General Anatomy, Physiology, and Histology
1/112
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Review for DLE 2025
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
113 Terms
What is the name of the combination of Stratum basale and Stratum spinosum?
Stratum germinativum or "Malphigian Layer”
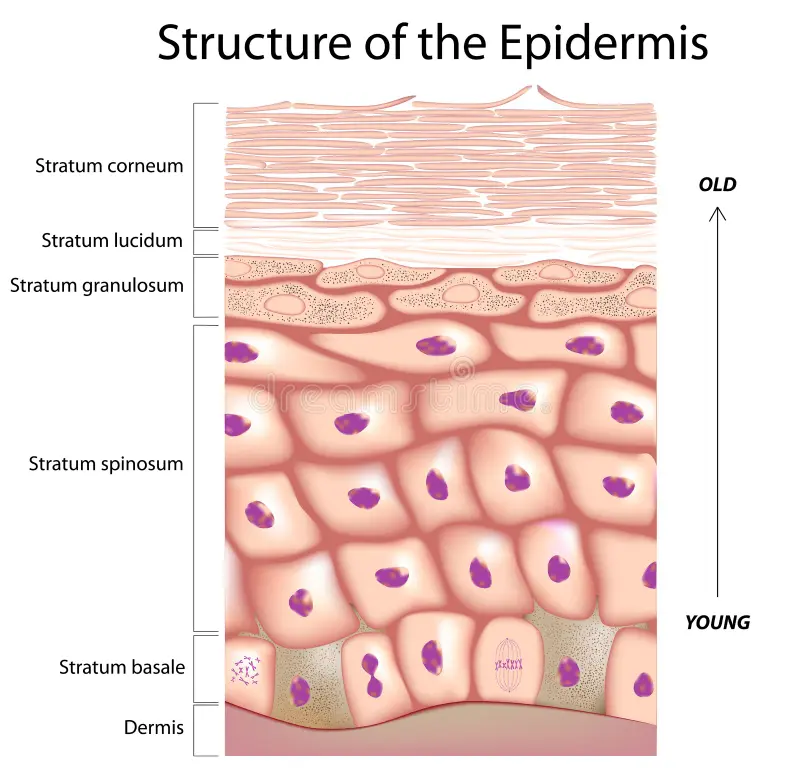
Most numerous cells in epidermis
Keratinocytes
Most numerous protein in the body
Collagen
Mechanoreceptor of skin that has the function for hot and stretch
Ruffini corpuscle or Bulbous corpuscle
Mechanoreceptor of skin that has the function for cold
End-bulb of Krause
Mechanoreceptor of skin that has the function for pressure and proprioception
Pacinian Corpuscle
End product of Vitamin D synthesis
Calcitriol
The following are common causes of blue baby syndrome EXCEPT:
a. Methemoglobinemia
b. Erythroblastosis fetalis
c. Thalassemia
d. Congenital heart defects
c. Thalassemia
Ergocalciferol is also known as
Vitamin D2
Cholecalciferol is also known as
Vitamin D3
Other name for freckles
Ephelis or Ephelides
SCALP stands for…?
Skin
Connective tissue
Aponeuroses
Loose connective tissue
Periosteum
What type of collagen does the bone have?
Type 1 collagen
What type of bone cell that is for bone growth and repair?
Osteogenic or osteoprogenitor cell
What is the difference between between bone and osteoid?
Osteoid - non-mineralized
Bone - mineralized
Other name of alveolar bone proper?
Bundle bone + Cribriform plate
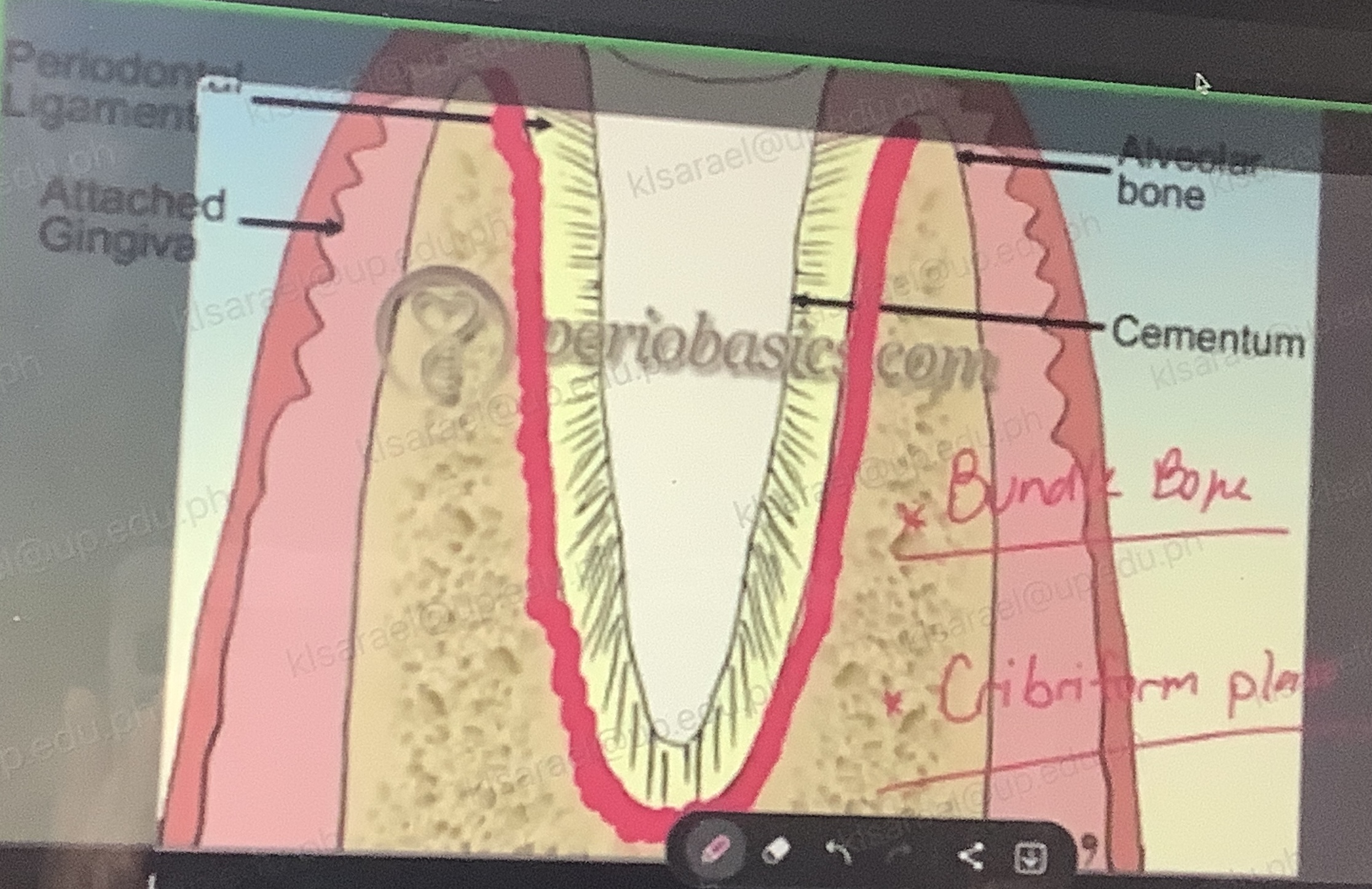
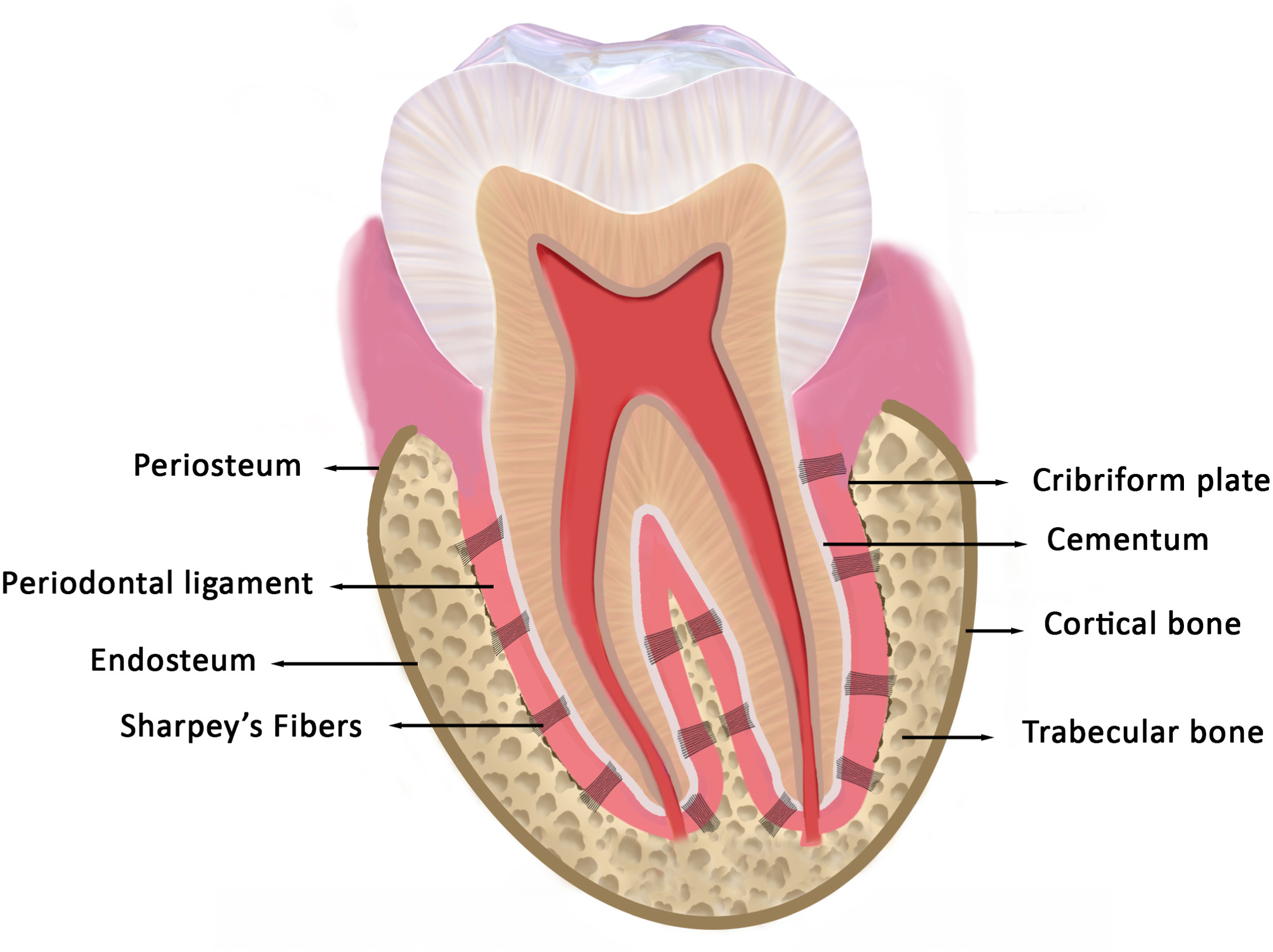
Mineralized ligaments penetrating the bone tissues are known as?
