Psyc 134: Knowledge, Visual Imagery, and Language
1/65
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Flashcards for key vocabulary and concepts from the lecture notes.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
66 Terms
Conceptual Knowledge
Knowledge that enables us to recognize objects and events and to make inferences about their properties.
Concepts
Categories of objects, events, and ideas (provides “rules” as to what is a category)
Categories
All possible examples of a given concept.
Categorization
The process of assigning something to a category.

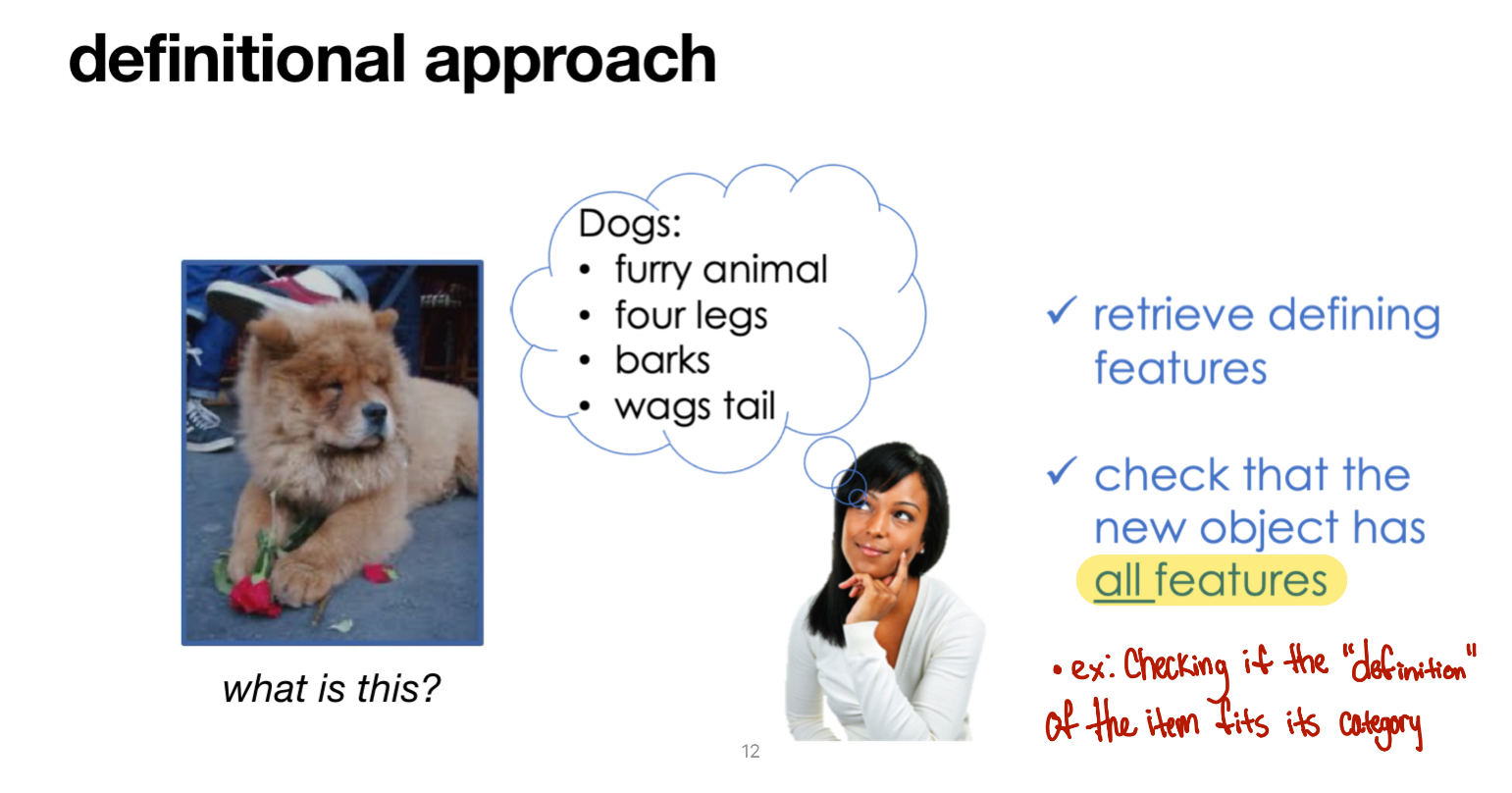
Definitional Approach
Determine category membership based on whether an item meets the definition of the category.
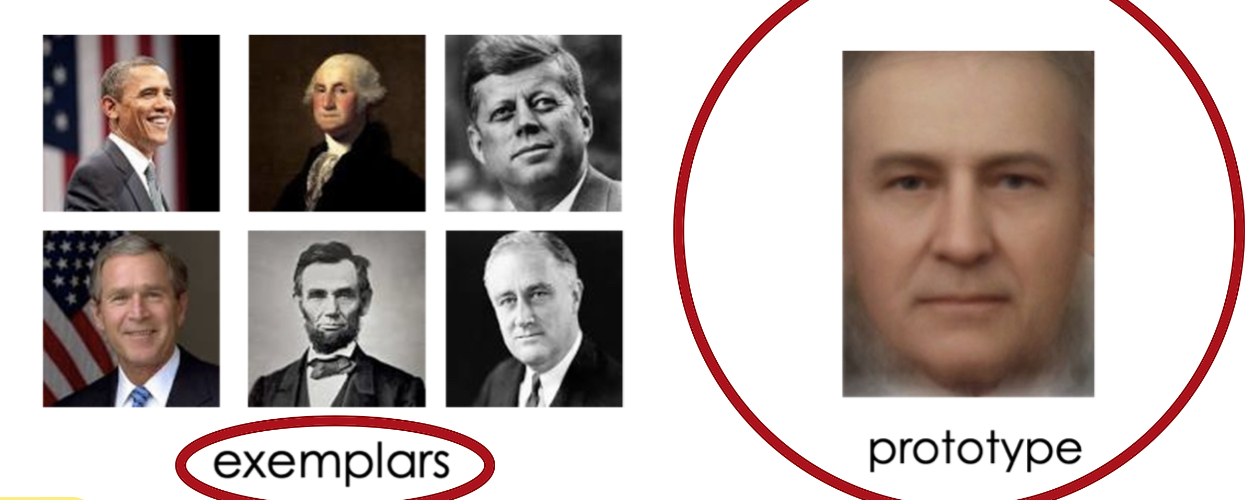
Prototype Approach
Determine category membership by comparing the item to a prototype that resembles the category.
Family Resemblance
Items in a category resemble one another in a number of ways.

