Chapter 2: The Chemistry of Life
1/151
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Merged flashcards from Chapter 2, McGraw Hill Anatomy and Physiology Ninth Edition, by Kenneth S. Saladin.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
152 Terms
Organic chemistry
The study of compounds containing carbon
Carbon molecule categories
Carbohydrates, lipids, proteins, and nucleic acids
Properties of carbon
Has four valence electrons to bind with each other and other atoms, can make groups with a carbon backbone
Macromolecules
Large organic molecules with high molecular weights
Polymers
Macromolecules made of a series of identical subunits called monomers (e.g. starch → 3000 glucose monomers)
Polymerization
Joining monomers to form a polymer
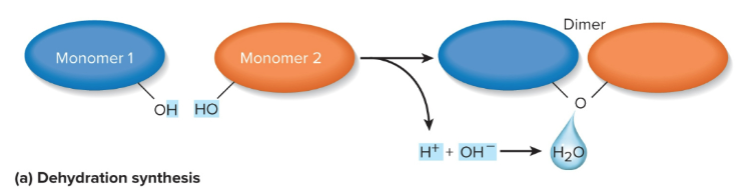
Dehydration synthesis
Covalently binding monomers to form a polymer; where OH and H groups are removed to make water as a byproduct
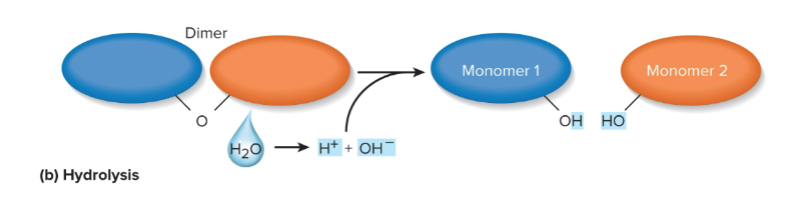
Hydrolysis
Splitting polymers into monomers with water; where OH and H groups are added to monomers that are broken through enzymes
Carbohydrates
Hydrophilic, organic molecules like sugars and starches that are converted to glucose and oxidized to make ATP; with a formula of (CH2O)n where n = number of carbon atoms
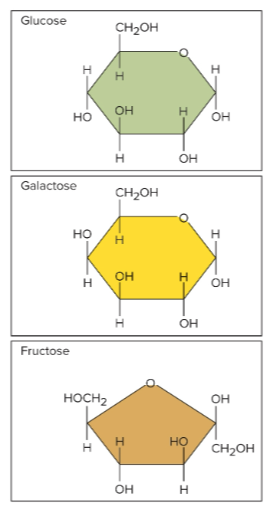
Monosaccharides
The simplest carbohydrates, they are monomers
Glucose, galactose, and fructose
The three important monosaccharides that are produced by digesting more complex carbohydrates; they are all isomers of each other with the formula C6H12O6
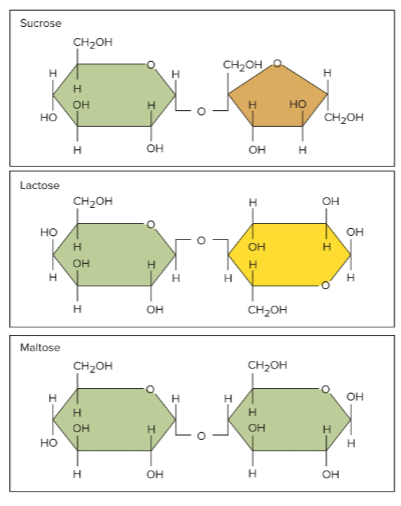
Disaccharides
Sugars made up of two covalently bonded monosaccharides
Sucrose (table sugar)
A disaccharide made up of glucose and fructose
Lactose (milk sugar)
A disaccharide made up of glucose and galactose
Maltose (sugar in grain)
A disaccharide made up of glucose and glucose together
Oligosaccharides