Sharpey’s fibers (mineralized PDL)
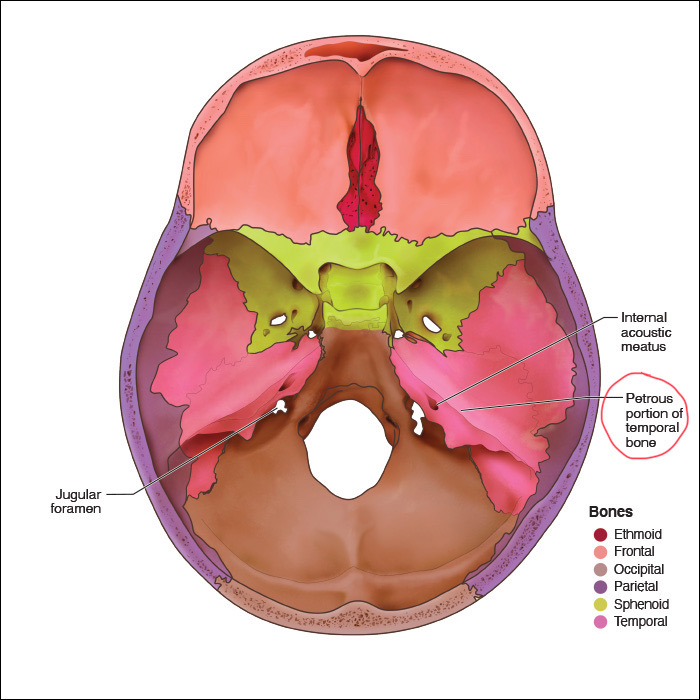
The following are considered having an endochondral bone growth EXCEPT:
a. Temporal bone
b. Condyle
c. Occipital bone
d. Ethmoid
a. Temporal bone
Petrous part of the temporal bone is the only endochondral bone
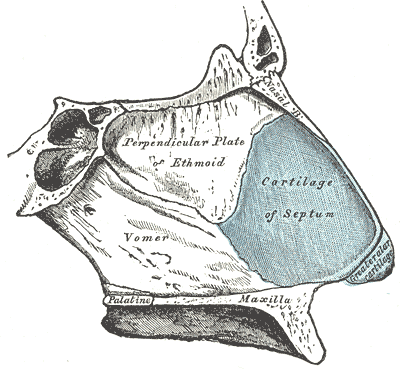
The septal cartilage is made up of
a. Elastic cartilage
b. Hyaline cartilage
c. Fibrocartilage
d. Collagen cartilage
b. Hyaline cartilage
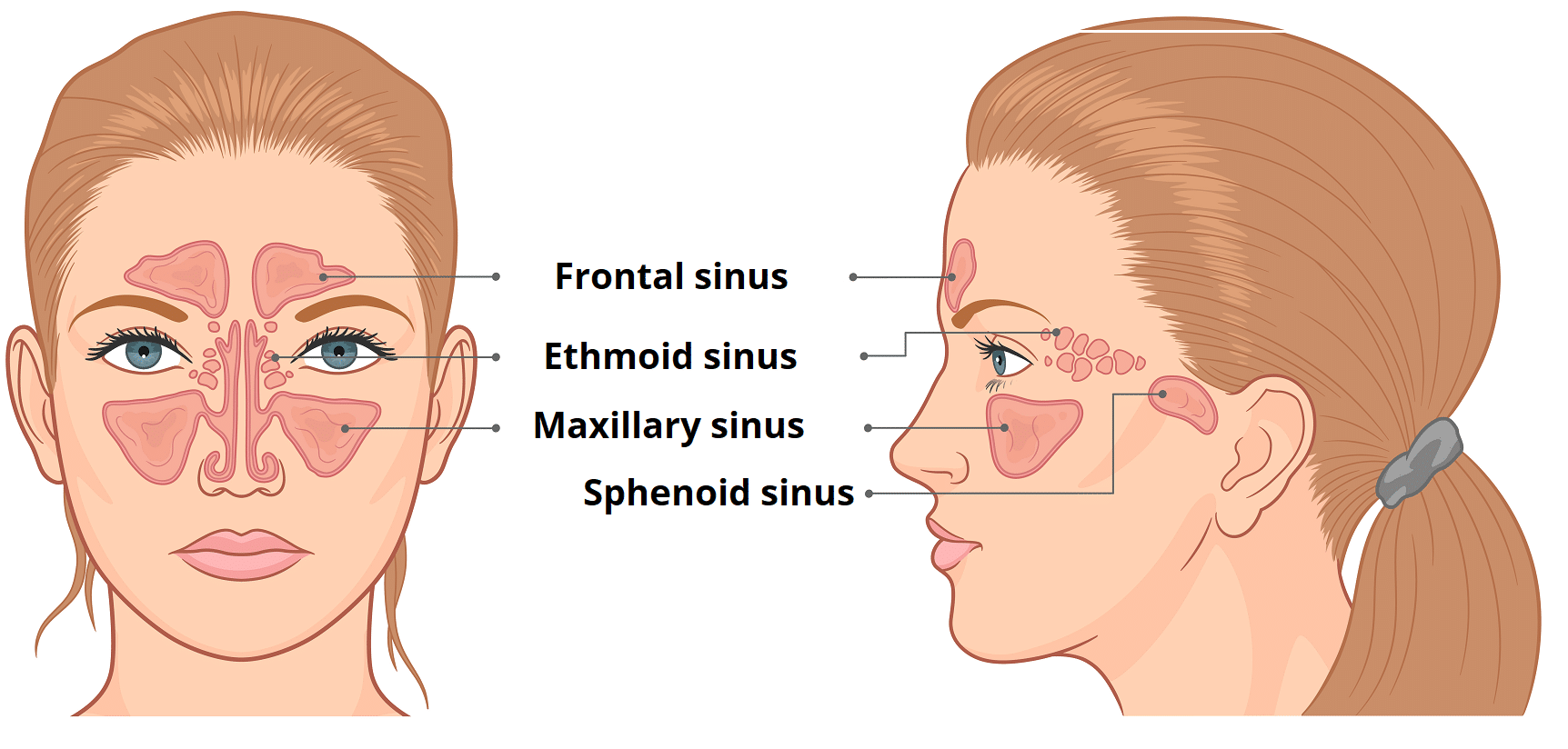
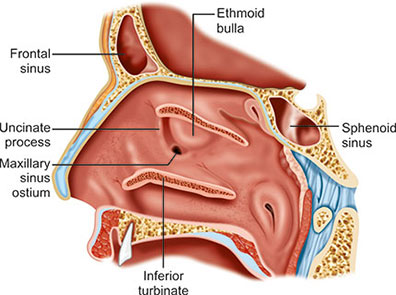
Where does the frontal sinus drain to?
Infundibulum towards Hiatus semilunaris of Middle meatus in the nasal cavity.