Prototype
Typical member of a category that has most of the characteristic features.

Typicality
How closely a category member resembles the category prototype.

Sentence verification technique
Read a statement and judge whether or not it is true

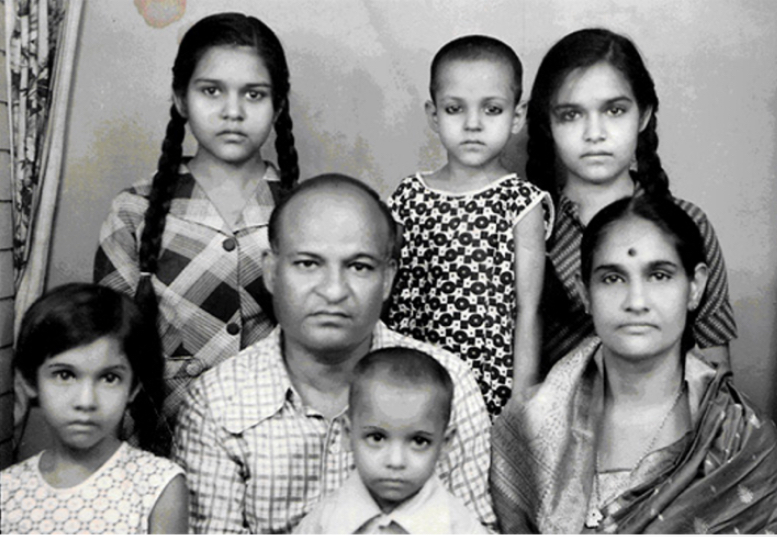
Exemplar Approach
Determine category membership by comparing the item to exemplars of the category.
Exemplar
Previously encountered member of a category.

