IB Macroeconomics Objectives and GDP-Triol
1/62
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
63 Terms
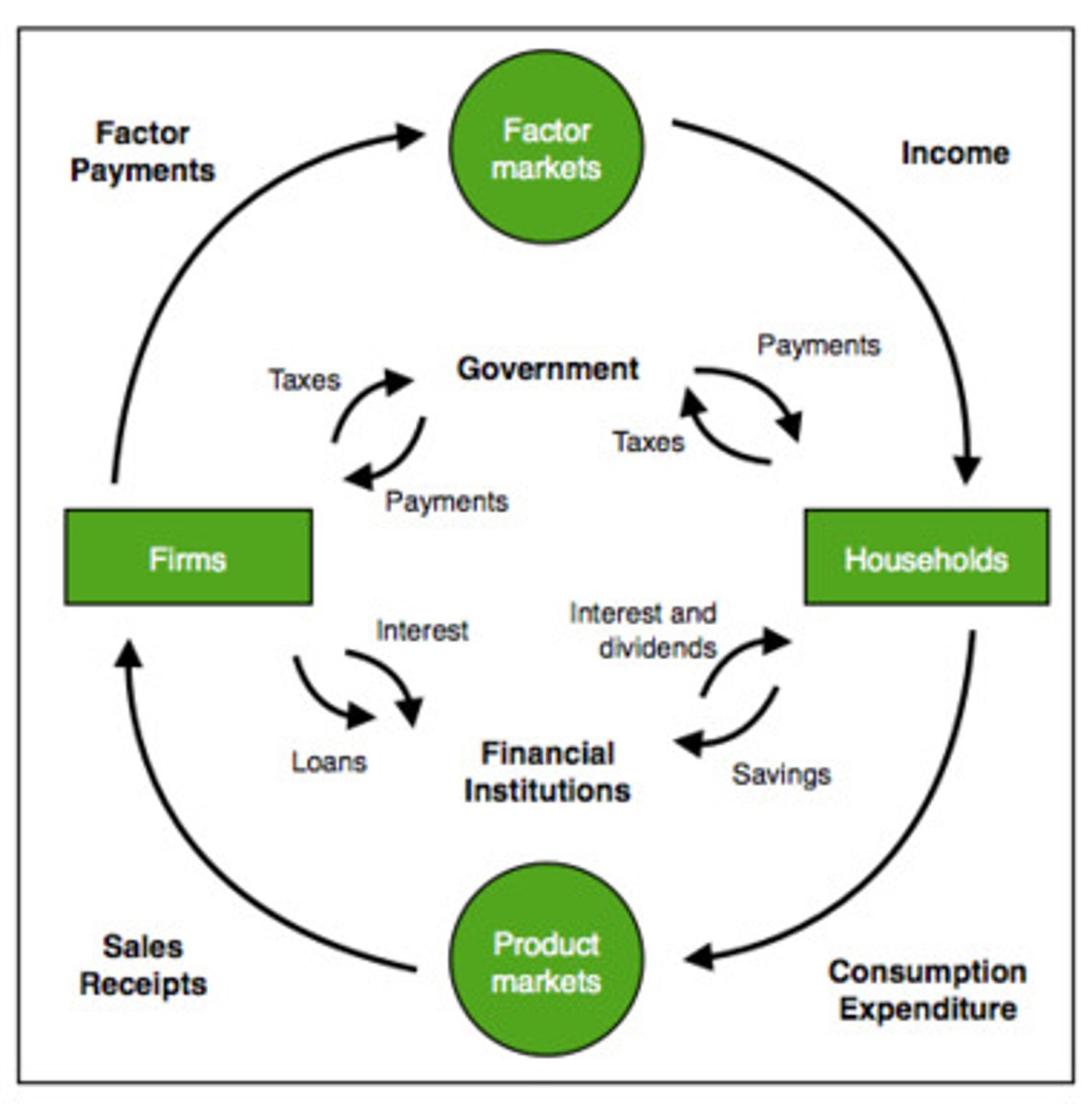
Circular Flow of Income
a simplified model of the economy that shows the flow of money through the economy
Gross Domestic Product
the total money value of all final goods and services produced in an economy in one year
Gross National Product
the total money value of all final goods and services produced in an economy in one year, plus net property income from abroad (interest, rent, dividends, and profit)
Net National Product
NNP is GNP minus depreciation (capital consumption)
Nominal GDP
GDP not adjusted for inflation
Real GDP
GDP, adjusted for inflation
Per Capita GDP
the total money value of all final goods and services produced in an economy in one year per head of the population
Human Development Index
a composite index that brings together measurements of life expectancy at birth, literacy rate, school enrollment rate, and GDP per capita to measure relative development
Aggregate Demand
the total spending in an economy consisting of consumption, investment, government expenditure and net exports
Consumption
spending by households on consumer goods and services over a period of time
Investment
the addition to the capital stock of the economy in the form of factories, offices, machinery, and equipment, which is used to produce goods and services. A fast food retailer, for example, builds a new outlet
Business Cycle (Trade Cycle)
shows fluctuations in the level of economic activity in an economy over time and suggests that the changes are cyclical. There a four stages: depression (slump), recovery, boom, and recession.
Demand-Side Policies
any government policies designed to influence AD in the economy, thus affecting the average price level and real national output
Fiscal Policy
A policy using changes in government spending and/or direct taxation to achieve economic objectives
Monetary Policy
a policy using changes in the money supply or interest rates to achieve economic objectives
Aggregate Supply
the total amount of domestic goods and services supplied by businesses and the government, including both consumer goods and capital goods
Short-Run Aggregate Supply (SRAS)
the Aggregate Supply that carries with the level of demand for goods and services and that is shifted by changes in the costs of factors of production
Long-Run Aggregate Supply (LRAS)
the Aggregate Supply that is dependent upon the resources in the economy and that can only be increased by improvements in the quantity and/or quality of factors of production
