male reproductive system
1/146
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
147 Terms
the purpose of the reproductive system is to produce what?
gametes (specialized cells)
Gametes must come together through sexual intercourse which is also called what?
copulation
What is the first cell of a new individual called & what is it made of?
zygote, combined sperm & egg
what is the development of a fetus called?
gestation
What are the male gonads?
testes
Where are the testes found?
within the scrotum (testicles)
where is sperm produced?
testes
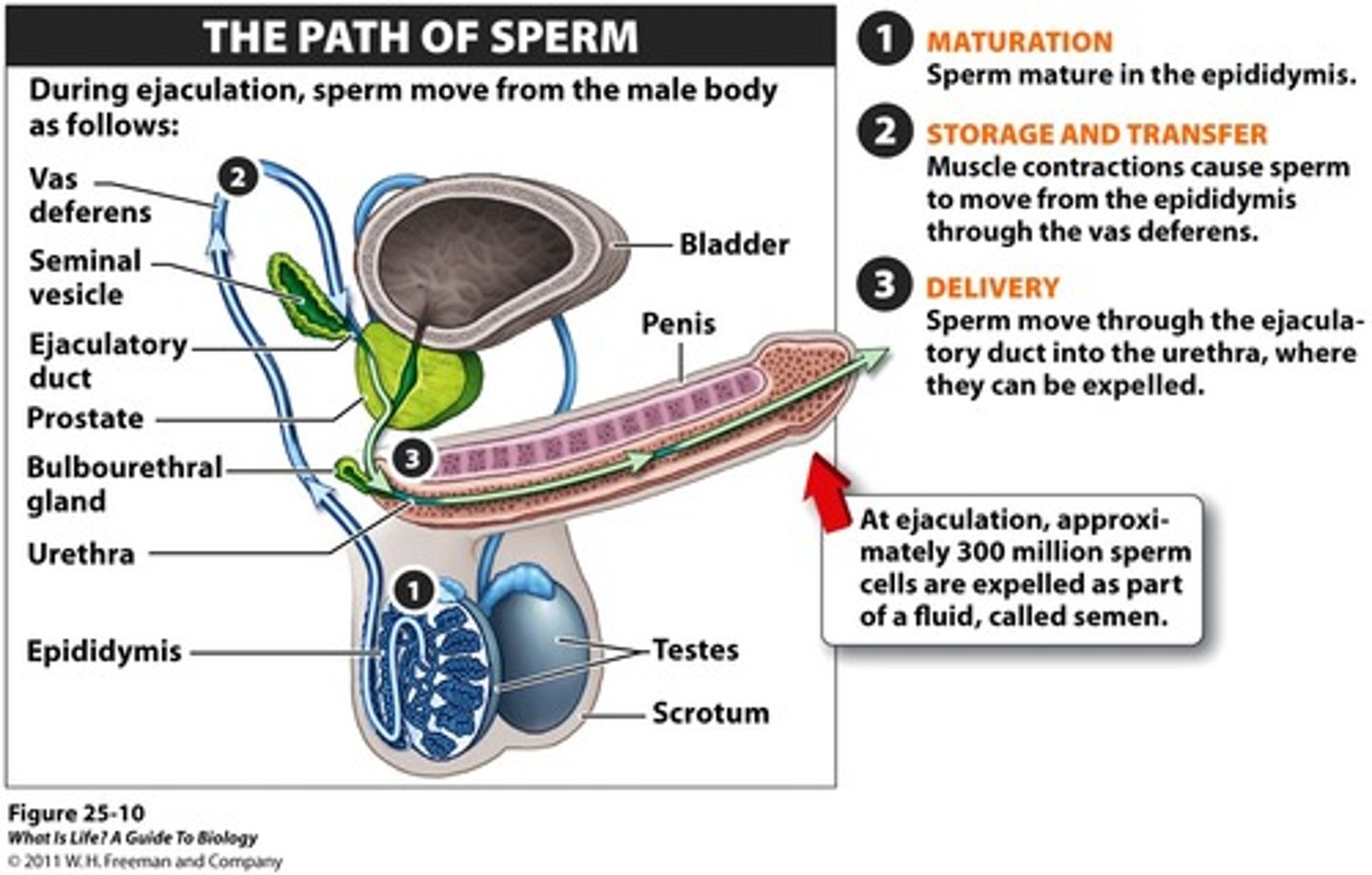
What is the path of sperm?
testes, epididymis, ductus (vas) deferens, ejaculatory duct, urethra
what are the accessory glands of the male reproductive system that help the sperm mature & fertilize an egg?
seminal vesicles, prostate, bulbourethral glands
In the male, the urethra is the same duct that carries what at different times?
semen & urine
After sperm is made in the testes, how does it flow through the body?
through the inguinal canal
into the pelvic cavity
up, over & behind the bladder
what is the scrotum?
sac of skin, fibrous membranes & fat which protect the testicle
For sperm to be viable, what temperature must it be kept at?
3 degrees lower than core body temperature
What structures divide the scrotum into two cavities?
scrotal septum
What is the dartos muscle?
smooth muscle that wrinkles scrotal skin to tighten & toughen the scrotum
What is the function of the wrinkles created by the dartos muscles?
trap warm air to help regulate temperature
What are the cremaster muscles?
skeletal muscles that elevate or lower the testes to maintain the proper temperature
If the temperature gets cold, the cremaster muscles will do what?
contract & pull the testicles closer to the body
If the temperature gets too warm, the cremaster muscles will do what?
relax & testicles are lower than the body
What are the testes surrounded by?
two tunics (tunica vaginalis and tunica albuginea)
What is the outermost layer of the testes?
tunica vaginalis
What is the innermost layer of the testes?
tunica albuginea; forms a fibrous capsule of the testes
What is the pampiniform venous plexus?
blood vessels & nerves merge to enter the testicle
How many lobules are in the testes?
250
What are the seminiferous tubules?
site of sperm production
Seminiferous tubules are separated into ______________ with a septum in between
lobules
Where does the sperm go after it travels through the seminiferous tubules?
rete testes then head of the epididymis
Where are immotile sperm stored?
epididymis within testicular fluid
How long is the epididymis when uncoiled?
20 feet
What moves sperm as they mature from the head to the body and finally to the the tail of the epididymis?
smooth muscle contractions
What happens when more sperm is produced than can be used?
epididymis will reabsorb some & return nutrients to the body
What happens when sperm mature after 20 days?
move into ductus deferens
What is the ductus deferens?
thick muscular tube that contracts by peristalsis
What encloses the ductus deferens?
connective tissue (spermatic cord)
Describe the path of the ductus deferens.
up through inguinal canal, into pelvic cavity, wraps around back of bladder
What is the structure called when the seminal vesicle duct & ductus deferens connect?
ejaculatory duct
When the fluid from the seminal vesicle has been conjoined with the sperm, what is produced?
semen
The urethra is the result of two __________________ __________ (left & right) joining.
ejactulary ducts
What is the prostatic urethra?
passes through the prostate gland
What is the function of the prostate?
adds secretions to the semen
When the prostatic urethra exits the prostate what is called? Is it long or short?
membranous urethra, short
When the urethra enters the penis, what is it called?
spongy urethra
What is the tissue called that surrounds the spongy urethra?
corpus spongiosum
What is the last accessory gland that adds secretions to the semen (it is located at the root of the penis)?
bulbourethral gland
During development, the testes form in the pelvic cavity & around the 7th month migrate through the inguinal canal. If they do NOT descend, what happens to the sperm?
will be too warm for sperm to mature & male becomes sterile
If the tests do not descend, what treatment is available?
surgery to remove testes out of pelvic cavity
What is a vasectomy?
cutting and ligating the ductus deferens (used to be called vas deferens)
Once the ductus deferens is cut, sperm CANNOT be ejaculated. The man still produces semen but is now what?
sterile
The sperm gets pushed into what structure during ejaculation?
ductus deferens
What does the ductus deferens & the duct of the seminal vesicle form?
ejaculatory duct
What do the seminal glands do?
contains smooth muscle that contracts during ejaculation so seminal fluid is added to sperm
The seminal fluid makes up what percentage of the semen?
