Ocular Anatomy and Embryology in Pediatric Optometry
1/87
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
88 Terms
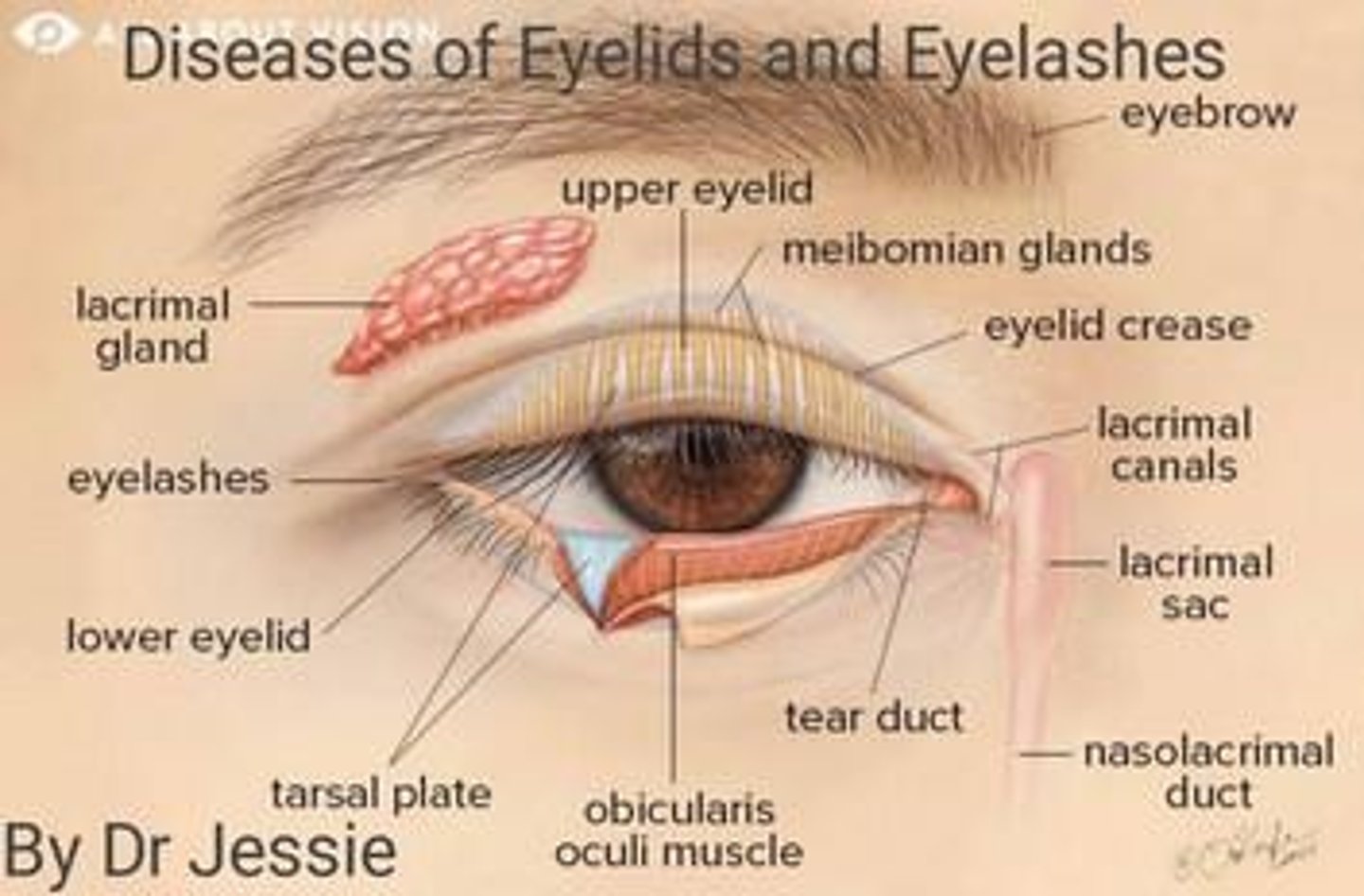
Eyelid
The fold of skin that covers and protects the eye, playing a crucial role in maintaining moisture and removing debris.
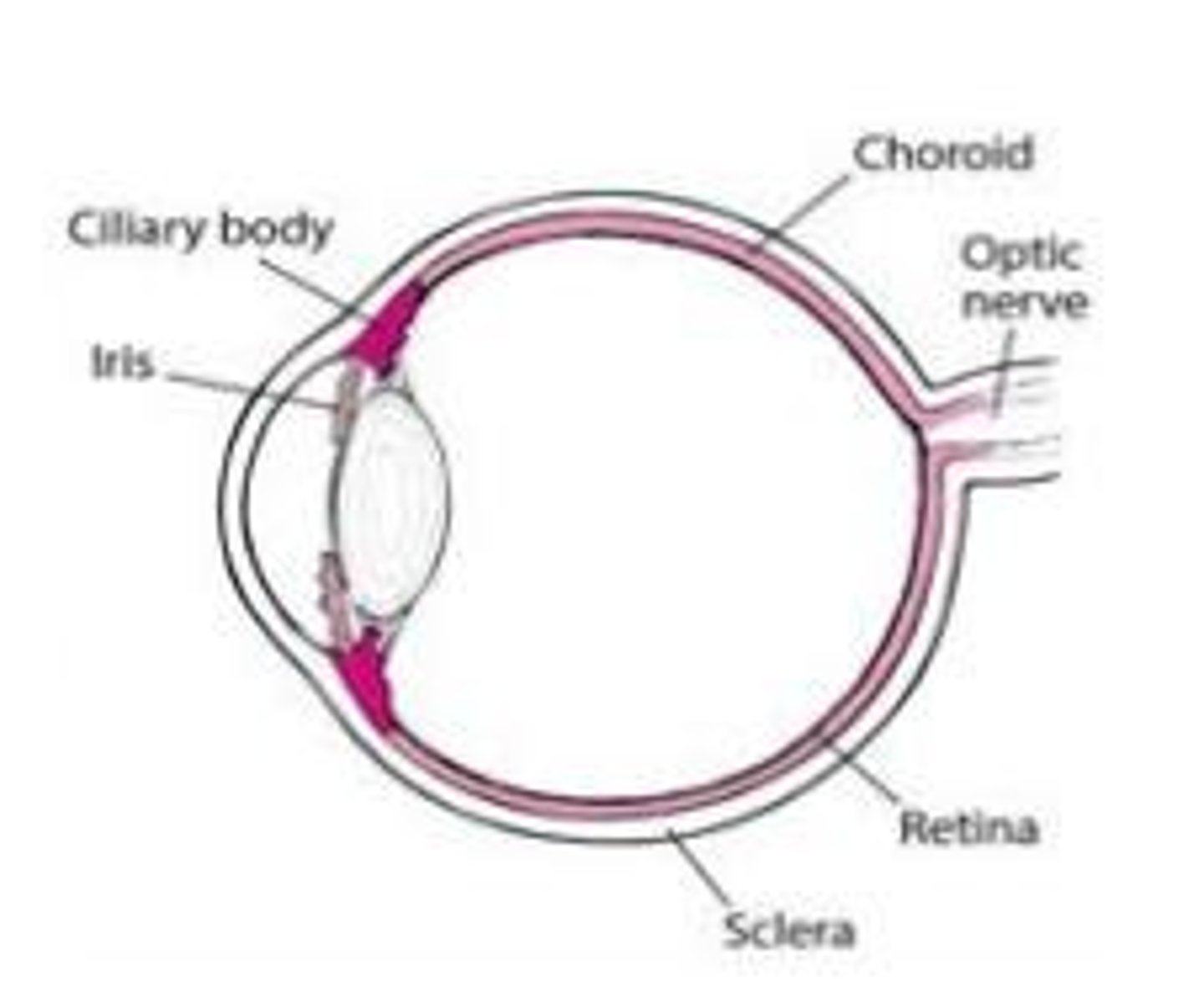
Ciliary Body
A structure in the eye that produces aqueous humor and contains the muscles that control the shape of the lens.
