McKenzie Approach for the Lumbar Spine
1/25
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
26 Terms
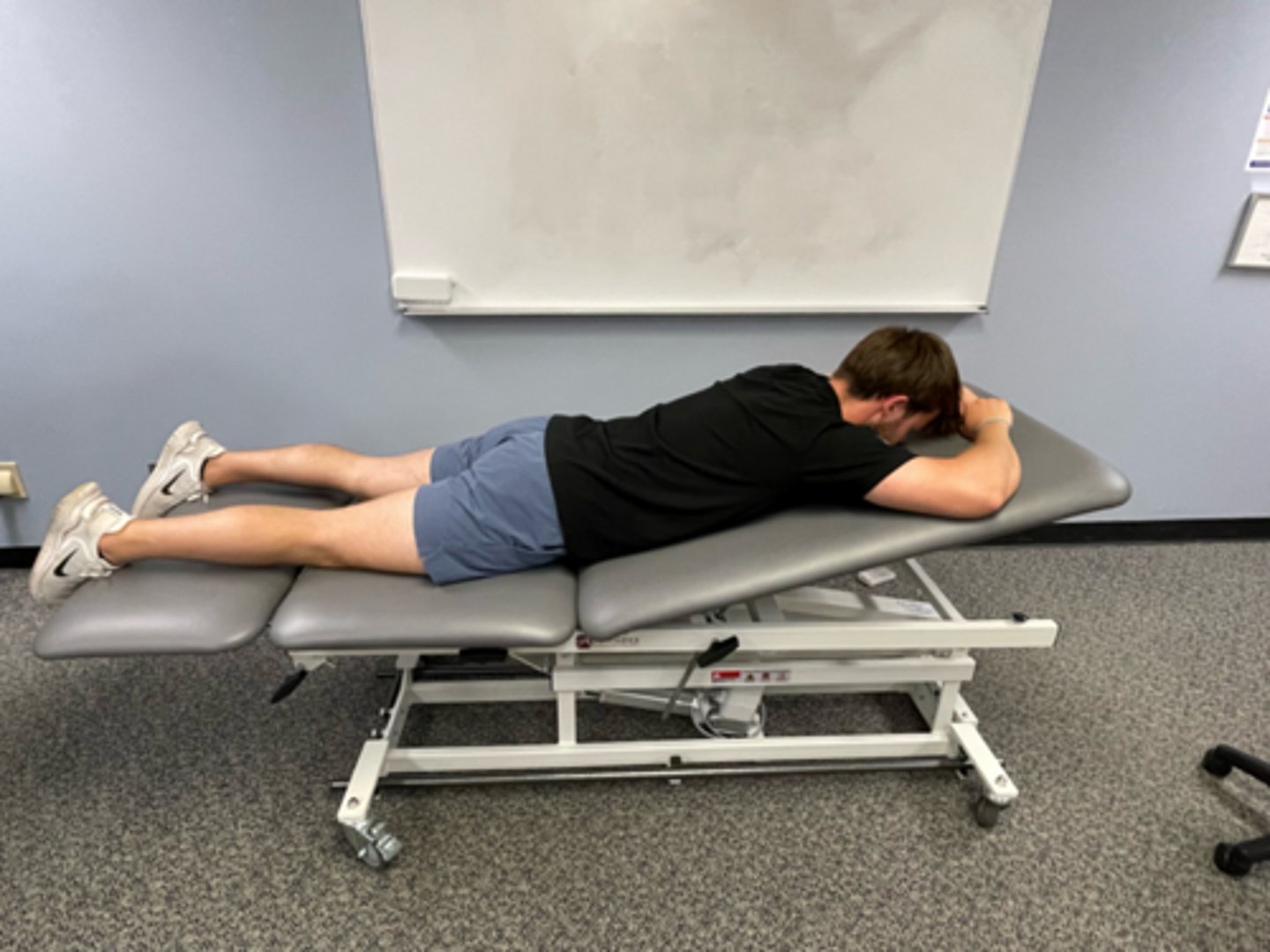
prone lying
extension bias
progress toward extension
particularly after prolonged flexion or first thing in the morning, the patient may need time in prone before attempting extension in lying (EIL)
-> prone -> prone on elbows /pillows under chest -> plinth raised --> this is recommended progression for Pt presenting with back dominant pain, presenting "stuck" bent forward in flexion
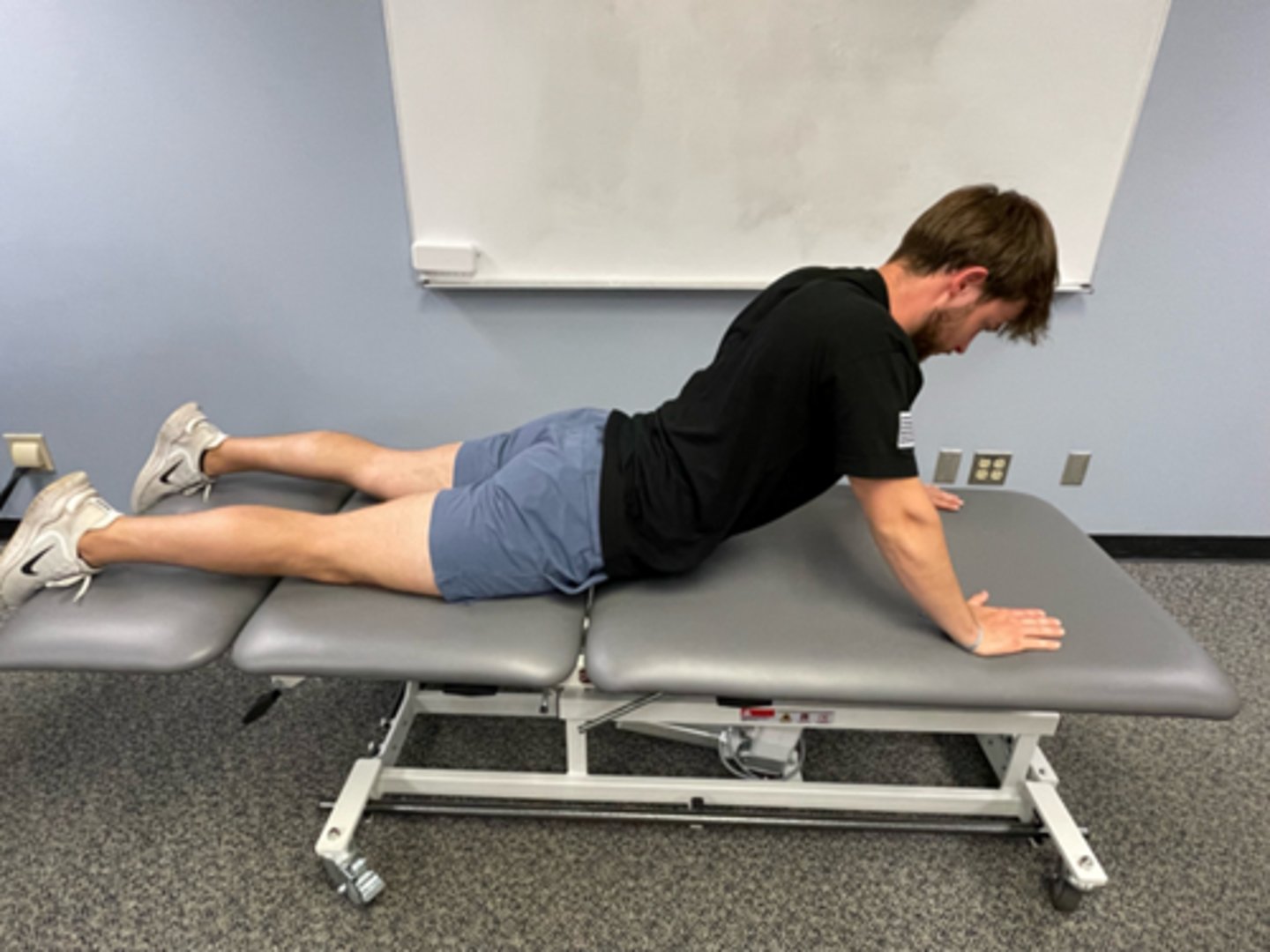
repeated extension in lying (REIL)
extension bias
press ups
self overpressure can be given with the “sag,” exhaling at end
self overpressure for lower regions: raising Pt legs or moving arms back
self overpressure for upper regions: moving arms forward
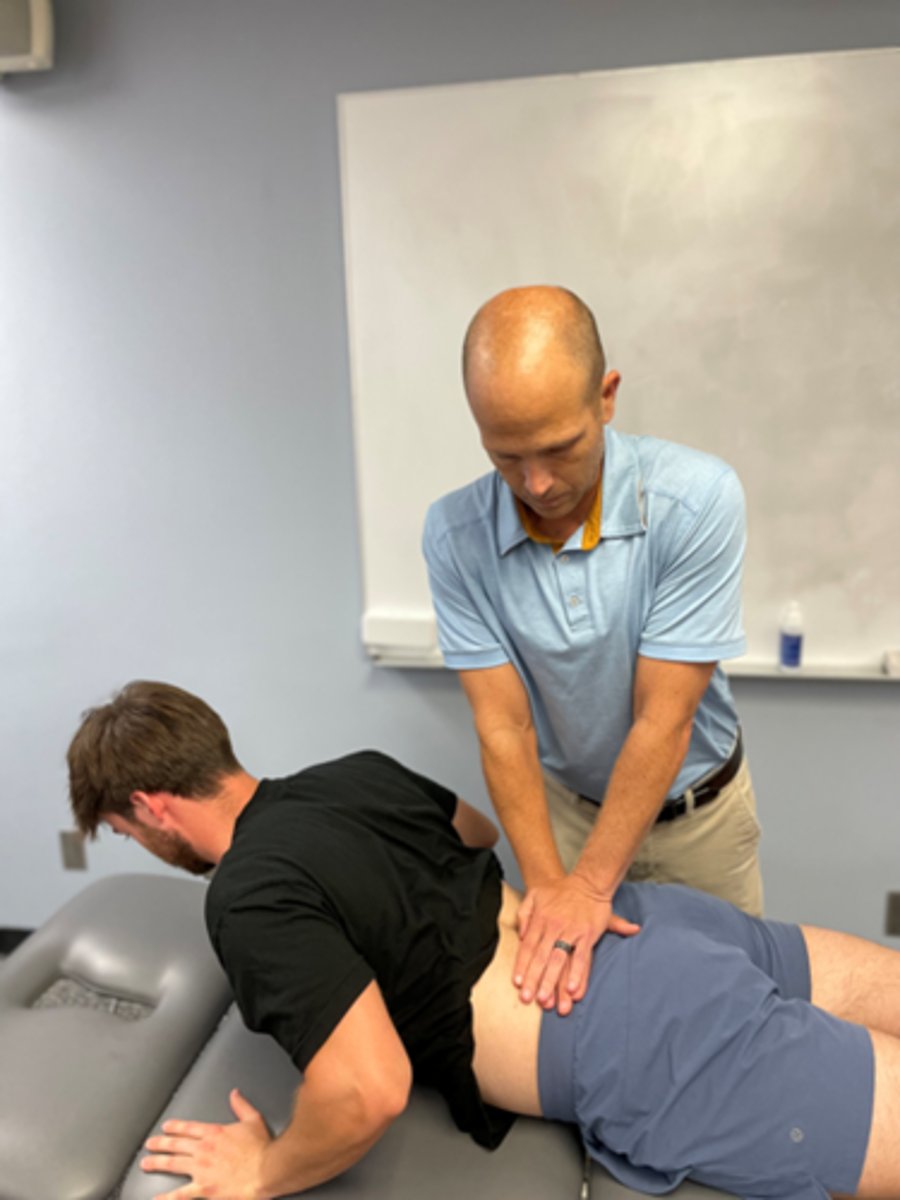
REIL with overpressure (manual fixation)
extension bias