60-70%
What does the seminal fluid contain to provide nourishment for the sperm?
fructose
What does the seminal fluid contain to stimulate peristalsis along the male & female reproductive tracts?
prostaglandins (helps to ensure sperm + egg physically meet)
What does the seminal fluid contain to temporarily clot inside the vagina?
clotting enzyme
What does the seminal fluid contain to neutralize the acids produced by the prostate gland + vagina?
alkaline fluid
Males have two of what structures? (hint: there are four different structures)
testicles, epididymis, ductus deferens, ejaculatory ducts
The ejaculatory ducts merge to form the ______________ ____________
prostatic urethra
What is the prostatic urethra surrounded by (this contracts during ejaculation)?
prostate
What does the prostate gland secrete?
a milky slightly acidic fluid that activates sperm a short after ejaculation (makes 20-30% of the semen volume)
What does the bulbourethral gland secrete?
pre-ejaculate alkaline mucus
What does pre-ejaculate do?
neutralizes traces of acidic urine in urethra & provides lubrication for sexual intercourse
What is the name of the structure that the sperm travels through (part of the membranous urethra)?
spongy urethra
What is the penis?
male sex organ designed to deliver sperm to the female reproductive tract
What three structures make up the penis?
root (near bulbourethral gland), shaft (body), glans penis (end)
There is one ___________ _________________ (the spongy urethra travels through this) and two _______________ _____________________.
corpus spongiosum, corpus cavernosa
What is the glans (of the penis)?
enlarged distal portion surrounding the opening of the urethra
What structure covers & protects the glans?
prepuce (foreskin)
The prepuce is sometimes surgically removed by what procedure (it is debated as it appears to be culturally driven)?
circumcision
What is an erection?
enlargement & stiffening of the penis due to more blood entering the erectile tissue that exits
Normally the arterioles within the penis are vasoconstricted, but during sexual excitement, the CNS activates what type of neurons?
parasympathetic neurons
What does the parasympathetic neurons release (in the penis)?
nitric oxide
What does nitric oxide do?
relaxation of smooth muscle, arterioles vasodilate, corpus cavernosa fills with blood
What is venous drainage blocked by?
enlarged corpora cavernosa (erectile tissue stays erect, corpus spongiosum keeps urethra open)
What happens during ejaculation?
movement of semen out of the body
What causes the ducts & accessory organs of the penis to contract?
sympathetic neurons
What constricts to keep urine from entering the urethra?
bladder sphincter
What might cause erectile dysfunction?
the parasympathetic nerves of the penis don't release enough nitric oxide, or problems with blood vessels
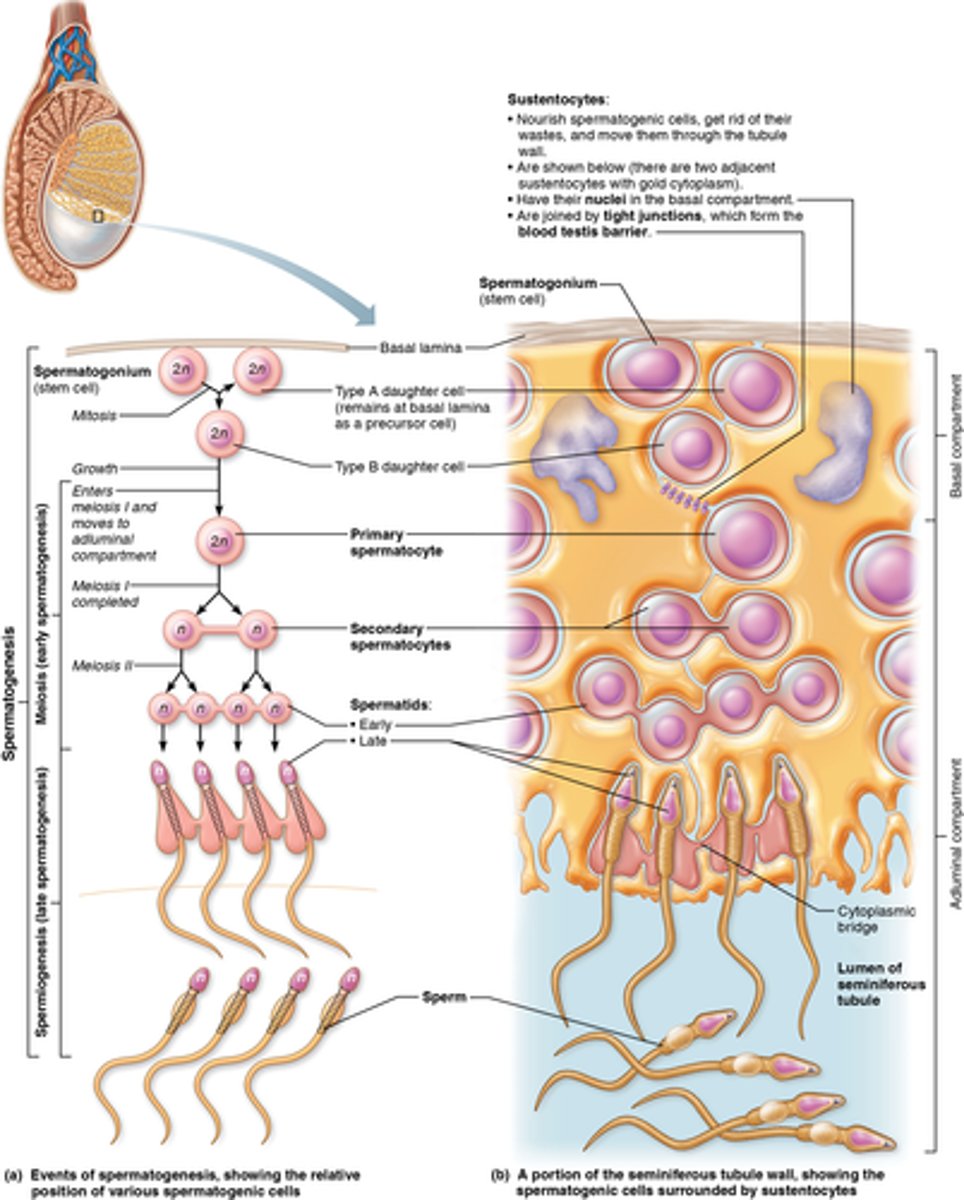
What is spermatogensis?
formation of male gametes (sperm)
Where does spermatogenesis occur (and when does it begin)?
seminiferous tubules (begins at puberty & through a male's life)
How much sperm does an adult male make in one day & how long does it take?