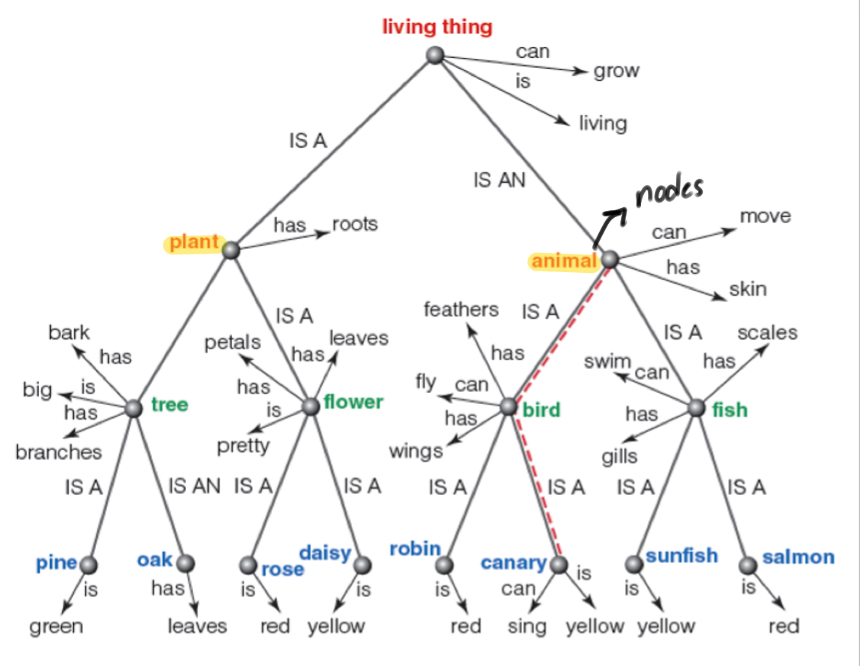
Hierarchical organization
Larger, more general categories are divided into smaller, more specific categories
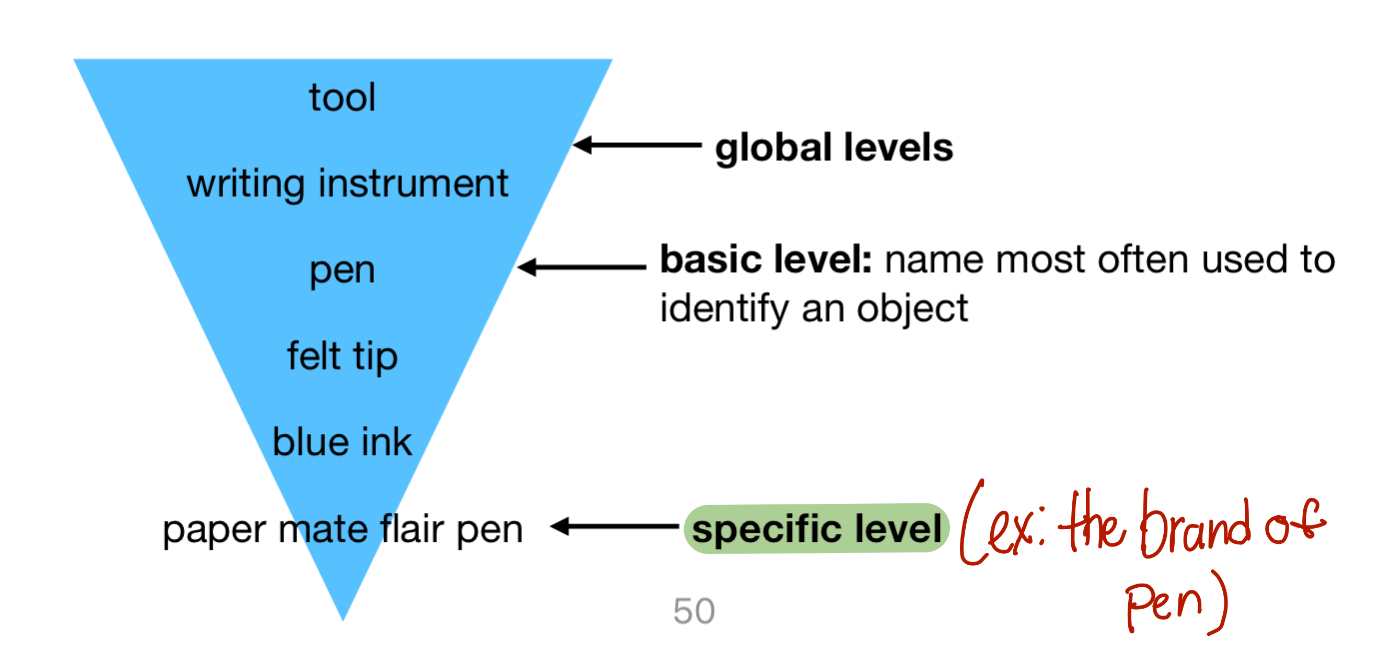
basic level
category members most often used to identify an object
Semantic Network Approach
Concepts are arranged in the mind as networks that connect related concepts.
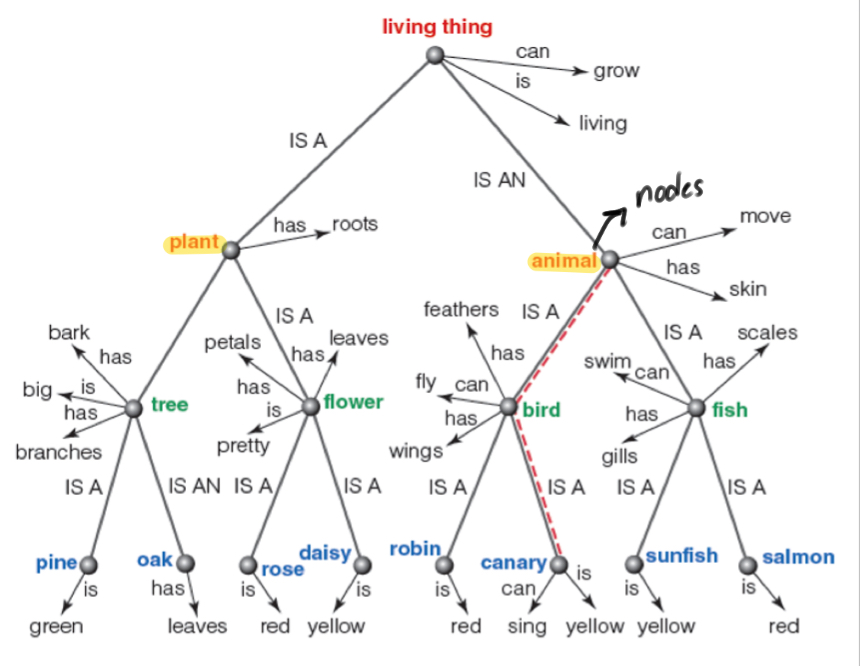
Nodes
Category or concept within semantic networks.
Lines
connect related nodes
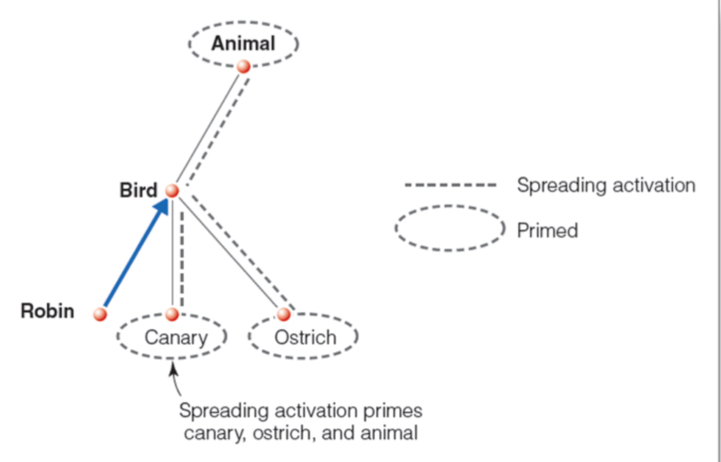
Spreading Activation
Activating' a node spreads to all connected concepts.
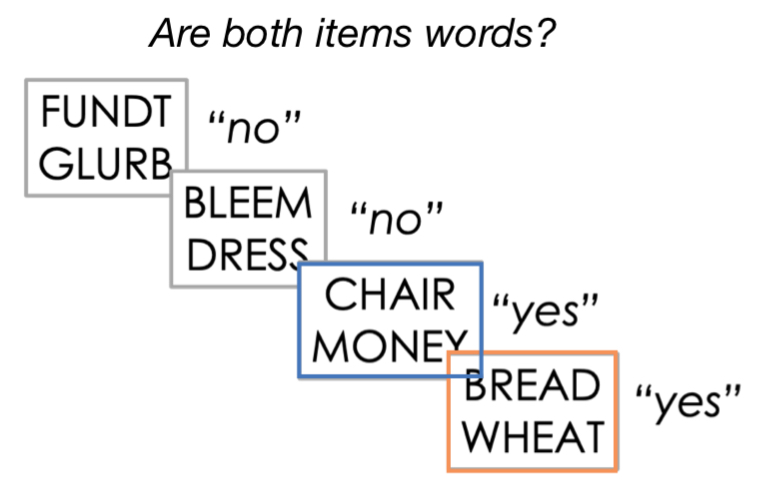
Lexical decision task
Participants indicate whether the stimuli are words or non-word
Cognitive Economy
Shared properties are stored just once at a higher-level node.
Connectionist Network
Concepts are represented as activity that is distributed across a network; also known as parallel distributed processing (PDP) models.
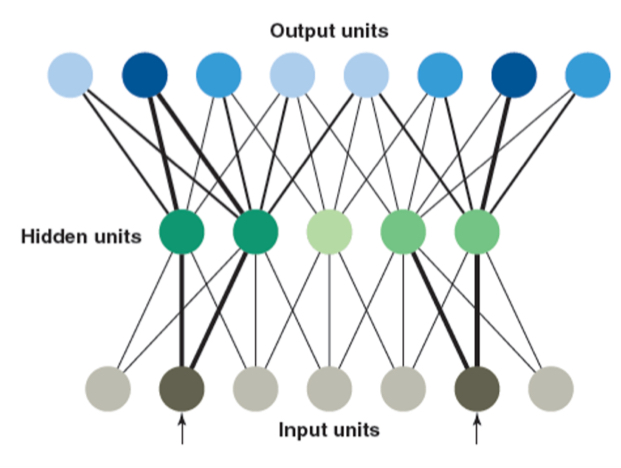
units, lines, and weights in a connectionist network
units: circles
lines: connects units
weights: strength of connections
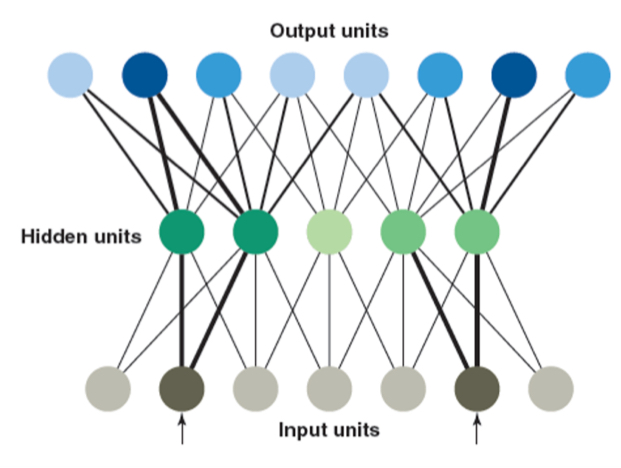
output units
Receive input from hidden units
Hidden units
Receive input from input units
input units
Activated by stimulation in the environment
graceful degradation
performance disruption occurs gradually as part of the system or damaged
generalization of learning
training system to recognize properties of one concept provide provides information about related concepts
Visual Imagery
"Seeing" in the absence of a visual stimulus (like seeing our kitchen) , Not always visual
Spatial Representation
Different parts of an image correspond to specific locations in space.

