GI Histology
1/77
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Year 1 - Semester 1
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
78 Terms
what type of epithelium is found in the oral mucosa?
keratinised stratified squamous
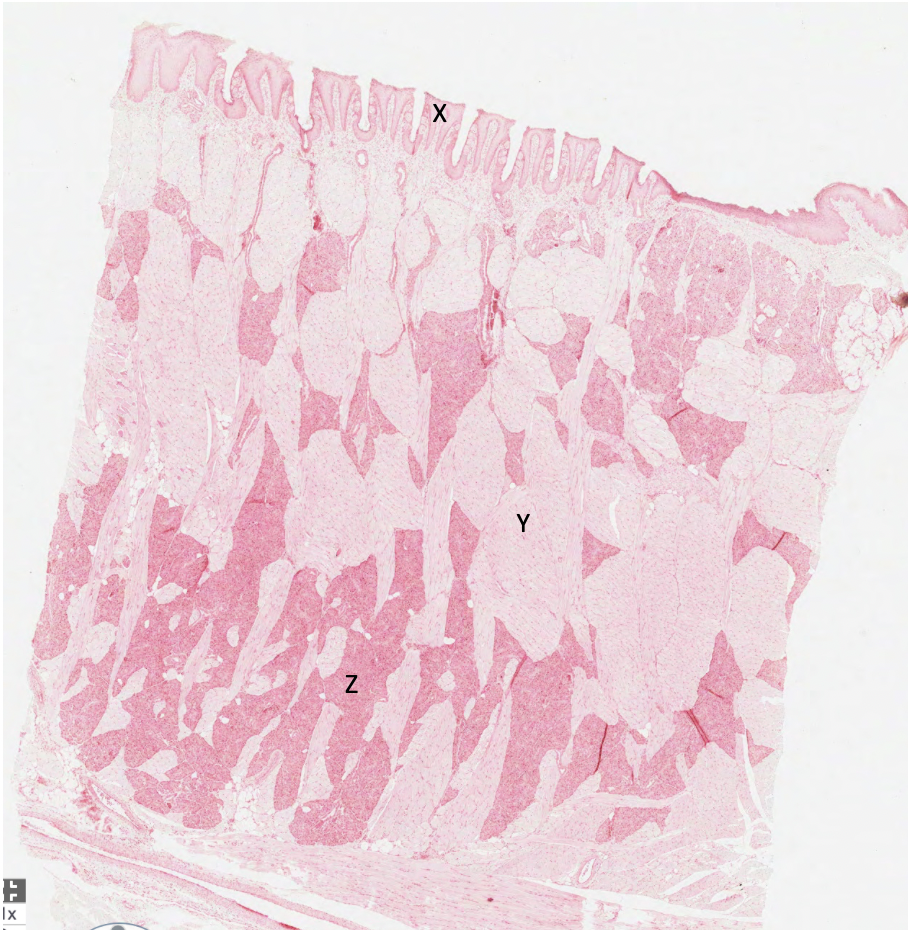
what does X represent in this rabbit tongue?
papilla lined by keratinised squamous epithelium
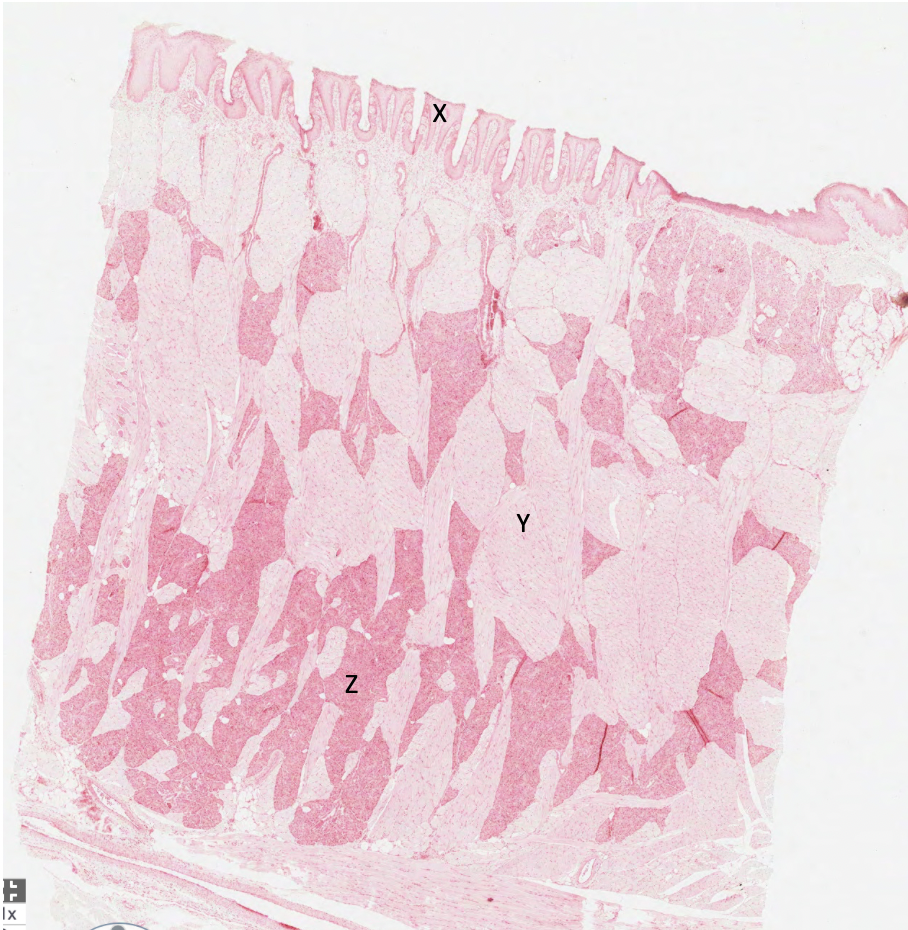
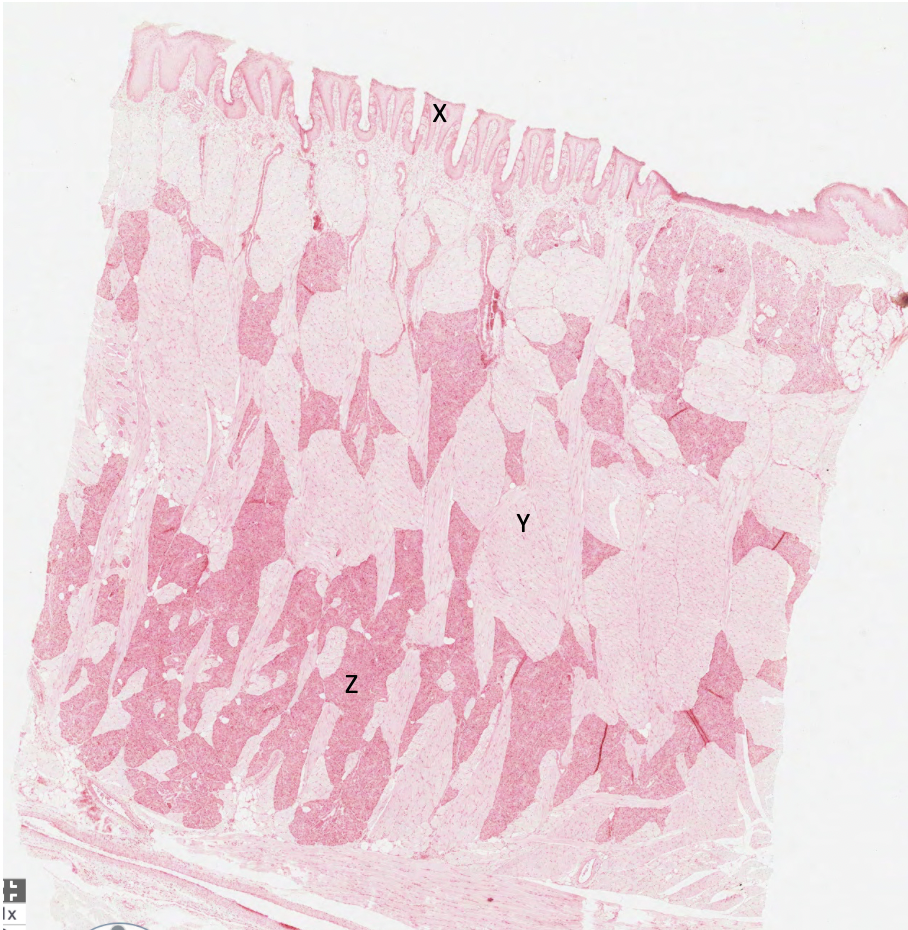
what does Y represent in this rabbit tongue?
skeletal muscle
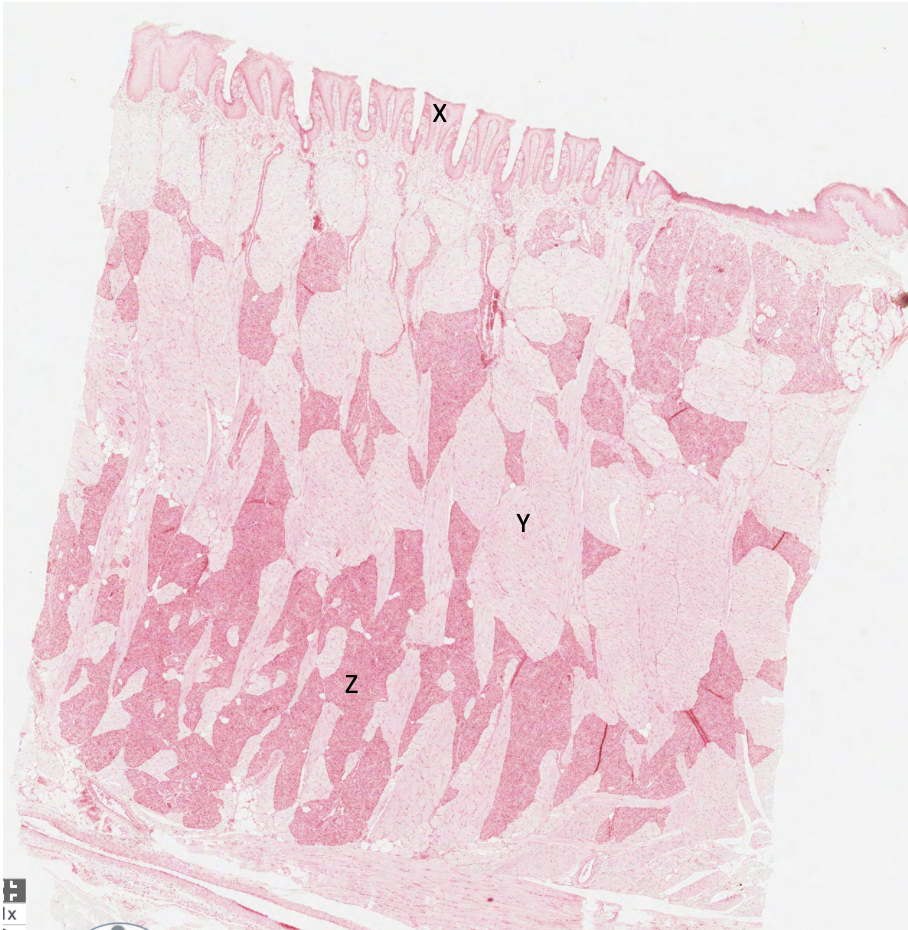
what does Z represent in this rabbit tongue?
serous glands
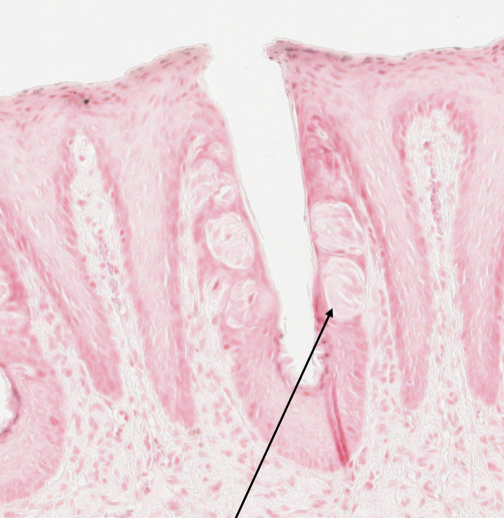
what structure in a rabbit tongue is shown by the arrow in this image?
taste bud
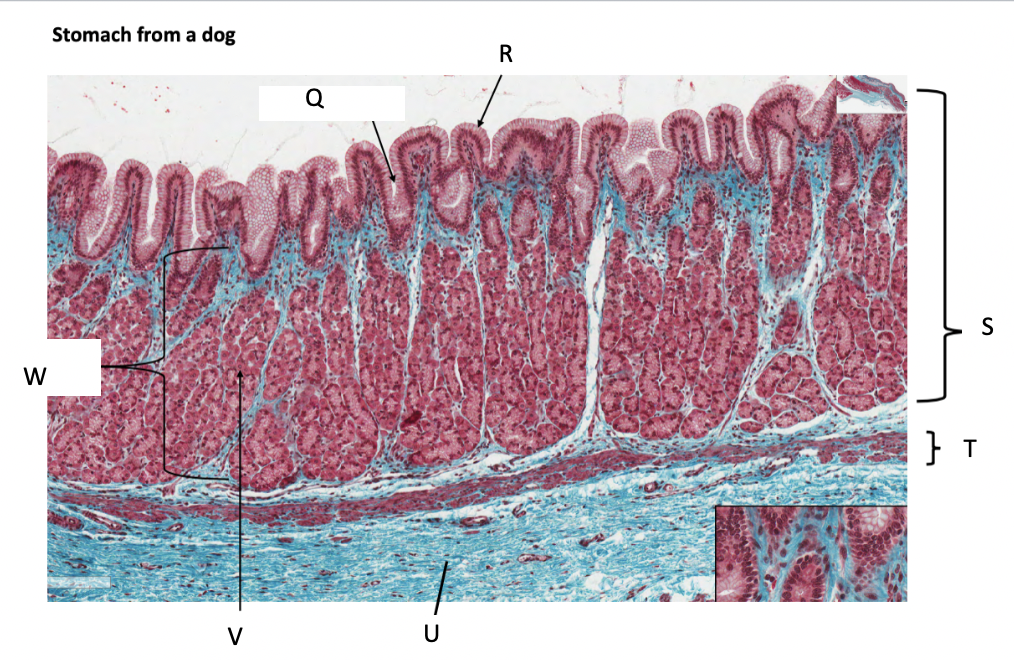
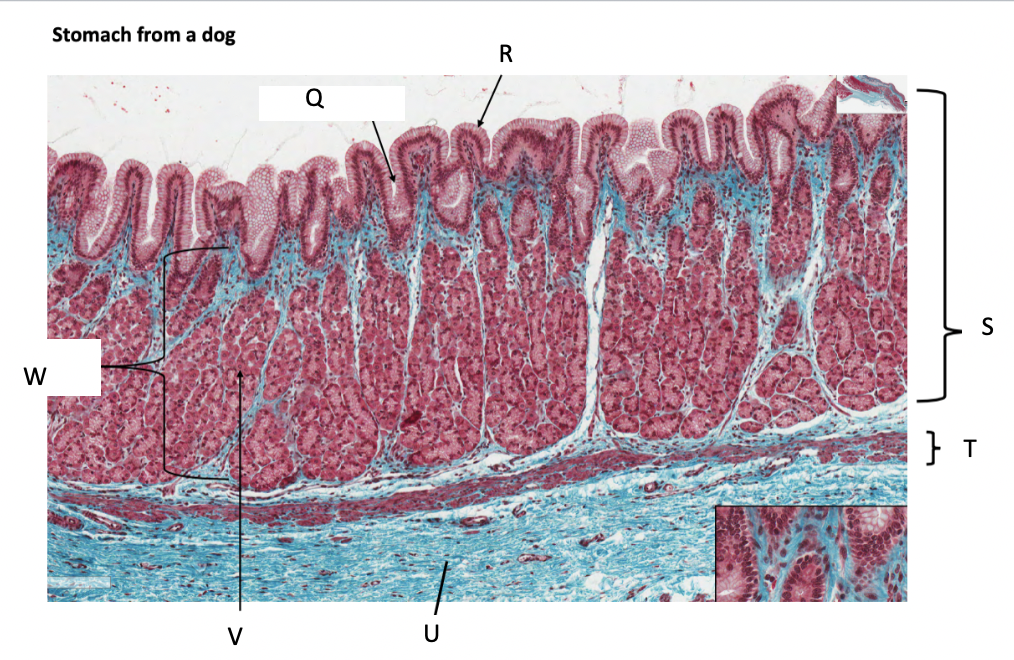
What is Q?
gastric pit
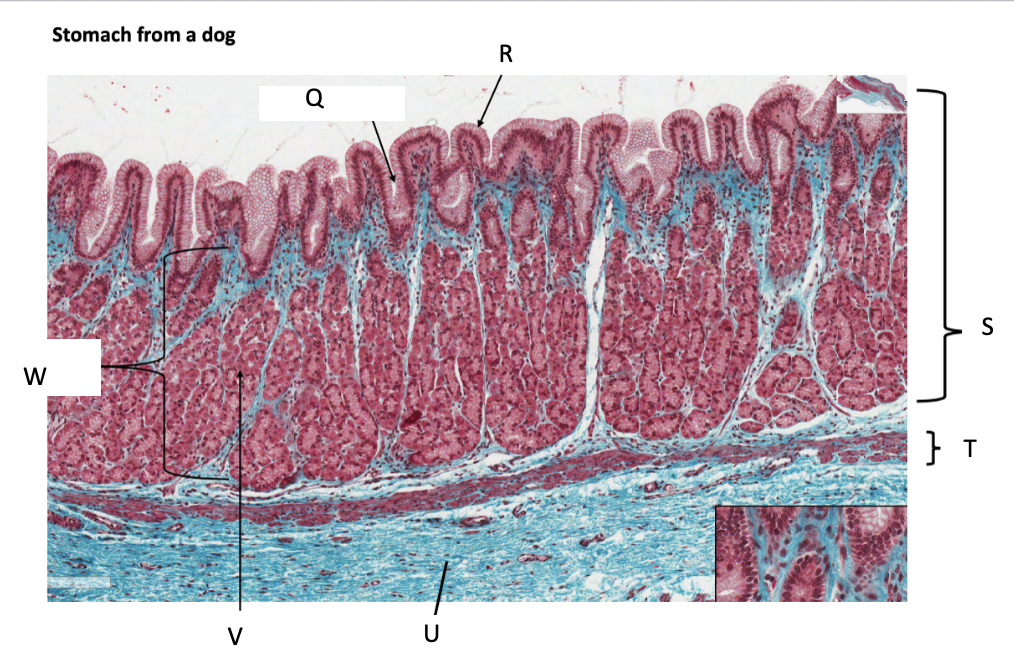
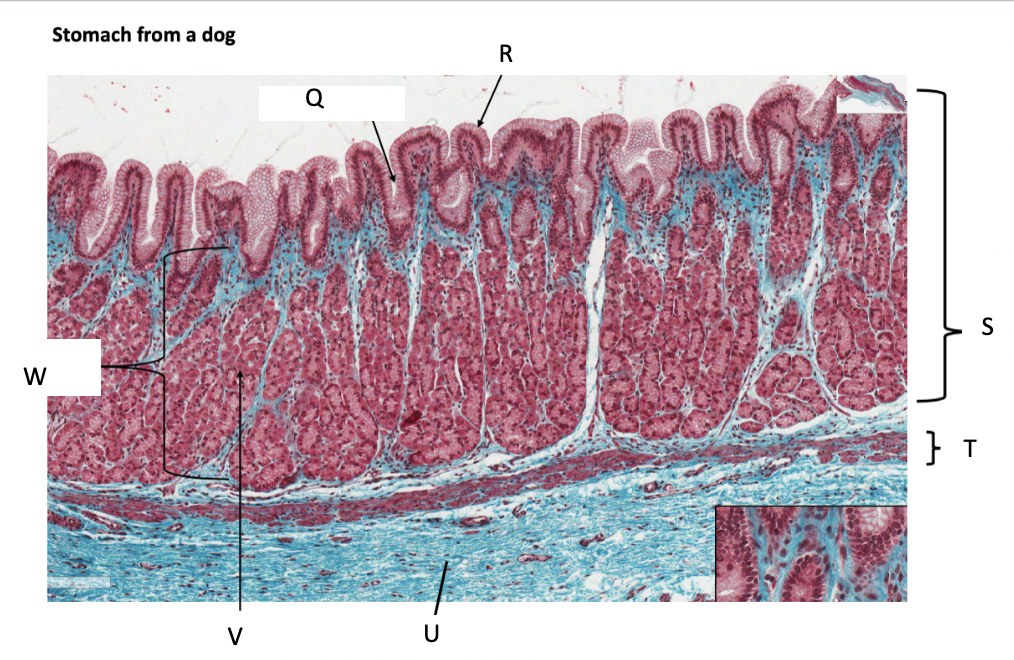
What is R?
simple columnar epithelium
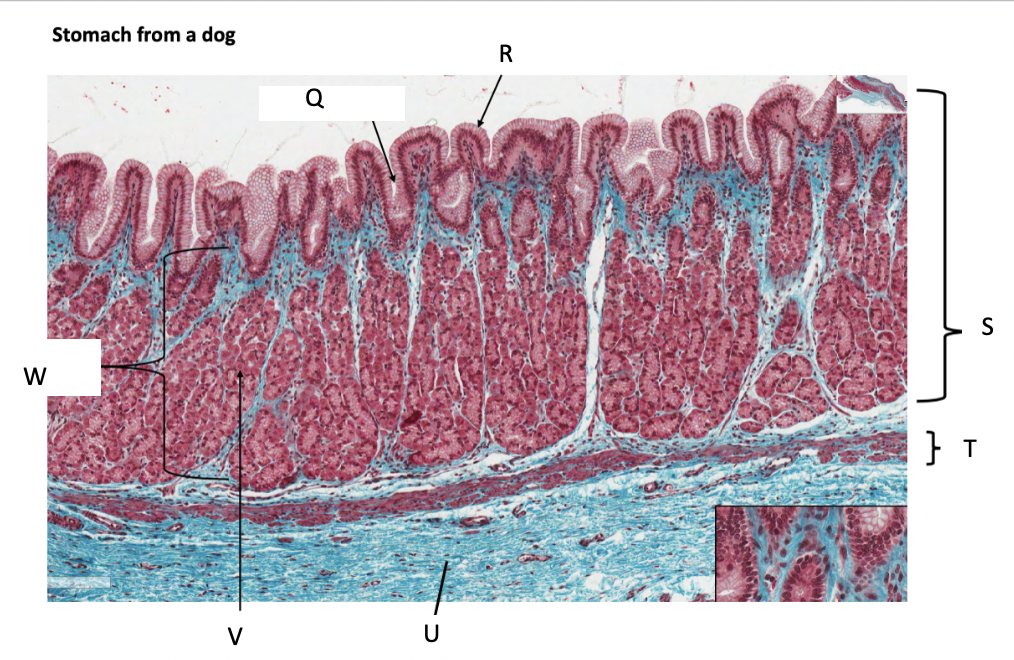
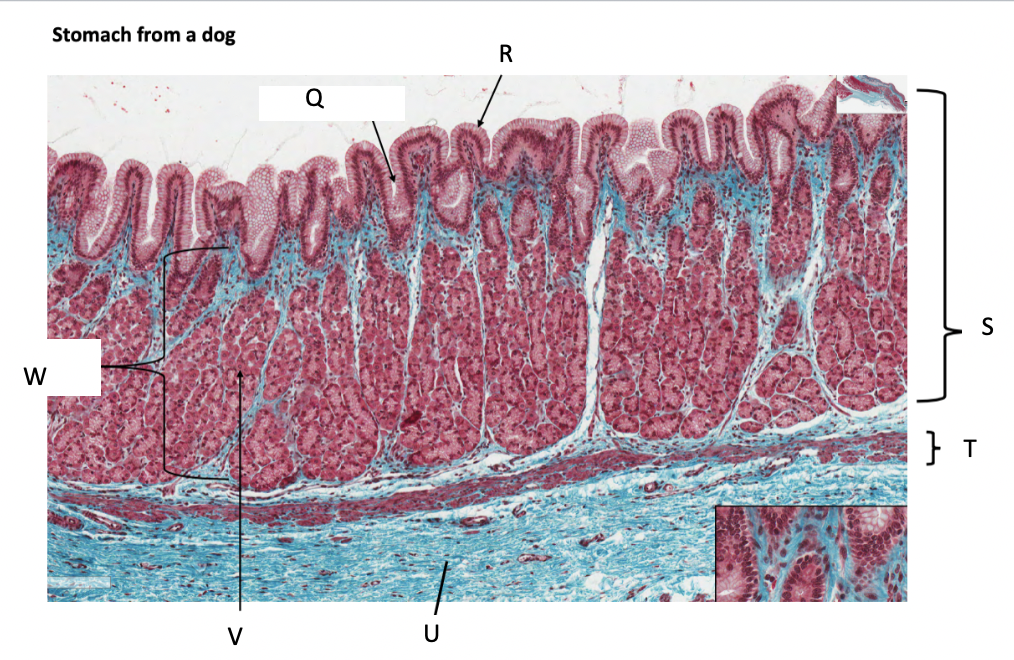
What is S?
