Plant Nutrition and Transport Mechanisms in Vascular Plants
1/71
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
72 Terms
Xylem
Vascular tissue transporting water and minerals upward.
Phloem
Vascular tissue transporting sugars from sources to sinks.
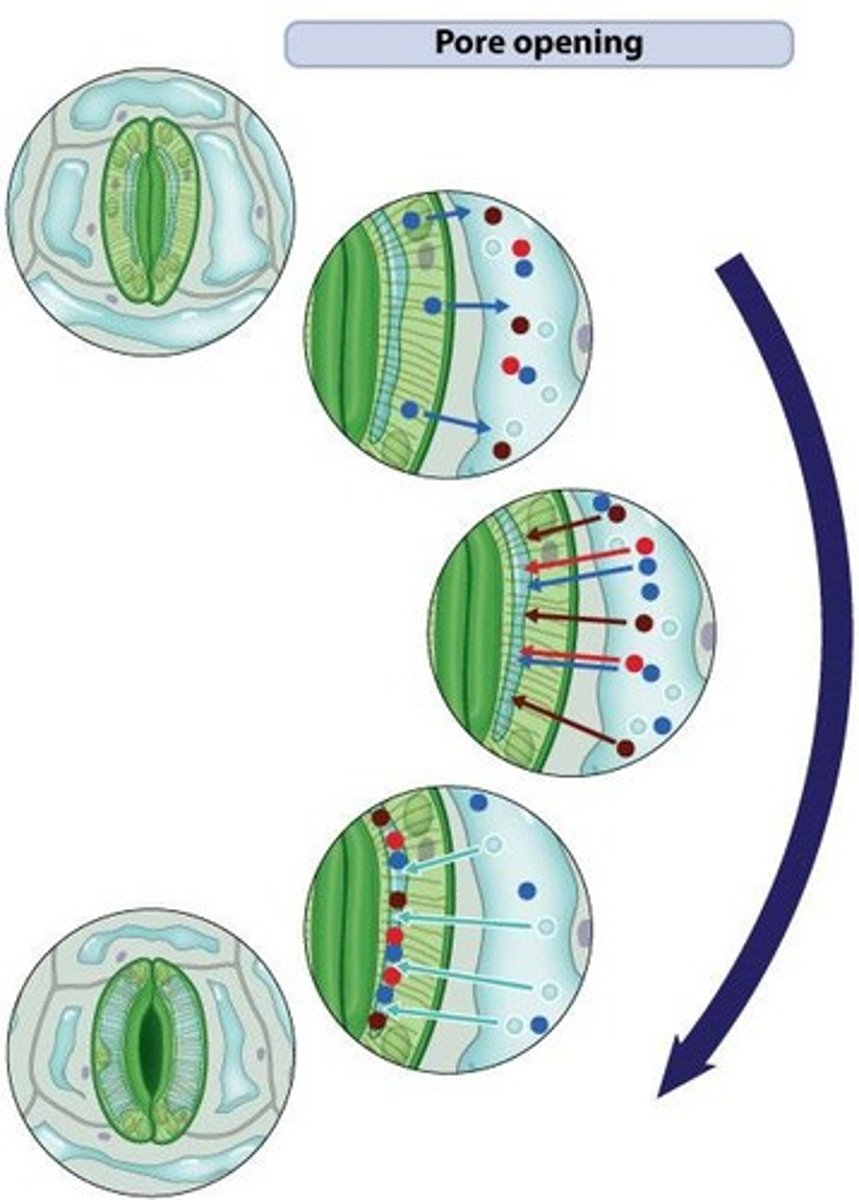
