Important Info
1/269
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
270 Terms
tumor necrosis factors
bind to cancerous cells to kill them
41s rule
reject when 4 consecutive controls exceed the mean ± 1sd
what is the inheritance pattern of HLA and Xga blood group system
Xga: X-linked dominant, so female passes to 50% of daughters and male would 100% pass it
HLA: codominant
what information is required on a completed laboratory report
patient’s name, DOB, other unique ID number, gender, collection date and time, time in and time out, correct units, result, age-approproate reference range, pertinent clinical info, name and address of testing lab, ordering physicians name, lab directors name, and testing tech initials
transforming growth factor (TGFs)
control proliferation and differentiation of cells
accuracy
the closeness to the target value (the mean)direct fluorescent antibody test
direct fluorescent antibody test
patient antigen is applied to a slide and a fluorescent-labeled antibody attaches
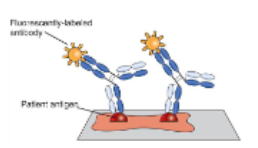
13s rule
reject when 1 control observation exceeds mean ± 3sd limit
resolution equation
(0.612 x wavelength (λ))/numerical aperture = resolution (microns)
precision
the ability to reproduce or repeat a test so you get the same answer
12s rule
a warning when 1 control observation exceeds (is outside of) the mean ± 2sd limit
interleukins (ILs)
help communicate between leukocytes and non-leukocytes in plasma, promote the development of differentiation of T and B cells and activate T-helper cells and promote inflammatory responses and fever
10x rule
reject when 10 consecutive control obserations fall above or below one side of the mean
aldosterone comes from the
adrenal cortex
colony stimulating factor (CSFs)
bind to surface receptors on hematopoietic stem cells and help in proliferation and differentiation
when blood pressure is high, what happens to sodium, water, and potassium
sodium and water get excreted
potassium is retained
when is ADH released by the posterior pitutary gland
when blood pressure in low (body will retain sodium and water and excrete out potassium)
a DAT involves what
RBCs and AHG
what is the significance of elevated levels of microalbumin
elevated levels of microalbumin show increased glomerular permeability (which allows more to get through), which could lead to end-stage renal disease
diabetic ketoacidosis (DKA)
a form of hyperglycemia in uncontrolled diabetes in which certain acids (ketones) accumulate when insulin isn’t available
what is the homeostatic range for blood glucose
70 to 110 mg/dL
what can cause sensitization of RBCs in vivo with the DAT test
hemolytic disease of the fetus and newborn
hemolytic trasnfusion reaction
autoimmune induced hemolytic anemia
drug-related hemolytic anemia
does glucagon inhibit or promote glycolysis
inhibits
type 1 glycogen storage disorder
the accumulation of glycogen in the liver and skeletal muscle
what causes type 1 glycogen storage disorder
a glucose-6-phosphate deficiency
3 hour GTT mg/dL per hour
fasting : ≥95 mg/dL
1 hr ≥180 mg/dL
2 hr ≥155 mg/dL
3 hr ≥140 mg/dL
if 2 out of 4 are observed person has GDM
a person can be diagnosed with whiple’s triad if
they have low blood glucose, classic symptoms of hypoglycemia, and have a relief of symptoms after plasma glucose level is raised
glucose disorder with 100-125 mg/dL
prediabetes for fasting glucose
does glucagon inhibit or promote glycogenolysis
promotes
insulin promotes or inhibits glycolysis
promotes
what are the four globin chain combinations for the four types of fetal hemoglobin
2 zeta 2 epsilon (Gower I), 2 zeta 2 gamma (Portland’s), 2 alpha 2 epsilon (Gower II), and 2 alpha 2 gamma (Hgb F)
IAT involves what
RBCs and IgG
what are the four types of globin chains for the four types of adult hemoglobin
2 alpha 2 beta (Hgb A), 2 alpha 2 beta-NH-glucose (Hgb A1c), 2 alpha 2 delta (Hgb A2), and 2 alpha 2 gamma (Hgb F)
hyperosmolar hyperglycemic syndrome
serious complication of type 2 DM where blood glucose levels are too high for a long period of time
what are five examples of what can cause a right (blue) shift in the ODC
low pH (acidic), increased CO2, high temp, high BPG, and Low O2 affinity Hb variants
CSF glucose levels
60% of serum or plasma level
insulin promotes or inhibits gluconeogenesis
inhibits
what are the implications of a right (blue) shift in the ODC
reduced oxygen affinity in the red cell and increased oxygen delivery to the tissues
2 hr GTT mg/dL per hour
fasting - ≥92 mg/dL
1 hr - ≥180 mg/dL
2 hr - ≥153 mg/dL
diagnosis made if 1 out of 3 is observed
what are the best lab tests currently available to detect mild to moderate glomerular damage
glomerular clearance tests
what are the components of the wright stain
methylene blue, eosin, and glycerin
diabetes insipidus
body can’t regulate its fluid properly because the body or kidneys don’t produce enough ADH (anti-diuretic hormone)
__________ reagent is recommended for enteribacterales for tube indole
kovac’s
citrate test principle
if organism can use citrate then ammonium hydroxide will be formed which is visualized by a blue color
why is Hgb effected by leukocytosis
the increased WBC count causes turbity which increases Hgb
what conditions are giant platelets associated with
thrombocytopenia, myelofibrosis, CML, and bernard - soulier syndrome
conditions associated with increased BUN levels
any disorder where there’s excessive portein breakdown (febrile illnesses, dehydration, corticosteroid or tertracycline therapy, or absorption of blood from the GI tract during GI bleeds and in the prescence of elevated thyroid hormones)
high protein diets/large ingestions of proteins
pregnancy (due to increased GRF)
hektoen inhibits
gram positive organisms
what happens to RBCs if the stain is too acidic
they look like stomtocytes
if glucose and lactose and/or sucrose fermented on triple sugar iron agar (TSI) then the tube shows