Short chains of three or more monosaccharides (at least 10); ____saccharides → a few
Polysaccharides
Long chains of monosaccharides (at least 50); ____saccharides → many
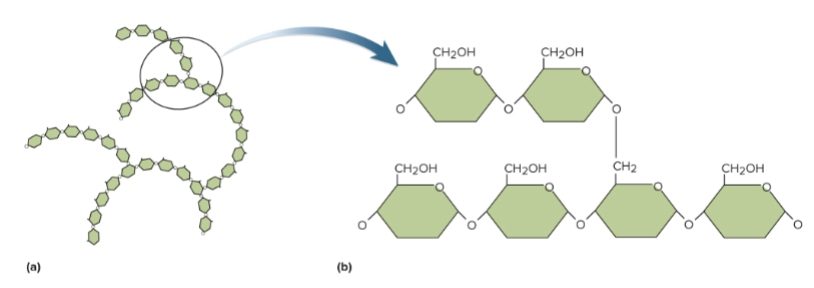
Glycogen
A polysaccharide that stores dense energy in the liver, muscles, and brain
Starch
Energy storage in plants that is digestable by humans
Cellulose
Structural molecule in plants that is important for dietary fiber but indigestible to us
Glycolipids and glycoproteins
Carbohydrates that are conjugated with lipids or proteins, where chains of sugars attach to these molecules
Proteoglycans
Gels that hold cells and tissues together and fill the umbilical cord and eye, and lubricates joints
More carbohydrate than protein
Lipids
Hydrophobic, organic molecules with a high ratio of hydrogen to oxygen - more calories per gram than carbohydrates
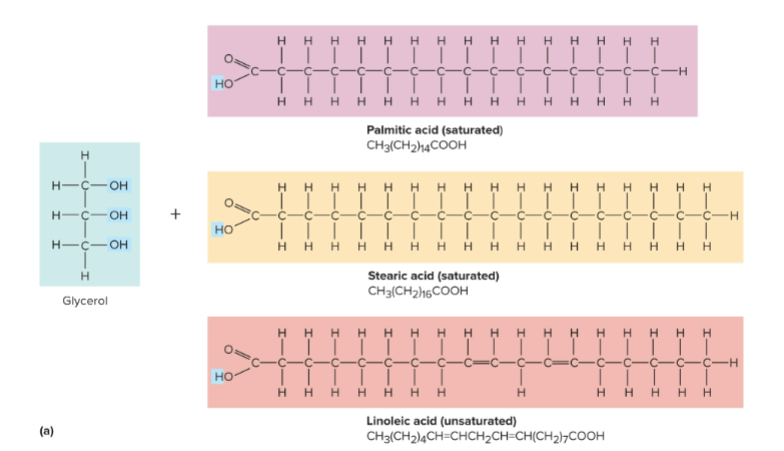
Fatty acids
Chains of 4-24 carbon atoms with a carboxyl and methyl group on the ends; they are obtained from food
Saturated fatty acids
Fatty acids with carbon atoms linked by single covalent bonds; “saturated” with as much hydrogen as possible
Unsaturated fatty acids
Carbon atoms linked by some double covalent bonds, has potential to add hydrogen
Polyunsaturated fatty acids
An unsaturated fatty acid with multiple double bonds between carbons
Triglycerides
Fatty acids linked to glycerol which store energy and help shock absorption
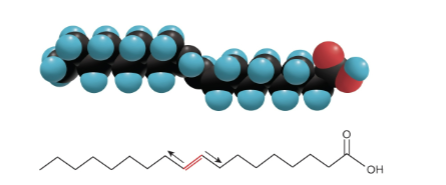
Trans-fatty acids
Fatty acids with two covalent C - C bonds in opposites on each side of the C = C double bond; they resist enzymatic breakdown in the body and deposit in the arteries
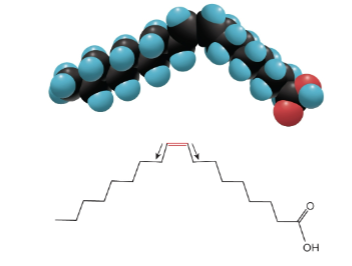
Cis-fatty acids
Fatty acids with two covalent C - C bonds in the same direction adjacent to the C = C double bond
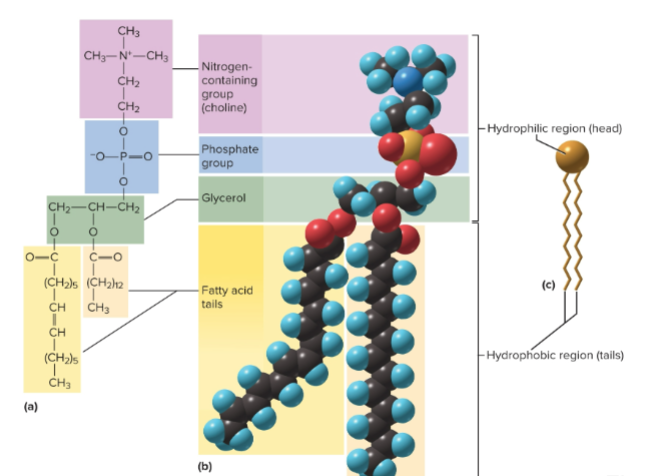
Phospholipids
