Alternatives to Agricultural Meat: Sustainability, Nutrition, and Ethics
1/61
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
62 Terms
What are some alternatives to reduce the negative impacts of producing and eating agricultural meat?
Eat insects, plant-based diets, plant-based meat analogues, lab-grown meat.
How does the carbon footprint of plant-based meats compare to that of beef?
The carbon footprint of plant-based meats is lower than that of beef and pork, and comparable to chicken.
What is the environmental impact of cell-cultured meat compared to traditional beef?
Cell-cultured meat is likely less carbon-intensive than beef and could be comparable to chicken if produced with clean energy.
What are some benefits of alternative meats?
They reduce land use and deforestation, protect biodiversity, produce less pollution, mitigate antibiotic resistance, lower public health burdens, and address animal welfare concerns.
What is entomophagy?
Entomophagy is the practice of eating insects and includes true insects and other arthropods like spiders and scorpions.
What types of arthropods are not included in entomophagy?
Entomophagy does not include crustaceans such as lobsters, crabs, and shrimp.
What are some examples of insect products available in Asian supermarkets?
Insect products such as snacks and food items are commonly found in Asian supermarkets.
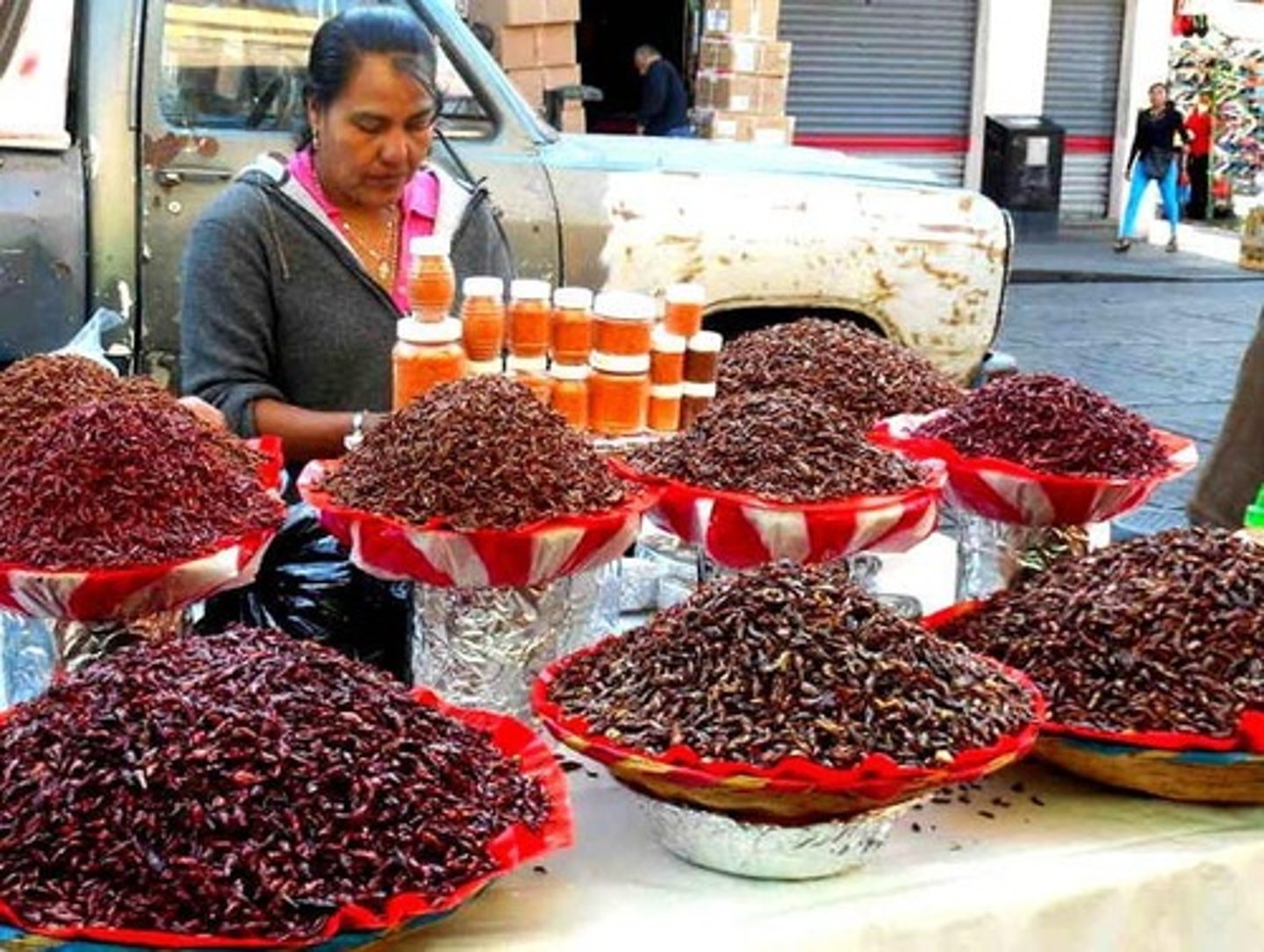

What is cochineal and where is it used?
Cochineal is an extract from the cochineal insect used to color ice cream, yogurt, fruit drinks, cheese, and cosmetics.
What is confectioner's glaze and its source?