90 million sperm per day, 9 weeks to make sperm
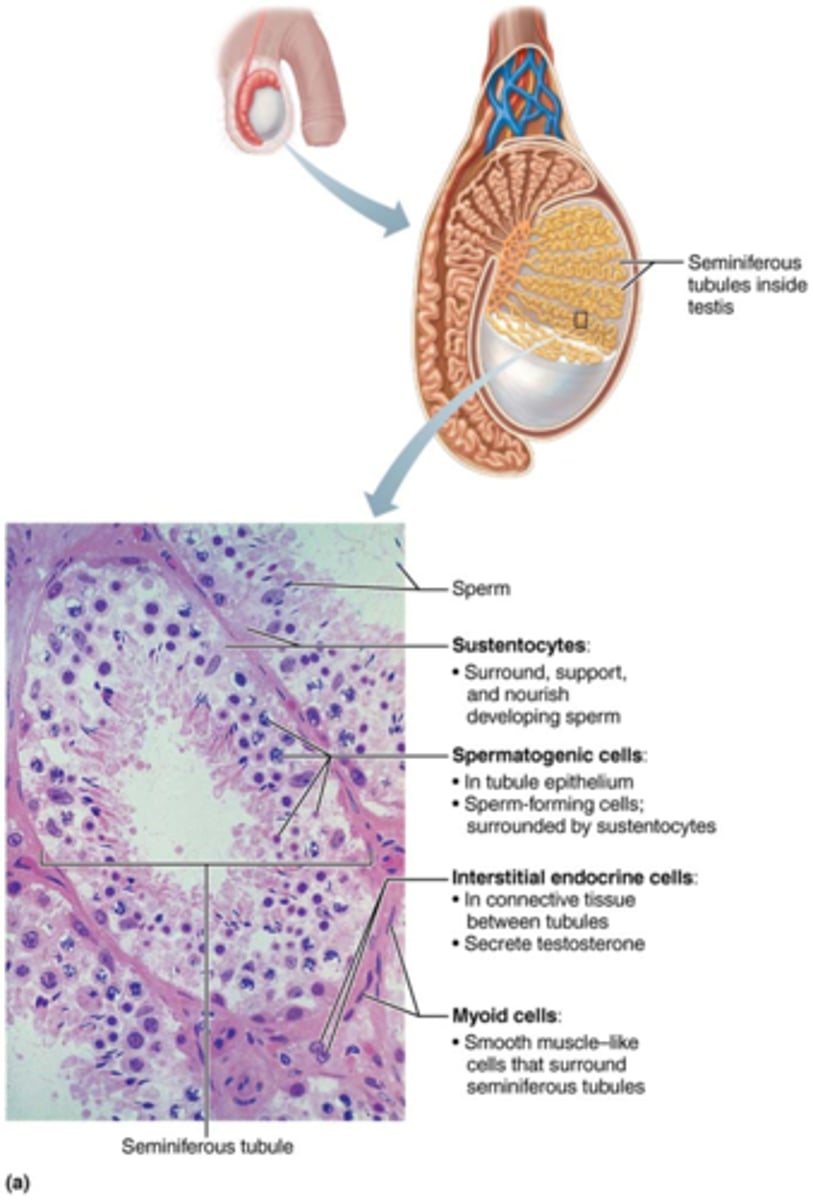
What are sustentocytes?
large columnar cells that nourish the developing sperm
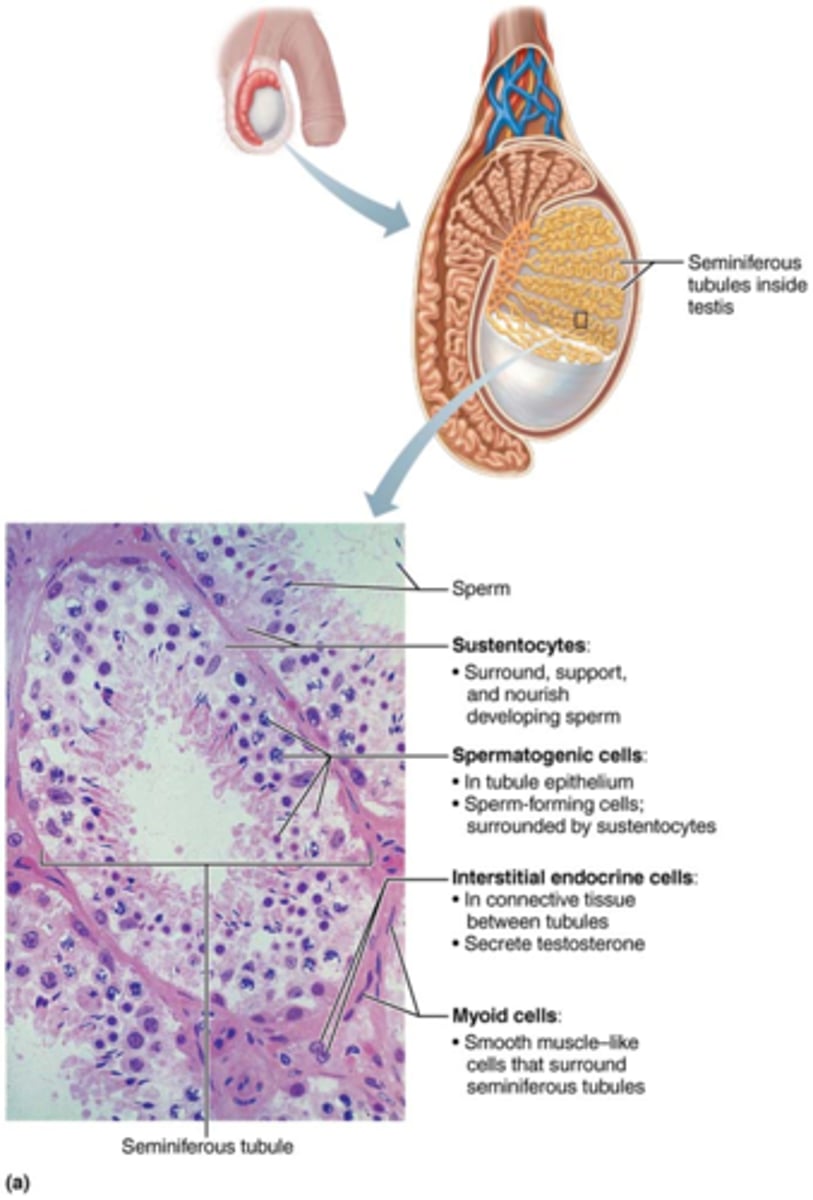
What are spermatogenic cells?