Similar to neutral fats, but one fatty acid is replaced by a phosphate group - the tails are hydrophobic, while the phosphate head is hydrophilic; making them good for cell membranes
Eicosanoids
20-carbon compounds derived from arachidonic acids; they send hormone-like signals between cells and include prostaglandins which plays an important role in inflammation
Steroids
Type of lipid with 17 carbon atoms in four rings
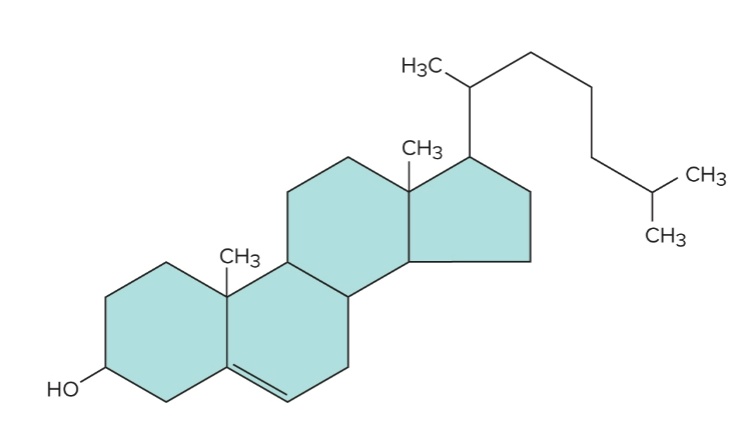
Cholesterol
The “parent” steroid from which other steroids are synthesized, they are important for nervous system function and cell membranes
High-density lipoproteins (HDLs)
“Good cholesterol,” has a lower ratio of lipid to protein and may prevent cardiovascular disease
Low-density lipoproteins (LDLs)
“Bad cholesterol,” has a lower ratio of protein to lipids and contributes to cardiovascular disease
Proteins
Polymers of amino acids, they are peptides with more than 50 amino acids
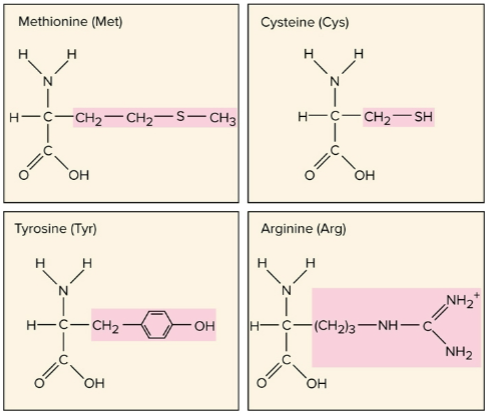
Amino acids
A carbon with amino (-NH2), carboxyl (-COOH), and radical (R) attachments; the R group determines the properties of this
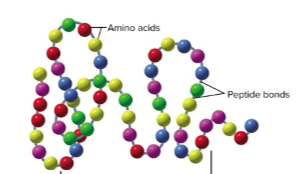
Peptide
Two or more amino acids joined by peptide bonds
Peptide bonds
Joins the amino and carboxyl groups of two amino acids through dehydration synthesis
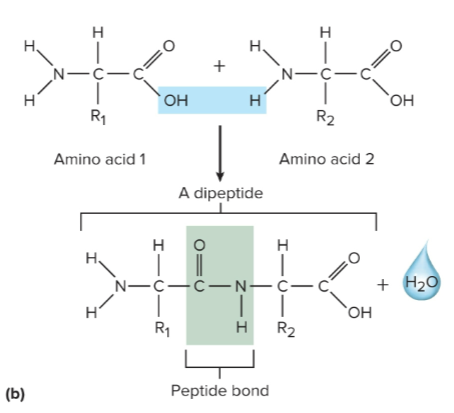
Dipeptides
A peptide with 2 amino acids
Tripeptides
A peptide with 3 amino acids
Oligopeptides
A peptide with between 3 and 15 amino acids
Polypeptides
A peptide with between 15 and 50 amino acids
Conformation
A unique, three dimensional shape of protein crucial to function; these are reversible to affect change
Denaturation
Extreme conformational change that destroys function; extreme heat or pH can cause permanent this
Primary structure
Structure comprised of a sequence of amino acids within a protein molecule; it is encoded by genes
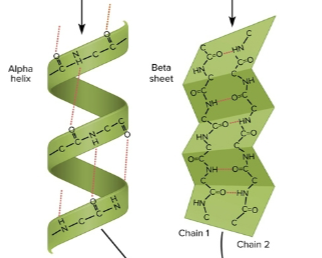
Secondary structure
Coiled or folded shape held together by slight hydrogen bonds between C = O and N - H
