Immunology: B-cell biology
1/28
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
29 Terms
Mature B activation takes place where.…? B cells first develop where though?
secondary lymphoid organs
primary lymphoid organ (bone marrow specifically)
describe the process of B cell development in the bone marrow
start as stem cell
Pre-B cells complete heavy chain rearrangement using “surrogate” light chain
most fail and die
Immature B cells complete light chain rearrangement (kappa or lambda) and express IgM on surface.
checkpoint for self-reaction (most fail and die)
Mature B cells express BOTH IgM and IgD
leave bone marrow and migrate to secondary lymphoid organs.
capable of being activated by antigen to proliferate (clonal expansion) and become plasma and memory cells
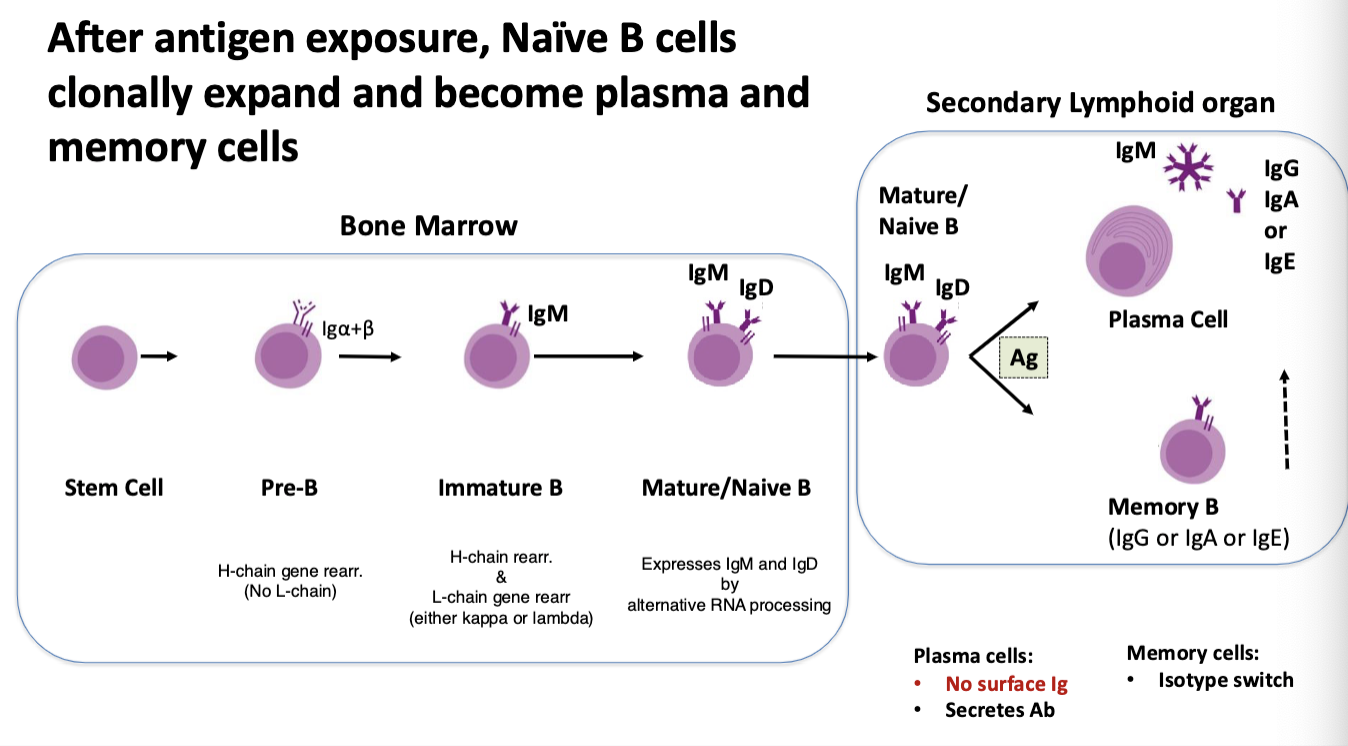
what are B cells that have been activated by antigen and synthesize large amounts of antibody?
plasma cells
what are long-lived B cells that result from the antigen-activation and clonal expansion of B cells?
memory cells
Memory B cells have usually undergone…? and express BCR consisting of which antibodies?
class switch recombination (class switching)
IgG or IgA or IgE.