A/(A) (yellow, acidic/yellow, acidic with gas produced)
where does urea (BUN - blood urea nitrogen) originate
it is synthesized in the liver
severe hypoproteinemia (>2.5 g/day)
hematuria
severe edema/weight gain/hypertension (losing fluid in BV)
hyperlipidemia/oval fat bodies/lipiduria
hyponatremia (Na+ seems low b/c of high water retention)
vision problems
lab values for nephrotic syndrome
what does chloride do for the body
regulates body fluid balance, maintains blood pressure, helps nerves and muscles function, and is crucial for digestion by forming stomach acid, and works with Na and K to regulate pH of the body
conditions associated with decreased chloride (hypochloremia)
prolonged vomiting, nasogastric suctioning, and diuretic use/abuse
conditions associated with elliptocytes
hereditary elliptocytosis and iron deficiency anemia
Which diego antibody can cause HTR or HDFN
Anti-Dia
medical conditions associated with microcytes
microcytic anemia
oliguria (some cases anuria) and azotemia
clinical symptoms of acute renal failure
do you start with the 5 drop method of the 2 drop method for the clinitest
5 drop, only do 2 drop if the pass through effect occurs
conditions associated with codocytes
hemoglobinopathies, thalassemia’s iron deficiency anemia, splenectomy, and obstructive liver disease
heinz bodies are made from
denatured hemeglobin
CIN
yersinia selective agar
what transmits ehrlichiosis
the bite of an infected tick
glomerulus, post-streptococcal damage, acute kidney infections, systemic autoimmune diseases, and hypersensitivity reactions to medications
causes of acute glomerular nephritis (autoimmune)
yersinia enterocolitica is motile at
25-32C
medical conditions associated with anisocytosis
blood transfusions
normal range for neutrophils
2500-7000/μl
pre-renal uremia, high protein intake in the diet or GI tract hemmerrhage
increased BUN:creatinine ratios with normal creatinine levels are associated with (ex: 30:1)
glomerular nephritis is the most common cause of
chronic renal failure requiring dialysis or renal transplantation
consequences of nephrotic syndome
glomerular membrane progressivly thickens to the point where there’s little glomerular filtration causing renal failure
normal range for lymphocytes
1000-4000/μl
S/S: vomiting, diarrhea, fever, chils after ingestion of oraganism
can be a carrier
not normal flora, always pathogenic
Salmonella
when preforming a RBC count, how many squares are generally counted in the centermost square
five, the four corners and the center squares
what are some abnormalities in peripheral stains caused by too alkline of a stain
causes RBCs to become crenated (puckers) and look like echinocytes (burr cells)
anything that would cause a build up of acids, uremia (urine in the blood), lactic acidosis (lack of O2 in tissues or lots of exercise), ketoacidosis (too many ketones), ingestion of toxic substances, large doses of antibiotics (breakdown into acidic byproducts), increased net protein charge (protein levels off, albumin is low, causes imbalance)
causes of an increased anion gap
azotemia
the retention of nitrogen containing products in the blood that should be filtered out (75%-80% of kidney lost)
how to differentiate citrobacter koseri and freundii with H2S
koseri is H2S negative
freundii is H2S positive
diabetic nephropathy and exposure to toxins
causes of acute glomerular nephritis (non-autoimmune)
normocytic
aldosterone originates in the
adrenal glands
diminihsed GFR
low urine volume
high cholesterol/triglycerides in the blood
low plasma levels of total protein and albumin
urinalysis shows 4+ proteinuria
hematuria
oval fat bodies and fatty casts in urine
lab results of diabetic nephropathy
what is the most common type of kidney stone found
calcium oxalate
what is the range for RDW
11.5-14.5%
E. coli is indole
positive
addison’s disease
(hypocortisolism) the adrenal glands are not porducing enough of the hormone cortisol
conditions associated with decreased BUN levels
cirrhosis of the liver
plasma and urine sodium and potassium levels for cushing’s disease
plasma Na+: increased (keeping Na+, water follows)
plasma K+: decreased (opposite of Na+)
urine Na+: decreased
urine K+: increased (being excreted)
if only glucose is fermented on triple sugar iron agar (TSI) then the tube shows
K/A (red, alkaline/yellow, acidic)
if hektoen is alkaline it’ll stay ___________ and if there’s a change in acidity the color will change to ___________________
green, yellow-salmon
enterobacterales are _______________ for the oxidase test with the exception of plesiomonas
negative
relative range for lymphocytes
20-40%
what are the alternate methods used to estimate the creatinine clearance in pediatric pateints
the schwarz formula (k x height)/creatinine
what type of anemias would hypersegmentation be in
megaloblastic anemias
conditions associated with stomatocytes
acute alocholism (screwdrivers), hereditary stomatocytosis, liver disease, corrhosis, hemolytic anemia, and artifact if staining is too acidic
relative range for monocytes
1-10%
gout
a disease where deposits of urates are deposited in body fluids
conn’s syndrome, cushing’s disease, diabetes insipidus, dehydration, extensive burns, excessive sweating w/o fluid replacement, dehydration due decreased water intake
same as hypernatremia but to lesser extent
conditions associated with increased chloride (hyperchloremia)
where does uric acid orginate
produced from the netural cellular breakdown in the body and some from the brekadown of dietary purines
plasma and urine sodium and potassium levels for diabetes insipidus
plasma Na+: increased (not retaining water so not retaining Na+)
plasma K+: increased
urine Na+: normal (problem in the blood not urine)
urine K+: normal (problem in the blood not urine)
what is the platelet estimation equation
{# of platelets in 10 fields/10 × 15} - 20