HS EOY Geography Revision
1/134
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
135 Terms
Describe the climate of a desert
Hot in daytime
Cool at night
Dry
What is a desert?
A hot or cold place that receives less than 250 mm of rainfall a year
Where are hot deserts mainly located?
15-30° north and south of the equator
How has the cactus plant adapted to the desert climate?
It stores water and has a thick, waxy skin
What are xerophytic plants?
Plants with adaptations that allow them to survive in hot and dry conditions.
What is the term for plants with adaptations that allow them to survive in hot and dry conditions?
Xerophytic plants
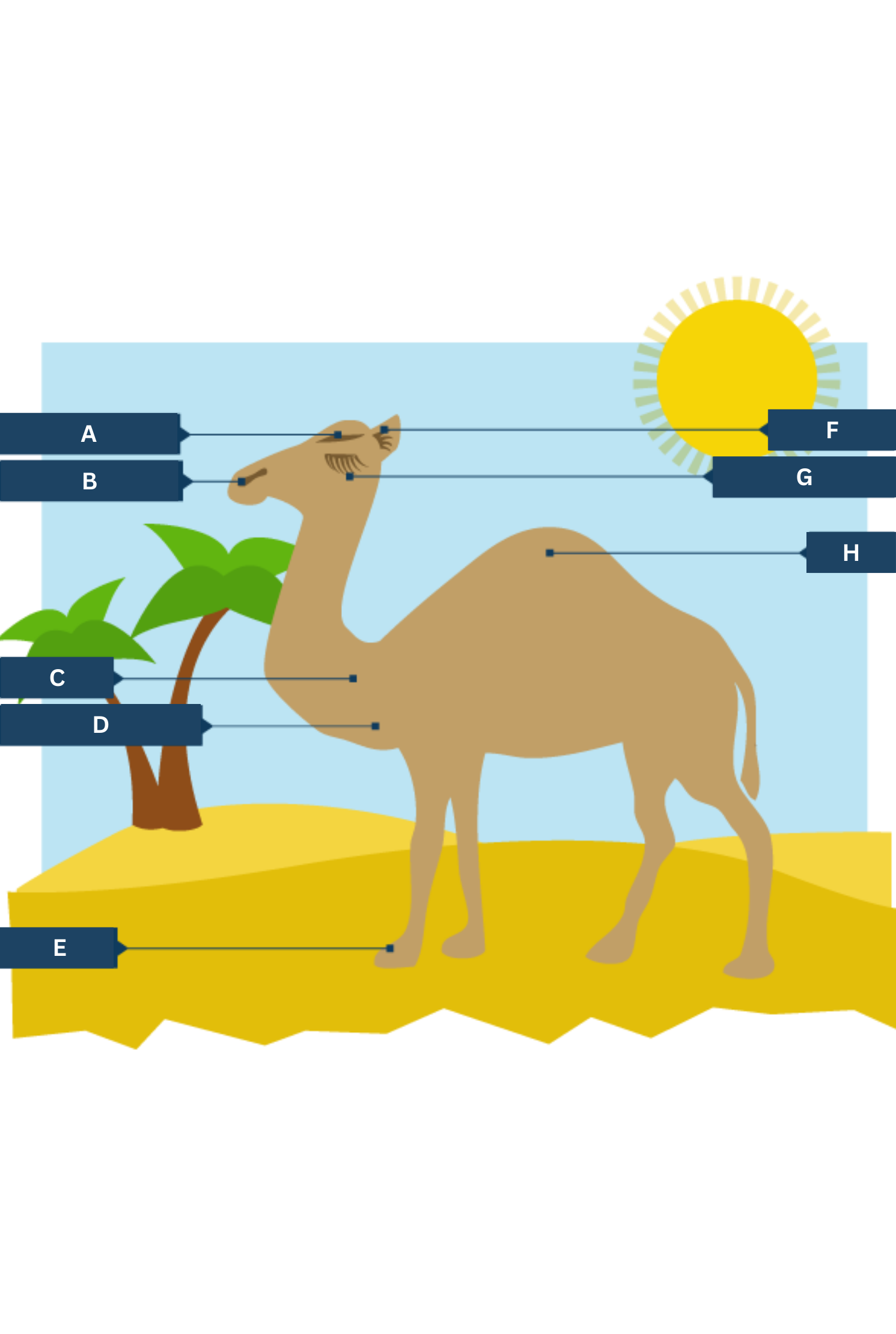
What is A on the camel adaptations diagram?
Thick eyebrows
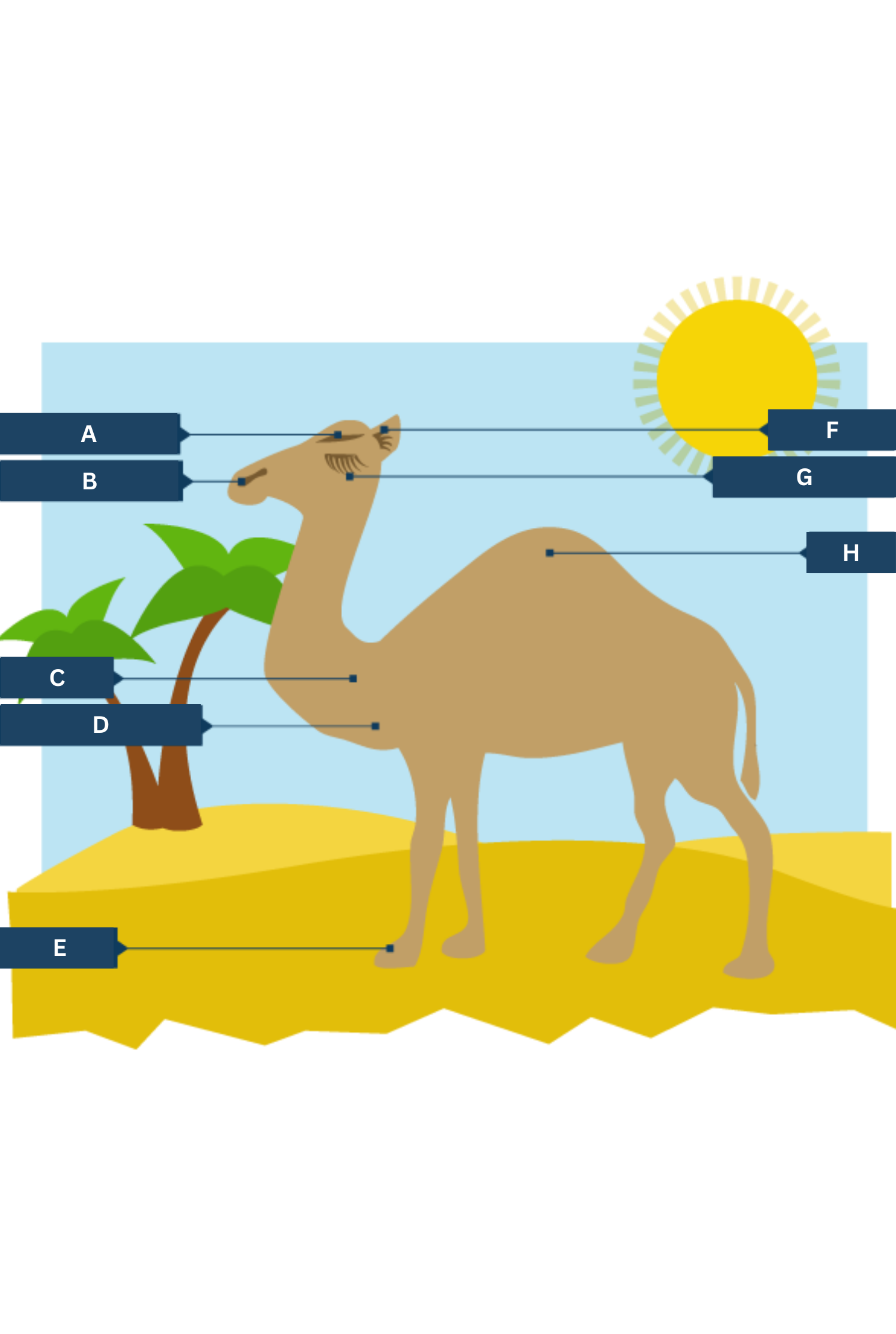
What is B on the camel adaptations diagram?
Slit-like nostrils - to help keep out sand
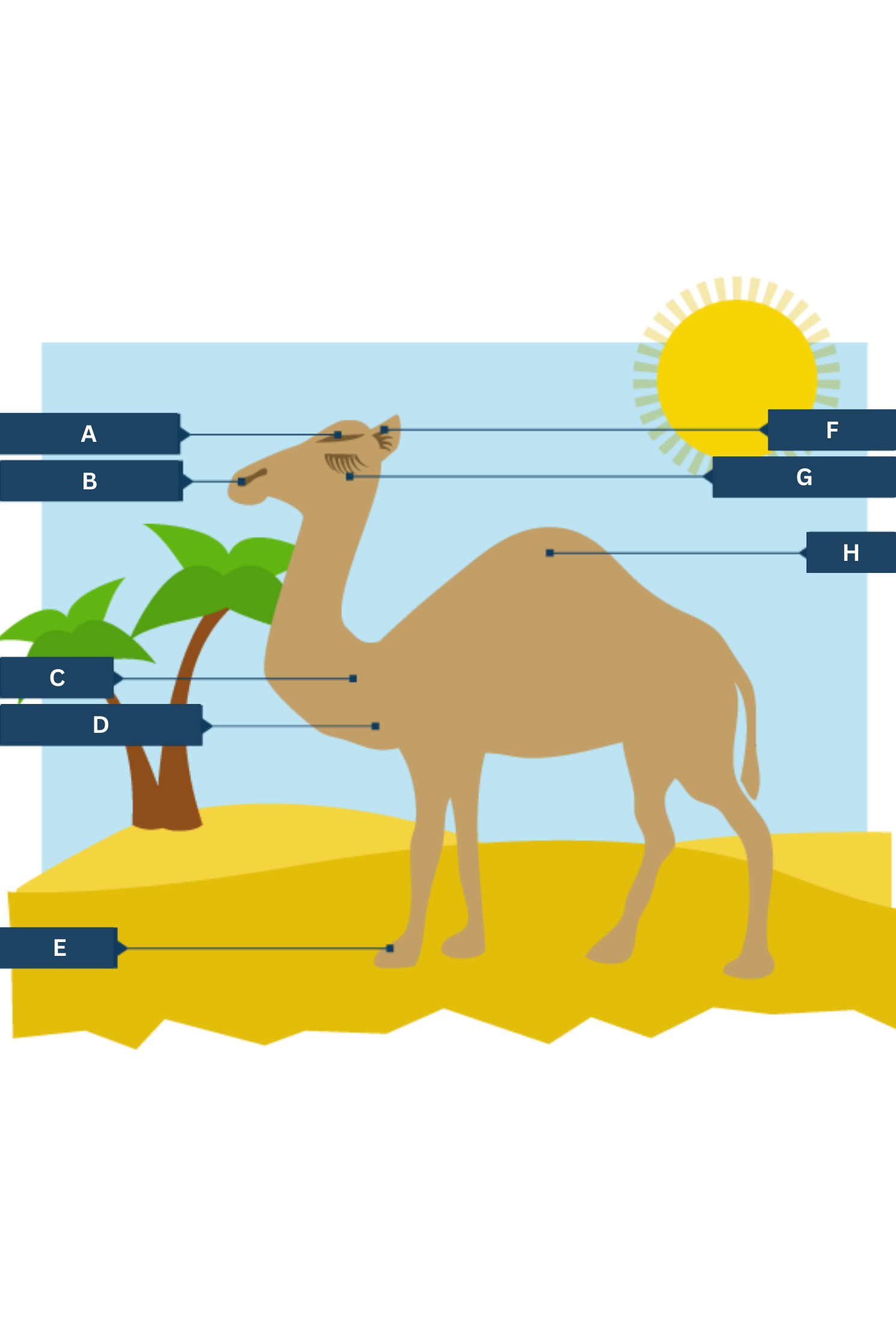
What is C on the camel adaptations diagram?
Thick fur on the top of the body for shade, and thin fur elsewhere to allow easy heat loss.
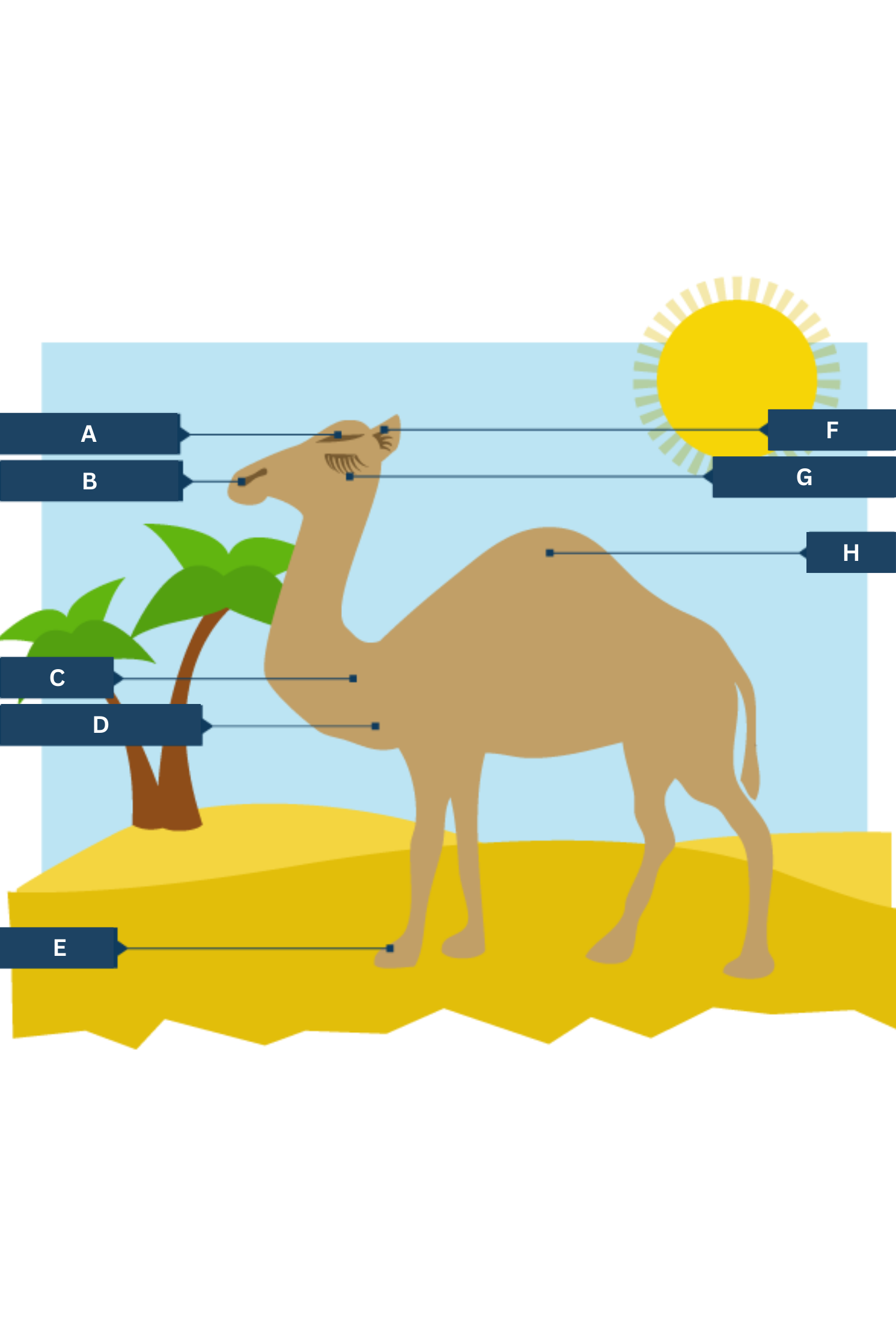
What is D on the camel adaptations diagram?
Well camouflaged
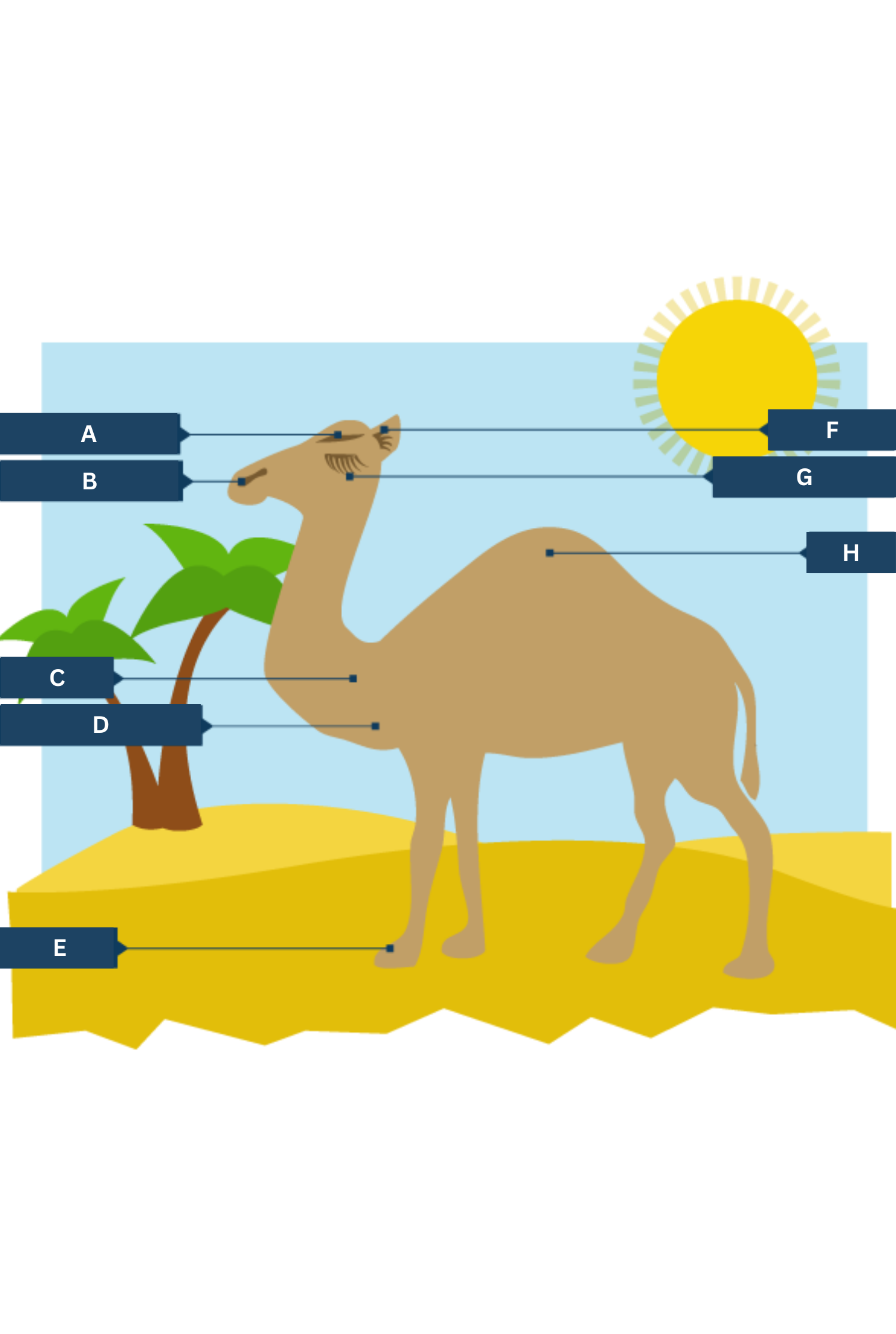
What is E on the camel adaptations diagram?
Large, flat feet - to spread their weight on the sand
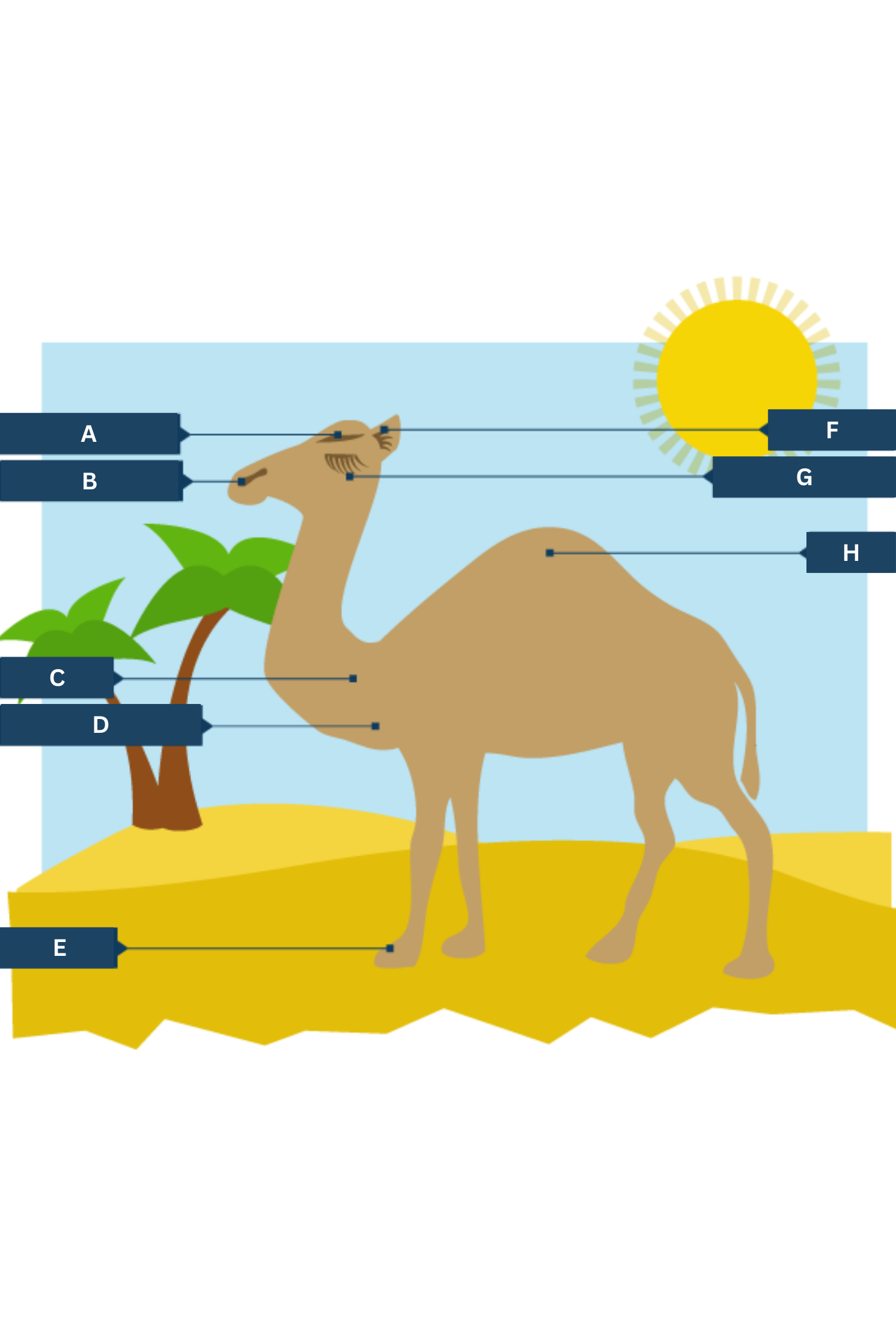
What is F on the camel adaptations diagram?