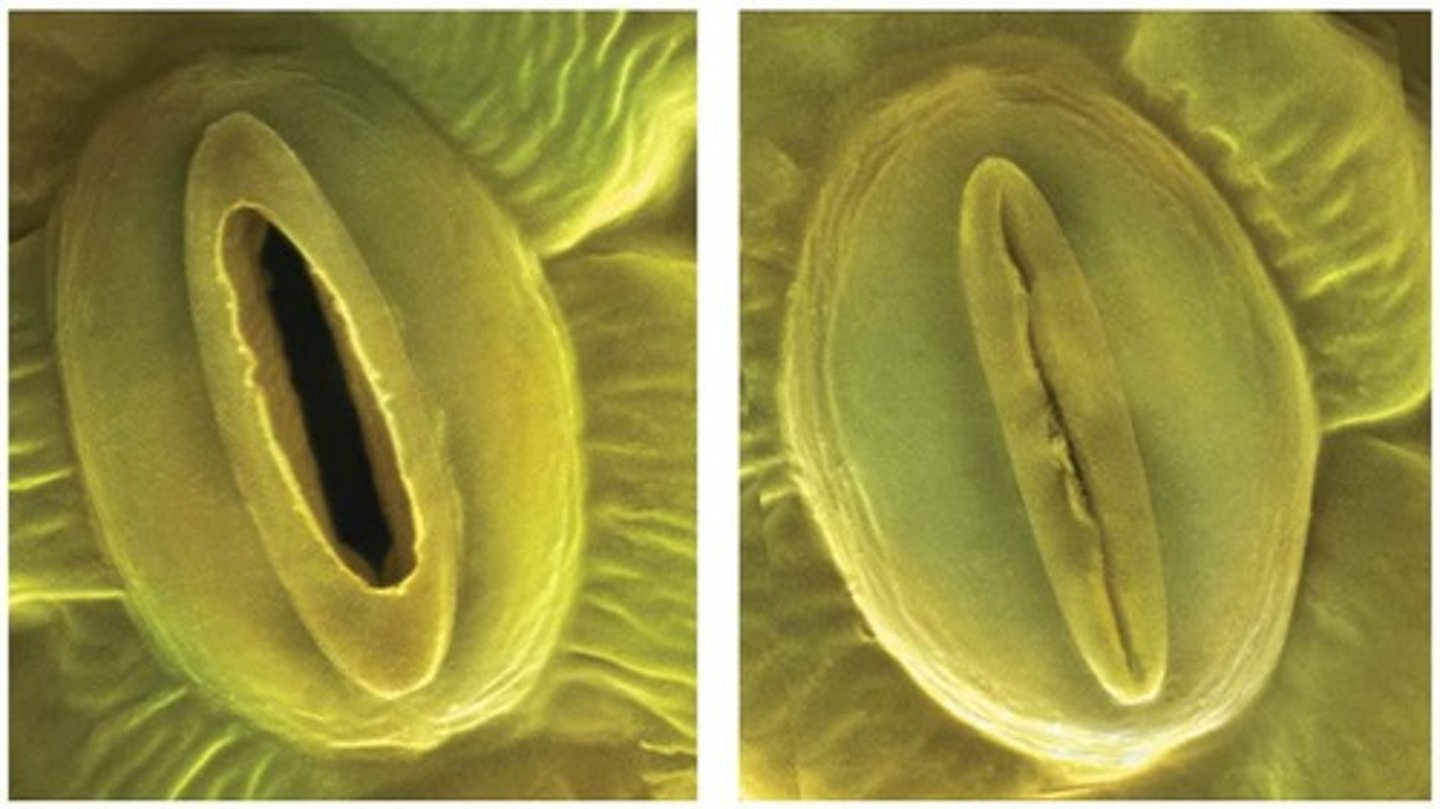
Stomata
Pores regulating gas exchange and water loss.
Root Pressure
Pressure pushing water upward in roots.
Transpirational Pull
Negative pressure created by water evaporation.
Transpiration
Water loss from leaves via stomata.
