AP Human Geography Unit 3 - Culture
1/104
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
105 Terms
examples of artifacts
clothing, architecture, art, weapons, tools, infrastructure, modes of transportation, etc.
examples of sociofacts
family, school, government, religious institutions, land use, gender roles, etc.
examples of mentifacts
language, religion, folklore and myths, traditions, taboos, morality and ethics, etc.
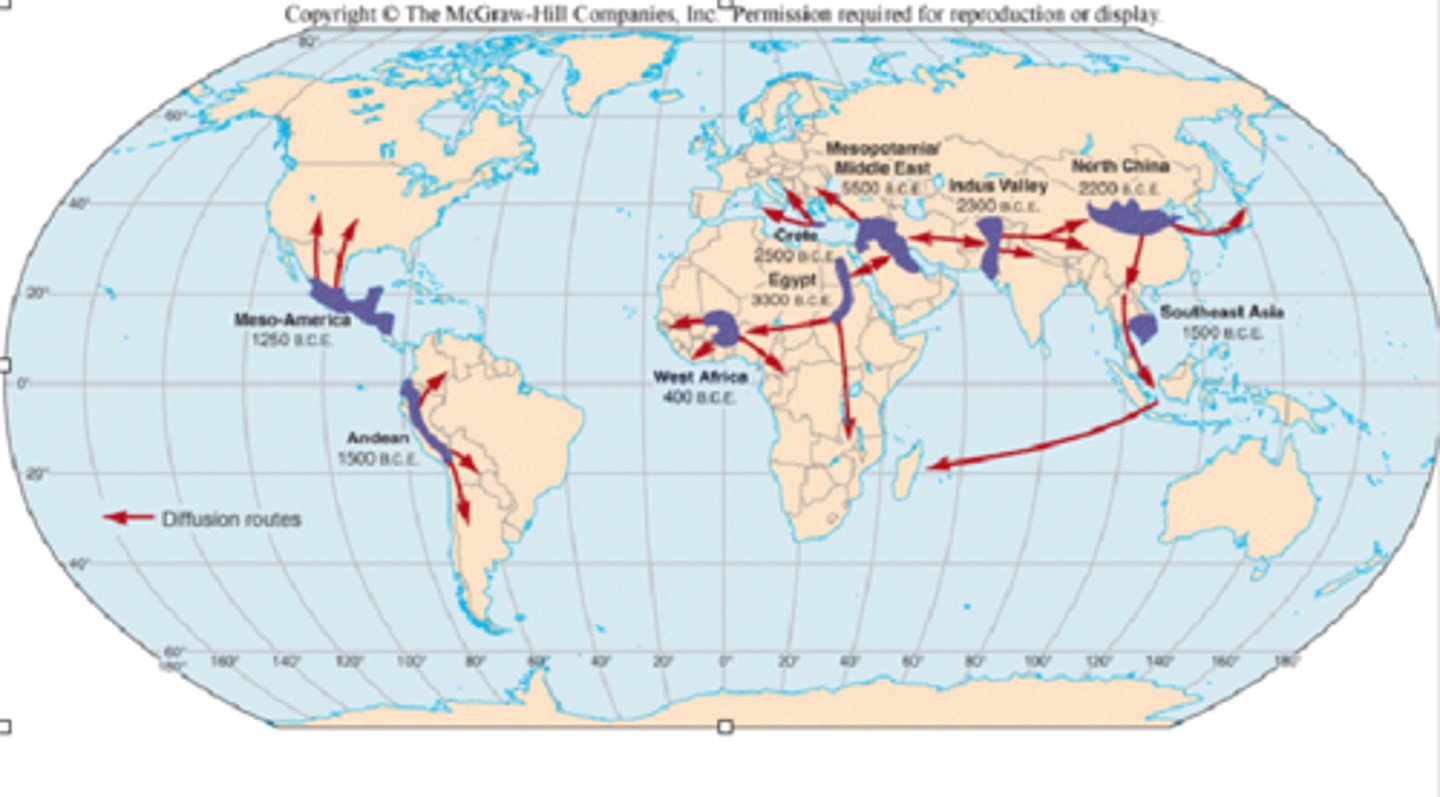
locations of the ancient cultural hearths
Mesoamerica, Andean America, West Africa, Mesopotamia, Nile Valley, Indus Valley, Wei-Huang River Valley, Ganges Delta
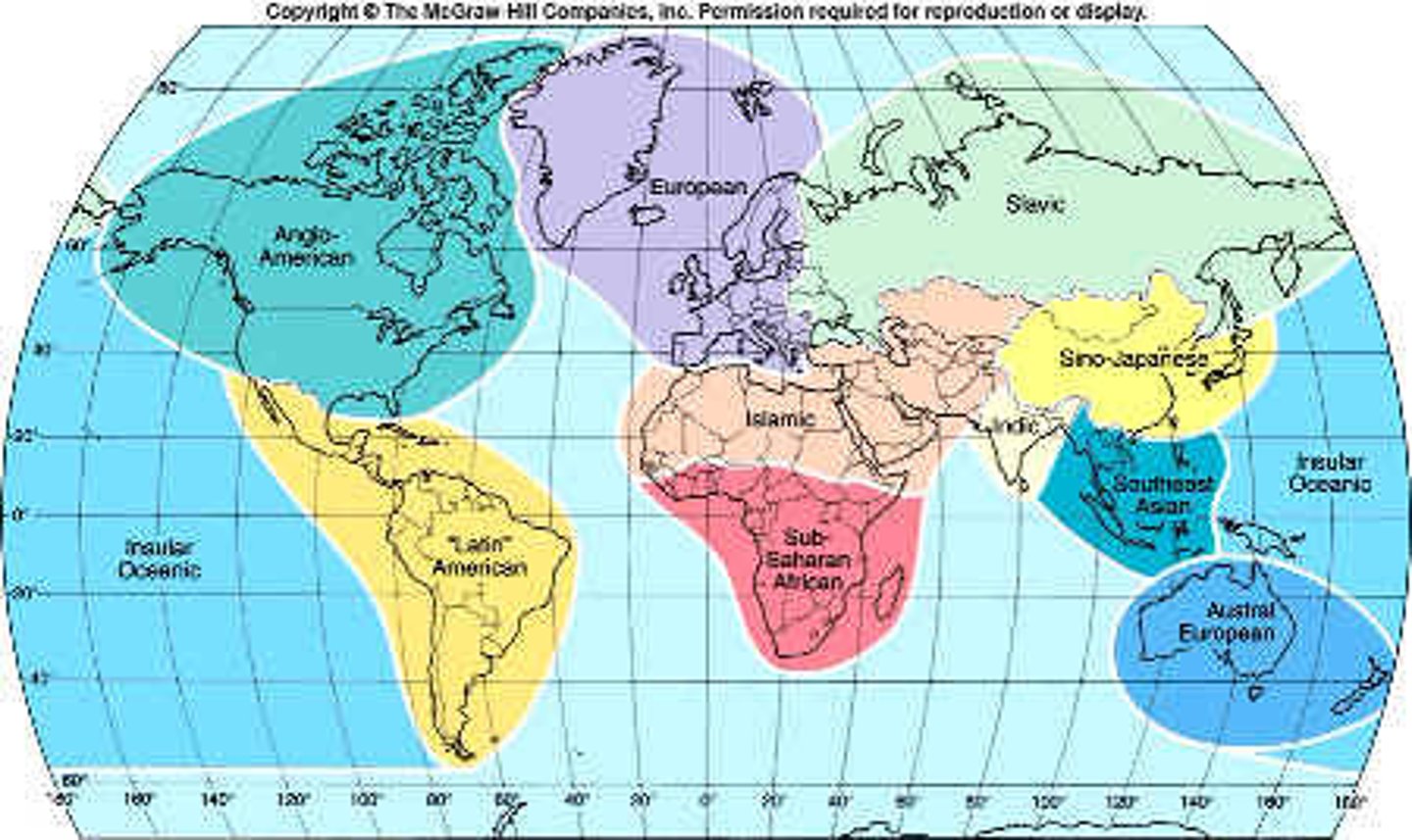
What are the cultural realms?
Anglo-American, Latin American, European, Islamic, Sub-Saharan African, Slavic, Sino-Japanese, Indic, Southeast Asia, Austral European
expansion diffusion
an idea or innovation develops in a hearth and remains strong there while also spreading outward
ideas/innovations move, not people
types of expansion diffusion
contagious, hierarchical, reverse hierarchical, stimulus
contagious diffusion
one person spreads an idea/innovation to multiple people, and those people spread it to multiple people, and so on and so forth
diffusion that uniformly affects all individuals/areas outward from the source
examples of contagious diffusion
disease, breaking news, internet memes, coffee culture
hierarchical diffusion
the spread of an idea from persons or nodes of authority or power to other persons or places of less power/authority
may only affect certain places
examples of hierarchical diffusion
fashion trends, phone trees, popular music, chains of command, rap
reverse hierarchical diffusion
diffusion up a hierarchy, such as from a small town to large cities
examples of reverse hierarchical diffusion
Walmart, thrifting
stimulus diffusion