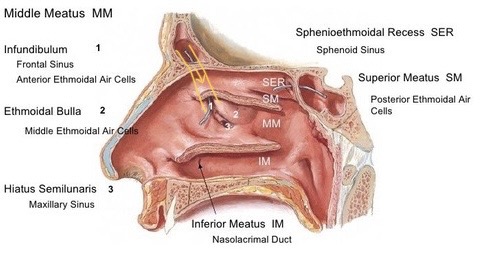
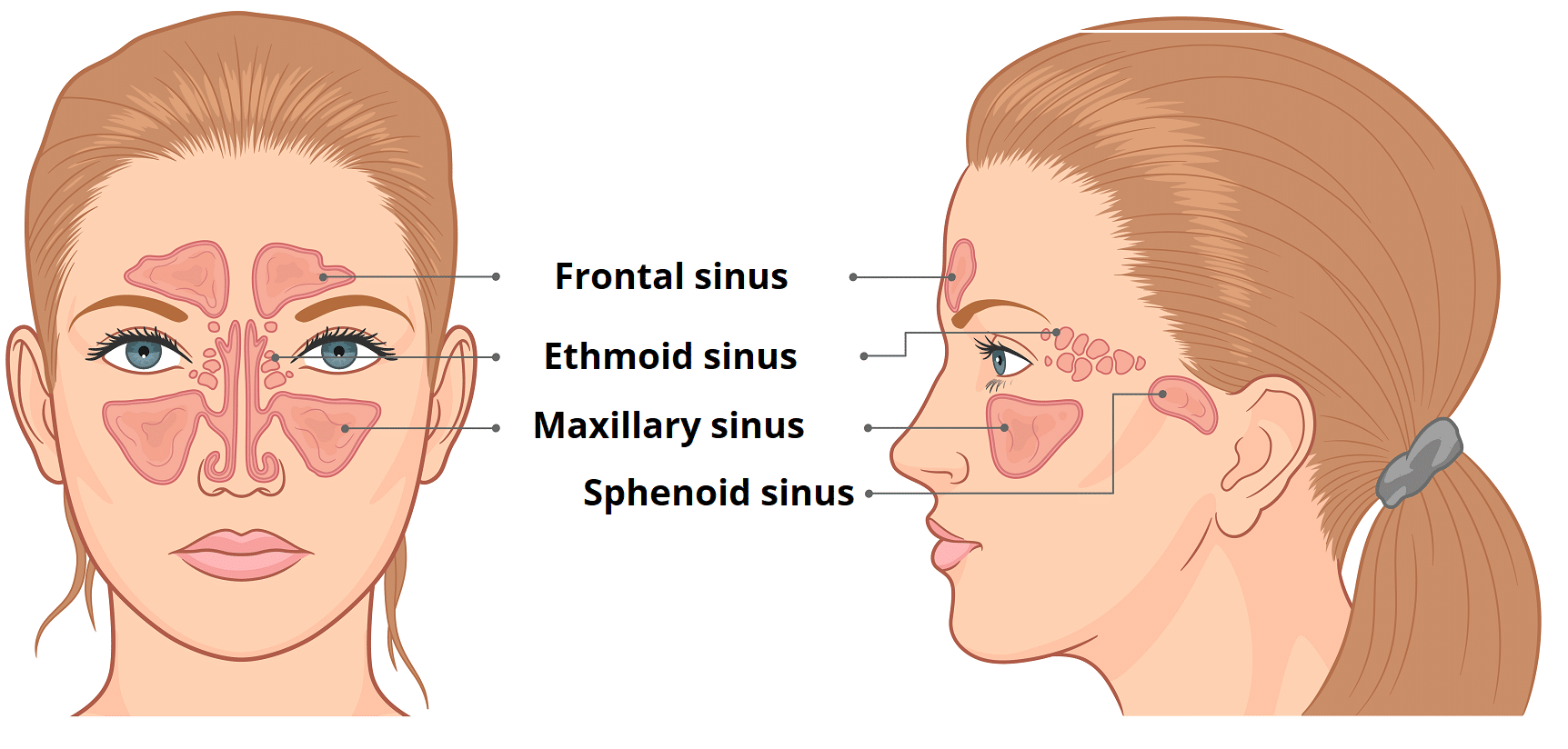
Where does the maxillary sinus drain to?
Ostium maxillare (opening of mx sinus that drains into the hiatus semilunaris of middle meatus of the nasal cavity)
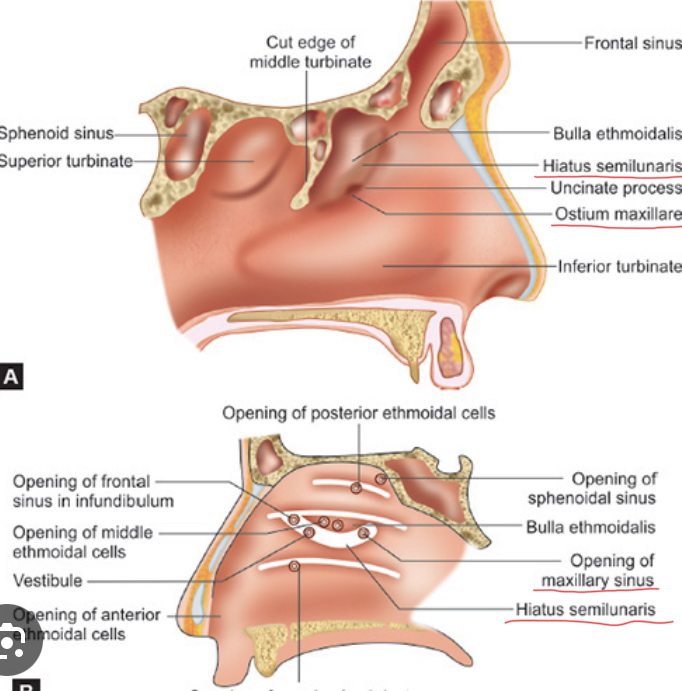
Mucous membrane covering the maxillary sinus cavity
Schneiderian Membrane
Procedure done to add bone between sinus and alveolar bone?
Sinus lift
Best 2D radiograph to assess maxillary sinus?
Water’s view
Technique used to open maxillary sinus through the canine fossa
Caldwell-luc
Drainage of middle ethmoidal sinus
Ethmoidal bulla in middle meatus
The only movable bone in the skull
Mandible
True or false: The palatine bone forms the floor of the orbit.
True
It is the framework or forerunner of the mandible (in formation).
Meckel’s cartilage
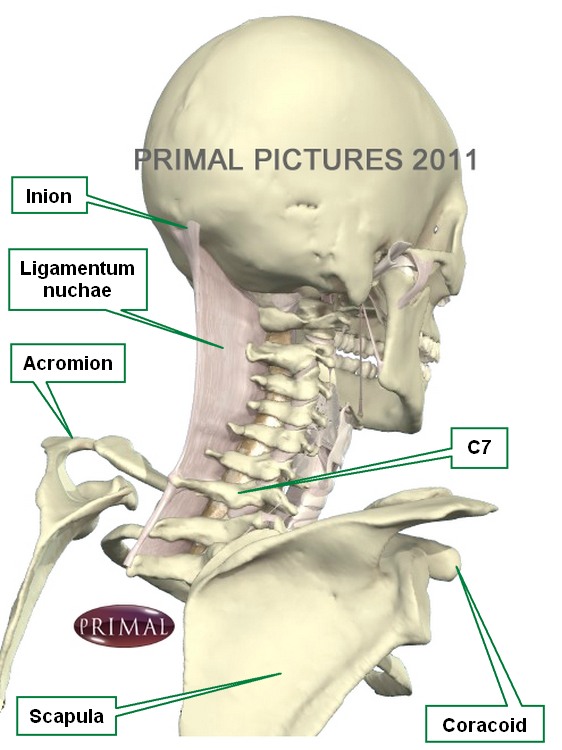
What is the ligament that connects the occipital bone to C7 in vertebrae?
Ligamentum nuchae
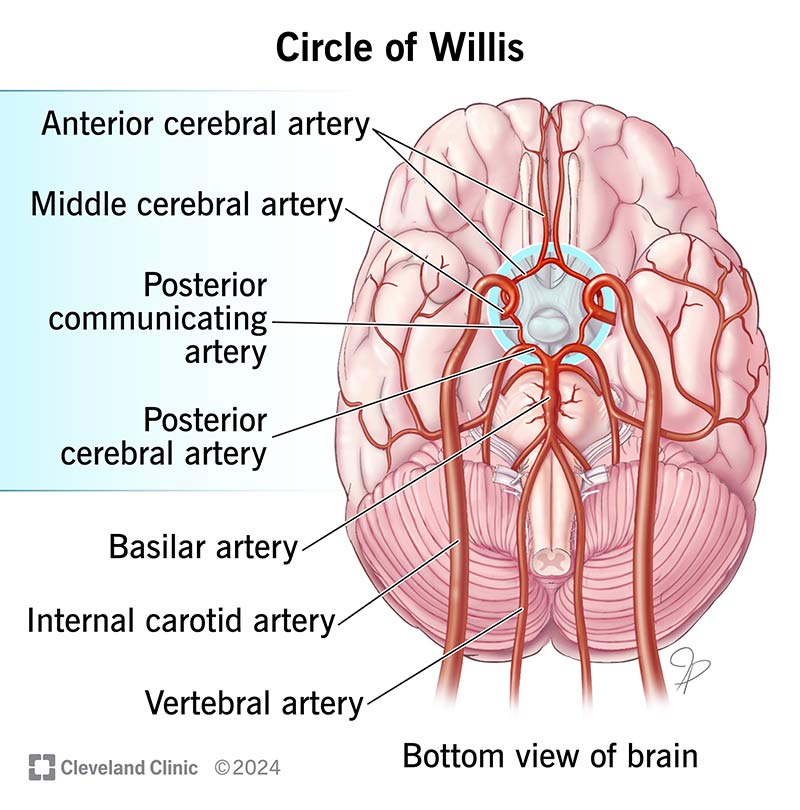
Pathway of primary blood supply of brain
Internal carotid artery to Circle of Willis
What nitrogenous bases are involved in uric acid formation?