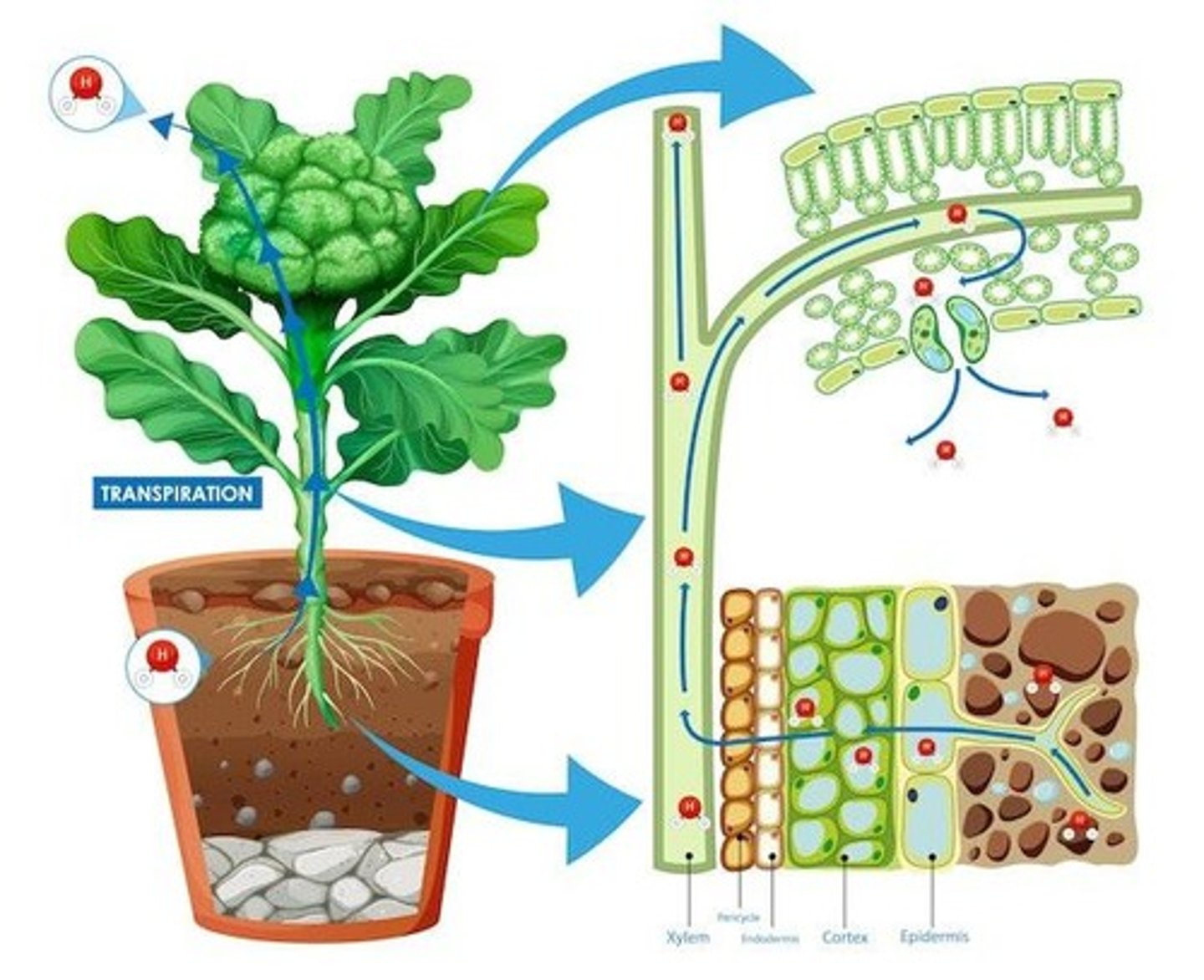
Translocation
Movement of nutrients through phloem.
Apoplastic Transport
Movement through cell walls and intercellular spaces.
Symplastic Transport
Movement through cytoplasm via plasmodesmata.
Transmembrane Transport
Movement across cell membranes.
Bulk Flow
Mass movement of water and nutrients.