sperm forming cells
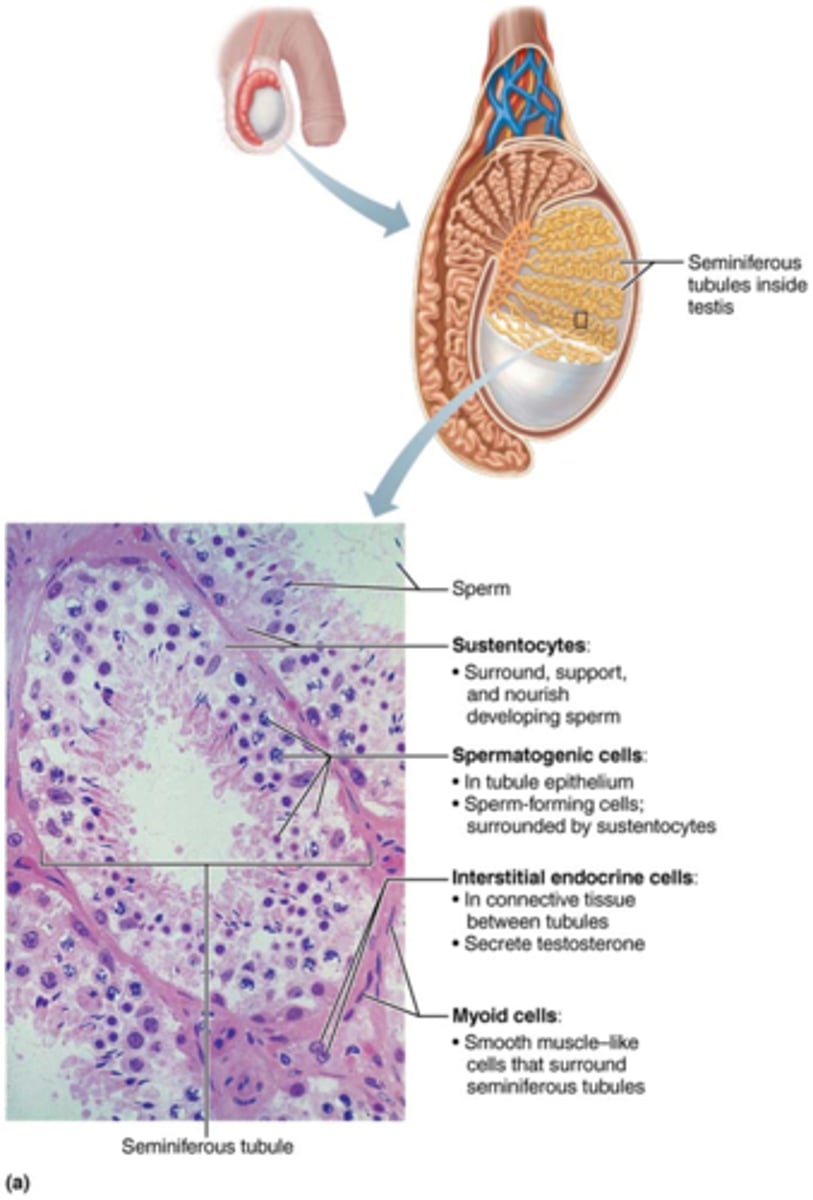
What are myoid cells and what do they do?
cells outside of the tubules & contract to squeeze sperm & testicular fluid through tubules
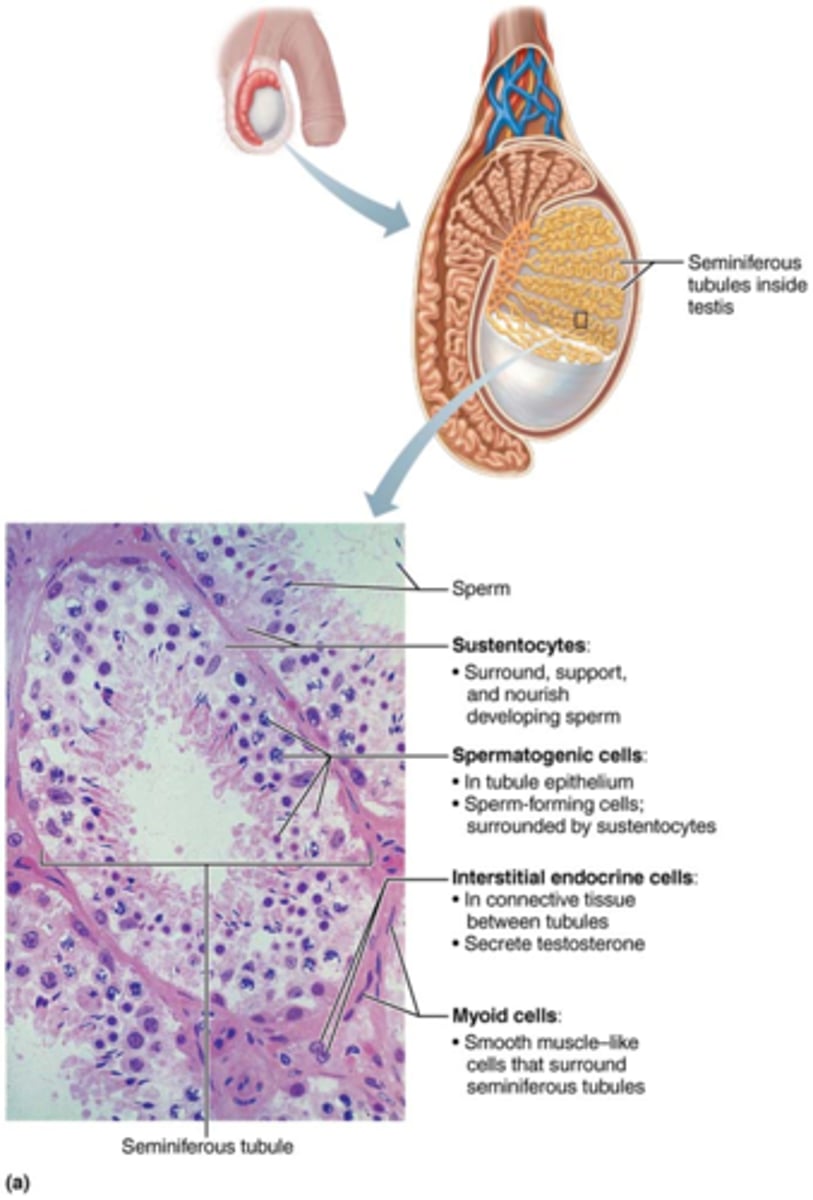
Where are interstitial endocrine cells (Leydig cells) located & what do they do?
located between tubules & produce androgens & some estrogen
If sperm cells haven't yet been made until puberty, then the immune system had no training to recognize them as self or non-self. What will the immune system consider sperm?
foreign
What is the job of the sustentocytes (in relation to the immune system)?
keep a blood testis barrier so no sperm cells escape into the blood & activate the immune system
What does androgen binding protein (ABP) do? What cells secrete ABP?
keeps testosterone levels high to stimulate spermatogenesis; produced by sustentocytes
What does inhibin do? What cells secrete ABP?
inhibits both FSH release & spermatogenesis
The ___________________________ __________ are in various stages of cell division as they become sperm.
spermatogenic cells
What is the process of mitosis?