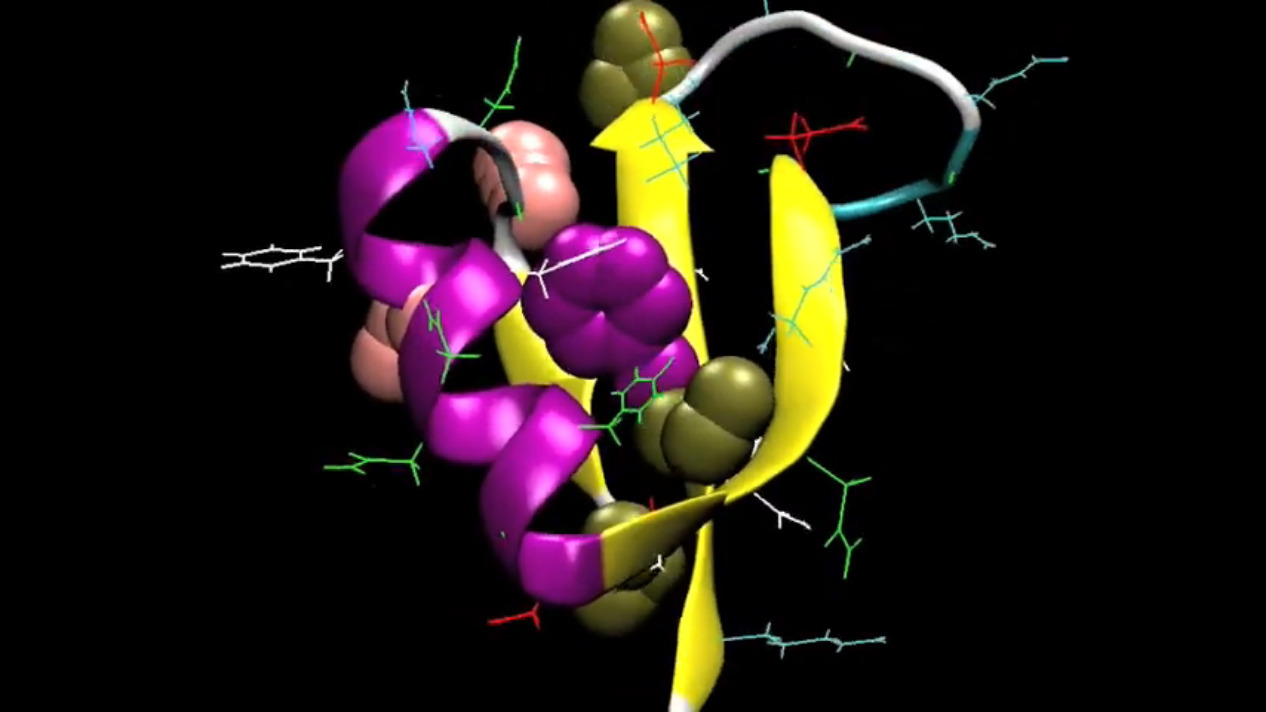
Tertiary structure
A structure made by further bending and folding of proteins into globular and fibrous shapes due to hydrophobic-hydrophilic interactions and van der Waals forces
Globular proteins
Proteins in a compact tertiary structure within the cell membrane and can move freely in body fluids
Fibrous proteins
Slender filaments suited for roles in muscle contraction and strengthening of skin and hair
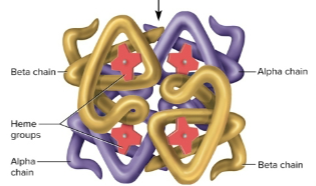
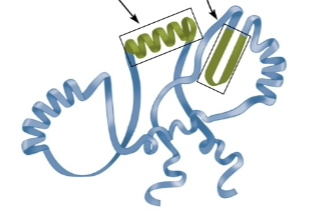
Quaternary structure
Structures comprised of two or more polypeptide chains due to ionic bonds and hydrophobic-hydrophilic interactions
Keratin
Tough structural protein of hair, nails, and skin surface
Collagen
Contained in deeper layers of skin, bones, cartilage, and teeth
Membrane transport
Diffusion of hydrophilic substances across cell membranes through protein channels
Enzymes
Proteins that function as biological catalysts to lower overall activation energy
They are named for the substrate with -ase as the suffix (e.g. lactase catalyzes the hydrolysis of lactose)
Substrate
The substance an enzyme acts upon
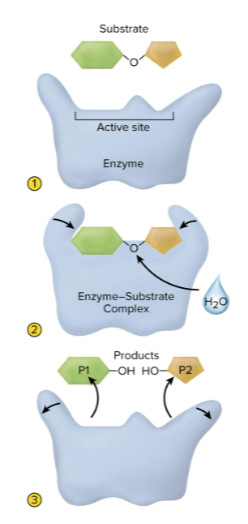
Steps to enzyme action
The substrate binds to the active site
The molecules form an enzyme-substrate complex
The enzyme releases reaction products
The enzyme repeats the process, as it is reusable
Optimal enzyme factors
Temperatures and pH (e.g. stomach vs salivary enzymes)
Cofactors
Non-protein “helper” molecules which are necessary for enzymatic functioning; includes minerals like iron, copper, zinc, and calcium
Coenzyme
Organic cofactors derived from vitamins (e.g. NAD+ which is derived from niacin and aids metabolism)
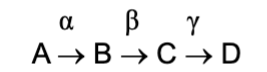
Metabolic pathway
The chain in which a reactant is modified by different enzymes to get an end product; the enzymes for each step are represented by Greek letters
