Test 1
1/409
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Chapters 1-6
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
410 Terms
Anatomy
The various structures of the body, and their relationship to one another
Gross anatomy
Structures visible to the naked eye
What is connected to what in which cavity
Regional vs Systemic
Microscopic anatomy
Structures that are microscopic
Not visible to the naked eye
Cells and tissues
Cytology vs histology
Physiology
How these individual body parts work (or function) on a normal level
Fixed in function
Mostly cellular and molecule
Cell are the ones producing products
What is the relationship between structure and function?
Principle of complementarity of structure and function
What a structure can do is dependent on its form
Change structure → change function
Structural organization of the human body
Chemical
Cellular
Tissue
Organ Level
Organ System
Organismal Level
Chemical level
Atoms combine to form molecules
The smallest structural organization
Cellular level
The smallest unit of life
The 2nd structural organization
Tissue level
Aggregation of living cells that carry out a similar function
Four basic types
The 3rd structural organization
Types of tissue
Muscle
Epithelial
Nervous
Connective
Organ Level
2 or more tissues operate together to preform a certain function
The 4th structural organization
Organ System
Multiple organs work together to accomplish a purpose
The 5th structural organization
Organismal Level
All organ systems working together to keep the organism alive
(you as a person)
The last structural organization
Necessary Life Functions