when something spreads but is changed by the people who adapt the idea/innovation
fundamental idea stimulates imitative behavior
adapted to meet needs of local culture
examples of stimulus diffusion
franchise restaurants w/ international locations (e.g. McDonald's), "Italian" food, Tex-Mex, gang culture
relocation diffusion
spread of an idea/innovation through the physical movement of people
not everyone along the path of achievement adopts the innovation
examples of relocation diffusion
crops & farming techniques, architectural styles, concepts of government, religion, missionaries/conquistadors spreading ideas, etc.
types of barriers to diffusion
physical, cultural, economic, political
examples of barriers to diffusion
mountains, oceans, deserts, religious beliefs, language, taboos, political boundaries, censorship, affordability of trends, etc.
historical causes of diffusion
trade, colonialism, war
contemporary causes of diffusion
globalization and urbanization
examples of folk culture
Amish, Native Americans, Cajun, Samui, Māori, Inuit, Romani
examples of popular culture
pop music, movies, fashion
folk culture
practiced by small, homogenous groups in isolated areas
anonymous origins with a heavier and stricter focus on tradition
transmitted slowly
traits and distribution characterized by local cultural and physical factors
often threatened by diffusion of popular culture, but continued use primarily for preservation or to attract tourists
popular culture
found in large, heterogenous societies
traceable hearths
typically follows hierarchical diffusion and distributes widely without barriers
sophisticated and complex products made by individuals, businesses, or factories; can also be imported
less influenced by environmental factors
diminishing ideas of gendered roles/spaces
when dominant, folk culture may been as controversial
Which religion is the largest religion with 2 billion followers?
Christianity
followers of Christianity
Christians
branches of Christianity
Catholic, Protestant, Orthodox
sacred text of Christianity
The Bible
key ideas of Christianity
Jesus is the son of God and savior of humanity. Core values are outlined in the Ten Commandments.
Christianity hearth
Eastern Mediterranean/Southwestern Asia/Present-Day Israel
Christianity diffusion
Contagious diffusion through Middle East, Europe, and Central Asia
Hierarchical diffusion via conquest/colonization
Relocation diffusion throughout the world via missionaries
Christianity distribution
Catholics dominate Southwest Europe and Latin America
Protestants dominate Northwest Europe and North America
Orthodox dominate Eastern Europe
Christianity place of worship
churches (architecture depends on location but often have a cross)
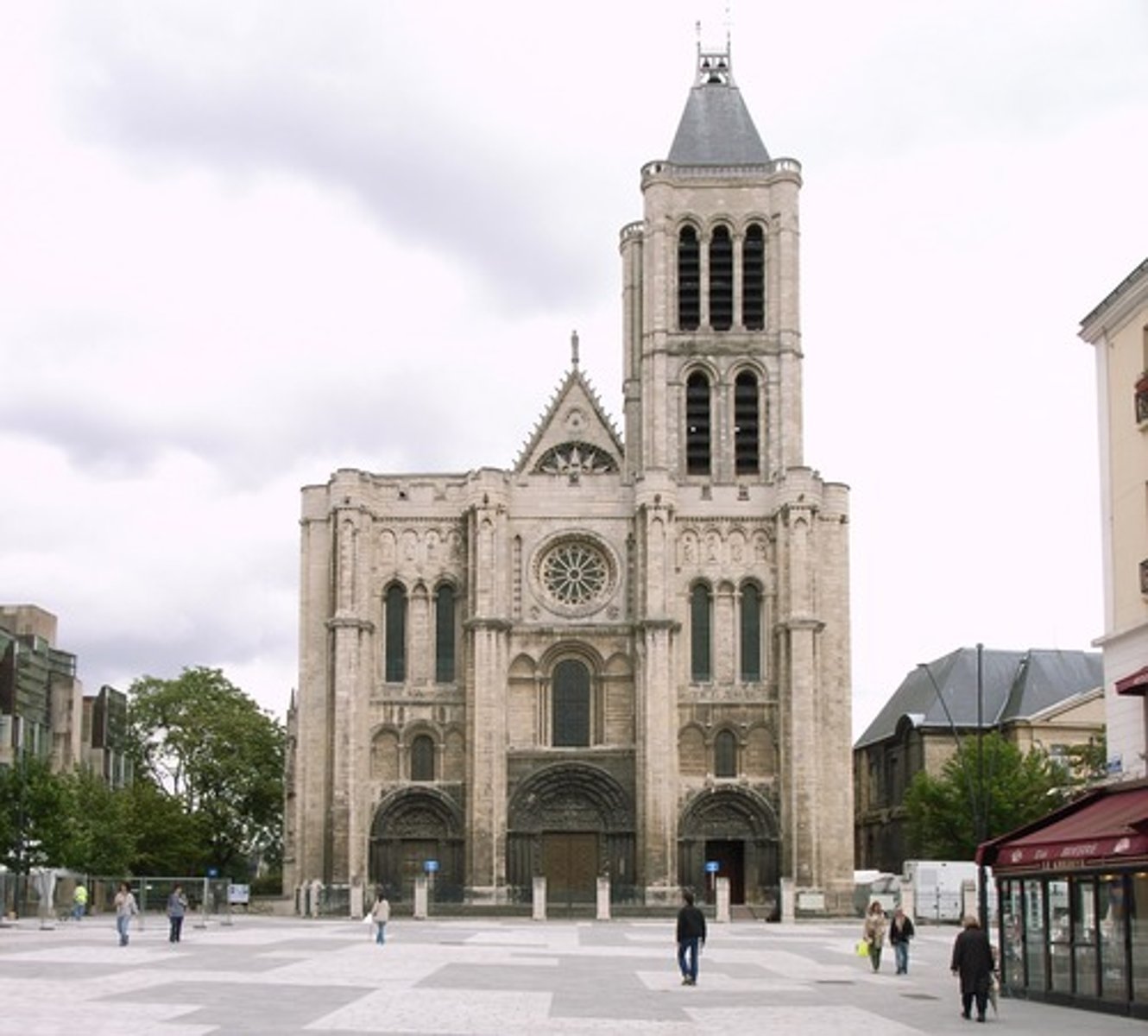

Which religion is the 2nd largest with 1.5 billion followers?
Islam
followers of Islam
Muslims
branches/denominations of Islam
Sunni and Shia
sacred text of Islam
Koran/Quran
key ideas of Islam
Allah revealed his teachings through a series of prophets, the last being Muhammad.
hearth of Islam
Southwestern Asia (Present-day Saudi Arabia)
Islam diffusion
Contagious diffusion by trade and military conquest to Spain, Africa, and much of Asia
Relocation diffusion throughout the whole world
Islam distribution
Dominant in the Middle East (from North Africa to Central Asia)
Islam place of worship
mosques (varies by location, but often with domes, thin towers, and ornate arches)
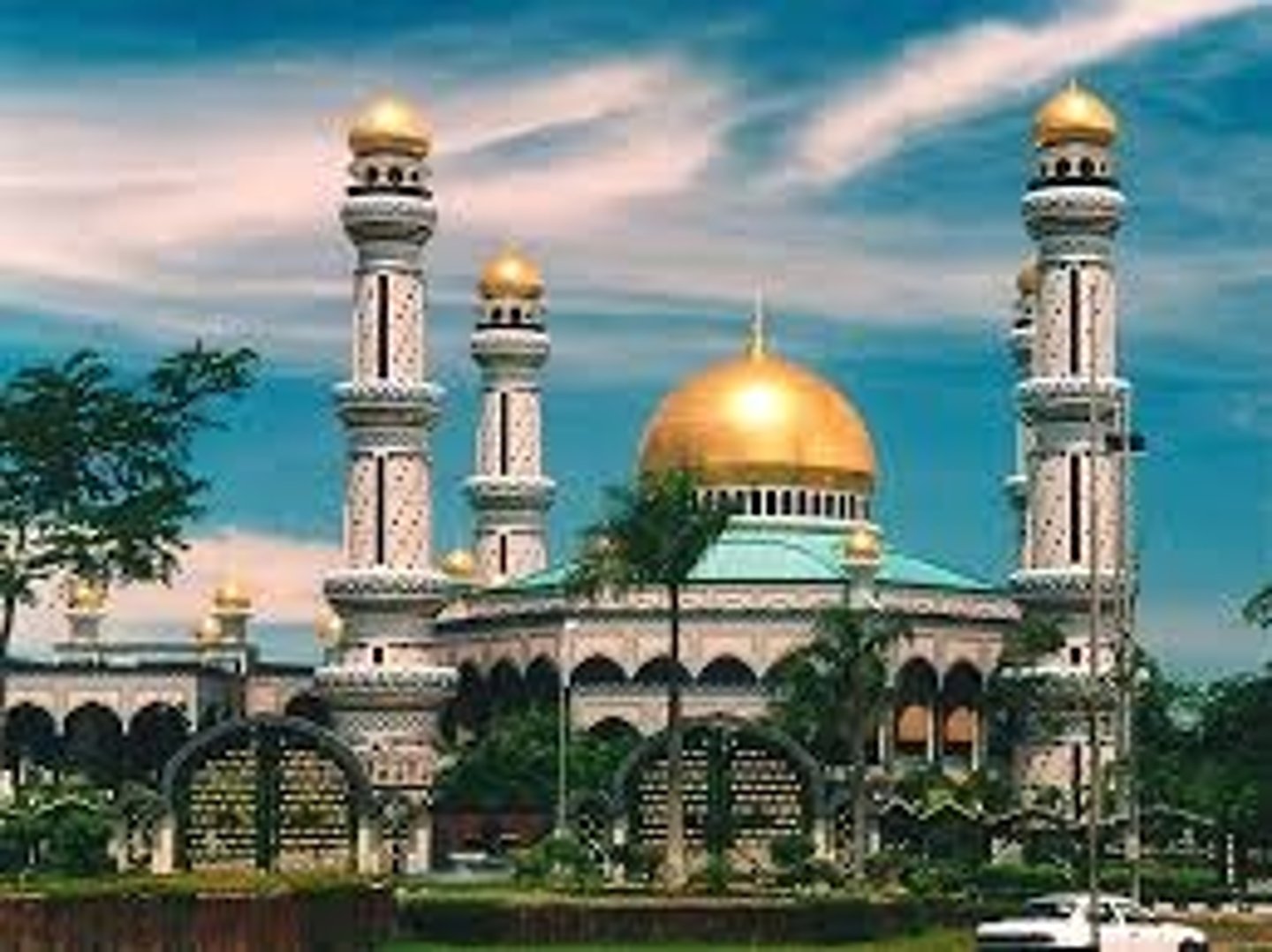

Which religion is the 3rd largest with 1 billion followers?
Hinduism
Hinduism branches
Vaishnavism, Shaivism, Shaktism, Smartism
Hinduism sacred text
The Vedas
key ideas of Hinduism
Belief in the power of meditation, karma, and reincarnation and associated with the caste system.
Hinduism hearth
South Asia
Hinduism diffusion
Contagious diffusion across Indian subcontinent
Relocation diffusion in recent decades to Europe and USA
Hinduism distribution
Vast majority of followers live in India, but there are significant populations in Bangladesh, Myanmar, Sri Lanka, and Nepal
Hinduism place of worship
temples (ornate and either colorful or monochromatic)
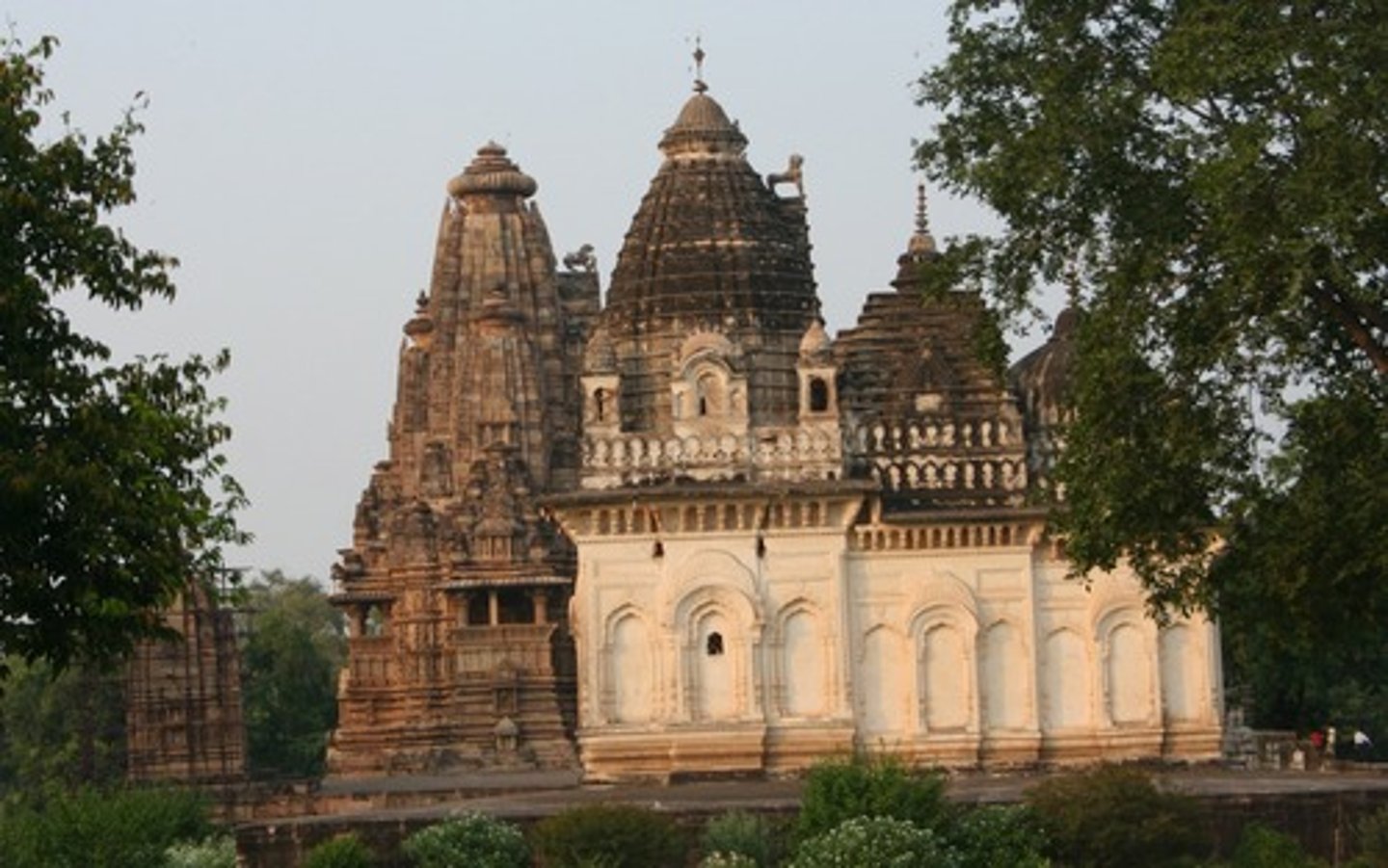

Which religion is the 4th largest with 350 million followers?
Buddhism
Buddhism followers
Buddhists
Buddhist branches
Mahayana, Theravada, Vajrayana
Buddhist sacred text
Tripitaka
key ideas of Buddhism
Core belief is reincarnation; followers pursue Nirvana (the ultimate enlightenment).
Buddhism hearth
South Asia in present day Nepal
Buddhism diffusion
Contagious diffusion as teachings spread throughout East and Southeast Asia via missionaries
Relocation diffusion throughout the world
Buddhism distribution
Significant presence in Southeast Asia, China, and Japan
Buddhist place of worship
temples (with sloping roofs)
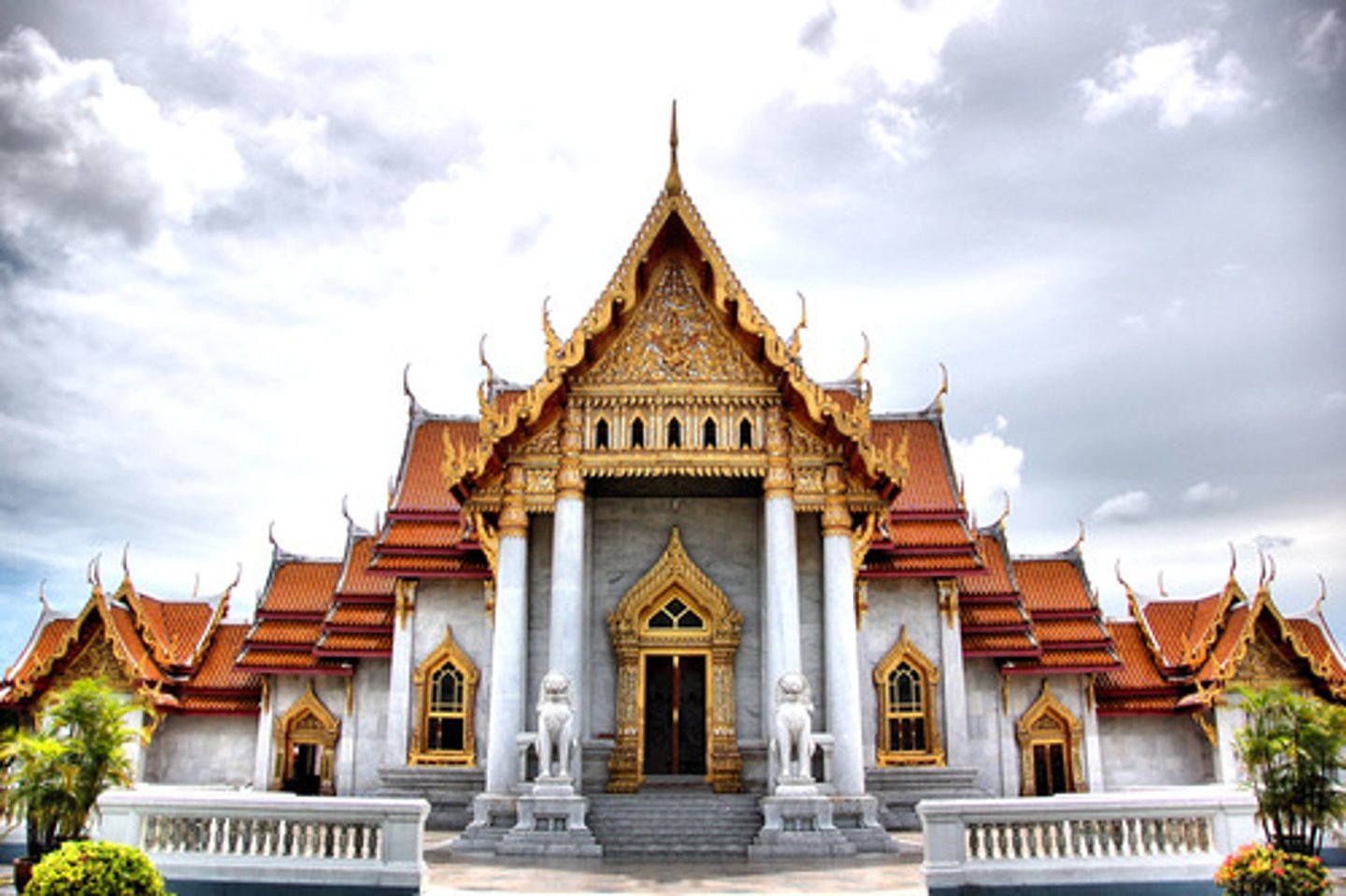

Which religion is the 5th largest with 30 million followers?
Sikhism
Sikhism followers
Sikhs
Sikhism branches
Udasi, Nirmala, Nanakpanthi, Khalsa, Sahajdhari, Namdhari Kuka, Nirankari and Sarvaria
Sikhism sacred text
The Guru Granth Sahib
key ideas of Sikhism
Meditation upon and devotion to the Creator, truthful living, and service to humanity
Sikhism hearth
Punjab, India
Sikhism diffusion
Hierarchical diffusion in Asia via missionaries
Relocation diffusion to North America, Europe, Oceania, and East Africa in more recent times
Sikhism distribution
primarily concentrated in India with significant populations in Canada, USA, and UK
Sikhism place of worship
Gurdwara (unique dome shape)
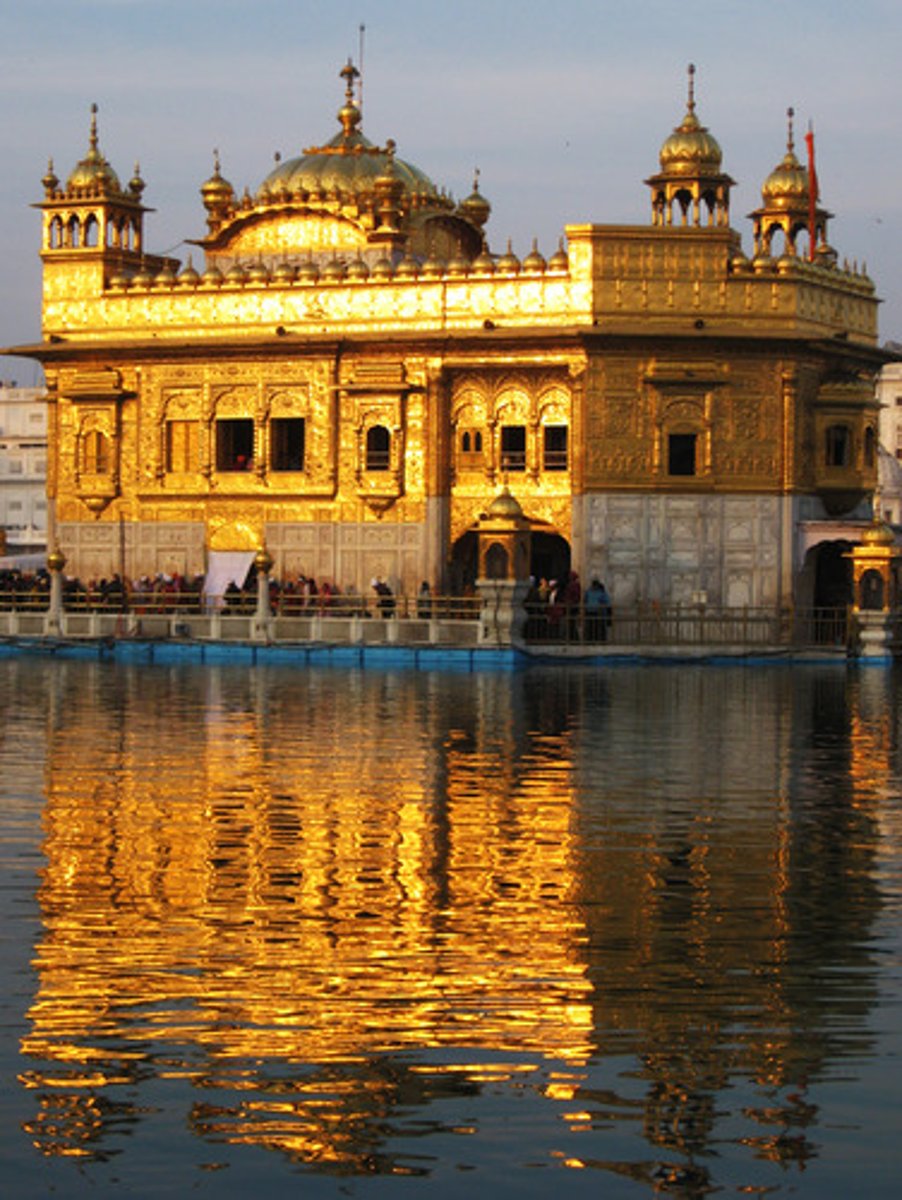

Which religion has 14 million followers?
Judaism
Judaism followers
Jews
branches of Judaism
Orthodox, Conservative, Reformed
sacred text of Judaism
Torah
key ideas of Judaism
There is one God who wants people to do what is just and compassionate
Judaism hearth
Eastern Mediterranean/Southwest Asia (Present-Day Israel)
Judaism diffusion
Relocation diffusion throughout North Africa and Europe forced by Romans beginning in 70 CE
Relocation diffusion to US and other countries largely due to persecution
Judaism distribution
Almost half of this religion’s population lives in Israel
1/3 live in the USA
The other portion is found spread throughout the Middle East, North Africa, and Europe
Jewish place of worship
synagogue (can vary greatly but may have prominent blue and white and/or Star of David)
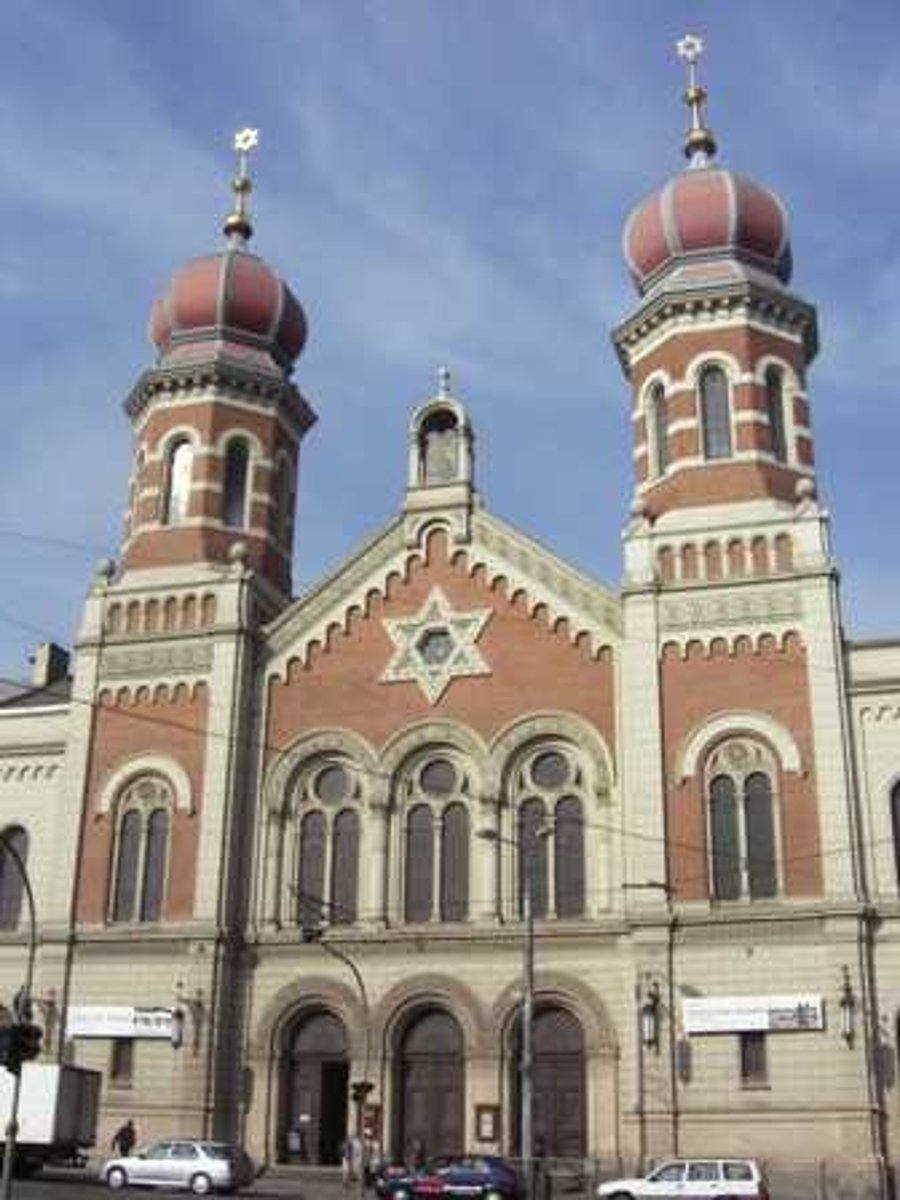

What are Abrahamic religions? Which religions fall under these?
trace origins back to the first 2 sons of Abraham (Isaac and Ishmael)
associated with Jerusalem
Christianity, Islam, Judaism
monotheistic religion(s)
Christianity, Islam, Sikhism, Judaism
polytheistic religion(s)
Hinduism
nontheistic religion(s)
Buddhism
universalizing religions
Christianity, Islam, Buddhism, Sikhism
ethnic religions
Hinduism and Judaism
most widely spoken languages
English, Mandarin, Hindi, Spanish, French, Arabic, Bengali, Russian, Portuguese, Urdu, Indonesian, German, Japanese (13)
examples of language families
Indo-European (3 billion speakers)
Sino-Tibetan (1.3 bil. speakers)
Niger-Congo family (437 mil. speakers)
examples of language branches
Romance (French, Spanish, Italian, Portuguese)
Germanic (English, German, Dutch, Swedish)
Indo-Iranian (Hindi, Farsi, Urdu, Kurdish)
examples of language groups
Afrikaans and Dutch
Proto-Indo-European language (PIE)
Because several language families have similar words, many people believe they must be descended from single common language
Linguists agree that it must have existed, but disagree about when/where it originated and how it diffused because there is evidence to support multiple theories
Nomadic Warrior Theory
aka conquest theory
Early Indo-Europeans were warrior pastoralists (herders); they domesticated animals and went out in search of areas to graze them
Spread to Europe, Middle East, Siberia, South Asia
Sedentary Farmer Theory
Language spread because of expansion of agricultures agricultural surplus led to more trade
Spread from Anatolia (Turkey) to Europe, Siberia, Middle East, South Asia
Why do some languages never diffuse widely?
not establishing colonies outside of country/continent
ex: Mandarin is the 2nd most spoken language, but it never widely spread because China never established colonies outside of Asia
examples of dialects
American vs. British English, Ebonics/AAVE, Southern vs. Boston American English
examples of isoglosses
y'all vs. you guys; soda vs. pop vs. coke
examples of creolized languages
French Creole in Haiti (French + African languages)
Papiamento in West Indies (Spanish + African languages)
Swahili in East/Central Africa (Bantu + Arabic)
Afrikaans in South Africa
List the Linguas Franca.
English, Arabic, Spanish, Swahili, Russian
examples of isolated languages
Korean, Basque, Sumerian
examples of endangered languages
Welsh, Celtic, Māori
examples of extinct languages
Gothic, many indigenous languages
examples of revived languages
Hebrew