cell divides into two identical cells (used to grow & replace worn out cells)
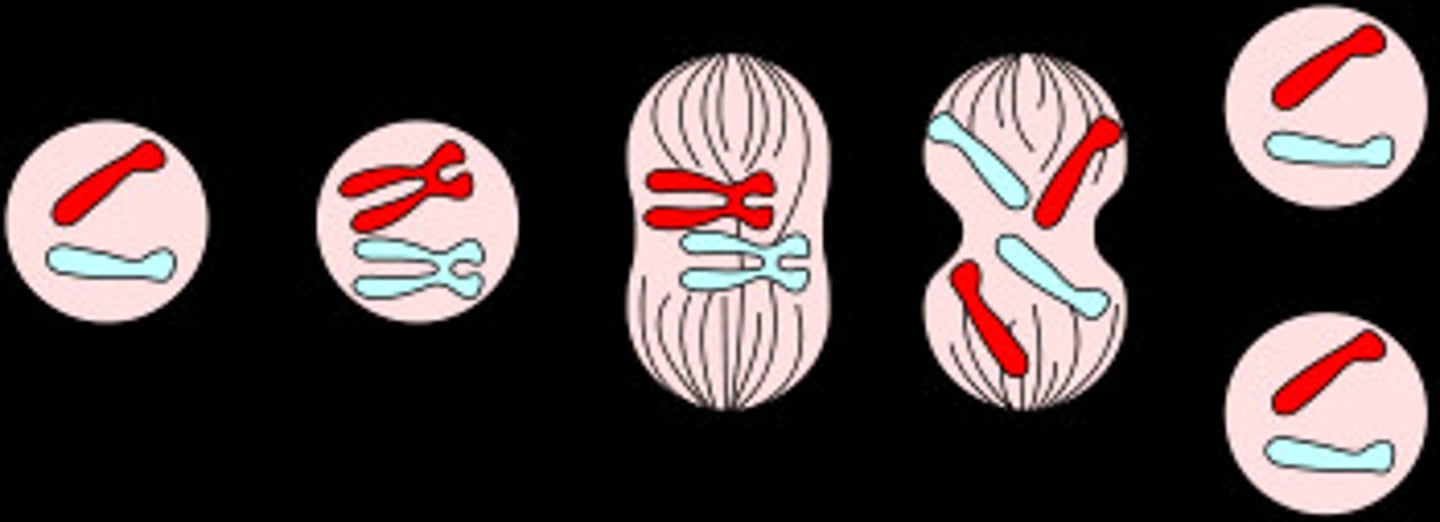
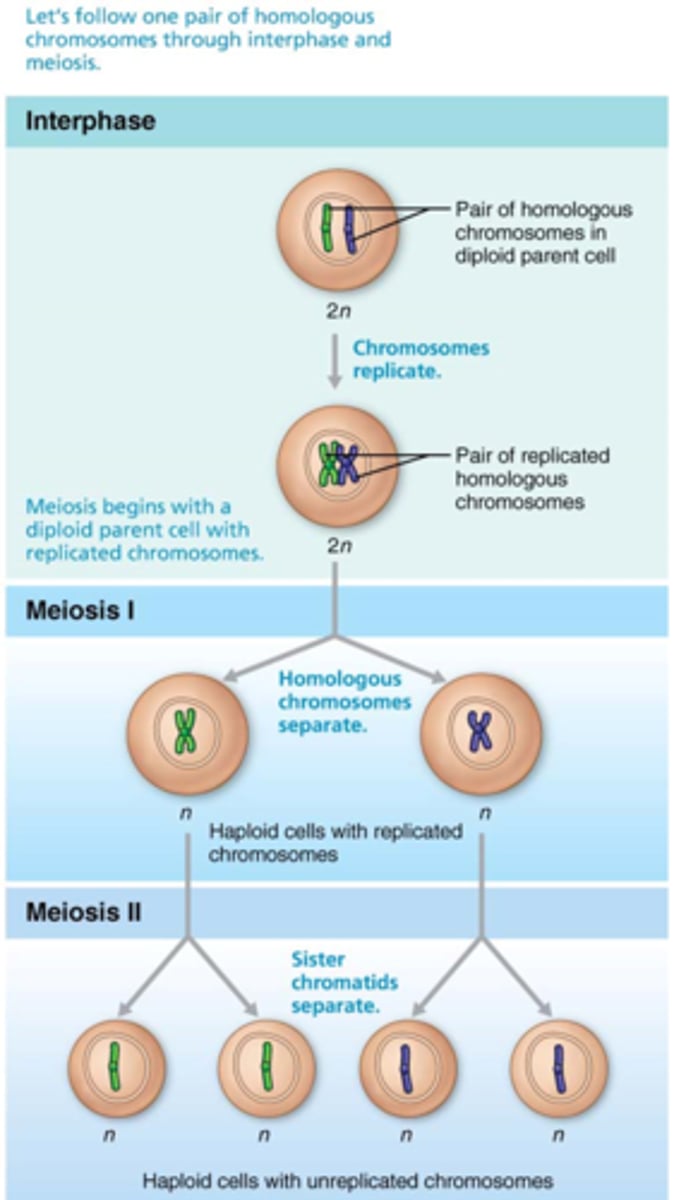
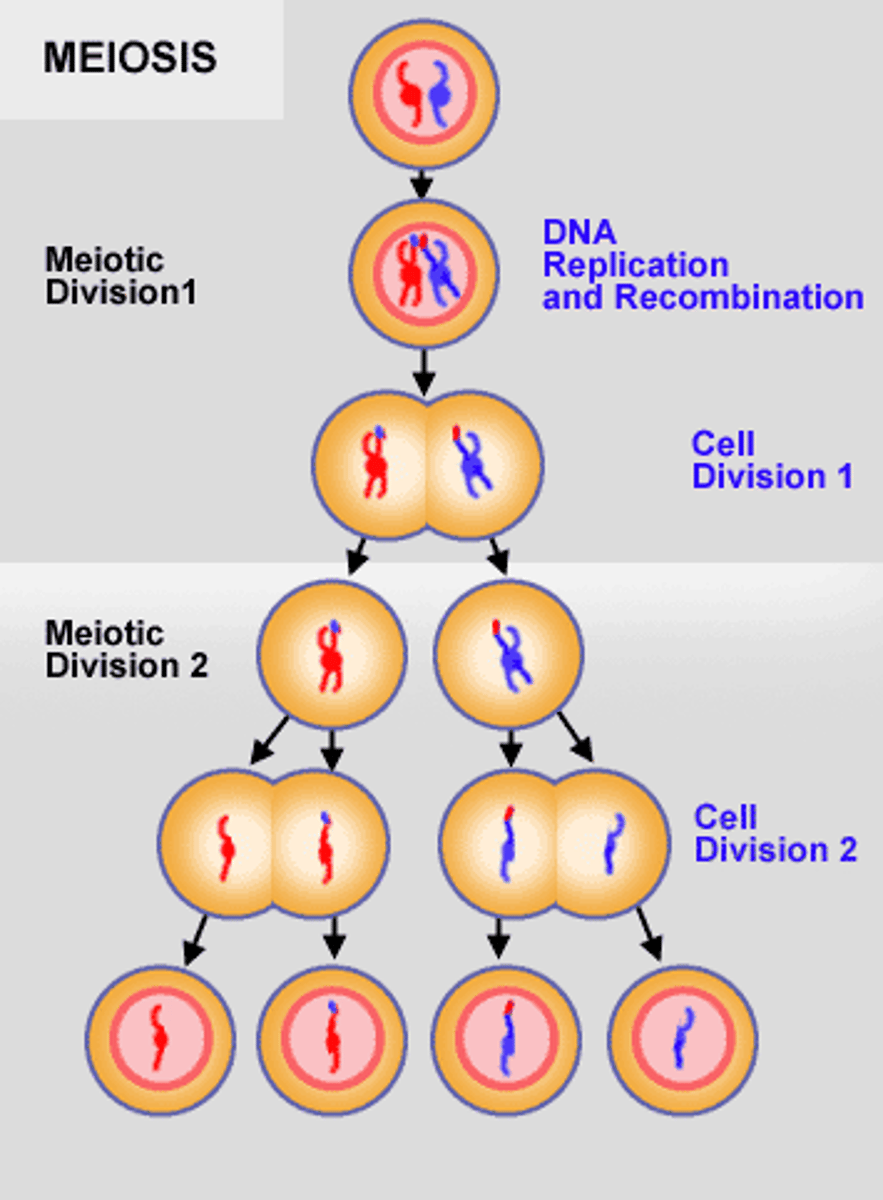
What is the process of meiosis?
