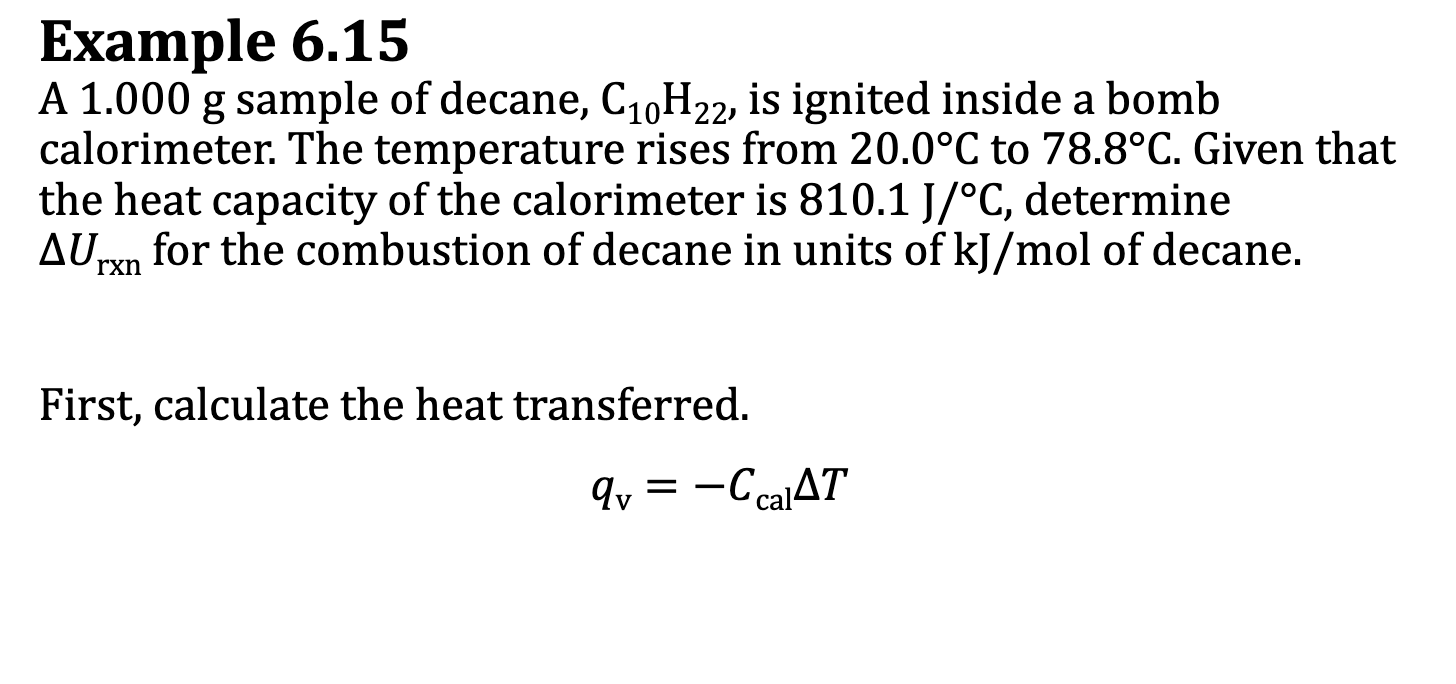
E.x. 6.15


Practice Problem 6.15

Constant V Equation
qrxn = -CcaldeltaT/qsoln
Constant P Equation
qrxn = -qsoln

E.x. 6.17

E.x. 6.18
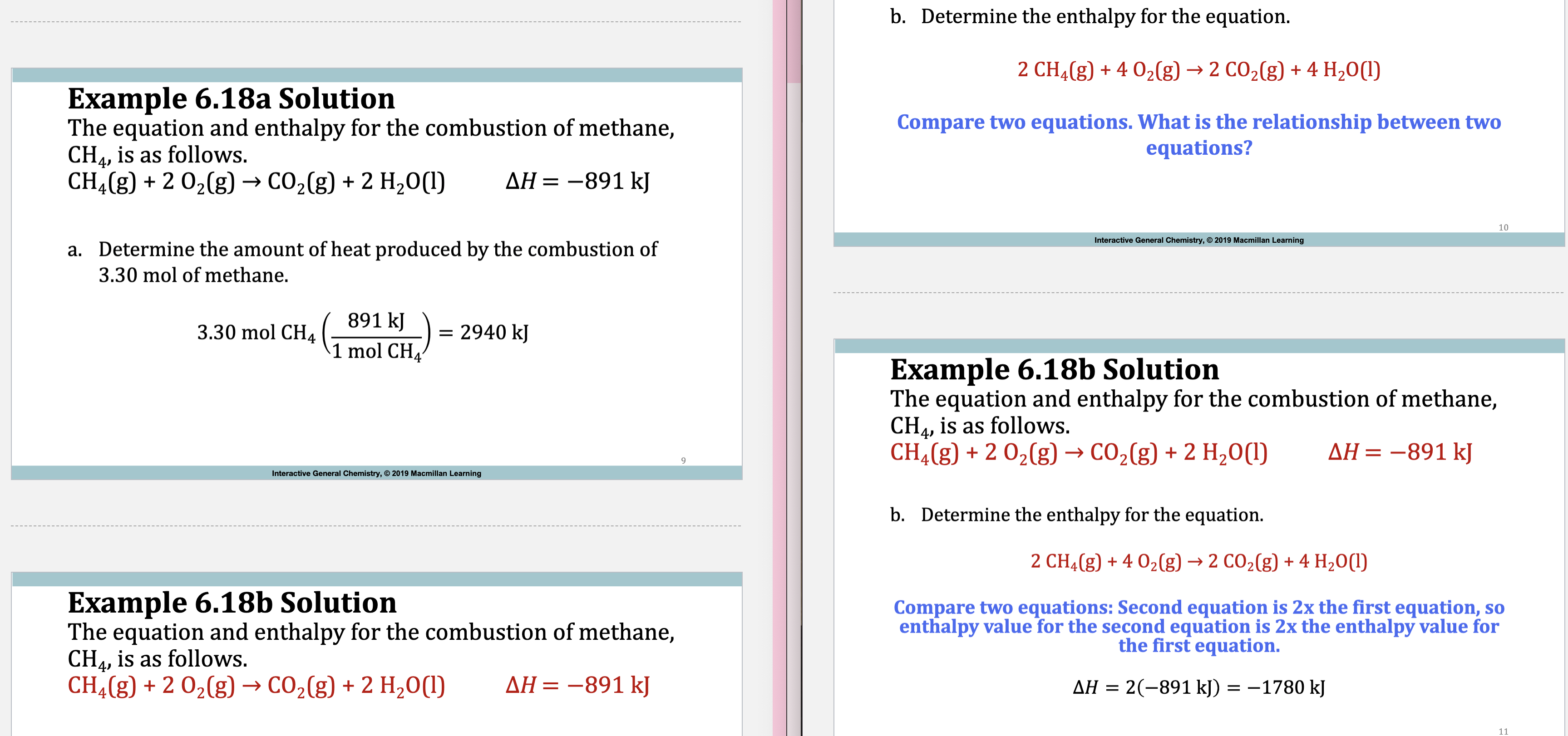

Your Turn

Hess’ Law