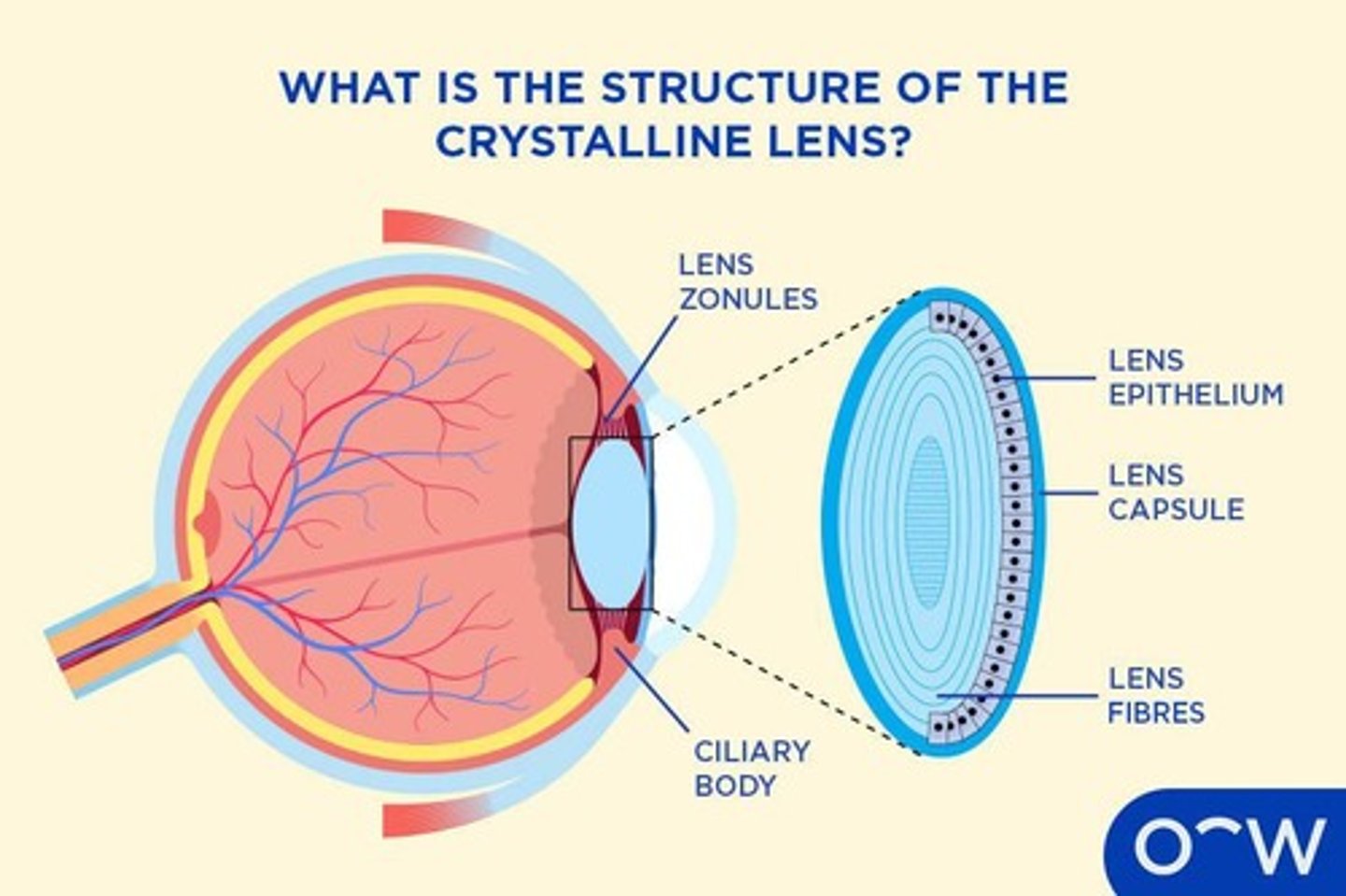
Lens
A transparent structure in the eye that focuses light onto the retina, allowing for clear vision.
Choroid
The vascular layer of the eye between the retina and the sclera, providing nourishment to the outer layers of the retina.
Retina
The light-sensitive layer at the back of the eye that converts light into neural signals for vision.
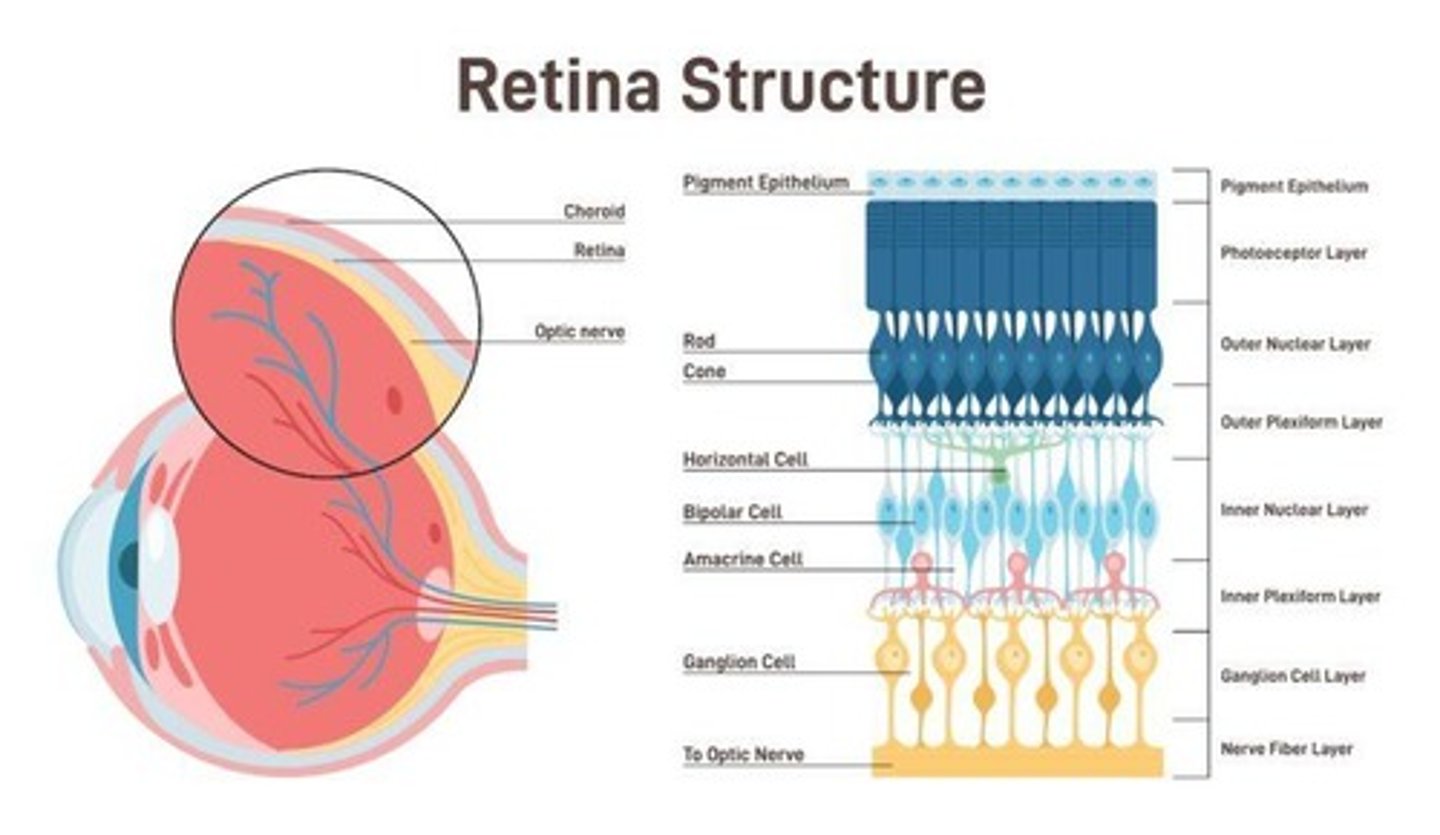
Sclera
The white outer coating of the eyeball, providing structure and protection to the inner components of the eye.
Cornea
The clear, dome-shaped surface that covers the front of the eye, playing a key role in focusing light.
Iris
The colored part of the eye that controls the size of the pupil and thus the amount of light entering the eye.
Pupil
The opening in the center of the iris that allows light to enter the eye.
Ectoderm
The outermost layer of the three primary germ layers in the embryo, which contributes to the formation of the nervous system and skin.
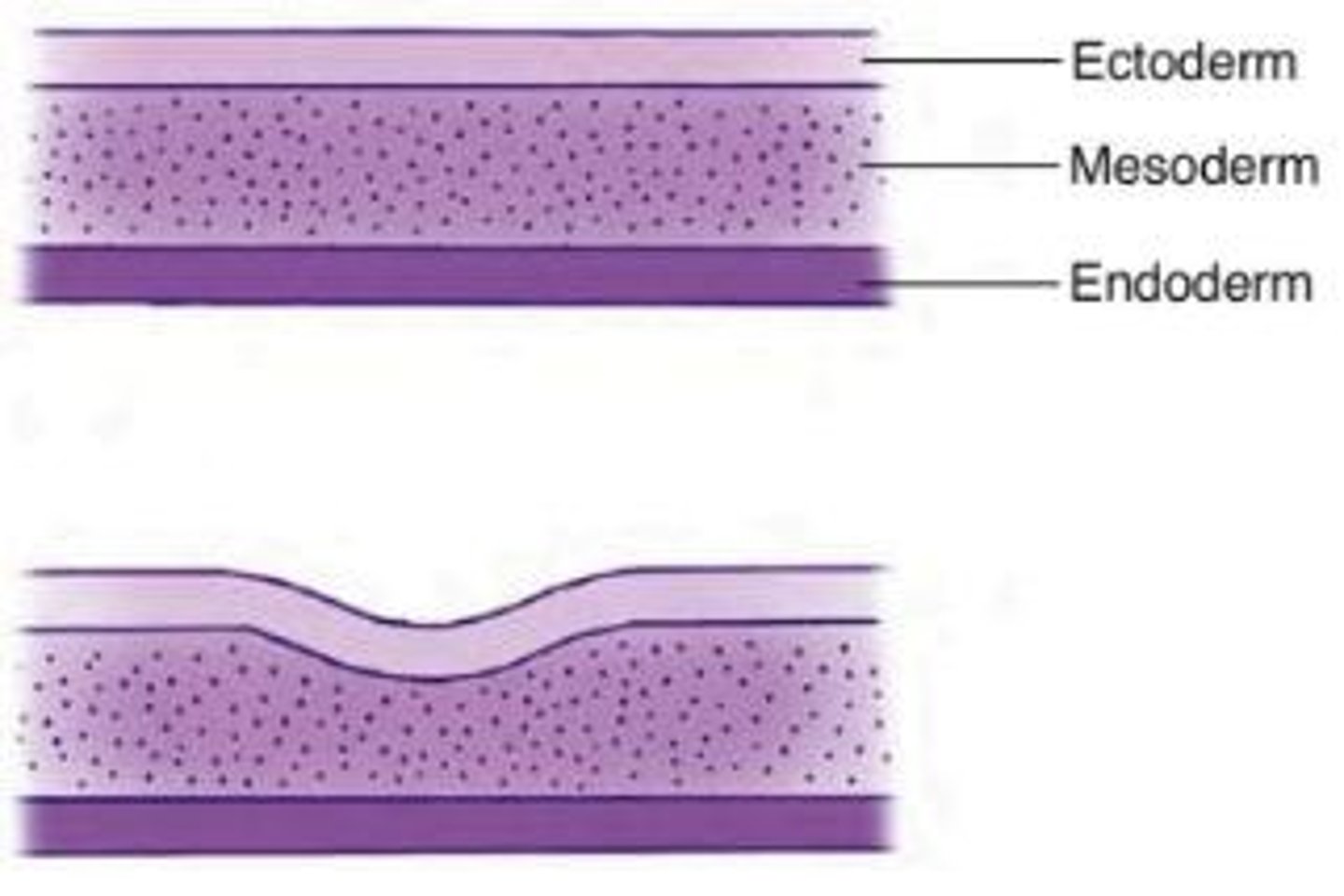
Mesoderm