the effect of overpressure is assessed by the therapist fixing the pelvis
or specific spinal segment using overlapping or crossed hand technique
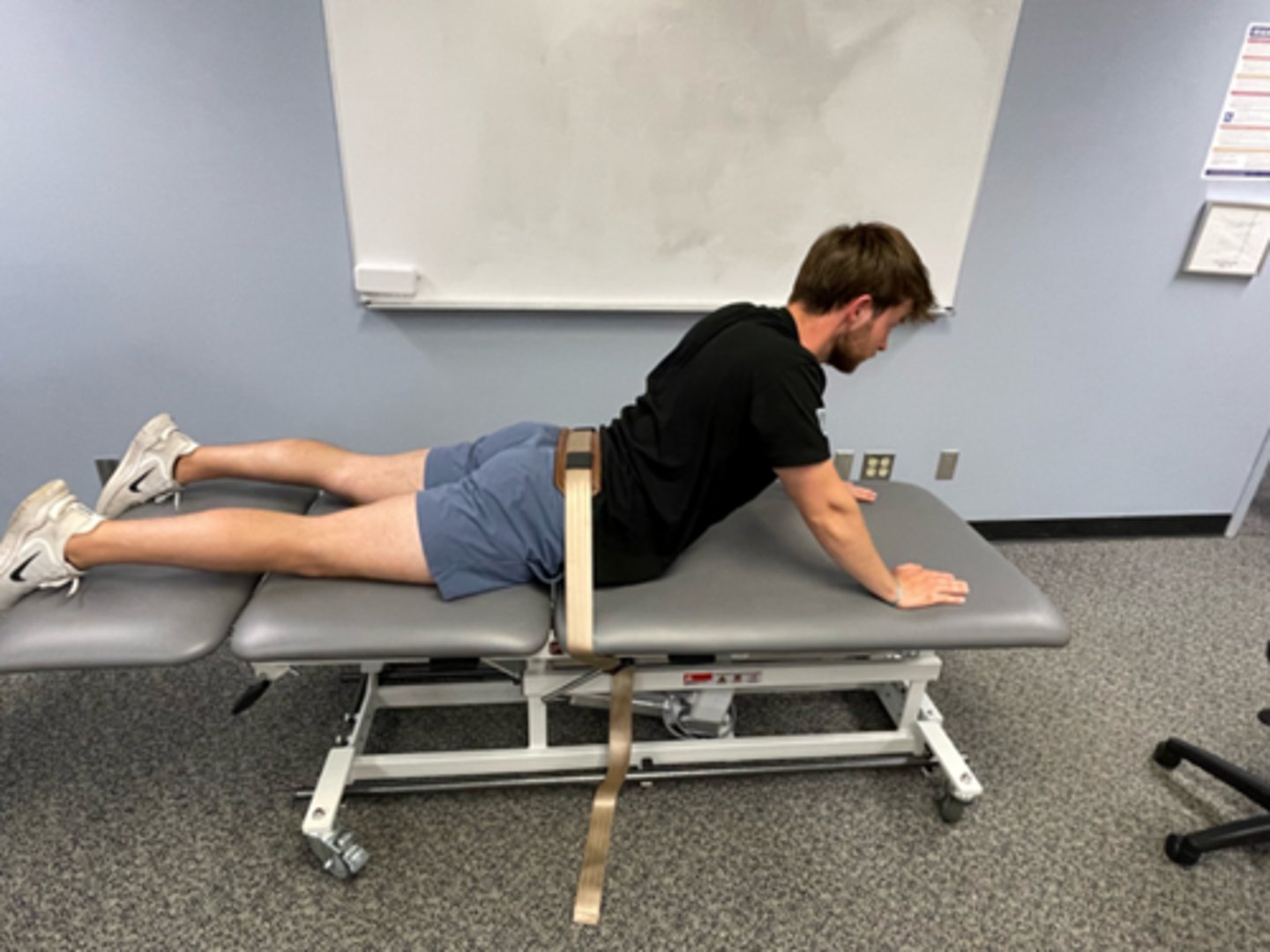
REIL with overpressure (belt fixation)
extension bias
belt fixation used to prevent hips leaving plinth
also used to localize self-stretch to a specific region of spine
patient extension with lateral component
extension bias
unilateral or asymmetrical symptoms not reduced with simple
usually move hips away from the side of pain
Progression --> therapist maintains lateral shift while pt extends (press up) or patient can maintain lateral shift while progressing into extension
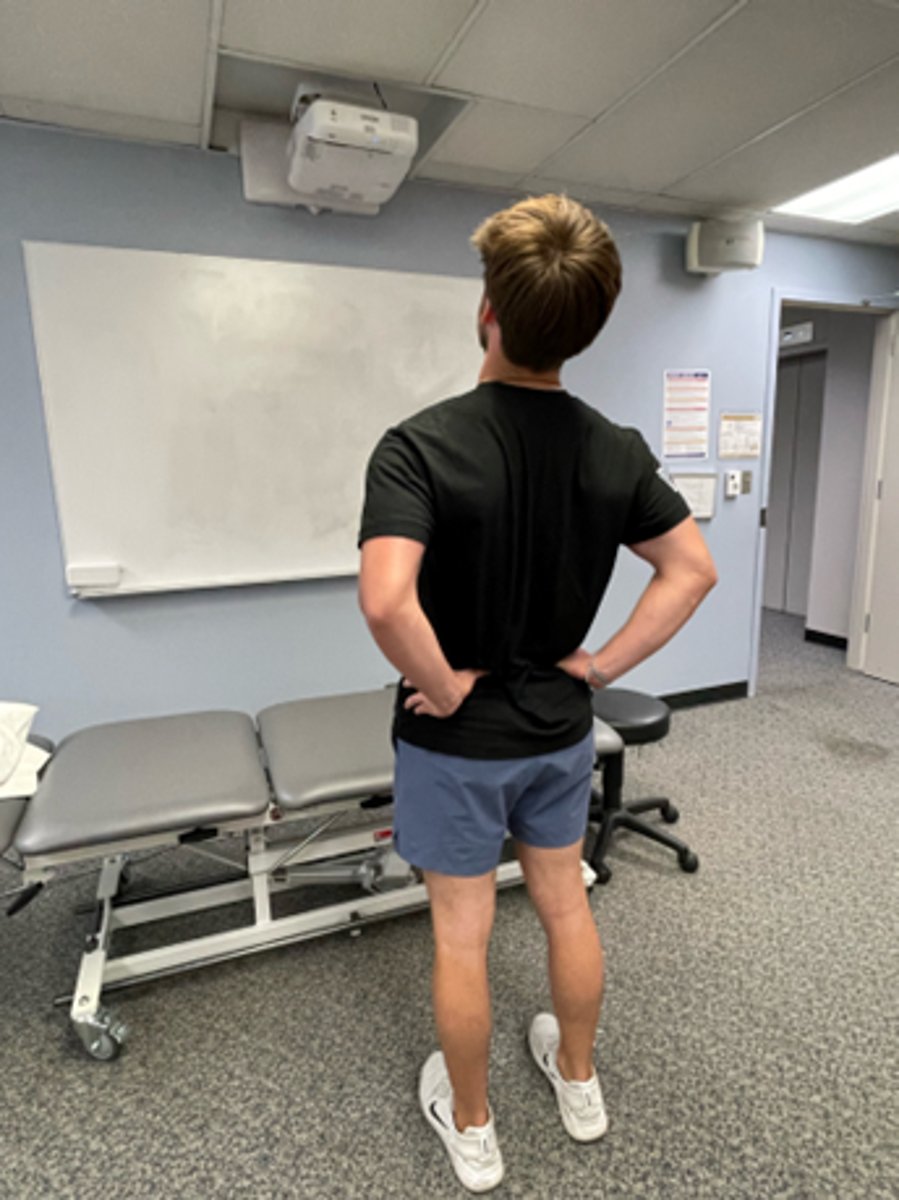
patient extension in standing (EIS)
extension bias
this is used as soon as possible, as it is easier for most patients to do during the day
wide BOS, look straight ahead, do NOT push hips forward