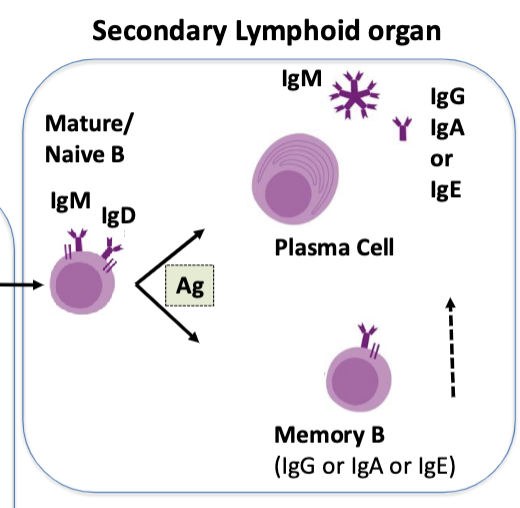
explain the concept of negative selection.
A B lineage cell that creates a self-reactive BCR and binds to self-Ag will undergo apoptosis in the bone marrow and will not continue development.
Important for preventing autoimmunity!
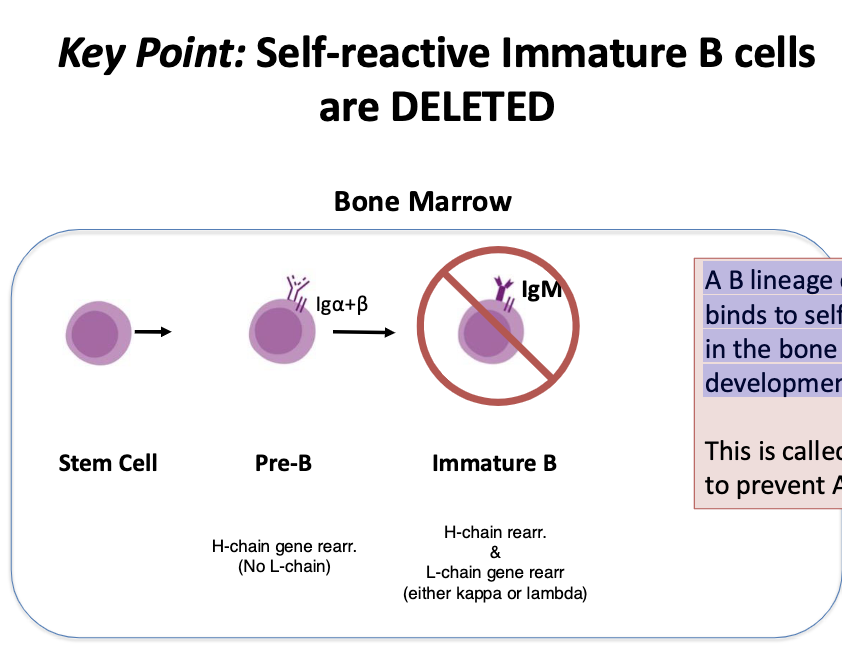
t/f: most developing B cells are self-reactive and are deleted!
true
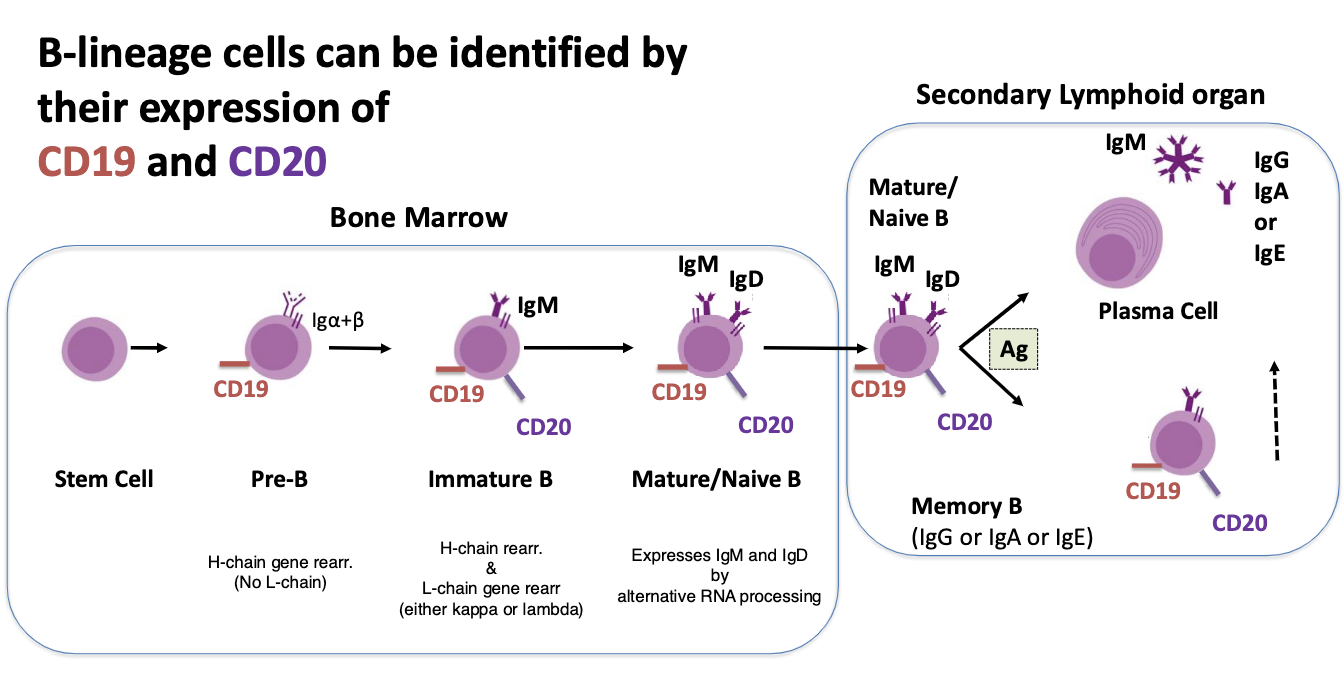
B-lineage cells can be identified by their expression of
CD19 and CD20
what type of immunity is immunization (vaccination)?
artificial active
what is active immunity?
response to an antigen
what is passive immunity?
transfer of pre-formed antibody from person to person
whay type of immunity is infection with pathogen?
natural active
what type of immunity is maternal IgG passed through placenta/milk?
natural passive
what type of immunity is injection of pre-formed immune globulin?
artificial passive
Antibodies that a person makes to an antigen are MONOCLONAL/POLYCLONAL. What does this mean?
POLYCLONAL
This means that many different B cell clones were activated and produce antibody specific for the antigen
It is possible to make MONOCLONAL/POLYCLONAL antibodies produced by cells grown in the laboratory.
MONOCLONAL
Thousands of such monoclonal antibodies (mAbs) are now available commercially and are used extensively in diagnostic medicine (and in home pregnancy tests)
The cancer multiple myeloma results from…?