Mental Scanning
We create mental images and then scan them in our mind.
Symbolic Distance Effect
We detect more details when we are closer to a stimulus.

Propositional Representation
Different parts of an image are represented by language or symbols.

Pegword Technique
"Hang" to-be-remembered words to "pegs" of concrete nouns that you use to create images.
Language
A system of communication using sounds or symbols that enable us to express our feelings, thoughts, ideas, and experiences.
Semantics
Meaning of a word, sentence, or passage.
Syntax
Rules that determine how words combine into sentences.

Phonemes
Smallest unit of speech sounds.

Morphemes
Smallest meaningful unit of language.

words
compromised of one or more morphemes

sentences
A meaningful collection of words
Lexical Semantics
Meaning of words.
Lexicon
All of the words we know.
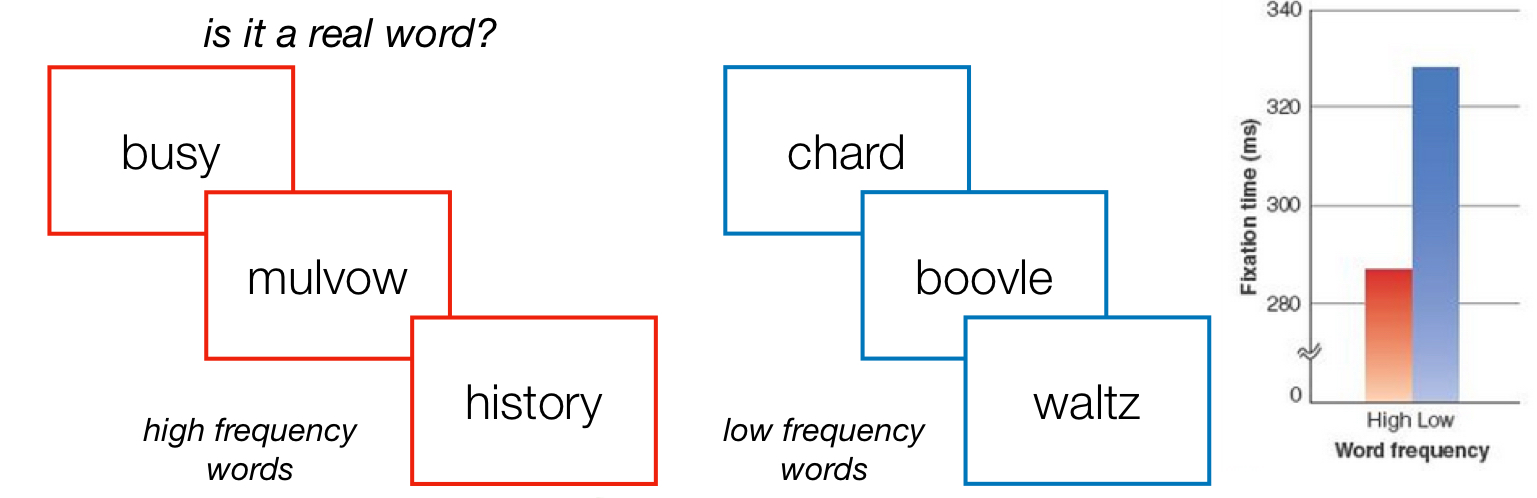
Word Frequency
How often words occur.