stomach mucosa
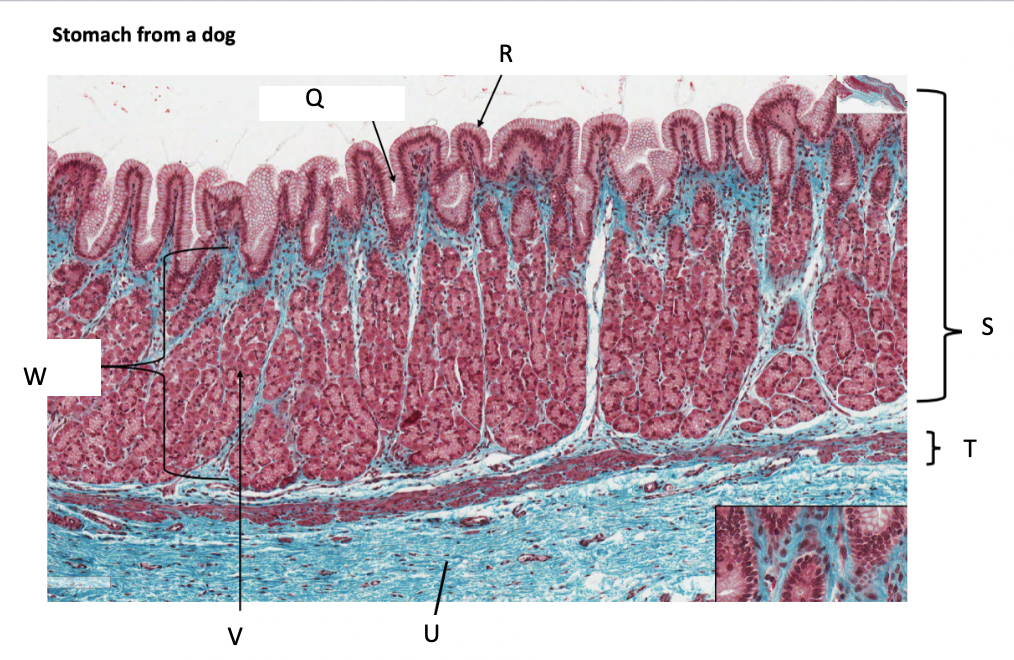
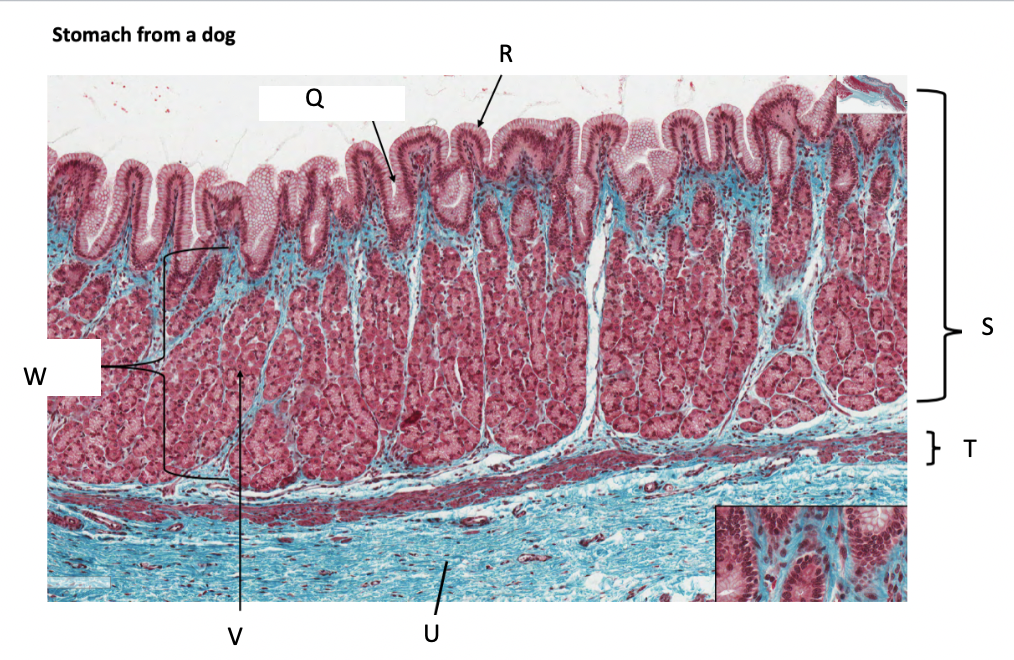
What is T?
muscularis mucosae
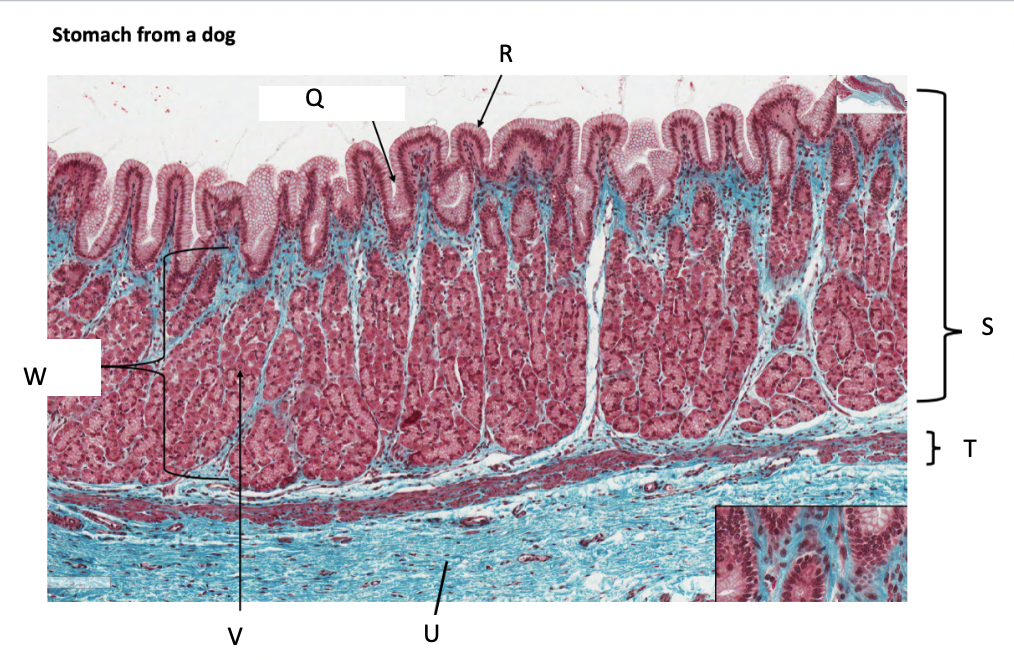
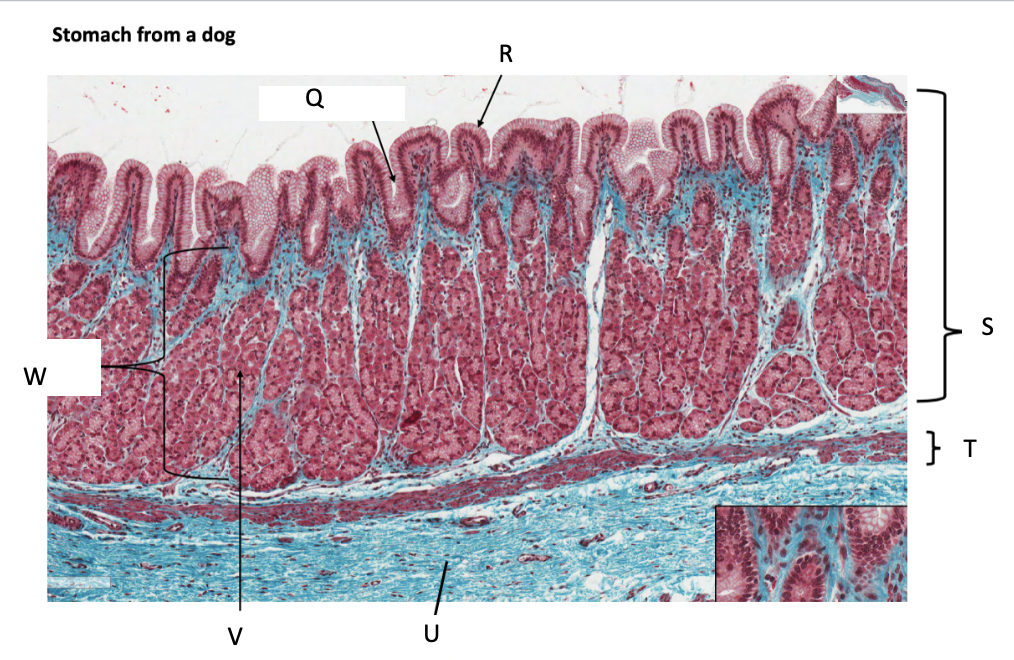
What is U?
submucosa
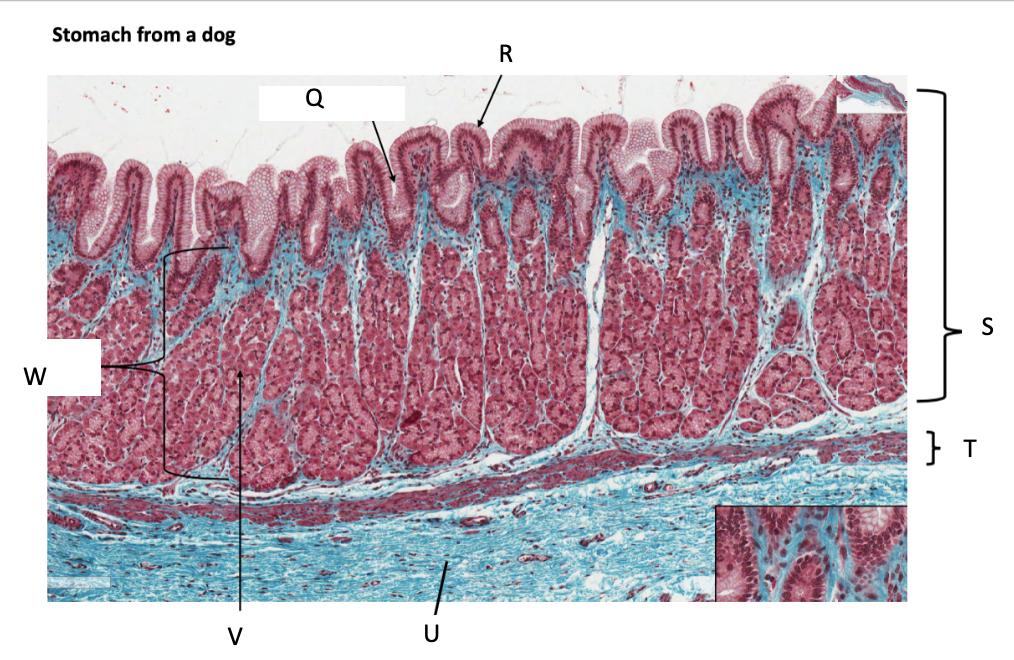
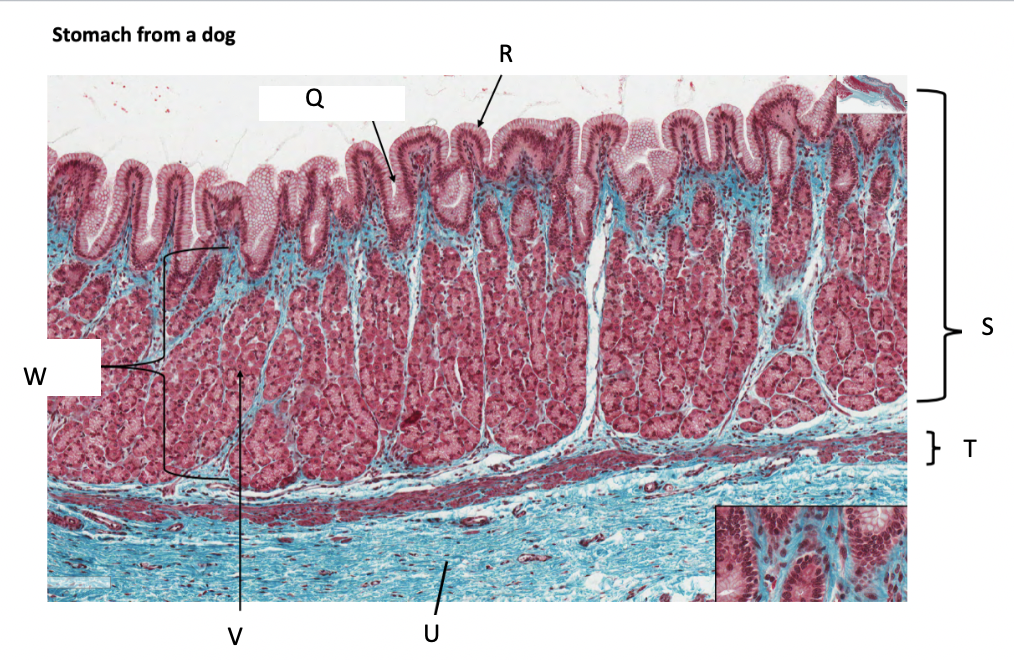
What is V?
parietal cells
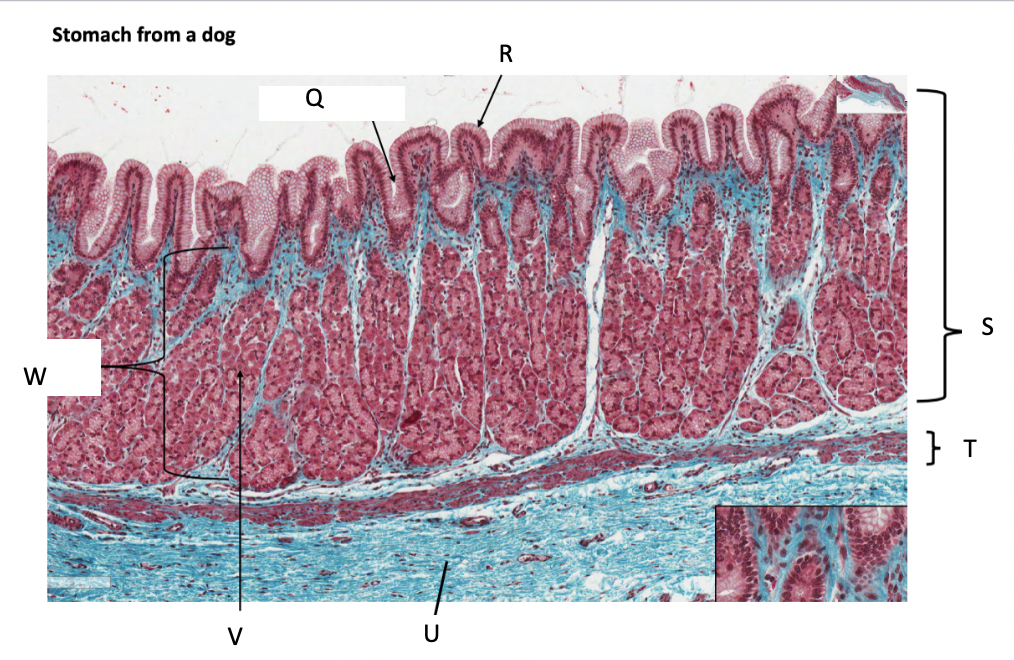
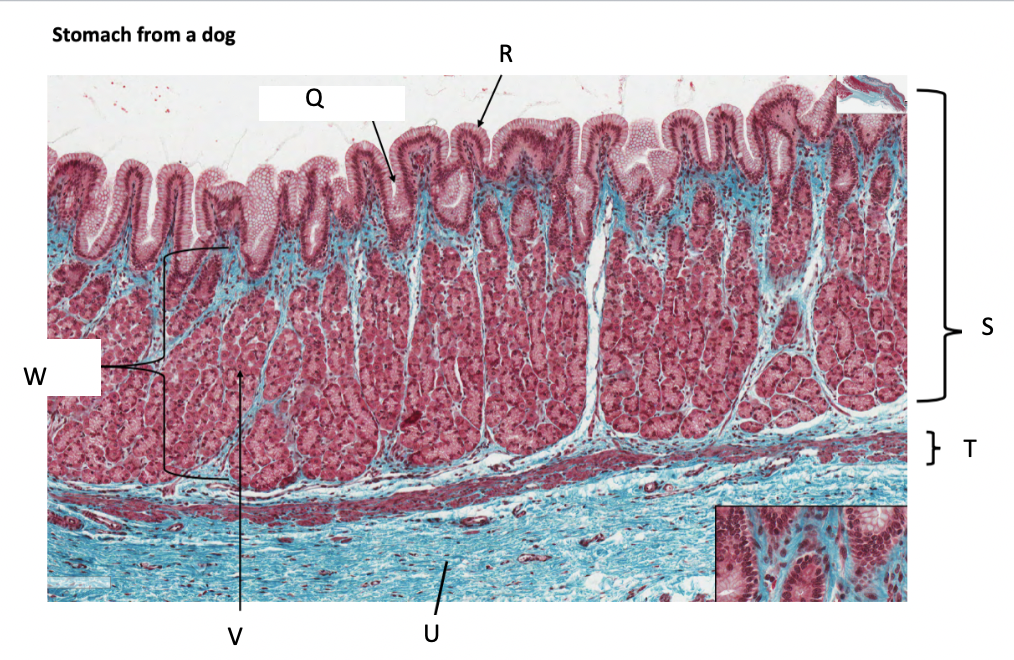
What is W?
lamina propria
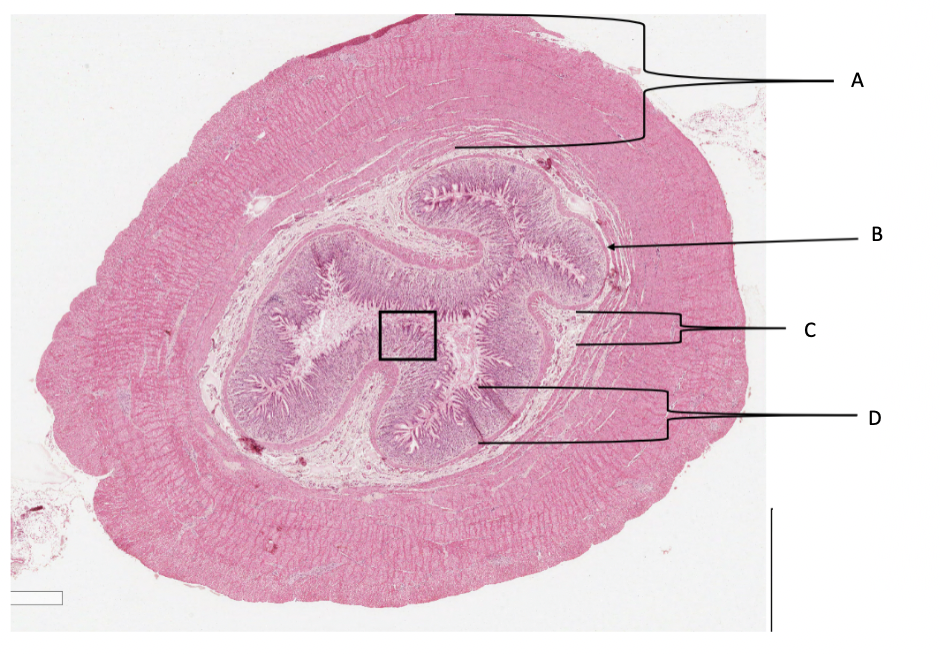
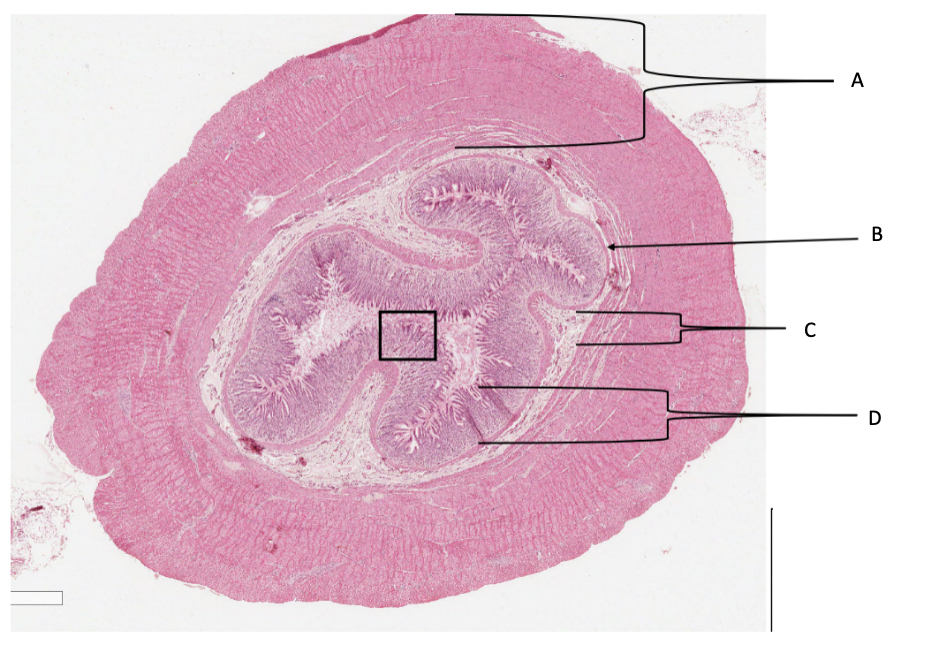
What is A in a cat stomach?