main preventative movement, to interrupt / reverse prolonged flexion activities before the pain reappears
EIS with belt
extension bias
Patient holds belt around target lumbo-sacral segment
Arms hold ends of belt in front with elbows bent
Arch backwards using the belt as a fulcrum to arch over
Often works better if patient pulls forward / upward with belt as they arch
This is a variation of a Mulligan SNAG
lateral shift in lying
extension bias
patient in sustained lateral shift, using pillows in side lying
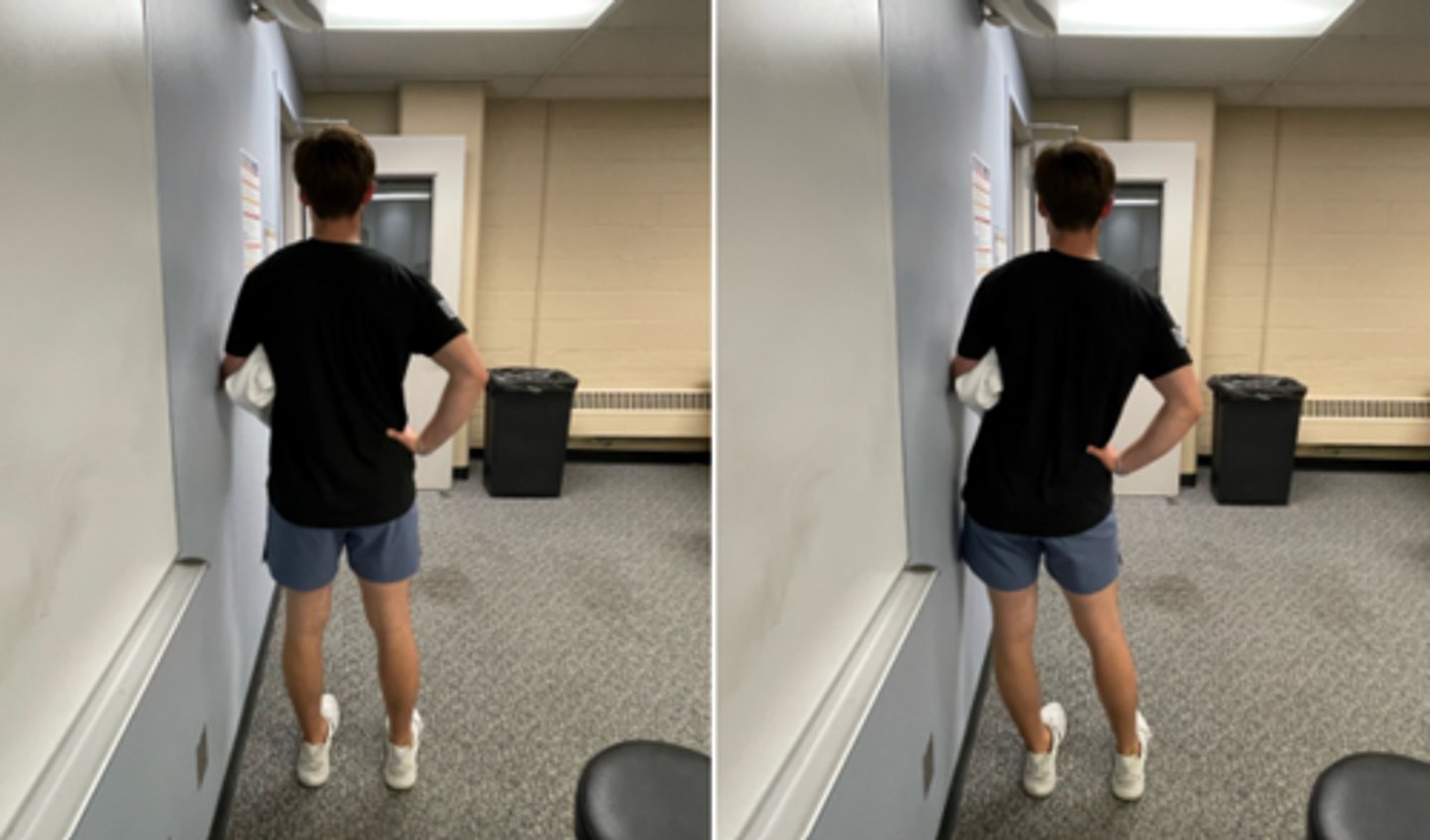
patient lateral shift in standing
extension bias
against wall, doorframe, with pillow to increase hip excursion
further away the pt leans, the more pressure from gravity
free standing, with one hand on hip, other on rib cage

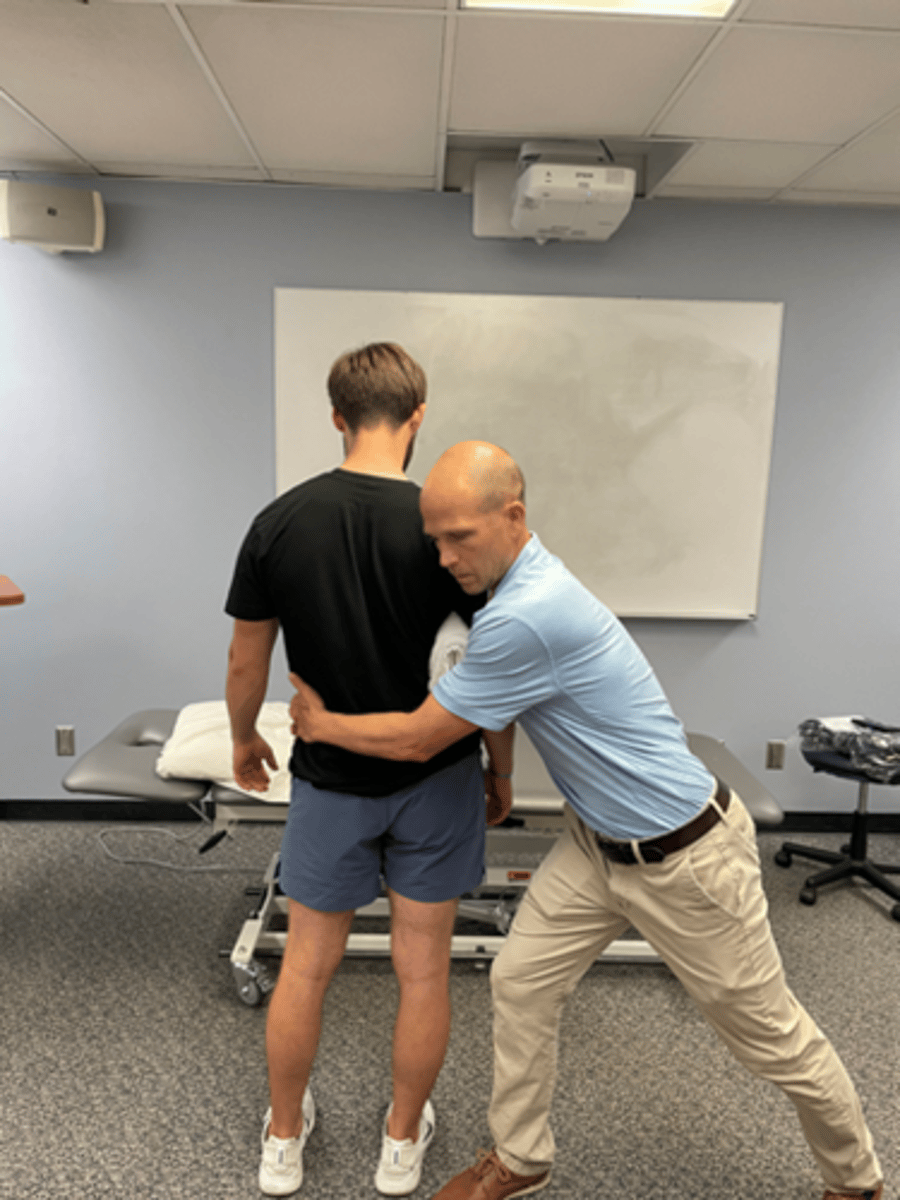
lateral shift with mobilization in standing
extension bias
wide BOS
stabilize pt’s trunk with therapist’s hands, using pt’s bent arm held into rib cage