word frequency effect
we respond Faster words that occur more frequently, We fix it less to Words that occur more frequently
word pronunciation
how we say words is affected by speech speed, accents, and word slurring
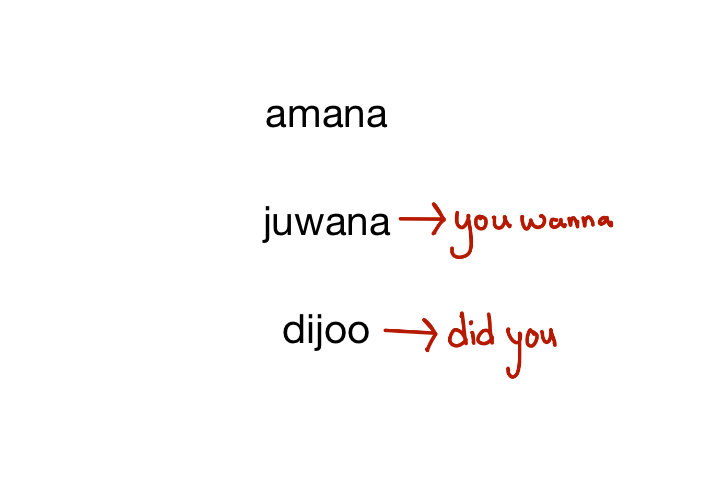
speech segmentation
we perceive individual words even though there are often no silences between them

