Molecular Cell Biology Lecture 1-2
1/21
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
22 Terms
What is the Raleigh equation used for in microscopy?
It calculates the distance between points resolved: Distance = 0.61 × wavelength of light / numerical aperture of lens
What is the resolution limit of optical microscopy?
200 nm (1000x magnification)
Describe how organelles and viruses can be separated using centrifugation.
By damaging the outer membrane and applying mechanical force (stirring, osmotic pressure, sonication, tissue homogenisers), followed by centrifugation techniques like differential ultracentrifugation and isopycnic centrifugation.
What does isopycnic centrifugation involve?
Spinning a gradient of glucose concentrations to separate organelles by density.
Name the three main components of the cytoskeleton and their sizes.
Microtubules: 25 nm, Intermediate filaments: 10 nm, Microfilaments (actin): 7–9 nm
What is the role of rhodamine-labeled phalloidin?
It binds actin filaments and allows visualization via fluorescent microscopy.
Describe the structure and function of actin in migrating cells.
Actin forms lamellipodia, filopodia, and stress fibers, aiding in cell movement and shape.
What is the role of the microtubule organizing center (MTOC)?
It originates microtubules and forms the mitotic spindle for chromosome segregation.
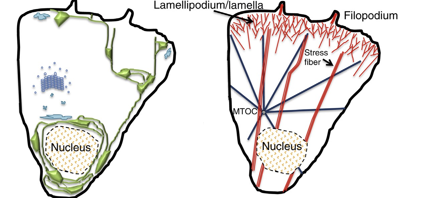
Describe the image showing cytoskeletal organization in epithelial cells.
The image illustrates the asymmetric shape maintained by cytoskeletal elements, showing actin and microtubule-based transport and polarity.
What is the critical concentration in actin polymerization?
The concentration at which G-actin monomers begin to polymerize into filaments.
What is treadmilling in actin filaments?
Subunits are added at the positive end and dissociate at the negative end, creating a dynamic flow.
How does cofilin affect actin filaments?
It binds between ADP-actin subunits, destabilizing and severing filaments.
What is the role of profilin in actin dynamics?
It promotes ADP loss and ATP binding, ensuring a supply of ATP-actin for polymerization.
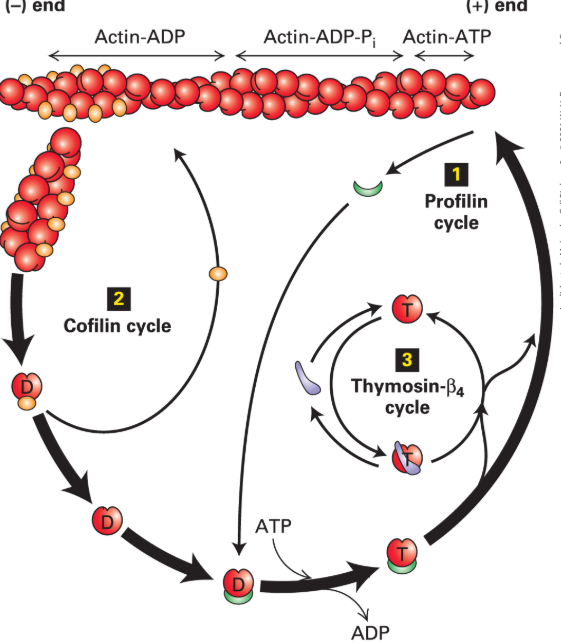
Describe the image showing cofilin and profilin interaction with actin.
The image shows cofilin severing filaments and profilin facilitating ATP-actin formation.
What proteins cap the ends of actin filaments?
CapZ (positive end), Tropomodulin (negative end)
What is the role of formin in actin nucleation?
It catalyzes nucleation of long filaments and protects the positive end from capping.
What does the Arp2/3 complex do?
It nucleates branched actin networks and requires activation by nucleation-promoting factors.
Which Rho GTPases are involved in cell polarization?
Cdc42: filopodia formation, Rac: lamellipodia formation, Rho: stress fibers and focal adhesions
What is the role of Rho kinase?
It mediates cell shape changes through actin/myosin contraction.
How does RhoGTP contribute to phagocytosis?
It promotes actin polymerization to form the phagocytic cup and stimulates superoxide production via Rac.
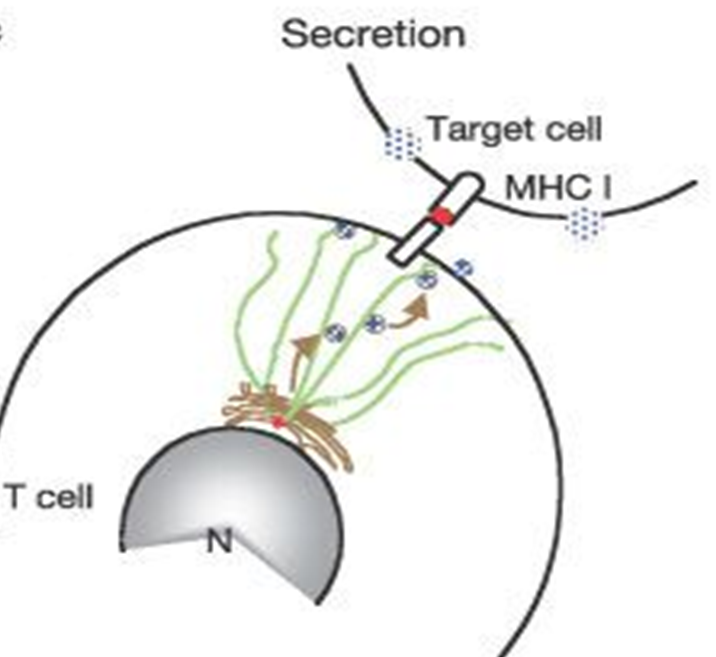
Describe the image showing RhoGTP in secretion.
The image shows microtubule re-orientation in cytotoxic T-cells for targeted granule delivery.
What is the role of RhoGTP in cell division?
It regulates cyclin expression and is required for actin-myosin ring assembly during cytokinesis.