one plasma cell becoming neoplastic. The uncontrolled proliferation of this single plasma cell results in a high concentration of a monoclonal antibody in the patient
what is a polyclonal antibody?
Antibodies made by plasma cells derived from many different B cell clones and recognizing multiple epitopes
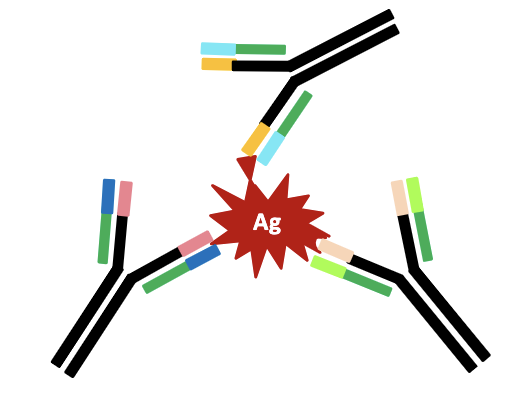
what is a monoclonal antibody?
All antibodies are from plasma cells derived from a single B cell. A MAb consists of identical antibodies that wrecognize the same epitope.
what is intravenous immunoglobulin (IVIG) used for?
prepared from pooled sera from 1000-10,000 donors (tons of antibodies for everything)
used as treatment for providing passive humoral immunity for those who can’t make it themselves
patients come in every 4 weeks (half-life of antibodies)
FDA approved uses for IVIG include providing passive humoral immunity for the treatment of what groups?
Primary humoral immunodeficiency diseases
Children with HIV
IVIG is also used to treat certain autoimmune and inflammatory diseases. However, the mechanism of the immunomodulatory effects of IVIG are not well understood.
what’s an example of Ig preparations with high titers for specific pathogens can also be used to provide passive humoral immunity? these are prepared using what?
Rabies immune globulin (RIG) is an Ig preparation for rabies virus prophylaxis.
Prepared using sera from donors who are immune to a particular pathogen.
what are examples of passive immunity and consist of polyclonal antibodies?