Hairy ears
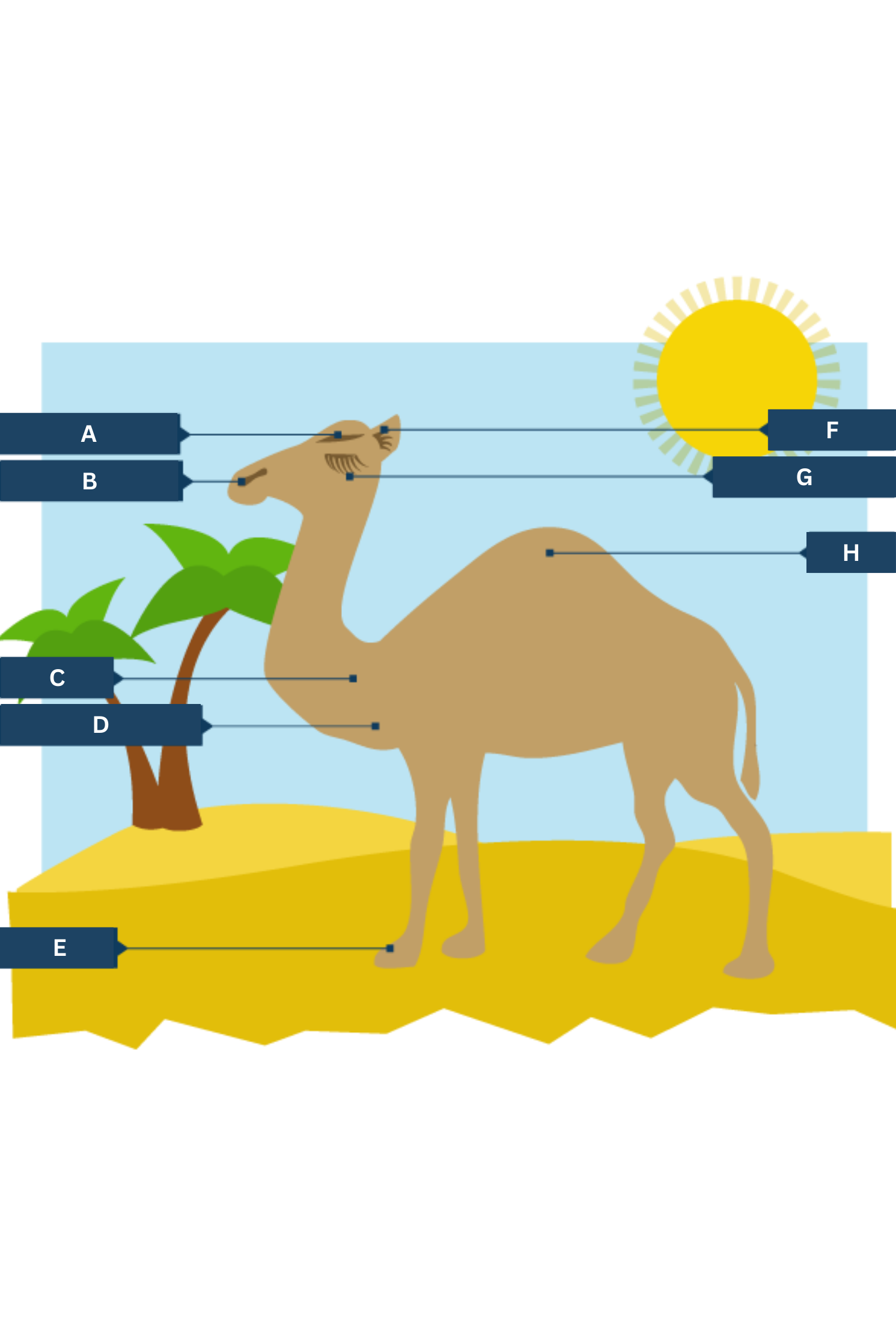
What is G on the camel adaptations diagram?
Two rows of eyelashes - to help keep out sand
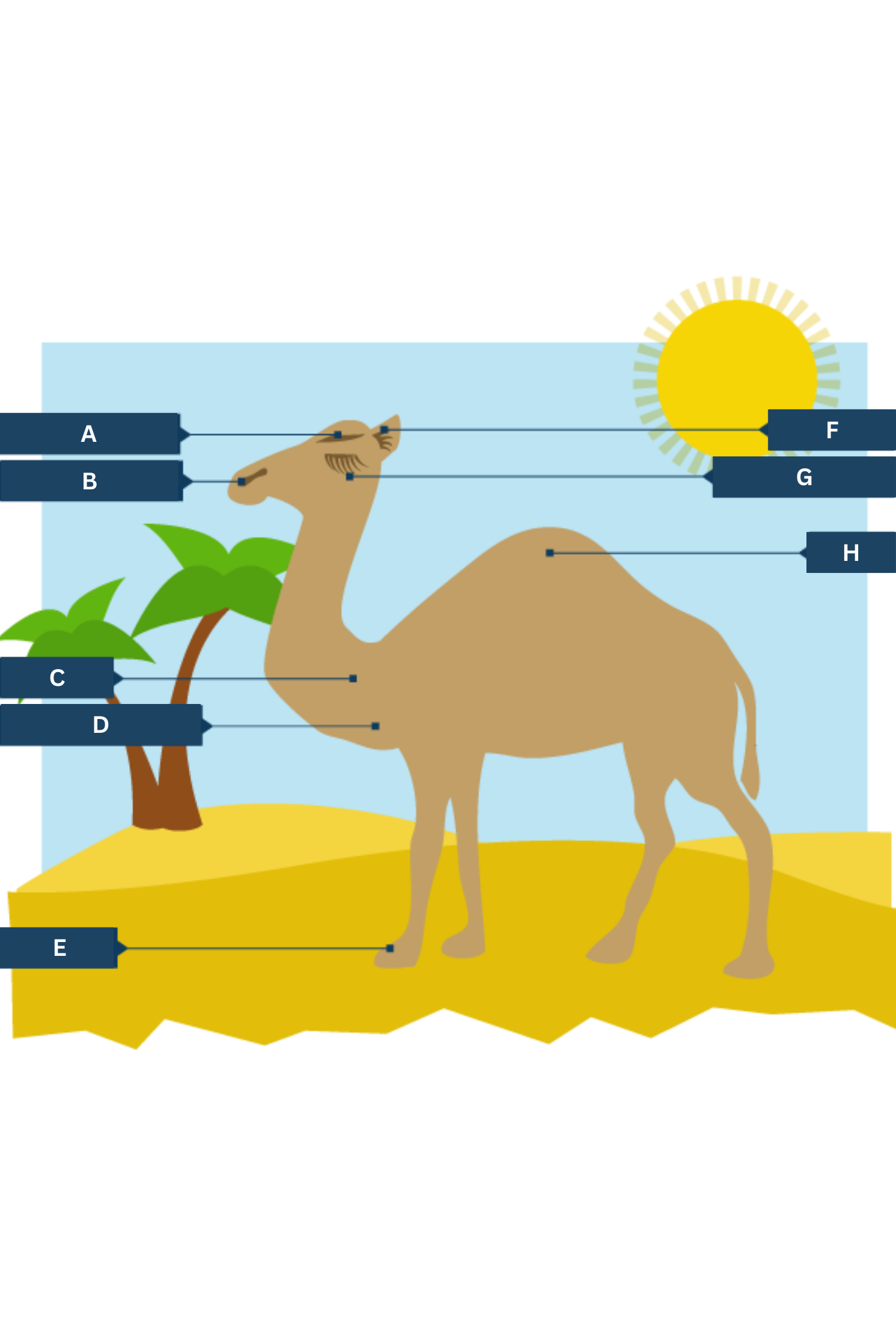
What is H on the camel adaptations diagram?
Hump - stores fat
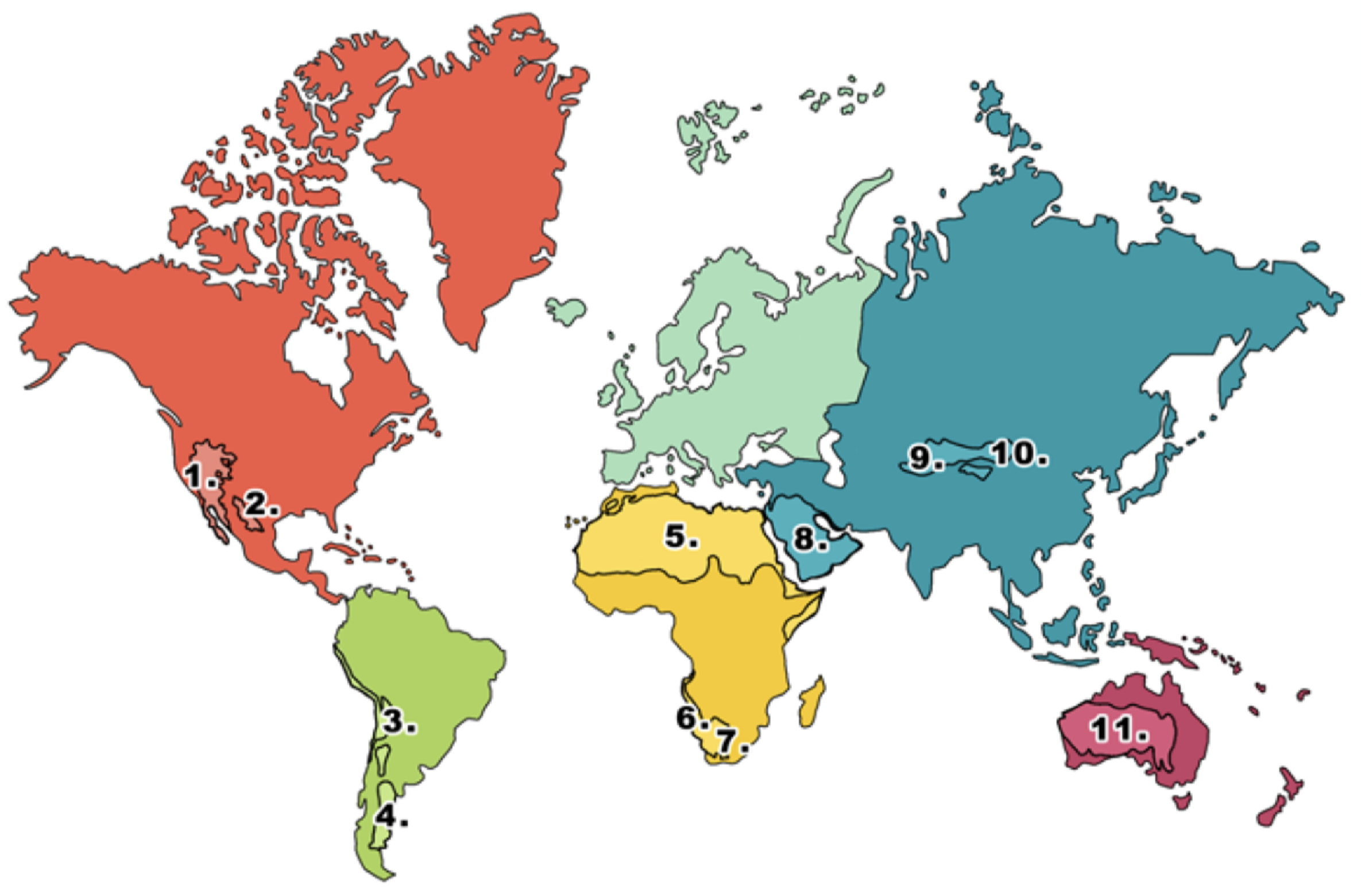
What is 1 on the deserts diagram?