The middle layer of the three primary germ layers in the embryo, which develops into muscles, bones, and connective tissues.
Endoderm
The innermost layer of the three primary germ layers in the embryo, which forms internal organs and structures.
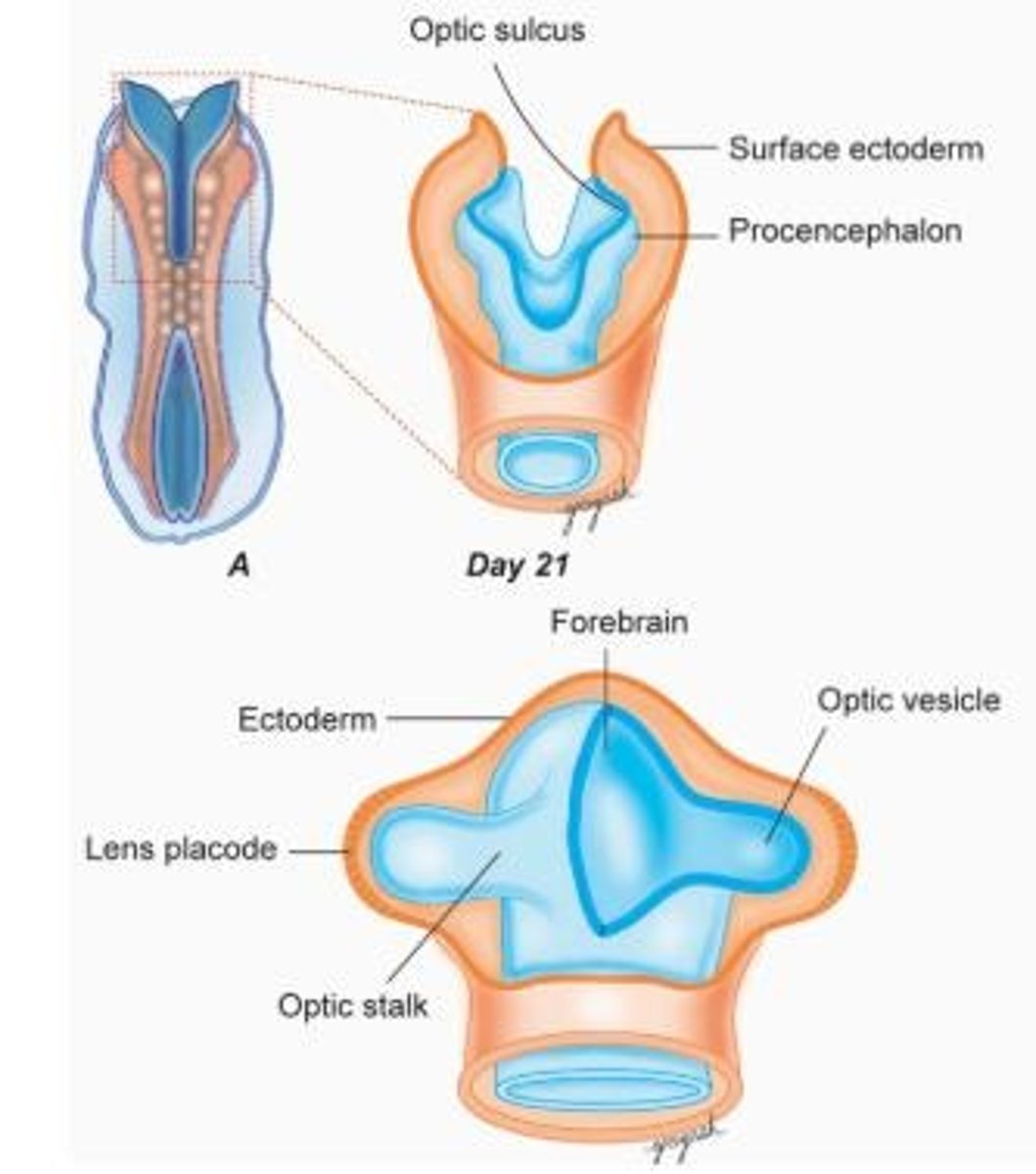
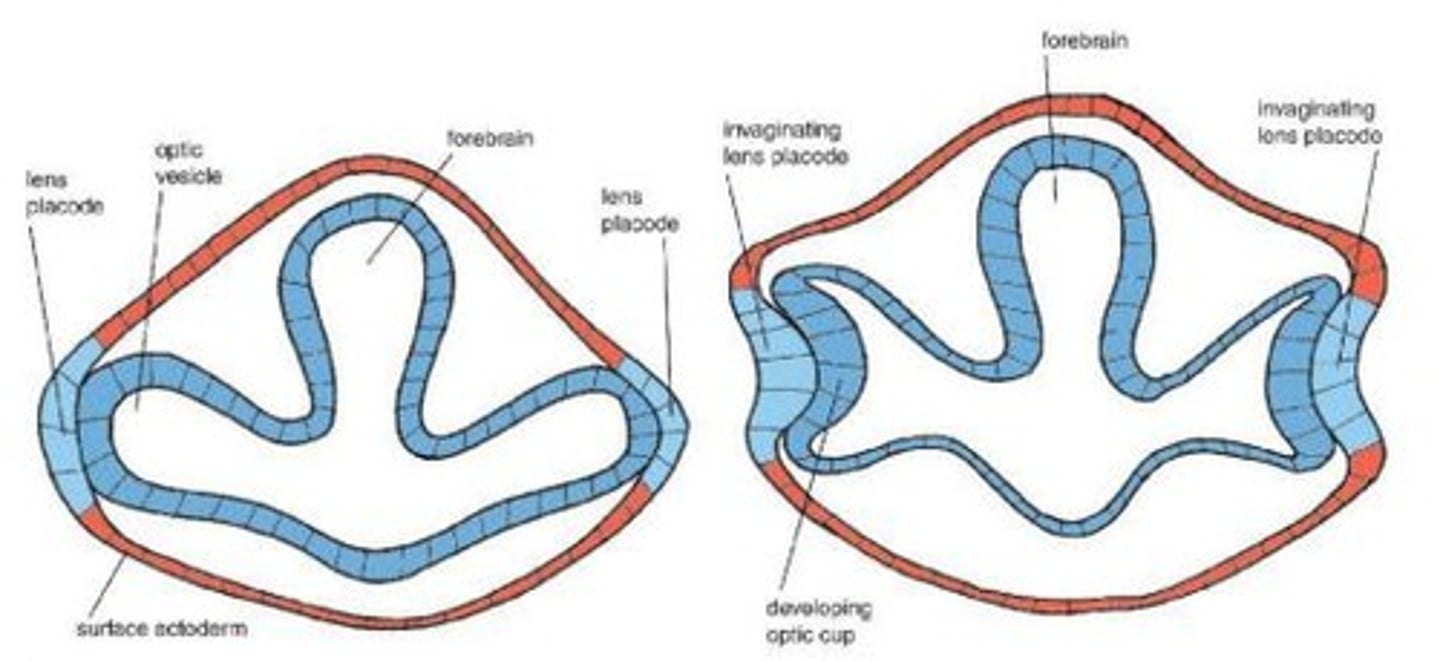
Optic Pits
Indentations in the forebrain that develop into optic vesicles, crucial for eye formation.
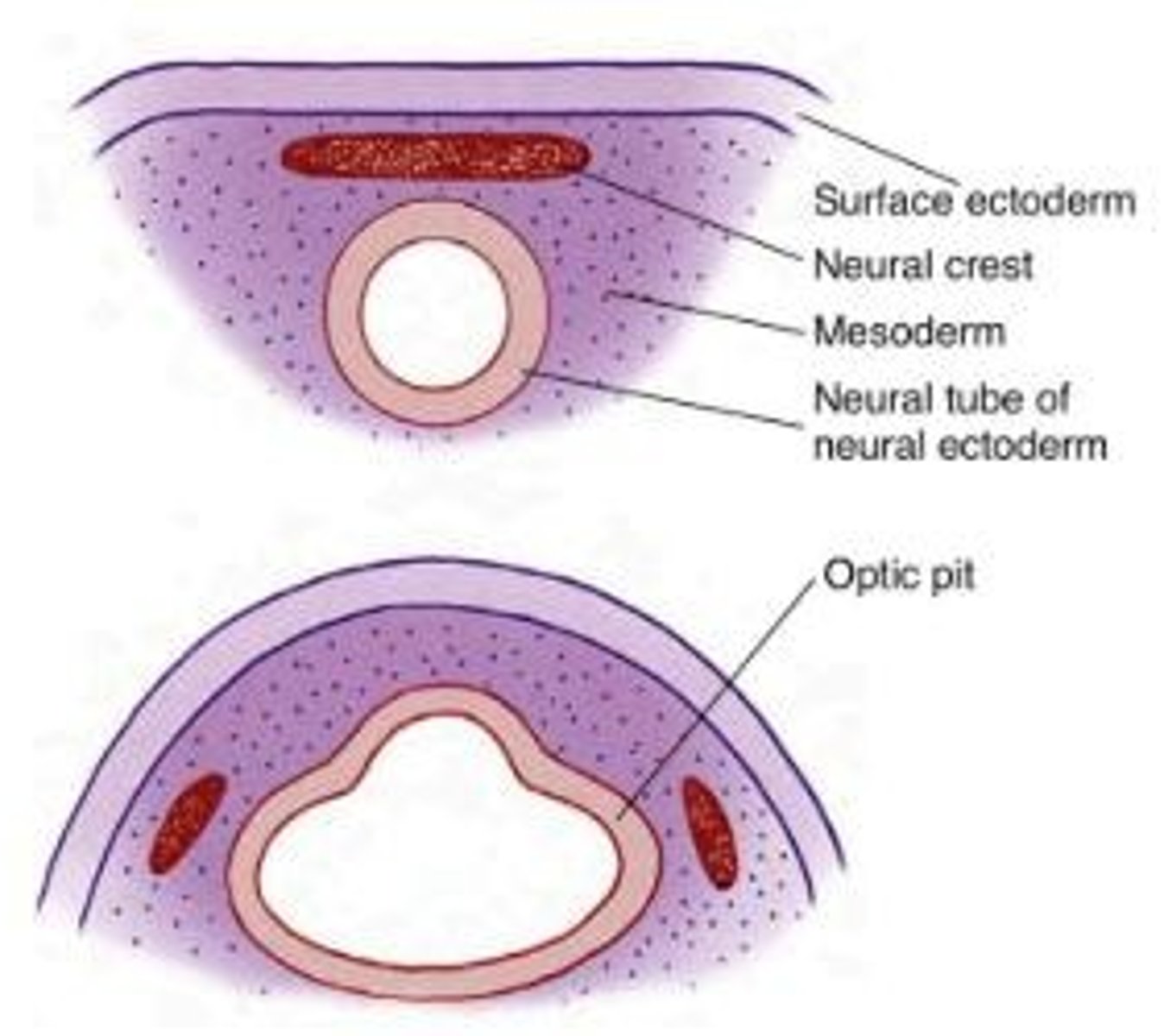
Optic Vesicles
Sac-shaped extensions that arise from the optic pits and give rise to structures in the eye.