Maintaining boundaries
Movement
Responsiveness
Digestion
Metabolism
Excretion
Reproduction
Growth
Mature Baboons Must Read Driving Manuals Especially Reverse Guides.
Maintaining Boundaries (as a necessary life function)
At the cellular level
Plasma membrane to keep contains of a cell together
At the organismal level
integument/skin
hold everything in
prevent exposure from environment and bacteria/viruses
Movement (as a necessary life function)
Cooperation of skeletal and muscular systems to coordinate actions
Conscious/voluntary
Skeletal muscular tissues
Not conscious/involuntary
Smooth muscle tissue (hallow organs)
Cardiac muscle tissues
Responsiveness/Excitability (as a necessary life function)
Sensing environmental changes both internally and externally and responding to them
Nervous system is primarily involved with excitability
Neurons
Highly specialized to be excitable
How brain perceives information and communicates with rest of body
Muscle tissue cells
Have to respond quickly to allow us to move fast
e.x: if we touch a hot stove
Digestion (as a necessary life function)
Absorb nutrients
Food is broken down to simple molecules to be absorbed to blood and delivered to various tissues
Metabolism (as a necessary life function)
Sun of all chemical reactions in organism
Catabolism
Break down
Take larger molecule and breaking it down into smaller part
ex: protien to amino acids
Anabolism
Build up
Take smaller molecules and combining them to make larger molecule
ex: amino acids to protein
Cellular respiration
Produce ATP
ex: glycolysis, Krebs Cycle, electron transport train,
Excretion (as a necessary life function)
Removal of waste produced during digestive and metabolic function
Forms
solid waste (digestive)
exhale (respiratory waste CO2)
nitrogenous waste (urinary system)
Built up waste can
kill a cell
interfere with cellular function
Reproduction (as a necessary life function)
Cellular level
cells must divide for organism to survive
Organismal
production of offspring
species survival
Growth
Increase in the number of body cells
Increase in size of individual cells themselves
Building must occur faster than breakdown
rate of anabolic > rate of catabolic
difference between survival need and life functions
The survival needs are required to be able to carry out life functions
Survival Needs
Nutrient
Oxygen
Water
Endothermy
Atmospheric Pressure
New Octopi Will Eat Anything
Nutrients (as a survival need)
Brought into body by ingestion
Includes macro nutrients: carbohydrates, fats, proteins
Need to bring them in at large amounts throughout the day
Includes micro nutrients: vitamins and minerals
Vitamins important for chemical reactions
e.g: B12 necessary for ATP products
Minerals (iron, zinc, calcium) are structural
Oxygen (as a survival need)
Cells can only survive a few minutes without oxygen
Electron transport train requires oxygen to make ATP
Electron transport train supplies >50% of our APT
Water (as a survival need)
We are 60% water
Provides environment for chemical reactions
Primary solvents for chemical reactions to occur in and use as part of the reactions
Hydrolysis
Fluid base for secretions and excretions
Difference between a secretion and excretion
Secretions
Removes something it produces
Excretion
Waste
Endothermy (as a survival need)
Body temperature must be maintained for chemical processes to occur
We produce our own body heat
Atmospheric Pressure
Required for respiratory function
Breathing and gas exchange
Changing altitude can effect humans
e.x: altitude sickness
Suddenly breathing in less oxygen concentration (thin air)
Homeostasis
Maintenance of a consistent internal state despite changes in external environment
Maintenance is not a static state, hover in a range of expectable levels
Accomplished by the work of virtually all organ systems
Control of homeostasis
Mostly regulated by central nervous system (almost always the brain) and the endocrine system (hormones)
Variable: what organ or function is being controlled or regulated, 3 parts involved in variable control
Receptor
Control Center
Effector
Controlled by negative feedback mechanism or positive feedback mechanism
Receptor (in control of homeostasis)
Some type of cell that receives information about the variable and sends a message to control center
Control center (in control of homeostasis)
Almost always the brain, sometimes the spinal cord
receives message from receptor, interpret it, then send out a response to an effector
Effector (in control of homeostasis)
Receives response from control center and carries it out
Negative feedback mechanism
Cause the variable to change in a direction that is opposite of the initial change
Prevents large changes, more stable
e.x: thermoregulation, most hormones
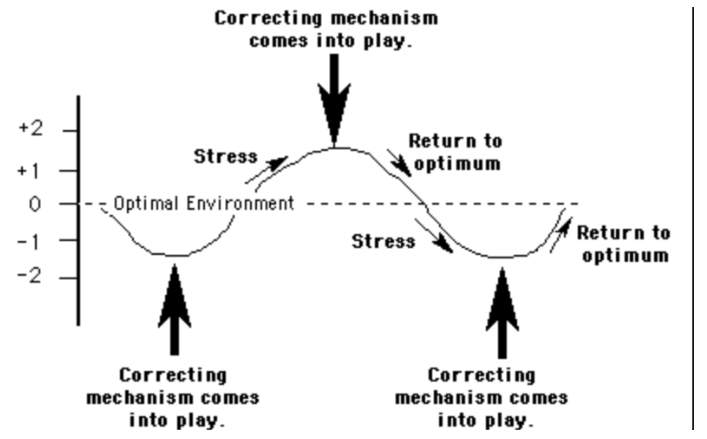
Positive feedback loop
Cause the original change of the variable to be enhanced (accelerates the change)