Mojave desert
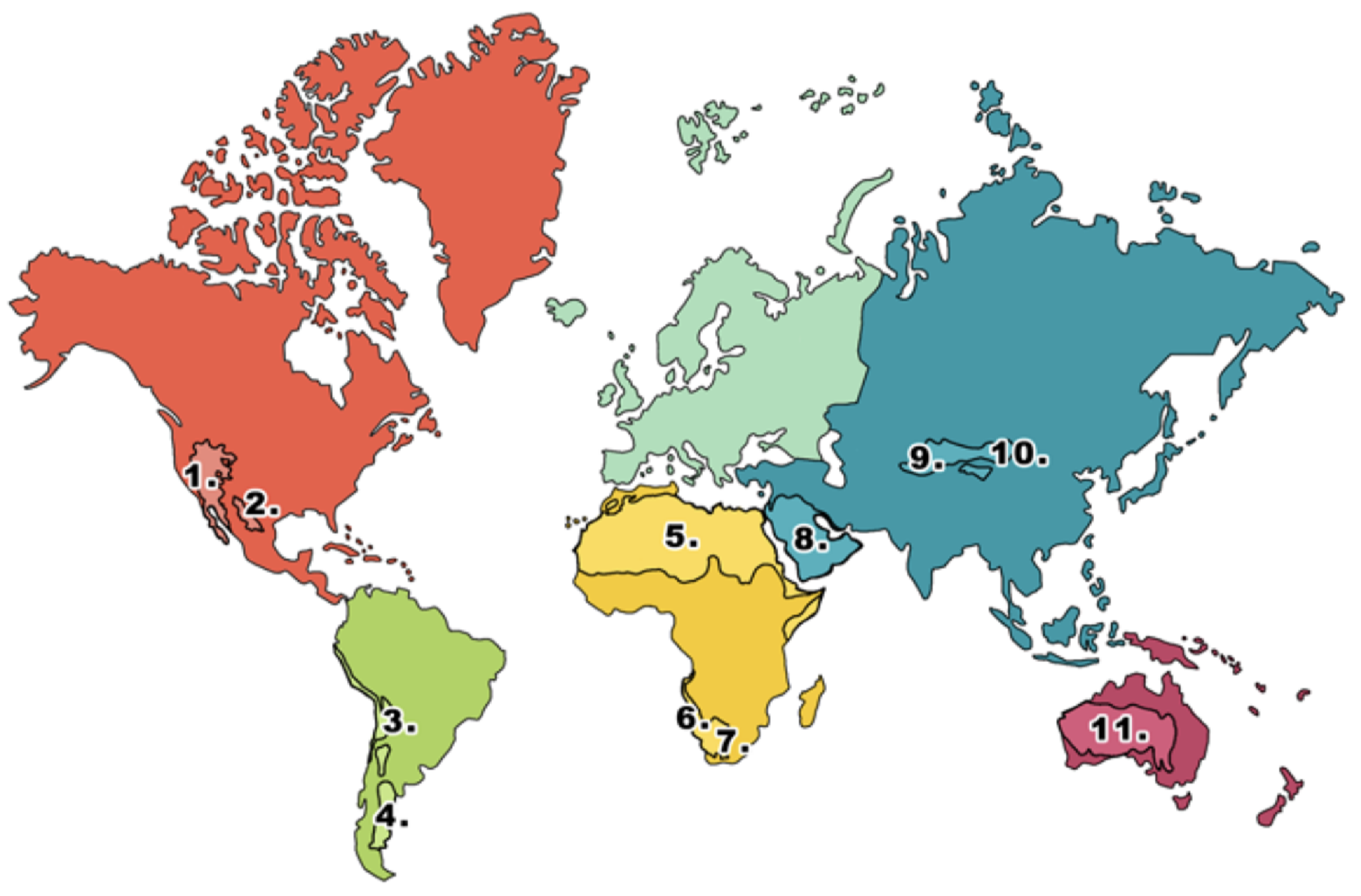
What is 2 on the deserts diagram?
Chihuahuan desert
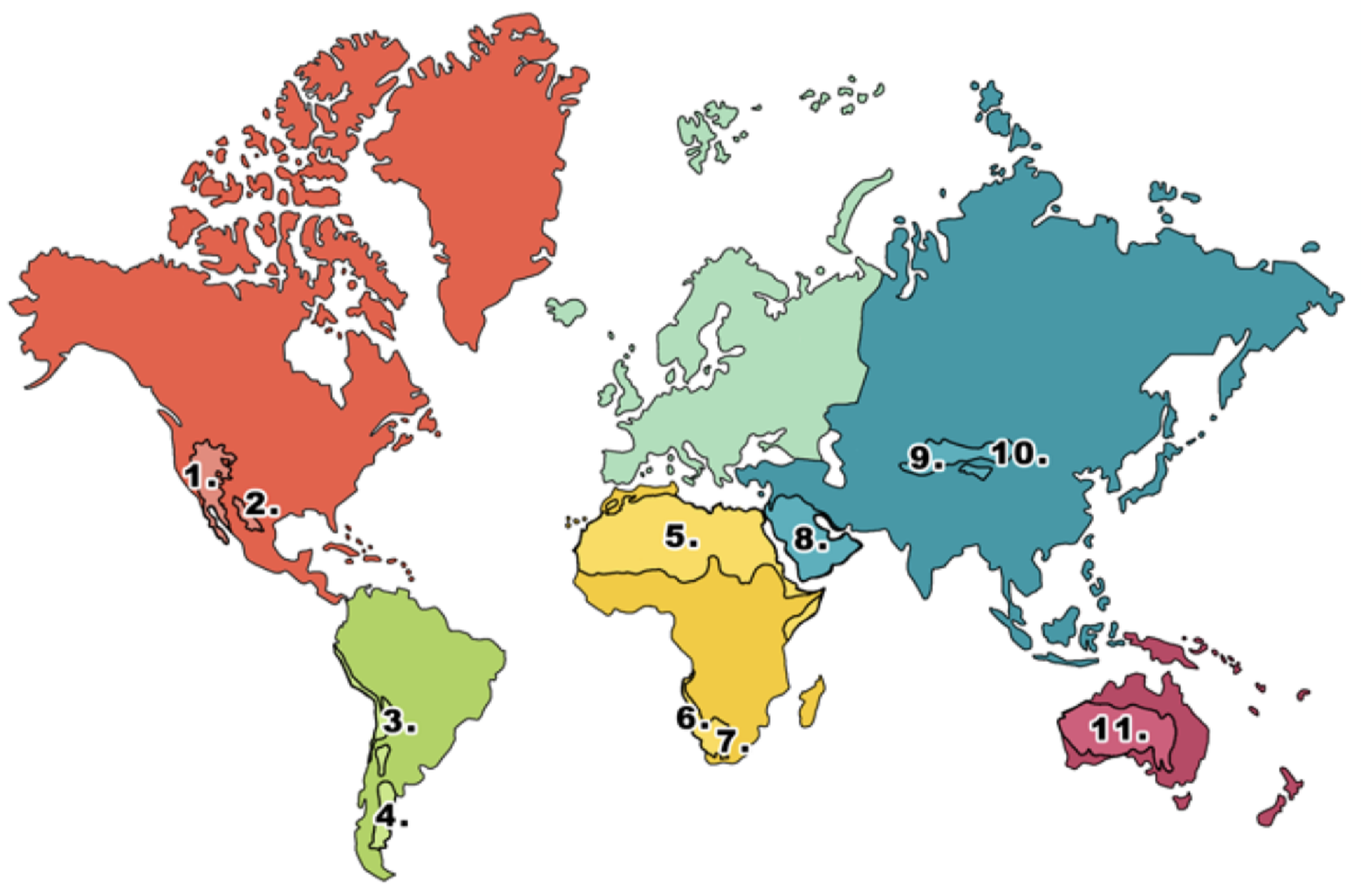
What is 3 on the deserts diagram?
Atacama desert
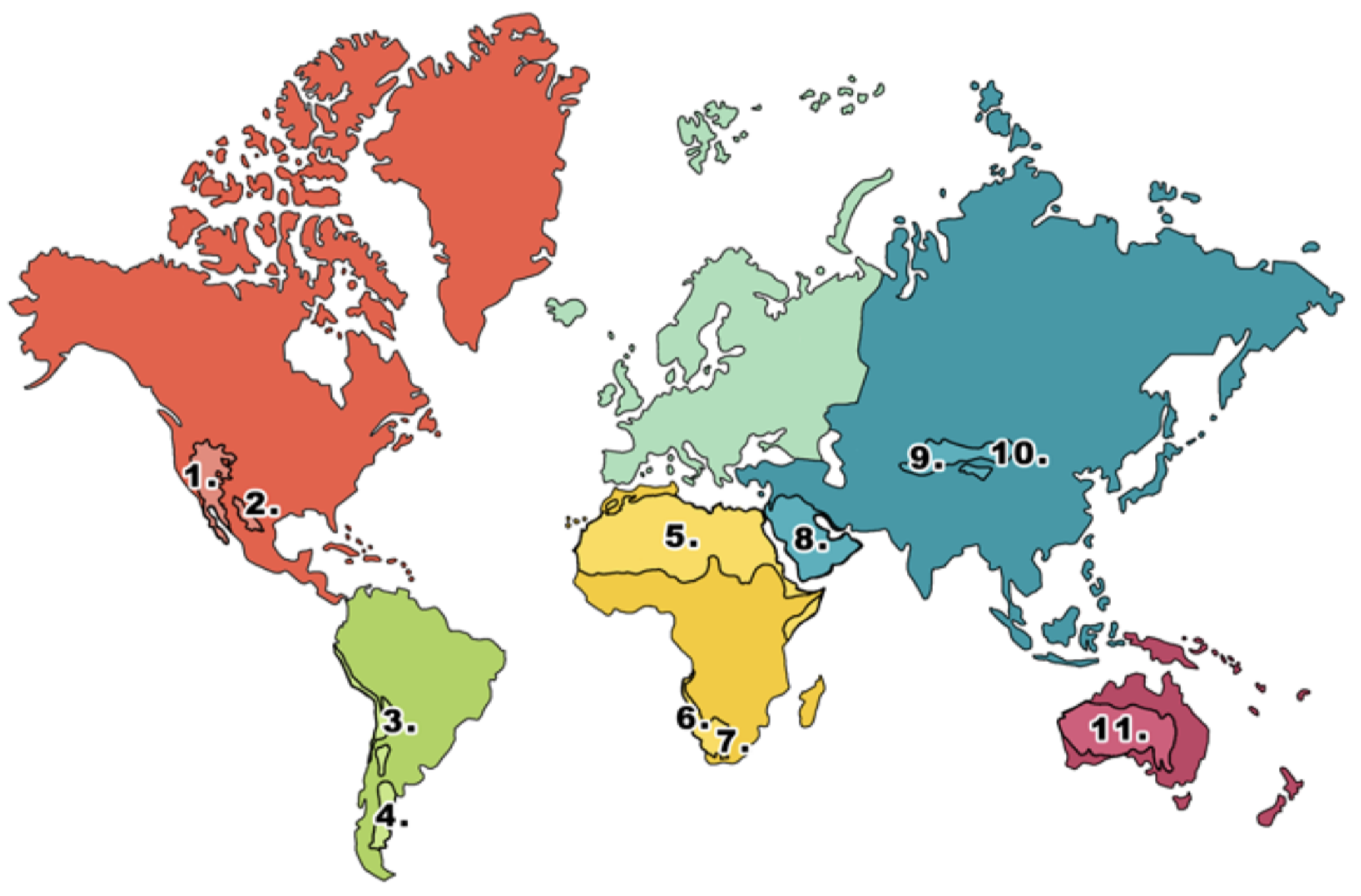
What is 4 on the deserts diagram?