muscularis layer
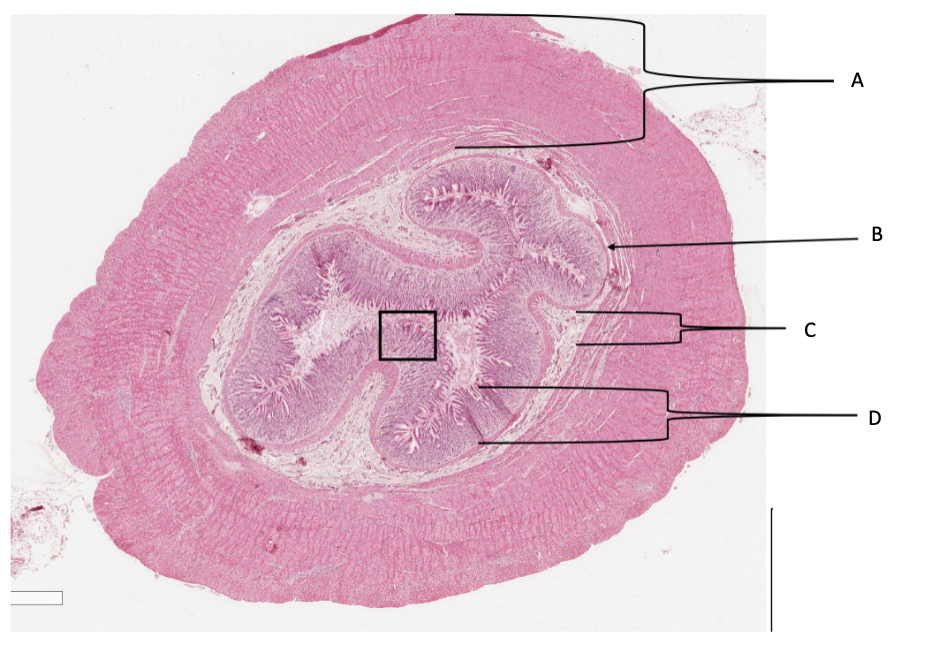
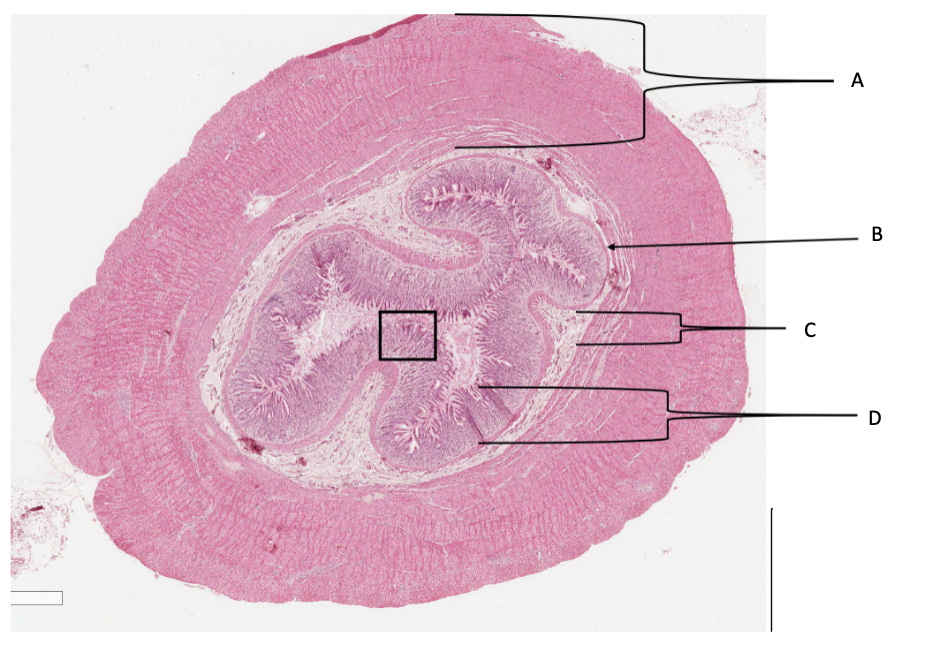
What is B in a cat stomach?
muscularis mucosa
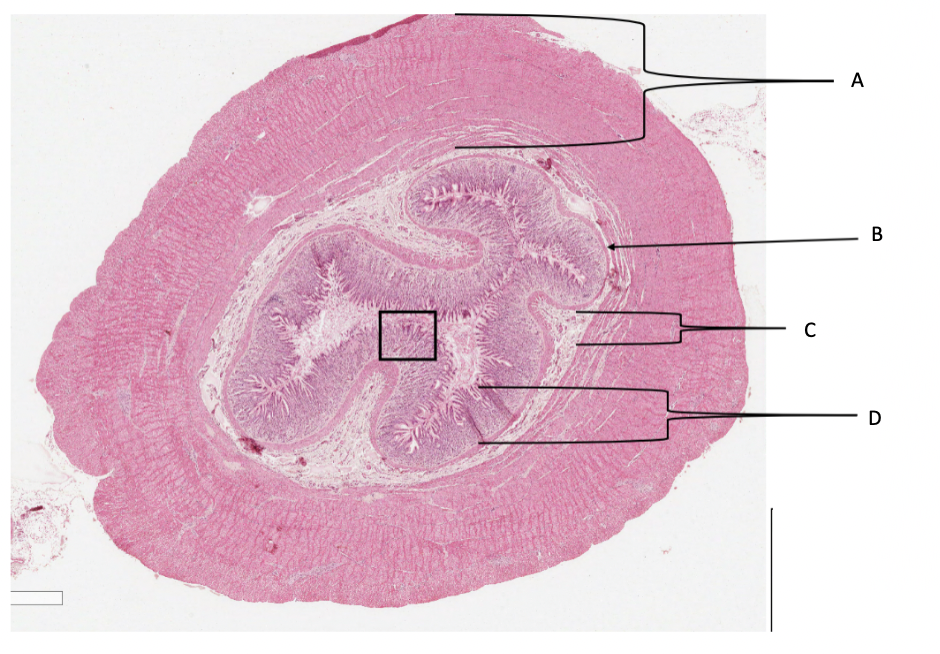
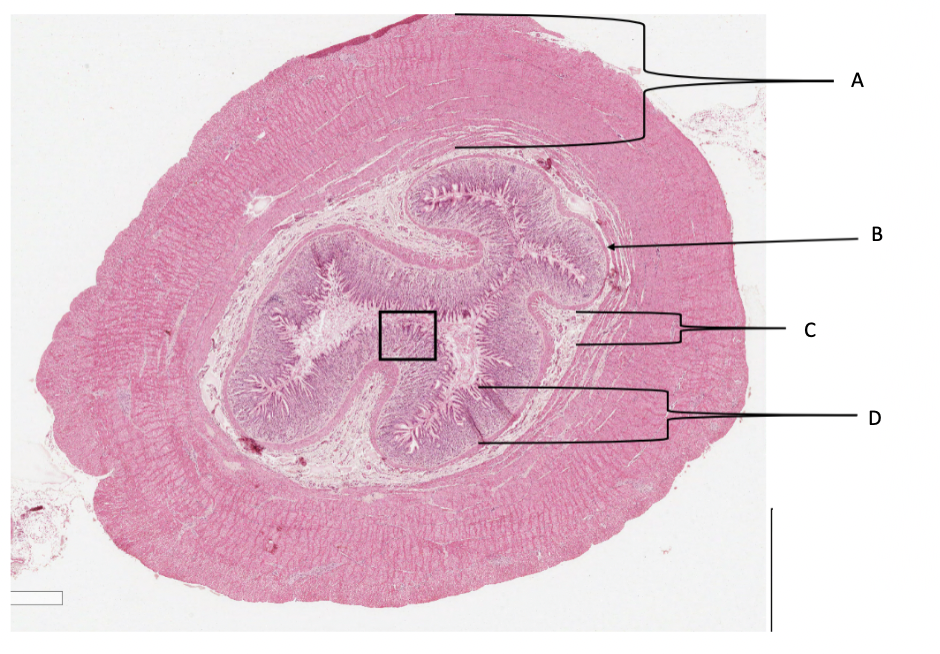
What is C in a cat stomach?
submucosa
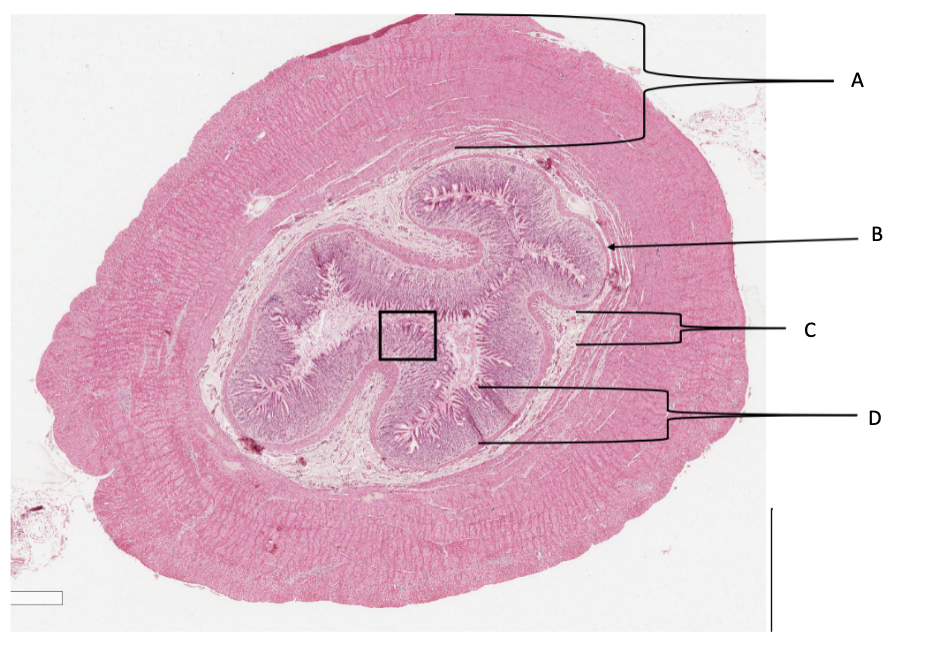
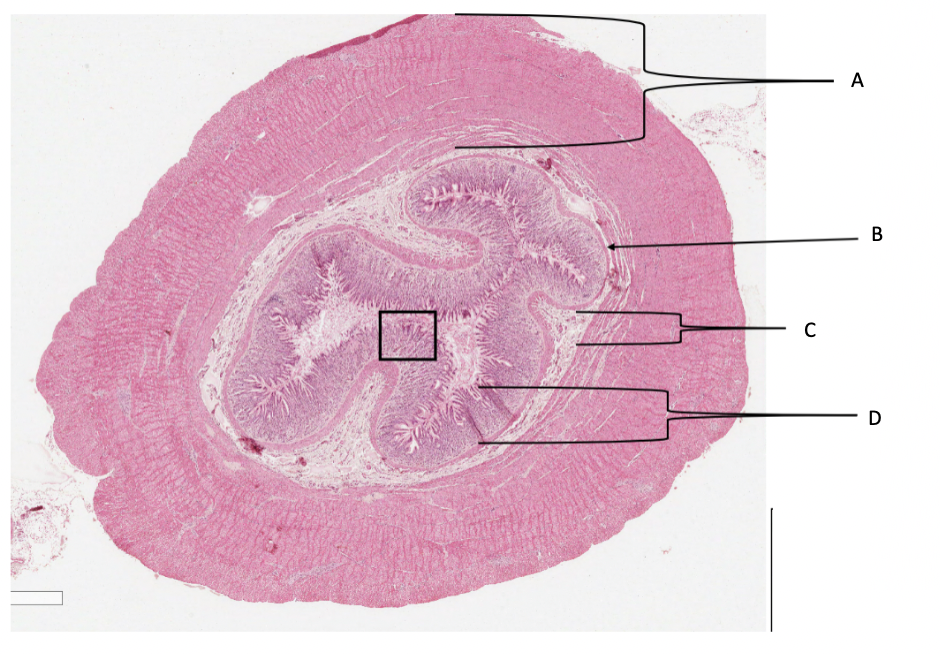
What is D in a cat stomach?
mucosa
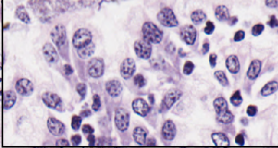
What are these cells from the abomasum of a sheep?
parietal cells
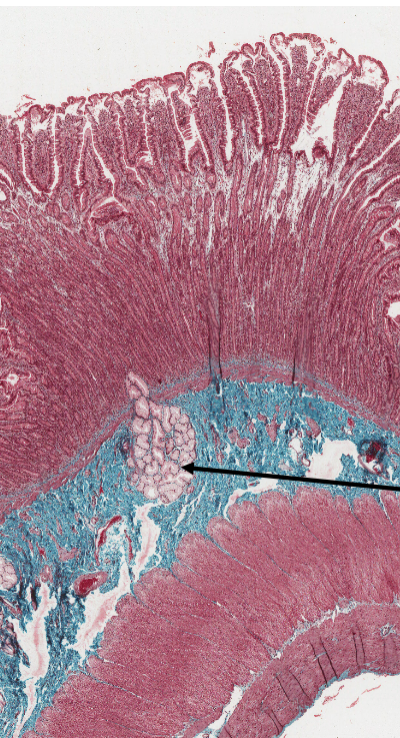
What is the structure marked by an arrow in the duodenum?
Brunner’s glands
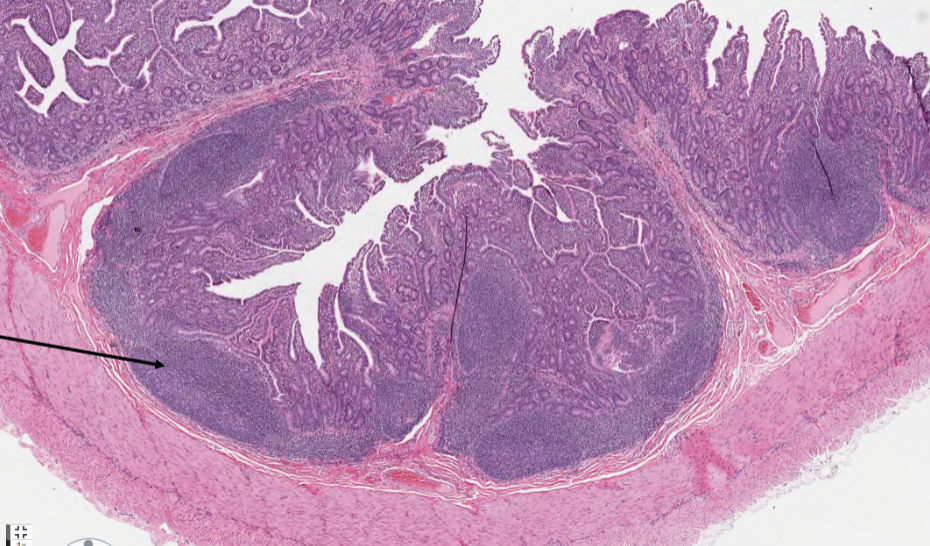
What is the structure marked by an arrow in a sheep ileum?
Peyer’s patch
function of Brunner’s glands
to secrete an alkaline mucus that protects the duodenal lining from the acidic chyme coming from the stomach
Peyer’s patches
organised lymphoid follicles in the lining of the small intestine which monitor intestinal bacteria and initiate immune responses against potential pathogens
what are the histological differences between the large and small intestine?
large intestine has more goblet cells, mucosa is arranged in colonic crypts in large intestine and in villi in small intestine
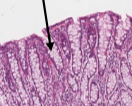
what cells are these in the colon mucosa?
goblet cells
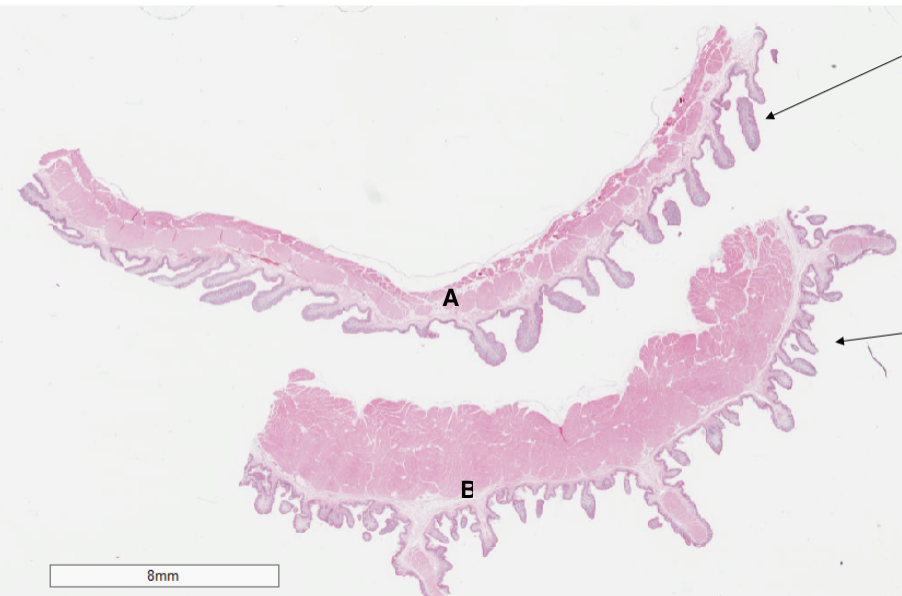
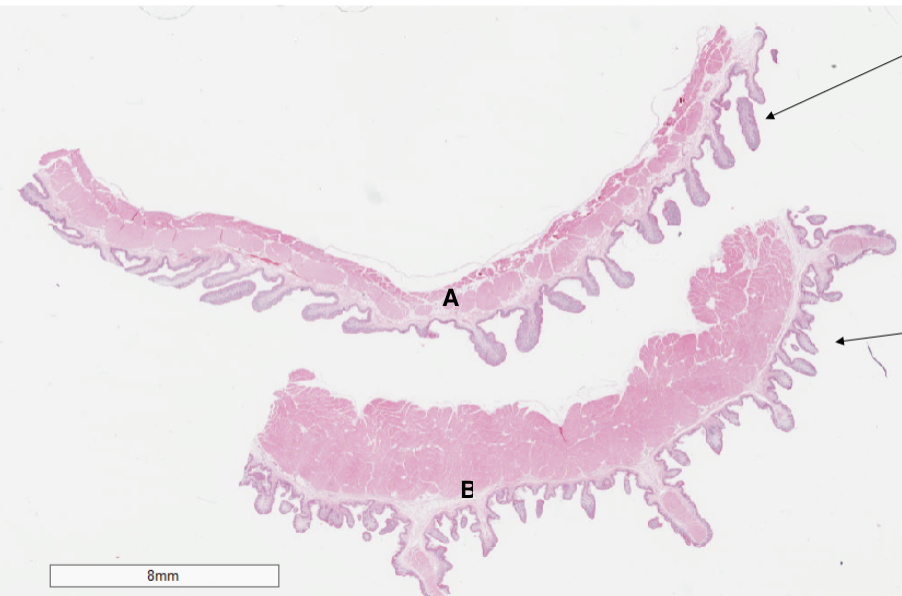
Which structure is a rumen?
A
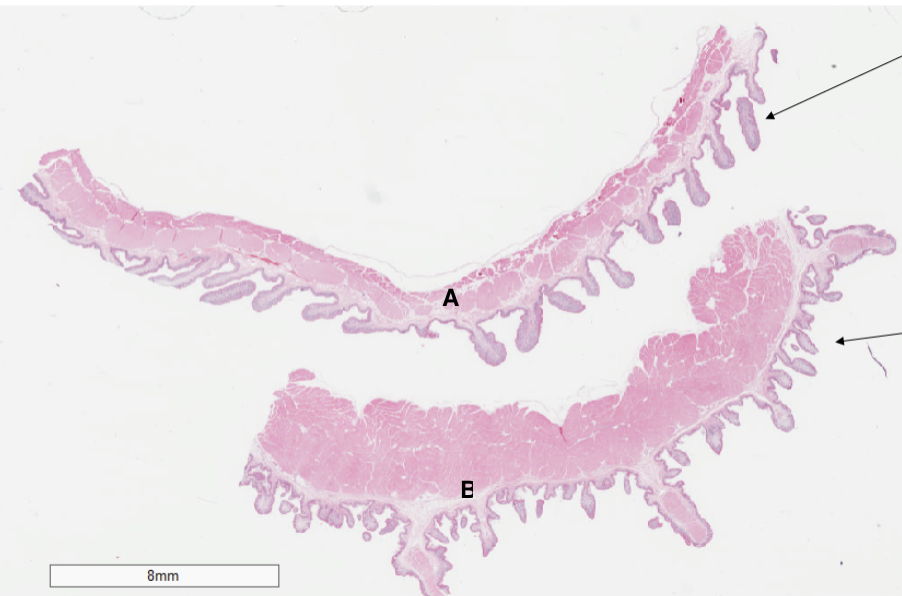
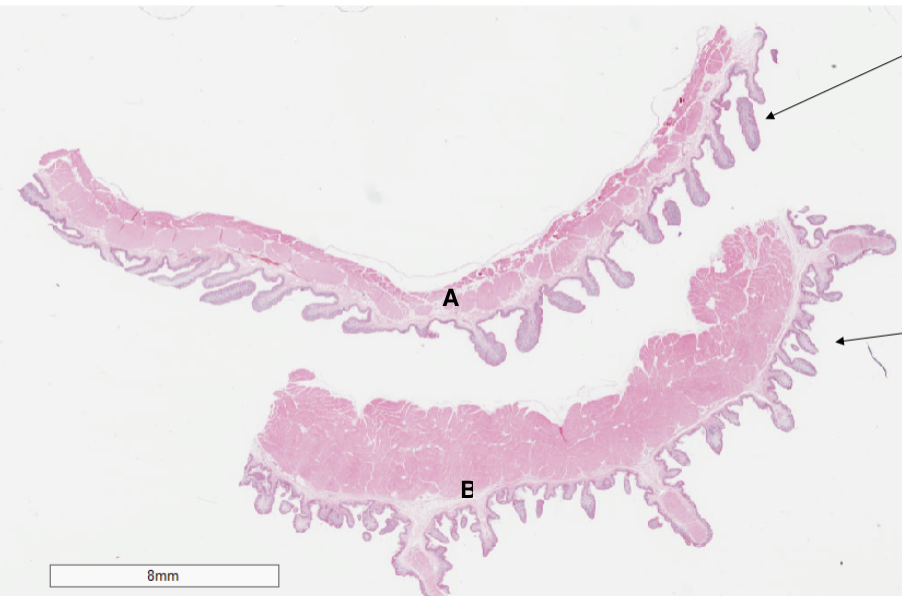
Which structure is a reticulum?
