Organic Chemistry Exam 5
1/48
Earn XP
Description and Tags
KILL ME
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
49 Terms
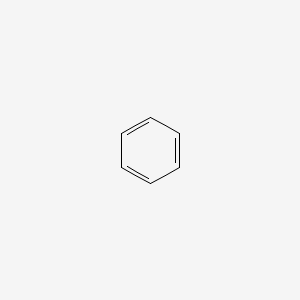
Benzene
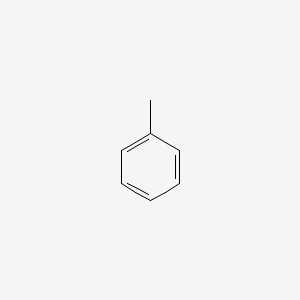
Toluene
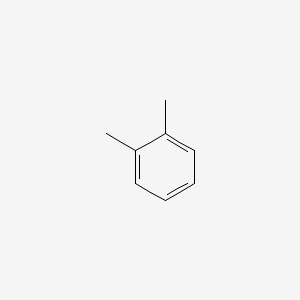
Ortho-xylene
Phenol
Aniline
Pyridine
Furan
Benzoic Acid
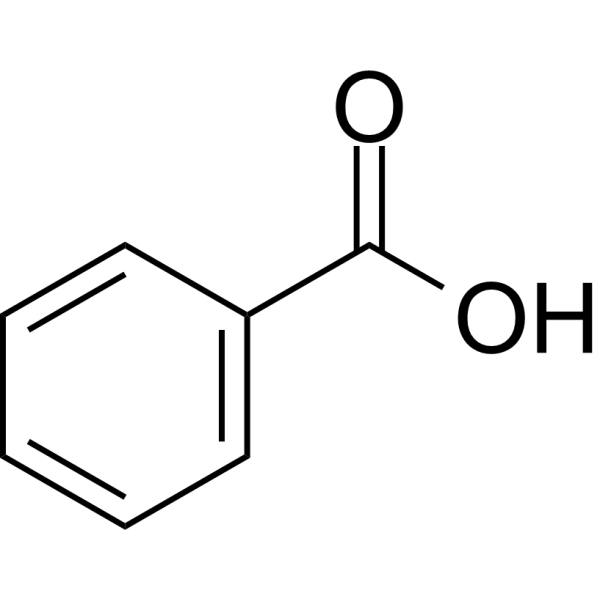
Benzaldehyde
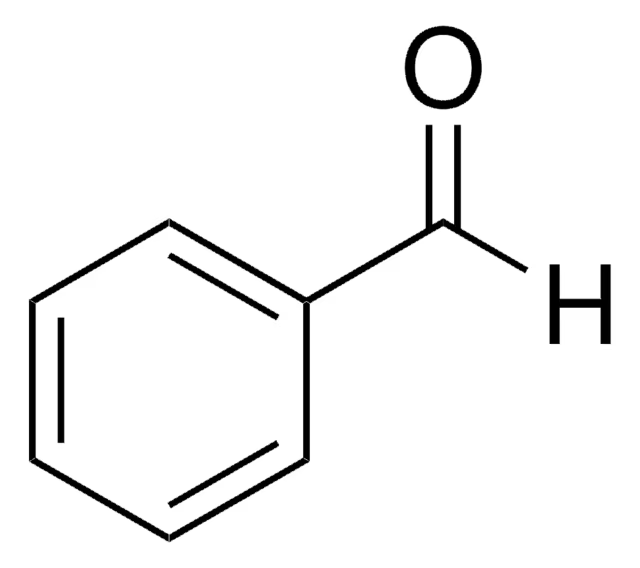
Acetophenone
Ortho-
Pre-fix for disubstituted benzene derivative.
Meaning branches at reference point and at one point beside it.