Negative Pressure Flow
Water movement due to negative pressure.
Positive Pressure Flow
Nutrient movement due to positive pressure.
Water Potential
Potential energy of water in a system.
Solute Potential
Effect of solute concentration on water potential.
Turgor Pressure
Pressure of cell contents against cell wall.
Pressure Gradients
Differences in pressure driving material transport.
Source
Location where nutrients are produced or stored.
Sink
Location where nutrients are utilized or stored.
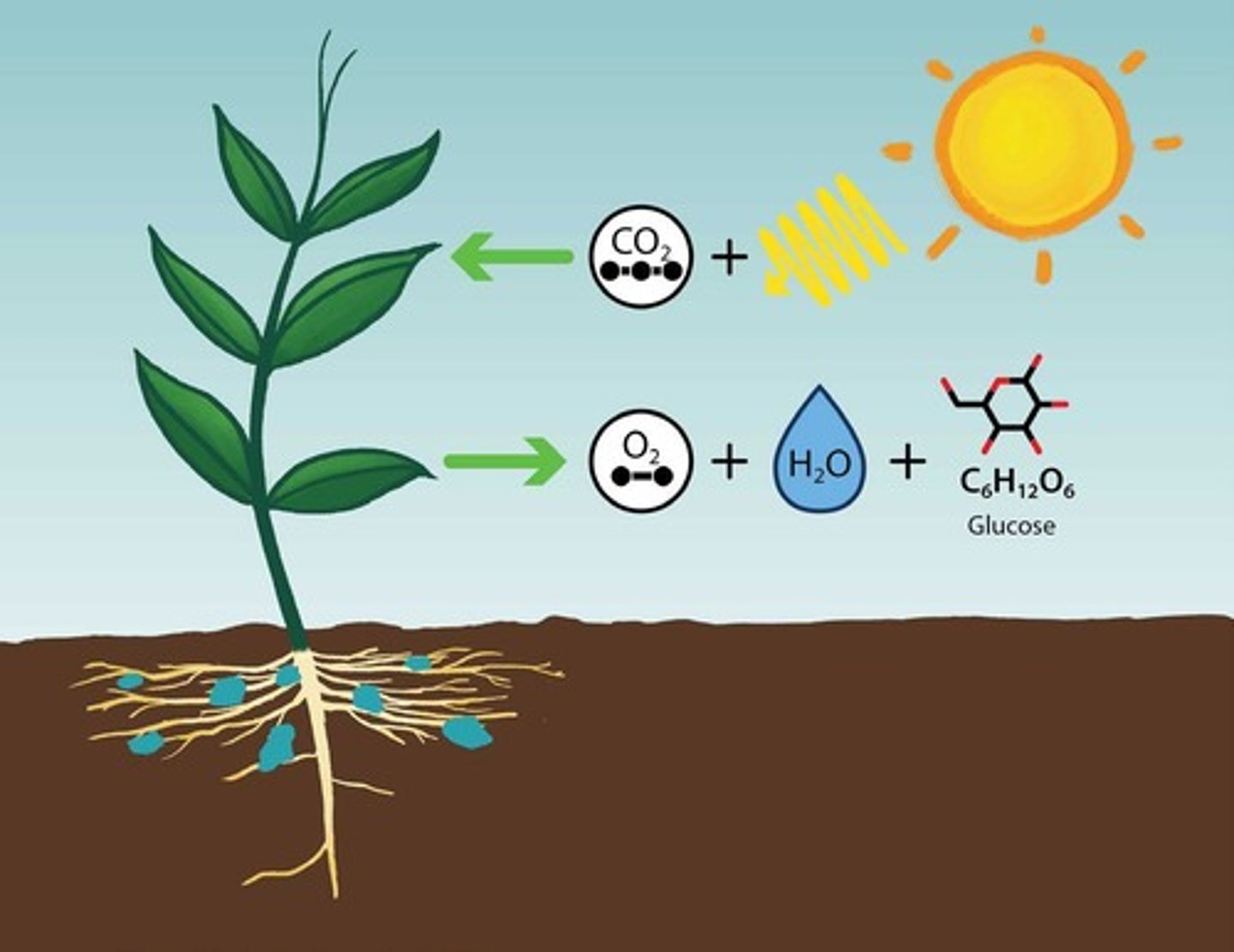
Photosynthesis
Process converting light energy into chemical energy.