Intravenous Ig (IVIG) and rabies immune globulin (RIG)
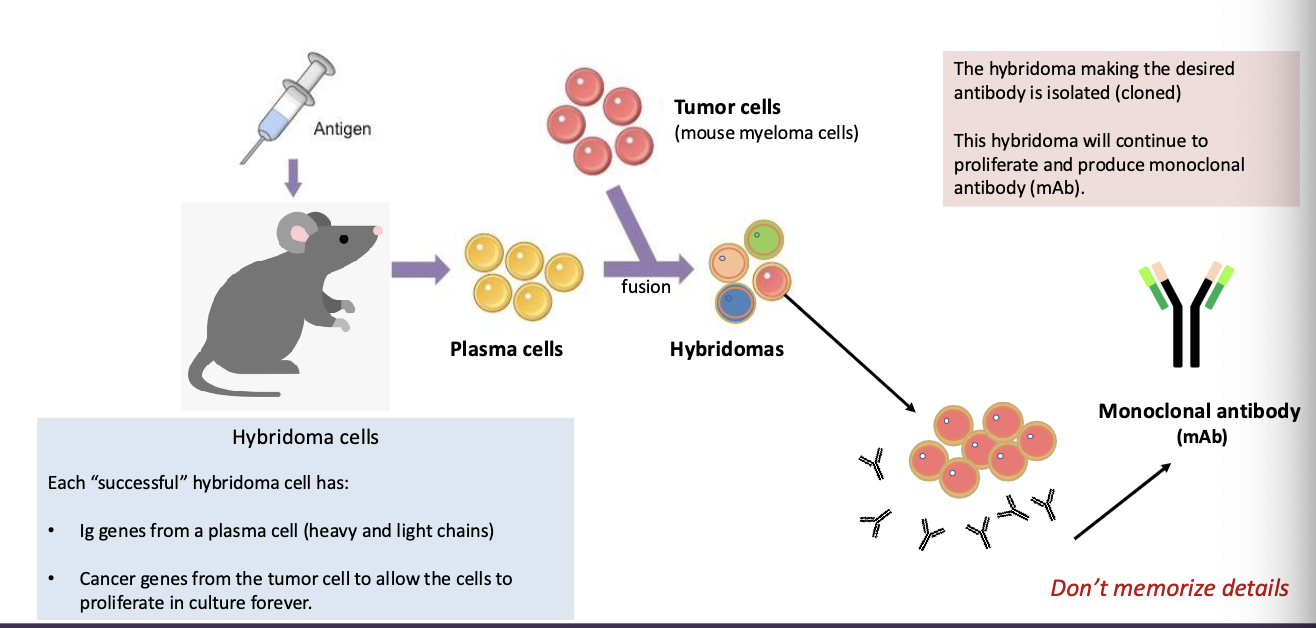
what is the key to making monoclonal antibodies in a lab?
hybridomas (fusion of plasma and tumor cells that make desired antibody)
Ig genes from plasma + cancer gene allows indefinite proliferation to produce monoclonal antibody (mAb)
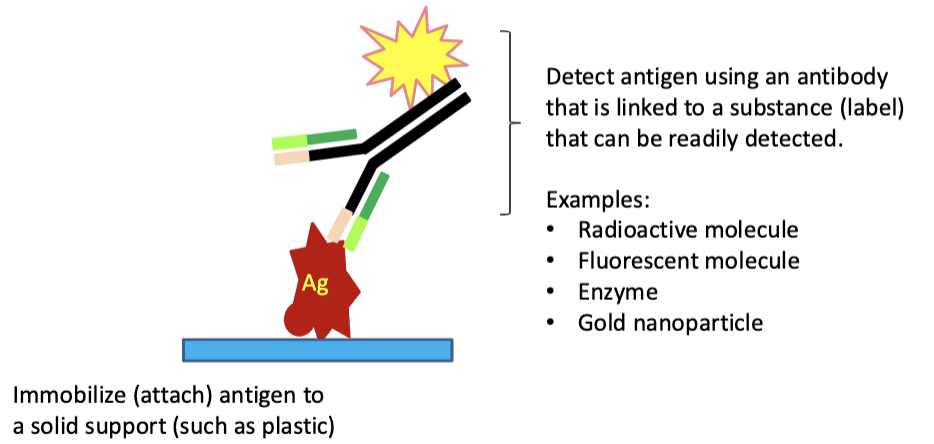
mAbs can be used for?
to detect and quantify antigen
(COVID-19 antigen test uses anti-SARS-CoV2 mAbs)
why are mouse monoclonal antibodies not useful as drugs for humans?