wrap arms around pt’s pelvis, pull hips toward you
may be oscillatory (slow) or sustained
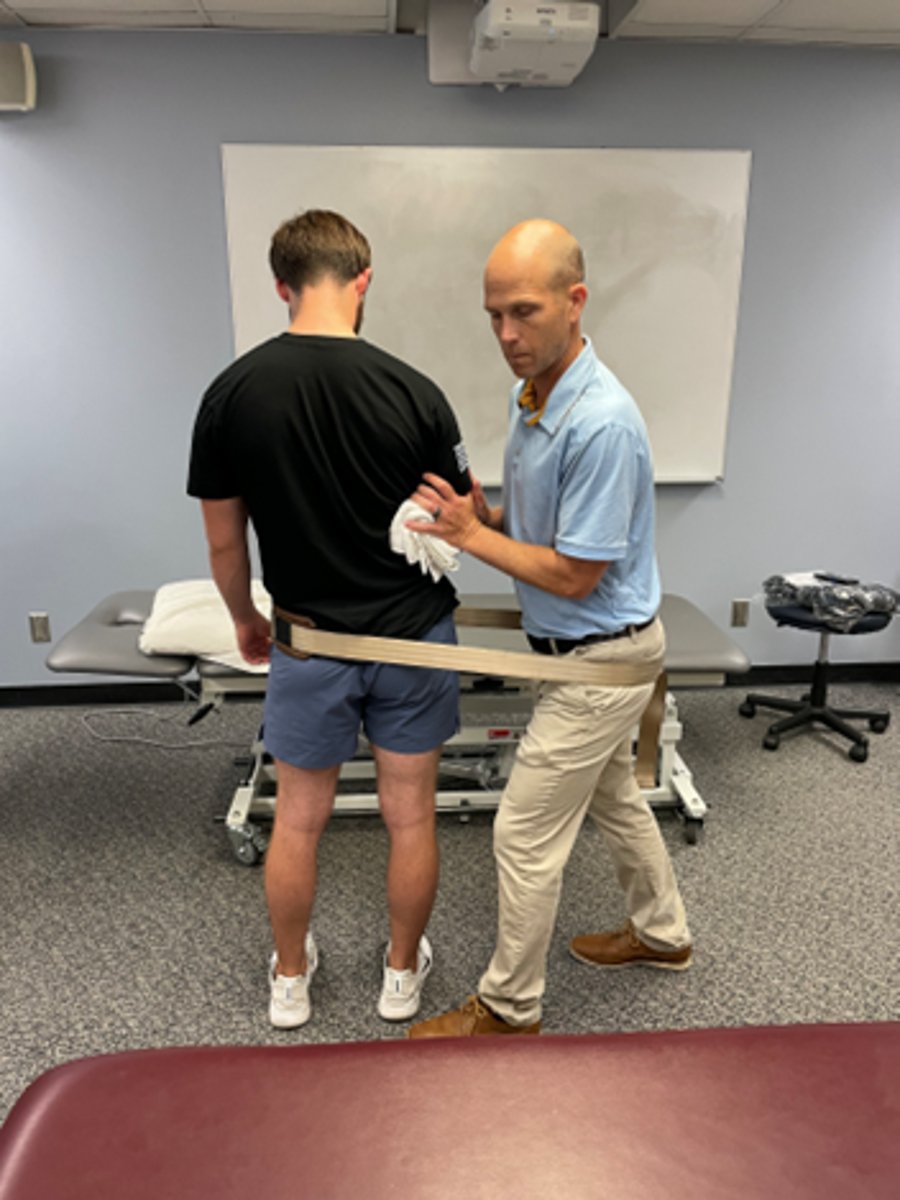
lateral shift with mobilization in standing (with belt)
extension bias
wide BOS
stabilize pt’s trunk with therapist’s hands, using pt’s bent arm held into rib cage
wrap belt around hips
should be side glide, not flex
patient rotation mobilization in flexion
flexion bias
flex first then rotate, (swing legs to side)
usually move legs towards painful side
may need to hold for several minutes

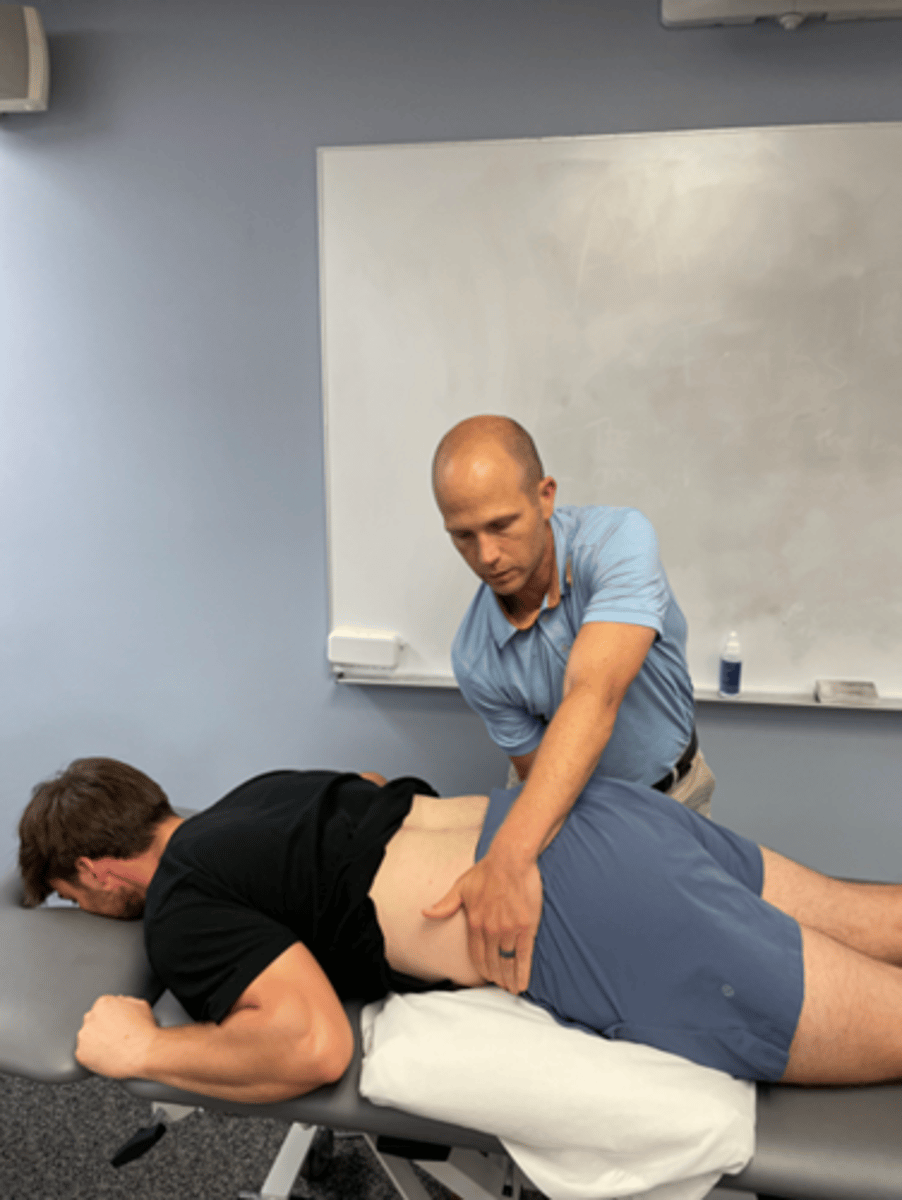
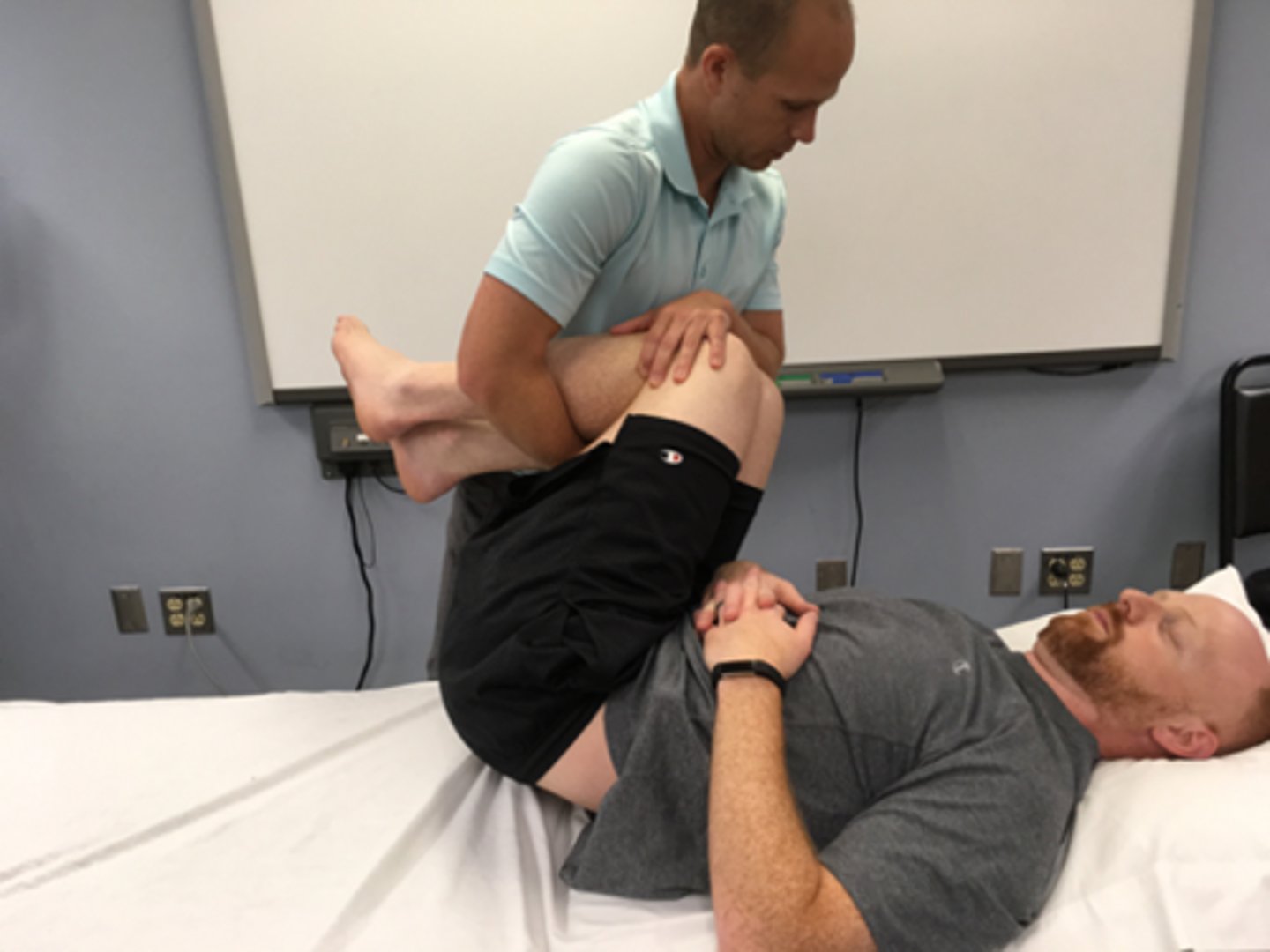
therapist rotation mobilization in flexion
flexion bias
flex first then rotate patient’s legs as above
usually move legs towards painful side
apply overpressure by holding down pt’s trunk / ribcage
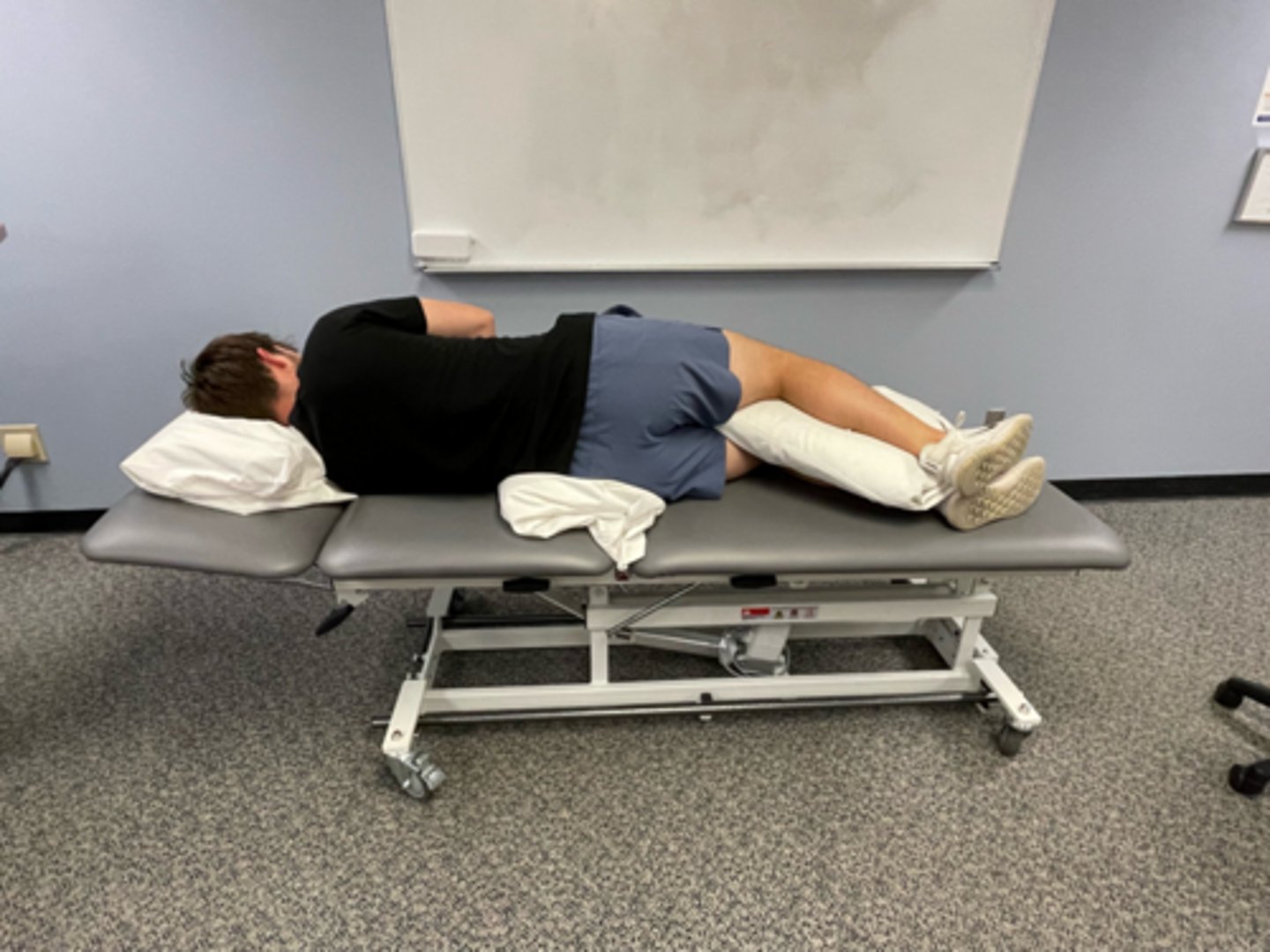
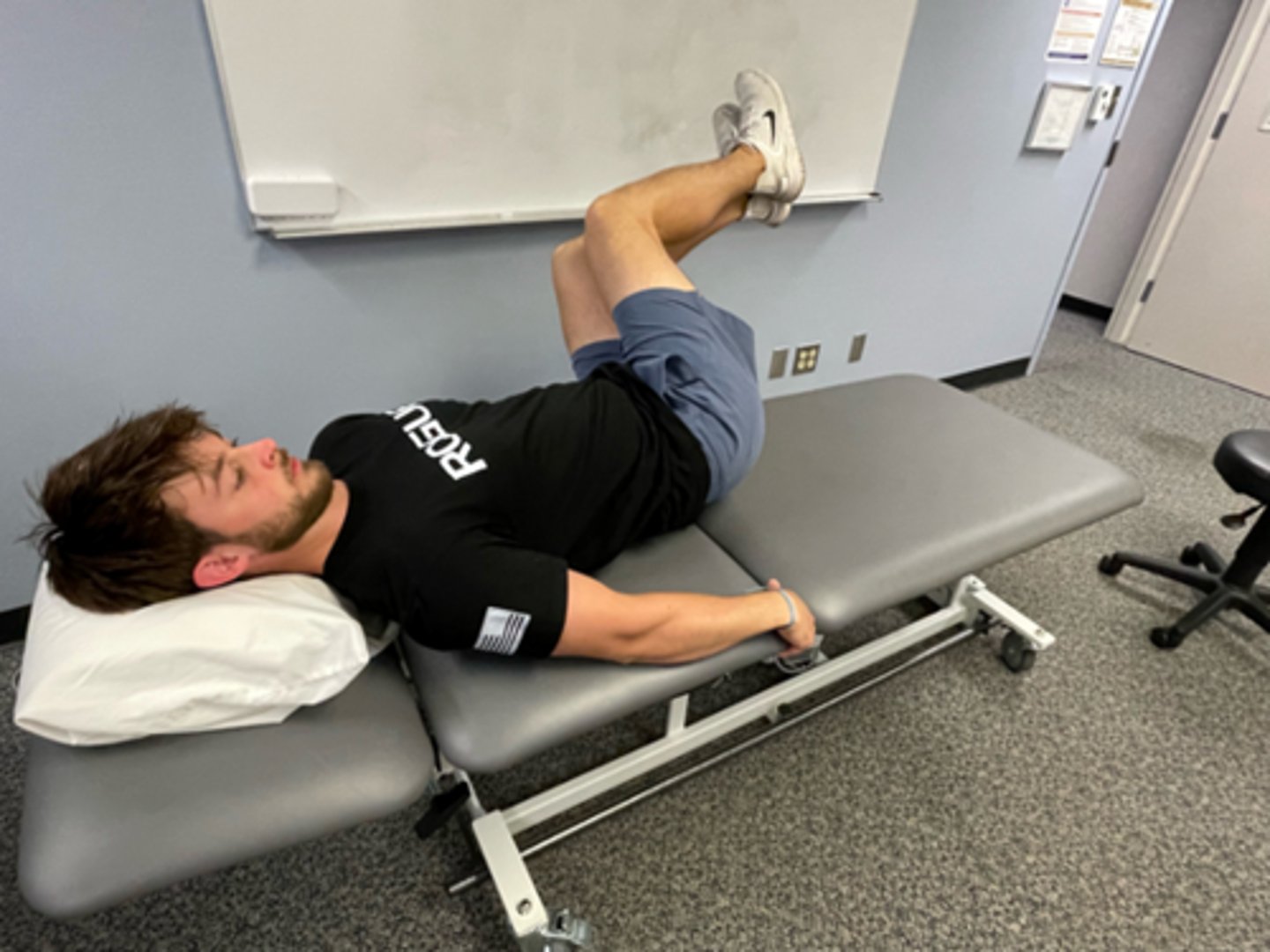