Adaptations
Traits enhancing survival and resource acquisition.
Aspen Leaves
Example of adaptation minimizing water loss.
Oxygen (O2)
Gas required for aerobic respiration in plants.
Carbon Dioxide (CO2)
Gas used in photosynthesis by plants.
Pressure potential
Physical pressure on a solution, can vary.
Turgid
Cell maximally filled with water, exerts pressure.
Root hairs
Increase surface area for water and mineral absorption.
Casparian strip
Waxy barrier controlling substance entry into xylem.
Apoplastic route
Pathway for water movement through cell walls.
Symplastic route
Pathway for water movement through cytoplasm.
Guard cells
Control stoma diameter by changing shape.
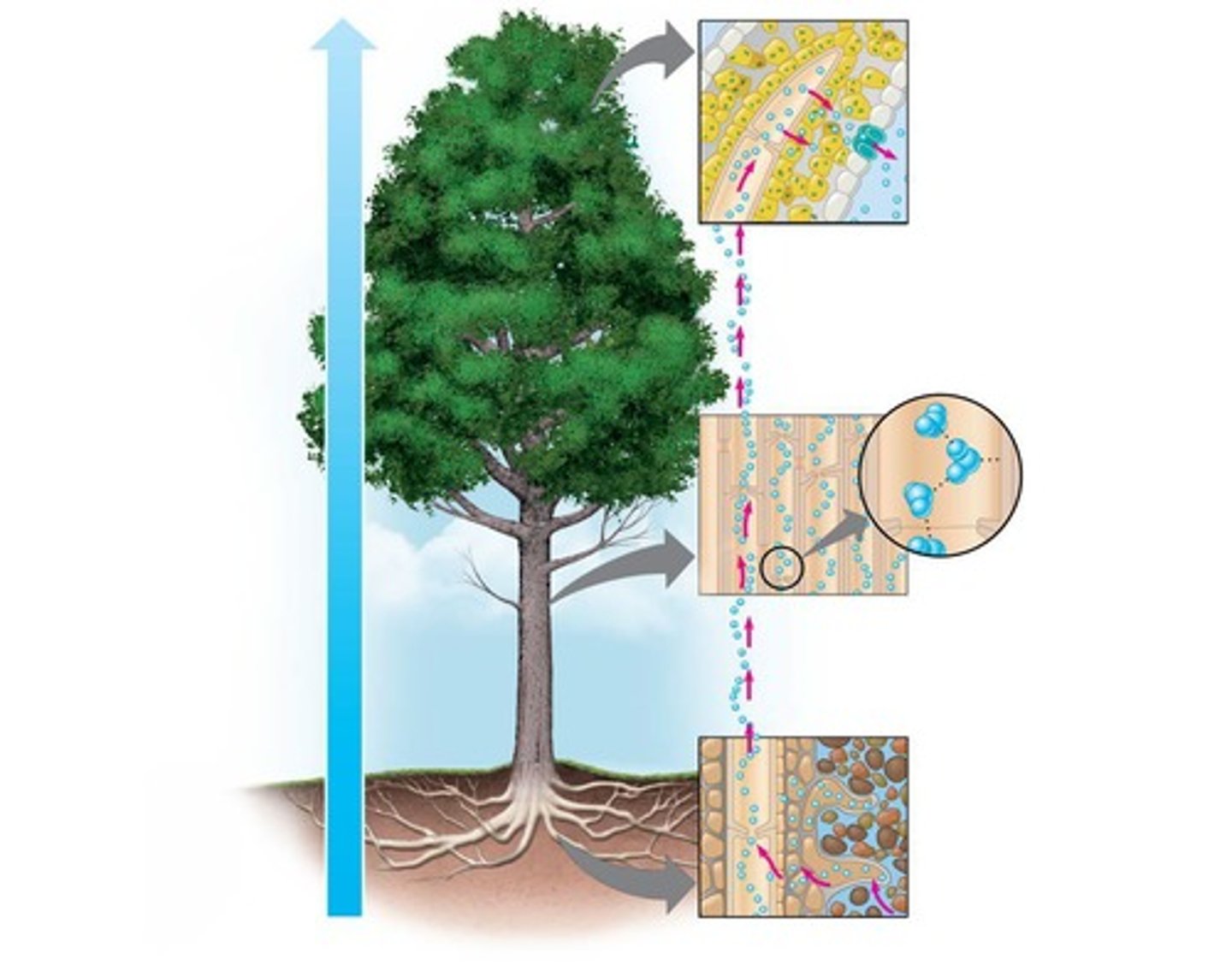
Cohesion-tension hypothesis
Explains water movement in plants via transpiration.
Evapotranspiration
Combined loss of water through evaporation and transpiration.
Wilting
Occurs when water uptake cannot replace lost water.
Xylem sap
Fluid transporting water and nutrients from roots.
Epidermis
Outer layer of roots, permeable to water.
Endodermis
Inner layer of root cortex, regulates water entry.