because humans will produce human anti-mouse antibodies (HAMA)
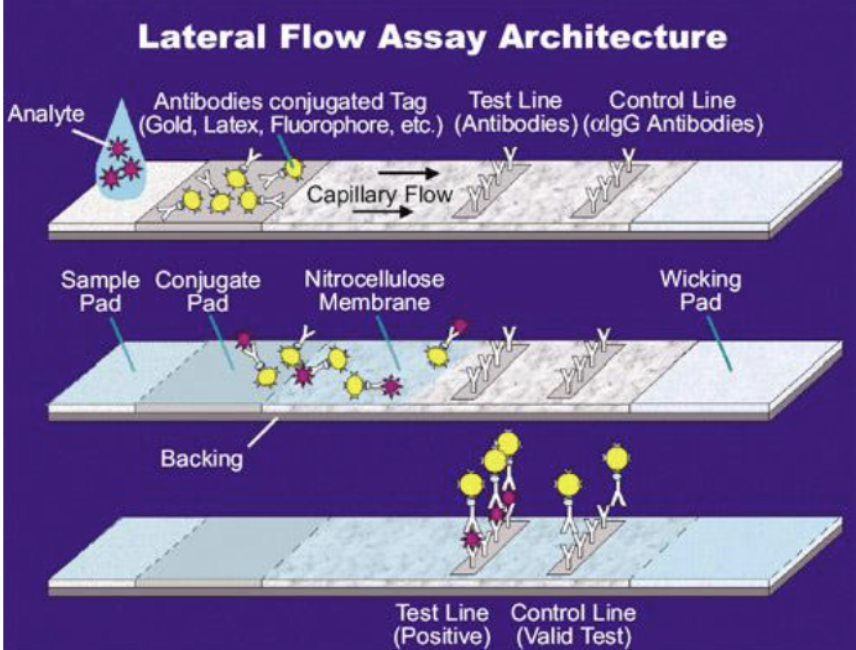
how does a lateral flow assay work?
mAb to viral epitope #1 captures the antigen (if present)
mAb to viral epitope #2 is labeled with an indicator molecule (gold nanoparticle)
test line shows positive when viral antigen is present
control line captures excess labeled antibody
if there’s no antigen present, mAb to antibody will bind the mAb with indicator molecule
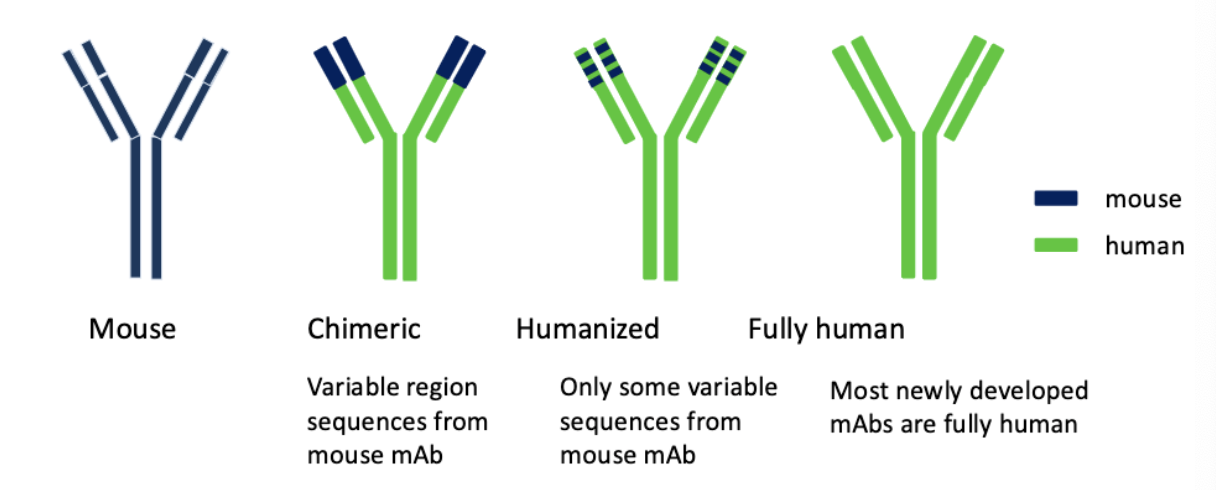
what can be done to therapeutic monoclonal antibodies derived from a mouse to be useful for humans?
often engineered as chimeric or humanized antibodies to reduce immunogenicity
what’s an important example of FDA approved therapeutic mAbs?
Nirsevimab (Beyfortes, anti-RSV) → RSV prophylactic for newborns