AP Psych - Unit 2 (things I forget)
1/76
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
77 Terms
sensation
detecting a stimulus
perception
interpreting a stimulus
top-down processing
use old information to understand things we are seeing… fast and with info we are familiar with
Like when you mis what you wrote on an essay because you think you already know what you wrote
bottom up processing
when stimuli is complex and unfamiliar… we have to interepret the stimulus as it comes to us… takes longer
schema
general idea of something
perceptual set
a mental shortcut that you use to quickly interpret something. The way you have lived determines the way you will analyze information given to you.
perception can be impacted by…
both internal and external factors.
selective attention
when you hone in on one stimulus and leave out the other ones. You are still recieving the stimuli, so if someone says your name you will respond, but your brain mutes them.
cocktail party phenomenon
to be able to focus on a single conversation ina. loud environment
blindess due to attention (there are 2)
Inattentional blindess: you miss things in your field of vision because you are focused on something else
Change blindess: fail to notice changes in an envionrment (spot the difference)
apparent movement
we perceive motion through still images.
Stroboscopic effect: seris of images in rapid succession appear to be moving
phi phenomenon: STATIONARY lights turn on and off to make a perceived motion
Induced movement: stationary object appears to move because of the movement of surrounding objects
autokinetic effect: stationary point of light in a dark environment appears to move
gestalt
how put things together in our mind ot form one big picture
Gestalt principles (6):
figure and ground: separates what we see into two categories
continuation: follow continous lines
Closure: fill in missing info
similarity: similar objects are one group
Thats why we notice anomalies (objects that stand out from a similar group)
Proximity: objects close together will be one group
Symmetry: symmetrical objects are perceived as one
Depth Perception:
Binocular:
retinal disparity (the slight difference both of our eyes see)
Monocular:
One eye, help wioth flat or 2D surfaces
Monocular cues (7):
Relative size: bigger objects are closer than smaller objects
Interposition: blocked objects are fartehr away
Relative height: objects higher in field of view are farther away than closer objects that are lower
Contour and Shading: less detail and more hazy means farther away. The more detailed means closer
texture and gradient: more detail is closer
Liner perspective: parallel lines seem to converge in distance proving distance
Motion parallax: closer objects seem to move faster than those that are farther away
perceptual constancy (4):
size
color: stays the same even in dif. light
shape: stays the same even at dif angle
lightness: the relative lightness or darkness of an object remains the same under dif amounts of light. Think hue
concepts
mental categories that we fit prototypes into.
Ex. ball is the concept… a basketball, bouncy ball, baseball, are all prototypes
prototype
most basic example of a concept. What you picture when you think of a concept
Schema
complex frameworks that organize and interpert information about the world.
groups of charcateristics that we associate with certain objects so that we can make mental judgements
assimilation
when we fit new information into existing schemas.
kid knows what a dog is, and sees a cat for the first time. “look a doggy!” they fit what they think it was a dog because it fit similar characterisitcs
accomodation
when we change a schema to fit new info
The kid learns that the cat is not a dog and makes a new, more specific, set of charactersitics for cats
representative heuristic
making judgments based on how much something represents a typical case or stereotype.
Thinking based on what we think the thing should be like, not based on the logic.
availability heustistic
making judgments based on how easliy you can think of examples
mental set
using past experiences to solve a new problem
priming
repetition priming: when you are exposed to a specific stimulus that makes it easier to recognize that same stimulus later
semantic: influence of one word on the interpretation of another
framing
the way info is presented can change the way we interpret it
divergent thinking
many possible solutions to solve one problem
convergent thinking
narrowing down the possibilities to identify the single best solution
Sternbergs 5 parts of creativity:
Expertise: more knowledge ona. subject means more likely to apply it in new and innovative ways
imaginitive thinking: must. be able to think about things in unique ways… leave traditional thinking behind
venturesome personality: must be willing to seek out new opportunities and embrace challenges that will help them grow
intrinsic motivation: internal drive for satisfaction
creative enviro: surround yourself with other creative people to foster innovation
gamblers fallacy:
if an event happens more often than normal during a given period, then it is less likely to happen in the future.
previous outcomes have no effect on future outcomes
sunk cost fallacy:
when you want to continue an action more the more time you have put into it… regardless of future value
memory
info that can be stored over time and retrieved when needed
metacognition
the awareness of your own cognitive processes
3 types of memory
explicit: consciously recall info with effort and thought
episodic: personal experience and events
semantic: knowledge facts and general info
Implicit: skills we learn without being fully aware
procedural: how to do tasks like motor skills and routines
Prospect: remembering to perform future actions
parallel processing
handling multiple streams of info at the same time
long term potentiation
Strengthening synaptic connections through repetition.