Patagonian desert
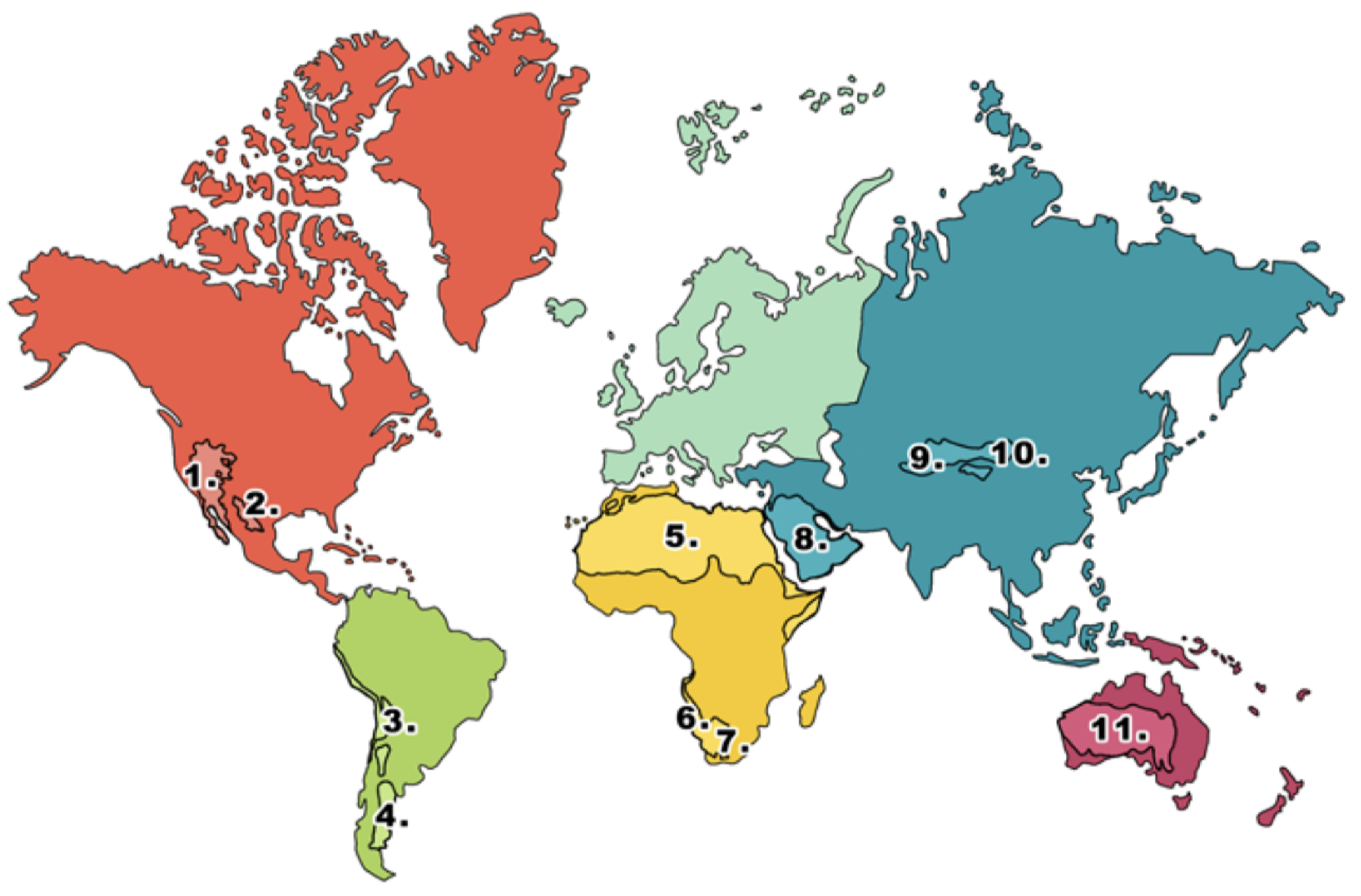
What is 5 on the deserts diagram?
Sahara desert
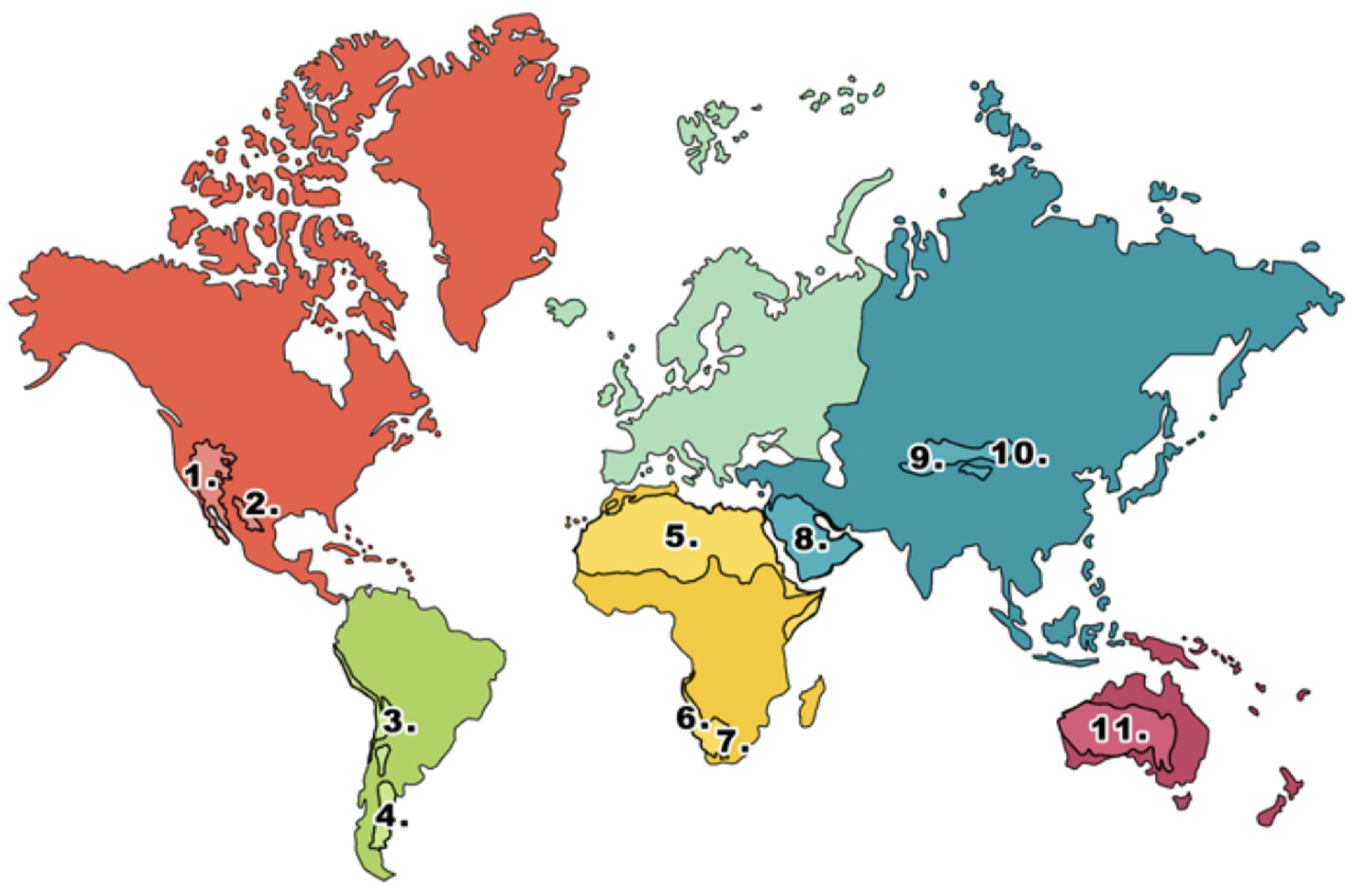
What is 6 on the deserts diagram?
Namib desert
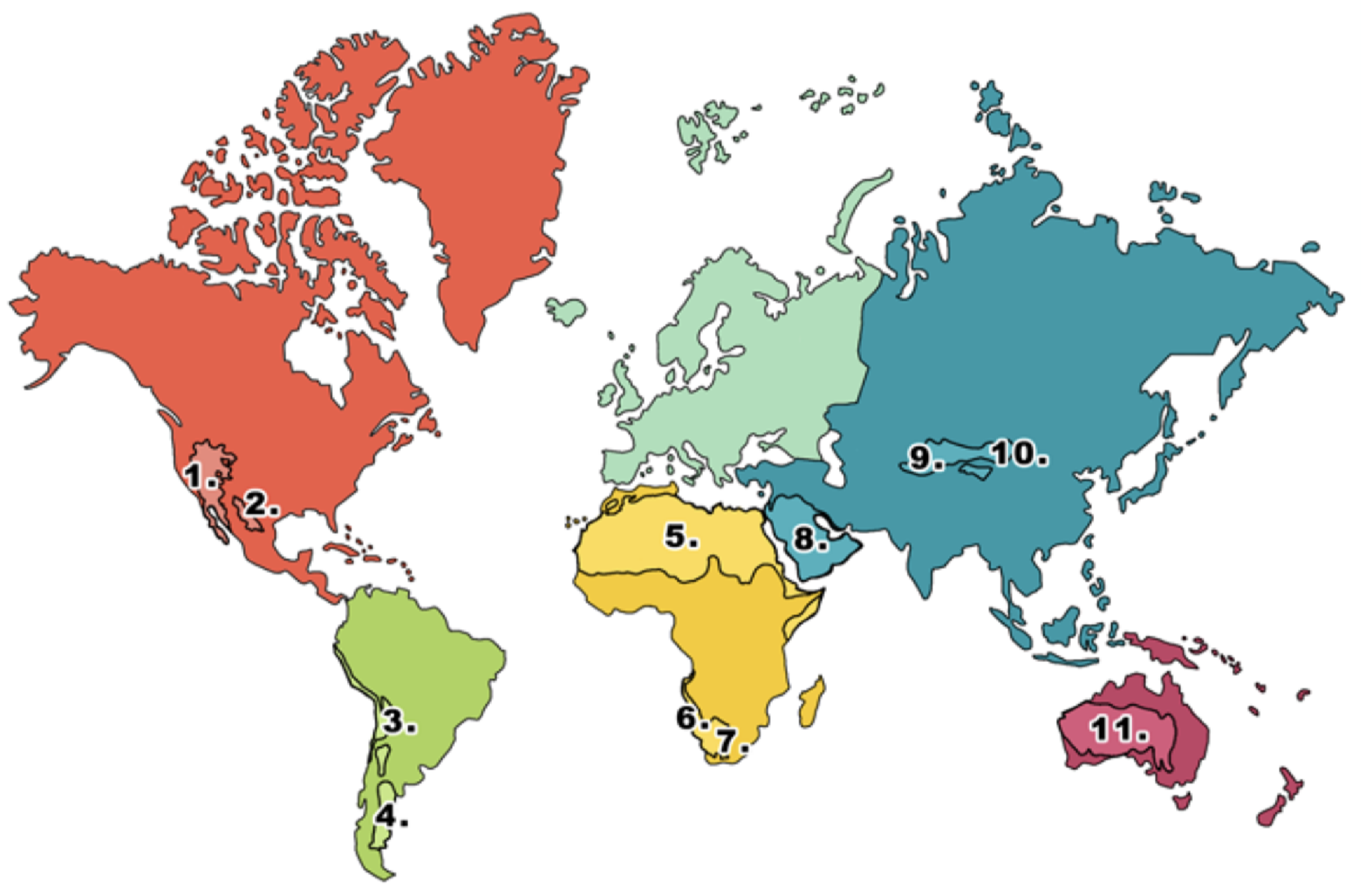
What is 7 on the deserts diagram?