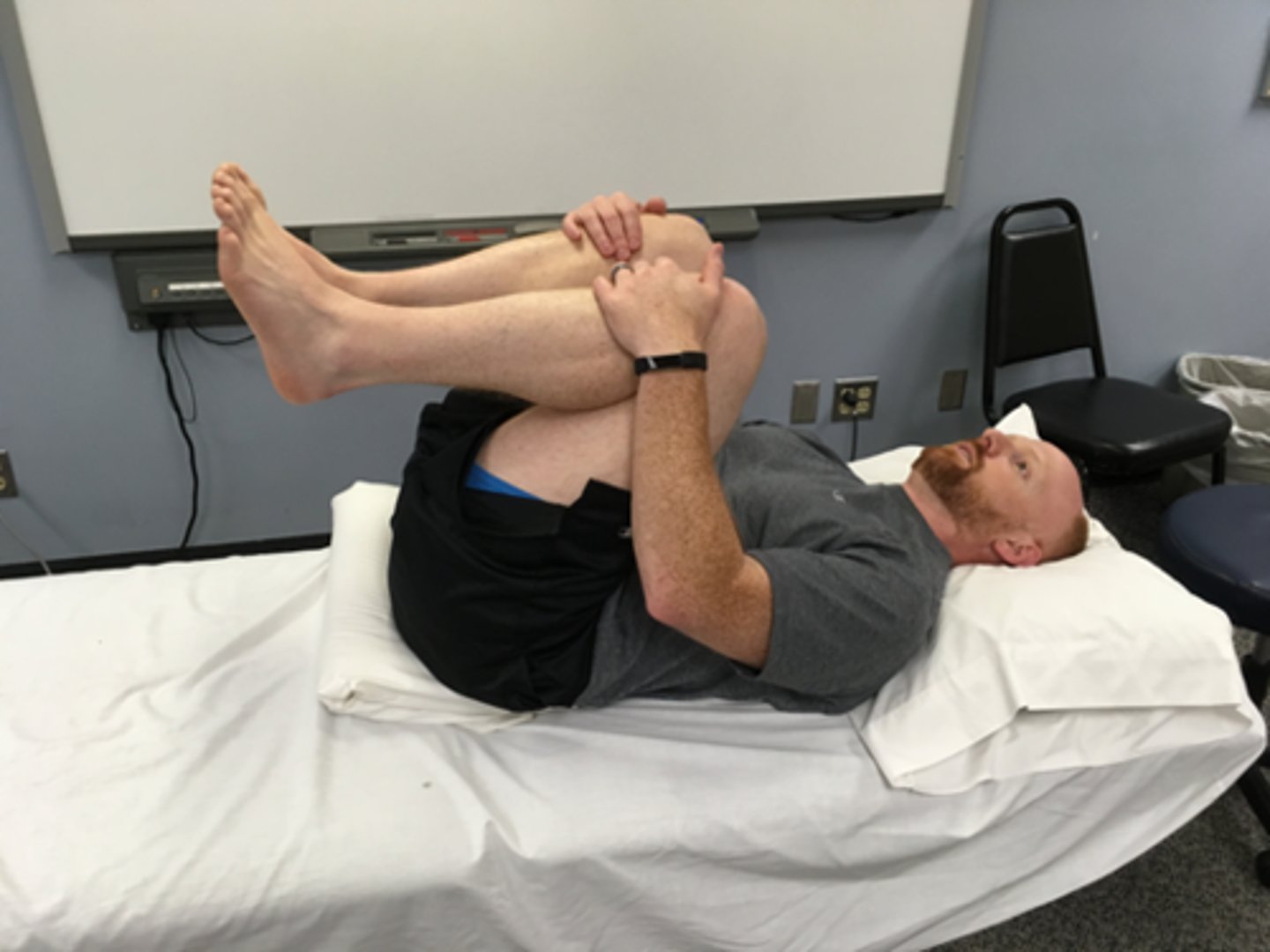
flexion in lying
flexion bias
may start with one leg, then both
extra ROM by abducting & rotating hips out
head stays on plinth
should be passive, using patient’s arms, not abdominals
stretch to lumbar spine increased by using pillow under pelvis
flexion in sitting
flexion bias
avoid sustained flexion, unless intended
alter seat height, position in chair
used for dysfunction and occasionally for acute derangements
overpressure with therapist fixation -> belt isolates lumbar motion
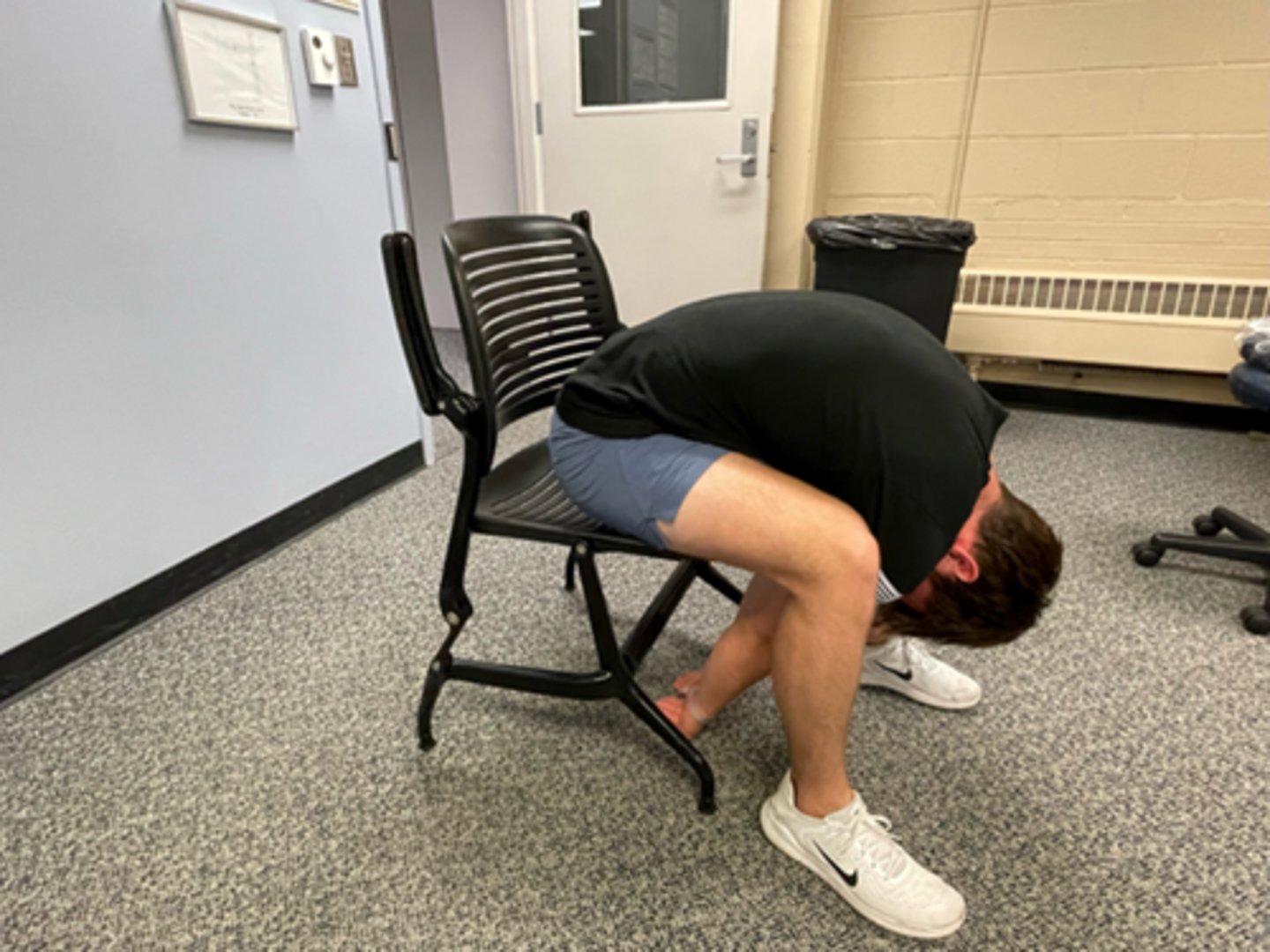

flexion in step-standing
flexion bias
used for asymmetrical dysfunction or adhered nerve root
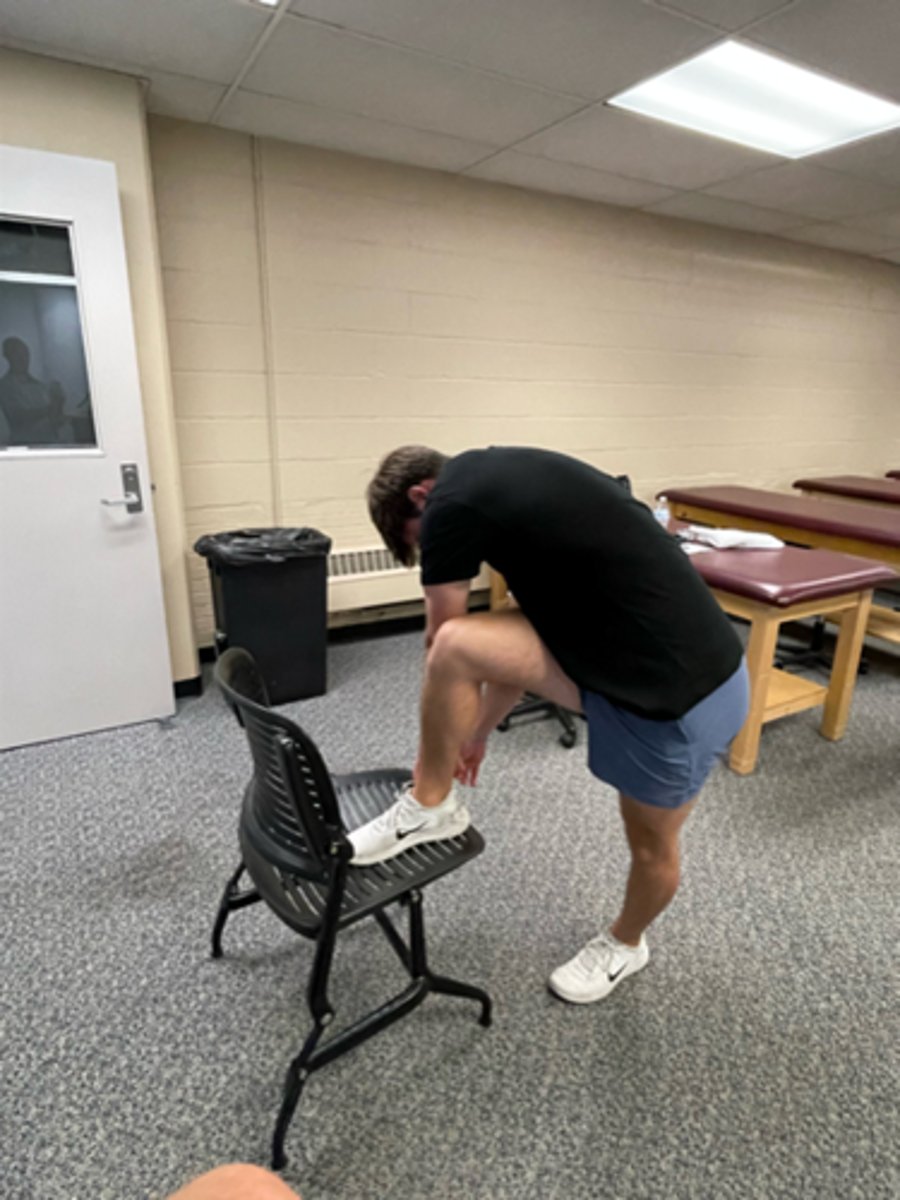

SNAG for extension in sitting/standing
SNAGS - lumbar/thoracic techniques:
Ulnar border of your hand is placed under the SP or TVP of target segment
Stand to the side of the patient (so as to not block extension)