B
What structure is this?
omasum
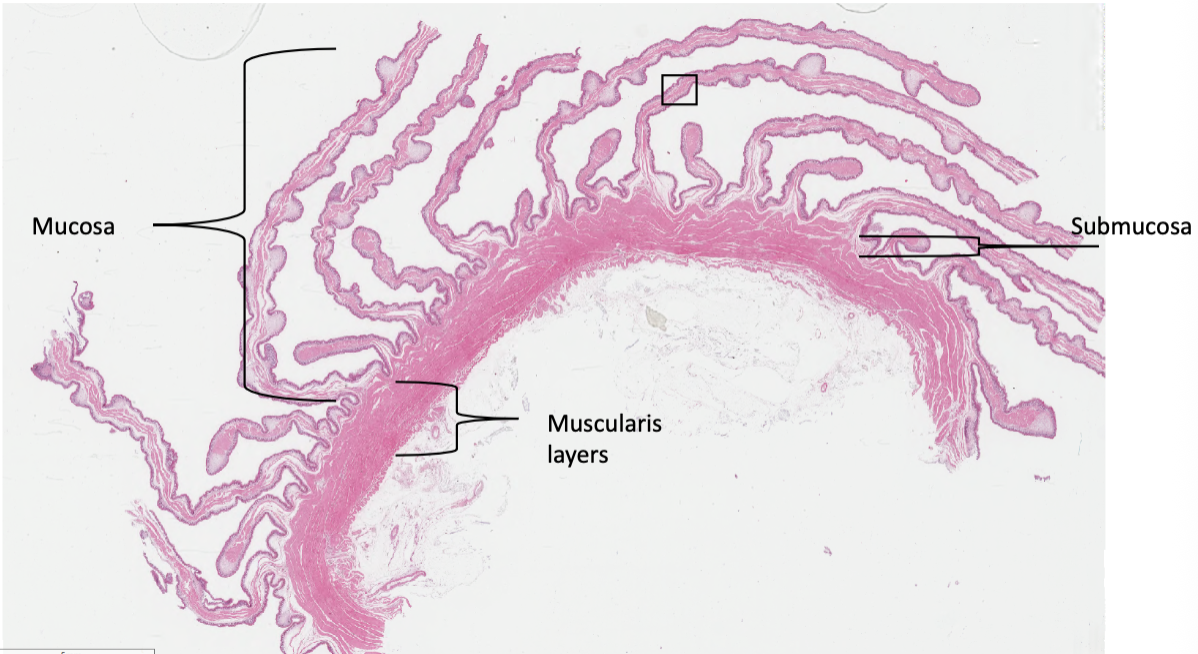
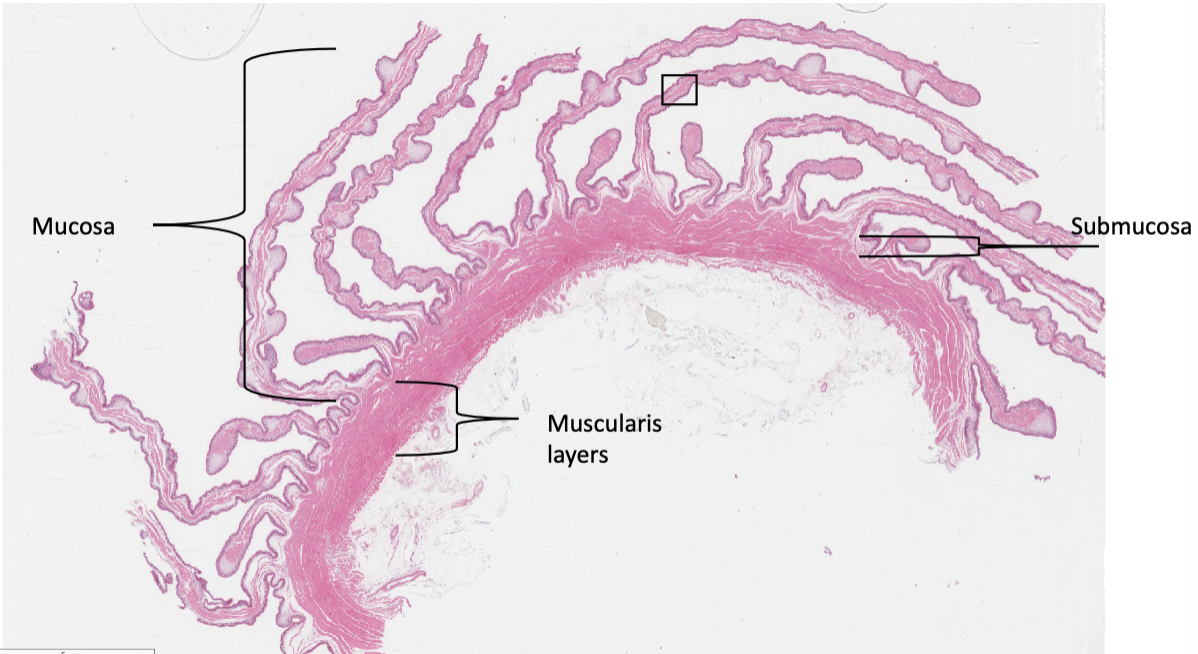
what are the histological differences between the rumen and the reticulum?
rumen has leaf-shaped papillae on inner lining while reticulum has primary and secondary folds that create a honeycomb pattern, the lamina propria in the reticulum contains smooth muscle and the rumen doesn’t, the tunica muscularis in the rumen has 3 smooth muscle layers and the reticulum has 2
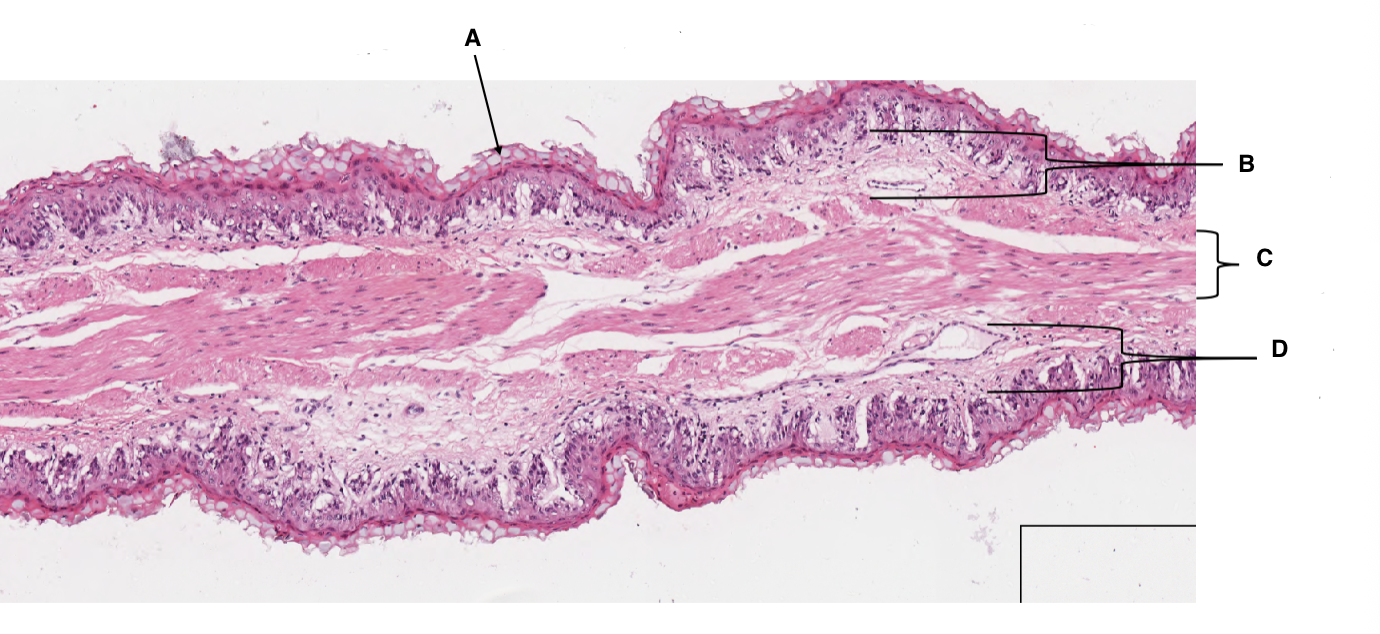
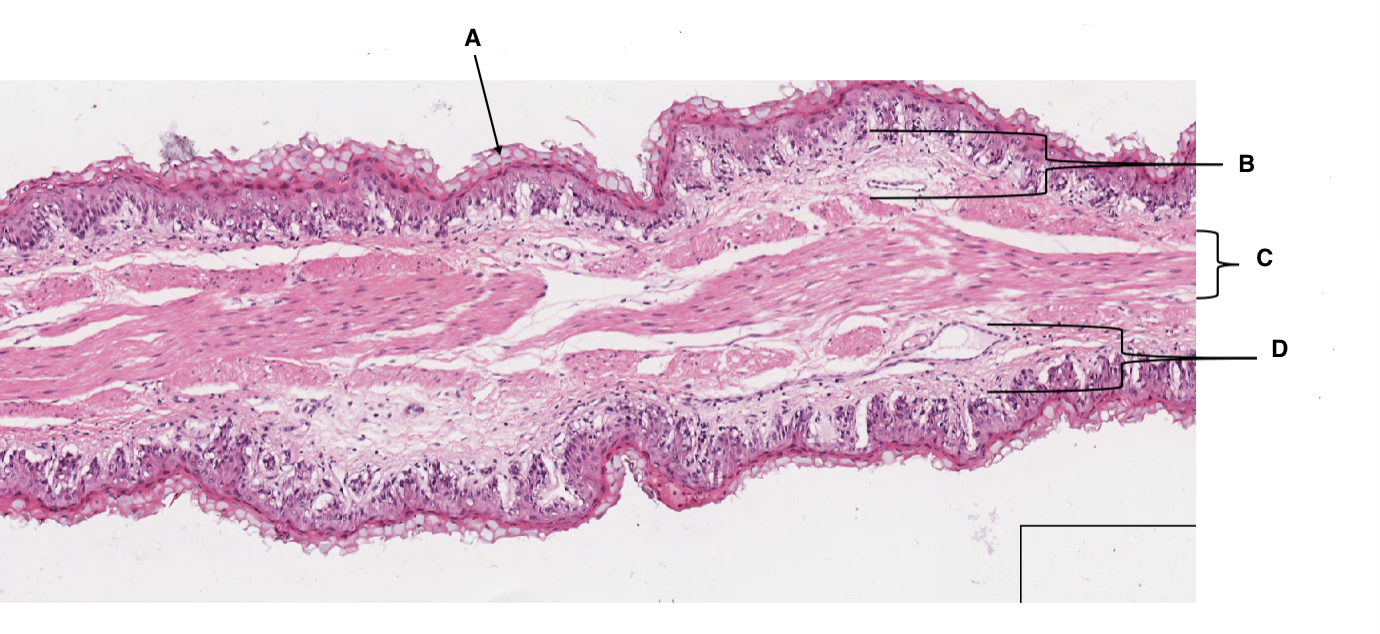
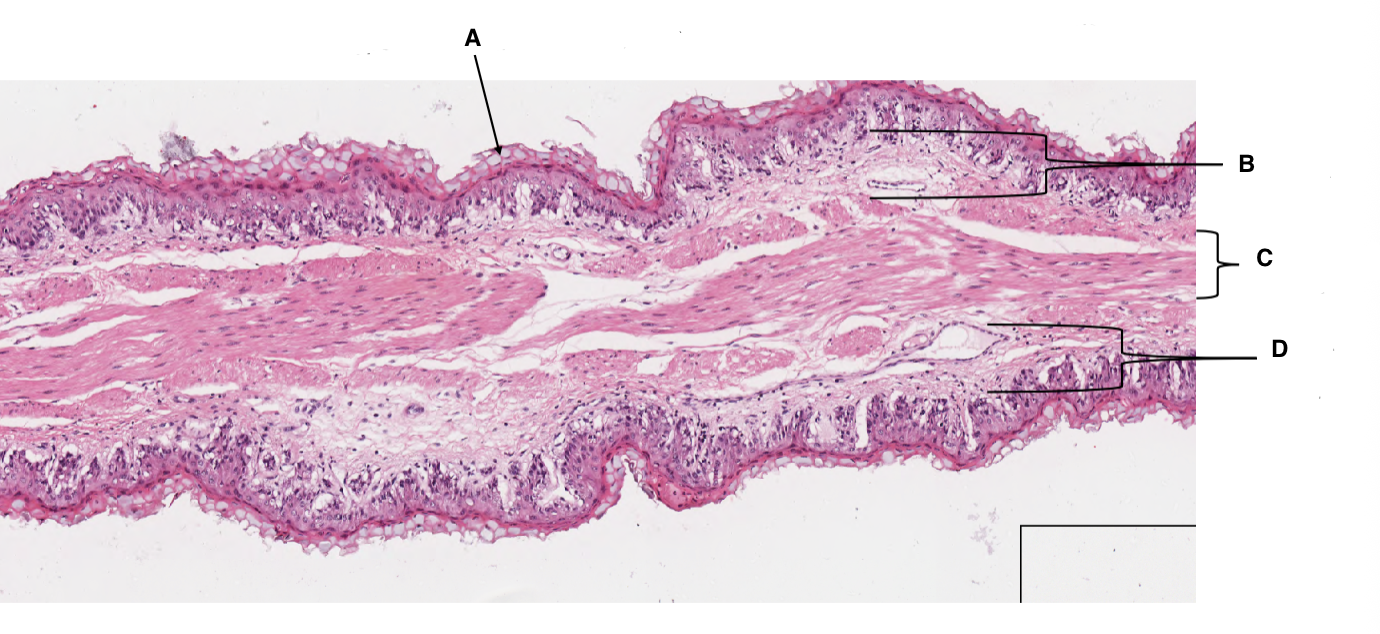
A
keratinised stratified squamous epithelium
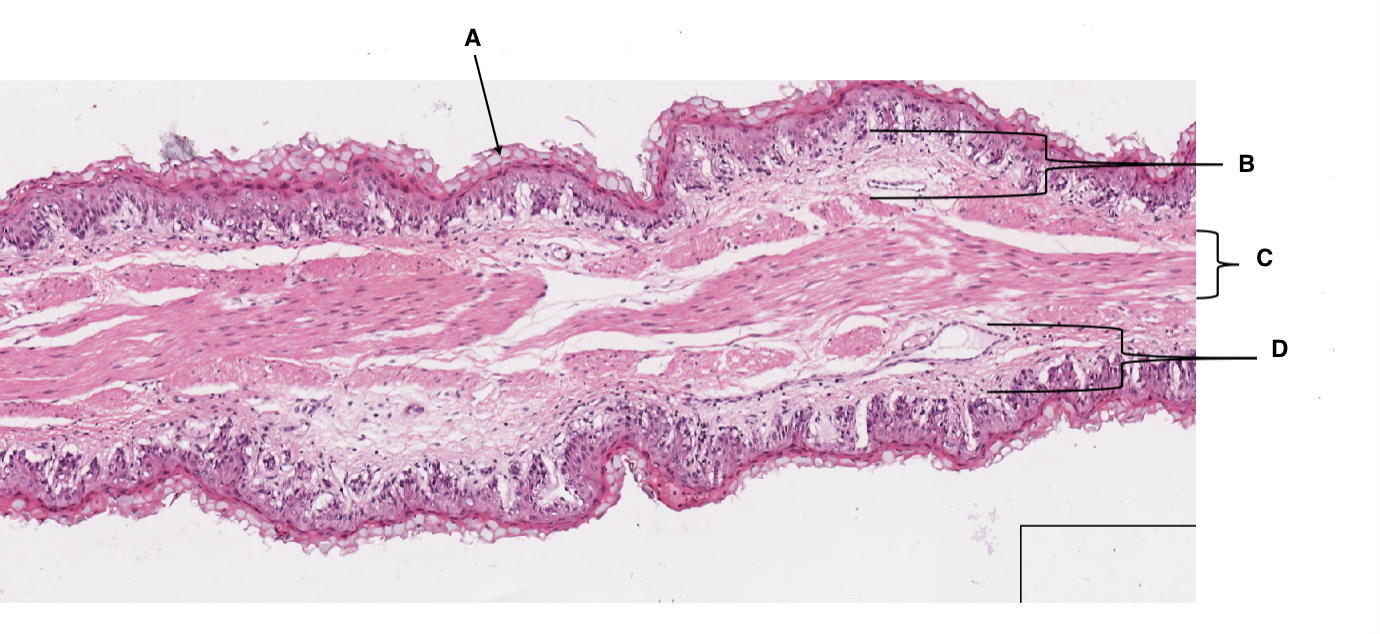
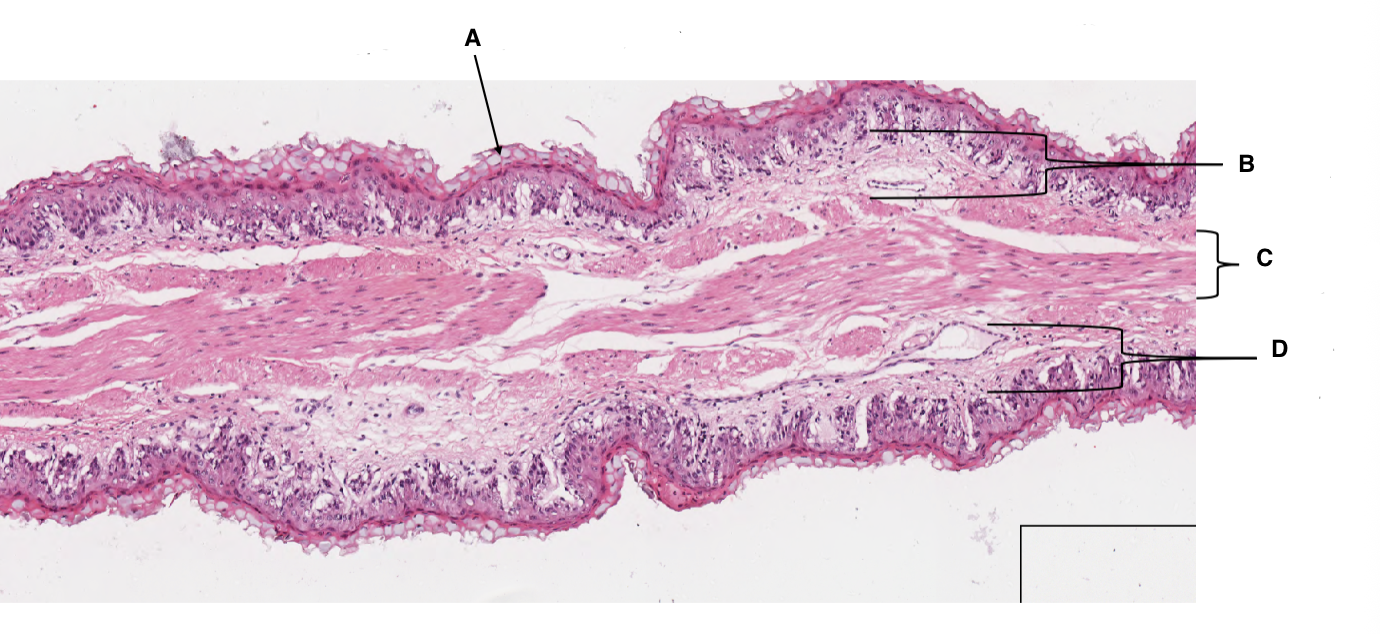
B
lamina propria
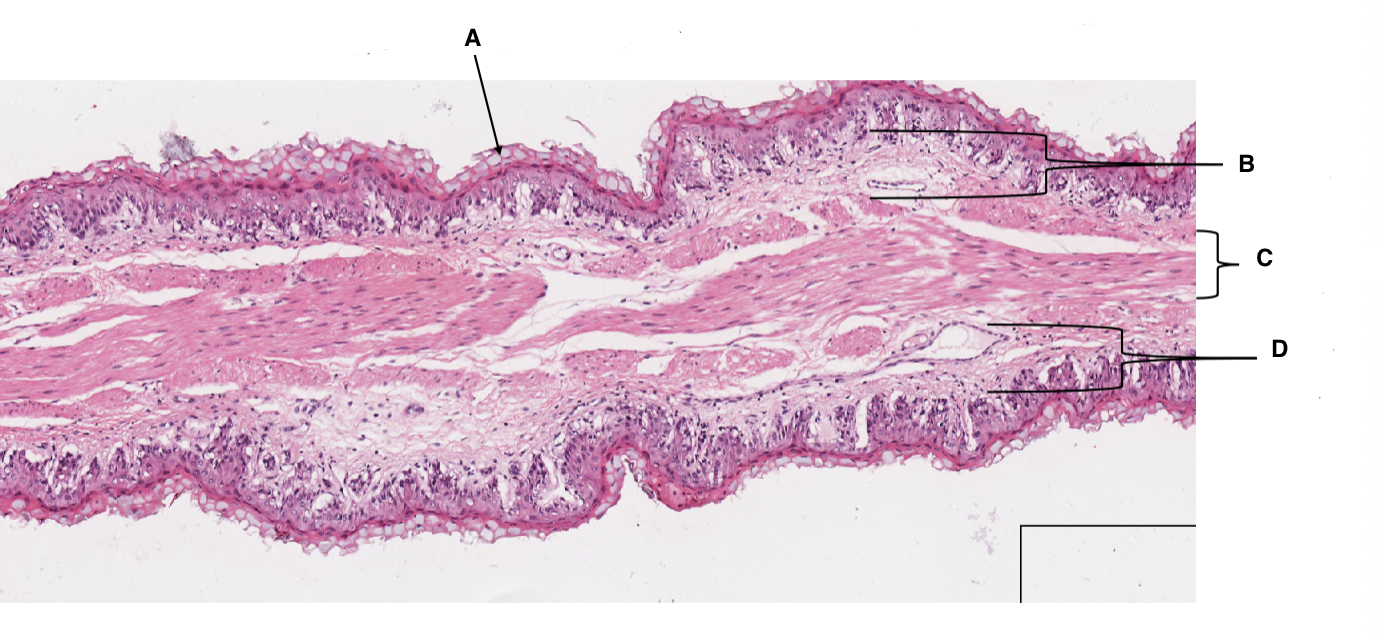
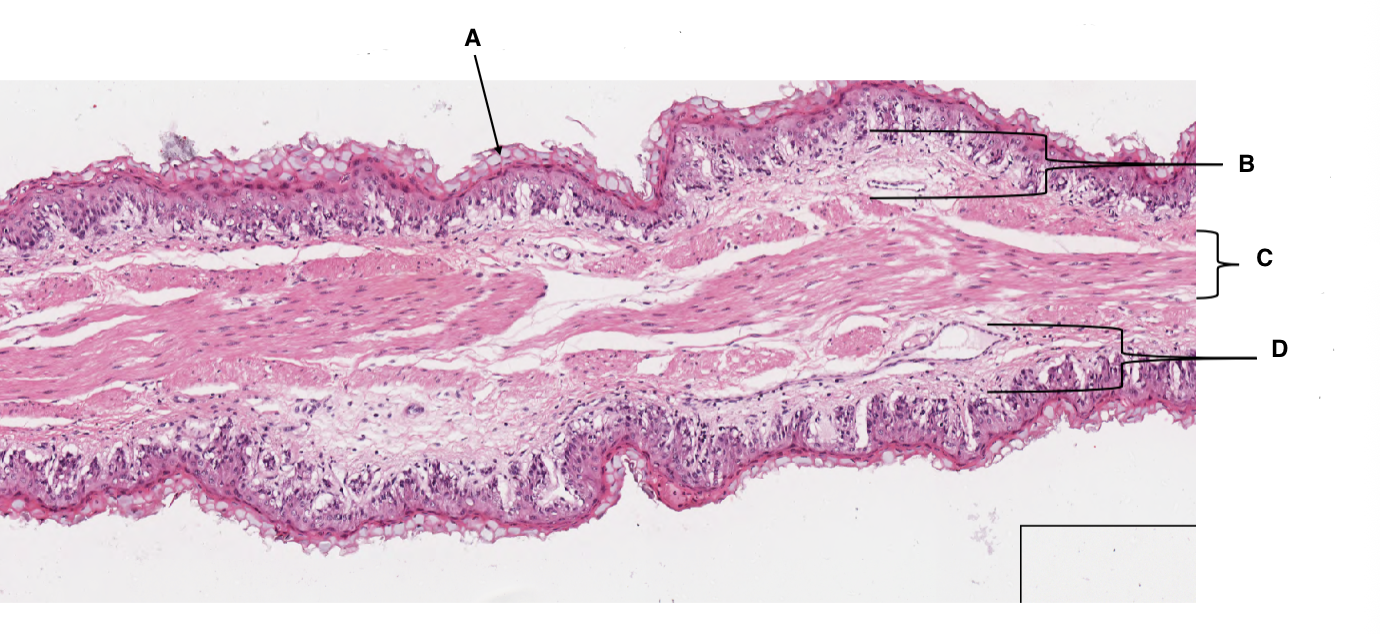
C
muscularis mucosa
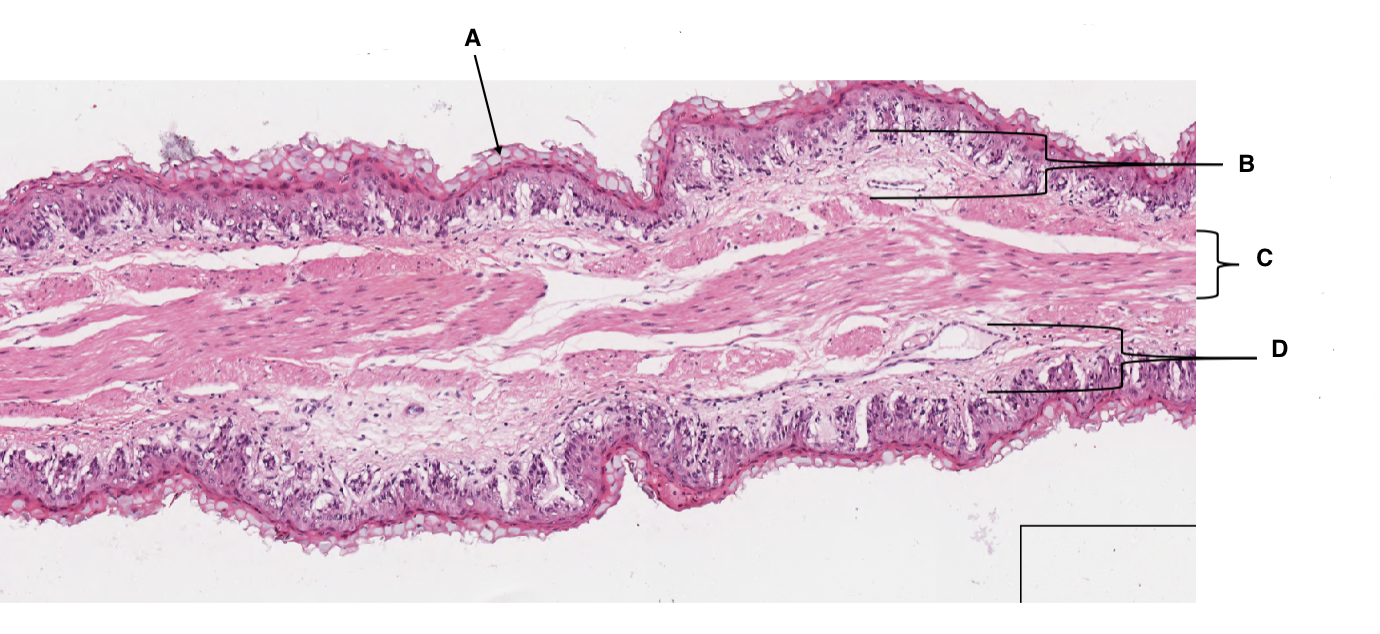
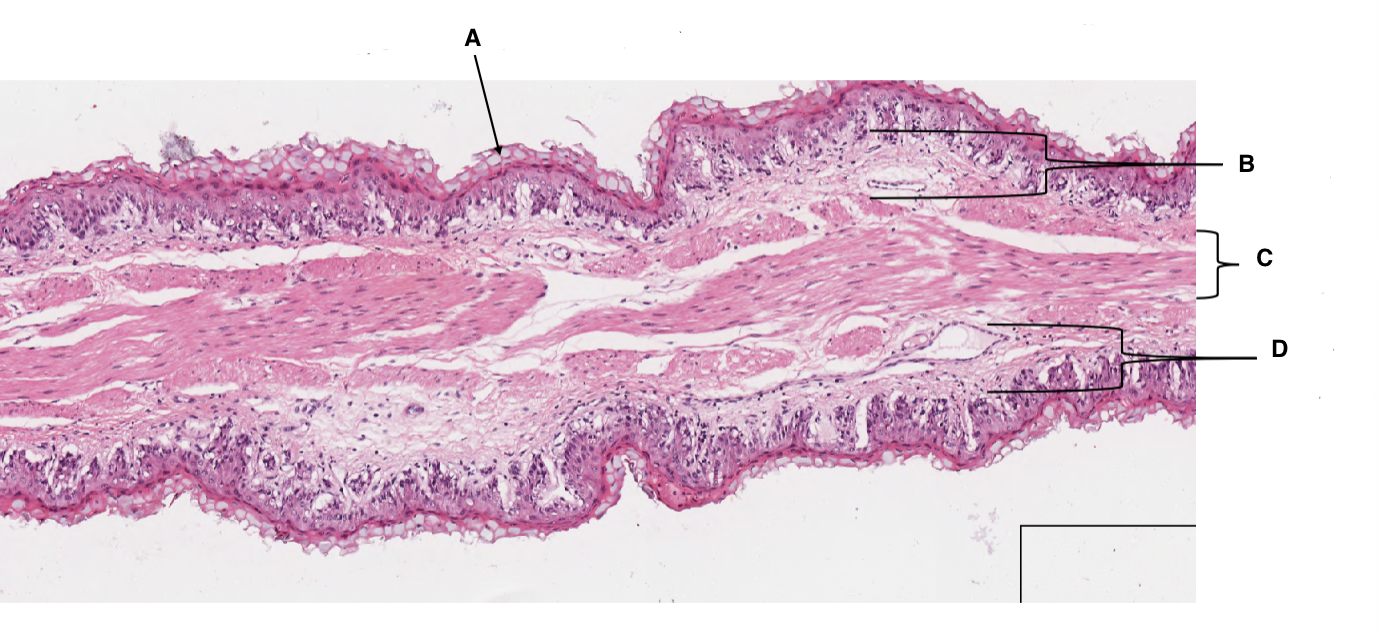
D
lamina propria
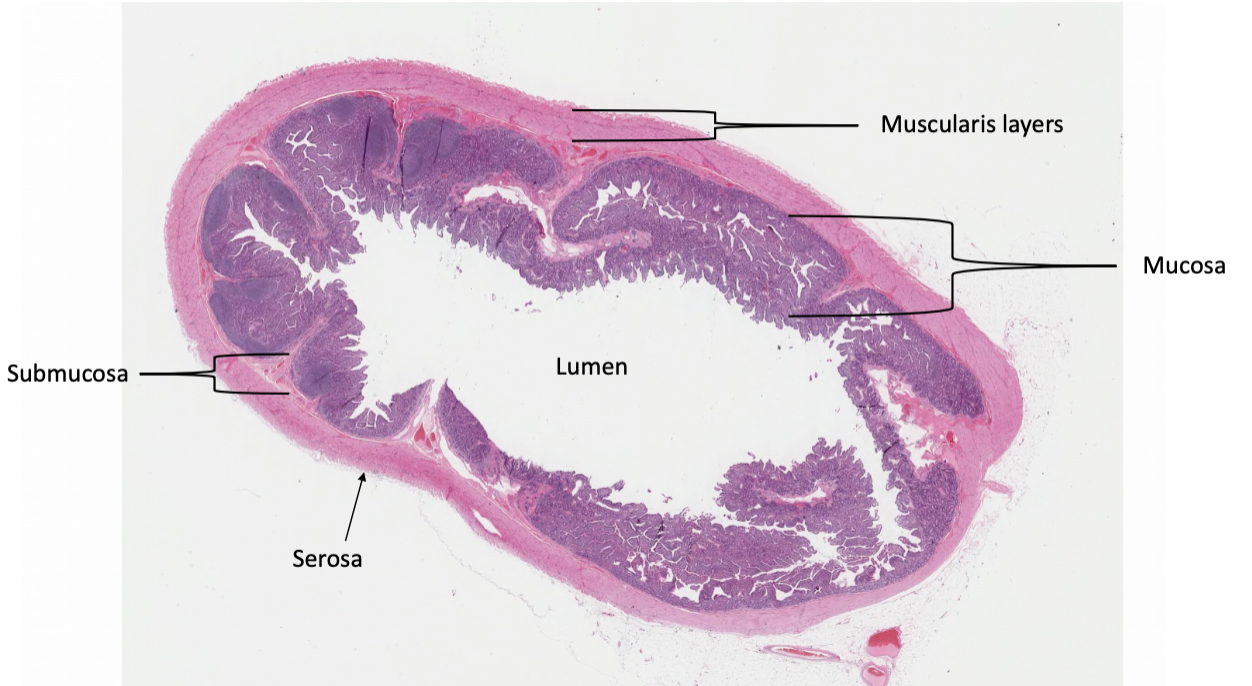
what organ is this slide from?
omasum
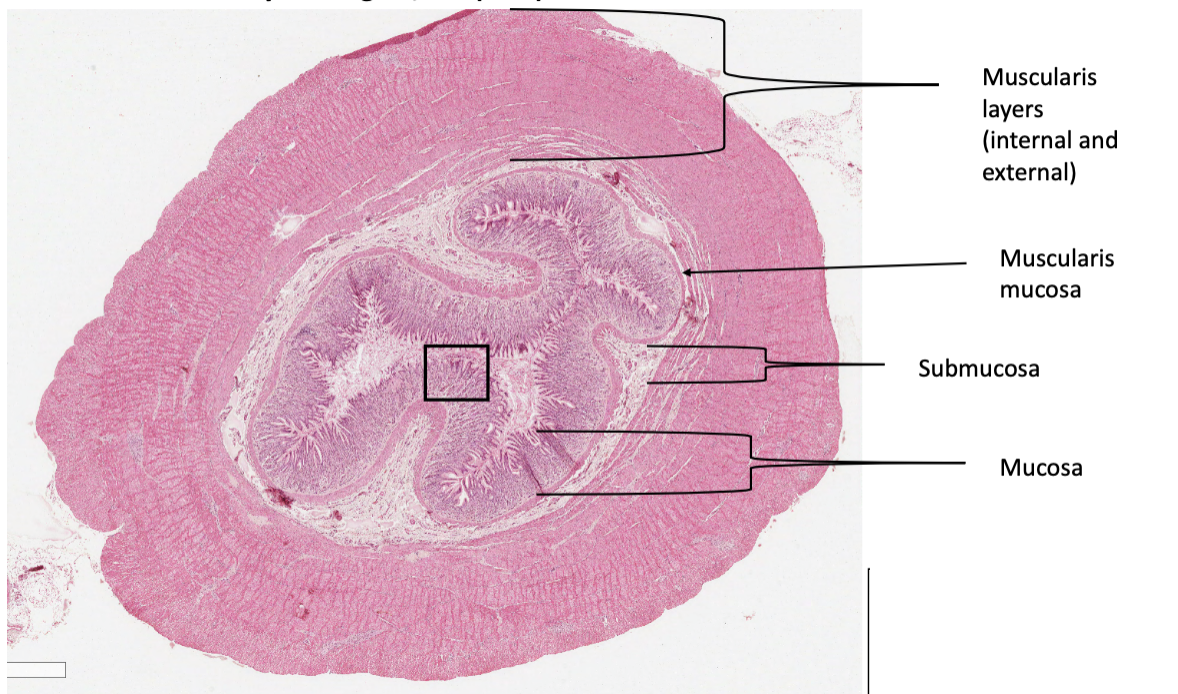
What organ is this slide from?
ileum
What organ is this slide from?
pyloric region of the stomach (cat)
histological features of the abomasum
simple columnar epithelium, mucus cells, parietal cells and peptic cells in gastric pits, tubular glands extending from the gastric pits, mucosa, submucosa, mulscularis, serosa
histological features of the ileum
