BIO MOLECULES EXAM, p.s you got this
1/58
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
59 Terms
science
is the orderly process of posing and answering questions about the natural world though repeated and unbiased experiments and observations.
hypothesis
a statement that clearly states the relationship between biological variables.
null hypothesis
it states there is no difference.
scientific method
effective for research and problem solving
treatments
the level in experiments, glucose, protein and control
Treatment variable
tested by the type of food (protein, sugars)
Response variable
CO2 production that inddicates yeast growth
Controls
verify that the biological response we measure is a functions of the variable being investigated? nothing else
replications
repeated measures of each treatment under the same conditions
Range
the highest & lowest values in a set of replicates
standard deviation
informative measure of variation
significantly different
differences between means must be due to the treatment
accuracy
measurement that is close to true/correct value
precision
measurement refers to how close one another in a series of measurements
Meniscus
the interface of air & water, surface tension and the adhesion of water to the sides of the cylinder.
mean
the arithermic average of a group of measurement
median
smallest to largest, the middle value that diviswa the set to two equal size
sum of squared deviation
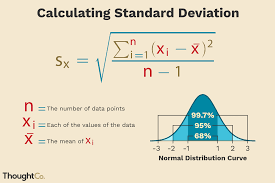
variance
sum of square deviation / N-1
Deviation
squared variance, just square the answer from SD
light microscope
a coordinated system of lenses arranged to produce an enlarged focusable image of a specimen
magnifies
it increases its apparent size
contrast
differences between the lightest and darkest parts of an image
condenser lens
located immediately below the specimen
condeser its diaphram
Khurled ring or lever that can be opened and closed to regulate the amount of light reaching the spicemen.
ocular
the lens that you look through
monocular
one ocular microscopes
binocular
two microscopes
Body tube
metal casing through which light passes to the oculars
stage
secures the glass side on which the specimen is mourried
field of view
the area that you can see through the ocular and objective
micrometers
field of view measurements
ocular micrometers
small glass disk with thin lines numbered and etched in a row
stage micrometers
calibrate the ocular micrometer by comparing its lines to those lines on a standard ruler
dissecting microscopes
offers some advantages over a compound microscope
working distance
the distance between the adjective lens and specimen
cytology
study of cellular structure and function
prokaryotes
bacteria & cyanobacteria
organelles
organized structures of macromolecules having specialized functions
cytoplasm
inside the plasma membrane, the liquid
Pili / flagellum
locomotion/ movement and attatchment to bacteria
ribosomes
synthesizes protein
plasma membrane
before cell wall
cyanobacteria
largest prokaryotes
thylalioids
the pigments held in photosynthetic membranes
nucilaginous sheath
to photosynthesize made them th primary contributers to the early oxygenatopn of the ancient earth’s atmosphere
nuclei
eukaryotic cells membrane - bound
cytoplasm
forms the matrix of the cells & contained by the plasma
chloroplasts
elipitical green organelles in plant cells
mitochondria
organelles found in plants & animal cells
protoplast
material & organelles contained by the plasma membranes
middle lanella
substance holding walls of two adjacent cells together.
Plasmadesmata
penetrate cell wall
stained
adding a dye that preferentially colors same parts of the specimen
cristae
inner membrane
plastids
organelles where food is made and stored
amoeboid movement
occurs by pseudopodia
Pseudopodia
temporary protrusions of the cell
contractile vacuole
accumalates and expels water & waste products