Glide vertebra upward as patient extends
Use belt to fix the pelvis if necessary
NOTE: patients must NOT lean back into your hand = rather they should extend over your hand
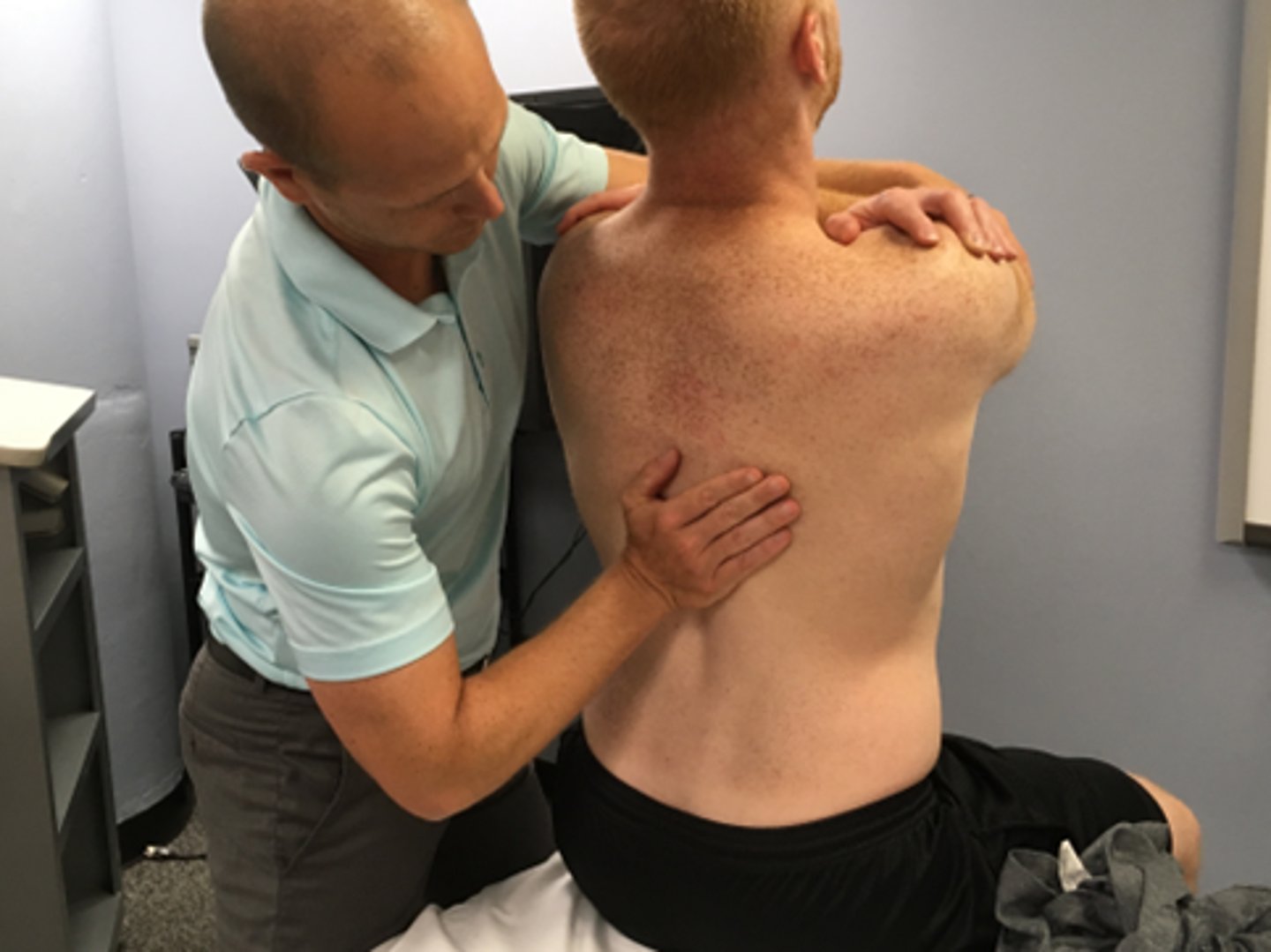
SNAG for flexion in sitting/standing
SNAGS - lumbar/thoracic techniques:
Ulnar border of your hand is placed under the SP or TVP of target segment
Stand behind the patient
Glide vertebra upward as patient flexes forward
Use belt to fix the pelvis if necessary
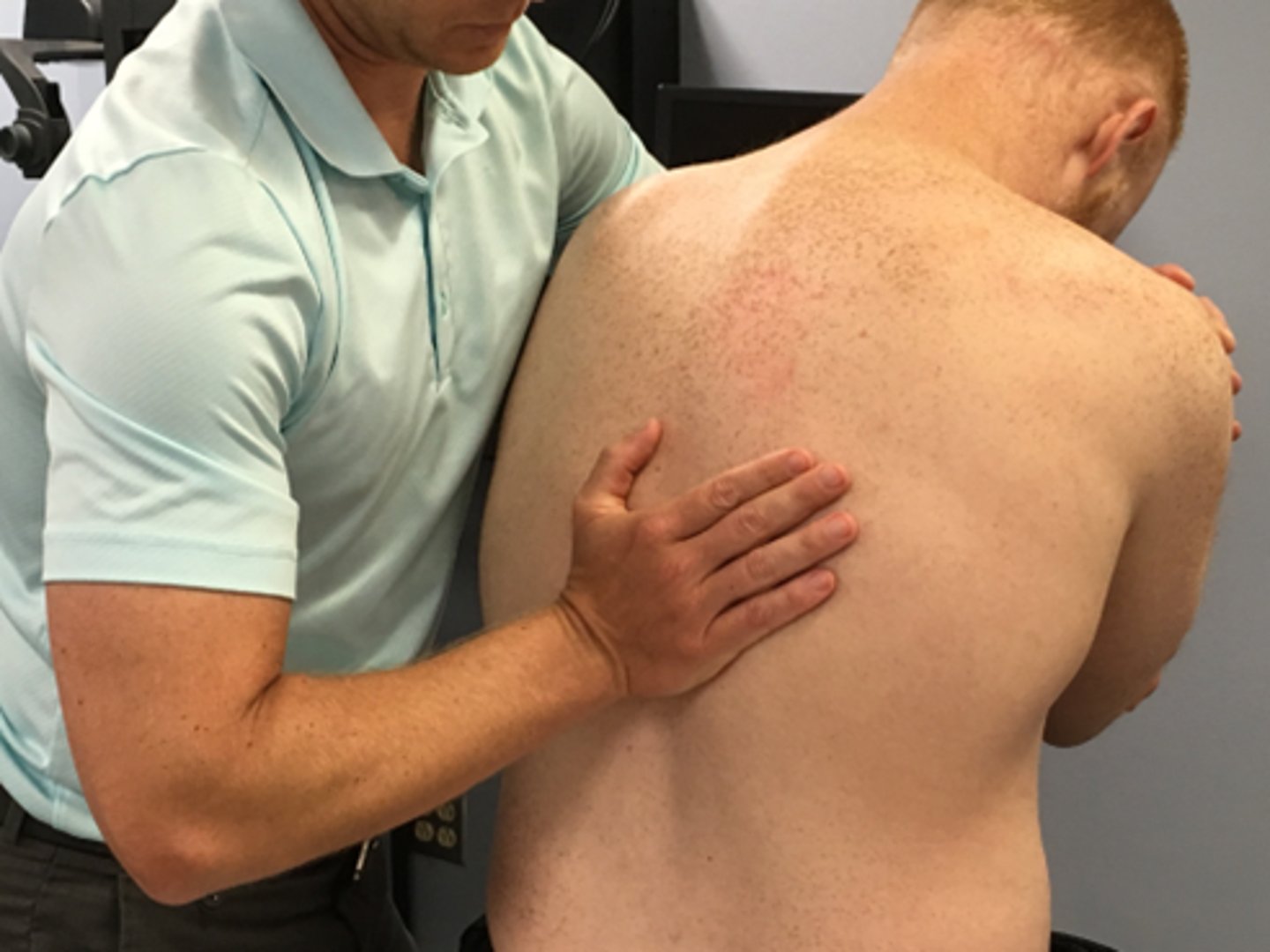
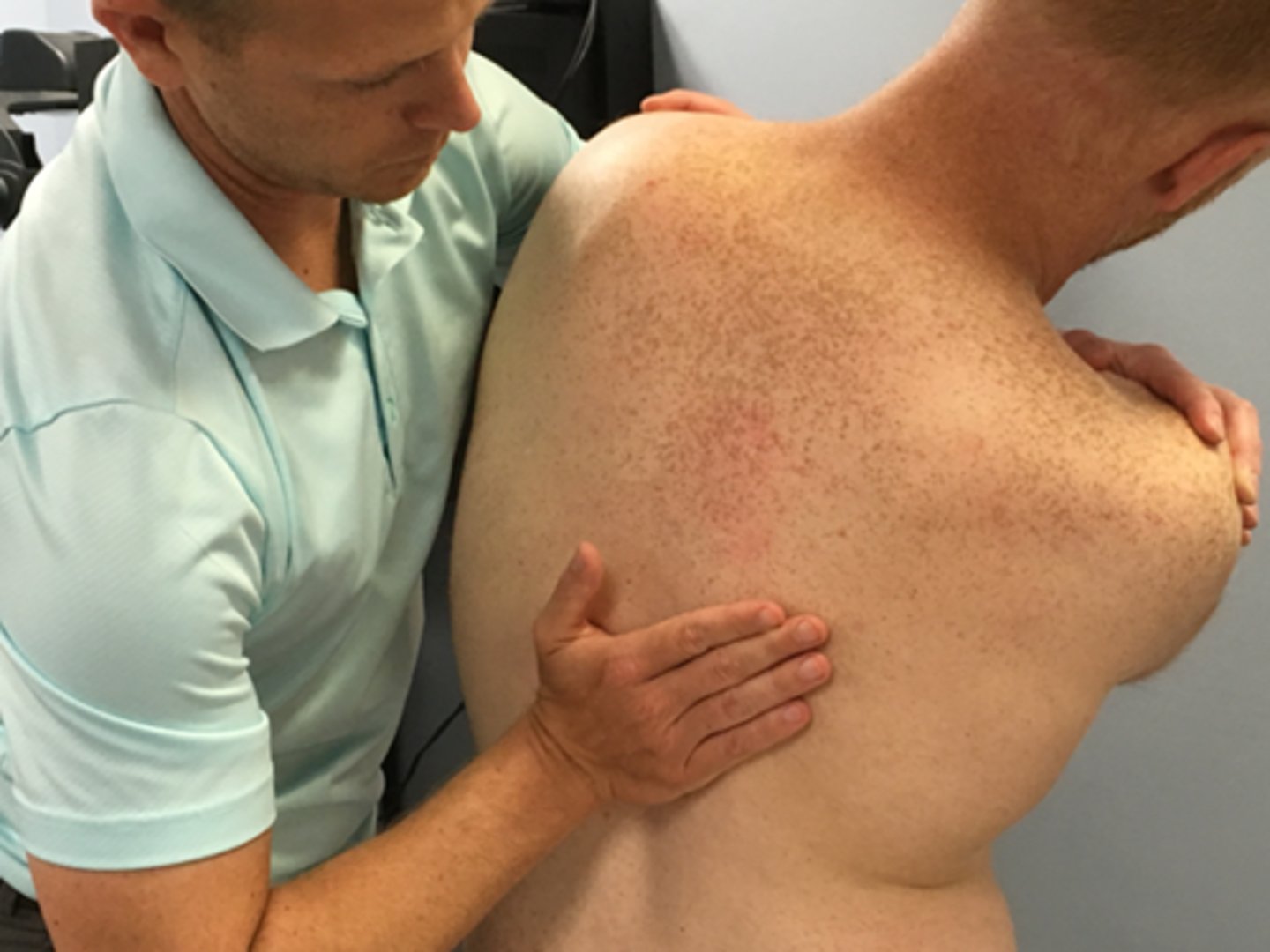
SNAG for side flexion in sitting/standing
SNAGS - lumbar/thoracic techniques:
Ulnar border of your hand is placed under the SP or TVP of target segment
Stand to the side of the patient (Opposite direction of movement)
Glide vertebra upward as patient side flexes
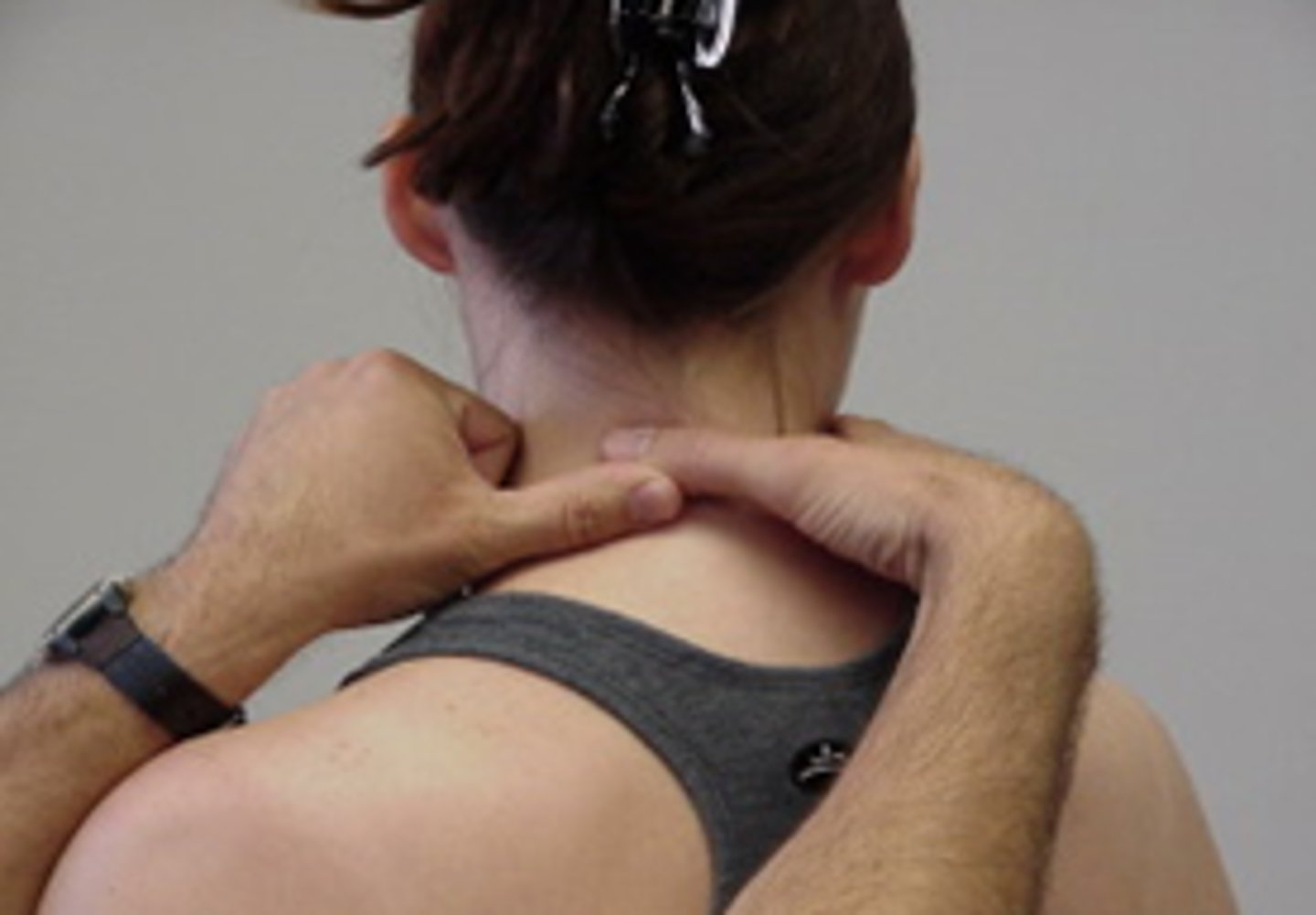
SNAG for rotation (using SP)
SNAGS - cervical techniques:
use edge of thumb on TP of target vertebra