Kalahari desert
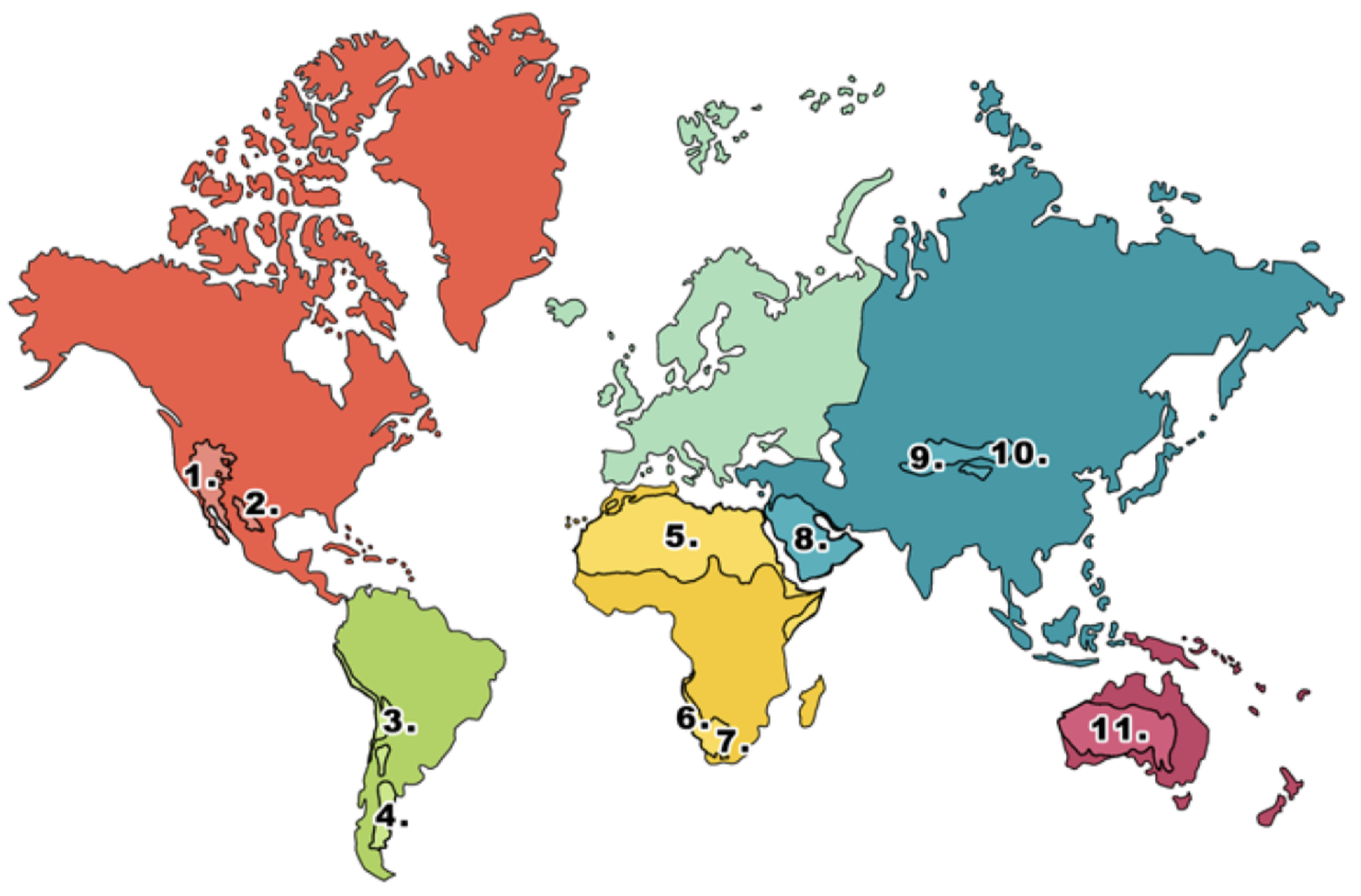
What is 8 on the deserts diagram?
Arabian Desert
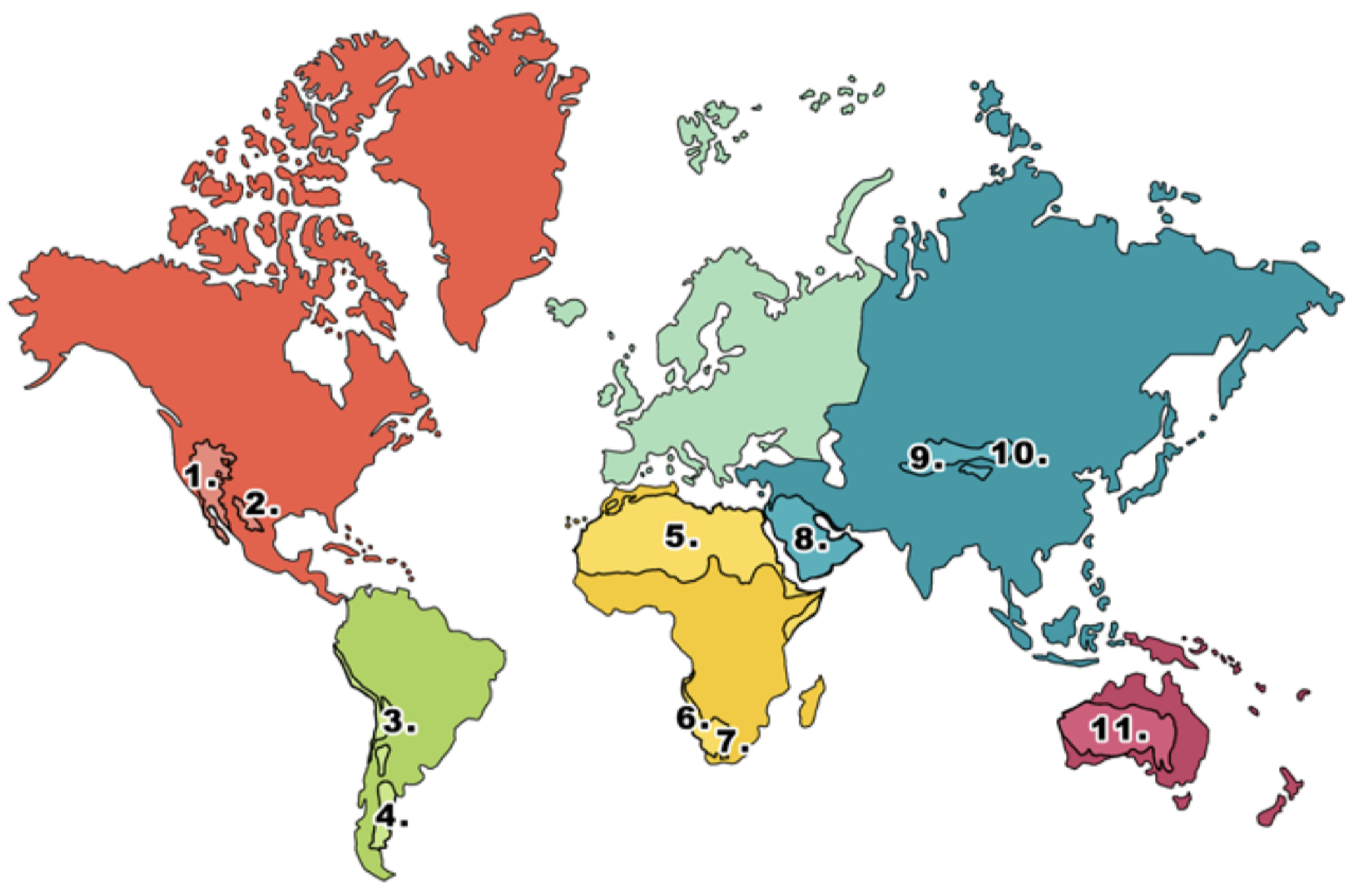
What is 9 on the deserts diagram?
Takla Makan desert
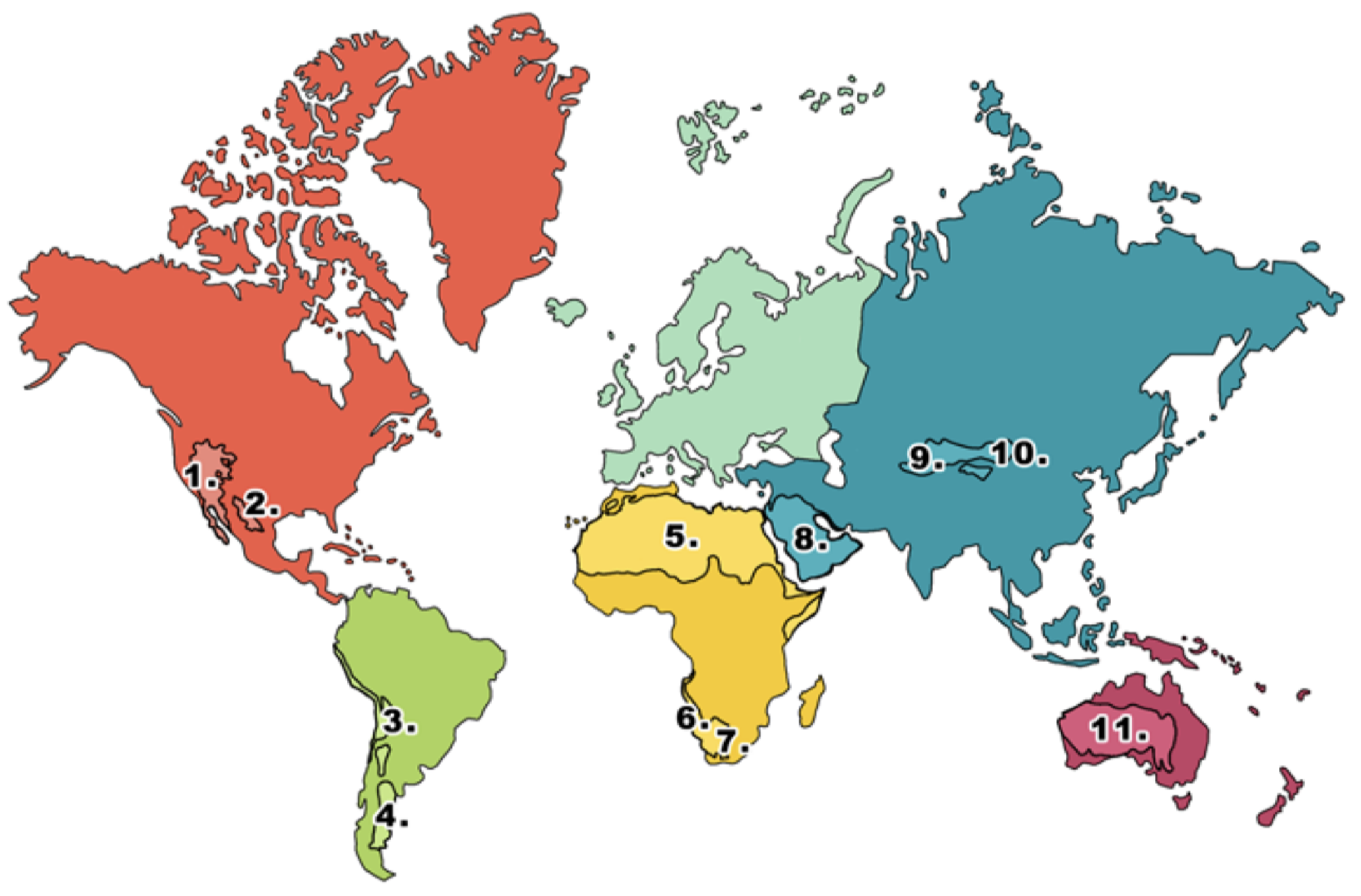
What is 10 on the deserts diagram?
Gobi desert
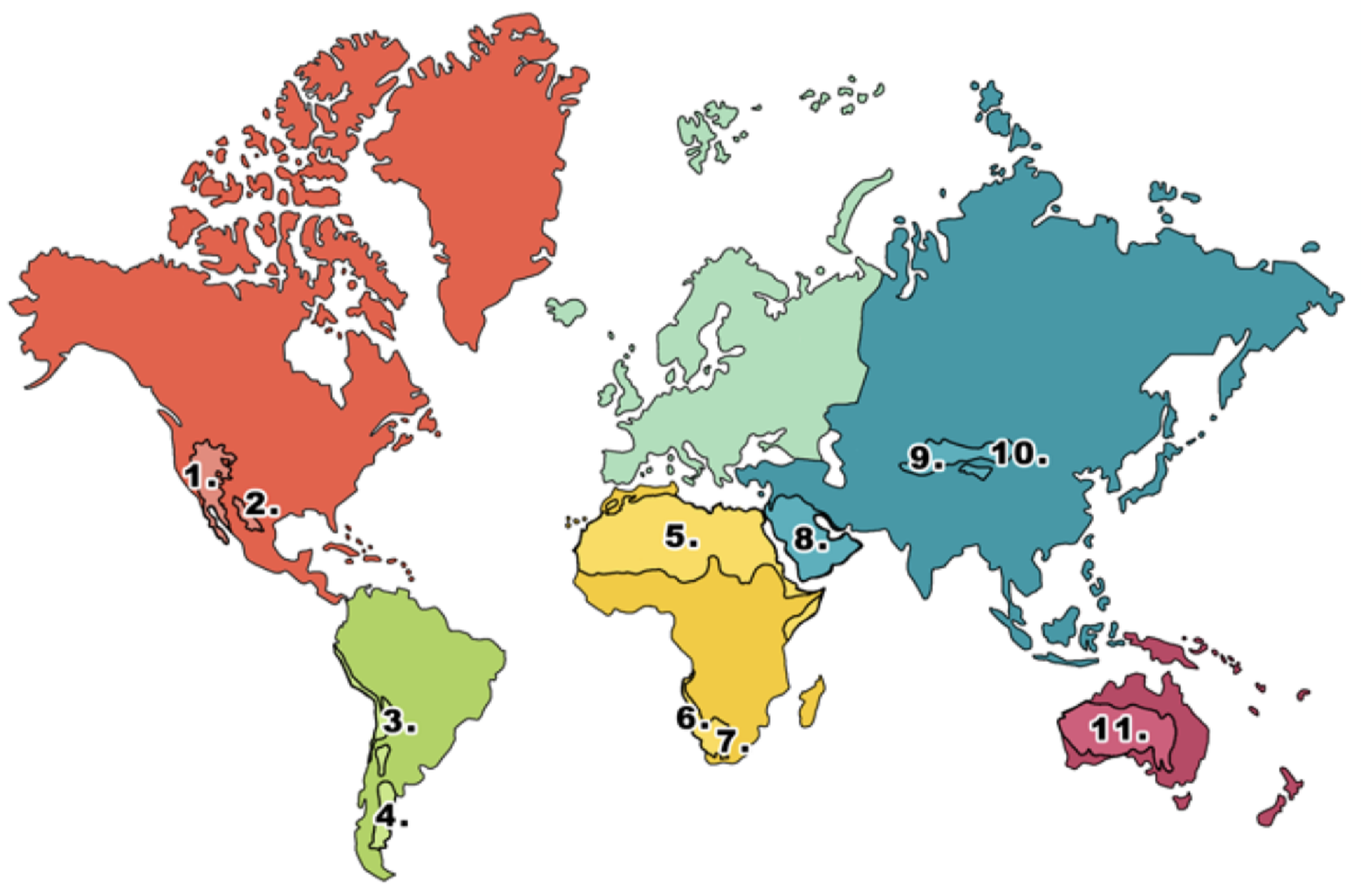
What is 11 on the deserts diagram?