Mondegreens
mishear something, slip of the ear

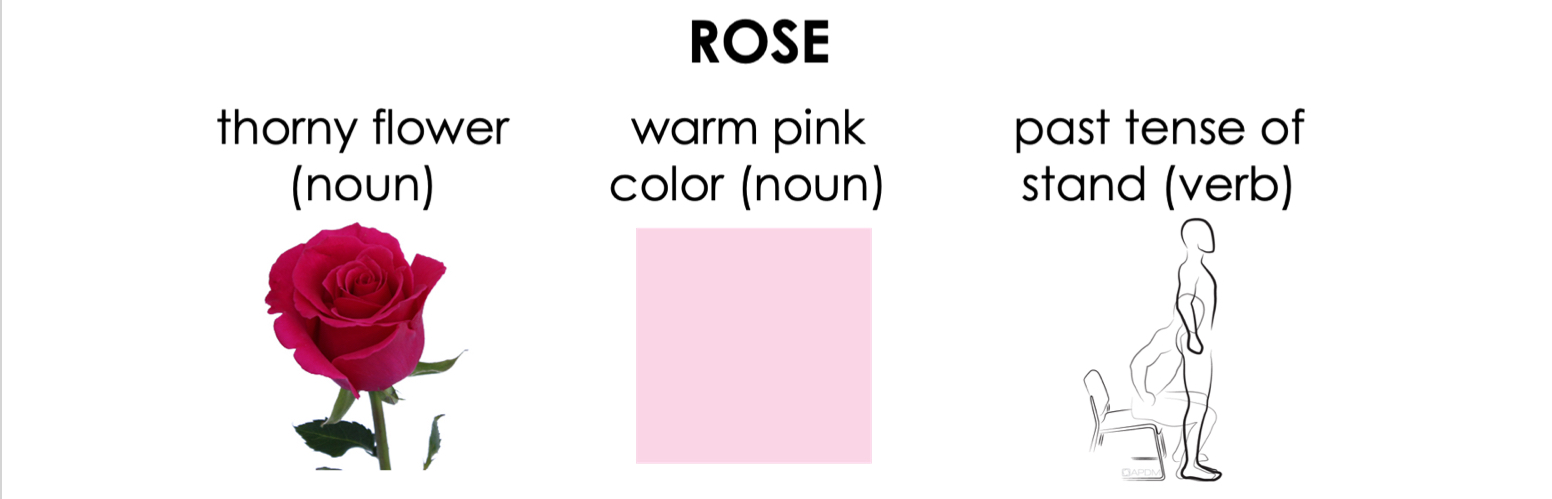
Lexical Ambiguity
Words often have more than one meaning.
Lexical priming task
read a priming sentence, followed by a probe word as quickly as possible
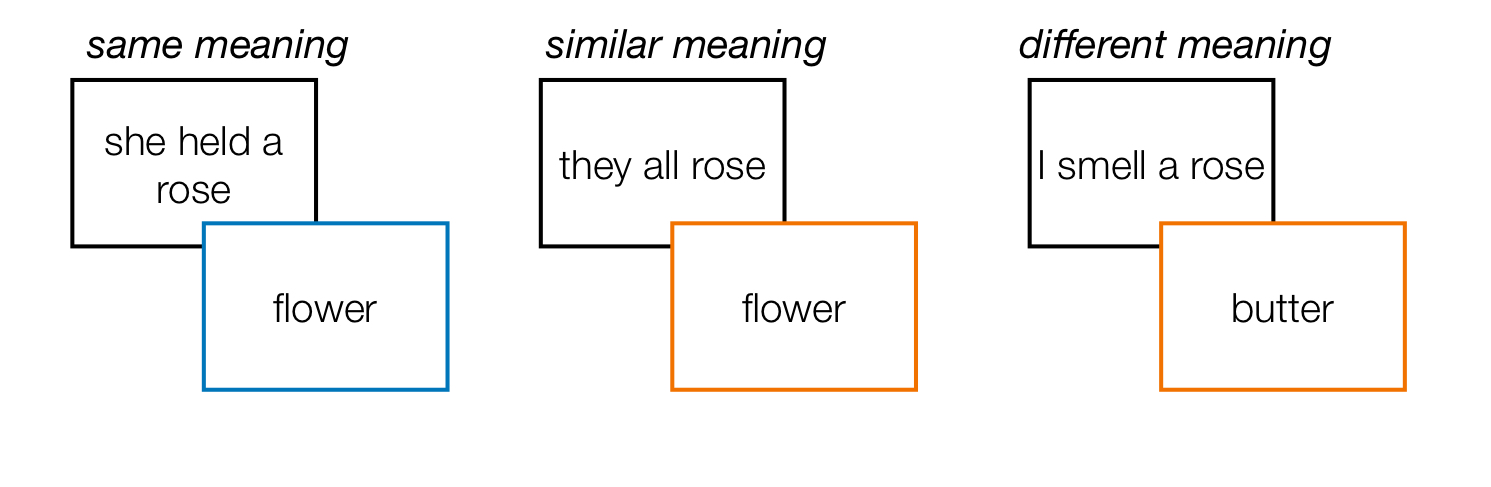
Priming effect
respond faster to probe words that have the same or similar meaning to the priming sentence
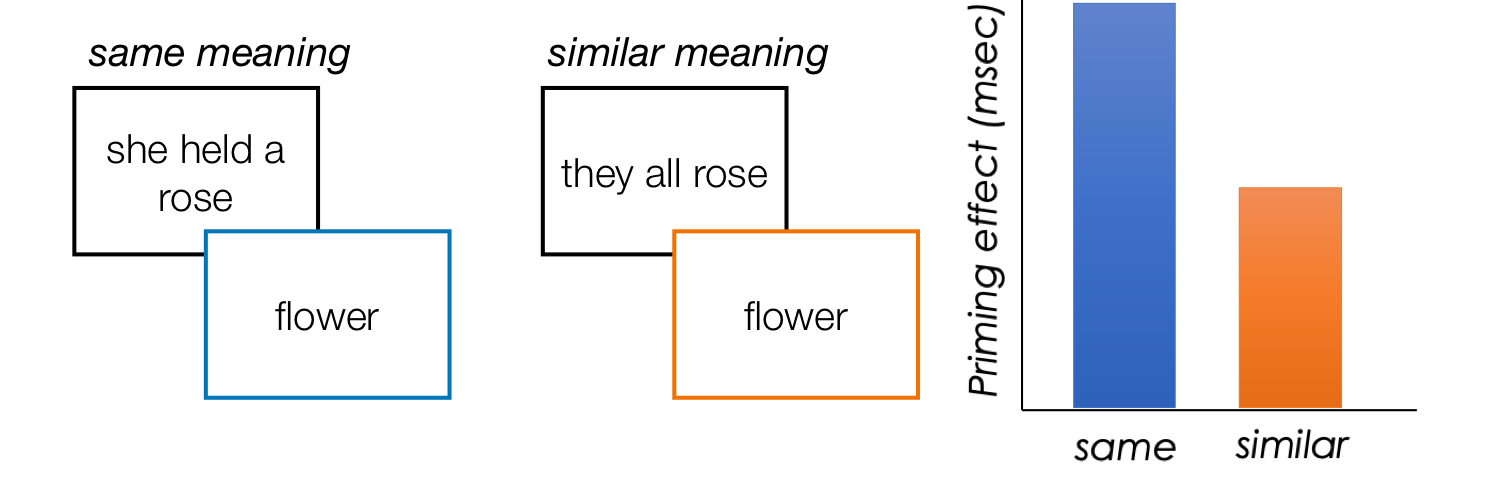
Biased dominance
One meaning, occurs more often than others

Phrasal Semantics
Meaning of sentences.
Parsing
Mentally grouping the words into phrases to create meaning.
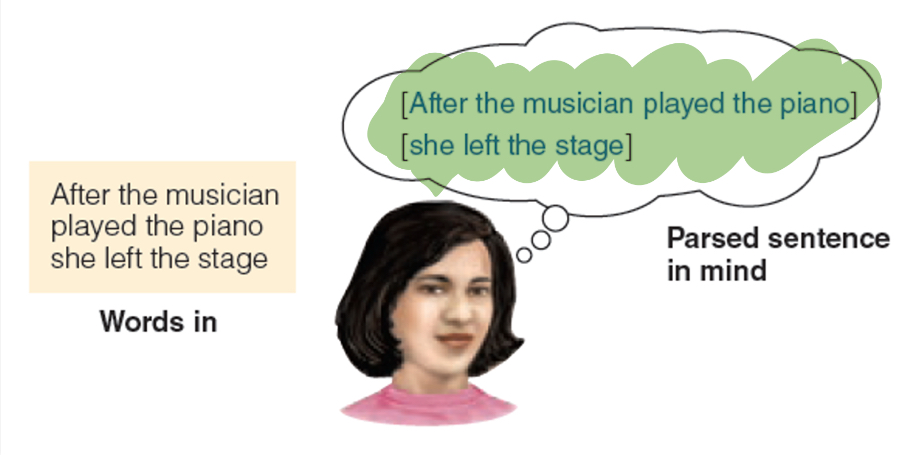
Garden Path Sentence
Sentences that begin by appearing to mean one thing, but end up meaning something else.