Supply-Side Policies
government policies designed to shift the LRAS curve to the right, thus increasing potential output in the economy
Unemployment
a situation that exists when people who are willing and able to work cannot get a job
Full Employment
when the number of jobs available in an economy is equal to or greater than the number of people actively seeking work
Underemployment
When workers are caring out jobs for which they are over-qualified, they are not using their full skills or abilities,
OR when workers are employed part-time, even though they are available for full-time employment
OR when workers in a planned economy are undertaking jobs that would not exist in a free market
Unemployment Rate
The number of unemployed workers expressed as a percentage of the total workforce
Structural Unemployment
Unemployment that exists when in the long term the pattern of demand and production methods change and there is a permanent fall in the demand for a particular type of labor. There is a mismatch between skills and the jobs available
Frictional Unemployment
Also: Search Unemployment
unemployment that exists when people have left a job and are in the process of searching for another job
Seasonal Unemployment
unemployment that exists when people are out of work because their usual job is out of season, for example a ski instructor in the summer
Demand Deficit/ Cyclical Unemployment
unemployment that exists when there is insufficient Aggregate Demand in the economy and real wages do not fall to compensate for this
Real Wage Unemployment
unemployment that exists when real wages (wages adjusted for inflation) in the economy get pushed up above their equilibrium, either by the government or by trade unions
Inflation
a sustained increase in the general (or average) level of price and a fall in the value of money
Demand-Pull Inflation
inflation that caused by an increase in aggregate demand without a corresponding increase in aggregate supply. Goods become scarce.
Cost-Push Inflation
inflation that is caused by negative supply shock, arising from sudden, unanticipated increase in costs of production for producers. Can be result of
Increase in wage rate
Increase in resource costs
Increased energy or transport costs
Increase regulation by gov
Increased business tax
Decreased exchange rate
Deflation
A decrease of average price level of goods and services in an economy. If CPI is smaller than a previous year, this indicates deflation. Is highly undesirable because it discourages investment and consumption, leading to recession and rising unemployment.