brush border of enterocytes, mucosa, submucosa, muscularis, serosa, abundant, large Peyer's patches in lamina propria, fewer, shorter villi than the jejunum, more stem cells and Paneth cells at the base of crypts, goblet cells
histological features of the large intestine
simple columnar epithelium, abundant goblet cells, deep crypts of Lieberkühn, no villi or Paneth cells, muscularis externa has an inner circular and an outer longitudinal layer, three distinct bands (taeniae coli) formed by outer muscularis layer
histological features of the duodenum
mucosa, submucosa, muscularis externa, serosa/adventitia, prominent Plicae Circulares (circular folds), leaf-like villi, Brunner's glands in the submucosa, brush border of enterocytes, goblet cells, enteroendocrine cells, paneth cells and stem cells at base of crypts
histological features of the jejunum
long, finger-like villi, no species-specific glands found in the duodenum (Brunner's glands) and ileum (Peyer's patches), brush border of enterocytes, goblet cells, intestinal crypts
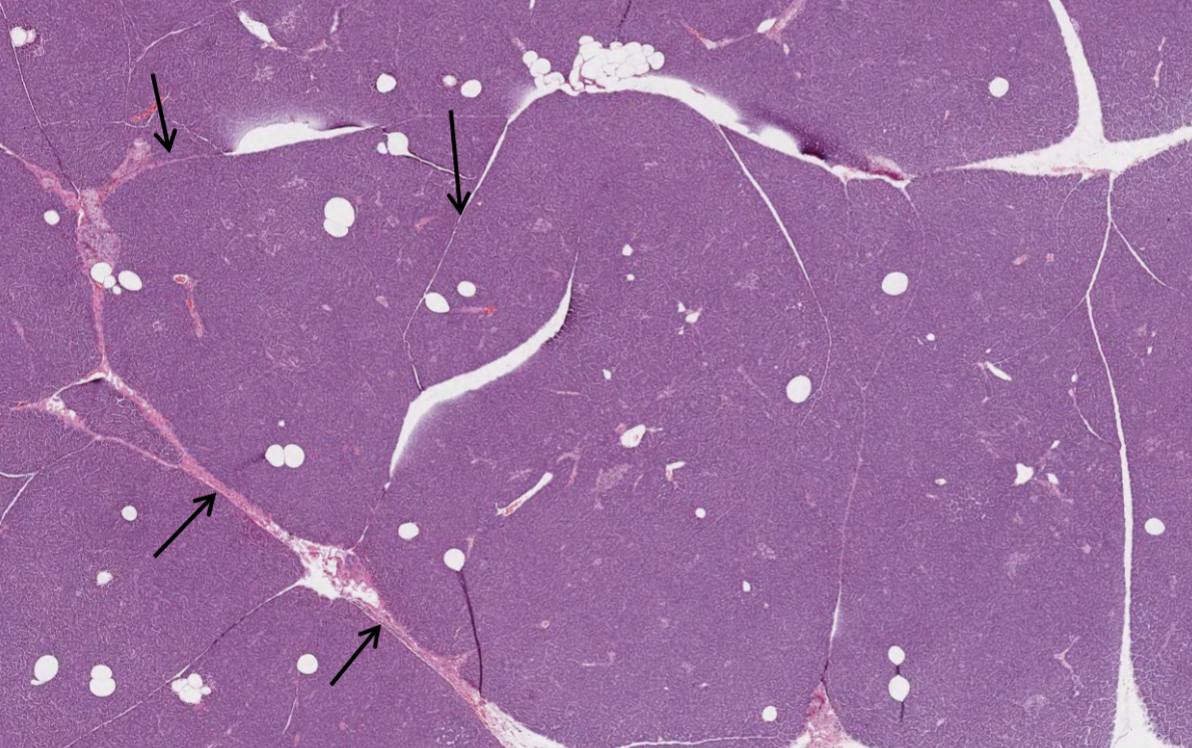
what do the arrows in this image of a pancreas indicate?
septa of connective tissue that divide the pancreas into lobules
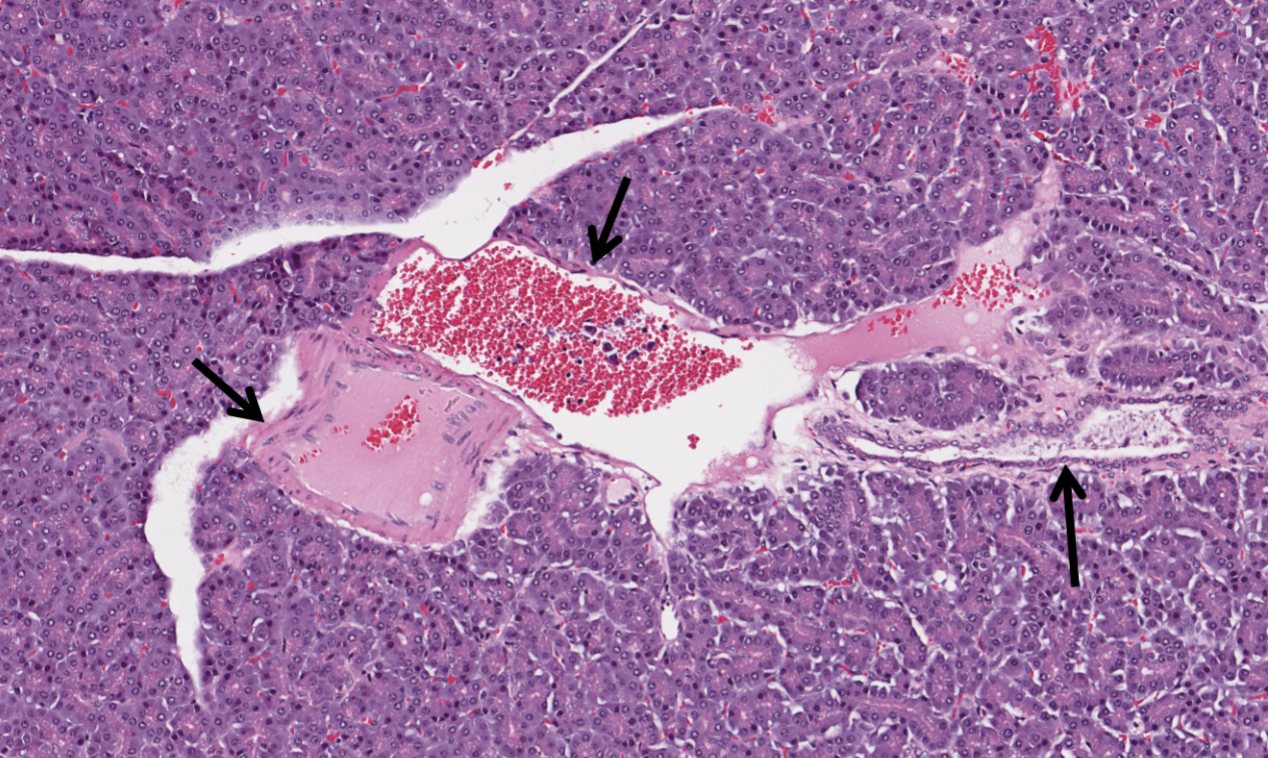
what is visible in this image of a pancreas?
pancreatic triad made up of an artery, vein and interlobular duct
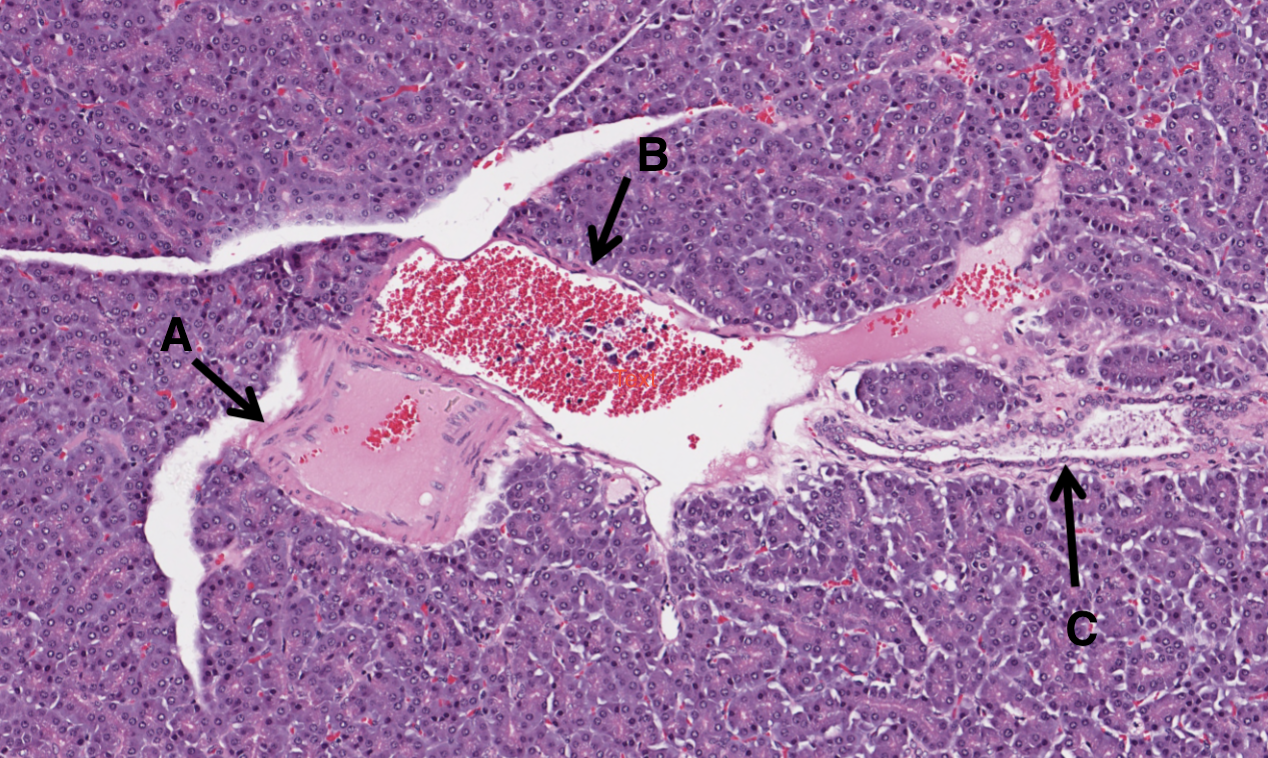
What is A in this image of a pancreas?
artery
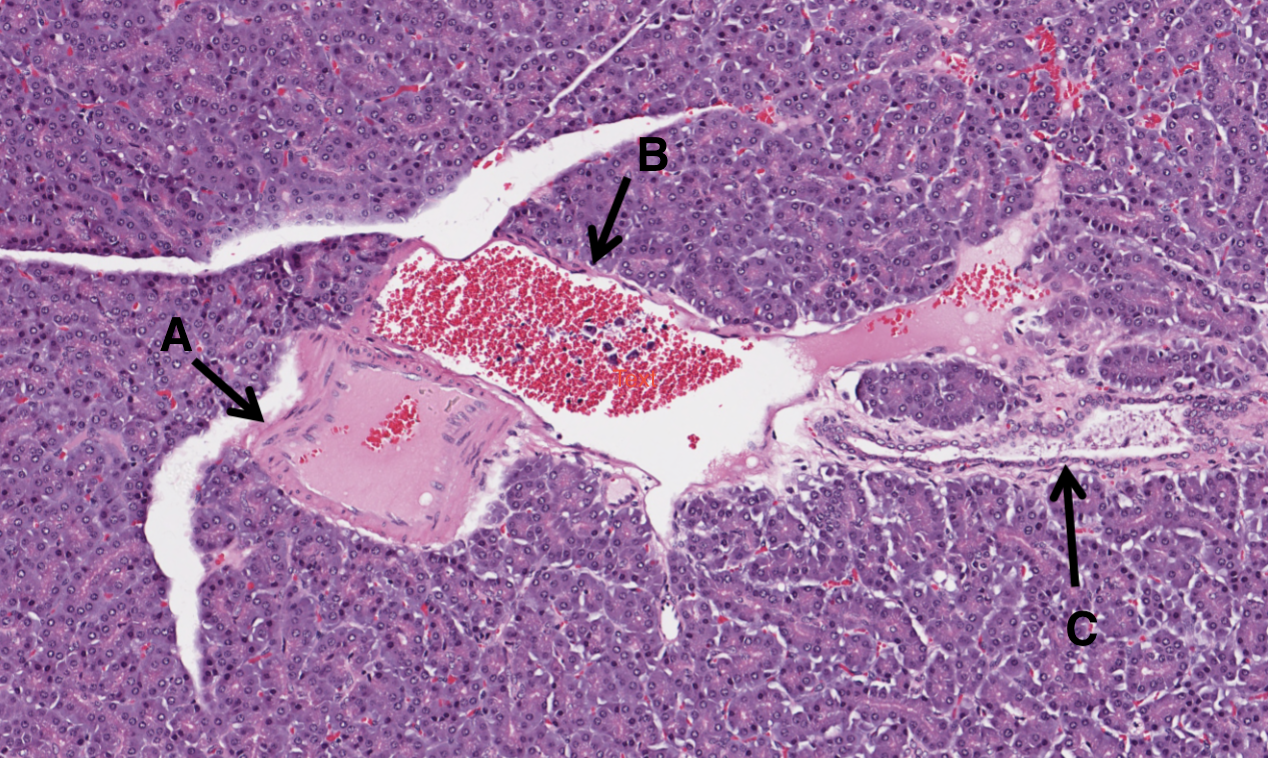
What is B in this image of a pancreas?
