Human Anatomy
1/755
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Flashcards from Human Anatomy Lecture Notes
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
756 Terms
Gross Anatomy
Study of visible structures (e.g., brain)
Microscopic Anatomy
Requires magnification (e.g., neurons, cytology, histology)
Regional Anatomy
Structures in a specific region (e.g., arm muscles, vessels)
Systemic Anatomy
Study by systems (e.g., cardiovascular)
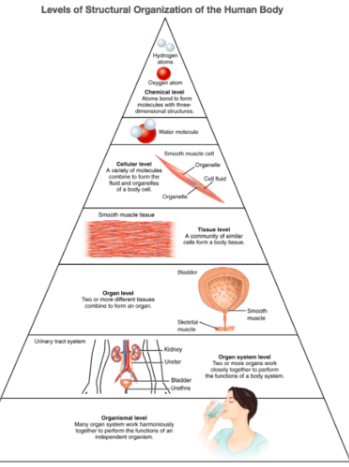
Structural Organization of the Human Body
Subatomic particles -> Atoms -> Molecules -> Organelles -> Cells -> Tissues -> Organs -> Organ Systems -> Organism
Cells
Smallest unit of life
Organelles
Specialized cell parts
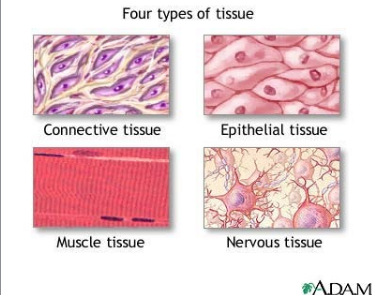
Tissues
Similar cells working together
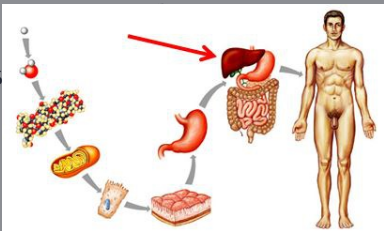
Organs
Groups of tissues
Organ Systems
Groups of organs working together
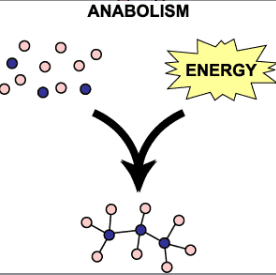
Anabolism
Builds up molecules (uses energy)
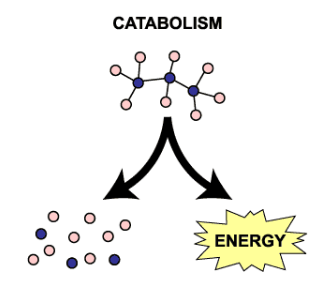
Catabolism
Breaks down molecules (releases energy)

Metabolism
Sum of anabolism + catabolism
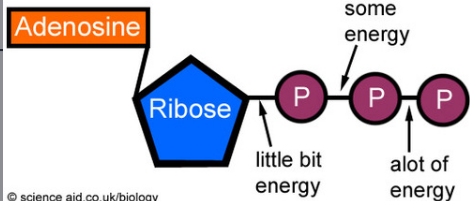
ATP
Cell's energy currency
Responsiveness
React to stimuli
Development
The body changes over time
Growth
Increase in size or number of cells
Differentiation
Cells become specialized
Reproduction
Formation of new organisms
Water
Essential solvent; 70% body mass
Energy-Yielding Nutrients
Carbohydrates, fats, and proteins
Micronutrients
Vitamins and minerals
Set Point
Ideal physiological value
Normal Range
Healthy fluctuation range
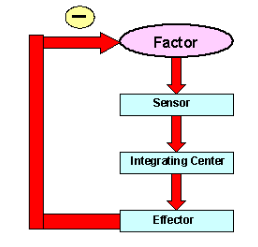
Negative Feedback
A mechanism that reverses a deviation from the set point.
Homeostasis is maintained by a negative feedback loop.
Ex: sweating
Components
Sensor -> Control Center -> Effector
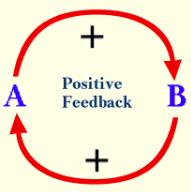
Positive Feedback
Amplifies change (e.g., childbirth)
A mechanism that intensifies a physiological condition in the body instead of reversing it.