Confectioner's glaze is an edible resin from the lac insect used as a glazing agent on candies and pills.
What are some common bee products consumed by Canadians?
Honey, beeswax in confectionery, and royal jelly as a nutritional supplement.

What is chitin and its uses?
Chitin is an insoluble fiber from the exoskeleton of arthropods, used as a nutritional supplement for weight loss and cholesterol management.
What insect content is allowed in Brussels sprouts?
An average of 30 or more aphids and/or thrips per 100 grams.
What is the maximum allowed insect content in canned citrus fruit juices?
5 or more Drosophila (fruit fly) and other fly eggs per 250 ml or 1 or more maggots per 250 ml.
What is the allowed insect fragment content in peanut butter?
An average of 30 or more insect fragments per 100 grams.
What is the maximum insect content in tomato paste?
30 or more fly eggs per 100 grams or 15 or more fly eggs and 1 or more maggots per 100 grams.
What is the allowed insect fragment content in wheat flour?
An average of 75 or more insect fragments per 50 grams.
What initiative did the Food and Agriculture Organization launch in 2013?
A program to encourage the breeding and consumption of insects as a sustainable food source.
What product does Loblaw sell that includes insects?
President's Choice cricket powder, marketed as high in protein with a neutral flavor.

What was the first bakery to offer bread made from ground crickets?
A Finnish bakery group in 2017.
What are some food products being developed from insects in Canada?
Snack foods and protein bars made with cricket powder and other insect ingredients.