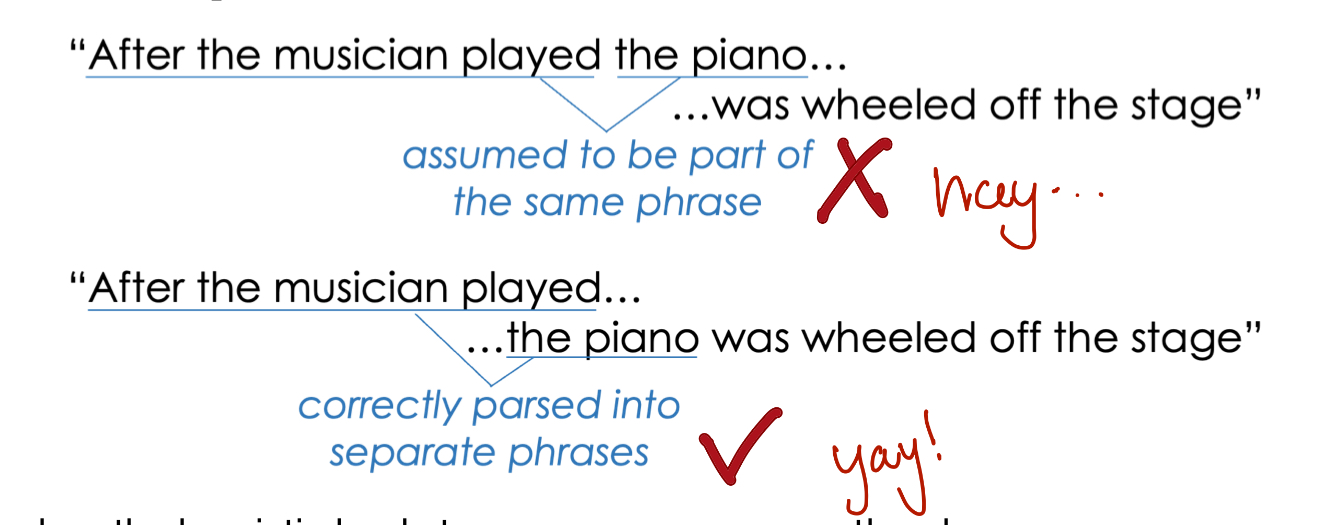
Garden path model of parsing
Listeners use heuristics (syntax based rules) to group words into phrases
Heuristics
Educated guesses, intuitive, judgments, or common sense used to solve problems quickly
late closure
Parser assumed each new word is part of the current phrase
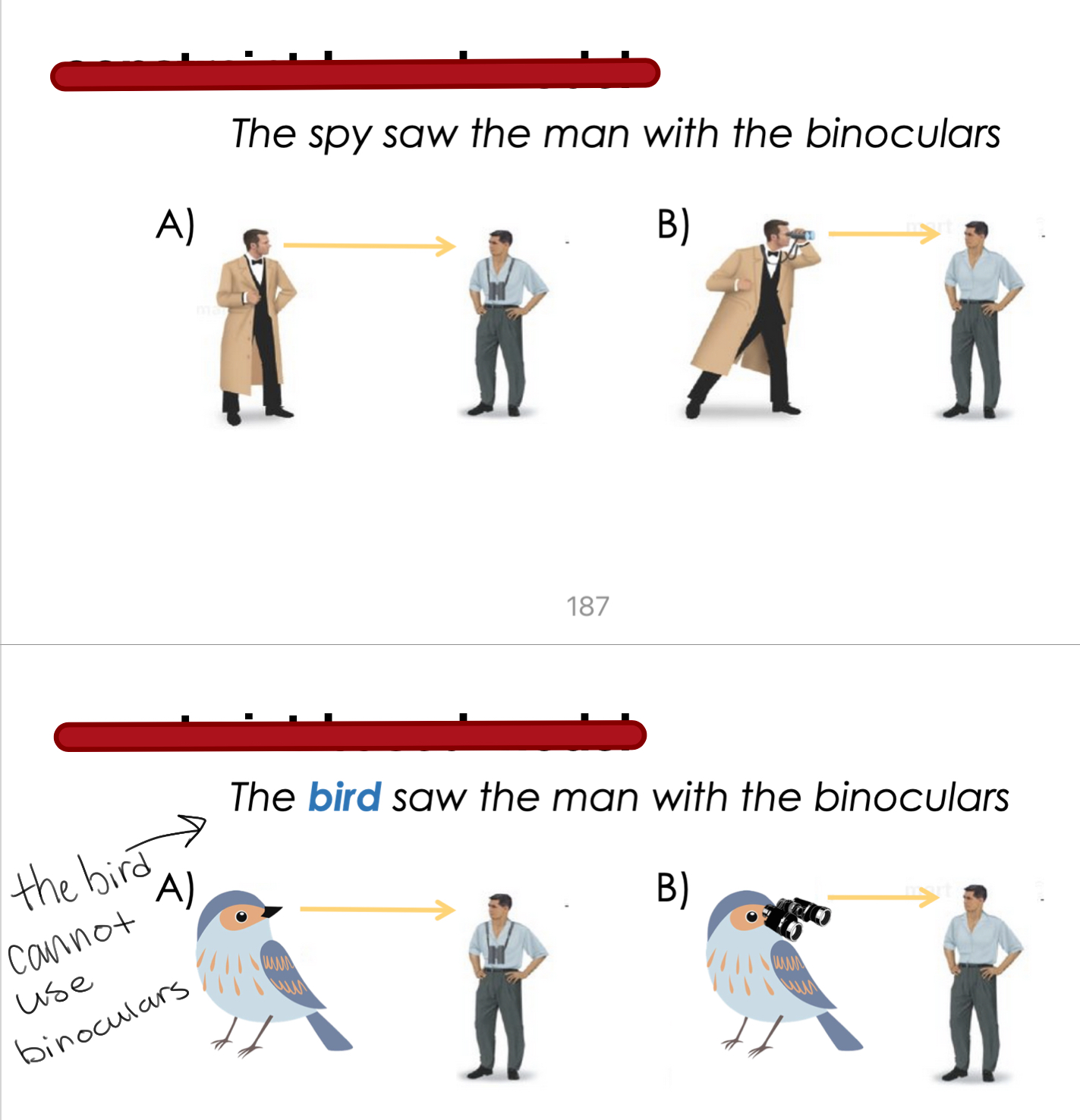
Constraint based approach to parsing
Listeners use syntax along with other information (word meaning, context, memory load) to group words into phrases
Visual word paradigm
View were seen and follow instructions
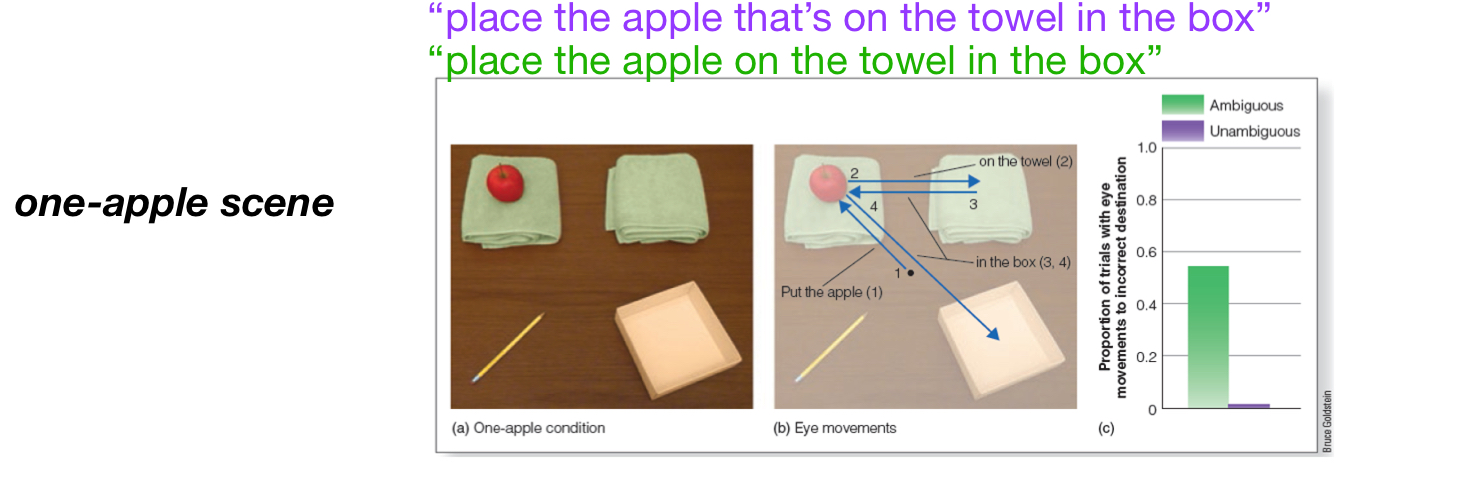
Given-New Contract
Speaker should construct sentences that include given information (that the listener already knows) and new information (that the listener is hearing for the first time).