Continues until a definite endpoint
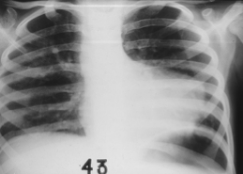
X-Ray
Produces 2D image
Uses: for hard tissues
Risk: Radiation
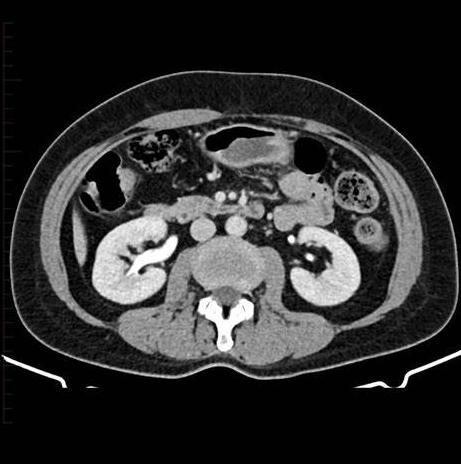
CT Scan
Produces cross-sectional
Uses: for soft tissues
Risk: High radiation
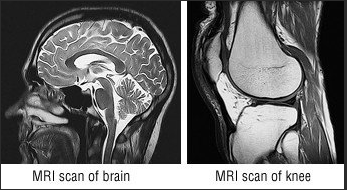
MRI (magnetic resonance imaging)
Produces magnetic imaging
Uses: tumors and soft external tissues
Risk: Expensive and no radiation
Integumentary System
Protects the body
sensory site
Organs: Skin, hair, nails
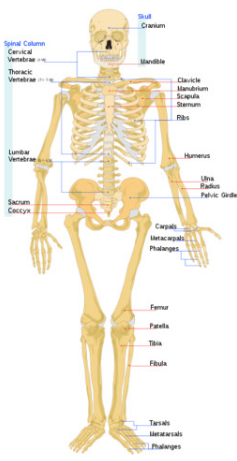
Skeletal System
Support and movement
Organs: Bones, cartilage
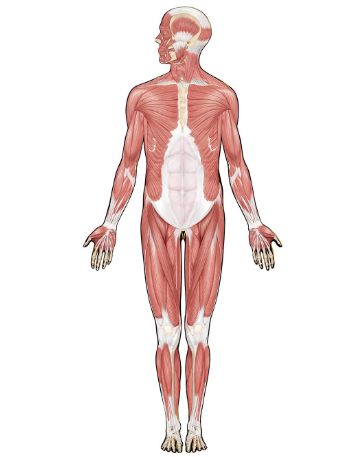
Muscular System
Movement and temp regulation
Organs: Muscles and tendons
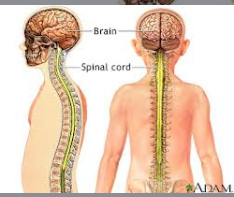
Nervous System
Process info and control
Organs: Brain, spinal cord, and peripheral nerves
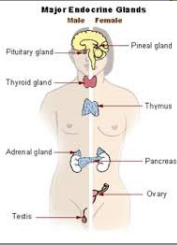
Endocrine
Secretes hormones and regulation
Organs: Pituitary gland, thyroid gland, pancreas, adrenal glands, testes, and ovaries
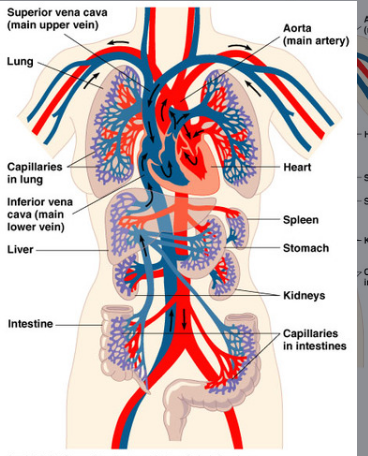
Cardiovascular System
Transport oxygen and nutrients and equalizes temp
Organs: Heart, vessels
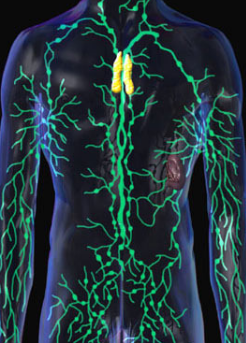
Lymphatic System
Immunity and fluid return
Organs: Thymus, lymph nodes, spleen, and lymphatic vessels
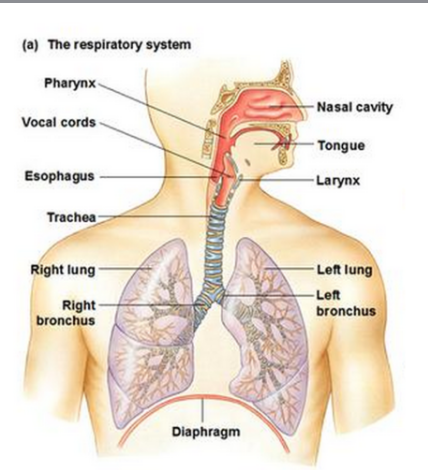
Respiratory System
Removes carbon dioxide and Delivers oxygen to the blood
Organs: Nasal passage, trachea, and lungs
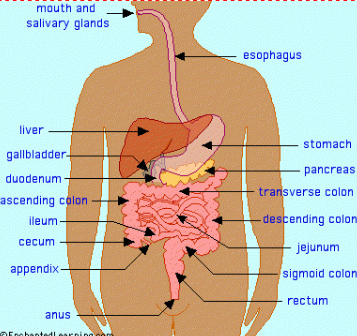
Digestive System
Responsible for nutrition and waste
Organs: Stomach, liver, gall bladder, large intestine, small intestine