vein
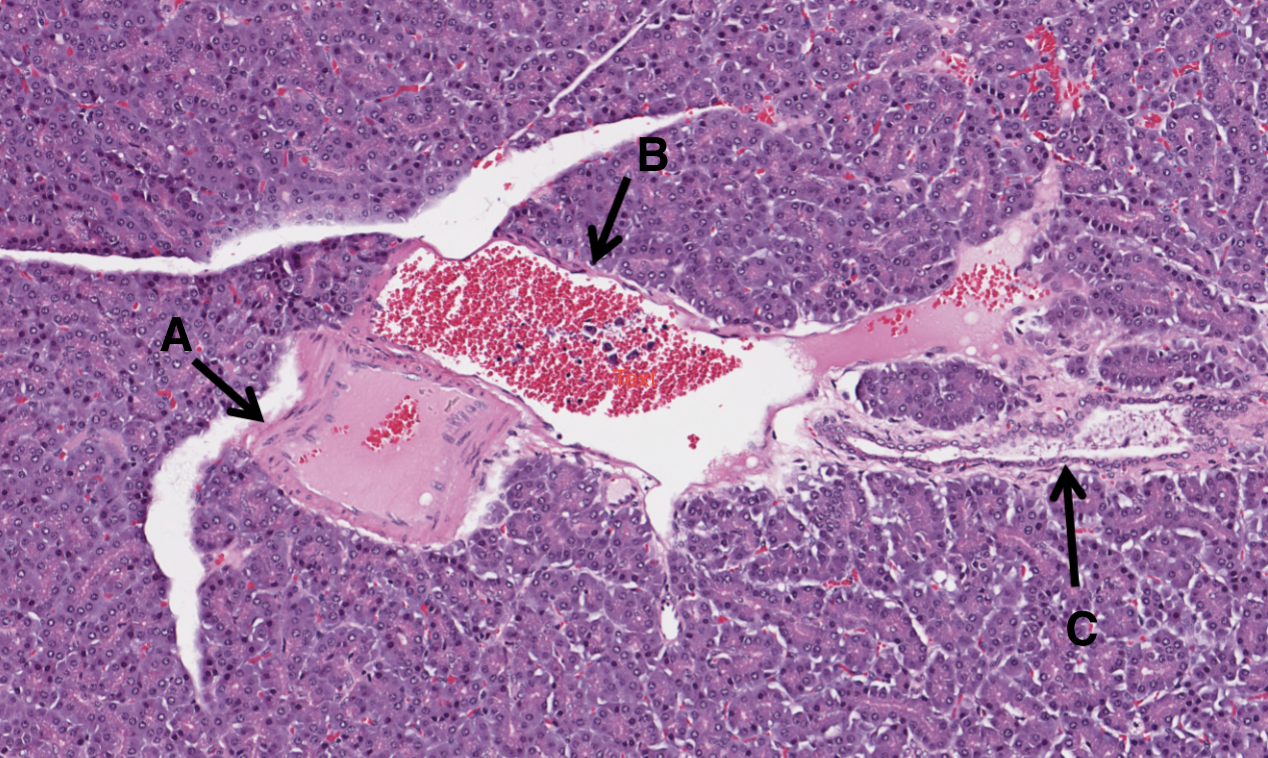
What is C in this image of a pancreas?
pancreatic duct
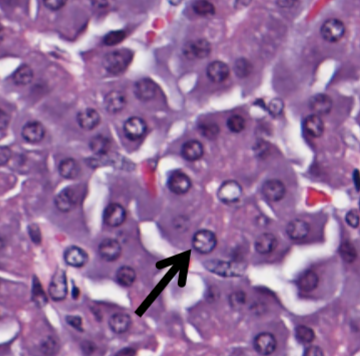
what structure in the exocrine pancreas is indicated by the arrow?
an exocrine acinus, consisting of a circular collection of exocrine glandular epithelial cells that secrete into the central lumen with peripheral nuclei
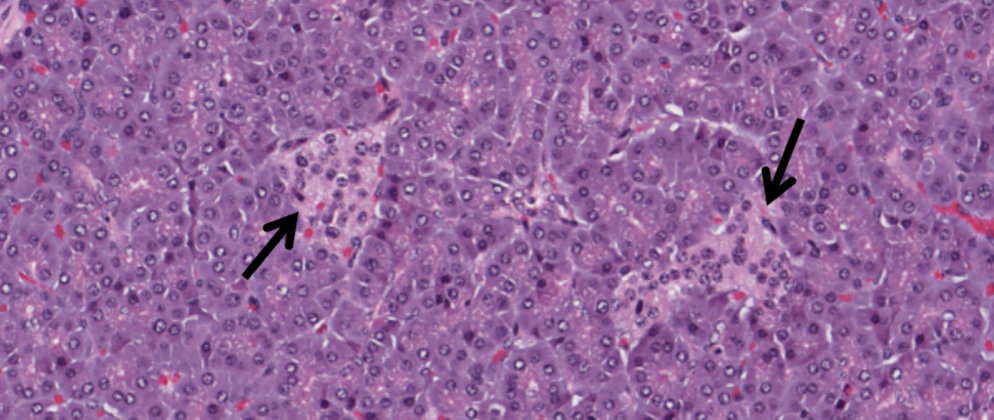
what structure in the pancreas is indicated by the arrows?
Islets of Langerhans
function of exocrine pancreas
to produce and release digestive enzymes and bicarbonate into the small intestine to aid in the breakdown of food
function of endocrine pancreas
to produce and release hormones that regulate metabolism
microscopic features of exocrine pancreas
groups of acini, cells contain zymogen granules, lumen between acinar cells, ducts
microscopic features of endocrine pancreas
islets of Langerhans made up of alpha, beta and delta cells
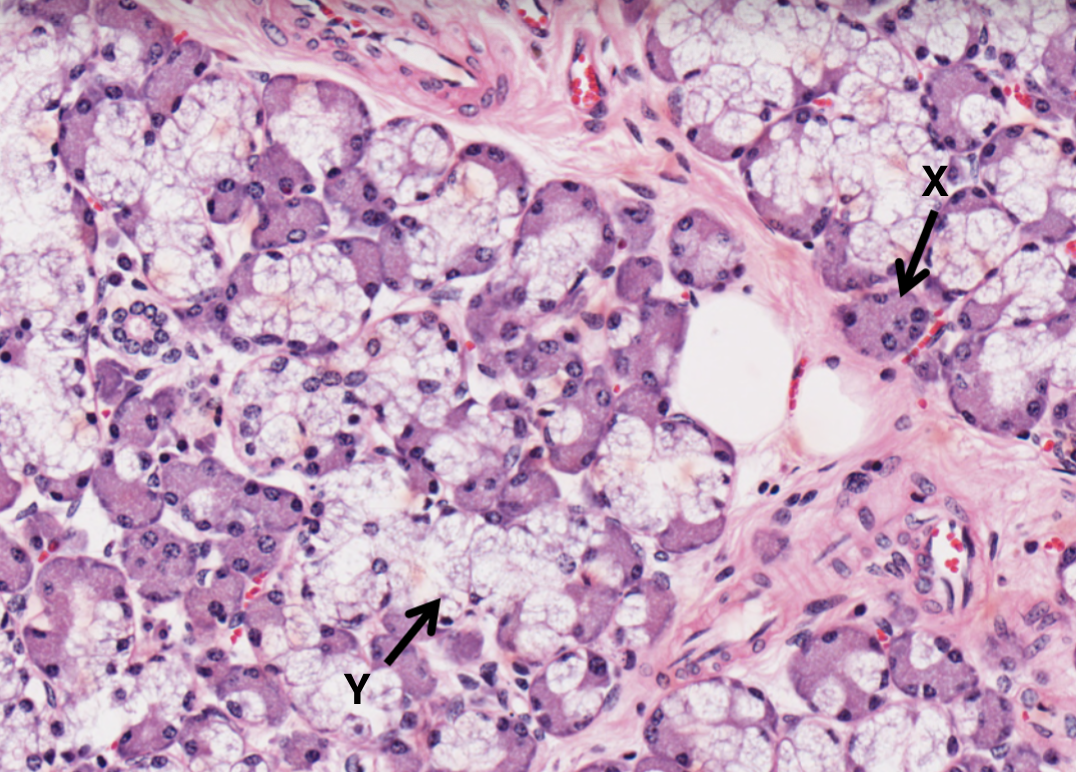
What type of cell is X in the salivary gland?
serous cell and acini
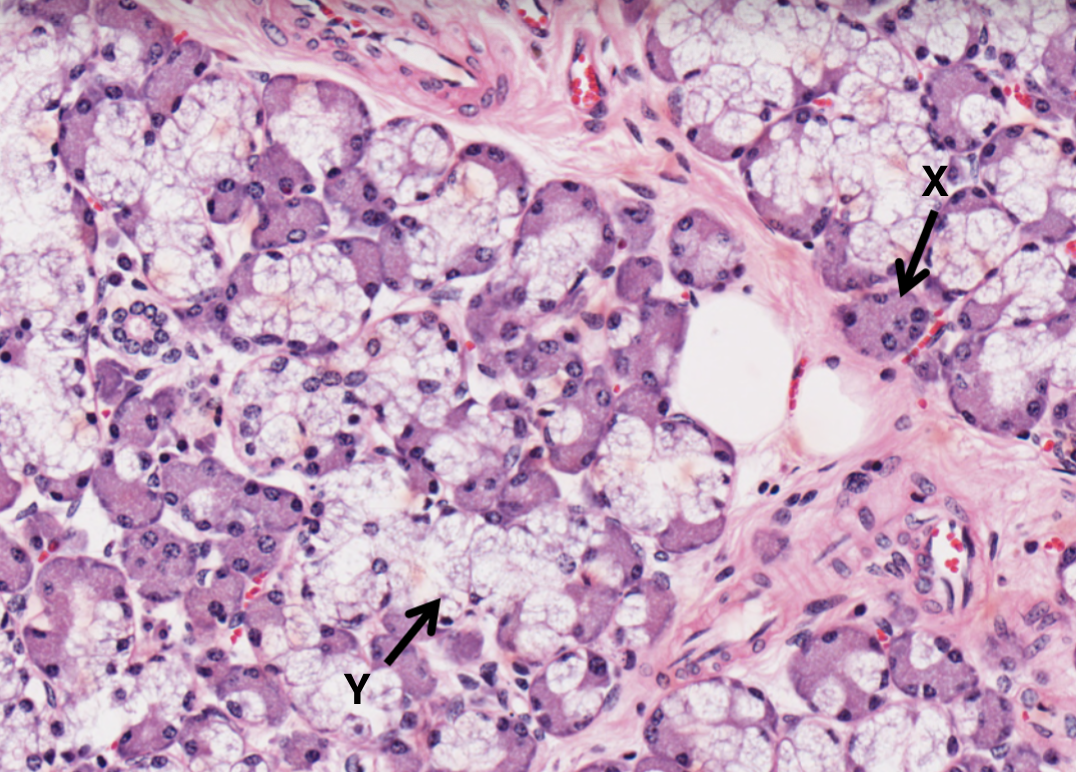
What type of cell is Y in the salivary gland?
mucous cell and acini
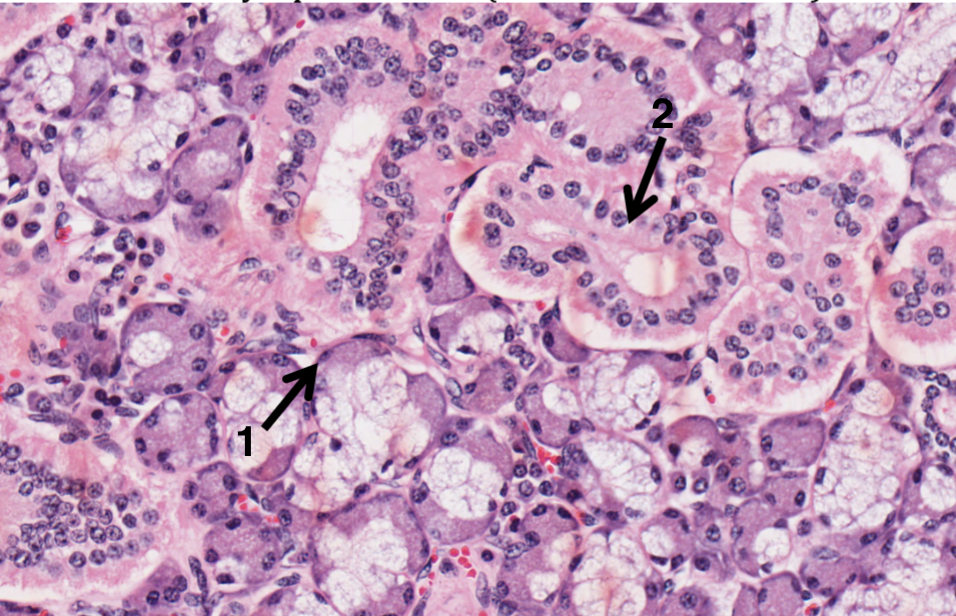
What does 1 represent in the salivary gland?
myoepithelial cells
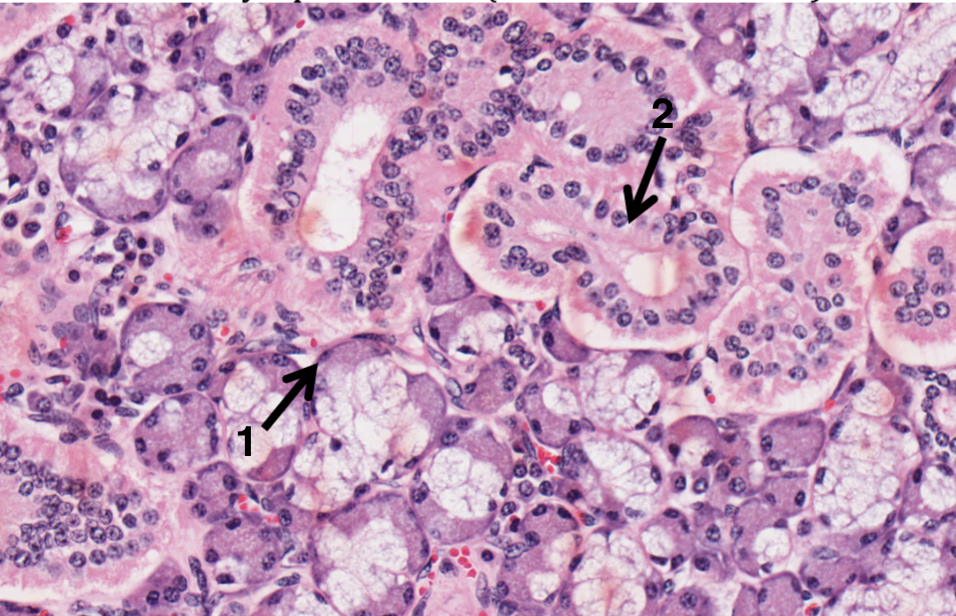
What does 2 represent in the salivary gland?
excretory duct
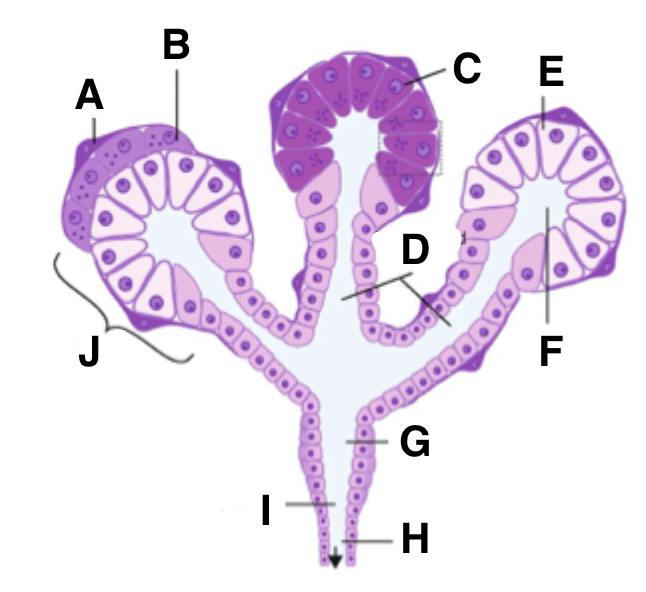
What is A in a salivary gland?
myoepithelial cell
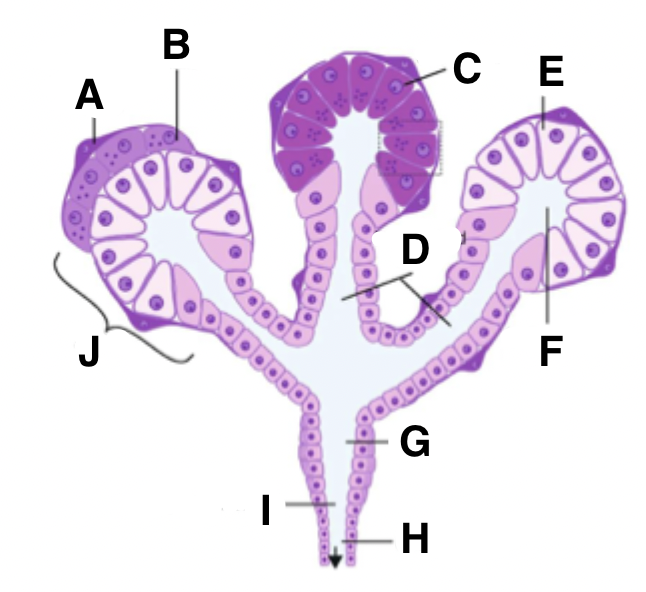
What is B in a salivary gland?
seromucous acinus demilune cell
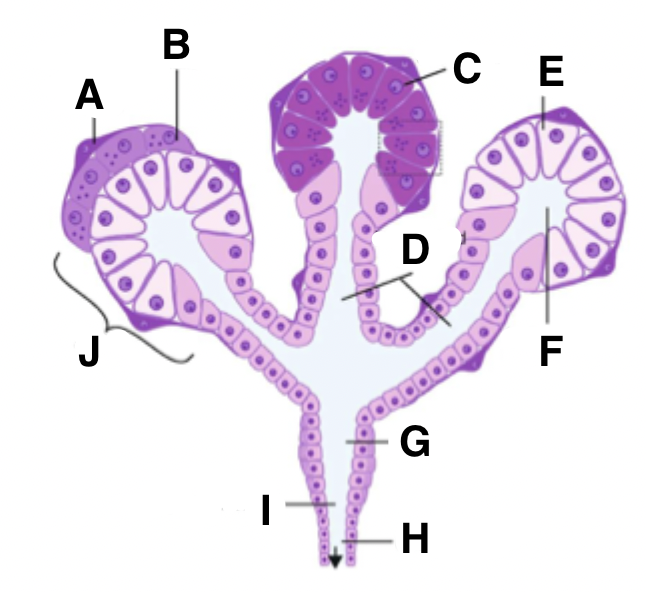
What is C in a salivary gland?
serous cell
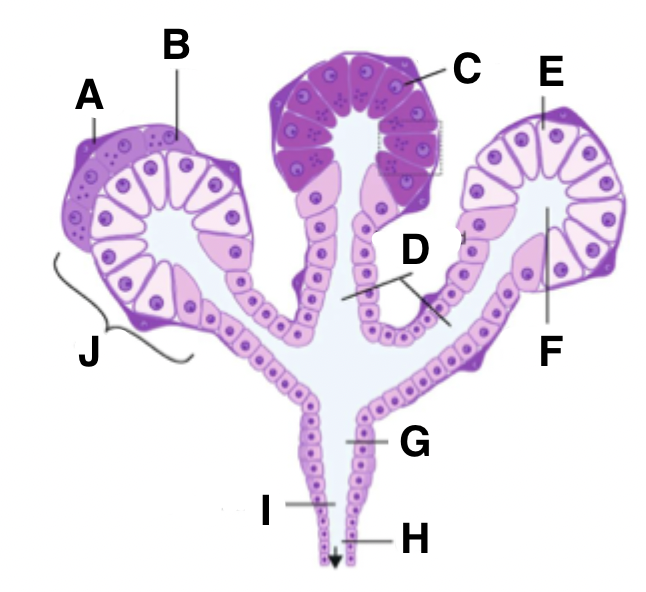
What is D in a salivary gland?
intercalated ducts
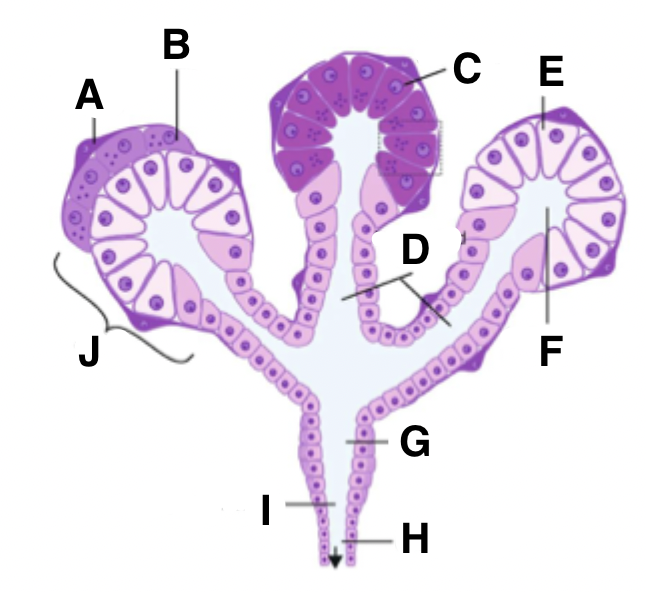
What is E in a salivary gland?
mucous cell
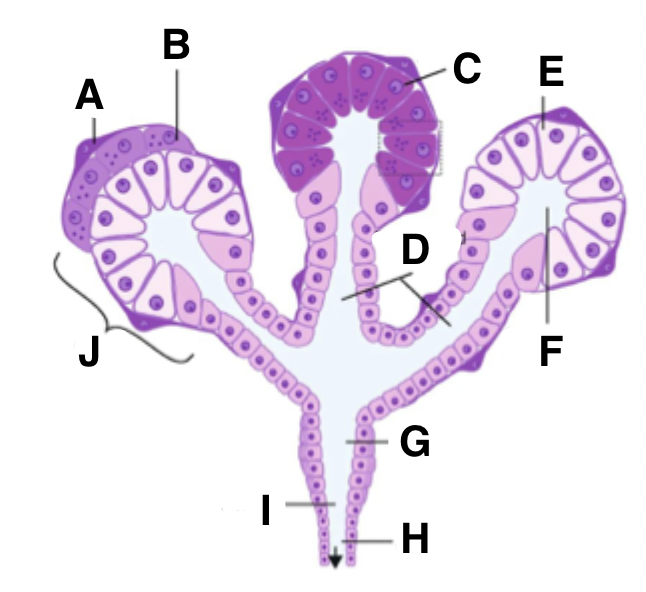
What is F in a salivary gland?
isotonic saliva
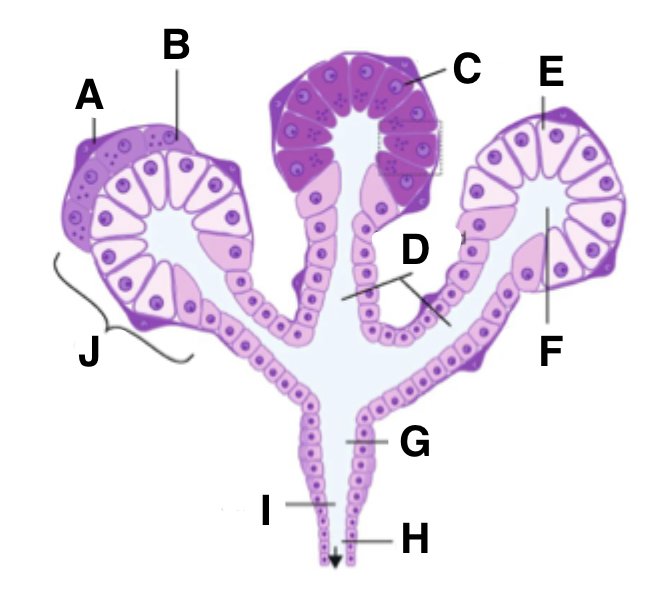
What is G in a salivary gland?