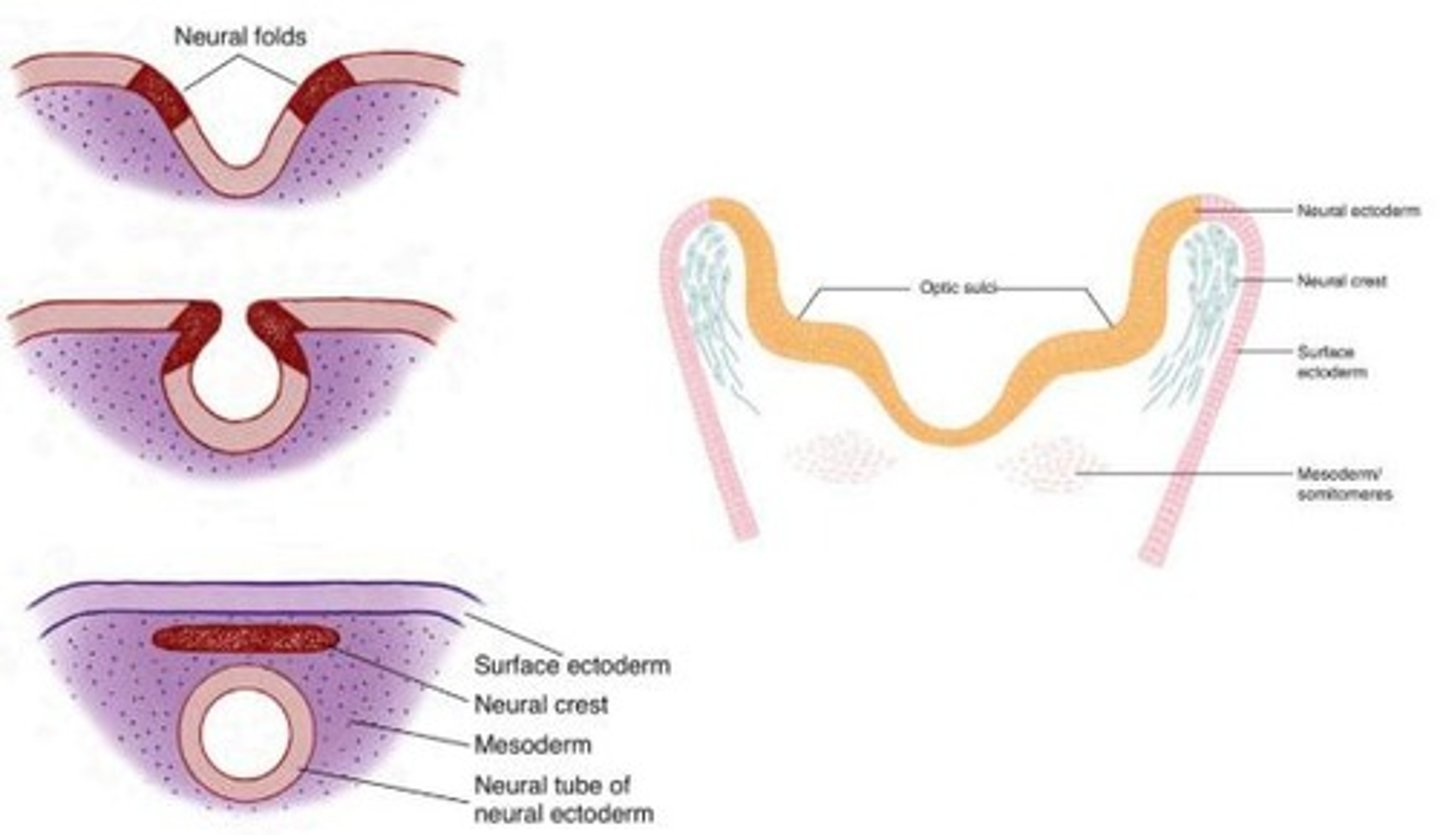
Neural Plate
A thickened region of ectoderm that forms the basis of the central nervous system, including ocular structures.
Neural Folds
The raised edges of the neural plate that eventually fuse to form the neural tube.
Neural Tube
The structure that develops from the neural plate and eventually forms the brain and spinal cord.
Mesenchyme
The loose connective tissue from which the connective tissues of the eye and orbit develop.
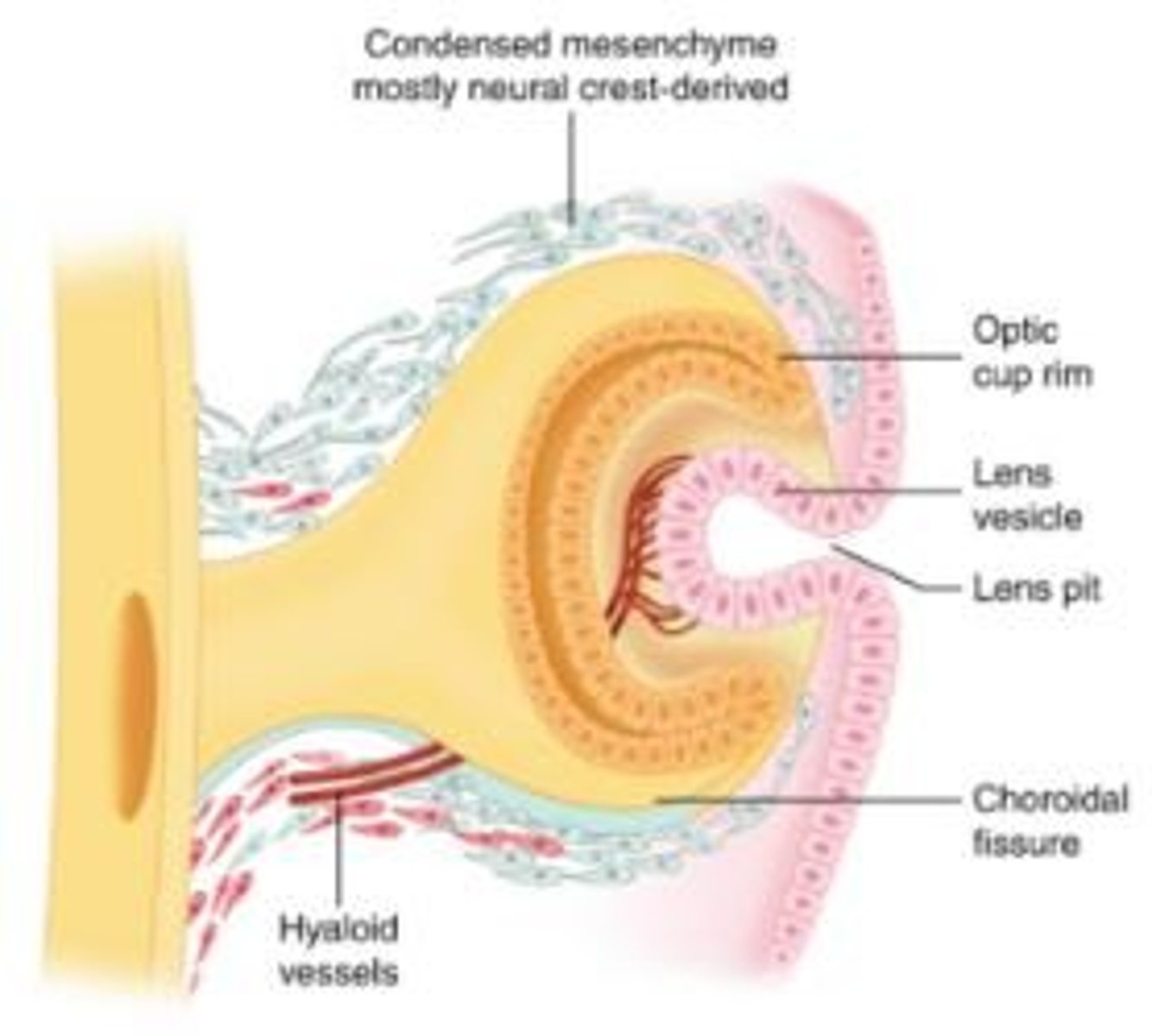
Neural Crest
Cells that separate from the neural folds and contribute to various structures, including parts of the eye.
Neural Ectoderm
The tissue that forms the neural tube, which gives rise to the central nervous system.
Surface Ectoderm
The outer layer of ectoderm that contributes to the formation of the lens and other ocular structures.