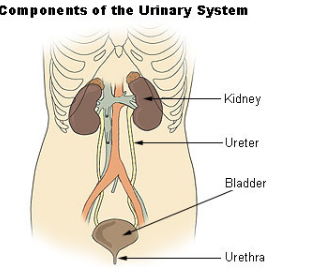
Urinary System
Waste excretion and water balance
Organs: Kidneys and bladder
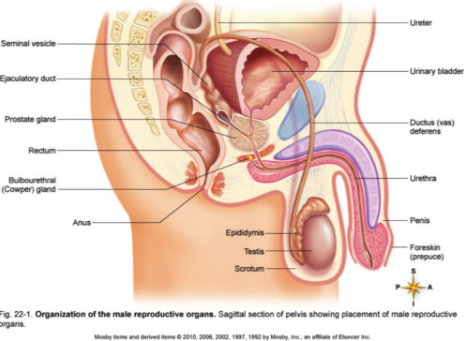
Male Reproductive System
Secretes hormones and gametes
Organs: Epididymis and testes
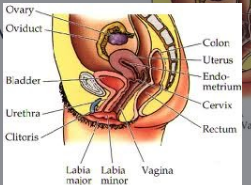
Female Reproductive System
Secretes hormones and gametes, supports infants, and produces milk
Organs: Mammary glands, ovaries, uterus
An organism's basic function:
An organism's basic function:
Consume energy and molecules from food to convert into fuel for movement, sustain its body functions, and build and maintain its body structures.
The requirements for life are oxygen, nutrients, and pressure.
The requirements for life are oxygen, nutrients, and pressure.
These are essential for maintaining cellular function and overall health.
Required chemical reactions in the body only take place when the body is within its narrow range temperature (Just below 37C (98.6F))
Required chemical reactions in the body only take place when the body is within its narrow range temperature (Just below 37C (98.6F))
Oxygen is a key component of chemical reactions, such as producing ATP.
Oxygen is a key component of chemical reactions, such as producing ATP.
Maintaining homeostasis requires that the body continuously monitor its internal conditions.
Maintaining homeostasis requires that the body continuously monitor its internal conditions.
In the heat, blood vessels dilate to release heat/ in the cold, blood vessels constrict to conserve heat.
In the heat, blood vessels dilate to release heat/ in the cold, blood vessels constrict to conserve heat.
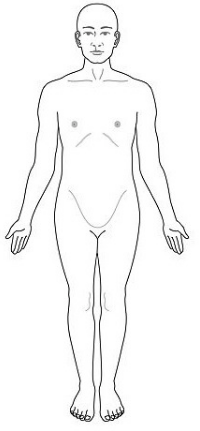
Anatomical Position
Anatomical Position
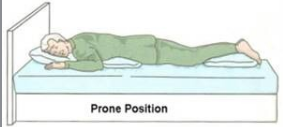
Prone
Face-down orientation
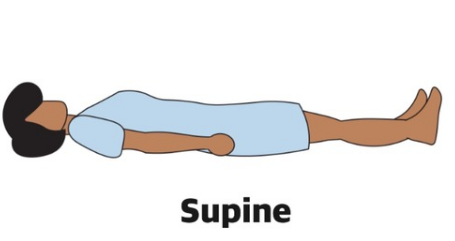
Supine
Face up orientation
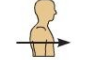
Anterior (or ventral)
Front of the body (facing forward) Ex:The toes are anterior to the foot
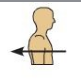
Posterior (or dorsal)
Back of the body (facing backwards) Ex: The popliteus is posterior to the patella.
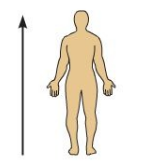
Superior (or cranial)
Position above/toward the head Ex: The orbits are superior to the oris
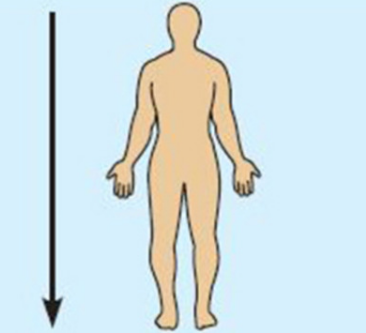
Interior (or caudal)
Position below or away from the head Ex: The pelvis is inferior to the abdomen.
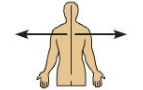
Lateral
The side or direction toward the side of the body Ex: The thumb (pollex) is lateral to the digits.
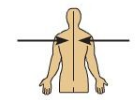
Medial
Position of in the middle or direction towards the middle of the body. Ex: The hallux is the medial toe
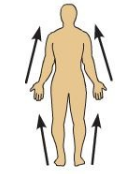
Proximal
The distance of a limb that is closer to the trunk or attachment to the body Ex: The brachium is proximal to the antebrachium
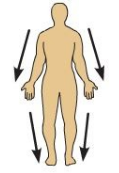
Distal
The distance of a limb that is farther away from the trunk or attachment to the body. Ex:The crus is distal to the femur.
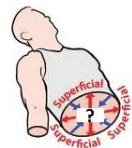
Superficial
Position closer to the surface of the body Ex: The skin is superficial to the bones.
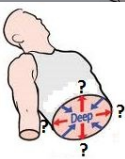
Deep
Position farther from the surface of the body. Ex: The brain is deep to the skull
Section
Two dimensional surface of a 3D structure that has been cut
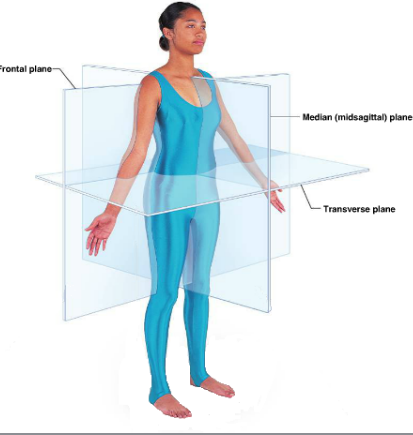
Plane
Imaginary two-dimensional surface that passes through the body.
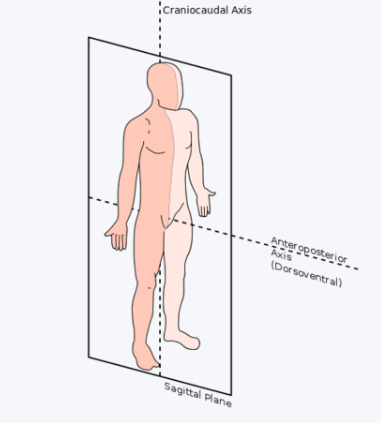
Sagittal Plane
Divides the body or organ vertically into right and left sides
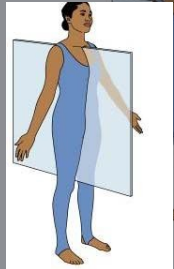
Midsagittal or median plane
Vertical plan directly down the middle of the body
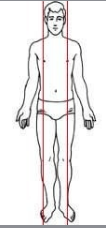
Parasagittal plane or longitudinal section
Unequal right and left sides plane or longitudinal section
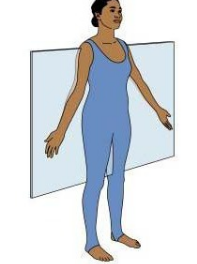
Frontal Plane
Divides the body or an organ into anterior (front) and posterior (back)
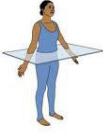
Transverse Plane
Divides the body or organ horizontally into upper and lower portions.
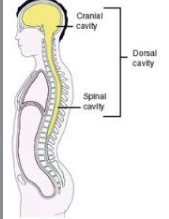
Dorsal (posterior) Cavity
Includes the cranial (brain) and spinal (spinal cord) cavities.
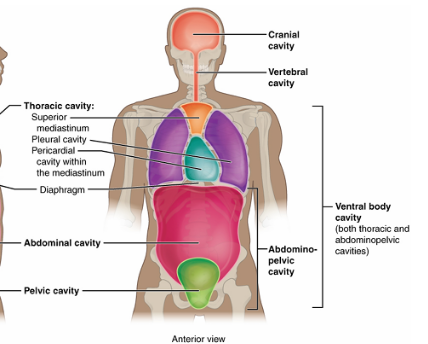
Ventral (anterior) Cavity
Includes the thoracic (the organs inside the rib cage and diaphragm) and abdominopelvic (abdomen and the top of the pelvis) cavities.
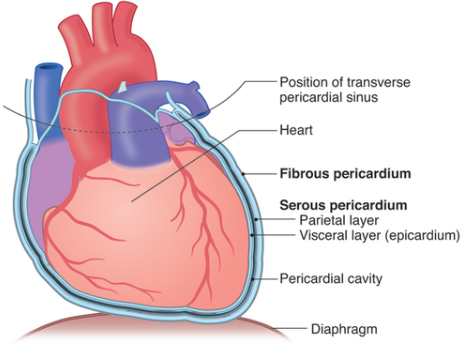
Serous Membrane
The thin membrane that covers the walls and organs in the thoracic and abdominopelvic.
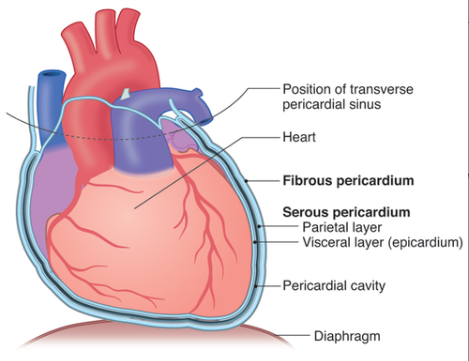
Parietal Layers
Membrane that lines the walls of the body cavity
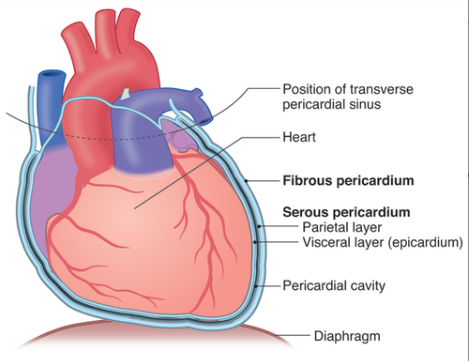
Visceral Layer
Membrane that covers the organs
Chemical Energy
Form of energy that is stored in chemical bonds.
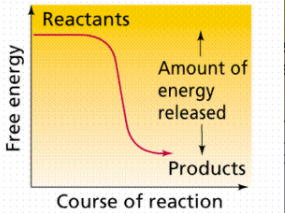
Exergonic
Chemical reactions that release more energy than they absorb. Ex: Catabolism
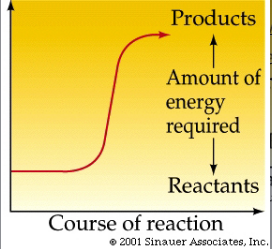
Endergonic
Chemical reactions that absorb more energy than they release.
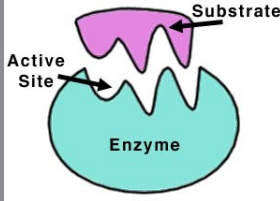
Enzyme
A catalyst composed of either a protein or a ribonucleic acid (RNA).
Works by lowering the level of energy needed to cause a chemical reaction.
Critical to the body's healthy functioning
Activation Energy
The threshold level of energy needed to break the reactant bonds.
Inorganic Compound
A substance that does not contain both carbon and hydrogen
Many contain hydrogen atoms (H2O and HCl)
Very little contain carbon atoms (CO2)
The three inorganic compounds that are essential to life are
Water, salts, acids and bases
The three inorganic compounds that are essential to life are
Water, salts, acids and bases
Organic Compounds
A substance that contains both carbon and hydrogen -Synthesized by covalent bonds within living organisms, including the human body.
Five functional groups that are important to human physiology
Hydroxyl, Carboxyl, Amine, Methyl, and Phosphate
Five functional groups that are important to human physiology
Hydroxyl, Carboxyl, Amine, Methyl, and Phosphate
Heat Sink
A substance or object that absorbs and dissipates heat but doesn't experience an increase in temperature Ex: water
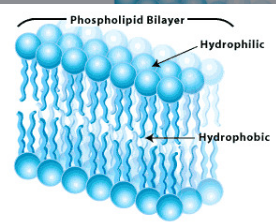
Hydrophillic
Dissolves in water (water loving)
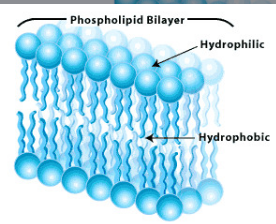
Hydrophobic
Does not dissolve in water (water fearing)
Salt
A substance that, when dissolved in water, dissociates into ions other than H+ or OH
Formed when ions make an ionic bond.
Dissociates into ions that are electrolytes and conduct electrical currents.
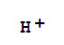
Acids
A substance that releases hydrogen ions in a solution -Proton donor -Strong acids release all their H+ in solution (they ionize completely) -Strong acids aid in digestion and kill ingested microbes.

Base
A substance that releases hydroxyl ions (OH-) in solution and accepts present H+ -Proton recipient -Removes H+ and reduces acidity.
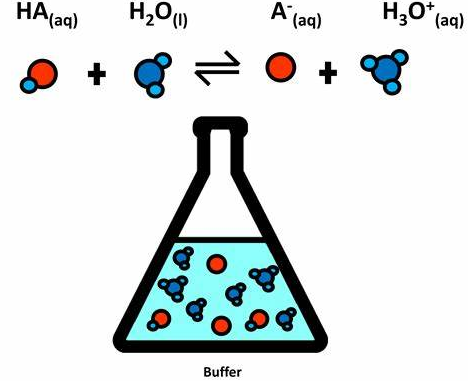
Buffers
A solution of a weak acid and its conjugate base.
Can neutralize small amounts of acids or bases in body fluids.
Carbohydrate
A molecule composed of carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen Also called sugars
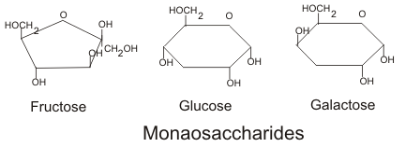
Monosaccharide
Monomers of carbohydrates. \Three of these are hexo sugars (6 carbons): glucose, fructose, and galactose Two are pentose sugars (5 carbons): ribose and deoxyribose
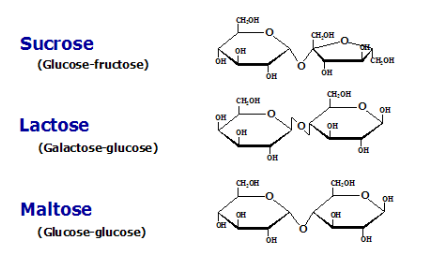
Disaccharides
Made of two monosaccharides -
Fromed through dehydration synthesis
Broken apart into monosaccharides in the digestive tract through hydrolysis
Three main sugars: sucrose (table sugar), lactose (milk sugar), and maltose (malt sugar)
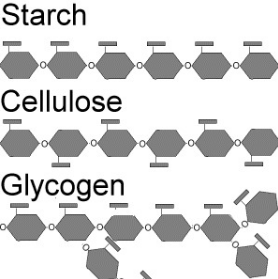
Polysaccharide
The polymers and consist of hundred to thousands of monomers or monosaccharides. -Three are important to the body: -Starches (polymer of glucose) -Glycogen (polymer of glucose) -Cellulose (fiber from plants cell wall)
Adenosine triphosphate (ATP)
Composed of a ribose sugar, an adenine base, and three phosphate groups -Releases free energy when phosphate bonds are broken and supplies cells with energy -Produced in the presence of oxygen
Lipids
One of a highly diverse group of compounds made up mostly of hydrocarbons. -Hydrophobic -Organic compound
Dietary fat assists in the absorption and transport of nonpolar fat-soluble vitamins
Stored body fat protects, cushions the bones and internal organs, and insulates to retain heat.
Dietary fat assists in the absorption and transport of nonpolar fat-soluble vitamins
Stored body fat protects, cushions the bones and internal organs, and insulates to retain heat.
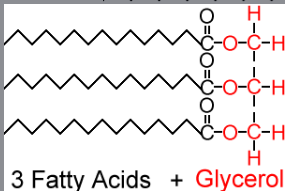
Triglyceride
One of the most common dietary lipid groups Formed through dehydration synthesis. -Major fuel source for the body.
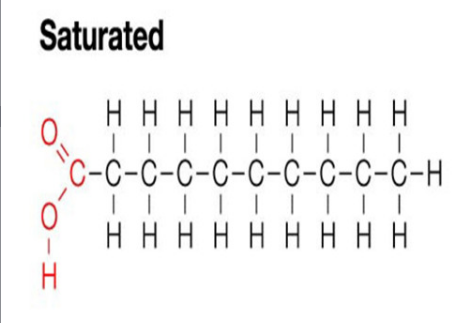
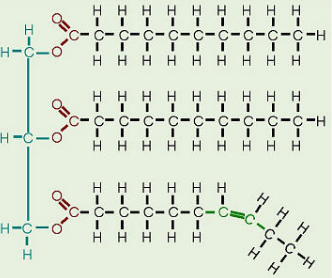
Saturated Fatty Acid
Fatty acid with no double carbon bonds -Sold at room temp -Ex: butter -Unhealthy
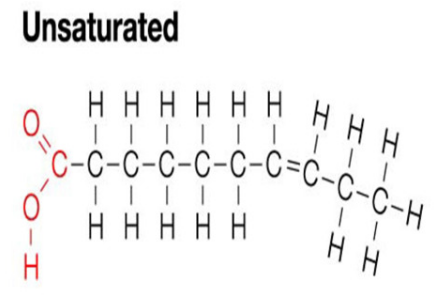
Unsaturated Fatty Acid
Fatty acid with double carbon bonds -Liquid at room temperature -Healthy
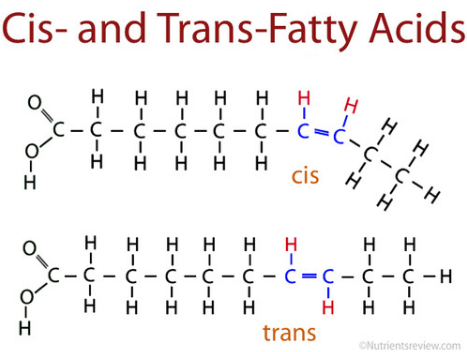
Trans fatty acids
Created from unsaturated fatty acids (such as corn oil) when chemically treated to produce partially hydrogenated fats. -Found in processed foods -Unhealthy and harmful to the heart and blood vessels.