a method to calculate deltaH values for rxns by manipulating the equations for other reactions with known deltaH values
Advantage: we don’t need to use actual calorimeter to collect any data needed for the calculations of deltaH values
Hess’ Law: Manipulating Chem Equations: Rule 1

Hess’ Law: Manipulating Chem Equations: Rule 2
same equation, diff quantities
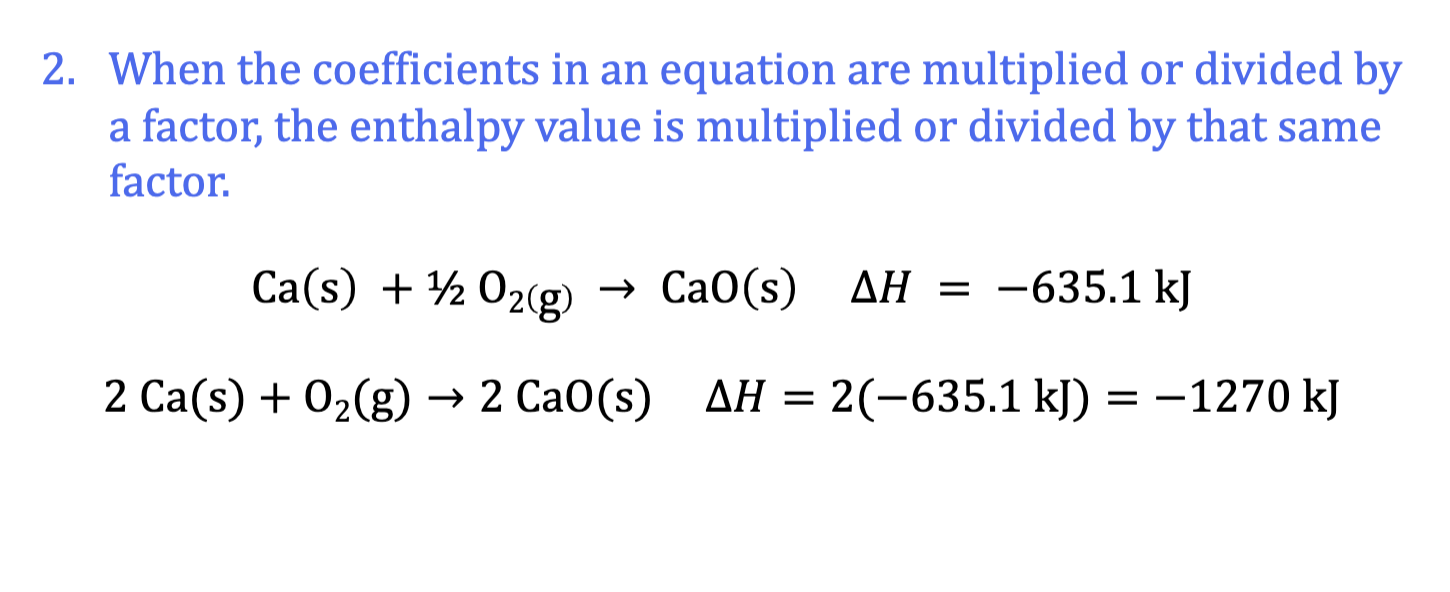
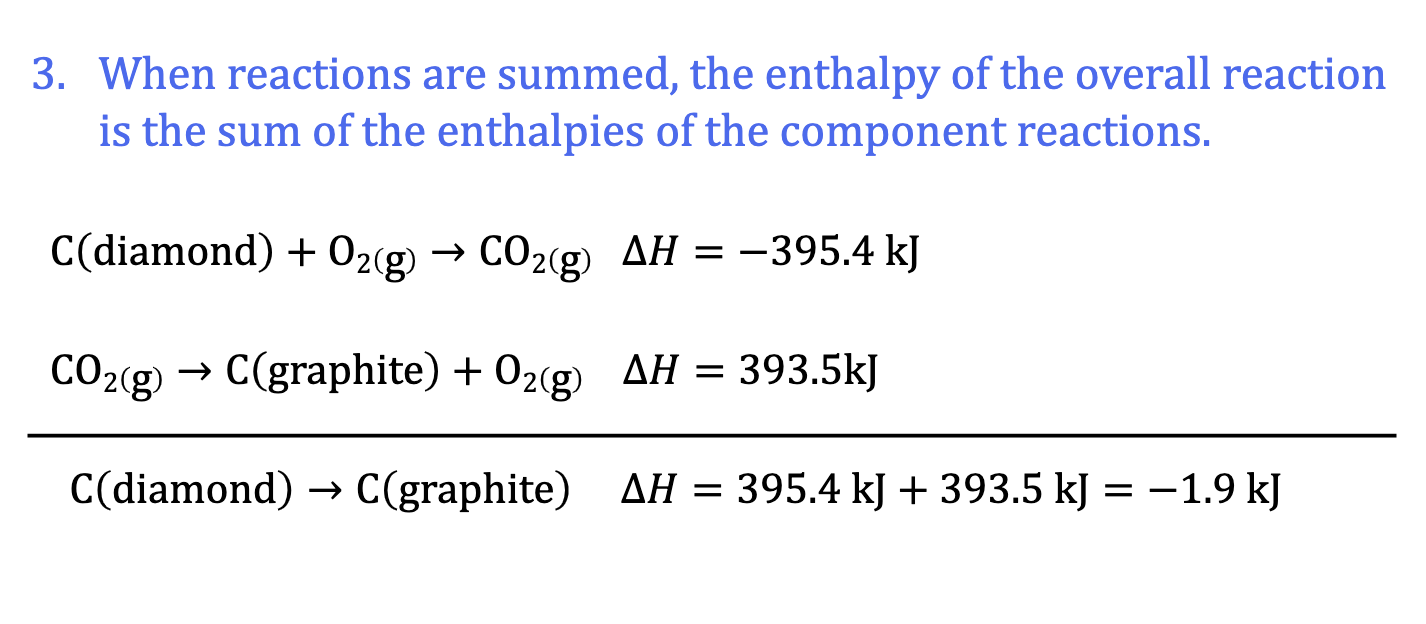
Hess’ Law: Manipulating Chem Equations: Rule 3
C(diamond) + O2(g) + CO2(g) → CO2(gr) + O2(g) add the two rxns
C(diamond) → C(graphite)
delta H = ?