Purine (adenine + guanine)
What condition that is caused by increased serum alkaline phosphatase in blood?
a. Osteitis
b. Rickets
c. Jacob’s syndrome
d. Paget’s disease
D. Paget’s disease
(or multiple myeloma if ito nasa choices)
Vitamin D/calcium deficiency AFTER epiphyseal closure (adult)
Osteomalacia
What is the stimulus for the sarcoplasmic reticulum to release calcium ions?
Action potential
What does the myosin head need to detach itself from actin?
ATP
Binding site of calcium in smooth muscle cells
Calmodulin
Blocks myosin head from binding to actin in smooth muscle cells
Myosin light chain kinase
How does Rigor mortis happen?
Calcium ions leak into cytoplasm
Hospitals use Succinylcholine/Suxamethonium (binds to Ach receptors; causes muscle paralysis/relaxation) for?
Laryngospasm
Skeletal fibers that are red in color, slow-twitch, fatigue-resistant
Slow oxidative fibers / Red muscle fibers
Skeletal fibers that are white in color, fast-twitch, fatigues quickly
Fast glycolytic fibers
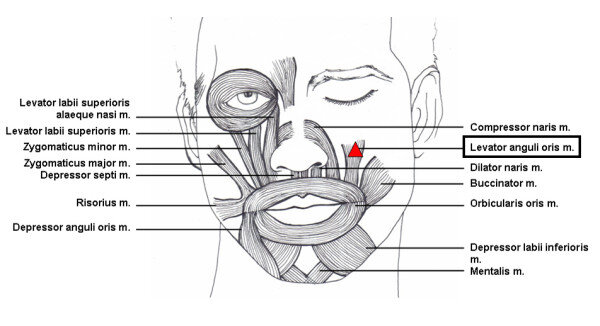
It is also called the “Caninus muscle” that elevates the angle of the mouth
a. Zygomaticus major
b. Levator anguli oris
c. Depressor labii inferioris
d. Levator labii inferioris
b. Levator anguli oris
During IAN block, we puncture these structures EXCEPT:
a. Buccinator muscle
b. Sphenomandibular ligament
c. Medial pterygoid muscle
d. Stylomandibular ligament
d. Stylomandibular ligament
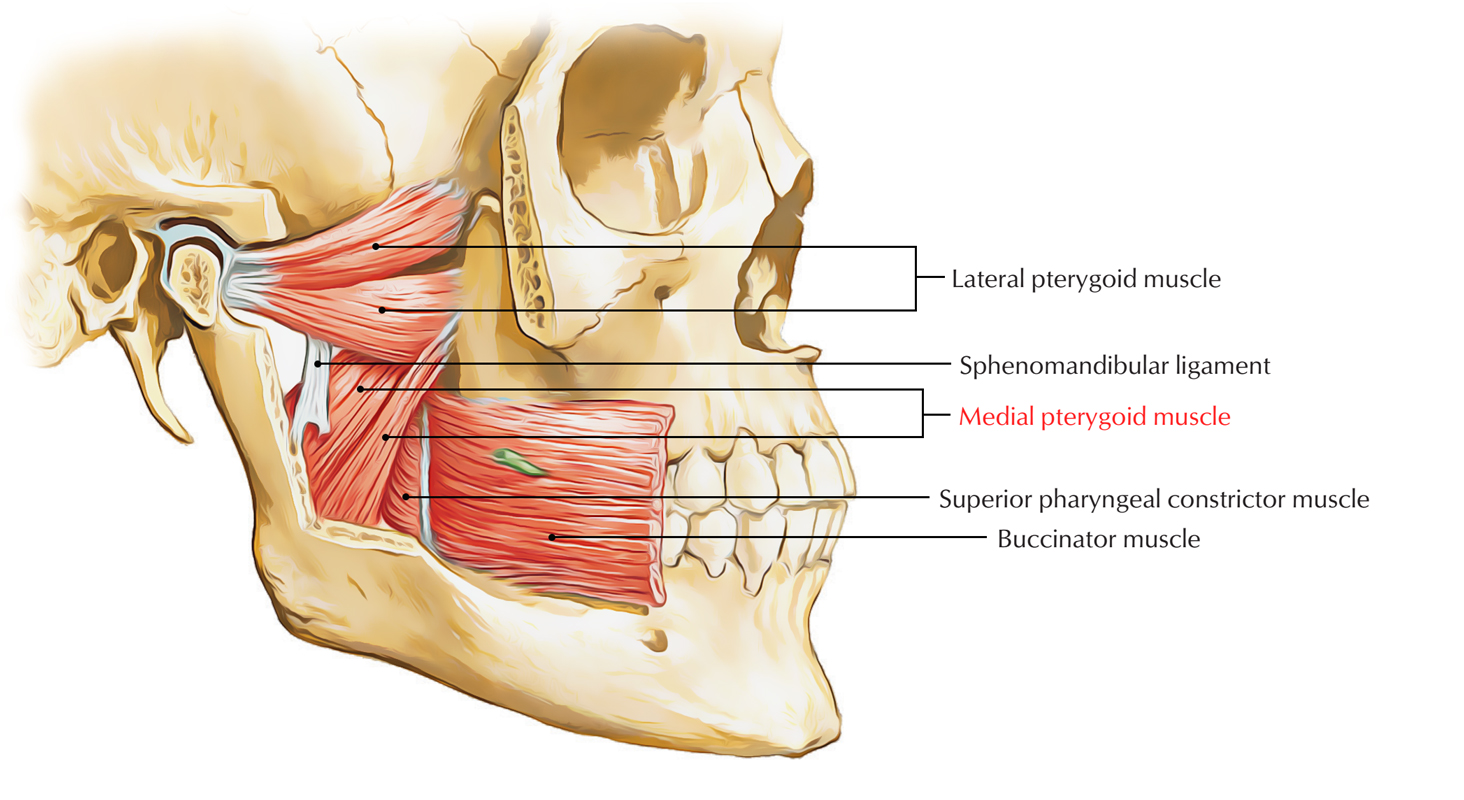
If there is abscess in the pterygomandibular space, which muscle shoud we incise to drain the content?
a. Masseter
b. Buccinator
c. Medial pterygoid
d. Risorius
b. Buccinator
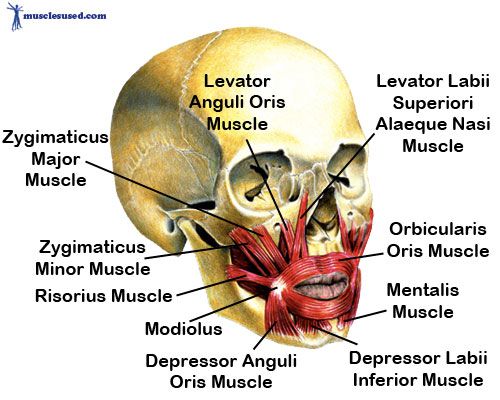
Structure where several facial muscles meet
Modiulus
What’s the muscle for the upper eyelid?
a. Levator palpebrae superioris
b. Superior tarsal plate
c. Corrugator supercilii
d. Orbicularis oculi
a. Levator palpebrae superioris
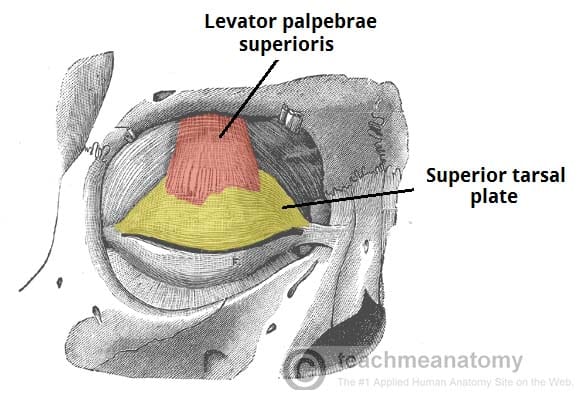
What cranial nerves innervate the muscles that (1) opens the eyes and (2) closes the eyes?
(1) CN 3
(2) CN 7
What is the structure in between the buccinator and superior pharyngeal constrictor?