Way less common, used in emerencys
Does not control events that require frequents, small adjustments
e.x: labor, blood clotting
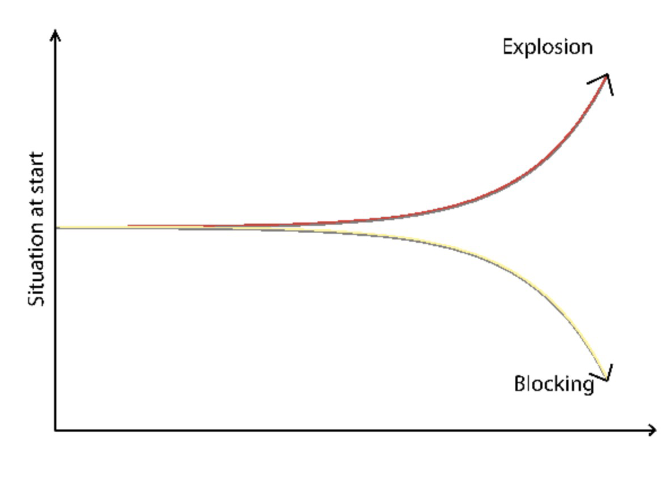
Imbalances in homeostasis
Causes:
aging leads to homeostatic imbalance
control systems become less efficient, making us more susceptible to disease
cascade of events caused by positive feedback mechanisms can overpower negative feedback mechanisms
Leads to disease or sickness
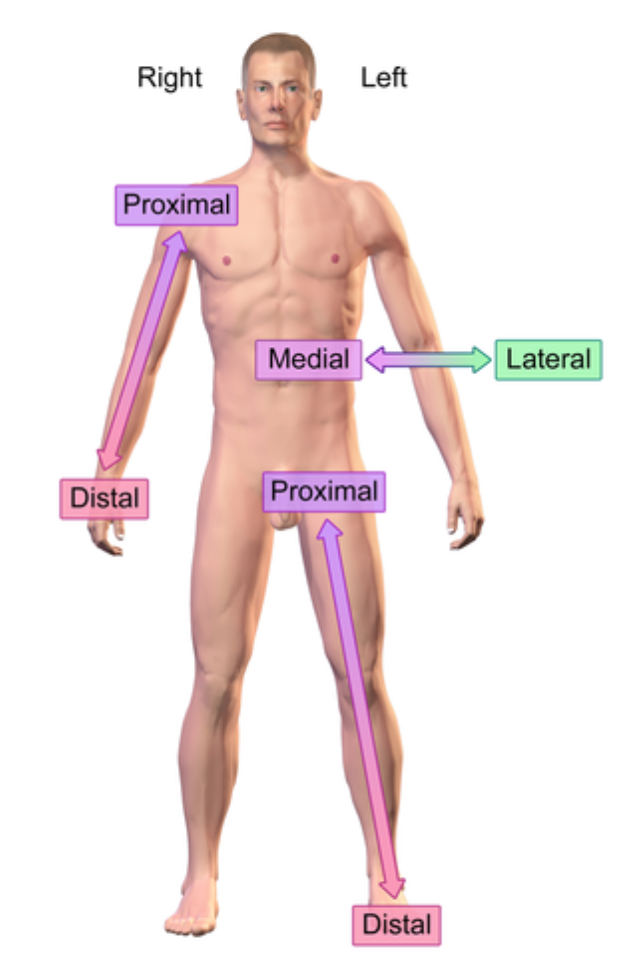
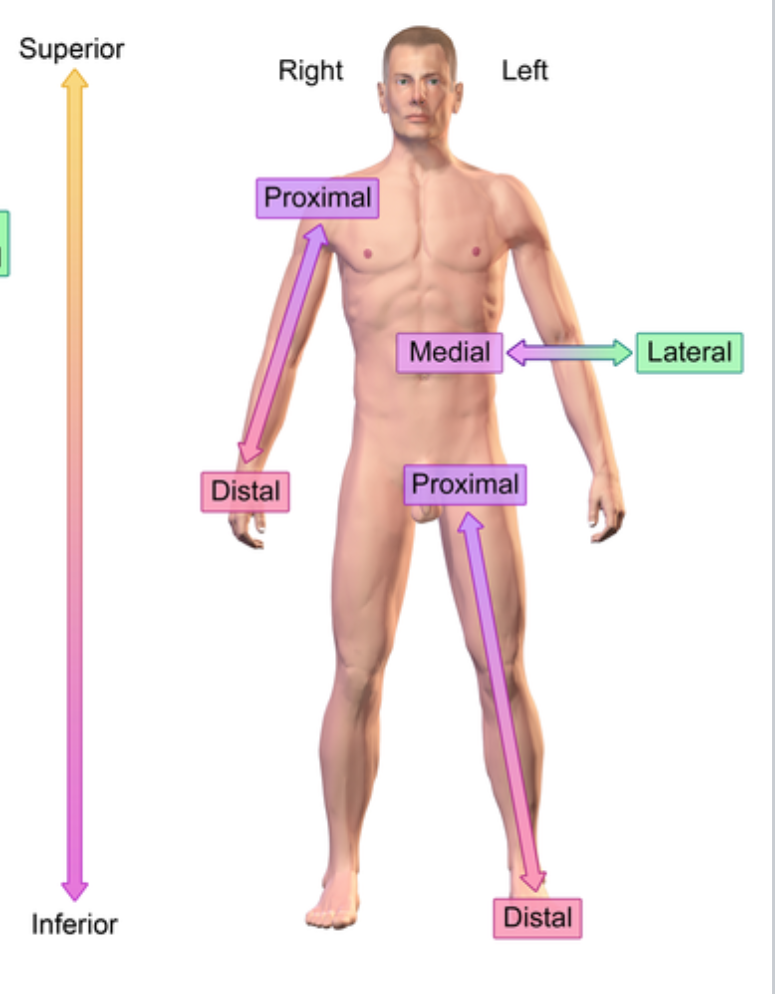
Reference point: anatomical position
Right vs left is always viewed in terms of the person being observed. not your own
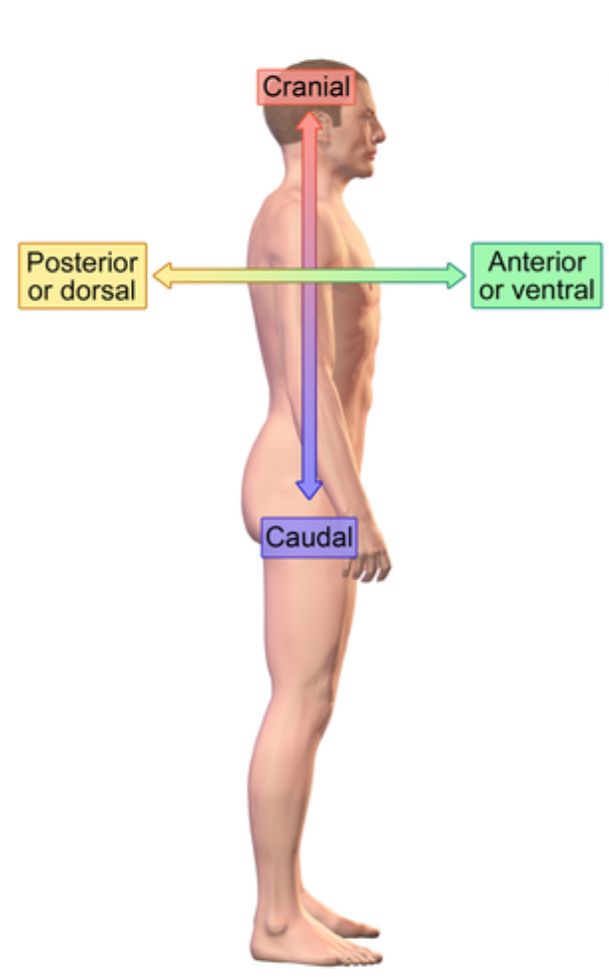
Dorsal (posterior) (anatomical term)
Backside
e.x: vertical column
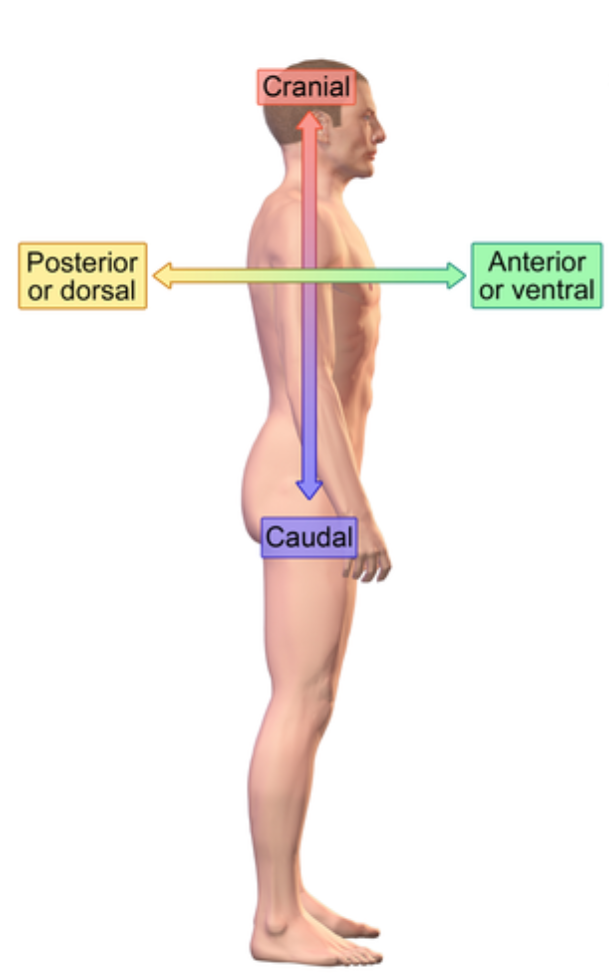
Ventral (anterior) (anatomical term)
Front/belly side
Lateral (anatomical term)
Further from the midline
e.x: ear is lateral to the eye
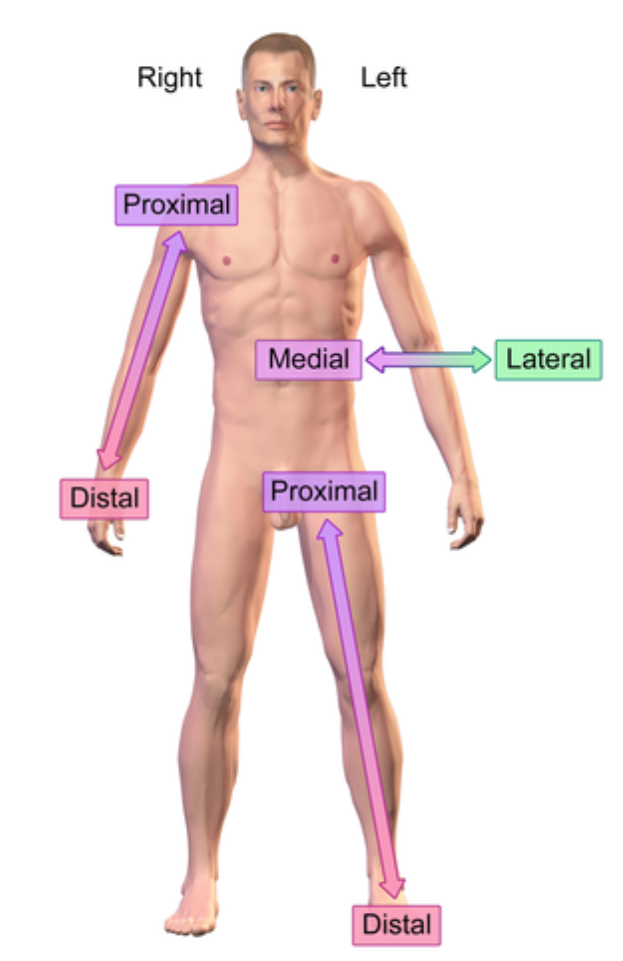
Medial (anatomical term)
Closer into the midline
e.x: eye is medial to the ear
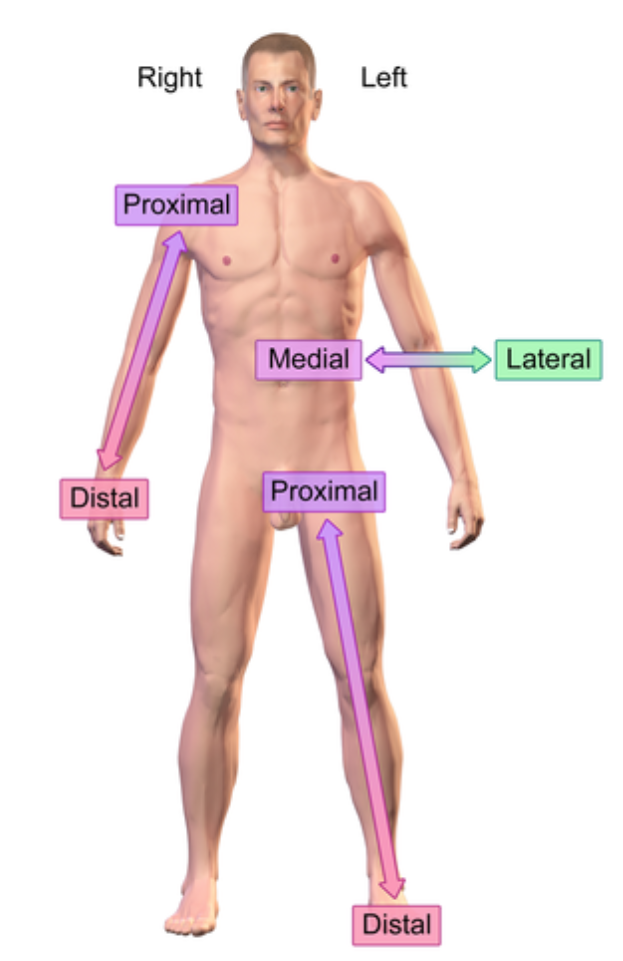
Distal (anatomical term)
further from the point of origin
e.x: Wrist distal to elbow (point of origin is shoulder)
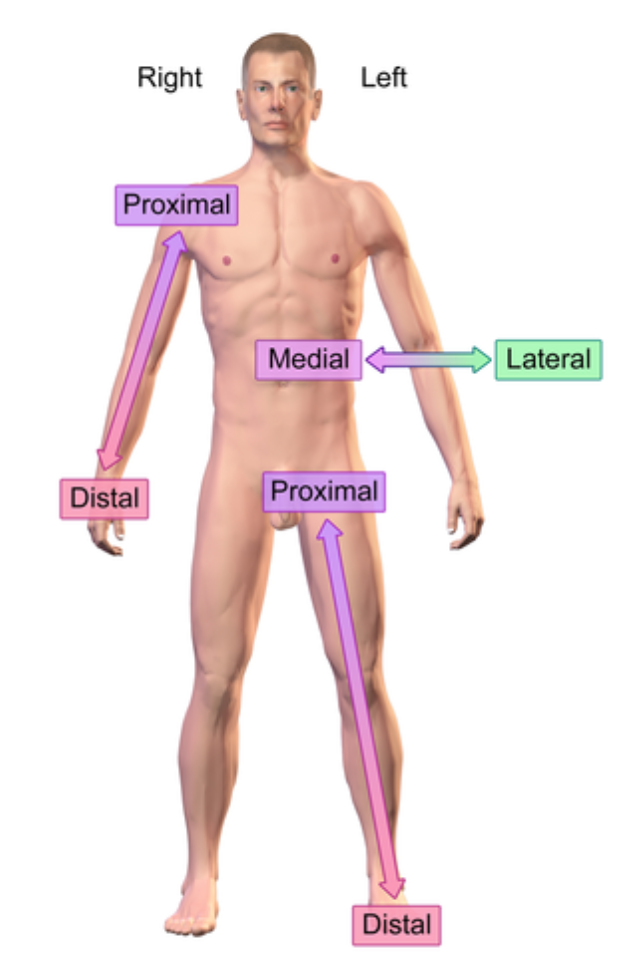
Proximal (anatomical term)
e.x: Elbow proximal to wrist (point of origin is shoulder)
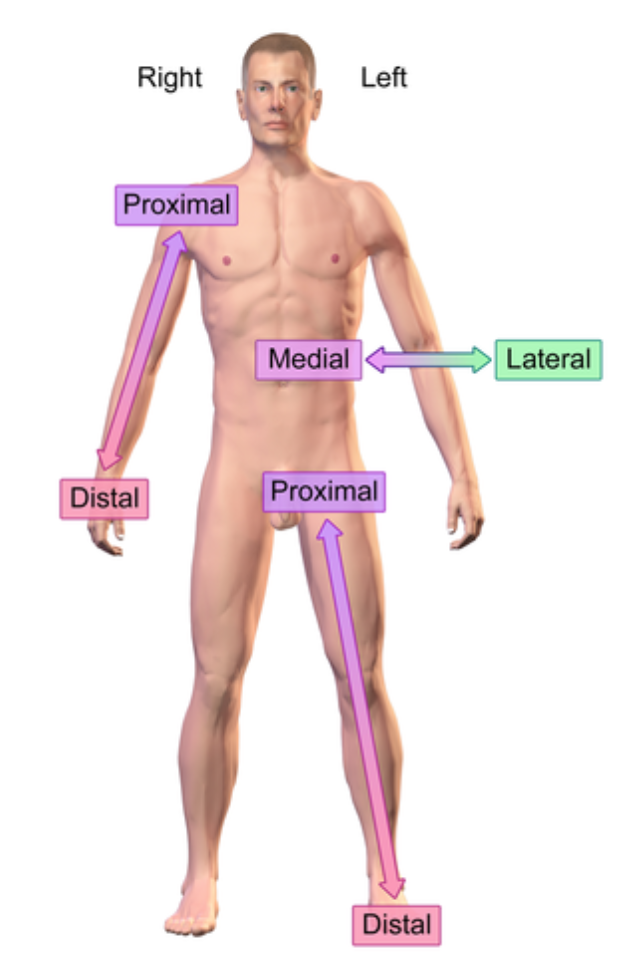
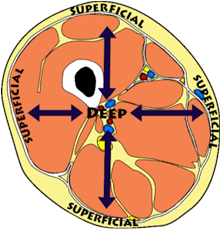
Deep (anatomical term)
Further from skin
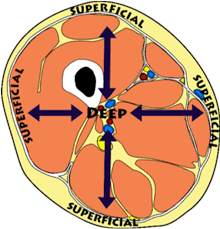
Superficial (anatomical term)
Closest to skin
Superior (anatomical term)
On top of
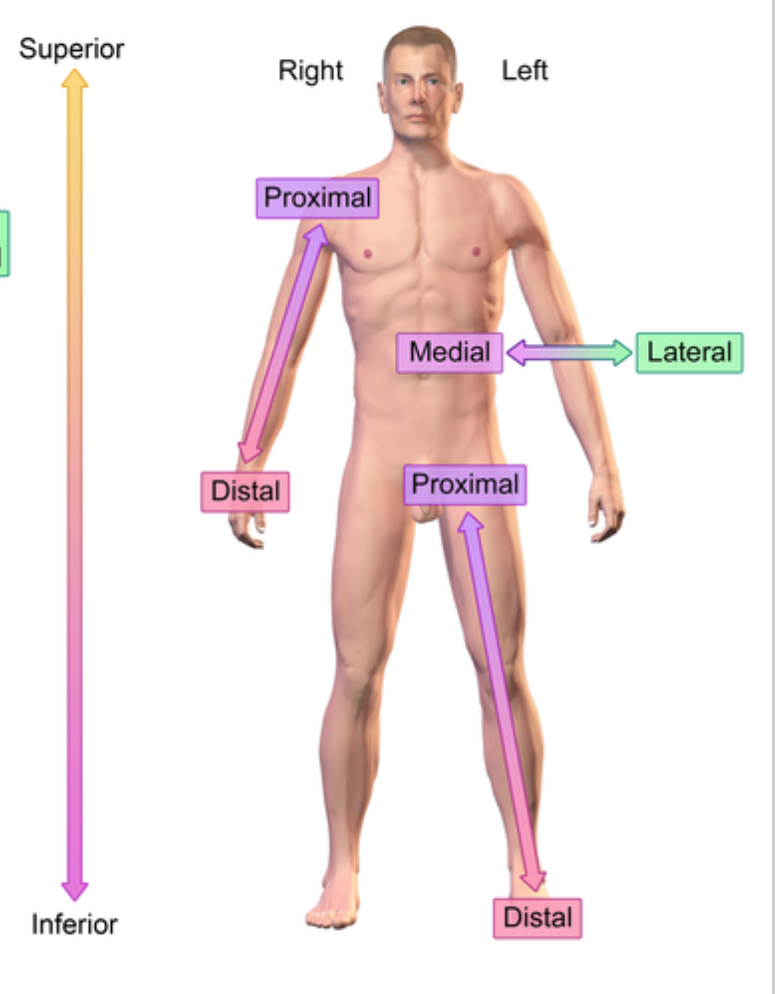