Another Example$
Reactants: C(s) + O2(g) + CO2(g)
Products: CO2(g) + CO(g)+1/2O2(g)
See what you can cancel out; the ½ O2 multiplies wit the other O2
What’s Left: C(s) + 1/2O2(g) → CO(g) (Target Equation)
DeltaH: Add the -393 and new DeltaH2 +283


E.x. 6.19
Try to see similarities between the I & II reaction and the Target reaction.
II reaction has a different product, this means it has to be reversed. (I rxn has the same product) This changes the sign of the deltaH
Determine Reactants and Products
Cancel Out any similarities
Target Equation is found

Standard State
standard state of a substance is the state in which the substance is most stable at 25ºC (298K) and 1 atm pressure
The standard state of a substance is the natural state of the substance
Standard state of Na (s) not Na (l)
Standard state of H2 (g) not H (g) or H (l)
Enthalpy of Formation + Enthalpy Change
The enthalpy change of the rxn below is called Enthalpy of formation, deltaHf
2H2(g) + O2 (g) → 2H2O (l)
The enthalpy change of the rxn below is called Standard Enthalpy of formation, delta H^0 subscript f
H2 (g) +1/2 O2(g) → H2O (l)
What is the Standard Enthalpy of Formation deltaHºsubscriptf
the enthalpy of formation of 1 mol of a compound from its constituent elements in their standard states (25ºC and 1 atm)
Note that the deltaHºf of any element in its standard state is 0
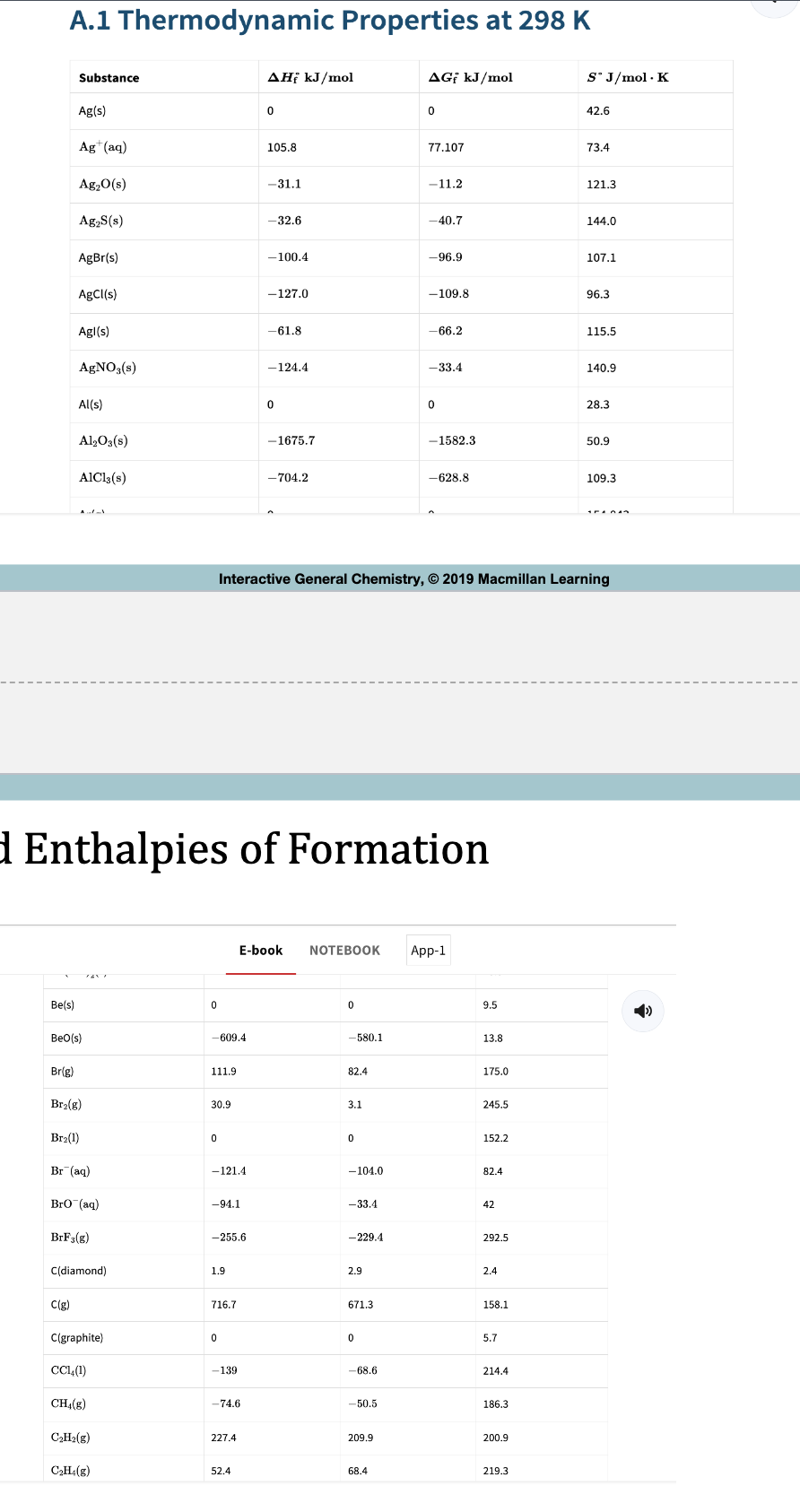
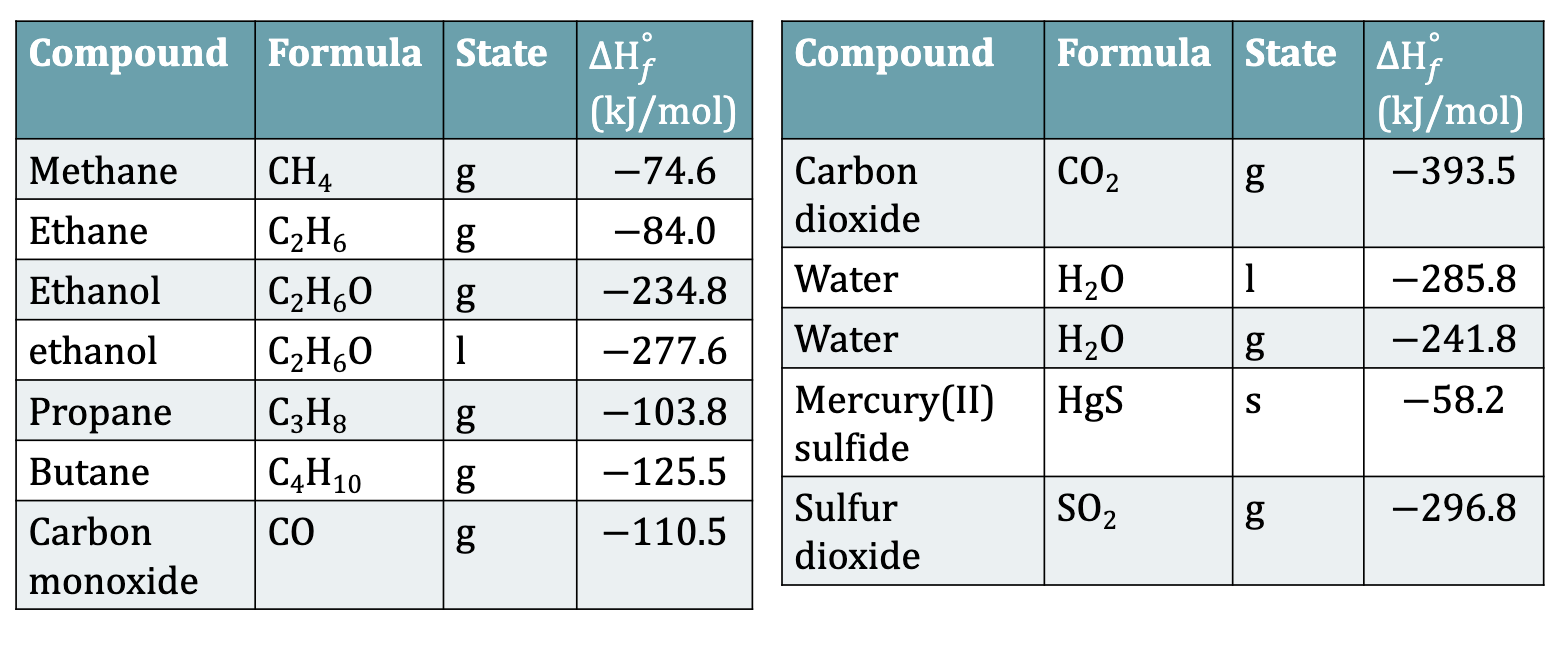
Standard Enthalpies of Formation