Pterygomandibular raphe
(also a landmark for IAN block)
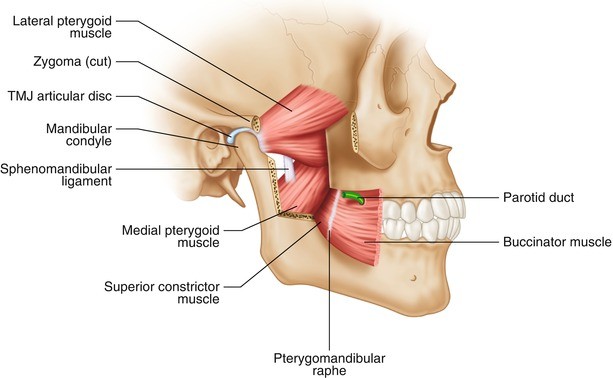
Which muscle is responsible for side to side movement of the mandible?
a. Masseter
b. Internal (medial) pterygoid muscle
c. External (lateral) pterygoid muscle
d. Temporalis
c. External (lateral) pterygoid muscle
Internal pterygoid can also move the mandible side to side but the primary muscle responsible for this is the External pterygoid muscle.
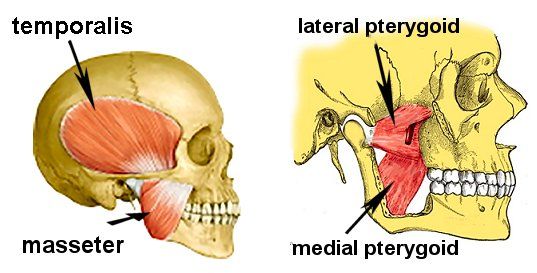
What is the major muscle for mouth opening?
a. Anterior belly of the digastric muscle
b. External pterygoid muscle
c. Posterior belly of the digastric muscle
d. Internal pterygoid muscle
a. Anterior belly of the digastric muscle
All of the following extrinsic tongue muscles are innervated by CN XII EXCEPT:
a. Genioglossus
b. Styloglossus
c. Hyoglossus
d. Palatoglossus
d. Palatoglossus - innervated by Pharyngeal plexus CN 9 & 10
All of the following are intrinsic tongue muscles EXCEPT:
a. Vertical
b. Inferior longitudinal
c. Horizontal
d. Superior longitudinal
c. Horizontal
VITS
Vertical
Inferior longitudinal
Transverse
Superior longitudinal
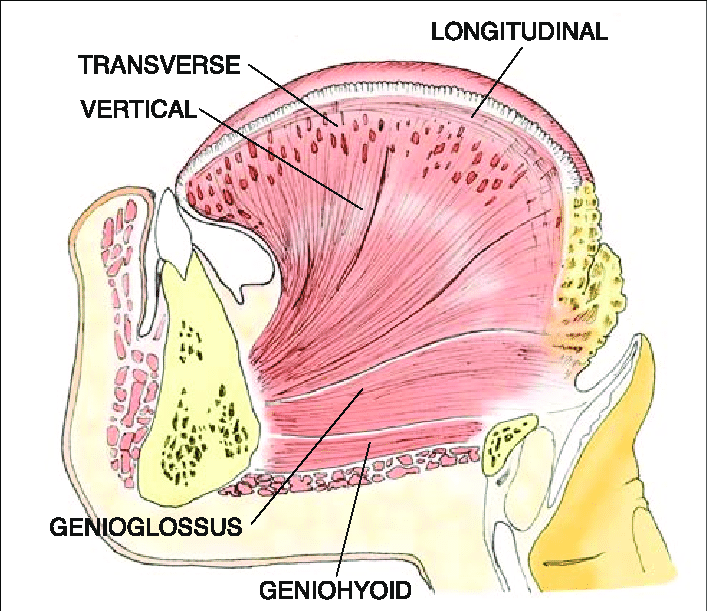
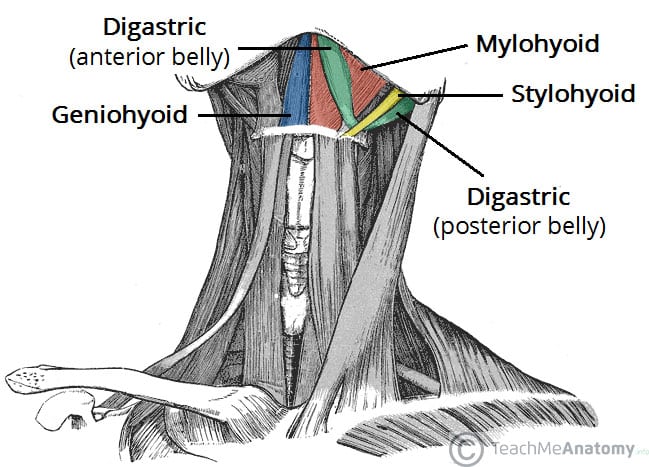
All of the following are suprahyoid muscles EXCEPT:
a. Digastic
b. Mylohyoid
c. Sphenohyoid
d. Geniohyoid
c. Sphenohyoid
Digastic
Mylohyoid
Stylohyoid
Geniohyoid