Inferior (anatomical term)
Below
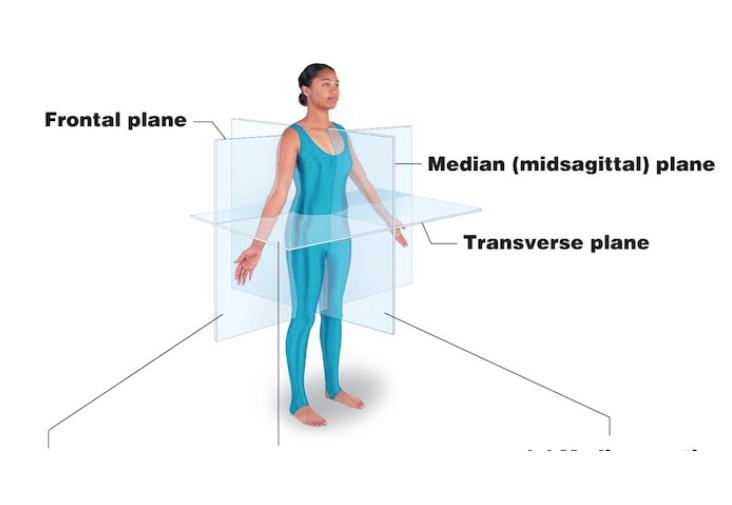
Body planes
Sagittal
Transverse
Frontal
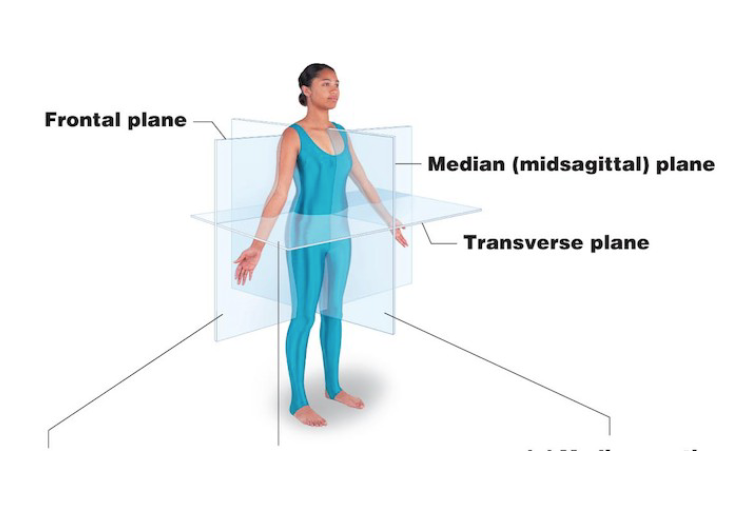
Sagittal
Divides body into left and right
Median/midsagittal plane divides the body exactly in half
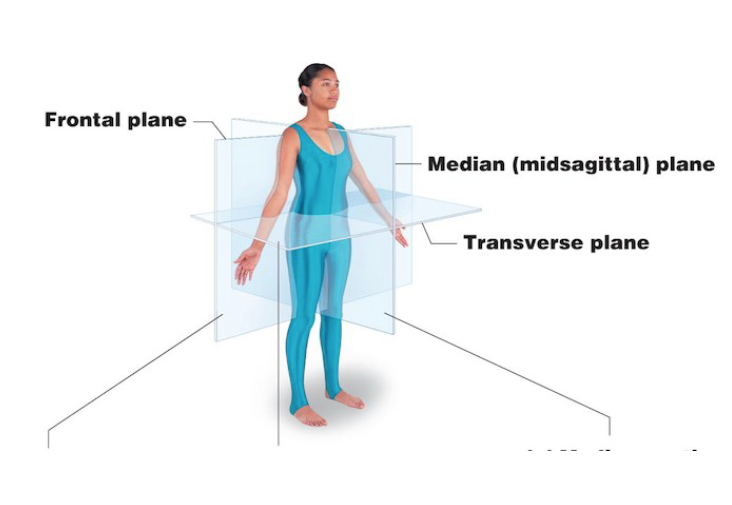
Frontal
Divides body into anterior and posterior
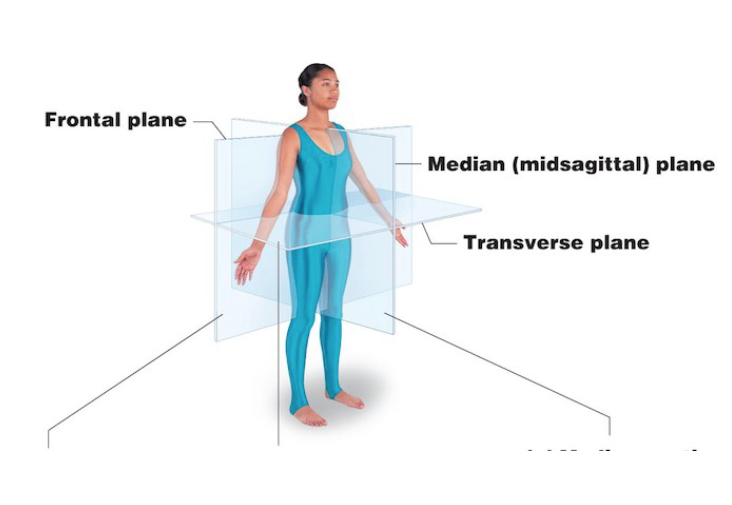
Transverse
Divides body in superior and inferior parts
Cross section
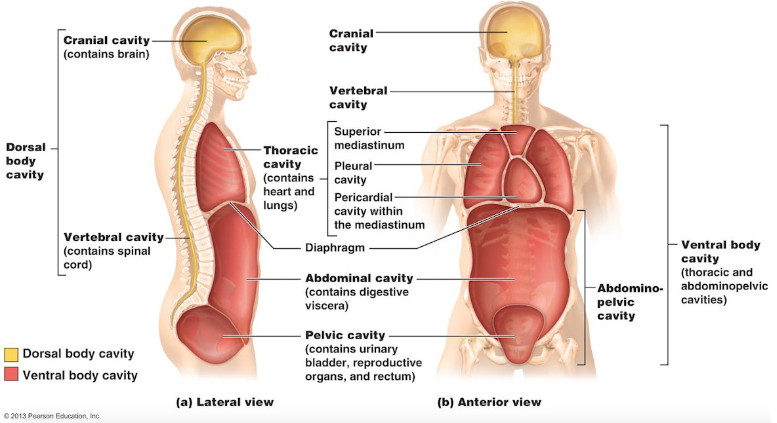
Body cavities
Most organs are found in one of the body cavities
Dorsal body cavity
Ventral body cavity
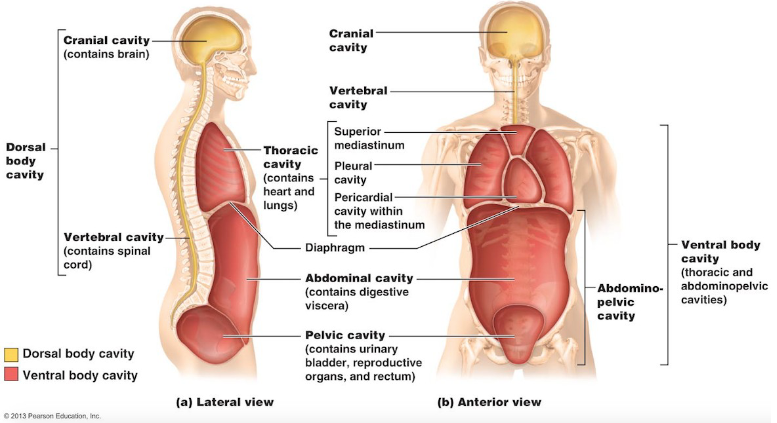
Dorsal body cavity
Protects organs of central nervous system
Composed of the cranial cavity and spinal
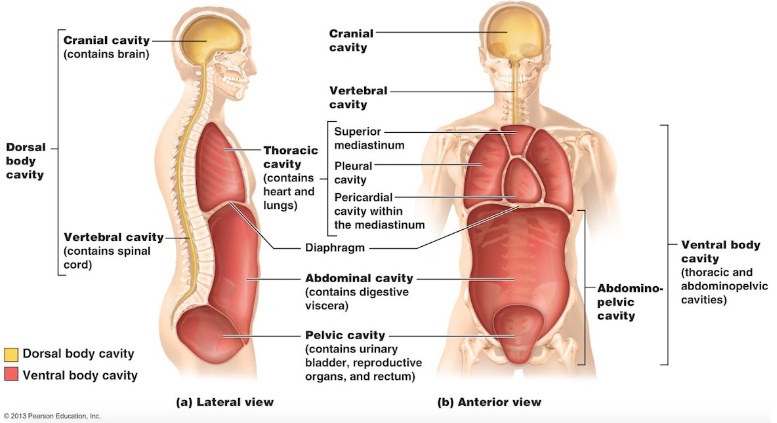
Ventral body cavity
houses visceral organs
Composed of:
Thoracic cavity: contains heart and lungs
Abdominopelvic cavity: separated from thoracic cavity by diaphragm
Membranes of the ventral body
Serous membrane
double-layered membrane
Serous membrane
Layers:
Visceral serosa: innermost layer covering the organ
Parietal serosa: outer layer lining the body wall of the cavity
layers are separated by a small amount of serous fluid
Named according to their location
Pericardium: surrounds heart
Pleura: surrounds lungs
Peritoneum: surrounds most organs of the abdominopelvic cavity
Visceral serosa
Innermost layer covering the organ
Parietal serosa
Outer layer lining the body wall of the cavity
Pericardium
Serous membranes surrounding the heart
Pleura
Serous membranes surrounding the lungs
Peritoneum