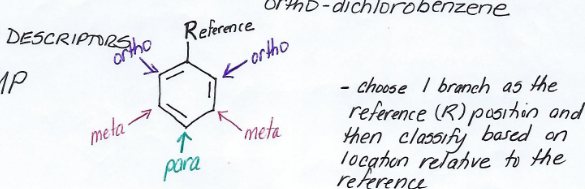
Meta-
Pre-fix for disubstituted benzene derivative.
Meaning branches at reference point and at one that is two points away.
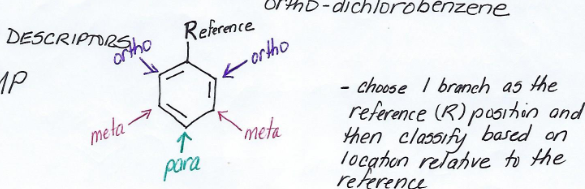
Para-
Pre-fix for disubstituted benzene derivative.
Meaning branches at reference point and at one directly opposite to the reference point.
Naming poly-substituted benzenes
Same IUPAC naming conventions as other compounds.
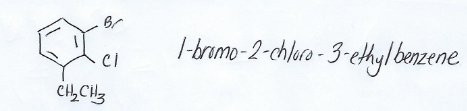
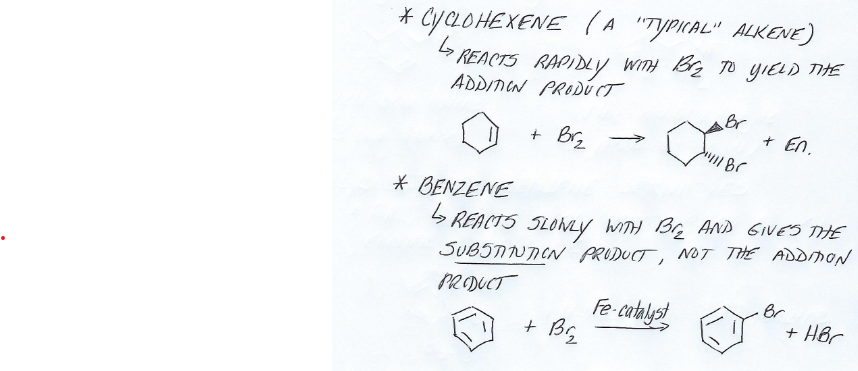
Benzene Reactivity
Much less reactive than typical alkenes. Fails to undergo typical alkene addition reactions.
Huckel’s Rule
Molecule must have a total of 4n+2π e- to be aromatic. Only applies to monocyclic compounds.
Three Criteria for Being Aromatic
Must be Cyclic + Planar
Each atom must have a p-orbital perpendicular to the ring (completely conjugated)
Must have a “huckel” # of delocalized e- (4n+2)
Aromatic
Meets all three criteria for aromaticity. Very stable
Antiaromatic
Meets first two criteria for aromaticity but has 4n π electrons. Very unstable
Nonaromatic
Does not meet 1st two criteria.
Rules for assigning hybridization
# of hybrid orbitals = # of attached atoms + # of lone pairs
Hybridization Exception
If an atom has one or more lone pairs AND is attached to an sp2 atom, then it is also sp2.
Completely Conjugated
Side to side overlap of P-orbitals at every atom of the ring.
Must have a p-orbital (Unhybridized) at every atom in the ring.
Huckel’s Rule for Polycylic Molecules
Orbitals that host π e- must be in closed p orbital loop.
If e- in question are in a π bond, both atoms must be a part of closed loop.
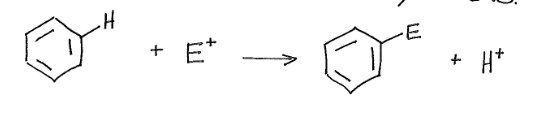
Electrophilic Aromatic Substitution
Reaction that occurs with benzene. An electrophile reacts with the nucleophilic aromatic ring and replaces one of the aromatic hydrogens.
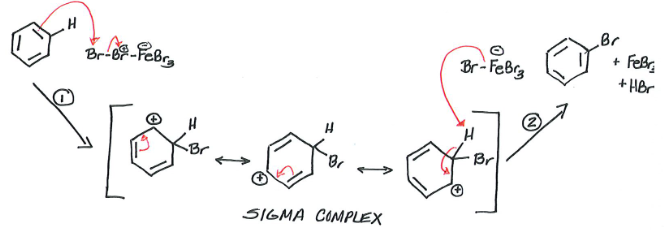
Halogenation of Benzene
Reagents: Benzene, Br2, FeBr3
Products: Bromobenzene (major) + HBr & FeBr3 (minor)
Br2 is not electrophilic enough to react with benzene, so catalyst (FeBr3) is combined with Br2 to create electrophilic reagent which allows for bromination.
Same reaction can occur with Cl2 and AlCl3
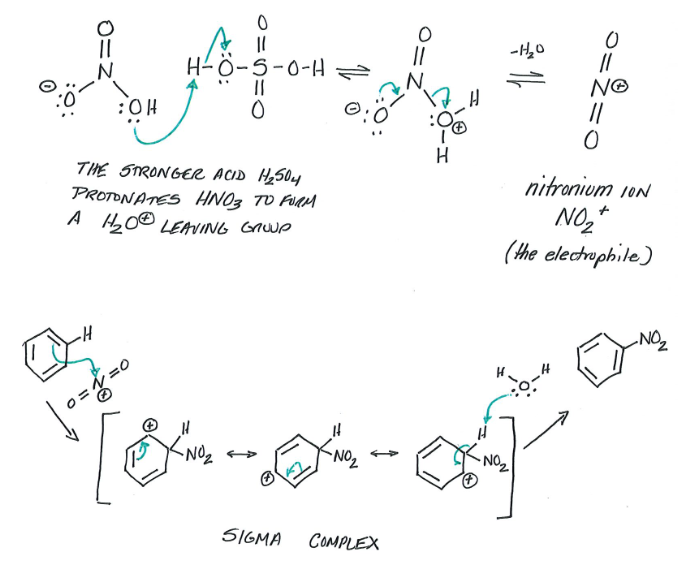
Nitration
Reagents: Benzene, Nitric Acid, Sulfuric Acid
Products: Nitrobenzene
NO3 and H2SO4 react and create Nitronium ion. This electrophile then reacts with benzene.
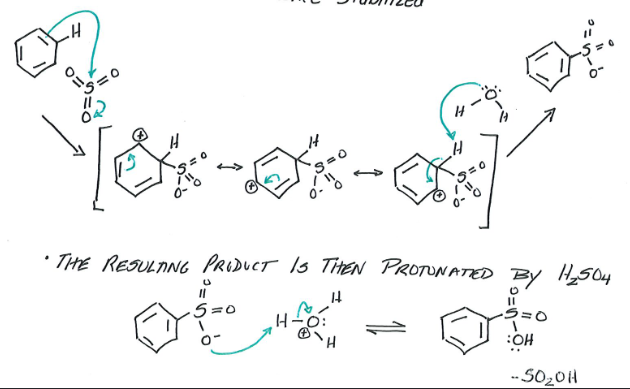
Sulfonation
Reagents: Benzene, Fuming sulfuric acid (mixture of H2SO4 and SO3)
Products: Benzene Sulfonic Acid
Fuming sulfuric acid creates Sulfur trioxide, which acts as a very powerful electrophile. This reacts with the benzene. The product of that then is protonated by H2SO4 to make Benzene Sulfonic Acid. Final product can be reversed to benzene by diluting with H2SO4.
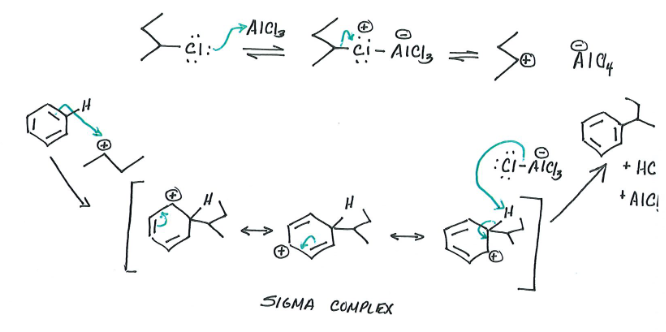
F-C Alkylation
Reagents: Benzene, Alkyl Group
Product: alkyl-benzene (major), HCl & AlCl3 (minor)
Add alkyl group onto aromatic ring. Carbon atom in alkyl group acts as electrophile
2° and 3° alkyl halides are used, not 1° (too high in energy).
Only efficient when substrate cannot undergo rearrangement.
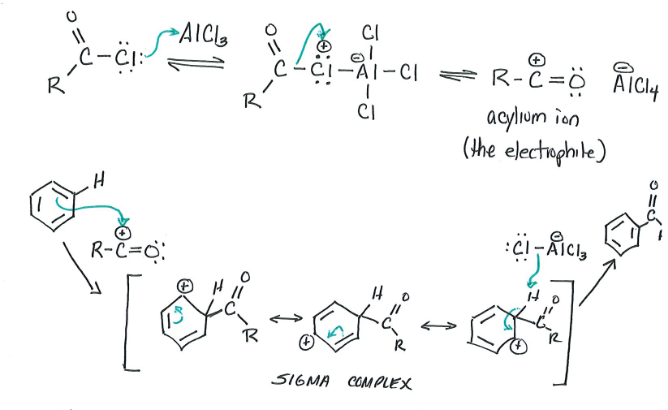
F-C Acylation
Reagents: Benzene, Acyl group
Products: Aryl Ketone (major),
Acyl chloride treated with lewis acid to form acylium ion. Acylium ion reacts with benzene.
Product can be reduced using a Clemmensen Reduction: Zn(Hg)/HCl + Heat
Substituents Affect on Reactivity
Some activate the ring (More reactive than benzene)
-OH makes ring 1000x more reactive
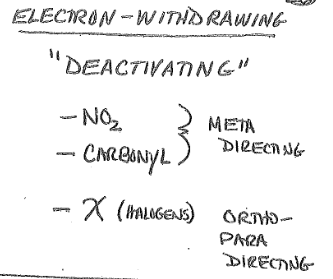
Some deactivate the ring (less reactive than benzene)
-NO2 makes ring 10 million times less reactive
-Cl makes ring 0.033x less reactive
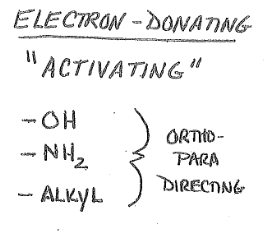
Ortho-Para Directors
Tend to be Electron-Donating Groups
Groups that direct incoming electrophile to the ortho and para positions
Meta Directors
Tend to be Electron Withdrawing Groups
Direct incoming electrophile to meta position
Three Main Rules for Tri-Substituted Benzene
If the directing effects of two groups reinforce each other (go to same position of the ring, single product is formed
If the directing effects oppose one another, the more powerful group has the dominant influence, mixture of products is formed.
When 2 groups are in the meta-disubstituted compound, it is rare for more substitution to occur between the two groups.
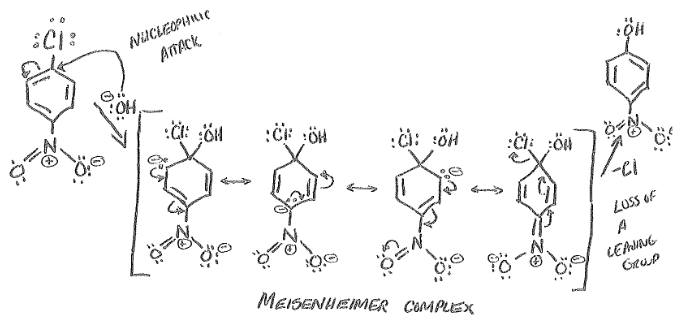
Three Criteria for Nucleophilic Aromatic Substitution
Ring must have a strong electron withdrawing group attached (like NO2)
The ring must contain a leaving group
The leaving group must be either ortho or para to the EWG
Nucleophilic Aromatic Substitution
Aromatic ring is attacked by nucleophile, then leaving group is expelled to restore aromaticity.
Side Chain: Permanganate Oxidation
Reagents: Benzene with alkyl halide side chain, KMnO4 or Na2Cr2O7
Products: Carboxylate Salt of Benzoic Acid
Benzene does not react with products attached to that are able to cleave C=C bonds. Alkyl halides react with oxidizing agents and are converted to -CO2H
Side Chain: Halogenation
Alkyl benzene undergo halogenation with abstraction of a H at a benzylic position.
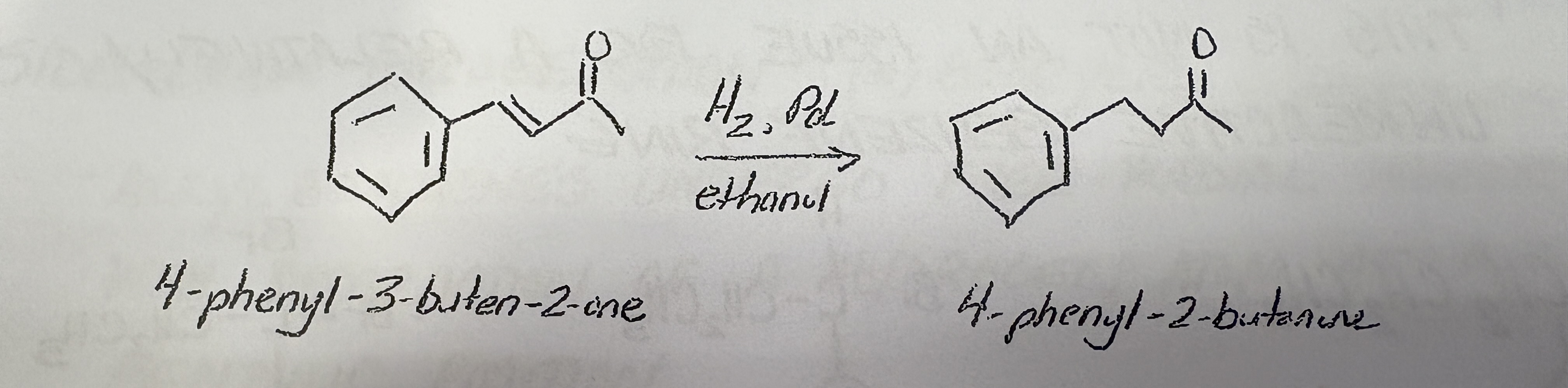
Aromatic Catalytic Hydrogenation
Reagents
Products
Rings inert to catalytic hydrogenation. Side chain reacts.
Birch Reduction
benzene derivatives reduced to non-conjugated cyclohexa-1,4-dienes by treatment with sodium or lithium in a mixture if liquid ammonia and an alcohol.
Strong Activators
-OH, -O, -NH2
Medium Activators
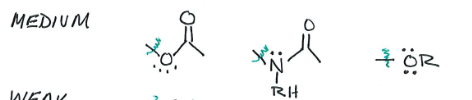
Weak Activators
-CH3,-CH2CH3
Weak Deactivator
-Cl, -Br
Medium Deactivator
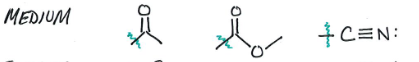
Strong Deactivator
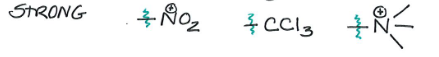
Activating Groups
Deactivating Groups