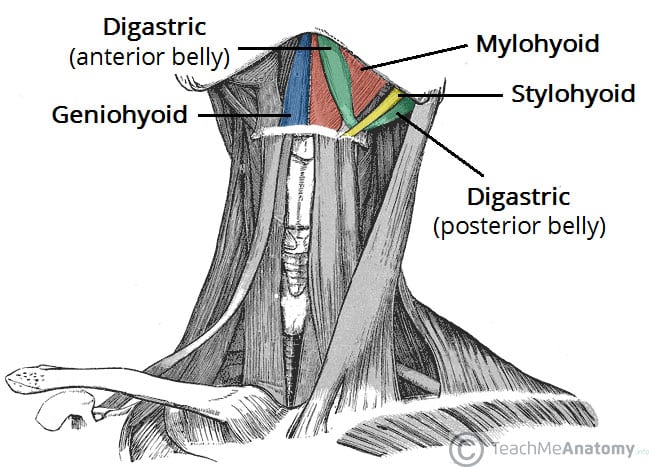
What muscle separates the submandibular gland into superficial and deep parts?
a. Geniohyoid muscle
b. Mylohyoid muscle
c. Digastic muscle
d. Sternothyroid muscle
b. Mylohyoid
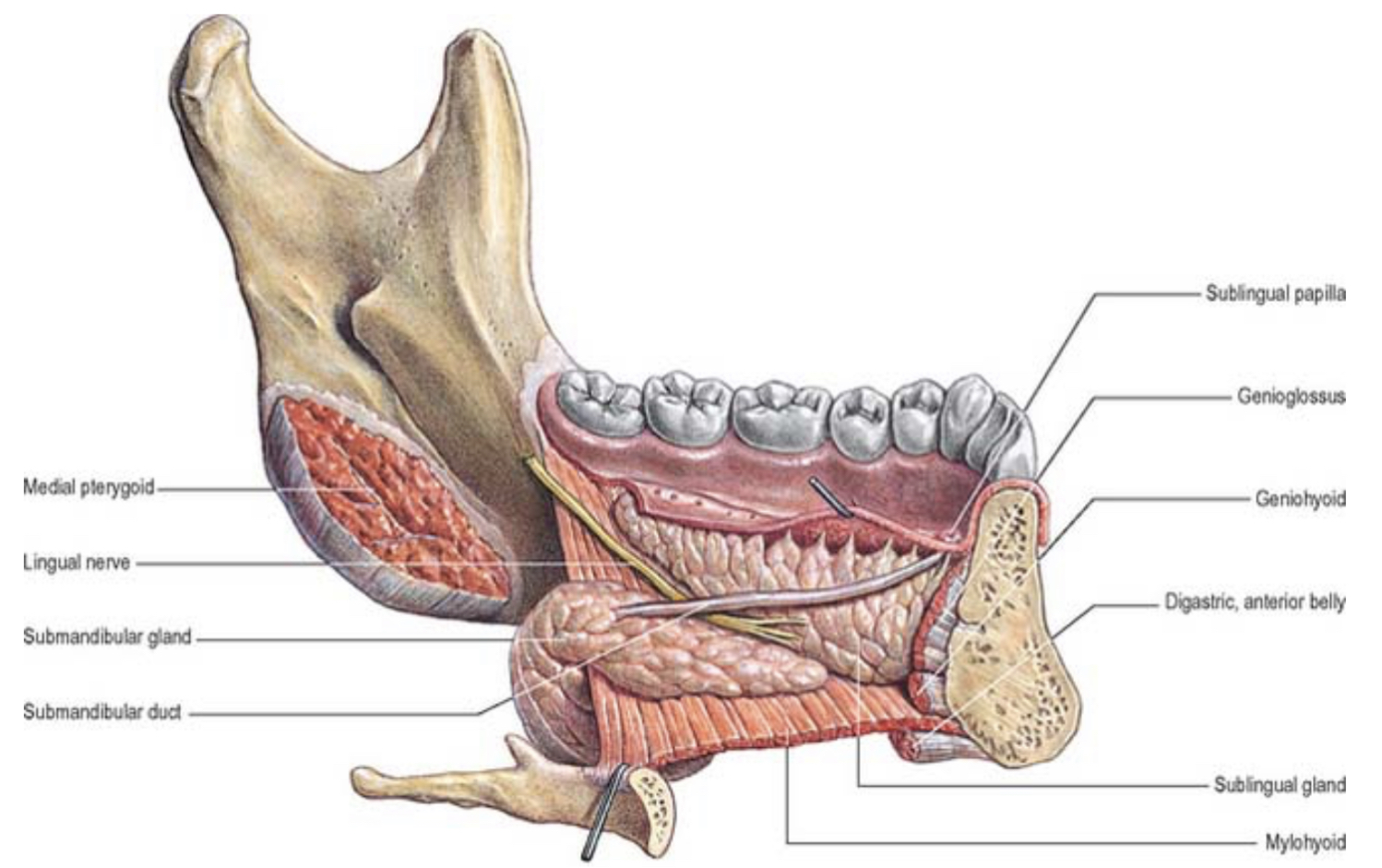
All of the following are infrahyoid muscles EXCEPT:
a. Sternohyoid
b. Omothyroid
c. Sternothyroid
d. Thyrohyoid
b. Omothyroid
Sternohyoid
Omohyoid
Sternothyroid
Thyrohyoid
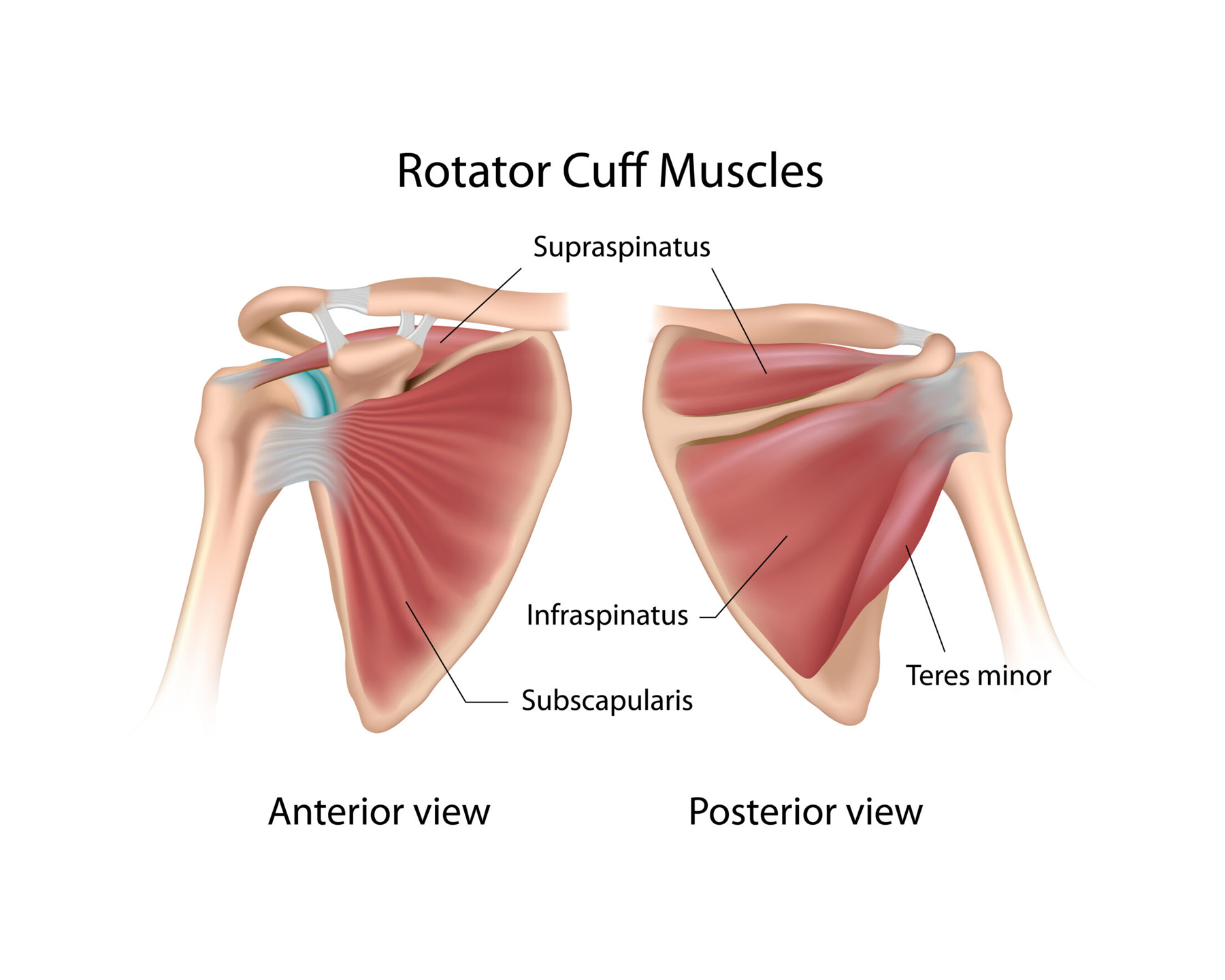
All of the following are rotator cuff muscles EXCEPT:
a. Supraspinatus
b. Infraspinatus
c. Teres major
d. Subscapularis
c. Teres major
SITS
Supraspinatus
Infraspinatus
Teres minor
Subscapularis
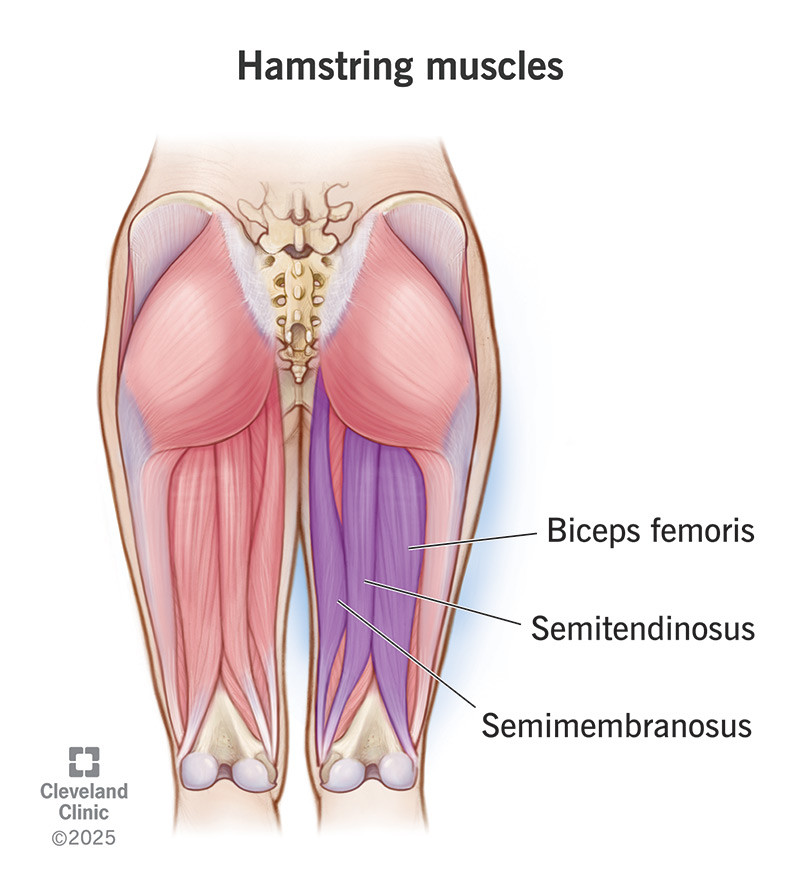
All of the following are hamstring muscles EXCEPT:
a. Semimembranosus
b. Biceps femoris
c. Semitendinosus
d. Semimedialis
d. Semimedialis
Hams3ngs - Bi Semi Semi
Biceps femoris
Semimembranosus
Semitendinosus
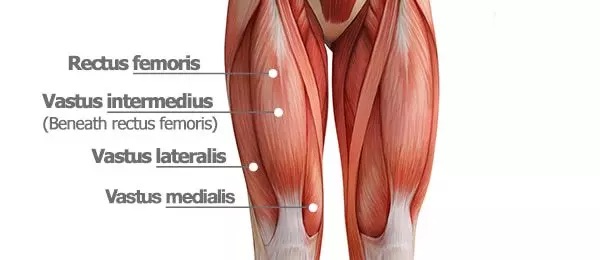
All of the following are quadriceps muscles EXCEPT:
a. Vastus intermedius
b. Rectus femoris
c. Semimembranosus
d. Vastus medialis
c. Semimembranosus
Sa Recto may 3 Vastus
Rectus femoris
Vastus lateralis
Vastus intermedius
Vastus medialis
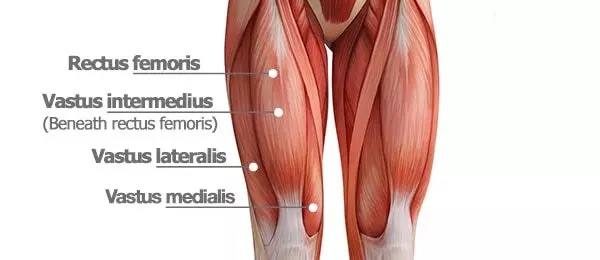
Most common muscle used in infants for drug administration
a. Vastus lateralis
b. Deltoid
c. Triceps
d. Gluetal muscles
a. Vastus lateralis
Which muscle flex the legs?