Common Ground
Knowledge and beliefs shared among conversation participants.

referential communication task
One person has to identify something, the reference, being described to them by someone else

Syntactic Coordination
Conversation participants coordinate their grammatical constructs.

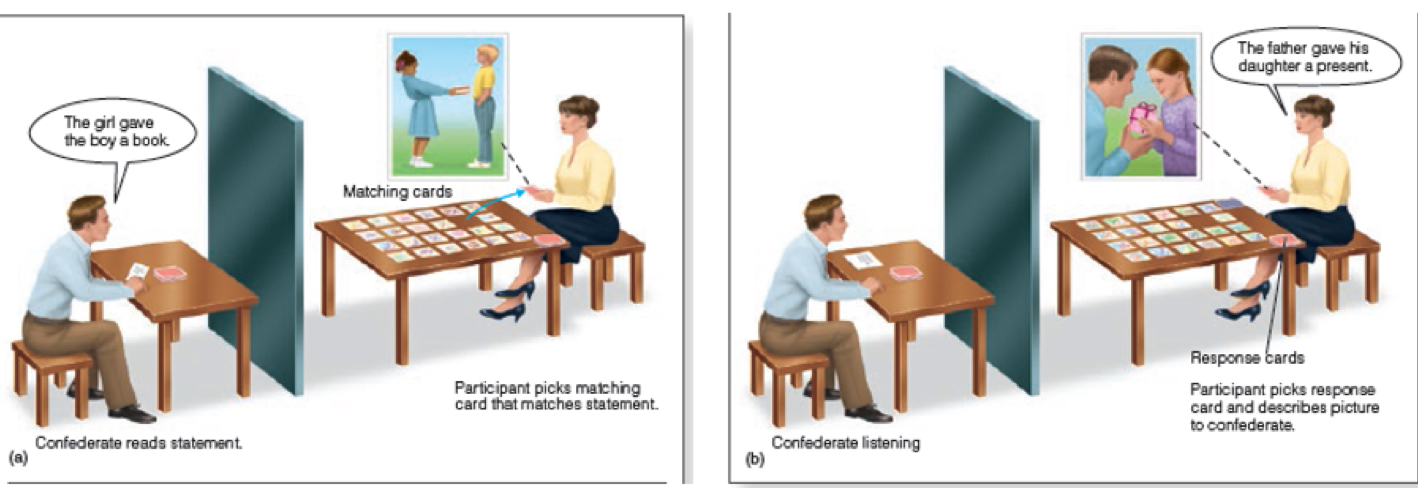
Syntactic priming
Hearing a grammatical construction increases the change that you will use it too
Theory of Mind
Being able to understand what others feel, think, or believe.

nonverbal communication
Being able to interpret and react to the person’s gestures, facial expressions, tone of voice, and other cues to meaning