Direct taxation
taxation imposed on people's income or wealth and on firms' profits
Indirect taxation
a tax on expenditure. It is added to the selling price of a good or service
Progressive taxation
A system of direct taxation where tax is levied at an increasing rate for successive bands of income. The marginal tax rate is higher than the average tax rate
Regressive Taxation
a system of taxation in which tax is levied at a decreasing average rate as income rises. This form of taxation takes a greater proportion of tax from the low-income taxpayer than from the high-income taxpayer
Proportional Taxation
a system of taxation in which tax is levied at a constant rate as income rises, for example, 10% of each increment of income as income rises
Lorenz Curve
A curve illustrating the degree of equality of income distribution in an economy. It plots the cumulative percentage of income received by cumulative shares of the population.
Causes of Cyclical Unemployment
Total demand of nation output falls, negative supply shock
Causes of Structural Unemployment
Technology used in production becomes capital intensive, cheaper foreign production, inadequate education and job training system.
Causes of Frictional Unemployment
Employers cannot be quickly and easily matched up firms demanding labour, resulting in higher and longer frictional unemployment.
Consequences of Unemployment for Individuals
decreased household income, increased psychological and physical illness
Consequences of Unemployment for Society
Increased poverty and crime, transformation of traditional societies
Consequences of unemployment for the Economy
Lower aggregate demand because of lower consumption, under-utilization of resources lowering production possibilities and living standards and downward pressure on wages for the employed.
consumer price index
Measures the price of a set basket of consumer goods that a typical household in a nation consumes between one time period and another.
The inflation rate
the percentage change in CPI between two years.
Low inflation
between 0 - 5% are considered desirable because stability over future prices is sound. Businesses and households can confidently invest, spend and save.
High inflation
greater than 5% will cause firms and households to spend their money quickly before its value drops. This causes AD to grow, reduces incomes and creates instability in the economy.
Lower real incomes (consequences of inflation)
A household's real income is its nominal income adjusted for any inflation in the economy. Their real income value falls as prices rise and a certain amount of income can buy less for households.
Lower real interest rates for savers (consequences of inflation)
The real interest rate is nominal interest rate - inflation rate.
Higher nominal interest rates for borrowers (consequences of inflation)
When banks anticipate inflation, they raise interest rates today.
Reduced international competitiveness (consequences of inflation)
Fall in demand for goods internationally because they are more expensive that other country's goods. Also reduces foreign investment as firms do not wish to produce expensively.
Economics Growth
an increase in the output of goods and services by a nation over time. Growth can also be defined as an increase in the per capita income of a nation over time.
Growth in total output
Measures the change in the total output of a nation between two periods of time
Per Capita Economic Growth
A better indicator of how the average person is doing, as it accounts for changes in nation's output AND the population
Economic Growth rate
Percentage change in GDP between two time periods. GDP2-GDP1/GDP1 x 100
Actual Output
• If an economy is producing at a level of output below its full-employment level and output increases, then the economy's actual output is increasing. This is a type of economic growth that occurs during the recovery of the business cycle.
Potential Output
• If an economy is producing at its full-employment phase level of output and output increases, this is the result of an increase in the nation's potential output, and is a form of long-run economic growth.
Physical capital and technology (sources of economic growth)
A nation's stock of physical capital is the quantity and quality of technology and infrastructure in a nation, such as internet access, transportation, sanitation, computer/communication technologies. It can only be accumulated through investment by private or public sector.
Human Capital and Productivity (sources of economic growth)
Human capital refers to the quality of the labour force in a nation. Can be improved through education and training of workforce by private or government sectors or both. Education, skills and access to technology increases productivity/output = higher average income.
Four factors of production
Land (natural resources), capital (physical assets and monetry resources), labour (transform raw materials to consumer goods) and entrepreneurship (ideas to create goods)
Problems with measuring unemployment
Overstating or understating unemployment. Does not include unrecorded legal or illegal employment, part-time work or discouraged unemployed people (not ACTIVELY seeking work)
production possibility curve
a graph that shows the combinations of output that the economy can possibly produce given the available factors of production and the available production technology