a. Hamstrings
b. Quadriceps
a. Hamstrings
Quadriceps EXTEND the legs
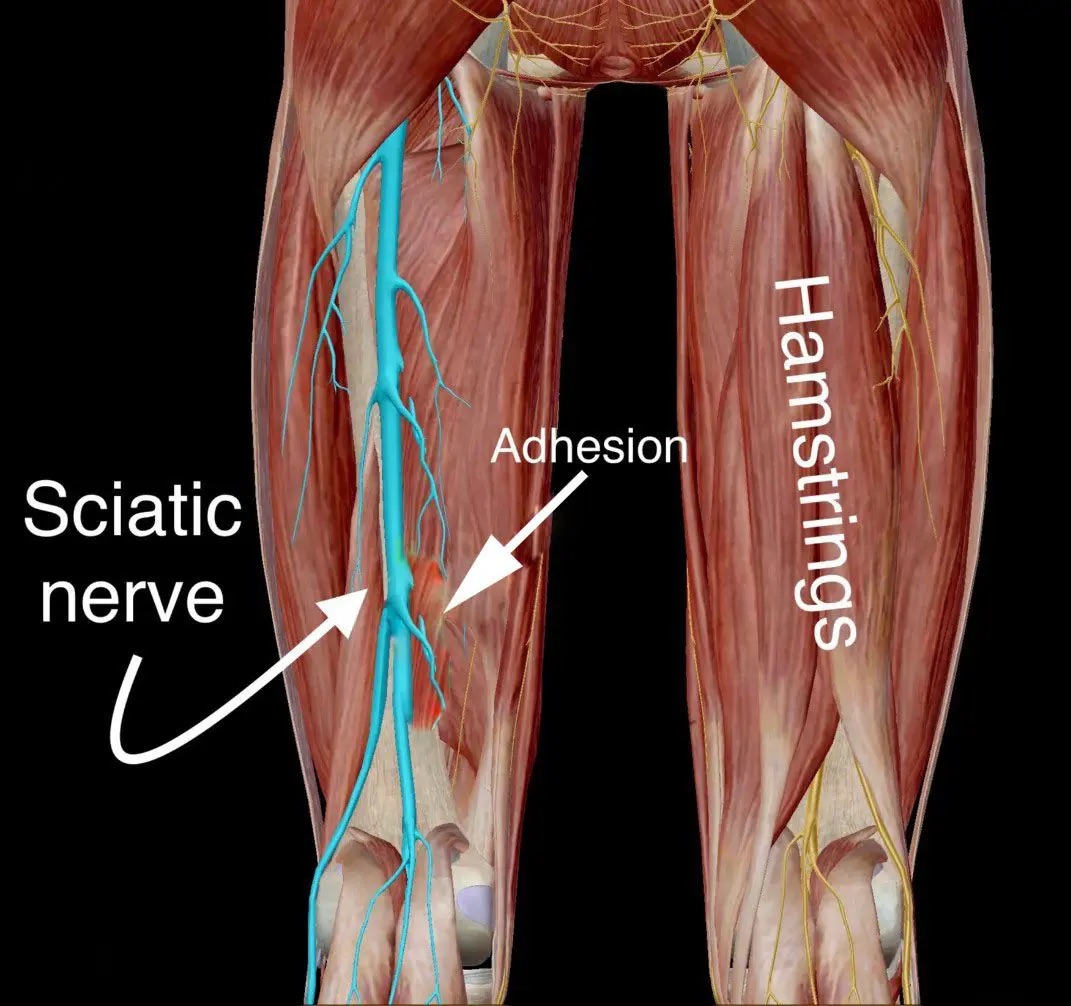
Which muscle is innervated by the sciatic nerve?
a. Hamstrings
b. Quadriceps
a. Hamstrings
Quadriceps is innervated by the FEMORAL nerve
What is the longest cranial nerve?
a. Abducens never (CN 6)
b. Vagus nerve (CN 10)
c. Trochlear nerve (CN 4)
d. Trigeminal nerve (CN 5)
b. Vagus nerve (CN 10)
What is the longest intracranial nerve?
a. Abducens never (CN 6)
b. Vagus nerve (CN 10)
c. Trochlear nerve (CN 4)
d. Trigeminal nerve (CN 5)
c. Trochlear nerve (CN 4)
What is the smallest cranial nerve?
a. Abducens never (CN 6)
b. Vagus nerve (CN 10)
c. Trochlear nerve (CN 4)
d. Trigeminal nerve (CN 5)
c. Trochlear nerve (CN 4)
What is the largest cranial nerve?
a. Abducens never (CN 6)
b. Vagus nerve (CN 10)
c. Trochlear nerve (CN 4)
d. Trigeminal nerve (CN 5)
d. Trigeminal nerve (CN 5)
Which is FALSE for serotonin?
a. Increases GI motility
b. Vasodilator
c. Makes you awake
b. Vasodilator
It is a vasoconstrictor
Opposite of melatonin
a. Histamine
b. Dopamine
c. Adrenaline
d. Noradrenaline
a. Histamine
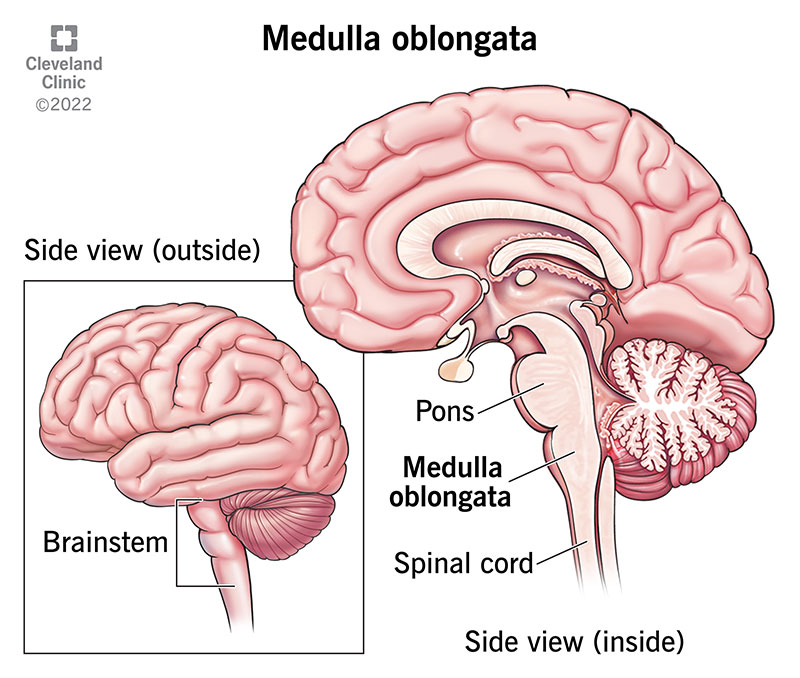
Respiratory center is found on what part of brain?
a. Metencephalon
b. Mesencephalon
c. Medulla oblongata
d. Diencephalon
c. Medulla oblongata
Pons varolii in Metencephalon also controls respiration, but Medulla oblongata is the primary respiratory center.
The central chemoreceptors is sensitive to the following EXCEPT:
a. Decreased O2 levels
b. Increased CO2 levels
c. Increased H+ levels
d. Decreased CO2 levels
d. Decreased CO2 levels
The central chemoreceptors are sensitive to:
1) Increased CO2 levels (hypercapnia)
2) Decreased O2 levels
3) Increased H+ levels
They are most sensitive to increased CO2 levels. If activated, there will be:
1) Increased breathing rate
2) Increased excretion of H+ in kidneys
General action of extrinsic muscles of tongue
Moves the tongue
General action of intrinsic muscles of tongue
Changes the shape of the tongue
The following are the components of the margin of the bony orbit, EXCEPT:
a. Frontal bone
b. Zygomatic bone
c. Maxilla
d. Nasal bone
d. Nasal bone
Which muscle is attached to malleus?
a. Stapedius
b. Tensor tympani
c. Levator angulii
d. Stapes
b. Tensor tympani muscle
Which of the two fontanelles is the first one to close during development?
a. Lambda
b. Bregma
a. Lambda
Lambda - closes at 12 mos
Bregma - closes at 18mos
How many pelvic bones are there in the body?
a. 1
b. 2
c. 3
d. 4
b. 2
Which of the following is not a component of the pelvic inlet?
a. Sacral promontory
b. Ileopectinal line
c. Symphysis pubis
d. Acetabulum
d. Acetabulum
What level is the carina located in thw ribs?
a. Transverse ridge / Sternal angle
b. Manubrium
c. Body / Corpus
d. Xiphoid process
a. Transverse ridge / Sternal angle
Which is more lateral, radius or ulna?