force is imparted with thumb of other hand
aim along facet planes
PT hands must follow movement
Pt provides own (pain free) overpressure
SNAG for rotation (unilateral)
SNAGS - cervical techniques:
top of thumb is lateral to SP of target vertebra
force is imparted with thumb of other hand
aim along facet planes
therapist hands must follow the patient's movement
Pt provides own (pain free) overpressure
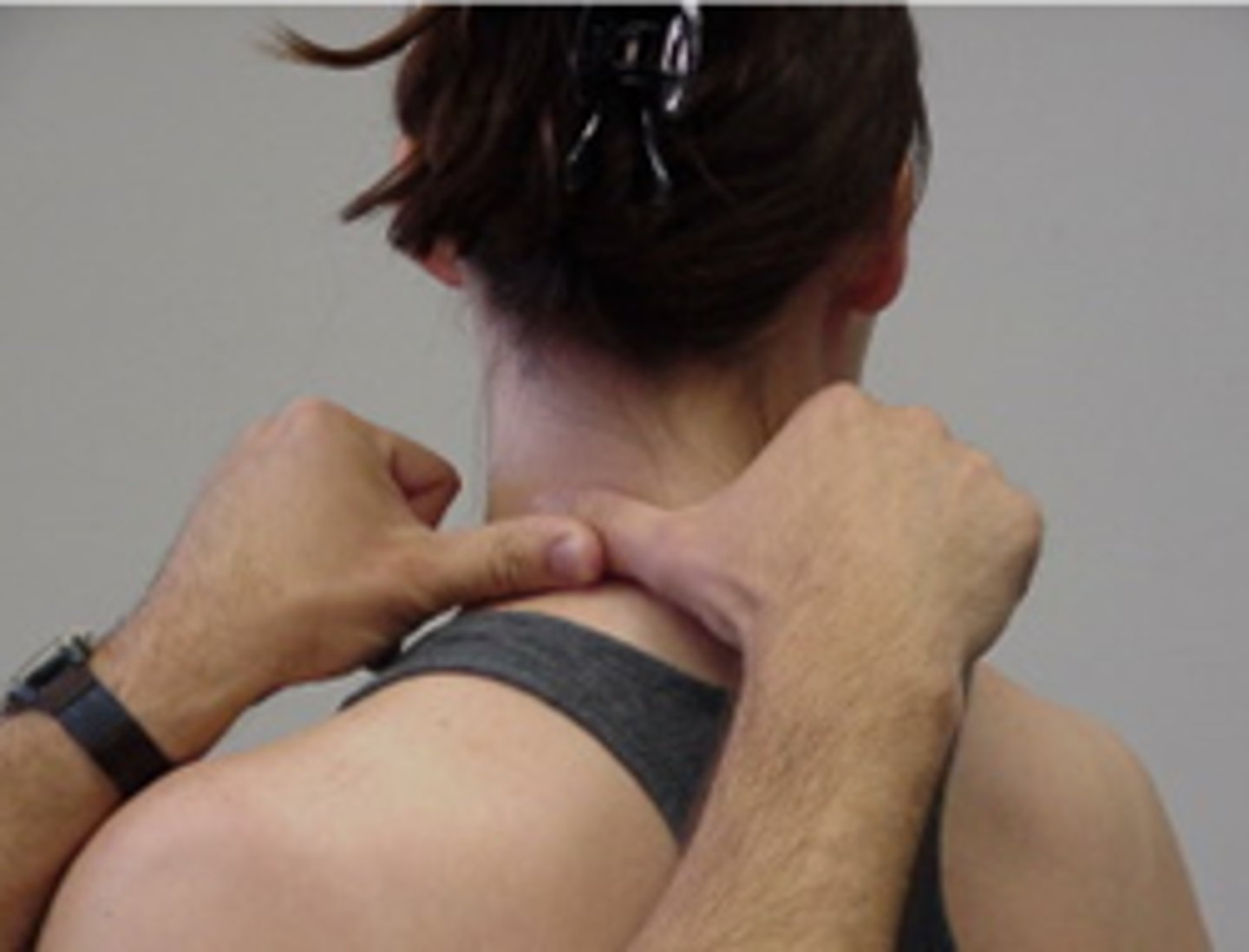
SNAG for side flexion (unilateral)
SNAGS - cervical techniques:
top thumb is lateral to TP of target vertebra
force is imparted with thumb of other hand
aim along facet planes
therapist hands must follow the patient's movement
Pt provides own (pain free) overpressure
can also use edge of thumb directly on SP of target vertebra
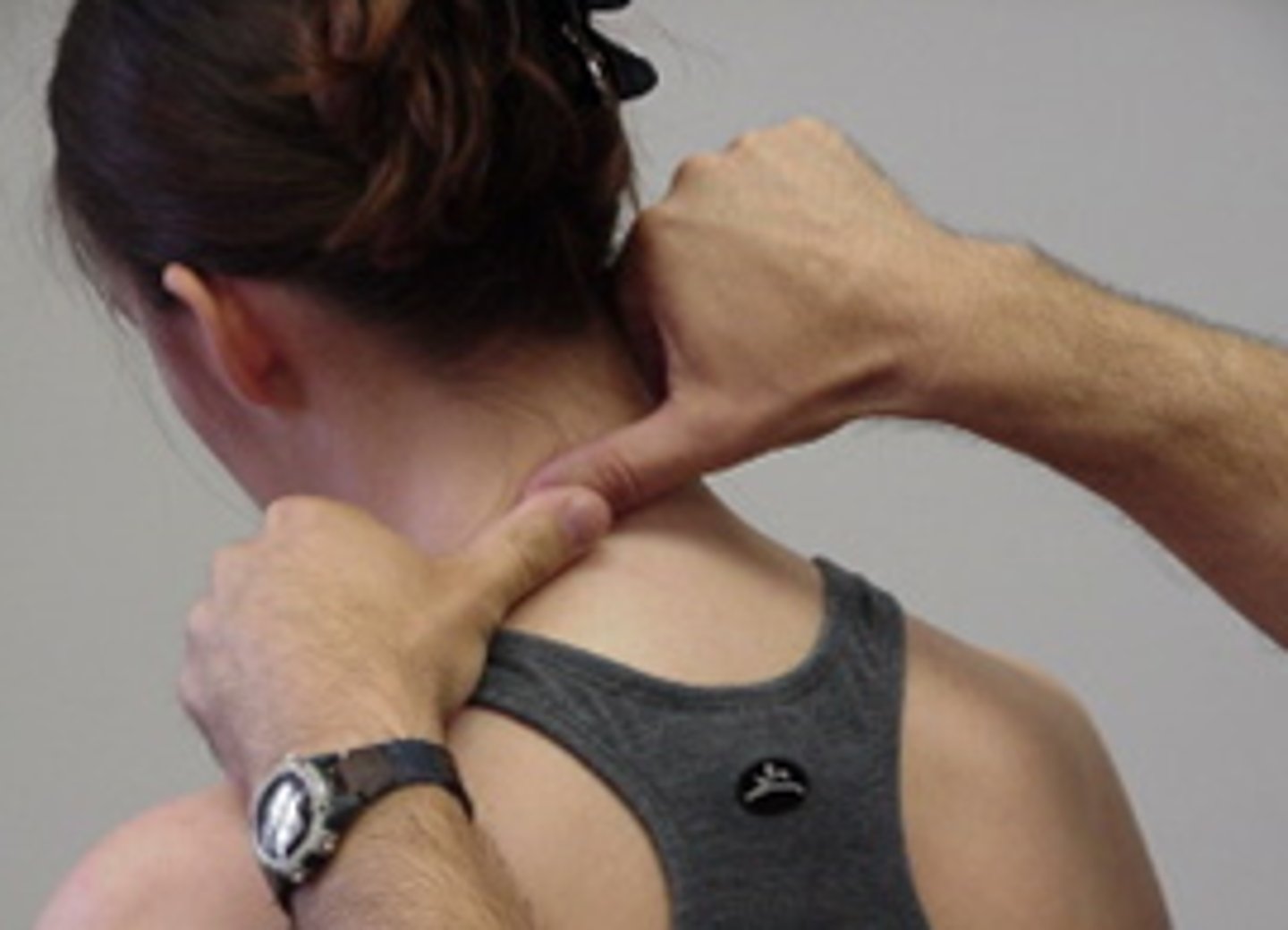
SNAG for extension (using SP)
SNAGS - cervical techniques:
use edge of thumb on articular columns of target vertebra