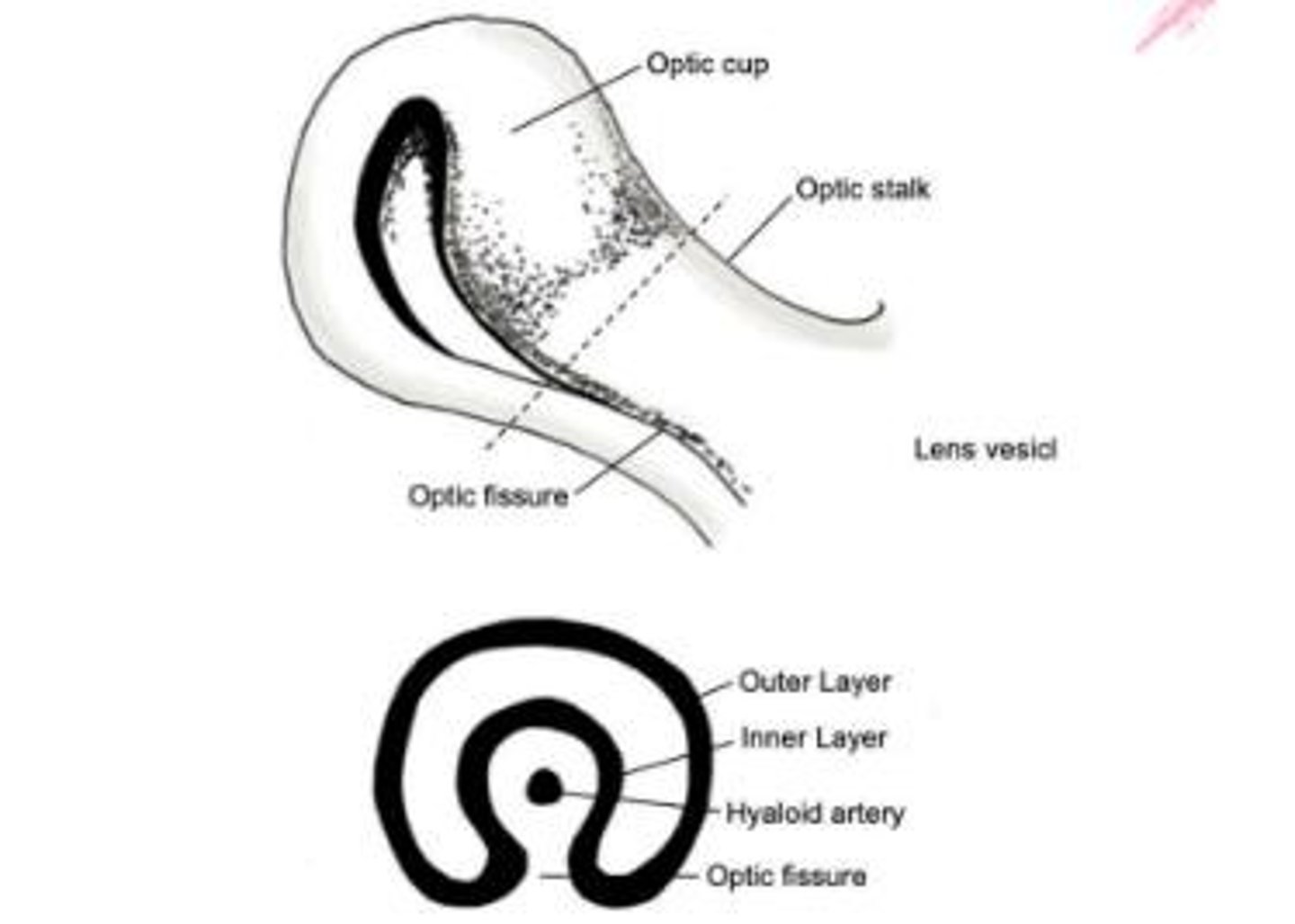
Optic Stalk
The structure that connects the optic vesicle to the neural tube, forming part of the developing eye.
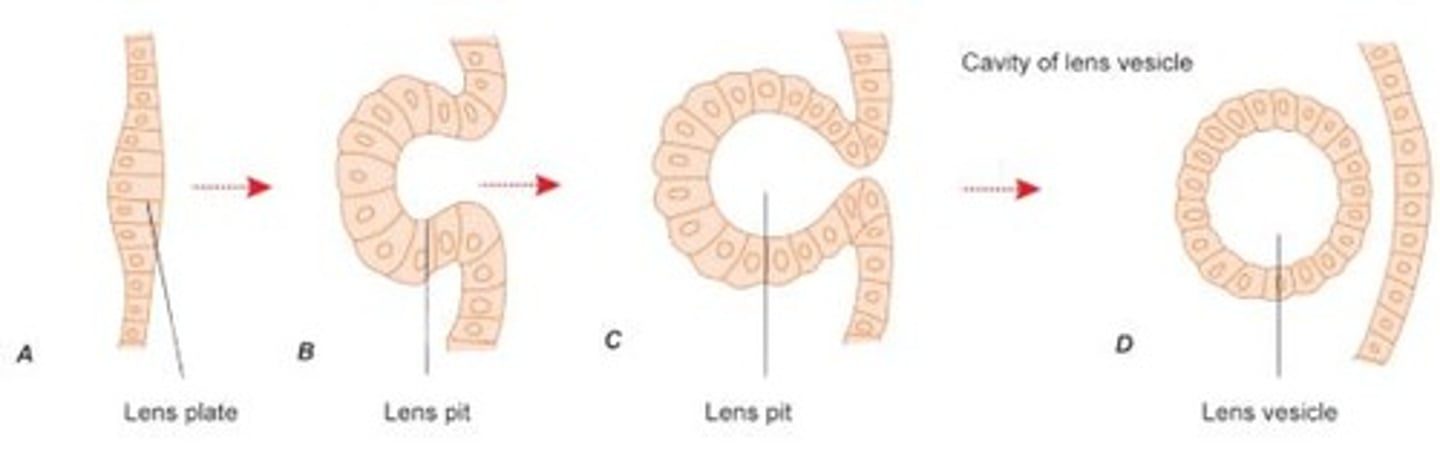
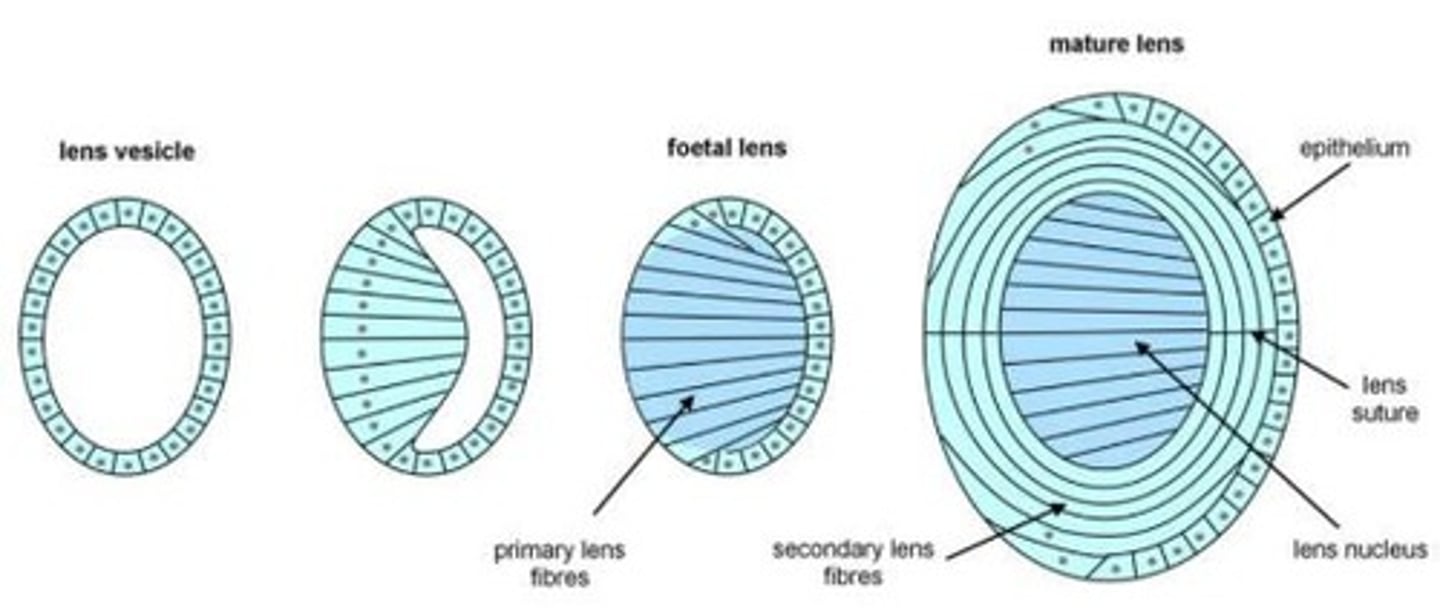
Lens Vesicle
A hollow sphere formed from the lens placode that eventually develops into the lens of the eye.