Serous membranes surrounding most organs of the abdominopelvic cavity
Do all organs have a serous membrane?
No, but most do
ex: Kidneys and esophagus do not
Mixtures
any substance containing 2 or more components physically intermixed
Can come in all phases: gas, solid, and fluid
Predominantly fluid in body
Types of mixtures
Solutions
Colloids
Suspensions
Solutions
Homogenous mixtures that can exist as a solid, liquid, or gras composed of very small particles that do not settle out
Composed of:
Solvent: dissolving medium
Solute: dissolved
Concentration expressed as:
Percent solution
Molarity (mol/L)
Important Example: saline solution (water and NaCl)
Solvent
the dissolving medium
Water is the body’s primary solvent
found in higher concentration
Solute
thing dissolved in the solvent
found in lesser concentration
does not settle, stays suspended
Percent solution
Way of describing the concentration of a solution
amount of solute dissolved is expressed as a percentage of the total solution volume
Molarity
mol/L
Way of describing the concentration of a solution
the number of moles of a substance per liter of solution
Reminder: a mole of any element or compound is equal to its molecular weight
Colloids
heterogenous mixtures composed of large solute particles that do not settle out
Larger particles compared to a solution
can undergo sol-gel transformation
Sol-gel transformation
can happen in colloids
mixture can change from a fluid state to more solid state (and back)
solid state is like jello
Depends on needs of the colloid
Ex: cytosol of cells changes consistency depending on certain cell activities (cellular division, change in shape, etc.)