striated duct
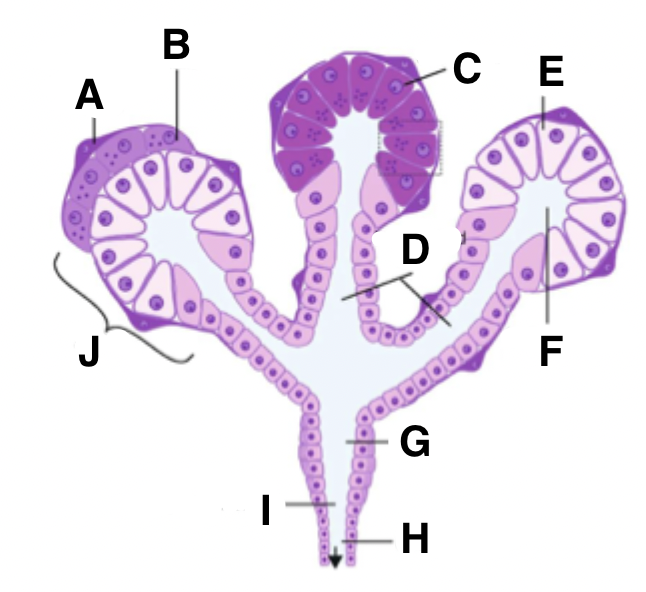
What is H in a salivary gland?
excretory duct
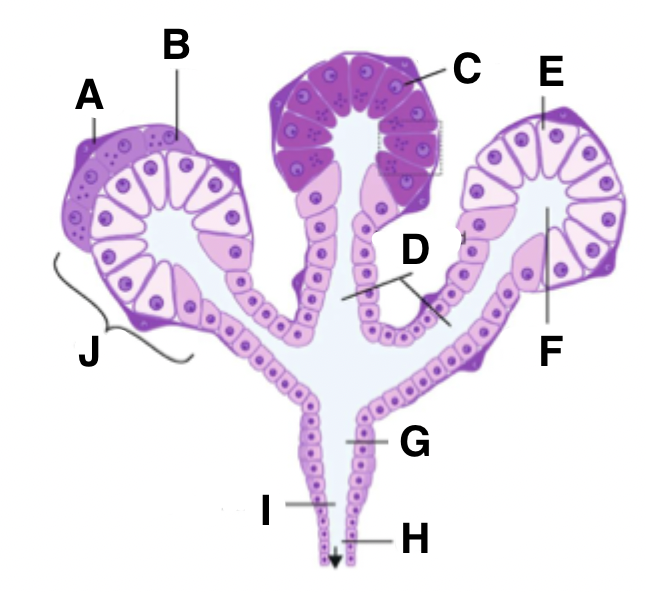
What is I in a salivary gland?
hypotonic saliva
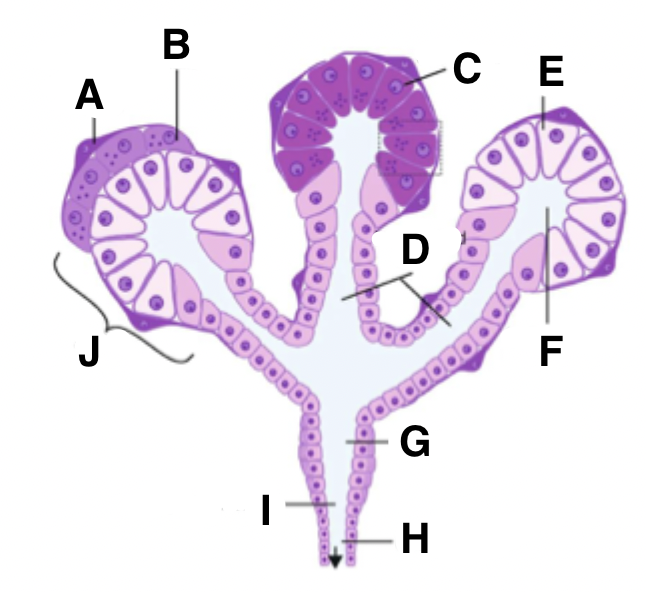
What is J in a salivary gland?
acinus
function of myoepithelial cells
to contract to squeeze secretions from cells into ducts
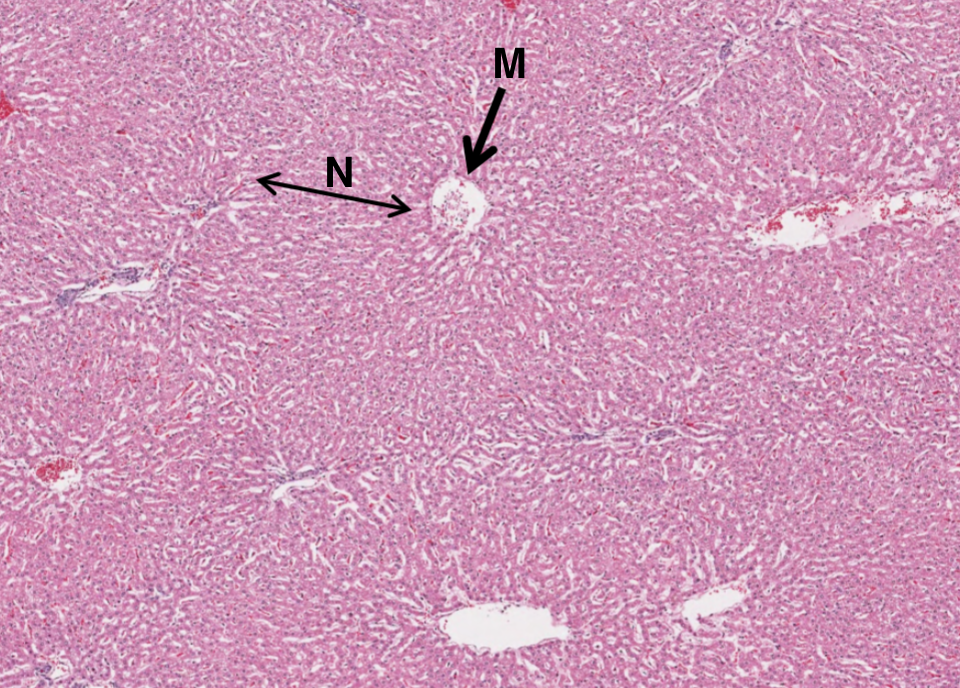
What is M in this image of the liver?
central vein
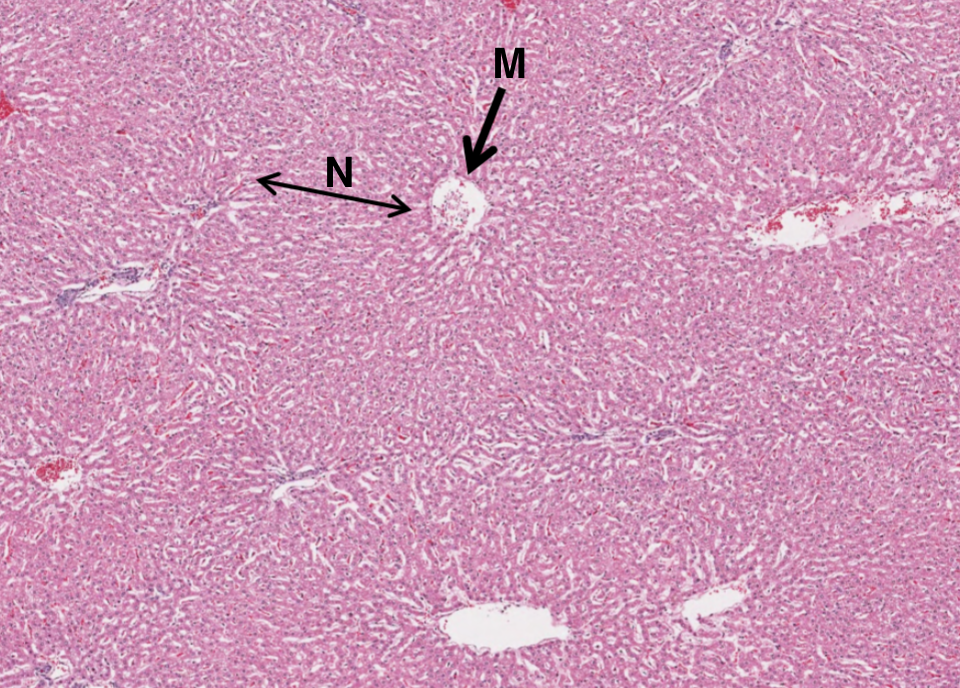
What is N in this image of the liver?
lines of hepatocytes which form hepatic lobules
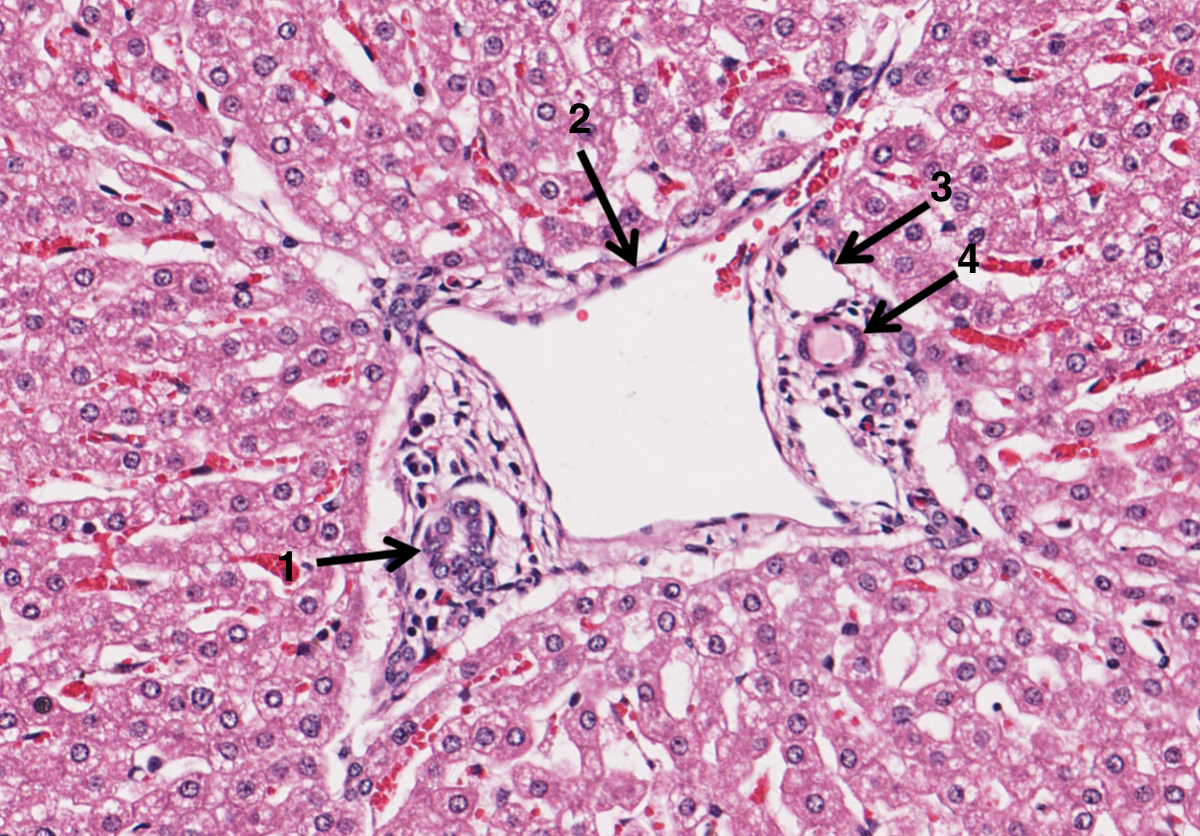
What is 1 in the portal triad of a liver?
bile duct
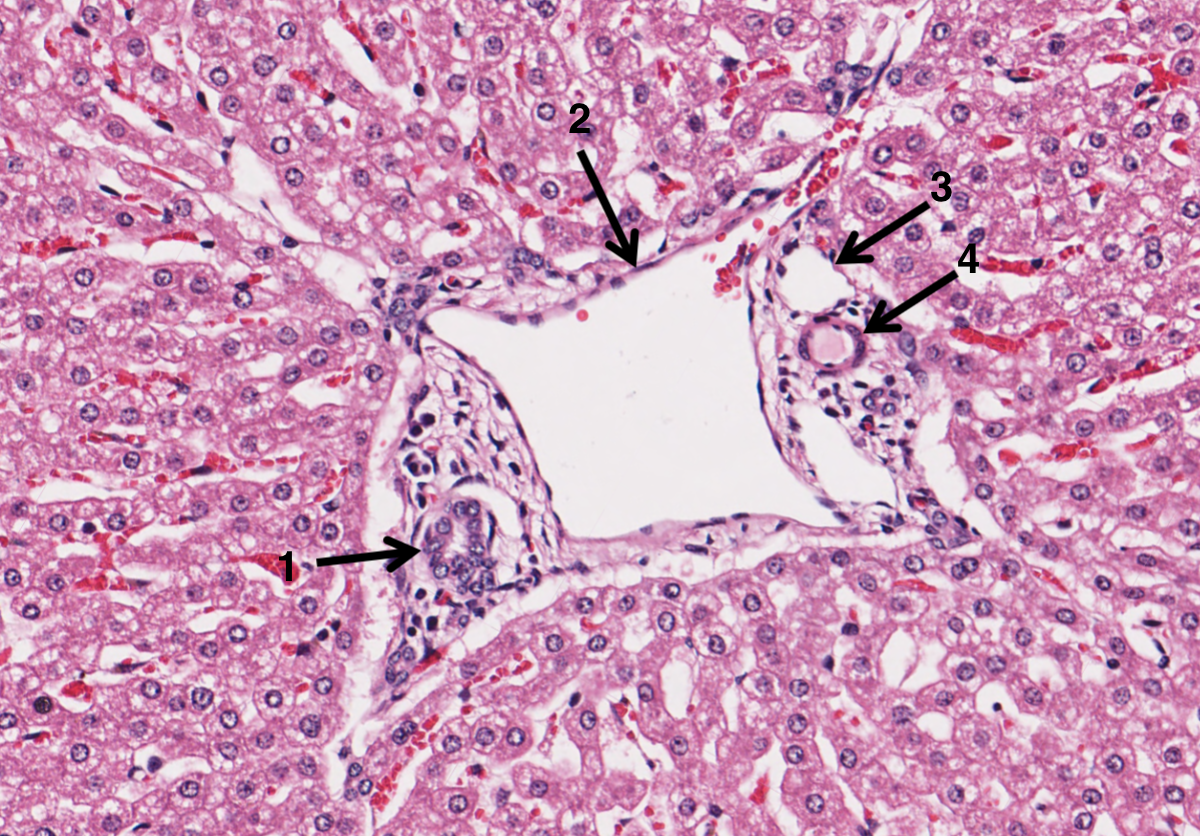
What is 2 in the portal triad of a liver?
hepatic portal vein
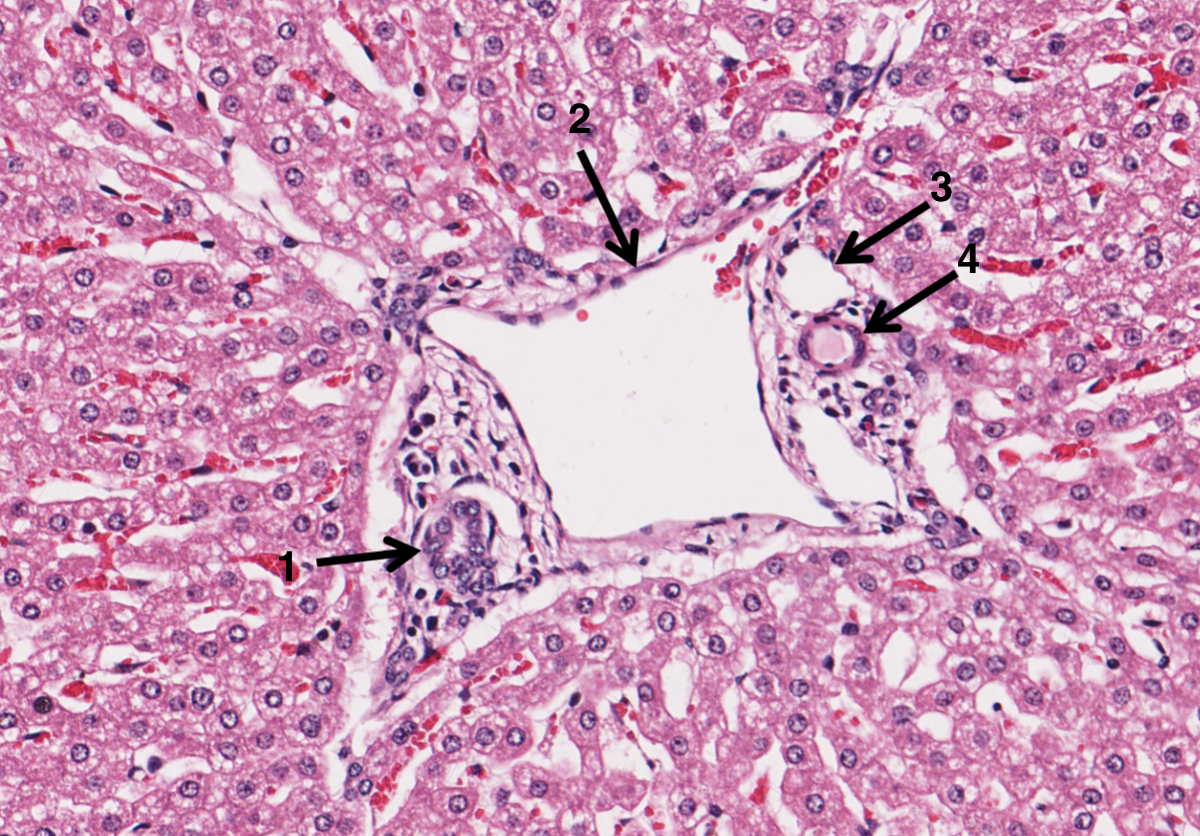
What is 3 in the portal triad of a liver?
lymphatic vessel
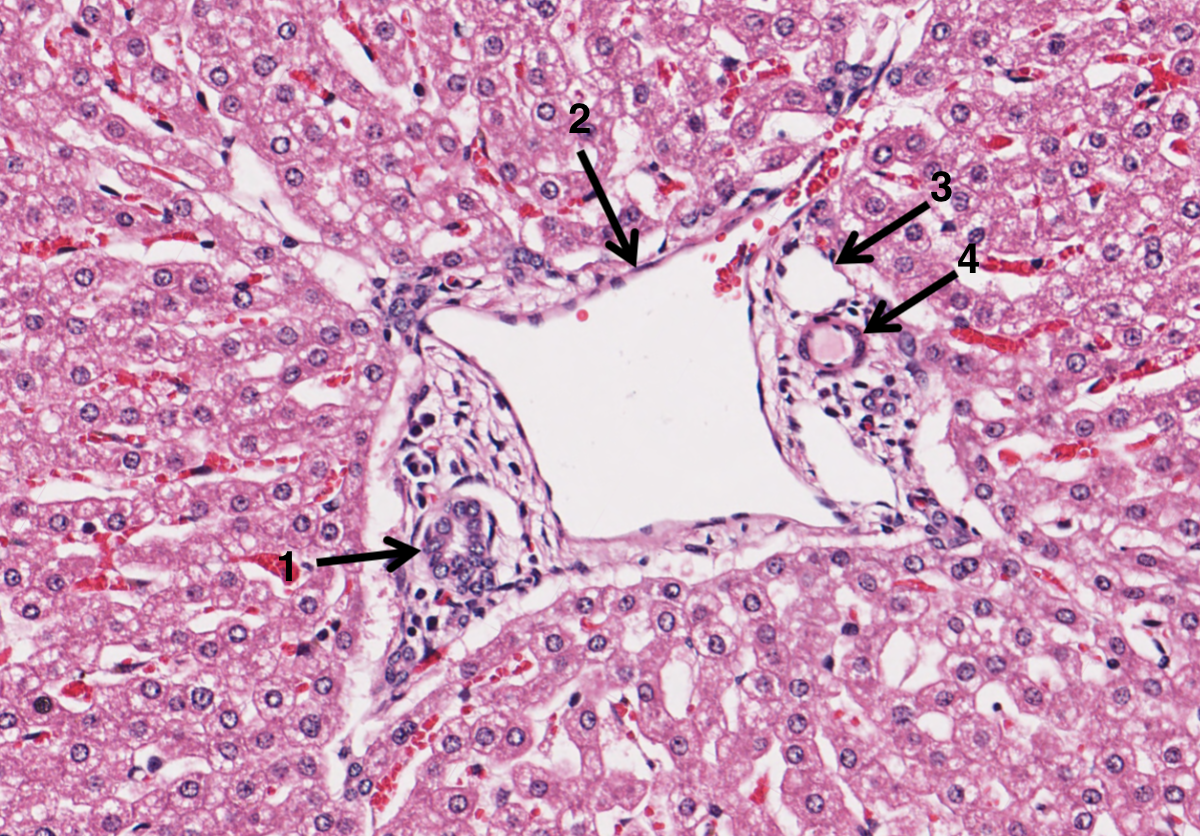
What is 4 in the portal triad of a liver?
hepatic artery
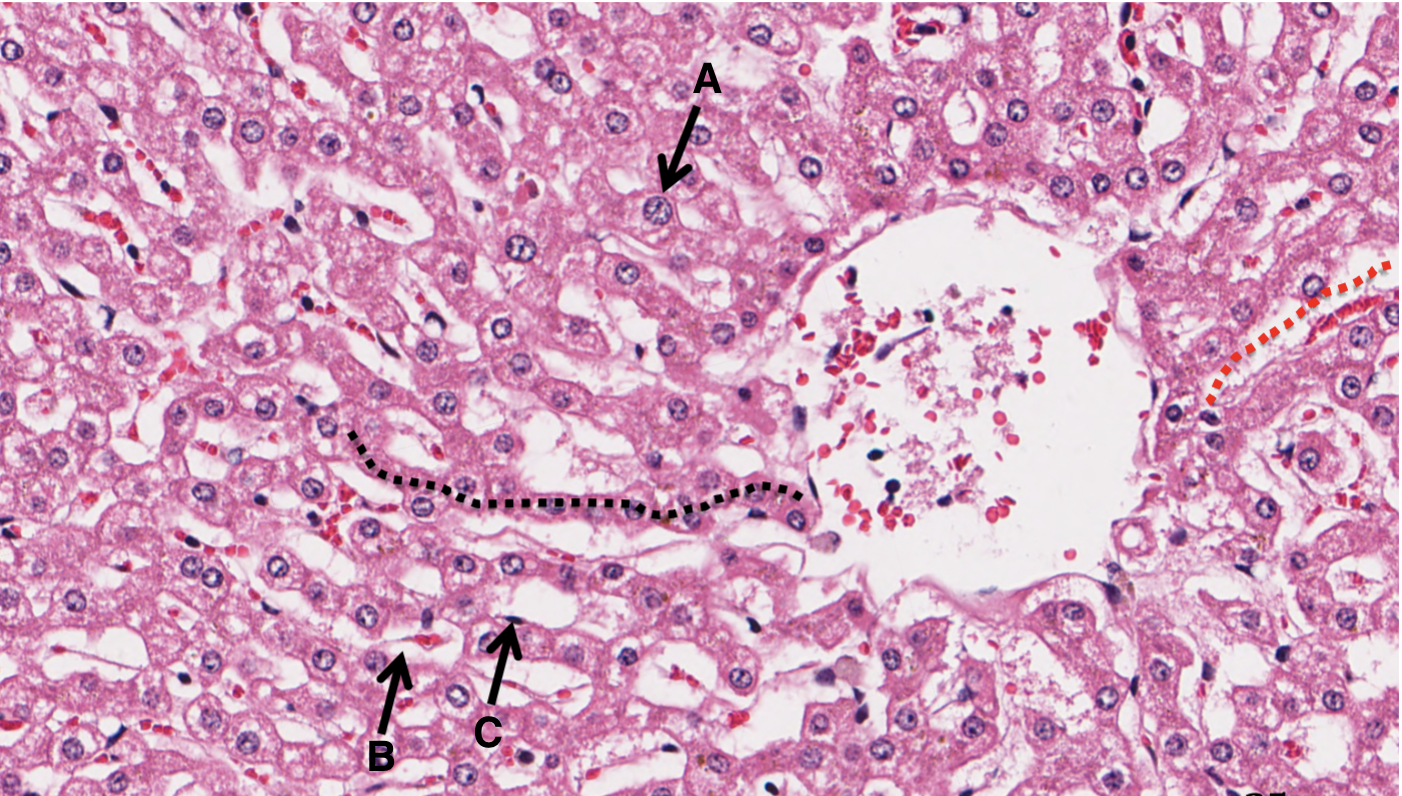
What is A in a liver slide?