Standard Enthalpy formation deltaHºf of water (l) is -285.8 kJ/mole
It means that H2(g) + 1/2O2 → H2O (l)
Since this rxn forms one mole of the product in the standard state, for this rxn deltaHºf = deltaHrxn
Table 6.4: Some Standard Enthalpies of Formation at 298K
Molar deltaH
find the deltaH and divide by the numbero f moles
dissolution proess; opposite of given (exo/endo) change in enthalpy changes
Use molar mass of given formula and the given mass to find the mole

Using deltaHºf to Calculate deltaHºrxn
deltaHºrxn = [sum of deltaHºf (products)] - [sum of deltaHºf (reactants)]
when the reaction involves multiple moles of products and reactants
deltaHºrxn = summation m [deltaHºf (products)] - summation n [deltaHºf(reactants)]
m = number of moles of each product
n = number of moles of each reactant

E.x. 6.21

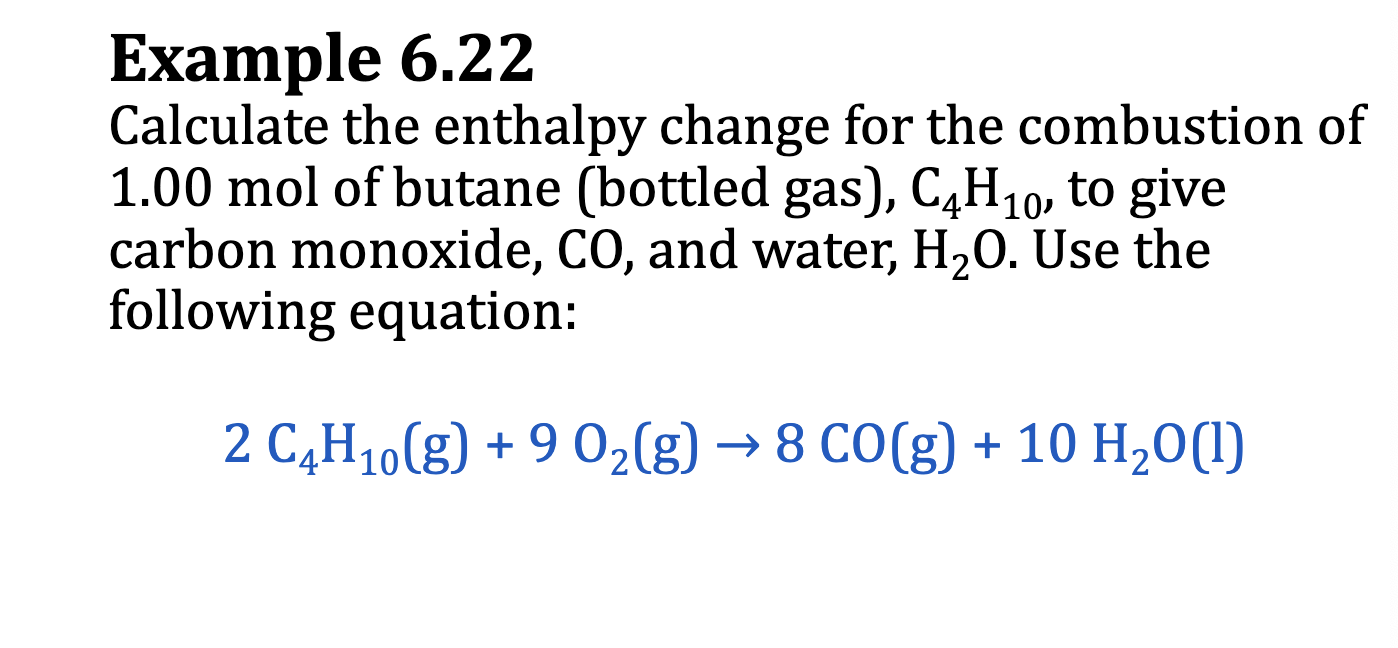
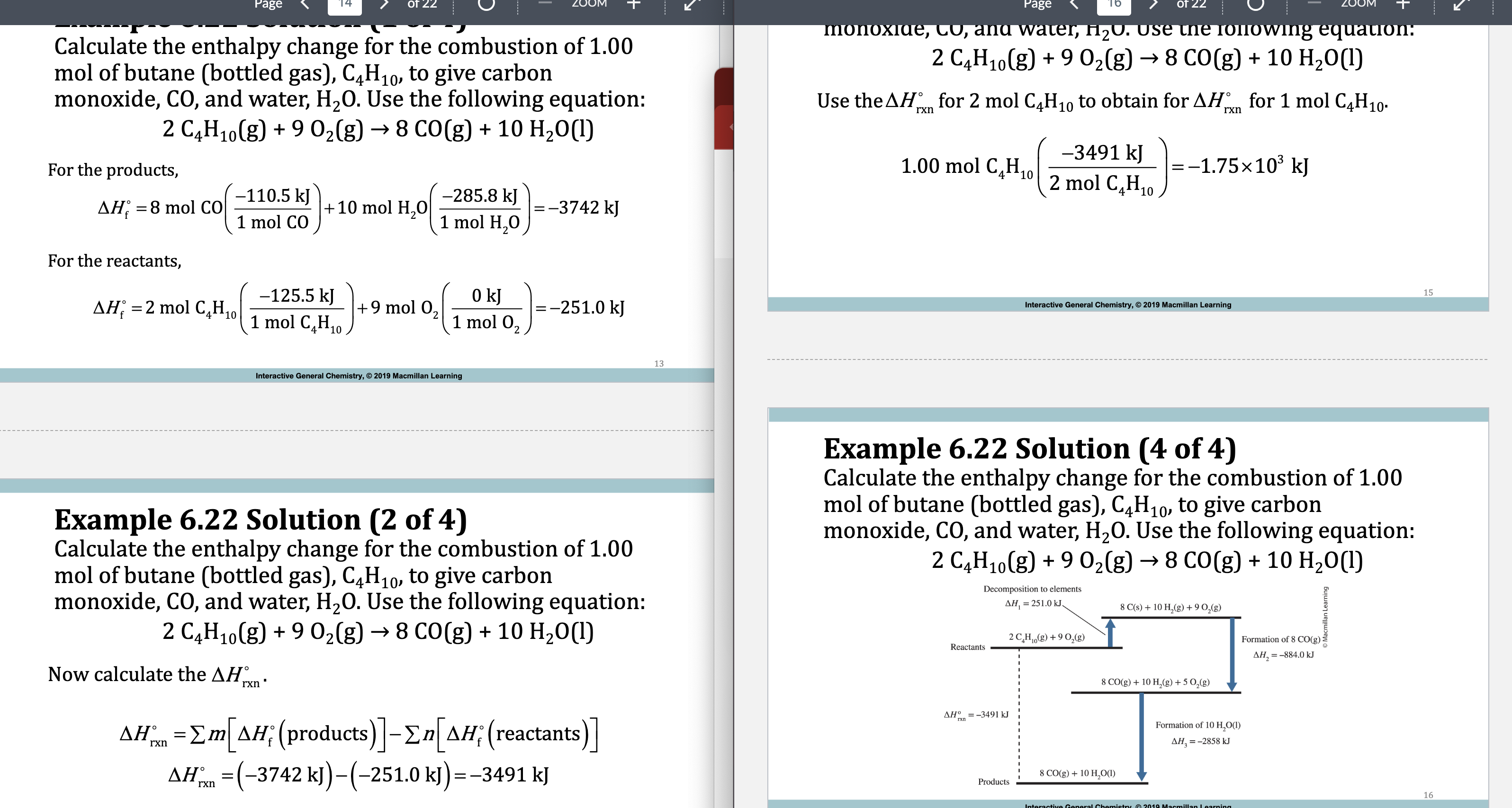
E.x. 6.22

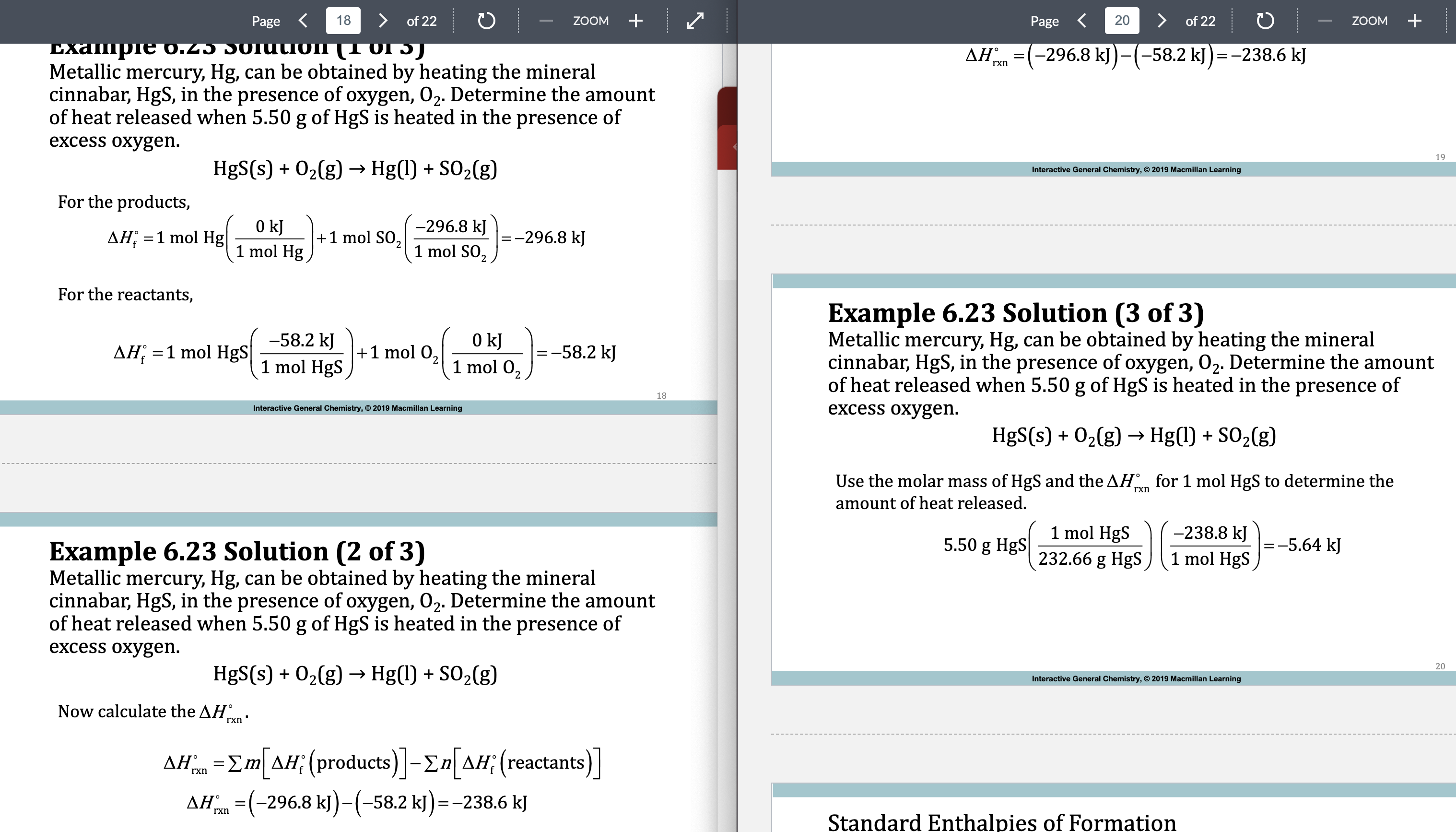
E.x 6.23
Standard Enthalpies of Formation