The chromosome number is reduced from 46 total chromosomes to 23 pairs, so when the egg and sperm unite in fertilization the zygote will have the correct number of chromosomes
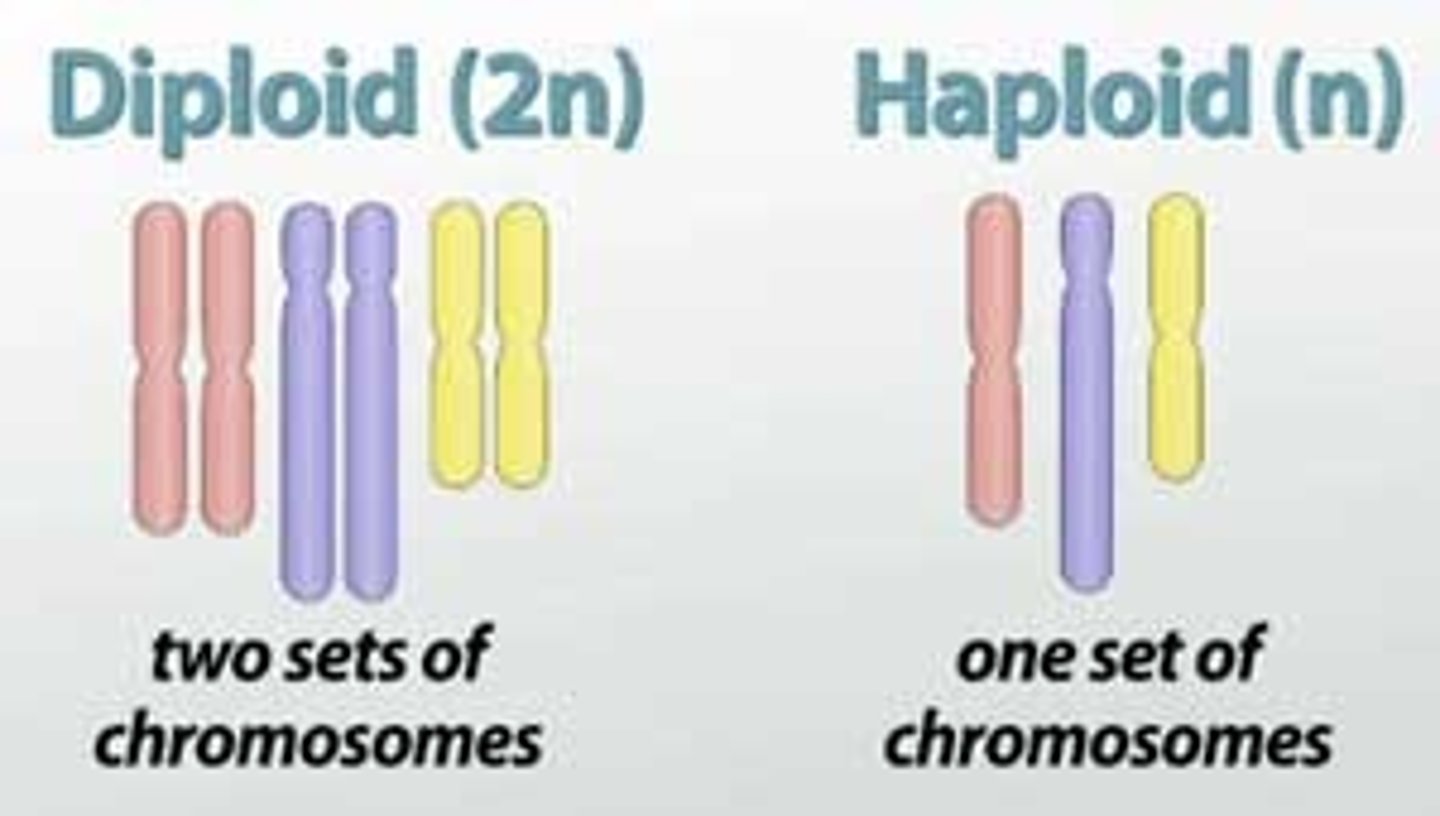
What is a cell with a complete set of chromosomes called?
diploid or 2n (the "2n" means you have two of each chromosome)
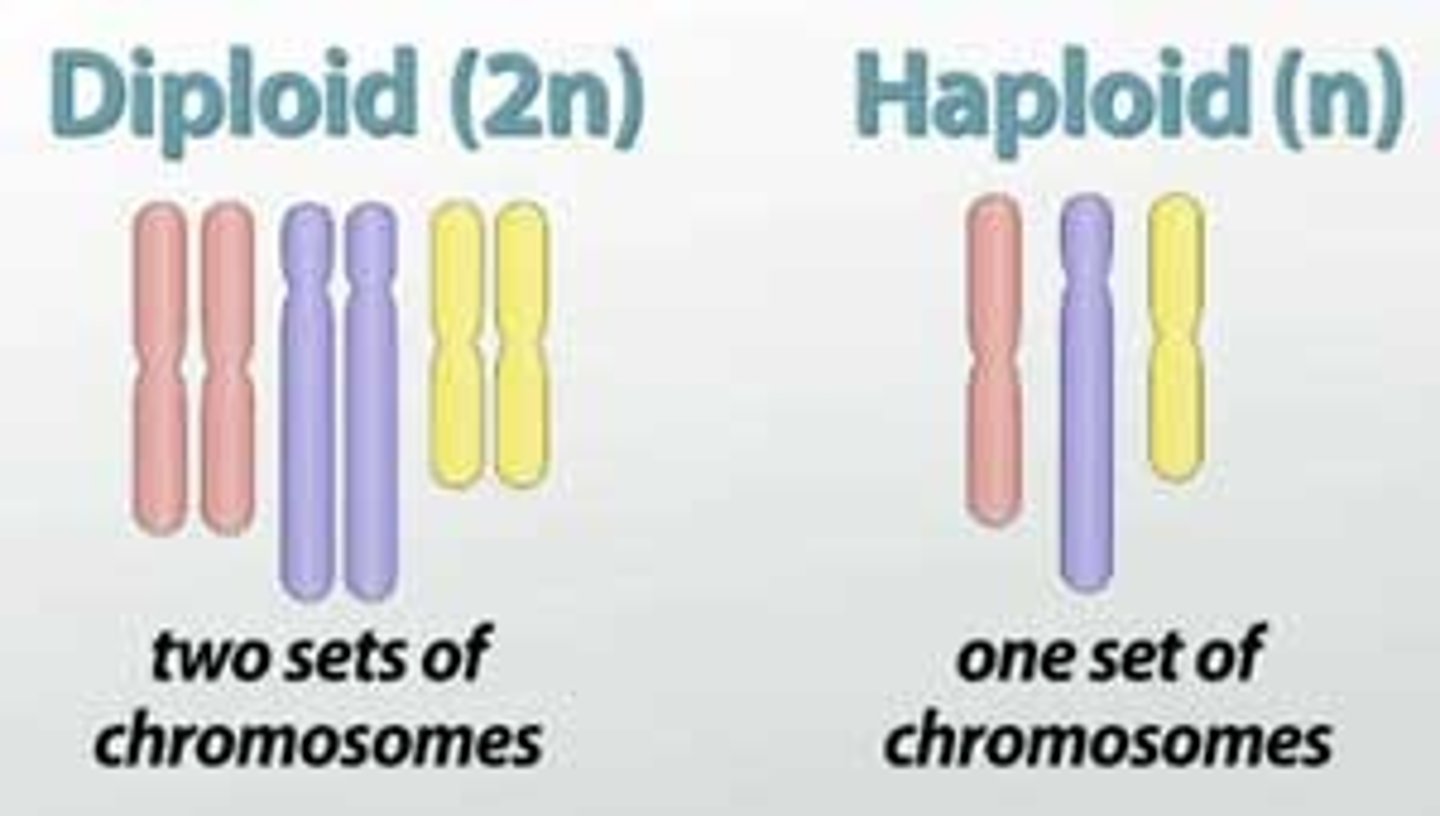
What is a cell with half the number of chromosomes called?