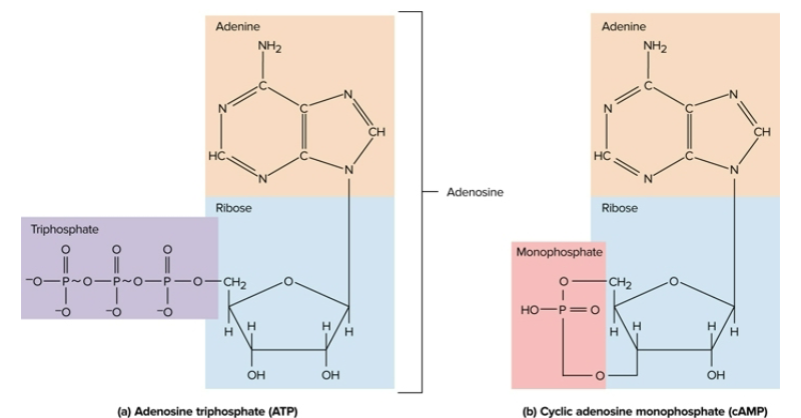
Nucleotides
Organic compounds with a nitrogenous base, sugar, and a phosphate group; examples include ATP and cAMP
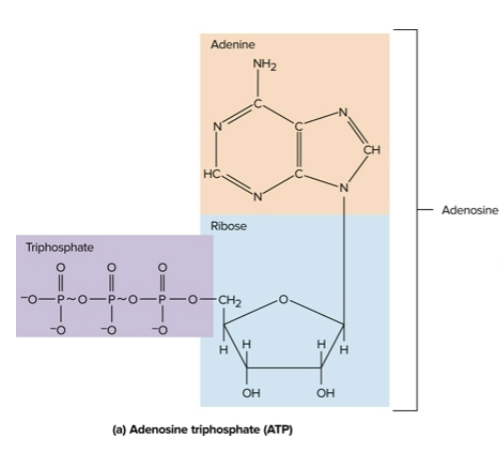
Adenosine triphosphate (ATP)
The body’s most important energy-transfer molecule; holds energy in covalent bonds between phosphates
Nucleic acids
Polymers of nucleotides; includes DNA for protein synthesis and RNA for genetic instructions
Energy
The capacity to do work; all body activities are work
Potential energy
Energy stored in an object but not currently doing work (e.g. water behind a dam)
Chemical energy
Potential energy in molecular bonds
Free energy
Potential energy available in a system to do useful work
Kinetic energy
The energy of motion which is doing work (e.g. water flowing through a dam)
Heat
The kinetic energy of molecular motion
Electromagnetic energy
The kinetic energy of moving packets of radiation called photons
Chemical reaction
Process in which a covalent or ionic bond is formed or broken
Chemical equation
Symbolizes the course of a chemical reaction; reactions on the left → products on the right
Decomposition reactions
Large molecule breaks down into two or more smaller ones; AB → A + B
Synthesis reactions
Two or more smaller molecules combine to form a larger one; A + B → AB
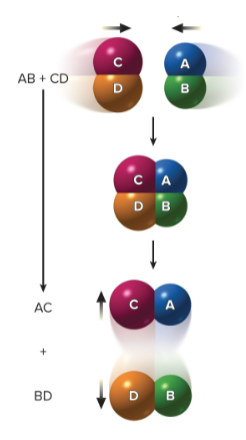
Exchange reactions
Two molecules exchange atoms or a group of atoms; AB + CD → ABCD → AC + BD
Reversible reactions
Reactions that can reverse under different circumstances; symbolized with a double-headed arrow
Law of mass action
Direction of reaction determined by relative abundance (quantity) of either side of equation
Increasing reaction rate causes
Rising temperature, concentrated reactants, catalysts like enzymes to lower the reaction energy
Metabolism
All chemical reactions of the body
Catabolism
Energy releasing (exergonic) decomposition reactions that break covalent bonds and produce smaller molecules