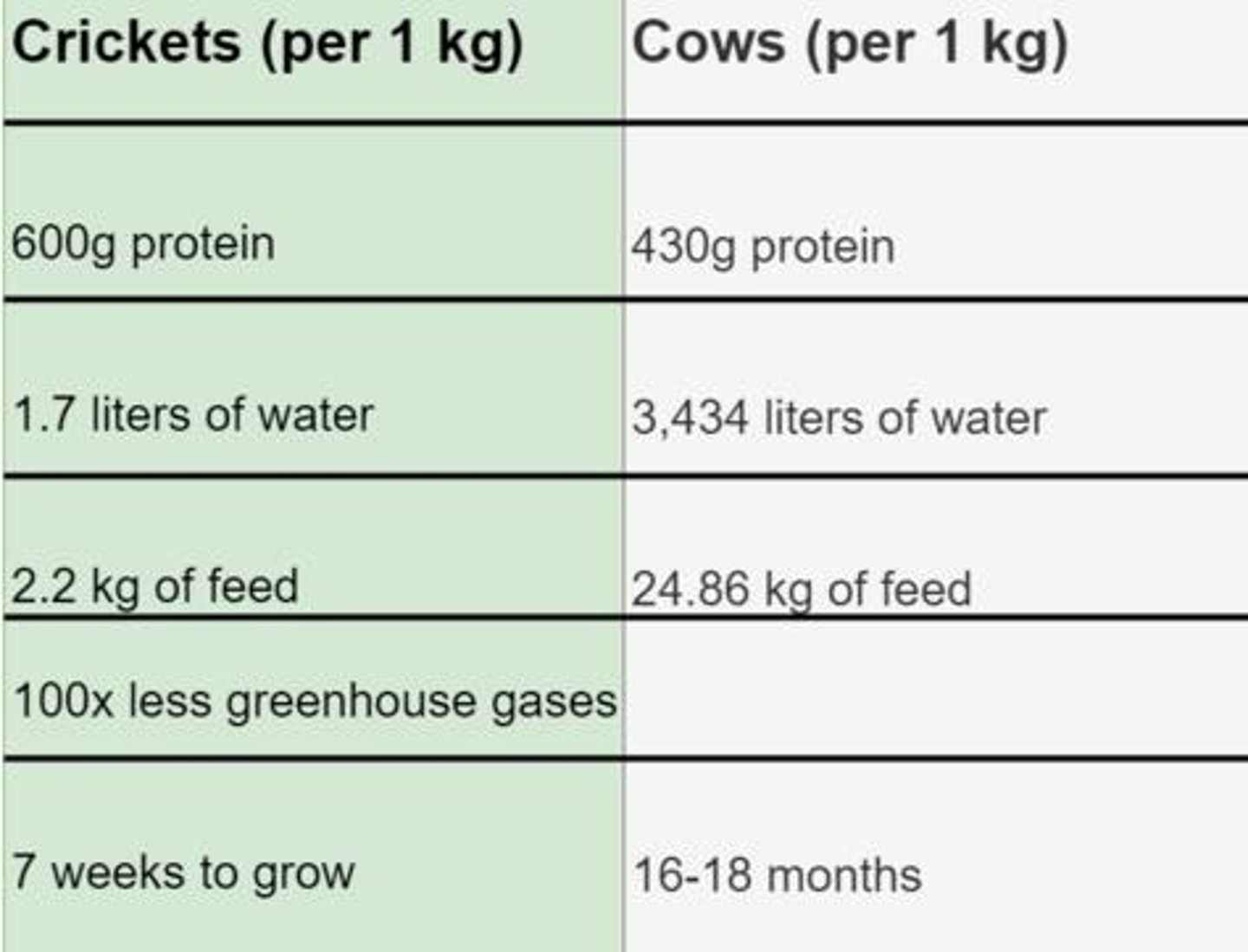
What are complementary amino acids?
A combination of meals made from legumes and grains that provide all nine essential amino acids in the proper amounts.
Which plant foods are generally lower in methionine?
Legumes
Which plant foods are generally lower in lysine?
Most other plant foods, except legumes.
What is the role of grains, nuts, and seeds in amino acid profiles?
They complement legumes by providing lysine and threonine.
What are some examples of plant-based meat alternatives?
Tofu (coagulated soybean curds) and Seitan (wheat gluten).
What is lab-grown meat?
Animal protein grown from animal muscle cells through tissue culture in controlled laboratory conditions.
What are the benefits of cultured meat?
Provides a safe meat source, eliminates the need to kill animals, reduces greenhouse emissions, and decreases zoonotic diseases.
What is the significance of cellular agriculture?
It is a stable and sustainable protein production system.
What is a common public perception of in vitro meat?
Many consumers consider it unnatural.
What percentage of US consumers had low or no willingness to try in vitro meat?