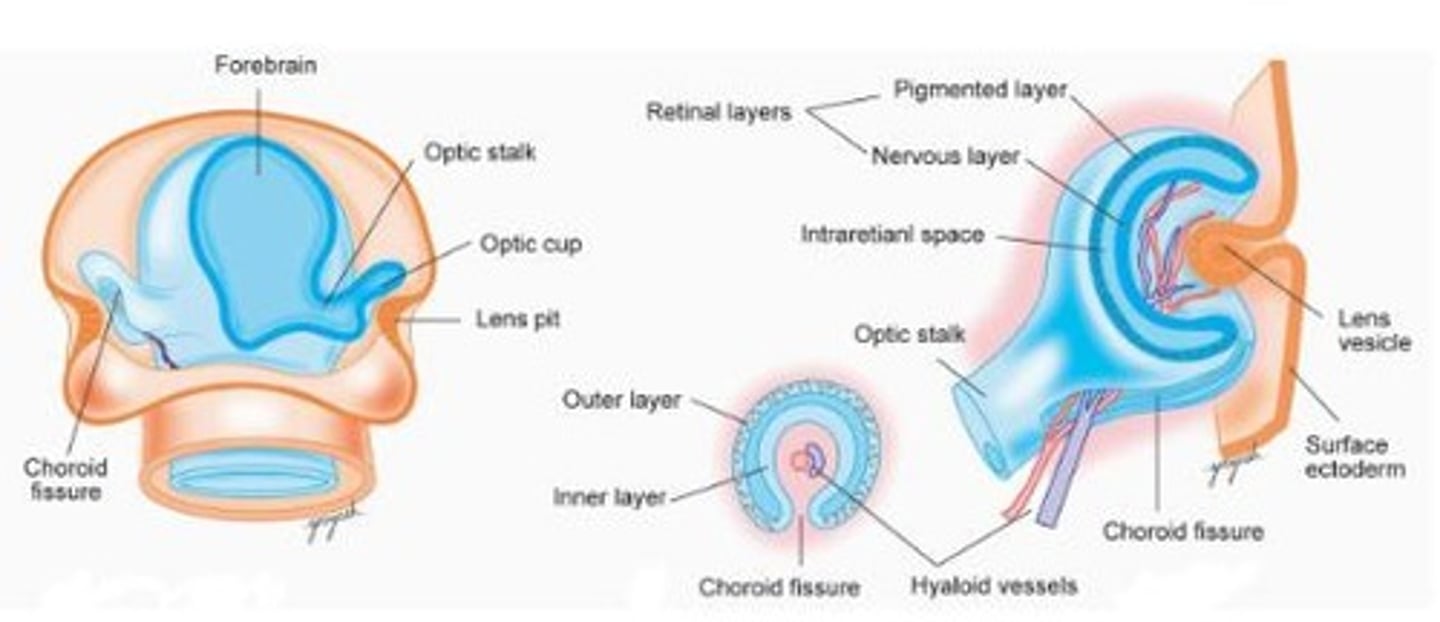
Optic Cup
A structure formed during embryonic development that gives rise to the retina and other parts of the eye.
Optic Fissure
A cleft formed during the development of the optic cup where mesenchyme enters to contribute to the formation of the eye.
Retinal Pigment Epithelium (RPE)
The outer layer of the retina that contains pigment cells and plays a crucial role in the health and function of the retina.
Neural Retina
The inner layer of the optic cup that develops into the neural tissue of the retina responsible for processing visual information.
Hyaloid Vasculature
A network of blood vessels that supplies nutrients to the developing lens and retina during embryonic development.
Anterior Iris Epithelium
The front layer of the iris that develops from the outer layer of the optic cup.
Ciliary Muscle
A muscle that controls the shape of the lens and is derived from neural crest cells during eye development.
Embryonic Nucleus
The central region of the lens formed by primary lens fibers during the early stages of lens development.
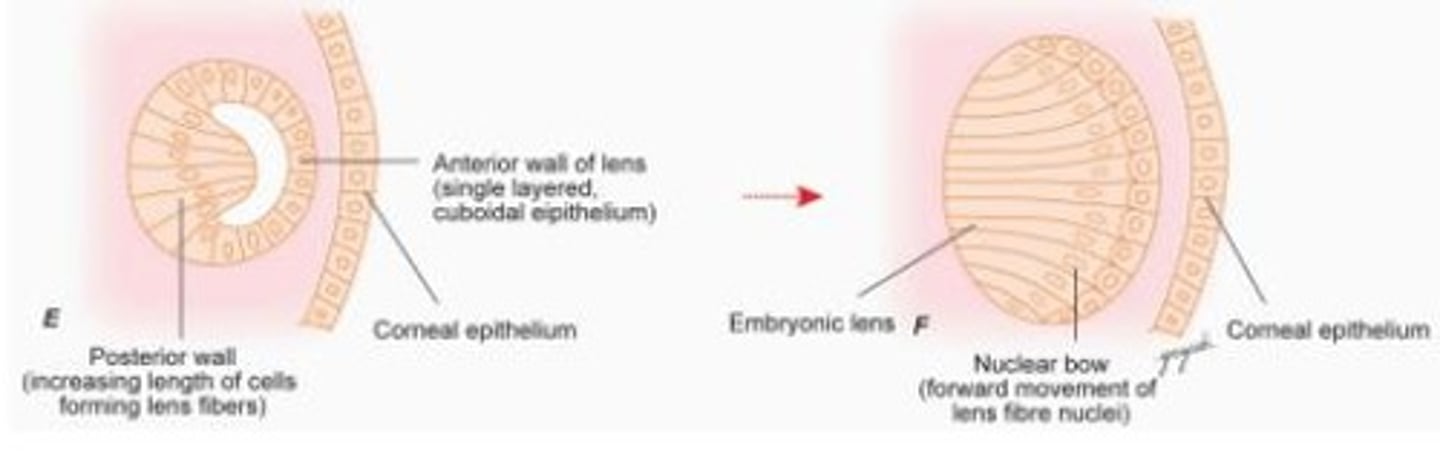
Secondary Lens Fibers
Cells that elongate and surround the embryonic nucleus, contributing to the growth and shape of the lens.
Basal Lamina
A thin layer of extracellular matrix that supports the cells of the optic cup and will become the lens capsule.
Vascular Endothelium
The inner lining of blood vessels that develops from mesodermal mesenchyme during eye development.
Striated Muscle Cells
Muscle cells that develop from mesoderm and are involved in the function of the eye's muscles.
Aqueous Humor
The clear fluid produced in the eye that nourishes the lens and cornea and maintains intraocular pressure.
Lens Capsule
A thin, transparent membrane that surrounds the lens, providing structure and protection.
Retinal Vasculature Development
The process by which blood vessels form in the retina, crucial for supplying nutrients and oxygen.
Marginal Zone
An anuclear region that serves as a precursor to the internal limiting membrane, separating the marginal zone from the vitreal cavity.
Transient Fiber Layer of Chievitz
A nucleus-free area located between the inner and outer neuroblastic layers during retinal development.
Neuroblastic Layers
Two layers formed during retinal development where differentiation of neural retinal cells occurs.
Ganglion Cells
Neurons in the retina that transmit visual information from the photoreceptors to the brain.
Müller Cells
Supportive glial cells in the retina that develop during the formation of the inner neuroblastic layer.
Apoptosis
A programmed cell death process that reduces the number of retinal cells, essential for proper retinal circuitry.
Photoreceptor Cells
Cells in the retina that detect light and are responsible for converting it into neural signals.
