neck masses and salivary glands HEENT
1/59
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
60 Terms
HIV parotitis S&S
nonpainful swelling of parotic gland or asymptomatic
parotitis in TB S&S
chronic nontender swelling of one parotid glands, lump within gland
uncommon
sjogren syndrome S&S
recurrent or chronic swelling of one or both parotid glands
discomfort is modest, dry mouth and eyes
associated with autoimmune
what’s the major salivary glands possibly involved in salivary gland stones (sialolithiasis)
parotid/stensen’s duct
submandibular/wharton’s duct
sublingual
salivary gland stones (sialolithiasis)
inflammation of salivary gland/duct
stagnation of salivary flow and Ca conc.
pathogenesis unknown
which gland is more prone to stone formation and why?
submandibular gland, flow of saliva is slow and against gravtiy
sialolithiasis S&S
sudden onset of swelling and pain in affected gland assoc. w/ eating and anticipation of eating
sialolithiasis Dx
clinical, history and PEx
sialolithiasis imaging?
CT w/o contrast for location of stone
solid = malignancy?, cystic = benign? (fluid, soft)
sialolithiasis Tx
conservative management - hydration, moist heat, massage gland
supportive: discontinue anticholinergic meds, NSAIDs PRN
complications of sialolithiasis
acute bacterial sialadenitis, abscess formation
acute bacterial sialadenitis
suppurative sialadenitis that can occur in absence of stone
most commonly involved gland in acute bacterial sialadenitis
parotid gland
most common pathogen in acute bacterial sialadenitis?
staph aureus
acute bacterial sialadenitis S&S
increased pain and swelling with meals
tenderness and erythema of duct opening
+pus = infxn
acute bacterial sialadenitis Tx
PO Abx
viral sialadenitis/viral parotitis - most common cause
mumps virus
viral sialadenitis (mumps) S&S
acute pain and swelling of one or both parotid glands
low-grade fever, malaise, HA, myalgia, anorexia
Tx of mumps/viral sialadenitis
self-limiting, supportive care
what is the most common type of benign salivary gland tumors?
pleomorphic adenoma
what is the most frequent site of salivary gland tumors?
parotid gland
what is the most common malignant salivary gland tumor?
mucoepidermoid carcinoma and adenoid cystic carcinoma
S&S salivary gland tumors
painless mass/swelling of the major glands
salivary gland tumor = parotid mass (+) is indicative of what?
facial nerve involvement, usually malignant
salivary gland tumor Dx
CT vs. MRI,
FNA bx, US Core Bx for definitive Dx
lyme disease bacteria
borrelia burgdorferi
what is lyme disease transmitted by?
Ixodes genus ticks
S&S lyme disease
facial paralysis, dysesthesias (decreased sensation CNVII), dysgeusia
HA, pain, cervical lymphaenopathy
cat scratch disease bacteria
Rochalimaea henselae (gram negative rod)
cat scratch disease S&S
cat scratch or bite, local papule/pustule/vesicle overlying scratch
persistent painful regional lymphadenopathy
cat scratch disease Dx
lab - skin test with antigen (Hanger-Rose skin test)
what is the most common form of congenital cyst in the neck?
thyroglossal duct cyst
thyroglossal duct cyst S&S
midline neck mass at level of thyrohyoid membrane, associated w hyoid bone
sinus tract may be present
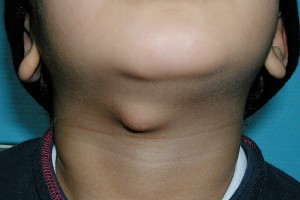
thyroglossal duct cyst Dx
CT/MRI/US, fistulography
FNA - definitive Dx
thyroglossal duct cyst Tx
surgical excision
branchial cleft cyst/fistula
congenital epithelial cysts in lateral part of the neck
branchial cleft cyst S&S
swelling in upper part of neck to SCM muscle,
± fistula to surface
branchial cleft cyst Tx
conservative vs. surgical excision
dermatoid cyst caused by
entrapment of epithelium in deeper tissue
dermoid cyst S&S
usually midline, nontender, mobile, submental neck masses
dermoid cyst Tx
surgical excision
lymphangioma
congenital malformation of lymphatic system
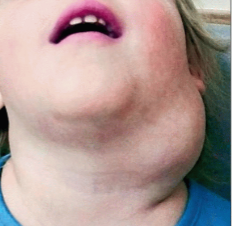
lymphangioma Tx
surgery, sclerotherapy, laser therapy
congenital torticollis
postural deformity of neck (lateral neck flexion and neck rotation)
contracted muscle appears like a mass
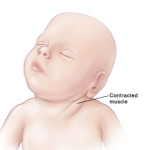
goals of congenital torticollis Tx
midline head position, posture symmetric, craniofacial symmetry improvement
teratoma
arises from pluripotential cells
classically large, encapsulated - cystic component
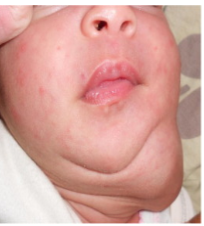
thymic mass
implantation of thymic tissue during embryonic descent
usually midline, angle of mandible to midline of neck
thymic mass Tx
surgical excision
which are rare causes of neck masses
metabolic and autoimmune
metabolic neck masses causes:
gout, sarcoidosis (granulomas tissue)
kimura’s disease, castleman’s disease
kimura’s disease
uncommon chronic inflammatory condition involve subcutaneous tissue
castleman’s disease
benign lymphoproliferative disorder that most frequently involves mediastinal lymph nodes
lymphoma
malignancy neck mass of lymphatic system (cancer)
what are the two types of lymphomas?
non-Hodgkins and Hodgkins
S&S lymphoma
painless swelling of lymph nodes, fatigue, SOB
B-symptoms: fever, night sweats, unexplained weight loss
lymphoma Tx
depends on: type of disease, aggressiveness, location, age, general health
Hodgkin’s lymphoma
younger usually
arise in neck, axilla, chest, Reed-Sternberg cell
non-hodgkin’s
older pts usually
arise in LN throughout body
dx at more advanced stage
which type of lymphoma has poor prognosis and why?
Non-Hodgkin’s due to delayed Dx
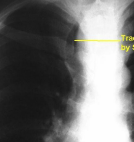
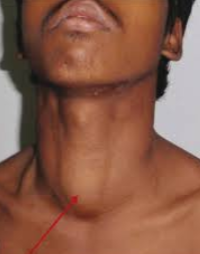
substernal goiter
trachea displaced