Textiles for Fashion - Exam Two
1/48
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Woven and Knit Fabrics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
49 Terms
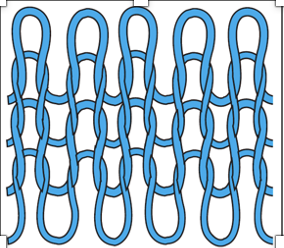
Knitting
Formed by a series of loops, intermeshing in rows, each hanging from the last.
Nonwovens
Fabrics made directly from solutions, fibers, or yarns; there is no processing of fibers into a yarn. (Not woven or knit).
Fabric
Pliable, planelike structure that can be made into two or three-dimensional products that require some shaping and flexibility.
Wale (Knits)
Vertical column of stitches in knits.
Lace
An openwork fabric with complex patterns or figures, handmade or machine-made on special machines or on raschel knitting machines.
Course
Horizontal row of stitches in knits.
Grain
Refers to the geometry or position of warp yarns relative to weft yarns in the fabric.
Composite Fabrics
Fabrics that combine several primary and/or secondary structures, at least one of which is a recognized textile structure, into a single structure.
Selvage
The lengthwise self-edge of a fabric that is formed when the weft yarn turns to go back across the fabric.
Warp (Wovens)
The yarns that run lengthwise (vertically) in woven fabrics.
Weft (Wovens)
The yarns that run crosswise (horizontally) in woven fabrics.
Weft (Knits)
Yarn is fed to the needles from the side, and loops are formed across a course; horizontal.
Weaving
Creating fabric by interlacing yarns together.
Spun Yarn
Yarns spun from staple fibers.
Wale (Weaving)
In a twill weave, each warp or weft yarn floats across two or more weft or warp yarns with a profession of interlacings by one to the right or left, forming a distinct diagonal line.
Warp (Knits)
Yarn is fed to the needles from the end, a separate yarn feed for each needle, so loops are formed in the direction of the wales; vertical.
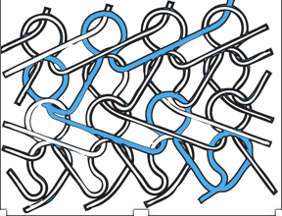
Loom
The machine that weaving is done on.
Stitch
Each loop in knitting.
Fancy Weave
Produces a design, text, or pattern that is an inherent and permanent part of the fabric's structure.
Fabrics from Solutions (fabrics made without yarn or fiber) Ex: Films, Foams
Fabrics from Fibers (fabrics made without yarn) Ex: Felt
Fabrics from Yarns (fabrics made with yarn) Ex: Braids, Lace
Composite Fabrics (fabric combinations) Ex: Quilted Fabrics
List the other 4 fabric fabrication methods and give an example of each:
Velvet
A fancy pile weave made with filament yarns. The pile breaks in crosswise rows because the warp tufts are interlaced with the ground weft yarns.

Velveteen
A fancy pile weave made with staple yarns. The pile breaks into lengthwise rows because the weft tufts are interlaced with the warp yarns.

Velour
A cut-pile fashion fabric used in men's and women's wear and in robes (Pile Knit).
Fabric Count
The number of warp and weft yarns per square inch of gray goods.
Count is written with the warp number first (80x76) or it may be written as the total of the two (156). The higher the count, the better the quality.
How do you determine fabric count in woven fabrics?
Balanced Plain Weave
Warp and weft yarns art the same size and same distance apart so that they show equally on the surface.

Plain Basket Weave
Made with 2 or more adjacent warps controlled by the same harness, and with two or more weft yarns placed in the same shed.
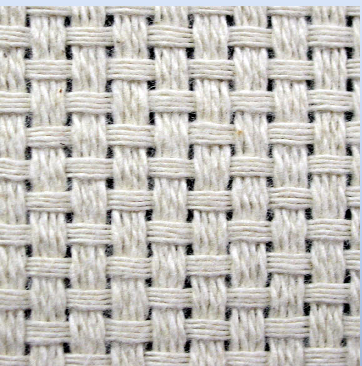
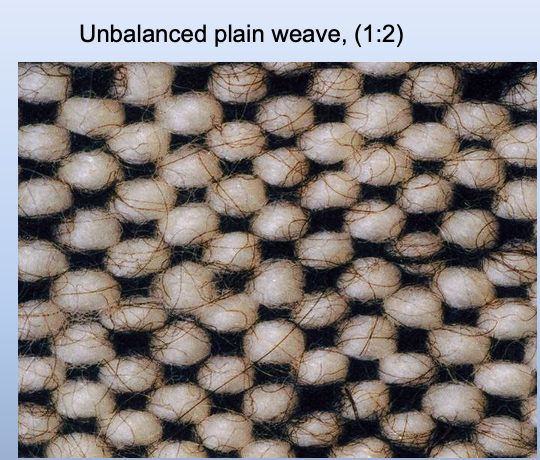
Unbalanced/Rib Plain Weave
Has significantly more of one set of yarns than the other (Broadcloth, 2:1)