Foveal Development
The process involving the displacement of inner retinal components, migration of photoreceptors, and maturation of these cells to enhance visual acuity.
Bipolar Cells
Retinal neurons that transmit signals from photoreceptors to ganglion cells.
Horizontal Cells
Retinal cells that integrate and regulate the input from multiple photoreceptor cells.
External Limiting Membrane
A structure formed by adhering junctions between photoreceptor cells, important for maintaining retinal integrity.
Cone Packing
The arrangement of cone photoreceptors in the fovea that increases visual acuity.
Inner Nuclear Layer
A layer in the retina containing the cell bodies of bipolar, horizontal, and amacrine cells.
Macular Area
The central region of the retina that is responsible for high-acuity vision.
Retinal Ganglion Cell (RGC)
The final output neurons of the retina that carry visual information to the brain.
Marginal layer
A layer in the developing retina where ganglion cells are displaced, allowing cones to be the only neural cell bodies in the center.
Cones
Photoreceptor cells in the retina responsible for color vision and visual acuity, which differentiate before rods during development.
Retinal vessels
Blood vessels that emerge from the hyaloid artery and supply the developing retina, completing their structure postnatally.
Corneal epithelium
The outermost layer of the cornea, formed from epithelial cells that align during early development.
Foveola
The central region of the retina responsible for sharpest visual acuity, which matures last during development.
Bowman's layer
An acellular layer of the cornea formed by fibroblasts and epithelial secretions, present by the fourth month of development.
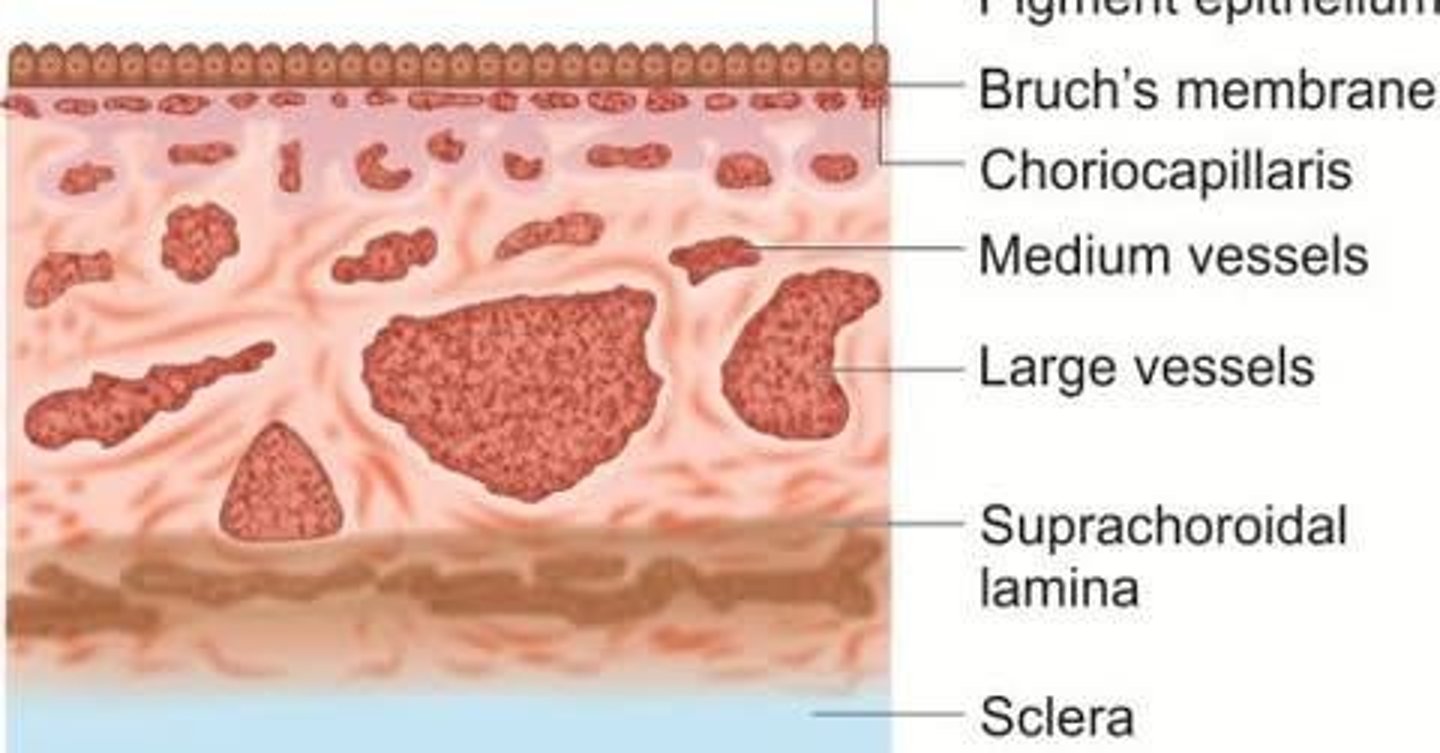
Choriocapillaris
A layer of capillaries in the choroid that must contact the developing pigment epithelium to differentiate properly.
Vitreous body
A gel-like substance filling the eye between the lens and the retina, which develops from both mesenchymal and ectodermal origins.
Pupillary membrane
A temporary membrane that forms between the lens and corneal endothelium during development, later replaced by the vitreous membrane.
Anterior chamber
The fluid-filled space in the eye located between the cornea and the iris, lined by a continuous endothelium.
Henle's fiber layer
A layer in the retina formed by the inner fibers of cones that adopt an oblique orientation to synapse with other retinal cells.
Tertiary Vitreous
A structure that arises in the vitreous during the 4th month of development, characterized by a triangular mass of mesenchymal cells.
Trabecular Meshwork
A network of tissue in the eye that facilitates the drainage of aqueous humor, becoming well developed by the 9th month of gestation.
Intratrabecular Spaces
Spaces formed within the trabecular meshwork, likely resulting from programmed cell death.
Tight Junctions
Specialized connections between endothelial cells that become evident in the canal's lining by the 4th month of development.
Meibomian Glands
Glands that develop from buds at the margins of the eyelid folds, contributing to tear film stability.
Neuroglial Sheath
The outer layer of the optic stalk that becomes the protective covering surrounding the optic nerve.
Programmed Cell Death
A biological process that occurs in developing tissues, including the eye, to remove unnecessary cells.
Myelination
The process of forming a myelin sheath around axons, which begins once the optic nerve fibers reach the lateral geniculate nucleus.
Eyelids
Structures formed from folds of surface ectoderm that grow toward one another and fuse during development.
Orbital Fat
Connective tissue derived from neural crest cells that supports the eye within the orbit.
Extraocular Muscles
Muscles responsible for eye movement, derived from mesoderm, with connective tissue components originating from neural crest.
Nasolacrimal System
The drainage system for tears that develops from a cord of surface ectodermal cells.
Uveal Pigment Cells
Cells that contribute to the pigmentation of the uveal tract in the eye.
Vascular Pericytes
Cells associated with blood vessels in the eye, derived from mesoderm.
Optic Nerve Fibres
Nerve fibers that transmit visual information from the retina to the brain.
Lamina Cribrosa
A sieve-like structure in the optic nerve head that supports the optic nerve fibers.
Corneal Diameter
The measurement across the cornea, which increases from about 10 mm at birth to adult size of 11.7 mm by age two.
Macula
A small area in the retina responsible for central vision, which fully develops between 4 to 6 months after birth.
Bruch's Membrane
The innermost layer of the choroid, which is avascular and provides support to the retinal pigment epithelium.
Conjunctiva
A thin membrane that covers the front of the eye and lines the eyelids, providing protection and lubrication.
Meibomian Gland
Glands located in the eyelids that secrete an oily substance to prevent tear evaporation.
Vitreous Humor
The gel-like substance filling the space between the lens and the retina, helping to maintain the shape of the eye.
Photoreceptors
Specialized cells in the retina that detect light; they include rods and cones.
Optic Nerve Head
The point where the optic nerve exits the eye, containing no photoreceptors, creating a blind spot.