Australian desert
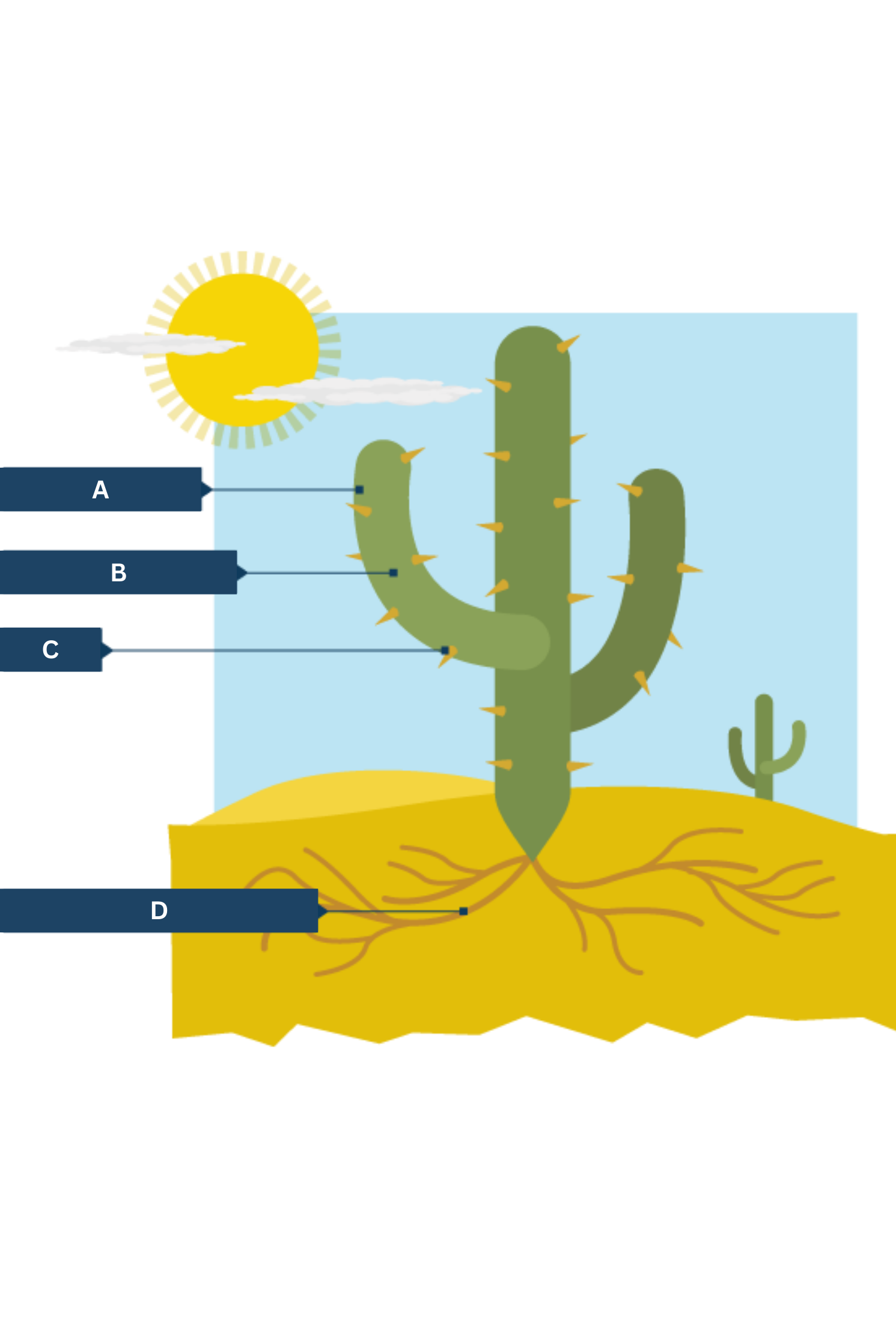
What is A on the cactus adaptations diagram?
Thick waxy skin - traps water inside plant
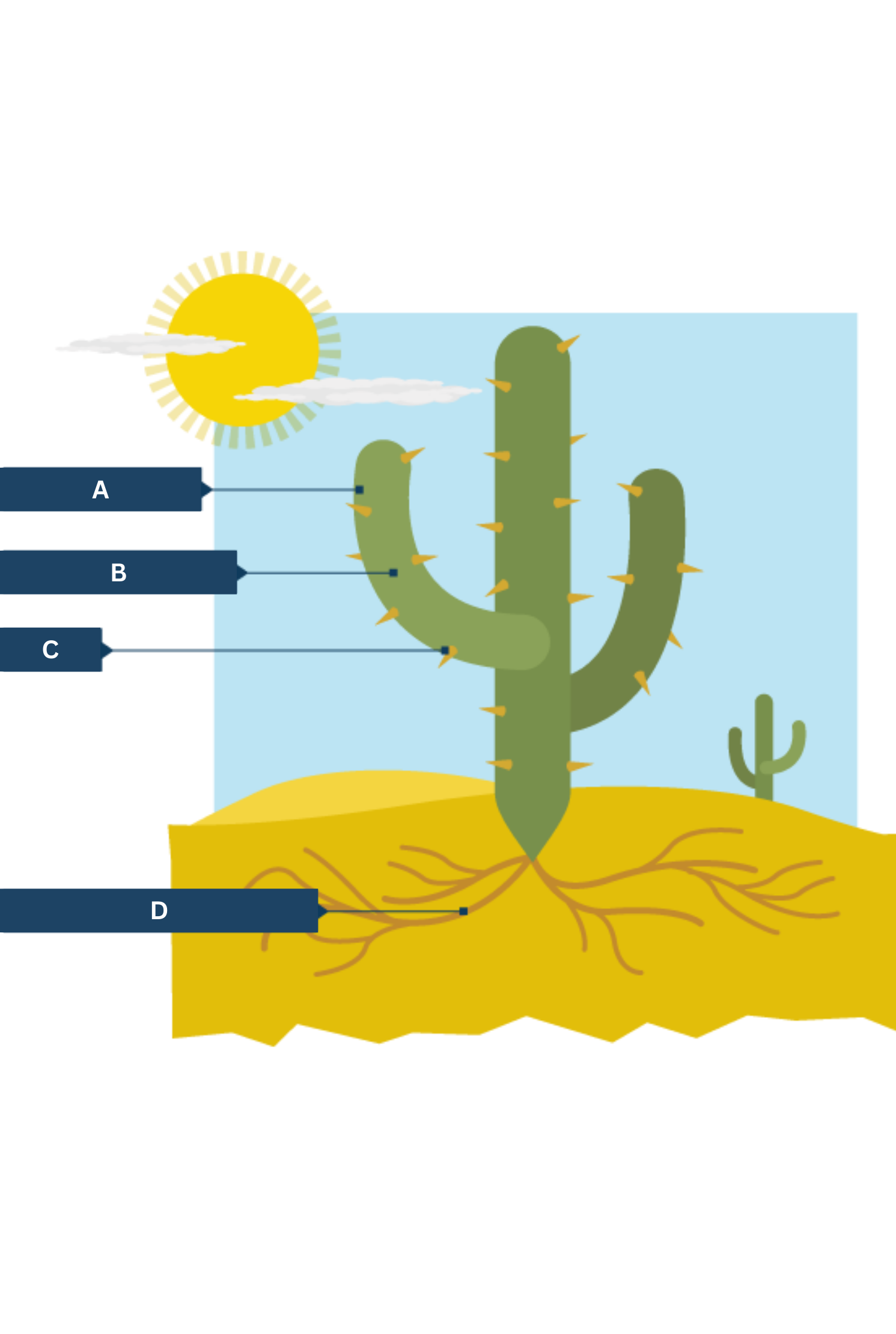
What is B on the cactus adaptations diagram?
Large, fleshy stems.
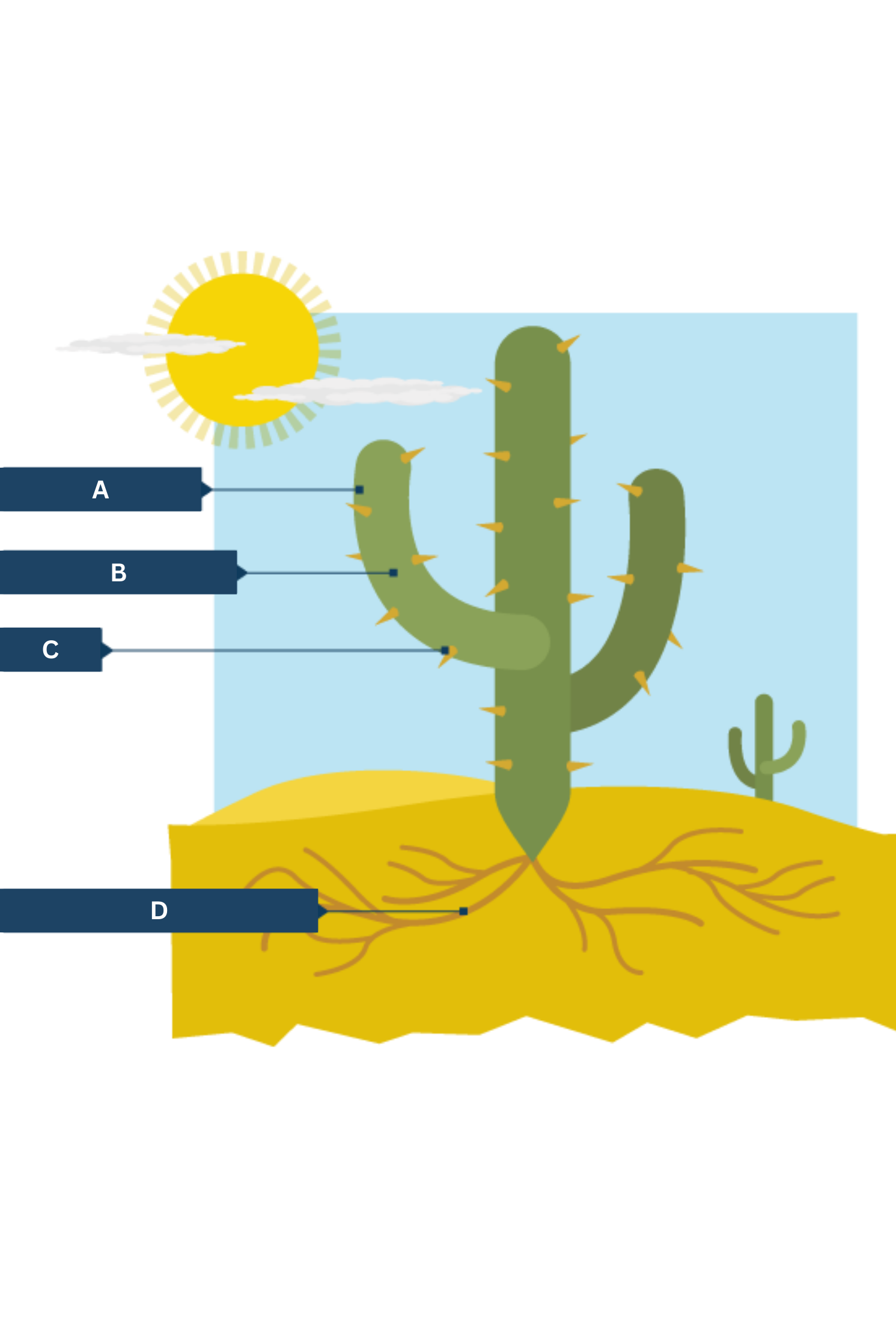
What is C on the cactus adaptations diagram?