Anabolic reactions
Energy storing (endergonic) synthesis reactions that require energy input (e.g. production of fat)
Oxidation
A chemical reaction in which a molecule gives up electrons and releases energy
Reduction
Any chemical reaction in which a molecule gains electrons or energy
Oxidizing agent or reduced molecule
The molecule that accepts the electrons; oxygen is often the acceptor
Reducing agent or oxidized molecule
The molecule that donates electrons
Oxidation-reduction (redox) reactions
Oxidation of one molecule (giving away electrons) is always accompanied by reduction of another (gaining electrons); electrons are transferred as hydrogen atoms
Mixtures
Substances that are physically blended but not chemically combined; most are body fluids with water
Properties of water
Solvency, cohesion, adhesion, reactivity, thermal stability
Solvency
The ability to dissolve other chemicals; water is the universal this
Hydrophilic substances
Substances that dissolve in water; molecules that are this are polarized or charged (like sugar)
Hydrophobic
Substances that do not dissolve in water; molecules that are this are nonpolar or neutral (like fats)
Hydration spheres
Ionic bonds being overpowered by hydrogen bonds from water
Adhesion
The tendency of one substance to cling to another; water does this in membranes
Cohesion
The tendency of like molecules to cling to each other; water does this due to its hydrogen bonds and makes surface tension
Chemical reactivity
The ability to participate in chemical reactions; water does this into H+ and OH-
Heat capacity
The amount of heat needed to raise the temperature of 1 gram of a substance by 1 degree C
Calorie
The base unit of heat that raises the temperature of 1 gram of water by 1 degree C
Thermal stability
The ability to stabilize the temperature of its surroundings; water can absorb high levels of heat and remove calories