Multiple Linear Regression
1/19
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
20 Terms
Limitations of MLR
conclusion & inferences made only valid for the data range used
Cant make causation statements (X causes Y)
High R² doesn’t guarantee it will be good fit for other data
R²
measures fit of regression line into the data
higher value shows large portion of variability in dependent variable
Standardized data
data than can be transformed to have a mean of 0 and a SD of 1 for each variable
Slope
shows increase change of y for one unit increase in x
Regression vs. residual
regression is a method used to find line of best fit (it is the line of best fit
residual is the distance of data pt from regression line
Coefficient table variables
Unstandardized Coefficient (B): shows that increase of 1 unit of the independent variable is equal to the B increase of dependent variable
Standardized Coefficient (β): shows 1 SD increase of indep. variable is equal to B SD increase of dep. variable
higher β = stronger effect
0.7 - 1+ β value is strong effect
Significant (p < ): shows statistical significant at lvl
R
represents correlation coefficient
shows strength & direction of linear relationship btenwee 2 variables
Durbin Watson
detects autocorrelation in the residuals of the linear regression model
examines if a residual is correlated with the previous residual
goes from 0-4, with 2 showing zero correlation
close to 2 - no correlation
2+ = positive autocorrelation (residuals similar over time)
2- = negative autocorrelation (residuals switch signs)
Pearson correlation
Tells strength and direction of linear relationship between 2 variables (-1, 0, 1+)
Simple linear regression equation to solve for mean
Y^= b0 + b1 * X
x = independent variable (waist circumference)
b0 and b 1= dependent variable points (fasting glucose)
Between Group Differences
Looking at differences between stuff
ex: one species of penguin heavier than others
other specie penguin have longer flippers
visual differences affects results (cant treat all penguins the same)
If differences are only in intercepts (start same with effect staying same across groups) the species is included as a main effect
If differences are also in slopes (effect changes depending on species) interaction term is added for moderaton
Within Group Differences
When relationship not same for each species, one line can’t be used for the species
different line for each species with intercept & own slope
“species moderate the relationship”: species changes the affect of variable
within group differences are the fuel as even with one type, the species is different
Multiple Linear Regression
Model to predict the value of 1 variable from another
used to predict values of an outcome from several predictors
Equation of the variation of a straight line
y = b0 +b1 * x
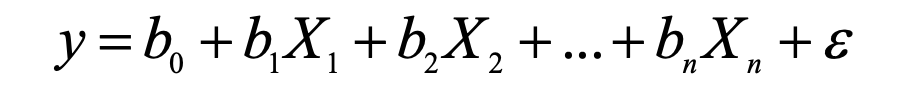
MLR Assumptions
Linear relationship between dependent & independent variables
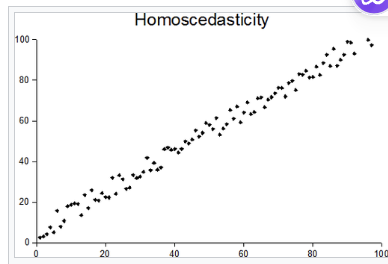
Homoscedasticity is assumed (spread of the data stays same at every lvl of independent variable)
data pts follow trend with same variance
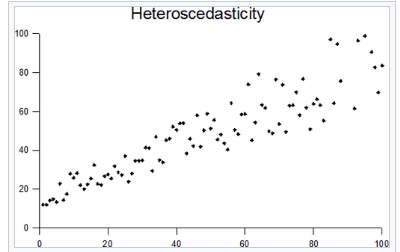
Heteroscedasticity
Data pts in mlr shows variance of y value of dots increase as x values increase
data points start getting more spread out but with same pattern
Collinearity
In a mlr where 2 or more predictors (independent) variables are highly linear related
1 variable can be almost perfectly predicted from another variable
Predictors in MLR
they are the independent variables (can be multiple like age, sex, etc.)
Multicollinearity
When predictors aren’t exactly, but highly, linearly related
Variance inflation factor (VIF)
Shows how much variance is inflated due to multicollinearity
VIF = 1 = no correlation with other vairables
VIF = 1 - 5 = moderate correlation
VIF > 5-10 = potential multicollinearity issues