33%
What was the percentage of respondents who would definitely try in vitro meat?
31.3%
What was the percentage of respondents who were unsure about trying in vitro meat?
11.7%
What is a potential barrier to consumer acceptance of in vitro meat?
The belief that it negatively impacts farmers.
What are ultra-processed meat analogues?
Highly processed products that do not resemble natural foods.
What is the relationship between lab-grown meat and regenerative medicine?
They use similar technologies for tissue growth.
What is the significance of the cultured meat schematic?
It outlines the steps in producing lab-grown meat without animal death.
What is the impact of cultured meat on global pandemics?
It may help prevent zoonotic diseases that could lead to pandemics.
What is the public's attitude towards in vitro meat based on past research?
Participants often view it as unnatural and have concerns about its impact on traditional farming.
What is the main concern regarding the production of cultured meat?
Finding a substitute for fetal serum to avoid animal deaths in the process.
What is meat?
Skeletal muscle and associated tissues harvested for human consumption from mammals, birds, reptiles, amphibians, and fish.
What are the two main types of meat?
Unprocessed meat (red meat and white meat) and processed meat.
What is red meat?
Muscle from mammals that has a high concentration of myoglobin, including beef, veal, venison, pork, lamb, mutton, horse, and goat.
What is white meat?
Muscle of poultry, sometimes classified as fish but nutritionally distinct from poultry.
What are processed meats?
Meat that has been transformed through salting, curing, fermentation, smoking, or other processes to enhance flavor or improve preservation.
What essential nutrients does red meat provide?
Vitamin B3 (niacin), vitamin B6 (pyridoxine), vitamin B12 (cobalamin), zinc, selenium, and heme iron.

What is the protein quality in meat?
Meat is a high-quality (complete) protein containing all nine essential amino acids needed for the body.
What are the classifications of amino acids?
Nonessential amino acids (11), essential amino acids (9), and conditionally essential amino acids (approximately 8).
What are limiting amino acids?
Essential amino acids present in the least amount relative to human requirements, making certain proteins incomplete.
What health risks are associated with unprocessed red meat?
May contribute to conditions like colon cancer and cardiovascular disease due to saturated fat and heme iron.
What compounds are formed when cooking meat at high temperatures?
Heterocyclic amines (HCAs) and polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs), which may be cancer-causing.
What health risks are associated with processed meat?
High in sodium, may lead to hypertension, and contains N-Nitroso compounds linked to colon and stomach cancer.
What is the World Cancer Research Fund's recommendation regarding red meat consumption?
Eat no more than moderate amounts of red meat and limit processed meat consumption.
What ethical problems are associated with raising animals for food?
Animal suffering, antibiotic resistance, greenhouse gas emissions, waste production, deforestation, and zoonotic disease transmission.
What are the environmental impacts of meat consumption?
Contributes to greenhouse gas emissions, deforestation, and loss of biodiversity.
What are the pros of consuming meat?
Nutritious, part of many cuisines, and has been consumed for hundreds of thousands of years.
What are the cons of consuming meat?
Overconsumption is associated with disease risk, environmental impacts, and ethical implications.
What is the significance of myoglobin in meat?
Myoglobin is a protein that gives red meat its color and is associated with the oxygen-carrying capacity of muscle tissue.
How does the protein content in animal flesh compare to vegetal proteins?
Animal flesh is a complete protein, while vegetal proteins are often incomplete due to limiting amino acids.
What is the role of L-carnitine in meat consumption?
L-carnitine can raise triglyceride and cholesterol levels, increasing the risk of atherosclerosis.
What is Neu5Gc?
A sugar found in red meat that may be associated with health risks.
What is the impact of industrial farming on antibiotic resistance?
Industrial farming practices contribute to the development of antibiotic-resistant bacteria.
What is the Planetary Health Diet?
A dietary guideline aimed at promoting health while reducing environmental impact, including recommendations for meat consumption.