haploid or n
Where are spermatogonium (in relation to the tubule wall)?
stem cell that stays along wall of tubule
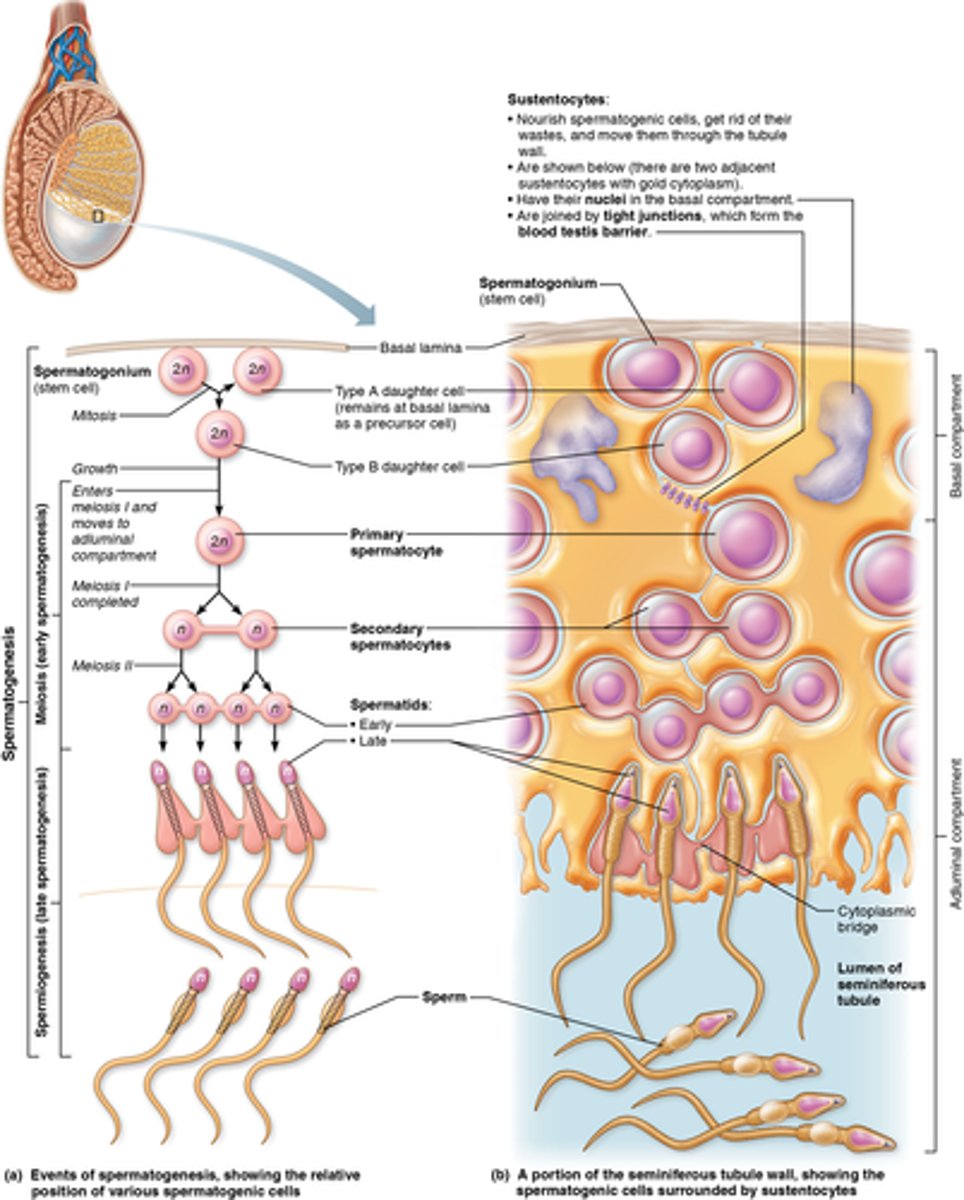
Where are primary spermatocyte (in relation to the tubule wall)?
pushed forward to the lumen
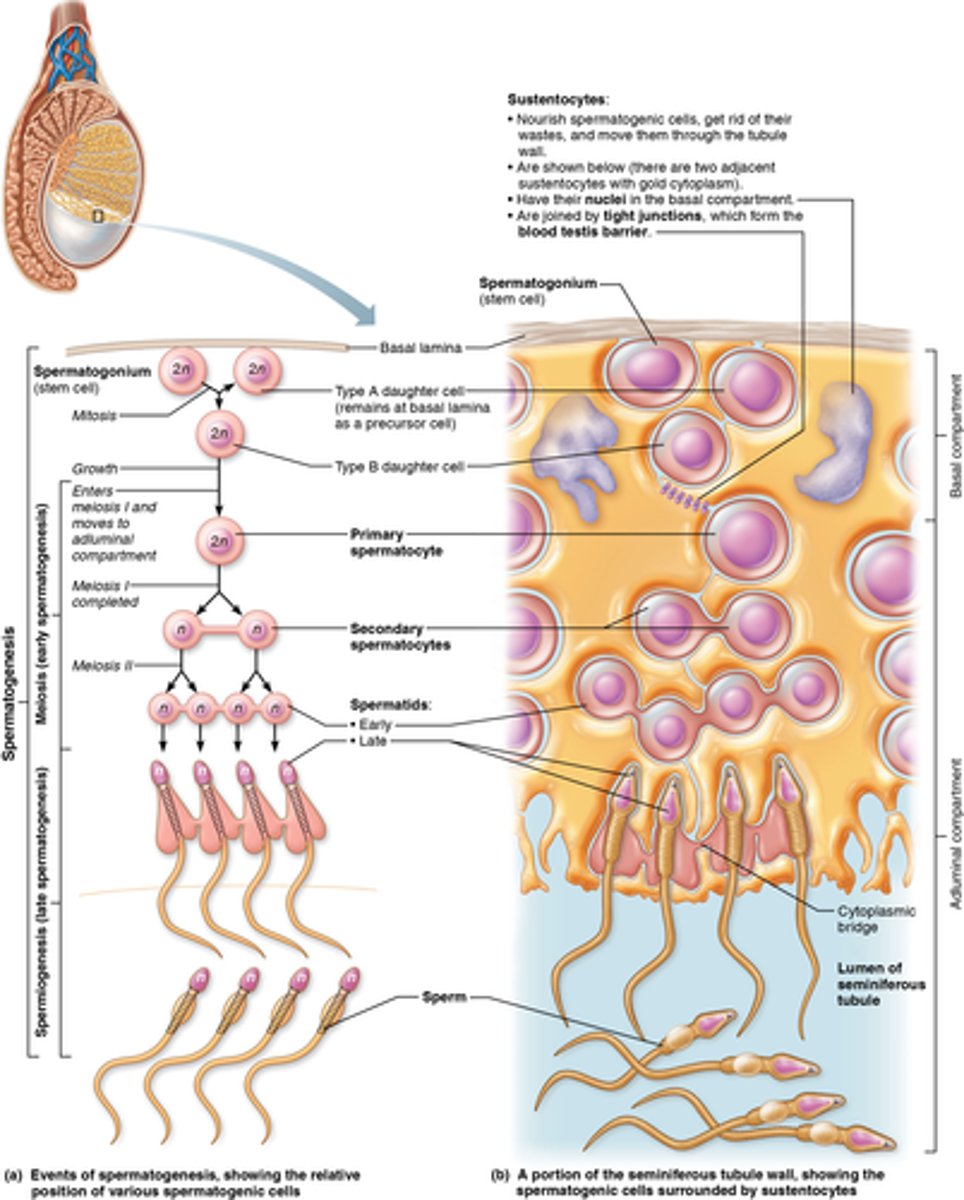
What is the process of spermatogenesis?