Suspensions
heterogenous mixture composed of large solute particles that do settle out
e.x: blood - contains a fluid portion (plasma) with various cell types (red blood cells, white blood cells, & platelets) suspended in it
Chemical Reactions
occur when chemical bonds are formed, broken, or rearranged
Bonds store energy
extremely important
Types of chemical reactions
Synthesis reaction
Decomposition reaction
Synthesis Reaction
Formation of bonds between atoms or molecules to form larger, more complex structures
Are endergonic - contains more energy after formation
ex: anabolic reactions in the body
Decomposition reaction
bonds are broken to create smaller molecules or individual atoms
are mostly exergonic - release energy when bond is broken
ex: catabolic reactions in the body
Inorganic compounds that are important to homeostasis
Water
Salts
Acid & Bases
Waters role in homeostasis
Makes up most of the total body mass and most of the volume of individual cells
Universal solvent
many reactions take place in water
transport water carries nutrients, respiratory gases, metabolic waste, etc.
water can surround some charged structure to prevent interactions with other charged particles
ex: proteins are wrapped in water so they do not react on the way to destination
High heat capacity (amount of heat a substance needs to absorb to raise it’s own temperature by 1°C)
can absorb and release large amounts of heat with little change to its own temperature
lots of things produce heat as a by product
skeletal and muscular system produces a lot of heat
helps prevent extreme changes in body temperature throughout the day
protection
water-based body fluids provide a “cushion” for internal organs
prevents damage from a physical blow
High heat of vaporization (amount of heat that needs to be absorbed to cause to material to evaporate)
Large amount of heat must be absorbed to break bonds and cause evaporation
Is why sweating absorbs a large amount of heat
Reactive
Water is used in several chemical reaction in the body
Hydrolysis: add water to break bond
AB + H2O → A-H + B-OH
Dehydration synthesis
A-H + B-OH → AB + H2O
Salts role in homeostasis
Dissociate in solution to form electrolytes
Examples:
Na+ and K+ allow for muscle contraction and transmission of nerve impulses
Fe+ used in red blood cells, is used to carry O2
Acids and Bases role in homeostasis
Also form electrolytes
Acids:
release H+ ions in solution
Cause pH to drop
Bases
release OH- ions in solution
Cause pH to increase
Optimal blood pH is 7.2-7.4
What happens if blood pH is off?
high/low pH disrupts cellular activity, hydrogen bonds, etc
What can cause this:
Prescription medications, certain foods
Solution:
Buffers
Weak acids release some (but not all) H+
Weak bases tie up excess H+ when pH becomes too acidic
Buffers prevent large changes in pH that could cause excessive damage in the body
All organic molecules found in the body contain _, why?
Carbon:
It is electroneutral, it neither gains nor lases electrons
Can form molecules of various shapes that all have specific functions in the body
Long chains
Rings (carbahydrates)
Macromolecules
Polymers that are made up of several smaller, identical subunits called monomers
3 types
carbohydrates
lipids
proteins
Carbohydrates
sugars and starches
monomer: monosaccharide
glucose
used for APT production **
fructose
galactose
can form disaccharides and polysaccharides
Used for other things
including polysaccharides are immune system marker that marks cells that belong to the body
major functions
fast, easy-to-use energy source
cell-cell interactions
carbohydrates attached to cell surface and are used to communicate
Types of lipids
Triglycerides
Phospholipids
Steroids
Triglycerides
Monomer: fatty acids and glycerol
Varieties
Saturated
Unsaturated
Trans fat
Omega-3 fatty acids
Functions
Protection
insulations
fast and easily accessible energy storage
Found
subcutaneous - right under skin
adipose tissues
Triglycerides: saturated
contain only single covalent bonds, molecules packed closely together
found in meat productions
only want low amounts
can build up in vessel walls and is solid
can lead to stroke and heart attack
Triglycerides: Unsaturated
contain 1 or more double covalent bonds
looser arrangement, molecules are more spread out
found in most plant-based oils
considered healthy
Triglycerides: trans fat
oil fats that have a H added at sites of double bonds
found in doughnuts and cookies
worst to consume
build up the most in vessels
Triglycerides: Omega-3 fatty acids
Oil fat found in cold-water fish
krill oil, fish oil capsulars
Phospholipids
modified triglycerides with 2 fatty acid chains and a phosphate group
fatty acid chains are hydrophobic
phosphate “head” is hydrophilic
function
used to build cell membranes
all cell membranes are phospholipid bilayer
Steroids
Most important steroid for life: cholesterol
Ingested in eggs, meat, cheese
Liver produces 85% of body’s need for cholesterol
Major functions:
structural component of cell membranes, makes them tougher
is “base” used by body to form other steroids (steroid hormones—testosterone & estrogens, corticosteroids)
Proteins
Monomers: amino acids
Specific amino acid sequence leads to large variety of protein functions
Structure determines function
Fibrous proteins
Globular proteins
Enzymes
Proteins: Fibrous
form long strands that can link together to form long, stable structures
Can be pulled without breaking and returns to original shape
Function
provide mechanical support & tensile strength, some contractile ability
Ex:
collagen*
skin
tendons
ligaments
joints
muscles
Proteins: globular
compact, spherical in shape
Chemically active
Function
transport molecules
immune defenses
regulation of growth & development
lipid based molecules bind to protein so they can travel in body when they need transport
Enzymes
biological catalysts
Function:
catalysts lower the activation energy of chemical reactions
Varying degrees of specificity
Some only catalyze 1 reaction, others can catalyze multiple reactions
Importance:
without enzymes, most reactions in the body would either not occur or would occur too slowly to sustain life
ATP & cellular energy
Adenosine triphosphate (ATP)
the energy transferring molecule of any body cell
glucose and O2 is used to make it
Has 3 phosphate tails
is a little unstable (high energy)
ATP has a triphosphate tail that has high bond energy
When a phosphate tail is transferred to another molecule, that molecule temporarily has more energy to do work
While doing the work, the molecule loses the phosphate group
ATP storage & release is similar to energy needed to drive most chemical reactions
have little ATP storage in body cells
only produce enough ATP so needed in moment
ATP requires ATP to be produces, so it just sitting around is a waste of energy
Importance:
without ATP, chemical reactions stop, cell transport stops, muscle cannot contract → death occurs
Neurons stop firing
without O2 → cant produce ATP → cells dies
Prefix for “the cell”
Cyto-