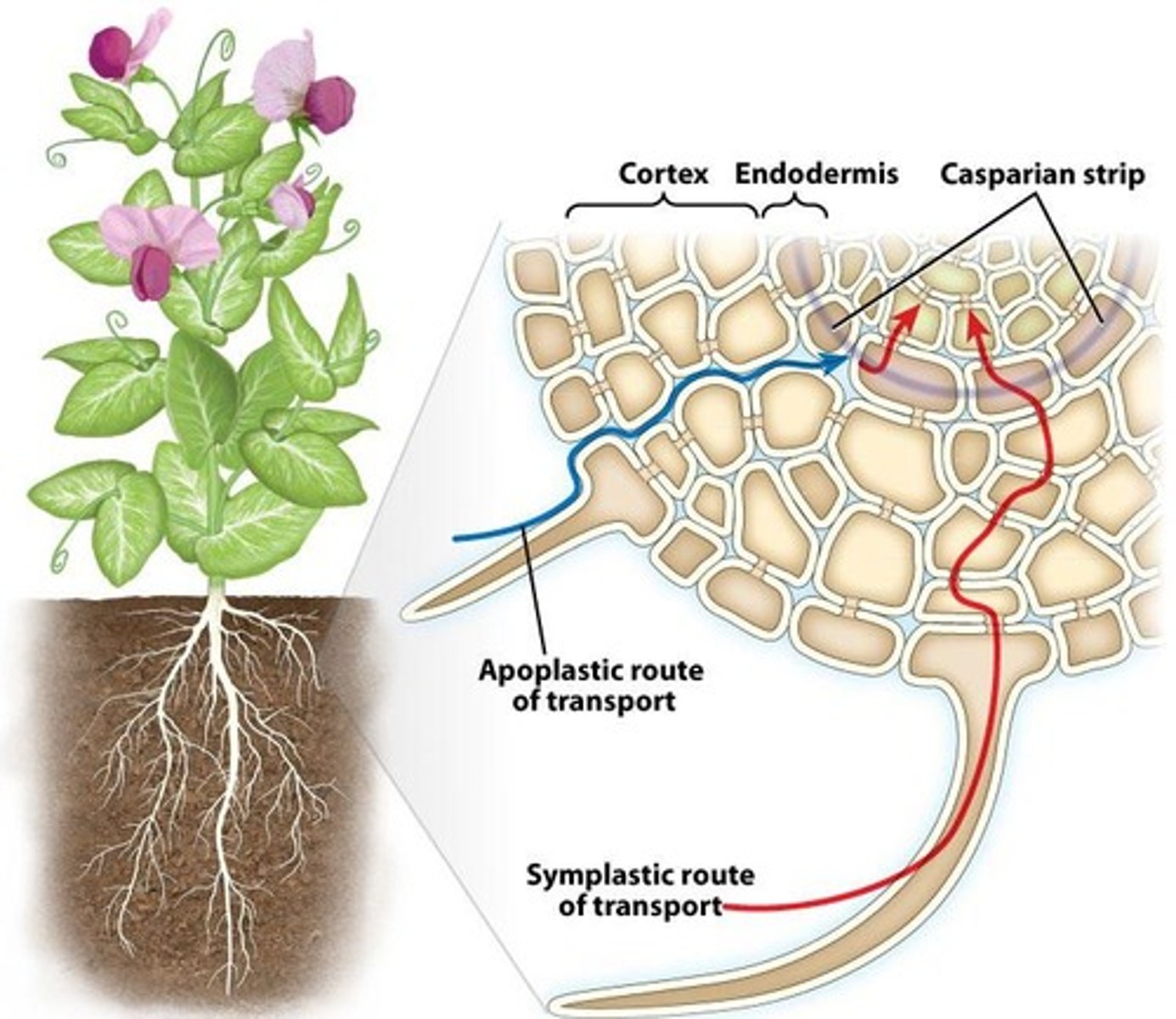
Vascular cylinder
Central part of root containing xylem and phloem.
Heartwood
Non-conducting central part of a tree's trunk.
Adhesion
Tension of water molecules to xylem walls.
Cohesion
Water molecules stick together via hydrogen bonds.
Stoma
Microscopic pores for gas exchange in leaves.
Mesophyll Cells
Leaf cells where photosynthesis occurs.
Photoautotrophs
Organisms that produce their own food using light.
Chloroplasts
Organelles where photosynthesis takes place.
Light Reactions
Convert solar energy to chemical energy.
Calvin Cycle
Light-independent reactions producing glucose from CO2.
NADPH
Electron carrier produced in light reactions.
ATP
Energy currency generated during light reactions.
Carbon Fixation
Incorporation of CO2 into organic molecules.
Grana
Stacks of thylakoids in chloroplasts.
Thylakoids
Membrane sacs where light reactions occur.
Stroma
Dense fluid within chloroplasts.
Chlorophyll
Green pigment that captures light energy.
Water Uptake
Process of water absorption by roots.
Water Potential Gradient
Difference in water potential driving water movement.
Photosynthesis Equation
6 CO2 + 6 H2O + Light → C6H12O6 + 6 O2.
Photosystems
Complexes of chlorophyll and proteins for light absorption.
Photosystem II
First photosystem in the light reaction sequence.
Photosystem I
Second photosystem in the light reaction sequence.
Electron Transport Chain
Series of proteins transferring electrons in thylakoids.
Proton Gradient
Difference in proton concentration across a membrane.
Chemiosmosis
Process of ATP production using a proton gradient.
Oxygen By-Product
O2 released during light-dependent reactions.
Glyceraldehyde 3-Phosphate (G3P)
Three-carbon sugar produced in the Calvin cycle.
Reduction Stage
Second stage; PGA converted to G3P using ATP/NADPH.
Regeneration Stage
Final stage; RuBP is regenerated for the cycle.
RuBP
Five-carbon sugar that accepts CO2 in Calvin cycle.
Rubisco
Enzyme catalyzing the first step of carbon fixation.
Sugar Source
Organ producing excess sugar, e.g., mature leaves.
Sugar Sink
Organ consuming or storing sugar, e.g., roots.
Pressure Flow Mechanism
Bulk flow of phloem sap driven by pressure differences.