force is imparted with thumb of other hand
aim along facet planes throughout the movement
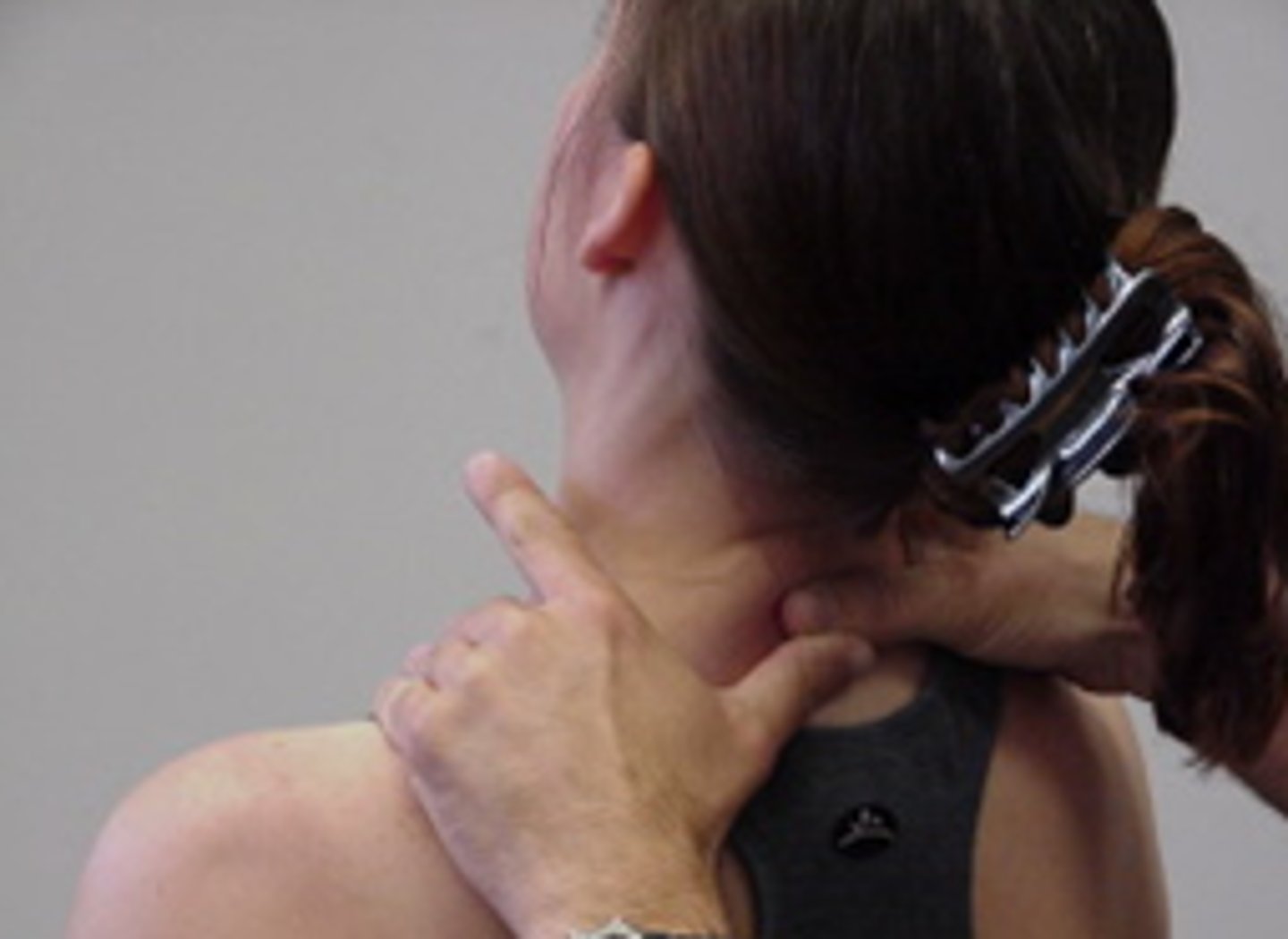
SNAG for rotation (bilateral)
SNAGS - cervical techniques:
alternate technique (usually more comfortable)
need to push anteriorly first to take up slack in soft tissues or won't be able to glide upwards
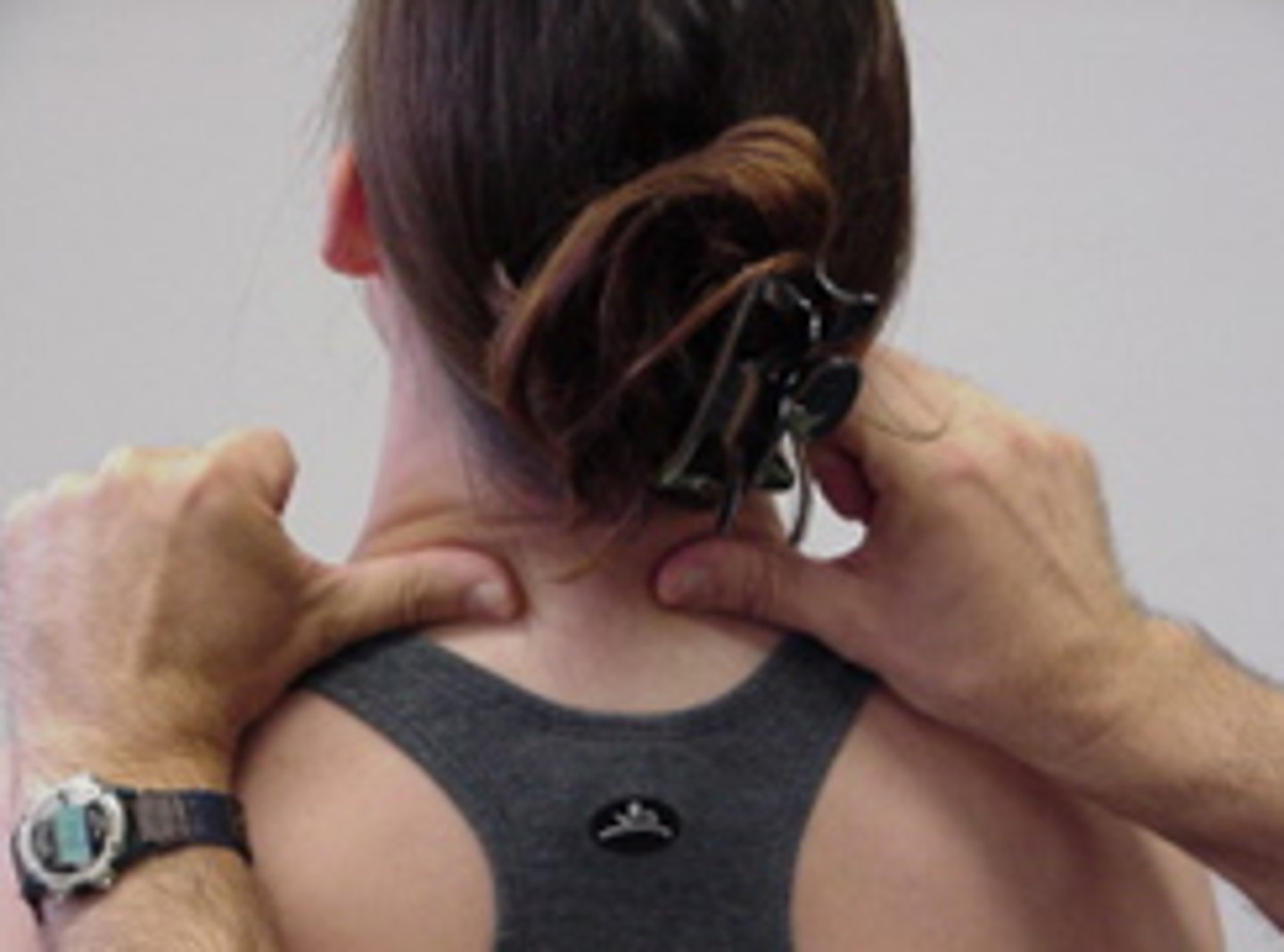
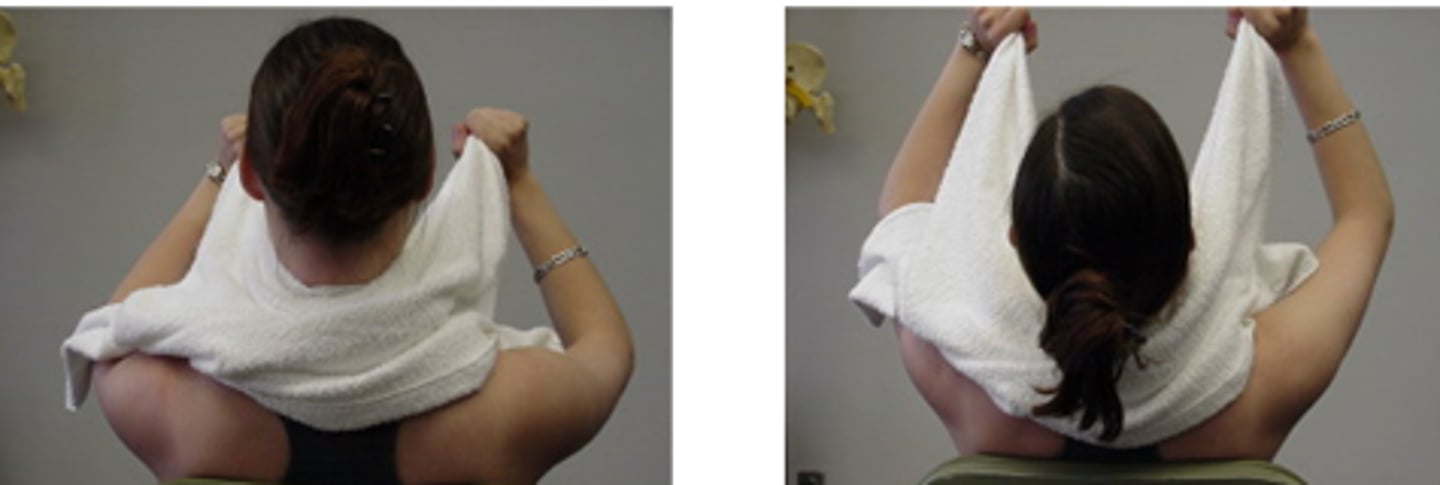
self-SNAG for rotation
SNAGS - self-techniques:
cross hands, with lower arm around chair back if possible to provide better fixation
upper hand aims towel edge along facet plane
Pt mut follow movement with upper arm
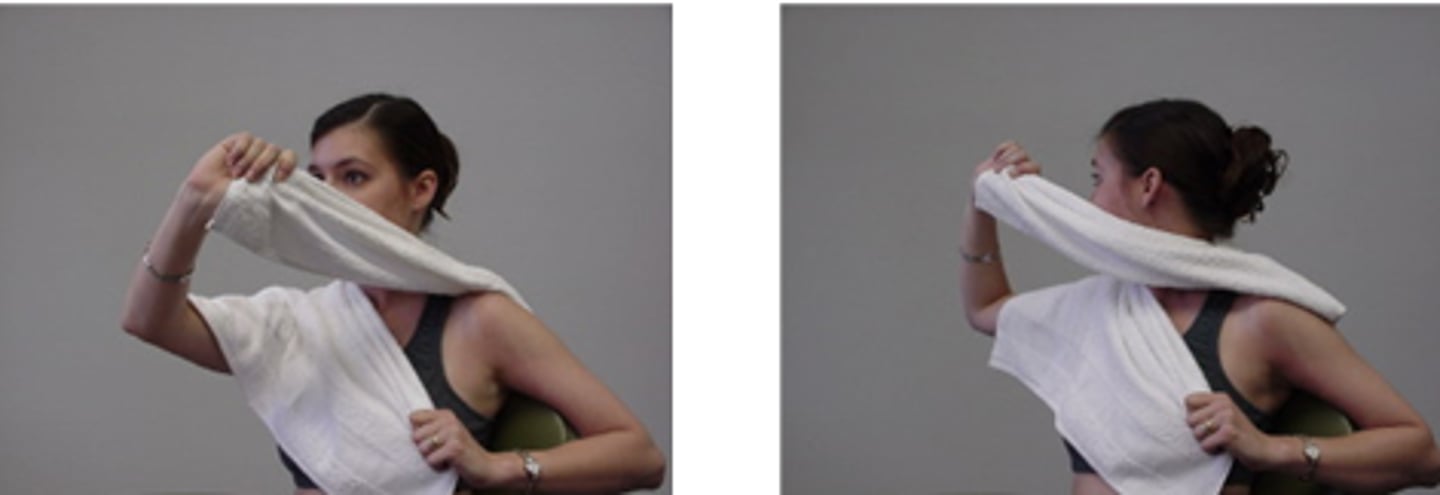
self-SNAG for extension
SNAGS - self-techniques:
edge of towel around target (lower) vertebra
Pt must raise arms to follow changing facet planes as they extend into pain free range
this is home exercise for Pts with ext block