Makes storing info easier
working memory model
visuospatial sketchpad: working memory that handles visual and spatial info… how we visualize things (the eye)
phonological loop:
phonological store: inner ear (holds sounds for a short period of time)
articulatory rehearsal process: inner voice, rpeat and rehearse verbal info
Central executive: control center of working memory. Attention focusing, task prioritizing, switching between dif activities, integrating information
episodic buffer: long term memory integrates with working memory. temporary storage system
what is working memory
short term memory
multistore model for memories
sensory memory:
Iconic: visual (<1 second)
Echoic: auditory (1-4 seconds)
Automatic porcessing… does not take much effort. If your brain wants the info it goes to working memory
Working memory (short term):
both types of rehearsal
maintenance
elaborative
Long term memory:
encoding (putting info into LTM)
maintenance rehearsal
when you go over info repititively to prevent forgetting it
elaborative rehearsal
connect info to something you already know so you remmeber it easier
encoding levels:
Structural: superficial and physical appearance on info
Phonemic: how a word sounds
Semantic: the meaning of the info or concept
method of loci:
associating information with a familiar place so it is easier to remember
chunking:
grouping info into chunks so its easier to recall
Short term memory
Hold 7±2 items for about 20-30 seconds
working memory
stores info and processes it. more updated form of STM
long term memory
Infinite space and stores info for long periods of time
memory consolidation
short term memories are transformed into long-term memories
flashbulb memories
very clear and specific memories that are generally stressful and extreme
autobiographical memory
memories connected to our own lives are more memorable because they have personal relevance
amnesia
loss of memory (temporary or permanent)
anterograde
can’t form new memories… porlly damage to hippocampus
retrograde
cannot retrieve past info
source
Remember info but not where/how they learned it
infantile
cannot remember info from early years of life
alzheimers
neurodegenerative disease
cannot store or retrieve new/old memories
recall
retrieve info without any cues
recognition
use cues to help retrieve info
context dependent memory
retrieval is improved when youre in same enviro that you first learned info
mood congruent memories
more likely to recall info that match your current moods
state dependent memory
retrieval is imporved if youre in the same physical or mental state as when the memory was encoded
forgetting curve (ebbinghaus)
can make it less drastic with rehearsal/review
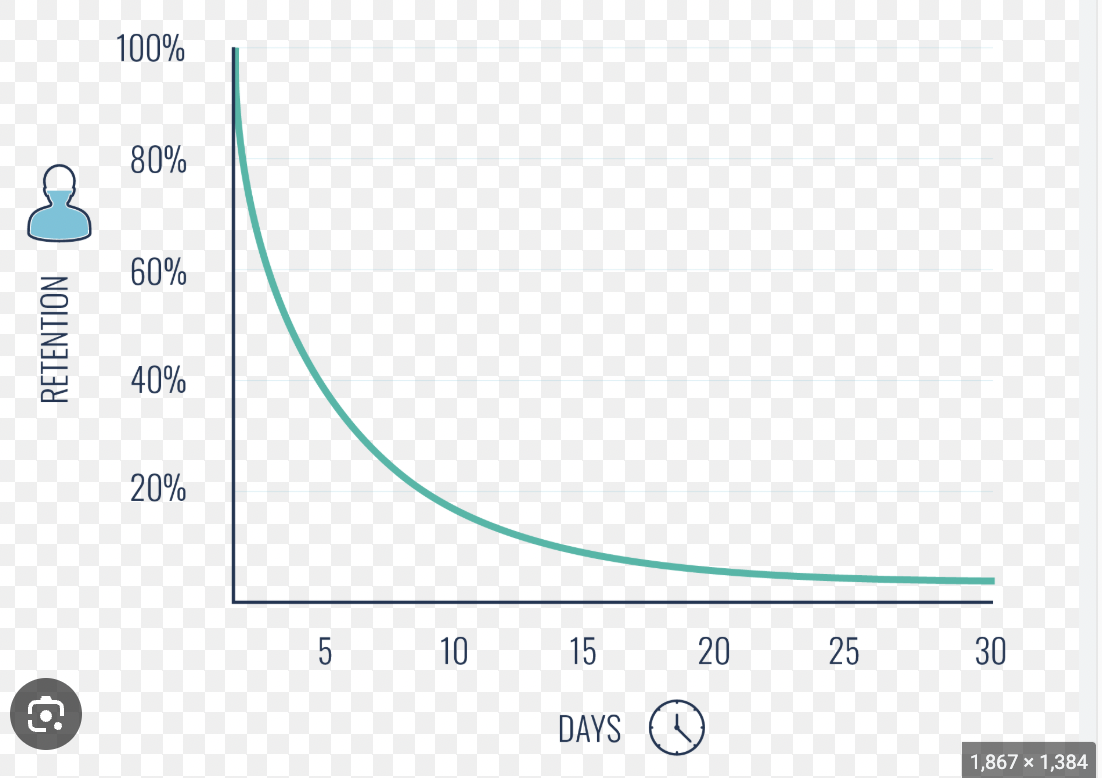
proactiver interference
old memories interfere with recall of new memories
retroactive interference
when new memories make it harder to recall old ones
distress
bad stress: caused by neagtive life events
eustress
good stress that is caused by positive life events
Freud’s Id, Ego, and Superego
ID - unconscious desires that are for pleasure (food and sex)
Superego - personal ideals and morals
Ego - The middle man between the Id and Superego. The “conscious” part that we use in reality
Defense mechanisms of the ID
How to protect itself and reduce anxiety
Repression: unconscious shielding of memories, but they can still have influence.
constructive memory
we do not remember things for basic facts, rather a combination of assumpations expectations, and new info. Our memories may not be 100% exact to what actually happened
Reconsolidation
altering memories before they are stored again
misinformation effect
altering a memory with false info
general intelligence (G)
the ability to be smart in all walks of life, its a combination of specific skills
specific intelligence (S)
Binet
Intoduced IQ and IQ testing.
IQ = Mental age/actual age x 100
arguments against IQ tests
stereotype threat: people are brought down by how they are stereotyped
Stereotype lift: people improve based on how they are stereotyped
good IQ tests need to follow psychometric principles
Reliability: will give the same results every time
test retest: when same person takes test, results should be similar
split half: two halves of the same test should give similar results
Validity: give accurate results
content: test asks questions that are on topic
construct: measures the trait its supposed to measure
criterion: correlates with outside variables
predictive: future performance (only when there is a large data set)
standardized: test is administered the same way every time
flynn effect
Iq is increasing generationally: better education and more resources
group Iq difference
the IQ difference within the same group is larger than the difference between two groups
achievement tests
how much someone knows at one point in time
aptitude test
predicts how someone will perform in the future