spermatogonia, primary spermatocyte, secondary spermatocyte, spermatid, sperm
As meiosis begins, each __________________ __________________ contains ________ individual chromosomes.
primary spermatocyte, 46
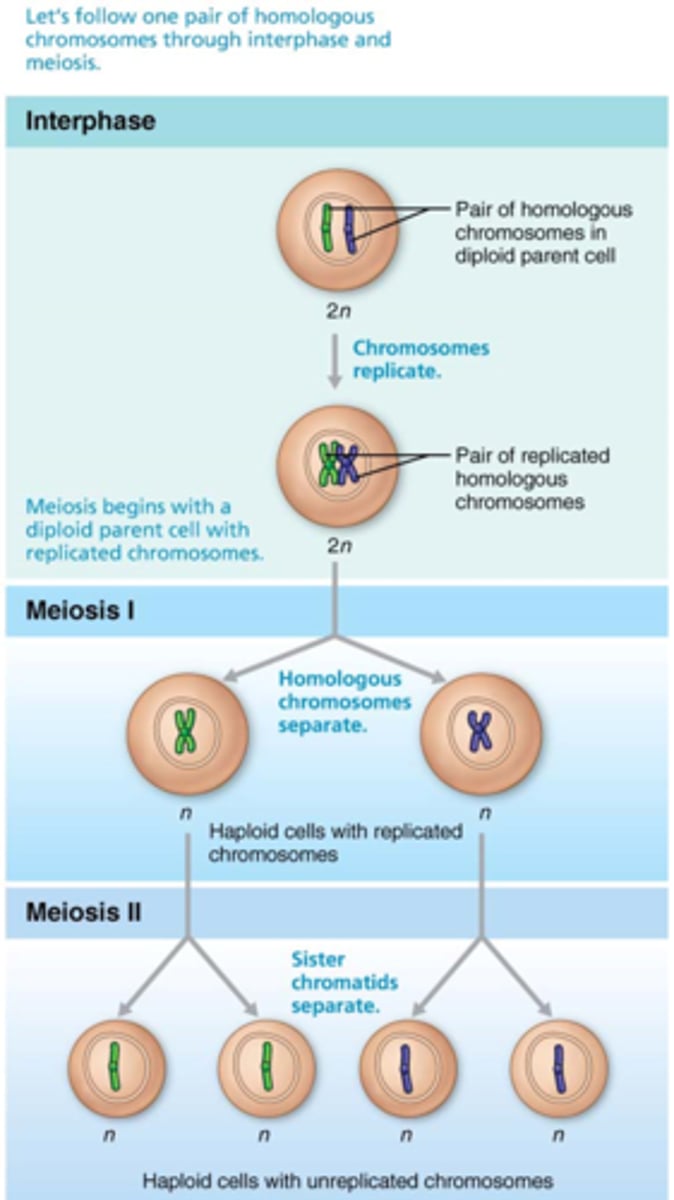
At the end of meiosis I, the daughter cells are called ________________ ______________________ and contain _____ chromosomes, each of which consist of a pair of duplicated chromatids.
secondary spermatocytes, 23
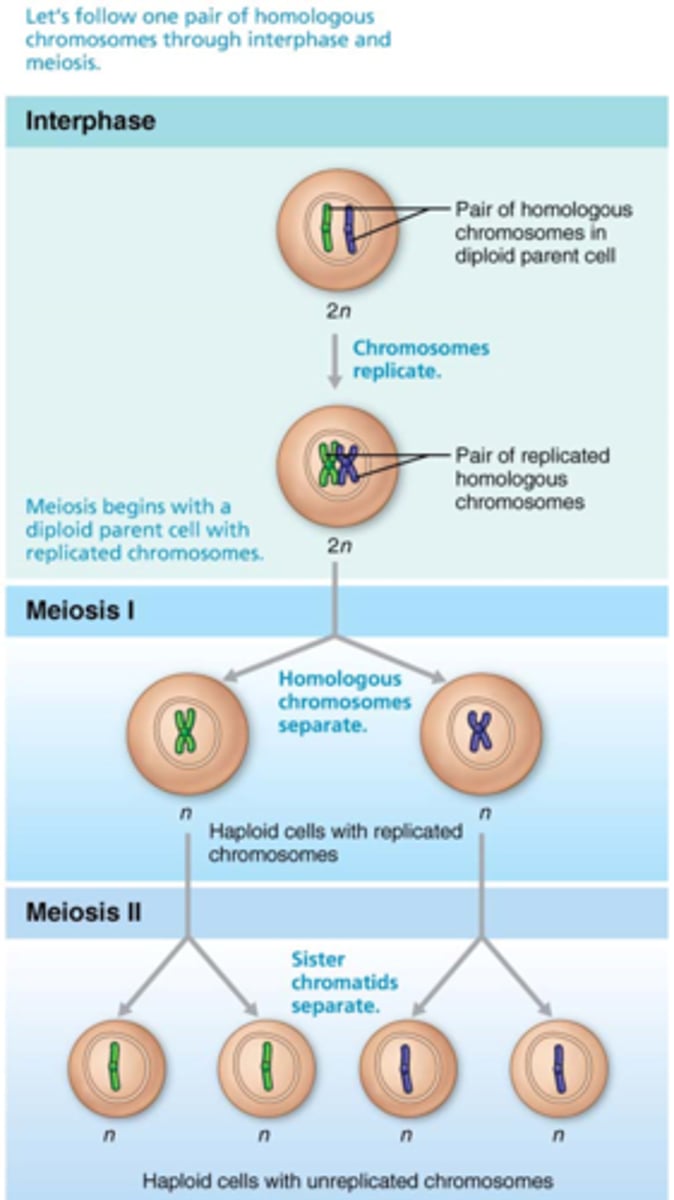
During meiosis II, the secondary spermatocytes will divide to become what?
4 haploid spermatids