a. Radius
b. Ulna
Radius
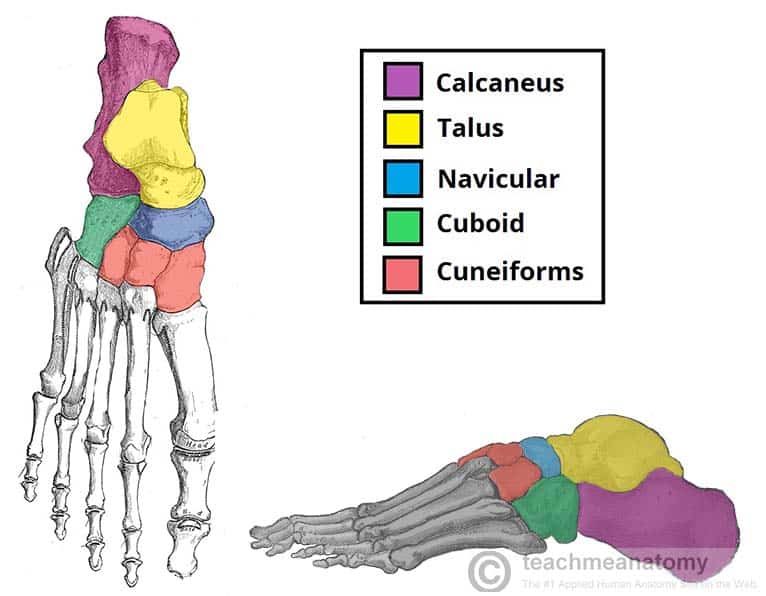
What is the most posterior of tarsals?
a. Calcaneus
b. Talus
c. Navicular
d. Cuneiform
a. Calcaneus
Which is the two (origin or insertion) moves less?
a. Origin
b. Insertion
a. Origin
If the molar % of adenine is 20%, what is the molar % of cytosine?
a. 40%
b. 30%
c. 20%
d. 10%
b. 30%
/Following Chargatt’s rule:
A (20%) - T (20%)
G (x) - C (x)
100% - 40% = 60%
60% / 2 = 30%
A (20%) - T (20%)
G (30%) - C (30%)
What is the strand A for this amino acid sequence?
Leu - Arg
5’ AAC GUC 3’ (tRNA)
a. 3’ GAC GUU 5’
b. 3’ GAC GTT 5’
c. 3’ TCC AAC 5’
d. None of the above
b. 3’ GAC GTT 5’
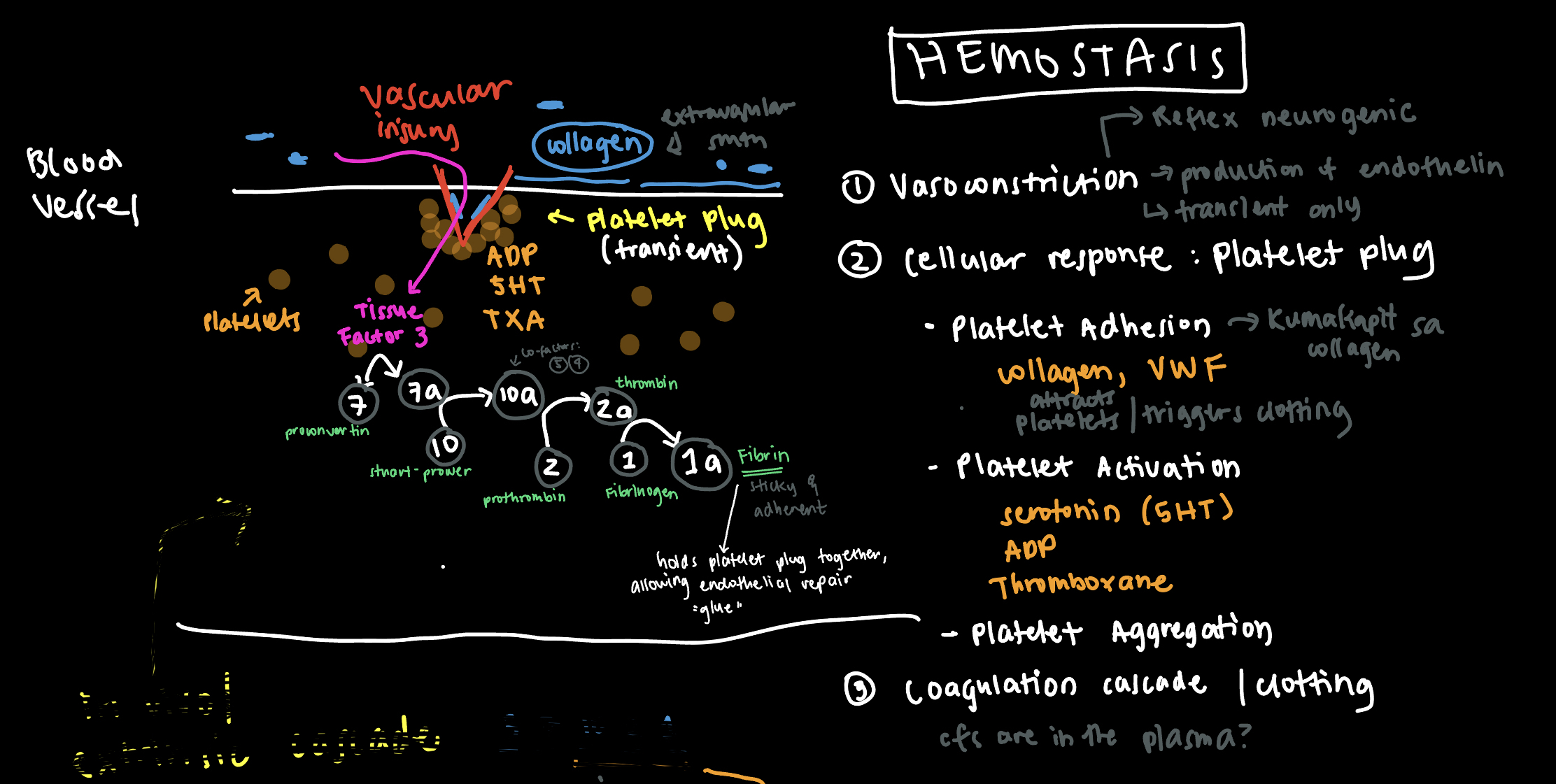
In hemostasis, which of the following activates Prothrombin?
a. Factor 5 - Labile factor
b. Factor 9 - Christmas factor
c. Factor 1 - Fibrinogen
d. Factor 7 - Proconvertin
a. Factor V - Labile factor
Proper answer is Tissue Factor 10. If TF 10 is not in the choices, we can choose its co-factors: Labile factor (factor 5) or Calcium (factor 4)
Prothrombin is Factor 2
Most common hemophilia
a. A (TF8 deficiency)
b. B (TF 9 deficiency)
c. C (TF 11 deficiency)
a. A (TF 8 deficiency)
TF = Tissue factor
How many of the cranial nerves has a sensory innervation?
a. 6
b. 7
c. 8
d. 9
b. 7
Which if the cranial nerves secremotor function of the parotid gland?
a. Facial
b. Glossopharyngeal
c. Trigeminal
d. Hypoglossal
b. Glossopharyngeal
(salivary glands)
All of the following are innervated by the spinal nerve except:
a. Chest muscles
b. Trapezius
c. Abdomen
d. Triceps
b. Trapezius
from Dr. Carigma: if Trapzius and Sternocleidomastoid are among the choices, it’s the answer. They are innervated by spinal accessory.
Which viral infection presents as painful blisters in a dermatomal pattern?
a. Ulticaria
b. Herpes labialis
c. Herpes zoster
d. Cellulitis
c. Herpes zoster (caused by Varicella zoster virus)
site of latency: dorsal root of ganglion
affecrs the sensory aspect of spinal nerve = presents in a dermatomal pattern
Which of the following gives you myelin in the central nervous system?
a. Oligodendrocytes
b. Schwann cells
a. Oligodendrocytes
How many nodes of Ranview should be blocked to halt impulse propagation?
a. 1 node
b. 2-3 nodes
c. 4-5 nodes
d. None
b. 2-3 nodes of Ranvier
How many millimeter of the axon should be blocked to halt impulse propagation?
a. 2-5mm
b. 8-12mm
c. 15-18mm
d. Doesn’t matter
b. 8-12mm OR 10-15mm
For every 4-5mm of the axon, there is a node of Ranvier. We need 2-3 nodes of Ranvier to block to halt impulse propagation.
Which has the faster conduction?
a. Myelinated axon
b. Non-mmyelinated axon
a. Myelinated axon
Conduction jumps from one myelin to another = faster
Which nerve fiber is blocked first?
a. Large, myelinated
b. Large, non-myelinated
c. Small, myelinated
d. Small, non-myelinated
d. Small, non-myelinated
Which myofilament is responsible for muscle elasticity?
a. Actin
b. Myosin
c. Titin
d. All of the above
c. Titin
Which of the following cartilages is the weakest?
a. Hyaline
b. Elastic
c. Fibrous
a. Hyaline
Which is responsible for mediating allergic reaction?
a. IgM, IgA, IgE
b. IgA, IgE, IgD
c. IgM, IgA, IgE
d. IgM, IgG, IgE
d. IgM, IgG, IgE
IgE - Type 1 hypersensitivity
IgM, IgG - Type 2 hypersensitivity
Which is responsible for opsonization (marking the pathogen for phagocytosis)of bacteria?
a. C5a
b. C3a
c. C3b
d. C5a
c. C3b
Which of the following is attacked by HIV?
a. Killer T cells or CD4
b. Helper T cells or CD8
a. Killer T cells or CD4
Which among the paranasal sinuses does not have a direct drainage to the middle meatus?
a. Frontal sinus
b. Ethmoid sinus
c. Maxillary sinus
d. Sphenoid sinus
d. Sphenoid sinus