Spikes - protection from hungry animals
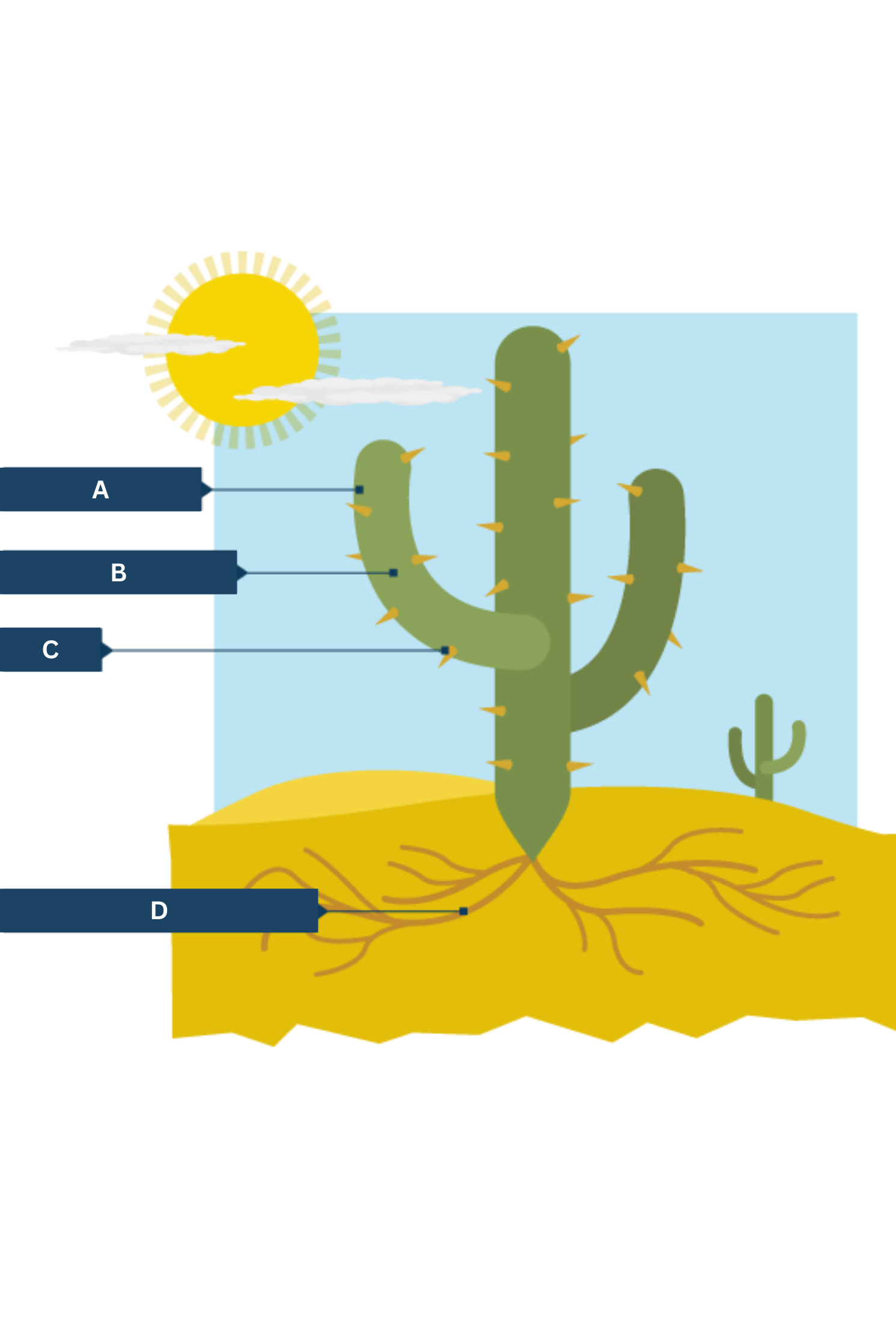
What is D on the cactus adaptations diagram?
Shallow, widespread roots
Define desertification
When a region loses its vegetation and becomes a desert
Where are deserts typically found?
15-30 degrees north and south of the equator
How does Dubai provide water in the desert?
By using energy-intensive desalination plants that convert seawater into freshwater.
How does Dubai deal with the extreme heat?
With widespread air conditioning, shaded buildings, and heat-reflective materials.
How is electricity supplied in Dubai’s desert environment?
Mostly through fossil fuels, though investment in solar power is growing.
What economic factors helped Dubai grow?
Oil wealth initially funded development, followed by diversification into tourism, finance, and trade.
How has Dubai built on sand?
By using advanced engineering techniques like deep foundations and soil stabilisation.
What is water scarcity?
A lack of sufficient water to meet the needs of people, agriculture, and the environment.
What is physical water scarcity?
When a region naturally lacks enough freshwater due to climate or geography (e.g. deserts).
What is economic water scarcity?
When water is available, but people can't access it due to lack of infrastructure or money.
Where is physical water scarcity common?
In arid regions like parts of the Middle East and North Africa
Where is economic water scarcity common?
In poorer areas, especially in Sub-Saharan Africa and parts of South Asia.
What is water stress?
Water stress occurs when the demand for water exceeds the available amount during a certain period or when poor quality restricts its use
What is water security?
The reliable availability of an acceptable quantity and quality of water for health, livelihoods, and production.
What is water surplus?
Where there is more water than needed
Define over-abstraction
Taking too much water from natural sources like rivers or aquifers, faster than it can be replaced, leading to water shortages.
What caused the Aral Sea to shrink?
Over-abstraction of water from its feeder rivers (Amu Darya and Syr Darya) for cotton farming during the Soviet era.
What is TEA in data analysis?
Trend, Example, Analysis
Has there been any recovery of the Aral Sea?
The North Aral Sea has seen partial recovery thanks to a dam built by Kazakhstan and international support.
What are the environmental impacts of the Aral Sea shrinking?
Loss of aquatic life, increased salinity, toxic dust storms, and desertification.
What are the human impacts of the Aral Sea disaster?
Collapse of fishing industry, poor health from dust pollution, and loss of livelihoods.
What is the Grand Ethiopian Renaissance Dam (GERD)?
A massive hydroelectric dam built by Ethiopia on the Blue Nile River to generate power and support development.
What is the Blue Nile?
A major tributary of the Nile River that originates in Ethiopia and contributes around 85% of the Nile’s water during the rainy season.
What is the White Nile?
A main tributary of the Nile, originating in East Africa (Lake Victoria), providing a steadier flow throughout the year.
Why is the GERD important to Ethiopia?
It aims to provide electricity for millions, boost the economy, and export energy to neighbouring countries.
Why is Egypt concerned about the GERD?
Egypt relies on the Nile for 95% of its water and fears the dam will reduce the river’s flow, threatening farming and water supply.
Why is Sudan involved in the GERD conflict?
Sudan is concerned about water flow and dam safety, but it could also benefit from cheaper electricity and regulated water flow.
What is the main issue of GERD causing tension?
Disagreement over how quickly Ethiopia fills the dam and how water will be shared during droughts.
Where in the UK has a water surplus?
North and West regions, including Wales, the Lake District, and parts of Scotland.
Where in the UK has a water deficit?
South East England, including London and surrounding areas.
What is the Kielder Water Transfer Scheme?
A system that transfers water from Kielder Reservoir in Northumberland to rivers like the Tyne, Wear, and Tees to support water supply in North East England.
Define forgery
Faking a document or signature
Define vandalism
Damaging things on purpose, for example, smashing up a phone box.
What is a traffic offence?
Offences to do with driving and parking vehicles
Define terrorism
Violent acts (such as bombings) carried out for political/ideological/religious reasons
Define environmental crime
An action such as illegal dumping of harmful waste in rivers
Define fraud
Making false claims, usually in order to make money
What is domestic violence?
Violence in the home; for example a man punching his wife
Define offender
A person who commits a crime (often used for people under 18)
Define criminal
Someone who commits a serious crime, or lives a life of crime
Define crime
An action that breaks the law
Define burglary
Breaking into a building to steal
What is common assault
Hitting or threatening to hit someone
Define mugging
Attacking a person in the street in order to steal something
What is built-in crime?
When poor design of buildings or public spaces makes it easier for crime to happen, like dark alleys or hidden entrances.
How can crime be reduced through design?
By planning spaces to make criminal activity more difficult or risky – this is known as "designing out crime."
Define target hardening
Making the 'target' harder to get at and involves the strengthening of security.
Define defensible space
A concept where the design of a space encourages residents to monitor and protect it, making it clear who owns and uses the area.
How do cul-de-sacs and changes to the road network contribute to reducing crime?
There is only one entrance/exit to the area, meaning burglars cannot escape easily/unnoticed.
How can we investigate crime in the local area?
By collecting and analysing data about the types, locations, and frequency of crimes, as well as people’s perceptions of safety.
What are Crime Statistics?
Official data from police reports showing types of crime, frequency, and when and where they occur. Can be found on sites like police.uk.
What is a Crime Hotspot?
A location where crime happens more often than in surrounding areas – often targeted for extra policing or prevention strategies.
What is primary data?
Data you collect yourself, e.g., surveys, interviews, observations – it's first-hand and up to date.
What is secondary data?
Data collected by someone else, e.g., websites, books, police records – it's second-hand but often easy to access.
Define Qualitative Data
Descriptive data based on thoughts, opinions, and feelings – often collected through interviews or open-ended questions.
Define Quantitative Data
Numerical data you can count or measure – like crime rates, number of burglaries, or survey percentages.
What is the main advantage of Primary Data?
It's specific to your study and up-to-date – you know exactly how and why it was collected.
What is the main disadvantage of Primary Data?
Time-consuming and can be expensive to collect, especially with surveys or interviews.
What is the main advantage of Secondary Data?
Quick, easy, and often free – lots of info already available from trusted sources.
What is the main disadvantage of Secondary Data?
May be outdated, biased, or not exactly relevant to your investigation.
What is the main advantage of qualitative data?
Gives detailed insights into people's thoughts, feelings, and experiences.
What is the main disadvantage of qualitative data?
Harder to compare, measure, or analyse statistically – can be subjective.
What is the main advantage of quantitative data?
Easy to analyse, compare, and spot trends – great for graphs and statistics.
What is the main disadvantage of quantitative data?
Lacks depth – doesn’t explain the “why” behind the numbers.
What was the main disadvantage of our field work?
The scoring system - each category had a different number of factors!
What is global energy demand?
The total amount of energy used by all countries around the world – and it’s rising due to population and development.
Define resource
Any physical material constituting part of Earth that people need and value
What is a Natural Resource?
A resource that comes from the Earth, like forests, fossil fuels, or water.
What is a Renewable Resource?
A resource that can naturally replenish over time, like wind, solar power, or timber (if managed sustainably)
What is a Non-renewable Resource?
A resource that cannot be replaced once it’s used up – like coal, oil, or natural gas
What is the main advantage of fossil fuels?
Reliable and produce a large amount of energy quickly.