Orgo Lab B: Synthesis of Aspirin
1/25
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
26 Terms
Aspirin: Background (3 points)
Patented by Bayer in 1893
One of the oldest and most consumed drugs
American consumption = 80 million pills/yr
Acetylsalicylic acid (aspirin) properties (3):
Analgesic
Antipyretic
Anti-inflammatory
Draw reaction scheme for synthesis of aspirin
Draw hydrolysis of excess acetic anhydride
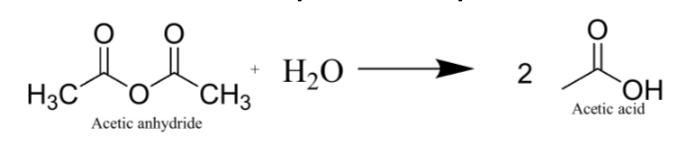
Why use an excess of one reactant (in this case, acetic anhydride)?
Using the excess of reactant favors formation of the other reactant
Calculation for mL of acetic anhydride

What produces a deep purple solution during the aq. FeCl3 purity check?
Purple indicates presence of a phenolic OH group, hence traces of Sa are present in the aspirin product.
Where do you dispose of chemicals containing ONLY C, H, and O?
Non-halogenated container
Where do you dispose of chemicals containing C, H, O, and Halogens?
Halogenated container
Where do you dispose of the solution containing ethanol?
Non-Halogenated Container
Where do you dispose of solutions from aq. FeCl3 purity check?
Specially labeled container “Aq. FeCl3 waste”
What are the 6 classifications of chemical hazards?
Flammable (low flash point) - lower flash point = easier to ignite
Corrosives - materials that can attack + chemically destroy exposed body tissues, causing chemical burns
Lachrymator - irritant taht causes tearing
Carcinogen - substance capable of causing cancer
Teratogen - drug/substance capable of interfering w/ development of an embryo fetus that may lead to birth defects.
Reactive - things that go BOOM.
What is a flash point?
Lowest temperature at which a liquid can form an ignitable mixture in air near the surface of the liquid.
What is the flash point of diethyl ether?
-45°C
What is the flash point of tert-Butyl methyl ether?
-33°C
What is the flash point of acetone?
-17.2°C
What is the flash point of gasoline?
-40°C
What is the flash point of ethylene glycol?
111°C
What are some examples of corrosives?
H2So4, NaOH, HNO3, Ca(OH)2, Br2
What are some examples of lachrymators?
Thionyl chloride, Acrolein, Methacryloyl chloride
What are some examples of carcinogens?
Benzene, Arsenic, Methylene chloride
What are some examples of teratogens?
Phenol, Benzene, Dinitrotoluene, Dioxane
What are some examples of reactives?
Na metal, sodium hydride, calcium carbide
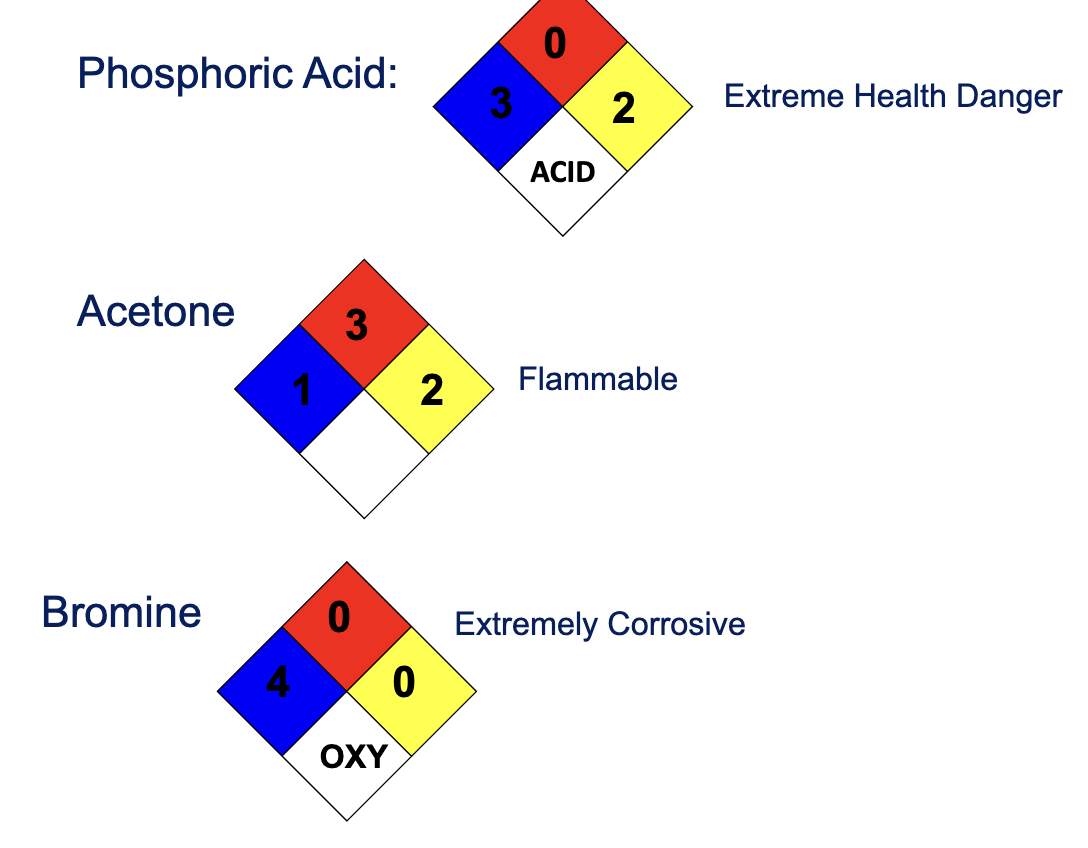
What are the 4 National Fire Protection Association (NFPA) Ratings?
Blue: Health Hazard
Red: Fire Hazard
White: Specific Hazard
Yellow: Reactivity Hazard
Name the 4 White hazard catagories
W: Water reactive
OX: oxidizing agent
ACID: acid
CORR: corrosive
Draw the NFPA for phosphoric acid, acetone, and bromine: