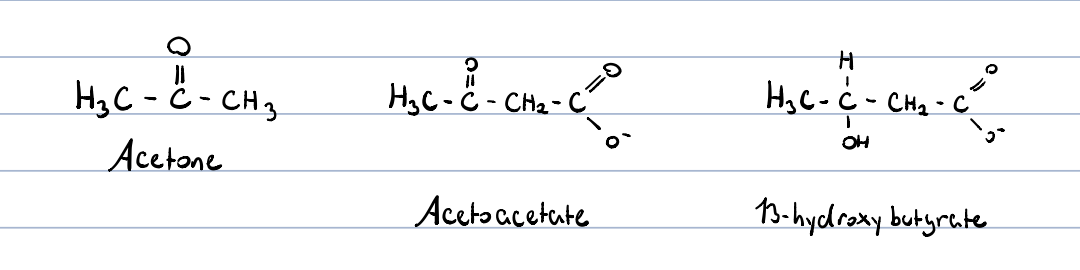3. Composition of simple and complex lipids, ketone bodies. biochemically important lipids
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/35
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Last updated 10:52 PM on 6/10/23
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
36 Terms
1
New cards
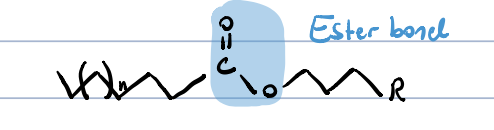
composition of simple lipids?
the simplest lipids are fats, oils and waxes
they are esters of fatty acids and alcohols, and does not carry any other group
they are esters of fatty acids and alcohols, and does not carry any other group
2
New cards
waxes?
esters of long carbon chain (C>20) monovalent alchols and long chain fatty acids
3
New cards
biological role of waxes?
protecting coating on skin, hair or feather
on fruits and on the leaves of plants to prevent water loss through evaporation
waxes are also used in pharmaceutical, cosmetic and other industries
on fruits and on the leaves of plants to prevent water loss through evaporation
waxes are also used in pharmaceutical, cosmetic and other industries
4
New cards
carnauba wax?
waxes and polishes
food products
pills
food products
pills
5
New cards
beeswax?
used in food, pharmaceuticals and cosmetics
6
New cards
lanolin?
wool-fat used as lotion for eczema
7
New cards
triacylglycerols?
esters of long chain fatty acids and trivalent alcohols
fats: solid triacylglycerols at room temperature, contain mostly saturated fatty acids
oils: liquids at room temperature, contain mostly unsaturated fatty acids. geometry of the double bond is cis
fats: solid triacylglycerols at room temperature, contain mostly saturated fatty acids
oils: liquids at room temperature, contain mostly unsaturated fatty acids. geometry of the double bond is cis
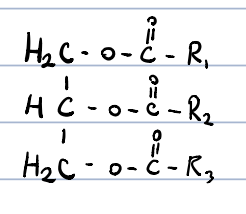
8
New cards
biological functions of TAG?
energy storage
* the carbons of fatty acids are more reduced than those in carbs, therefore oxidation of FA yields 2x the energy, gram for gram
mechanical protection and insulation
* the carbons of fatty acids are more reduced than those in carbs, therefore oxidation of FA yields 2x the energy, gram for gram
mechanical protection and insulation
9
New cards
glycerophospholipids?
esters of glycerol w. fatty acids and phosphoric acid, in which the phosphoric acid is also esterified by an other alcohol
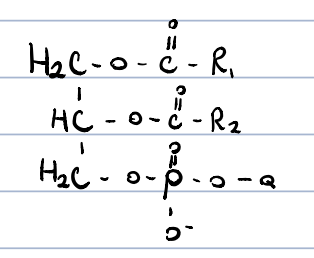
10
New cards
biological functions of glycerophospholipids ?
building blocks of the cell membrane
certain phospholipids functions as signalling molecules
certain phospholipids functions as signalling molecules
11
New cards
cephalin (phosphatidyl ethanolamine)?
main constituents of cell membranes
facilitates incorporation of proteins into the cell membrane
facilitates incorporation of proteins into the cell membrane
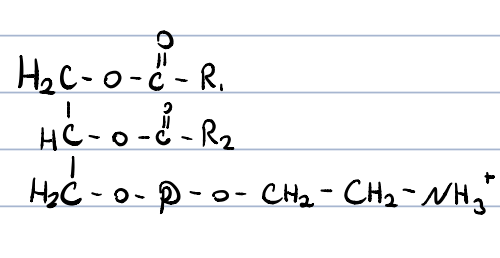
12
New cards
Lecithin (phosphatidylcholine)?
main constituents of cell membranes
occurs in high quantities in egg yolk and soya beans
in signal transmission
precursor of DAG
occurs in high quantities in egg yolk and soya beans
in signal transmission
precursor of DAG
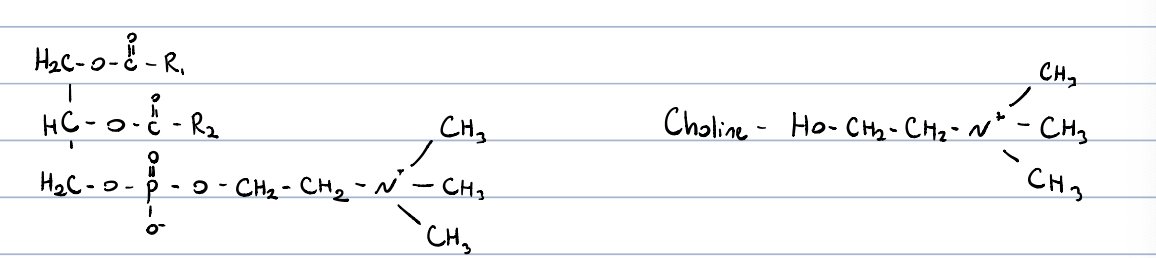
13
New cards
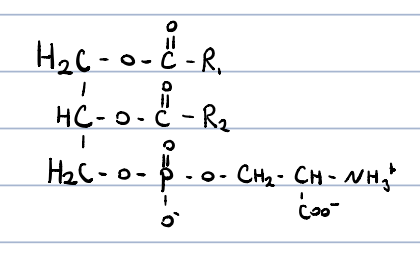
Phosphatidylserine?
constituents of cell membranes
it occurs in higher amount in myelin
it is the cofactor for PKC, has a role in blood coagulation and programmed cell death
can act as both a base and an acid
it occurs in higher amount in myelin
it is the cofactor for PKC, has a role in blood coagulation and programmed cell death
can act as both a base and an acid
14
New cards
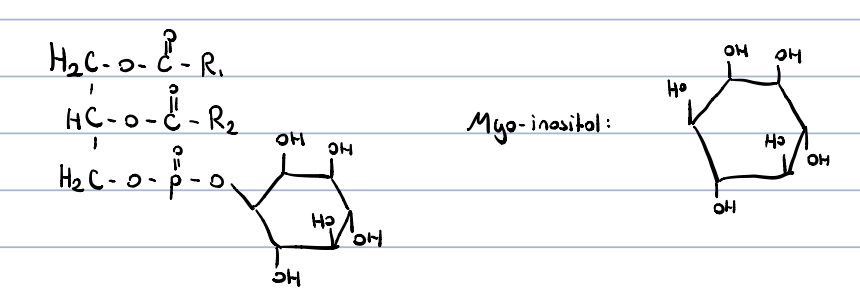
Phosphatidylinositol?
a constituent of cell membranes
very abundant in brain
main source of arachidonic acid
in signal transmission: gives diacylglycerols
very abundant in brain
main source of arachidonic acid
in signal transmission: gives diacylglycerols
15
New cards
cardiolipin (bisphosphatidylglycerol)?
two phosphatidic acids are linked through a glycerol
occurs in the inner mitochondrial membrane
necessary for proper function of the enzymes of the resp. chain
occurs in the inner mitochondrial membrane
necessary for proper function of the enzymes of the resp. chain
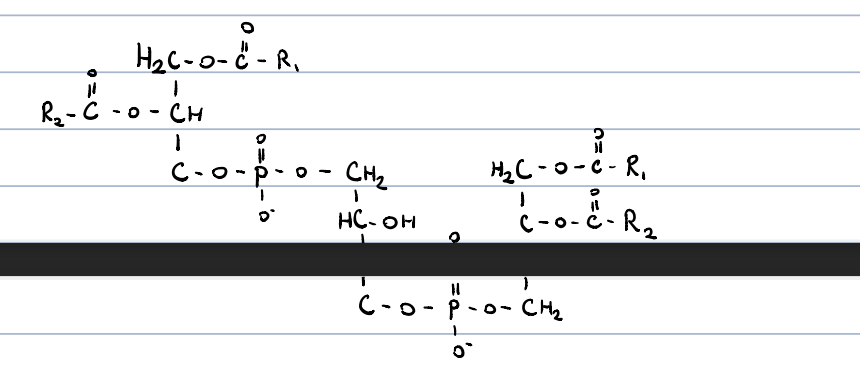
16
New cards
glycerophosphospholipids in signal transmission?
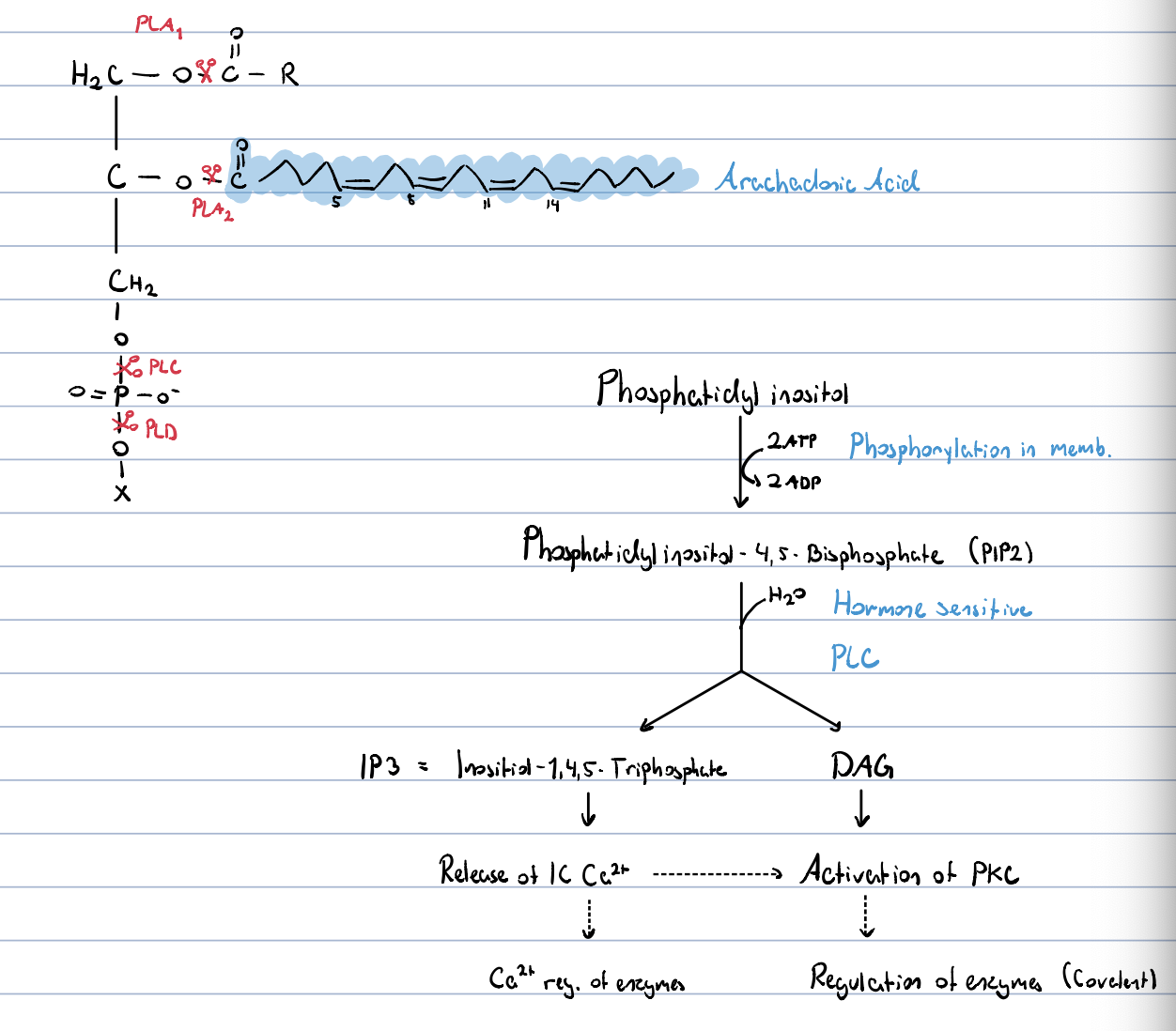
17
New cards
sphingolipids?
amides of FA and sphingosine which is linked to other polar groups
the fatty acid:
* saturated or contains 1 double bond, can have odd or even number of carbons, generally
* can contain OH group
* multisaturated FAs are rare in sphingolipids
backbone is not glycerol
the backbone is a long-chain amino alcohol
a fatty acid is joined to sphingosine via amide linkage
a polar head group is attached w. glycosidic or phosphodiester linkage
sugar containing sphingolipids occur mostly on the outer surface of plasma membranes
the fatty acid:
* saturated or contains 1 double bond, can have odd or even number of carbons, generally
* can contain OH group
* multisaturated FAs are rare in sphingolipids
backbone is not glycerol
the backbone is a long-chain amino alcohol
a fatty acid is joined to sphingosine via amide linkage
a polar head group is attached w. glycosidic or phosphodiester linkage
sugar containing sphingolipids occur mostly on the outer surface of plasma membranes
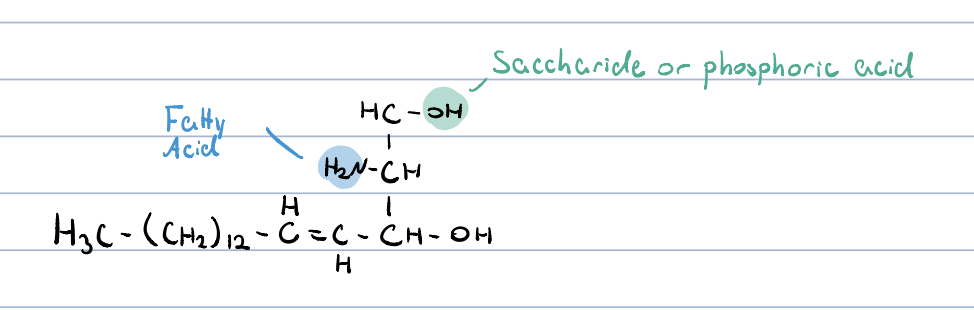
18
New cards
biological functions of sphingolipids?
the main constituent of the outer layer of the cell membranes
they occur mainly in nervous tissue, they have an important role in recognition
they occur mainly in nervous tissue, they have an important role in recognition
19
New cards
ceramides?
R-carbon chain of fatty acid
precursor of other sphingolipids
precursor of other sphingolipids
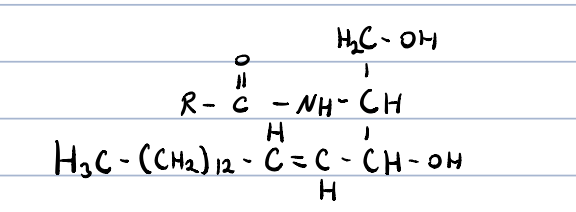
20
New cards
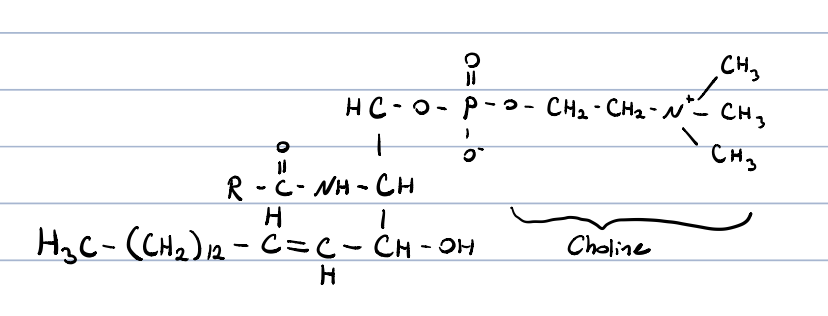
sphingomyeline?
the most abundant sphingolipid
occurs in lipid rafts
* lipid raft: 10-200nm, heterogenous, ordered structures in the membrane
occurs in lipid rafts
* lipid raft: 10-200nm, heterogenous, ordered structures in the membrane
21
New cards
classes of sphingolipids?
neutral glycophospholipids
sulphated glycolipids
gangliosides
sulphated glycolipids
gangliosides
22
New cards
neutral glycophospholipids?
the carbohydrate part doesn’t contain negatively charged groups
most frequent monosaccharides are:
* glucose
* galactose
* N-acetulglucosamine
* N-acetyl galactosamine
examples are:
* cerebrosides
* globosides
most frequent monosaccharides are:
* glucose
* galactose
* N-acetulglucosamine
* N-acetyl galactosamine
examples are:
* cerebrosides
* globosides
23
New cards
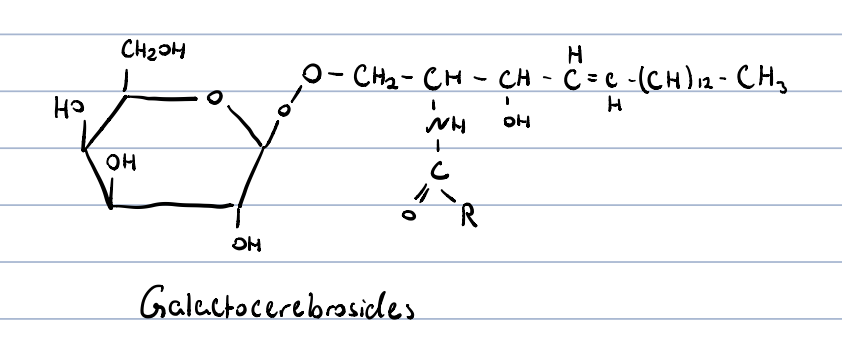
cerebrosides?
monoglycosyl ceramides
constituent of myelin in CNS, and lipid rafts
constituent of myelin in CNS, and lipid rafts
24
New cards
globosides?
ceramides of di- or oligosaccharides
e.g. blood type antigens
e.g. blood type antigens
25
New cards
sulphated glycolipids?
galactocerebrosides, in which the 3rd OH-group of galactose is esterified by sulphuric acid
constituent of myelin
constituent of myelin
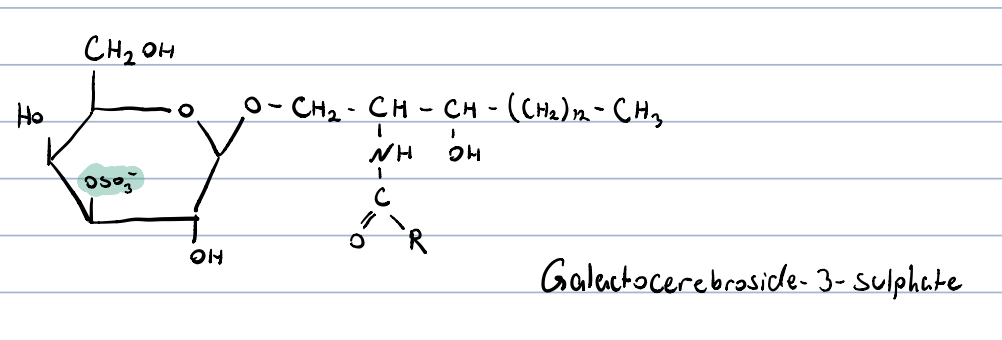
26
New cards
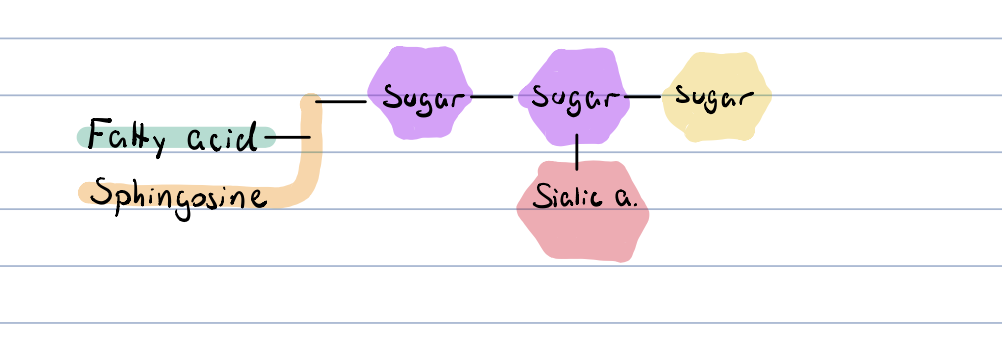
gangliosides?
the carbohydrate part is an oligosaccharide, which contains a negatively charges sialic (N-acetylneuraminic) acid moiety
occur in grey matter of brain
cell type specfic antigens, receptor
occur in grey matter of brain
cell type specfic antigens, receptor
27
New cards
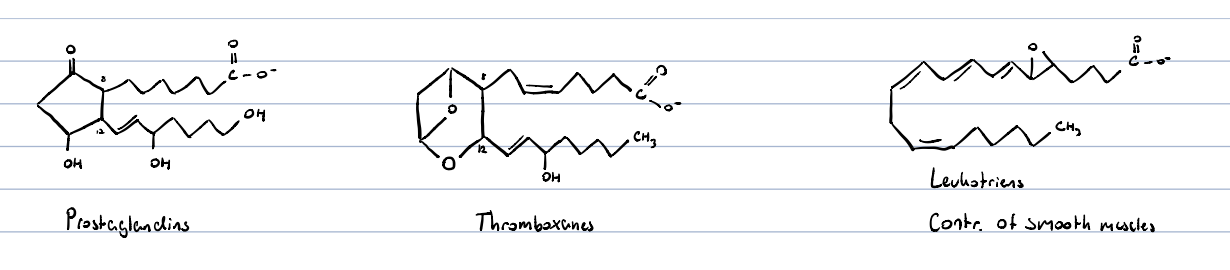
eicosanoids?
carboxylic acids of 20 carbons
enzymatic conversion of arachidonic acid yields:
* cyclooxygenase: prostaglandins, thromboxanes
* lipoxygenase: leukotrienes
enzymatic conversion of arachidonic acid yields:
* cyclooxygenase: prostaglandins, thromboxanes
* lipoxygenase: leukotrienes
28
New cards
biological role of eicosanoids?
paracrine hormones
mediators in healthy and pathological cells (reg. of blood pressure, clotting, contr. of smooth m.)
overproduction of prostaglandins → fever, inflammation, nausea, vomiting
mediators in healthy and pathological cells (reg. of blood pressure, clotting, contr. of smooth m.)
overproduction of prostaglandins → fever, inflammation, nausea, vomiting
29
New cards
prostaglandins?
20-C long carboxylic acid w. substituted cyclopentane ring
PGE and PGI2
PGE and PGI2
30
New cards
PGE?
stimulates contraction of smooth miscles in uterus
protects epithelium from gastric juice and reduce acid secretion
protects epithelium from gastric juice and reduce acid secretion
31
New cards
PGI2?
inhibits aggregation of thrombocytes
vasodilator
vasodilator
32
New cards
Biosynthesis of prostaglandins?
oxidation and cyclisation by cycloxygenase
reduction to 15-OH by peroxidase
reduction to 15-OH by peroxidase
33
New cards
thromboxanes?
produced by thrombocytes to initiate blood clotting
TXA2: induces aggregation of thrombocytes and is a vasoconstrictor
TXA2: induces aggregation of thrombocytes and is a vasoconstrictor
34
New cards
Leukotrienes?
they are produced in granulocytes and mast cells
mediators of inflammation and allergic reactions
mediators of inflammation and allergic reactions
35
New cards
terpenoids?
built from isoprene units
biological role:
* precursor of steroids and caratenoids
* hormones and vision
* anti-oxidants
* essential oils
biological role:
* precursor of steroids and caratenoids
* hormones and vision
* anti-oxidants
* essential oils
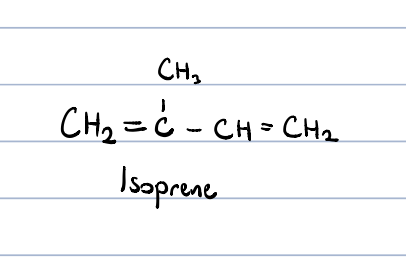
36
New cards
ketone bodies?
3 types of ketone bodies, where two can be utilized by our body for energy
* acetone
* acetoacetate
* β-hydroxybutyrate
* acetone
* acetoacetate
* β-hydroxybutyrate