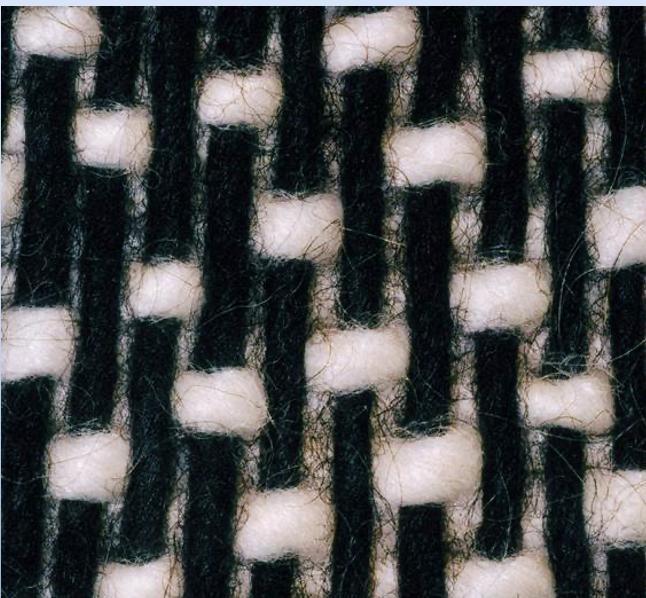
Twill Weave
Each warp or weft yarn floats across two or more weft or warp yarns with a progression of interlacings by one to the right or left, forming a distinct diagonal line (wale).

Satin Weave
Each warp yarn floats over four weft yarns 4/1 and interlaces with the fifth weft yarn, with a progression of interlacings by two to the right or the left.

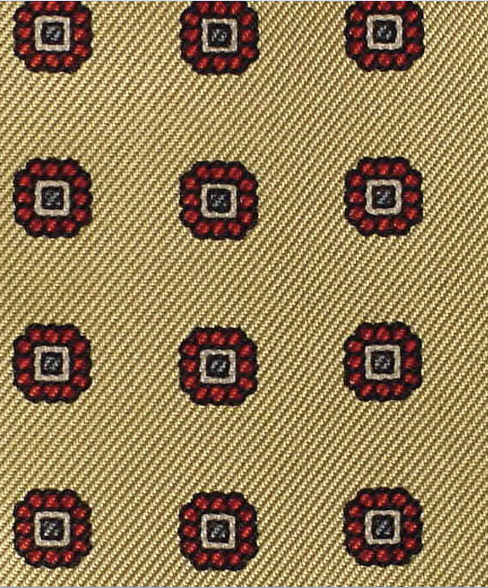
Jacquard Weave
Large figured designs that require more than 25 different arrangements of the warp yarns to complete one pattern repeat (Damask, Brocade, Brocatelle, Tapestry fabrics).

Crepe Weave
Also known as a momie weave. A weave that presents no wale or other distinct weave effect but gives the cloth the appearance of being sprinkled with small spots or seeds. Has irregular interlacings and a pebbly, uneven surface.
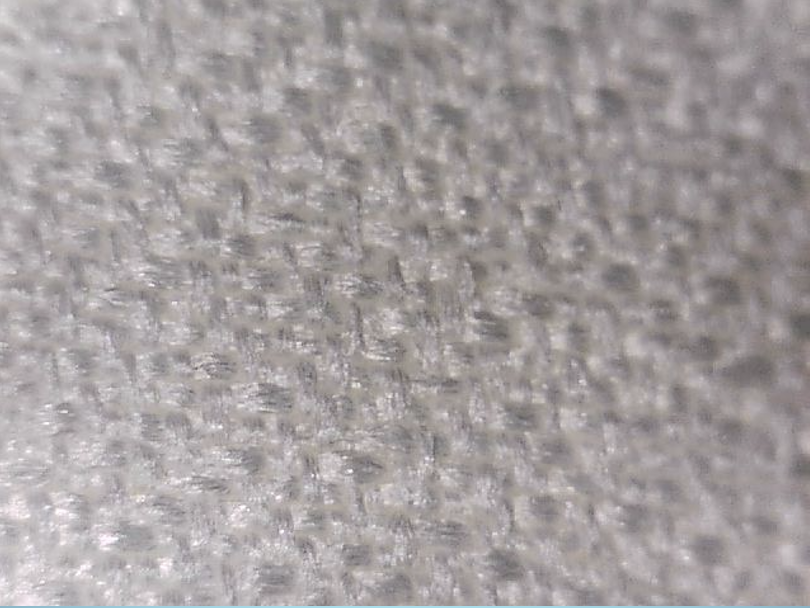

Dobby Weave
Small-figured designs, geometric figures (Bird's Eye, Huck-a-back, Waffle cloth).
Pile Weave
Three-dimensional structures made by weaving an extra set of warp or weft yarns into the ground yarns to make loops or cut ends on the surface (Corduroy, Velvet, Velveteen).

Slack Tension Weave
2 warp beams are used. Yarns on one beam are held at regular tension while the yarns on the other beam are held at slack tension. As the reed beats the weft yarn into place, the slack yarns crinkle or buckle to form a puckered stripe, and the regular-tensioned yarns form the flat stripe (Seersucker).

Extra Yarn Weave
When not used in the figure, extra warp or weft yarns float across the back of the fabric and are usually cut away during finishing (Traditional Dotted Swiss, Eyelash).
Nonwoven (Fabric from Fibers)
Felt (Fabric Structure?)
Pile Weave
Corduroy (Fabric Structure?)
Twill Weave
Herringbone (Fabric Structure?)
Twill Weave
Denim (Fabric Structure?)
Warp Knit
Machine-Made Lace (Fabric Structure?)
Nonwoven (Fabric from Solutions)
Film (Fabric Structure?)
Weft Pile Knit
Terry Cloth (Fabric Structure?)
Slack Tension Weave
Seersucker (Fabric Structure?)
Simple Weft Knit
Jersey Knit (Fabric Structure?)
Momie Weave
Crepe (Fabric Structure?)
Extra Yarn Weave
Eyelash (Fabric Structure?)
Twill Weave
Houndstooth (Fabric Structure?)
Warp Knit
Tricot (Fabric Structure?)