hepatocyte arranged in plates
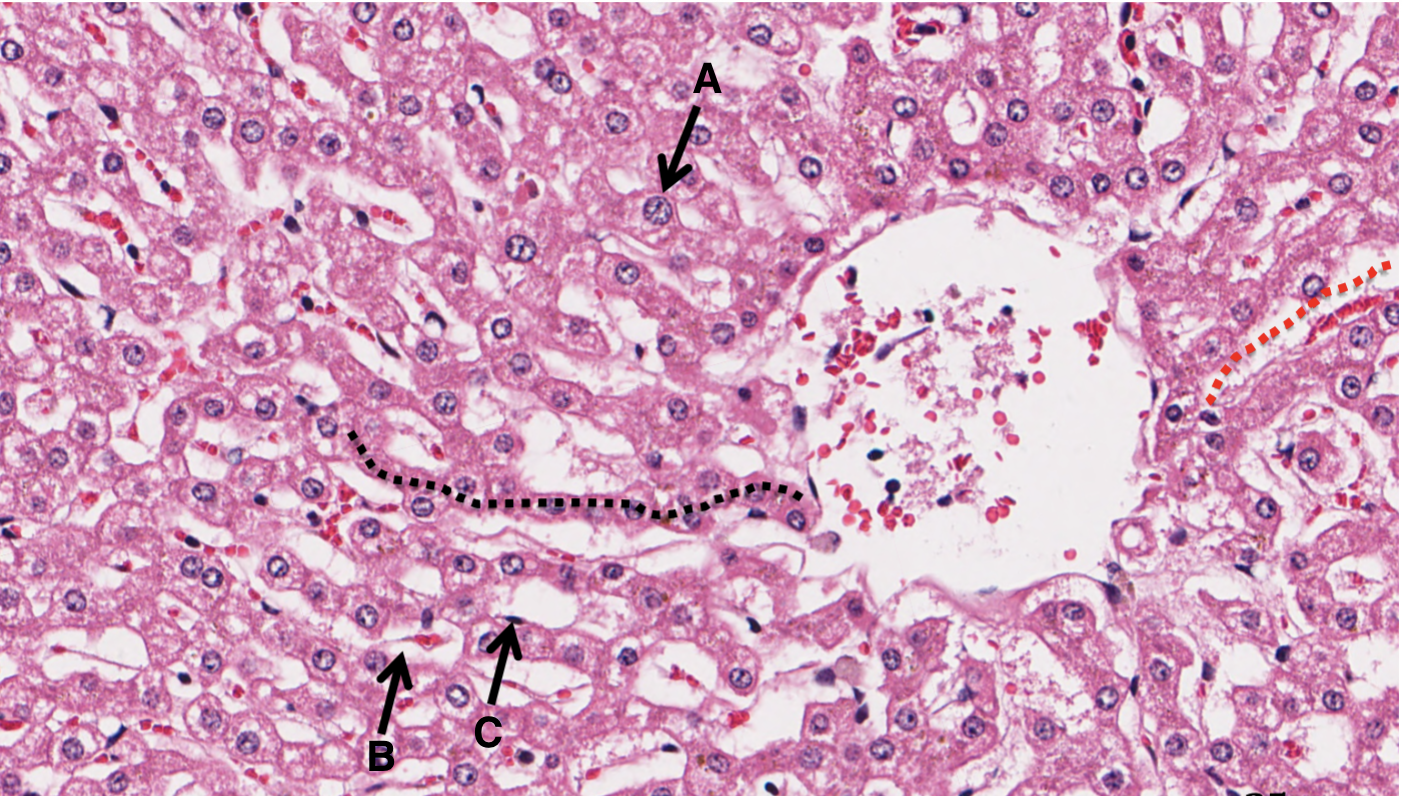
What is B in a liver slide?
sinusoid
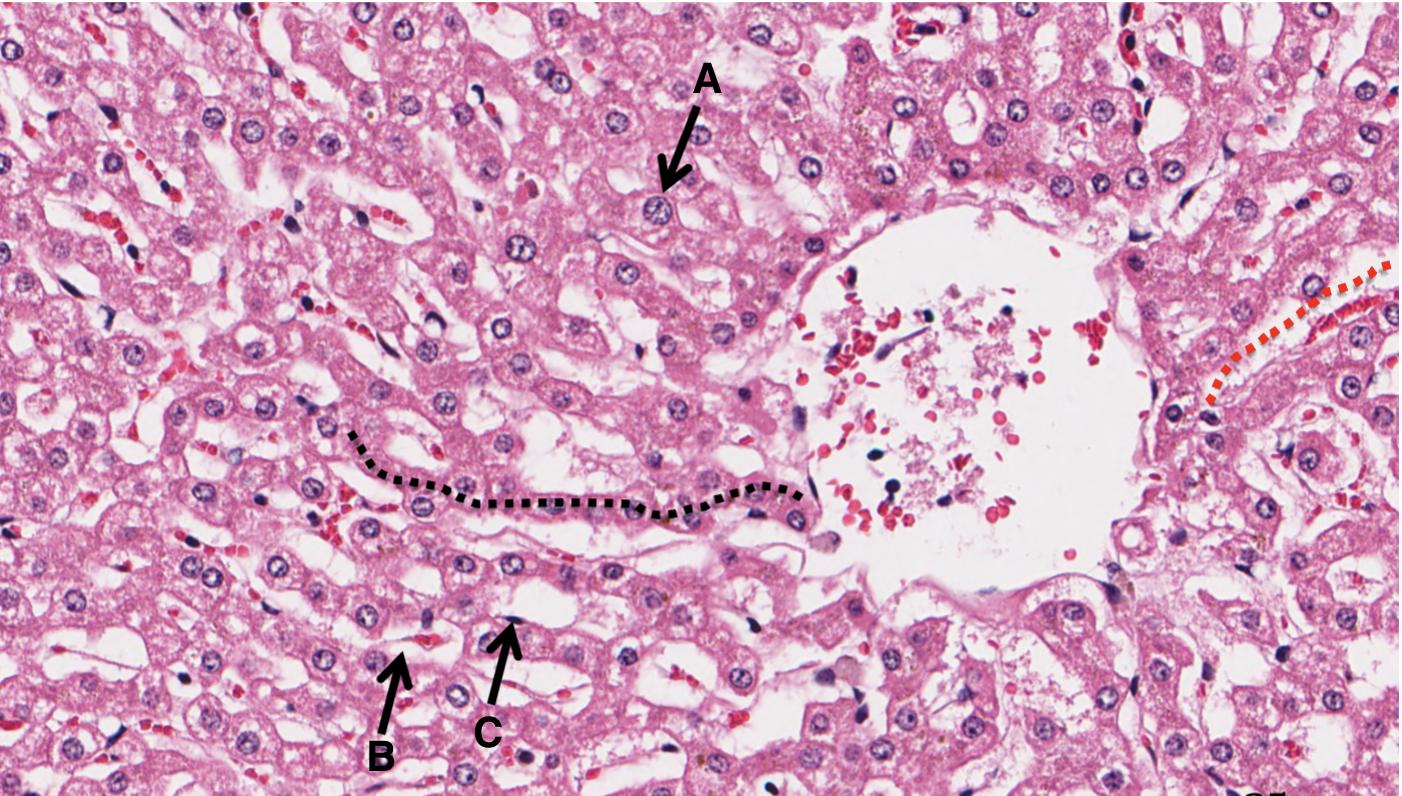
What is C in a liver slide?
Space of Disse
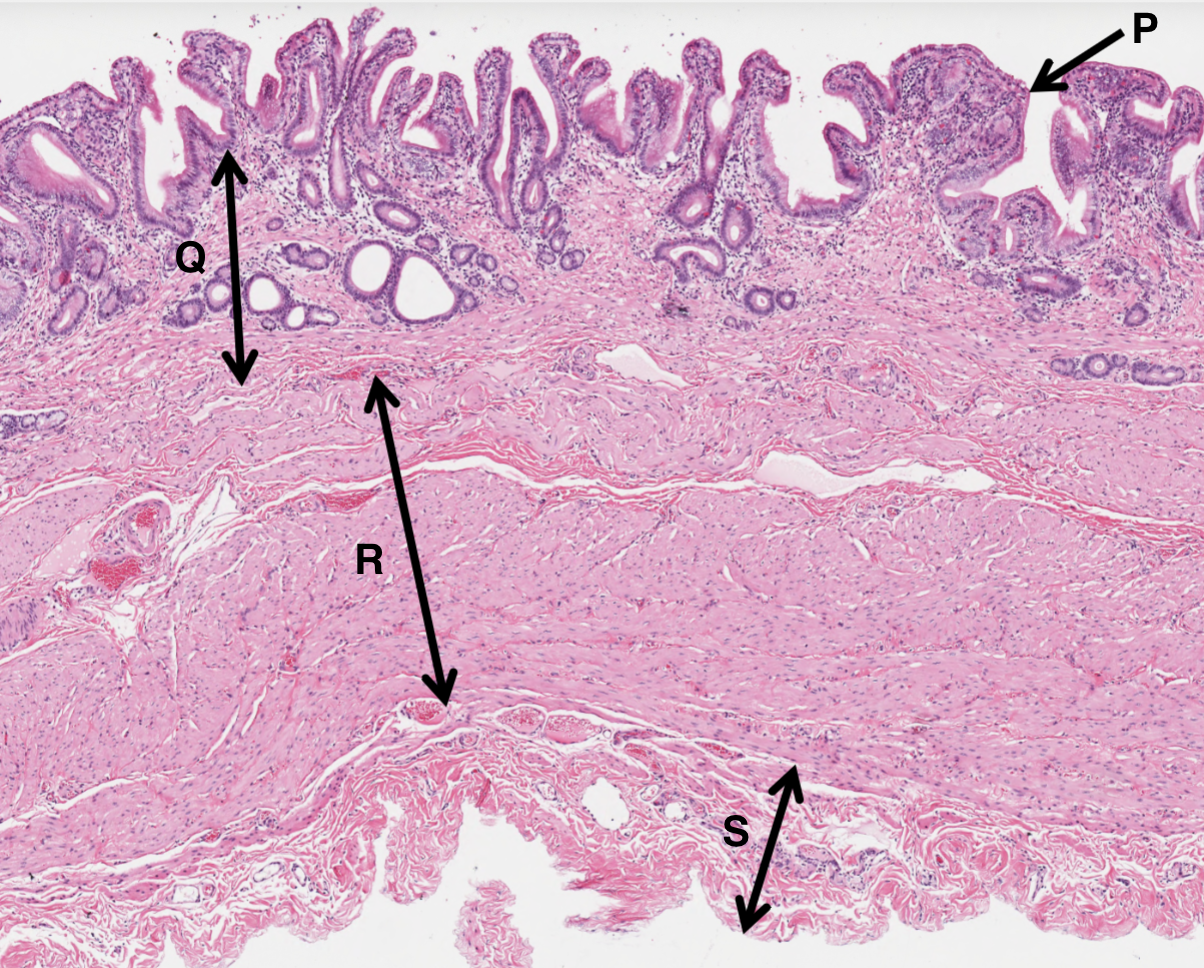
What is P from a gall bladder slide?
simple columnar epithelium
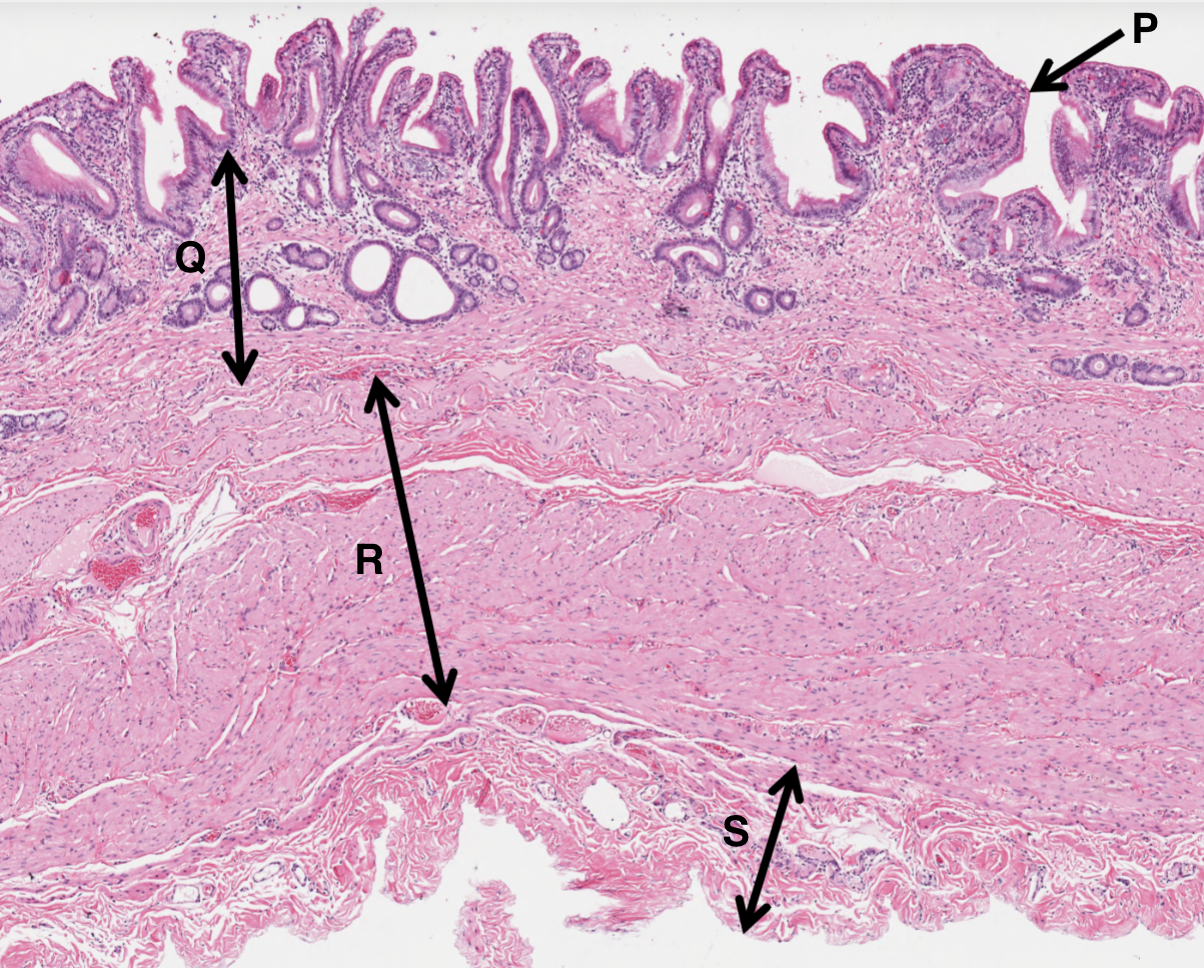
What is Q from a gall bladder slide?
vascular rich laminate propria
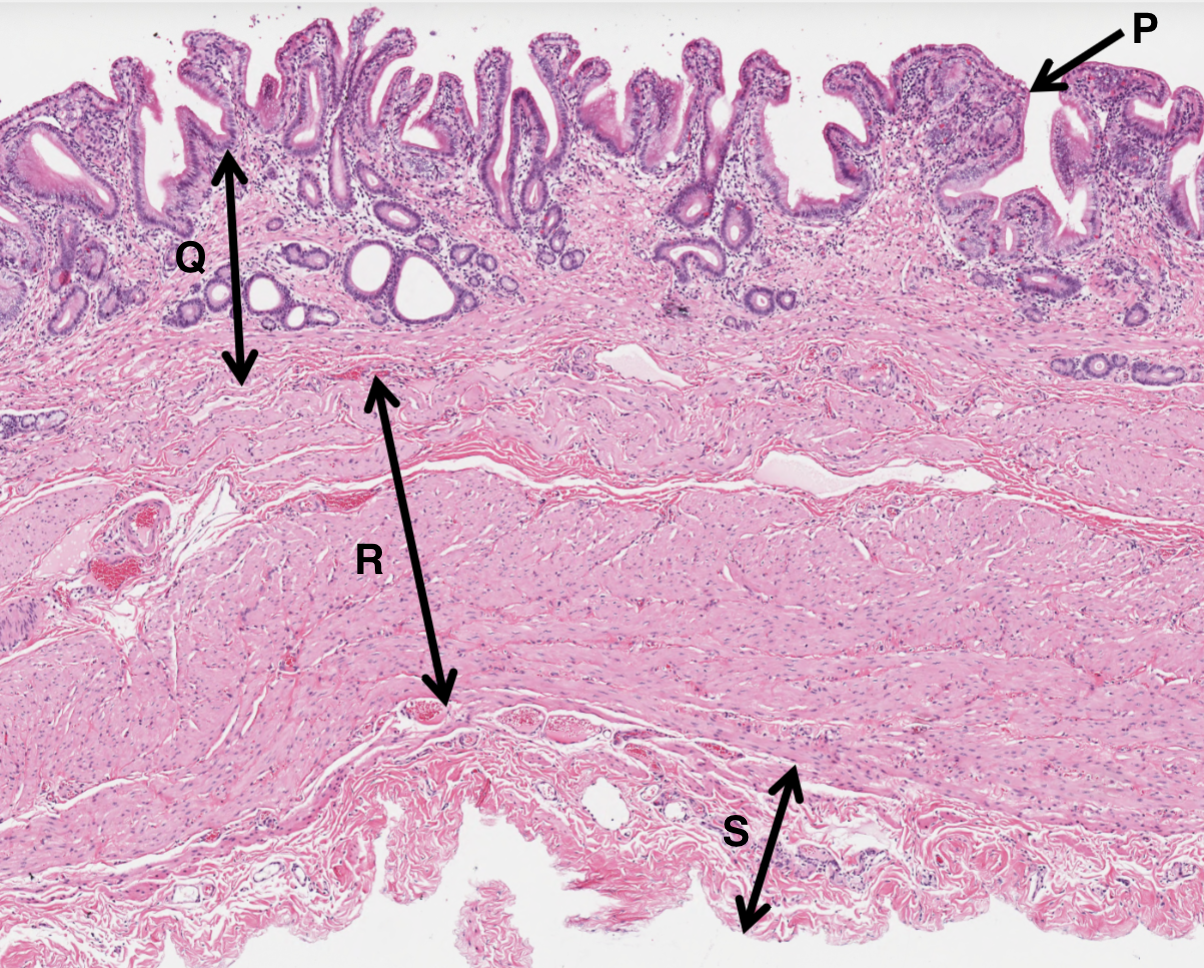
What is R from a gall bladder slide?
smooth muscle layer
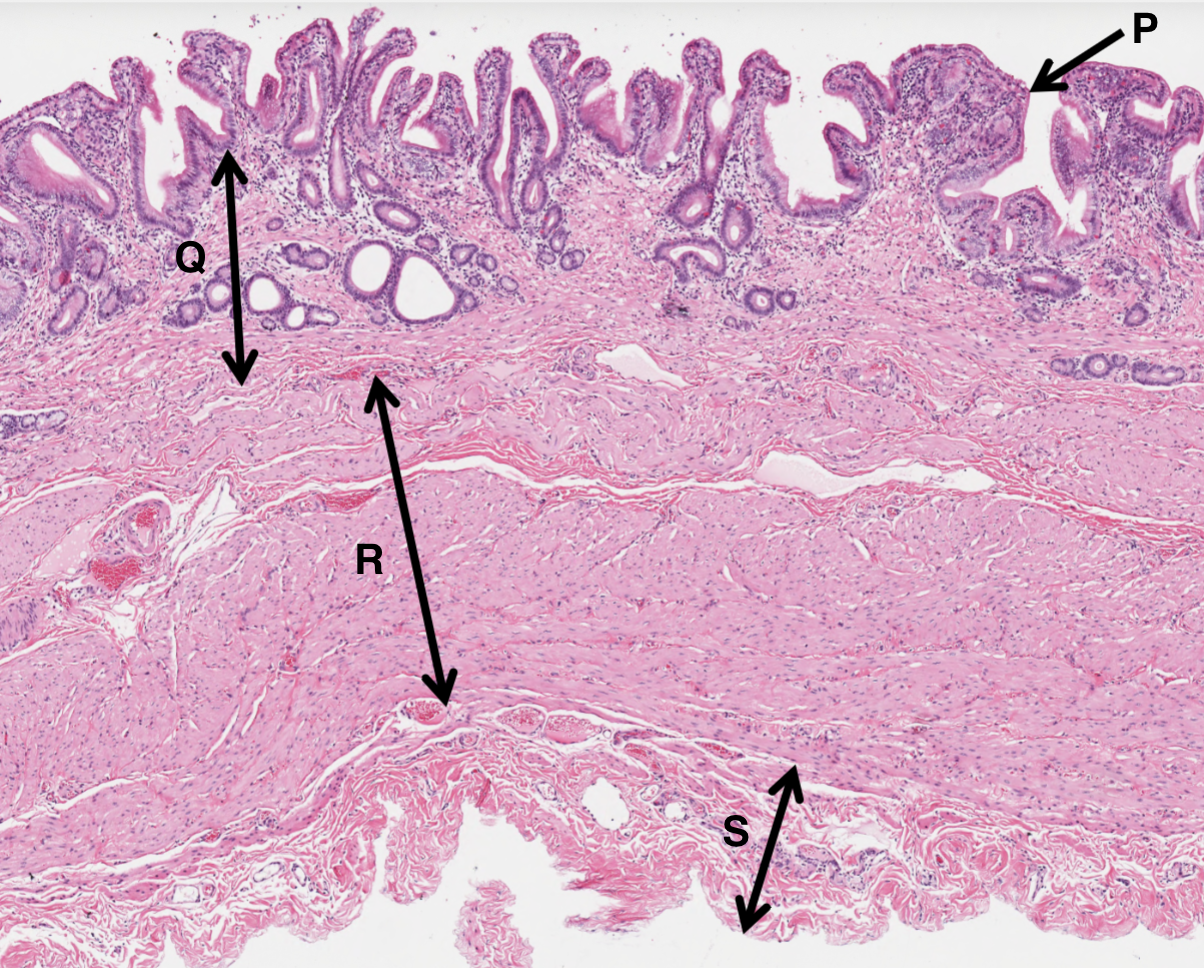
What is S from a gall bladder slide?
adventitia