Biochemistry Unit 2 Dr.Lee
1/181
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
182 Terms
Carbohydrates
provide the energy to power all biochemical processes that take place inside a cell or organism; break down glucose to provide energy
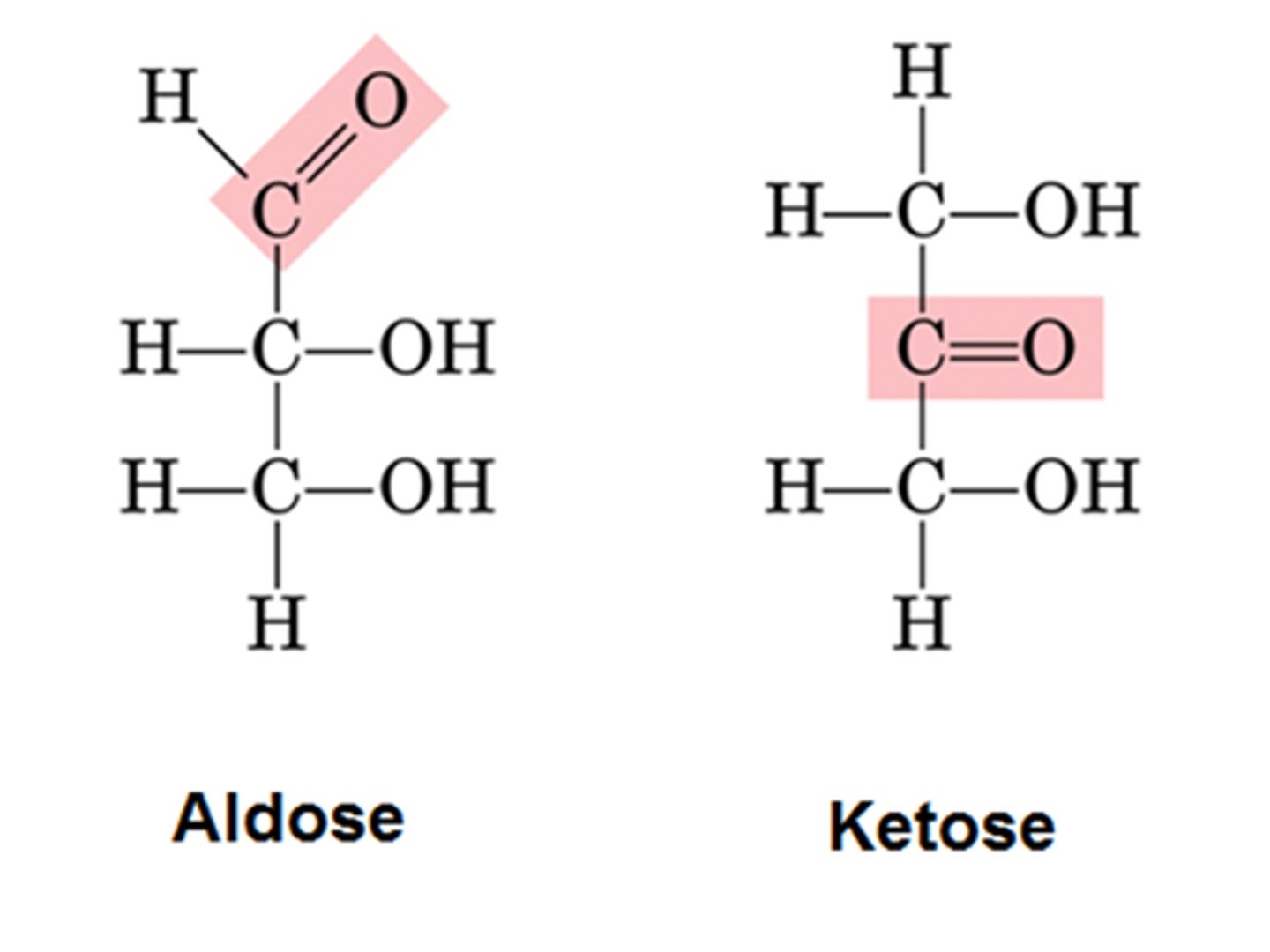
Aldose
aldehyde + sugar
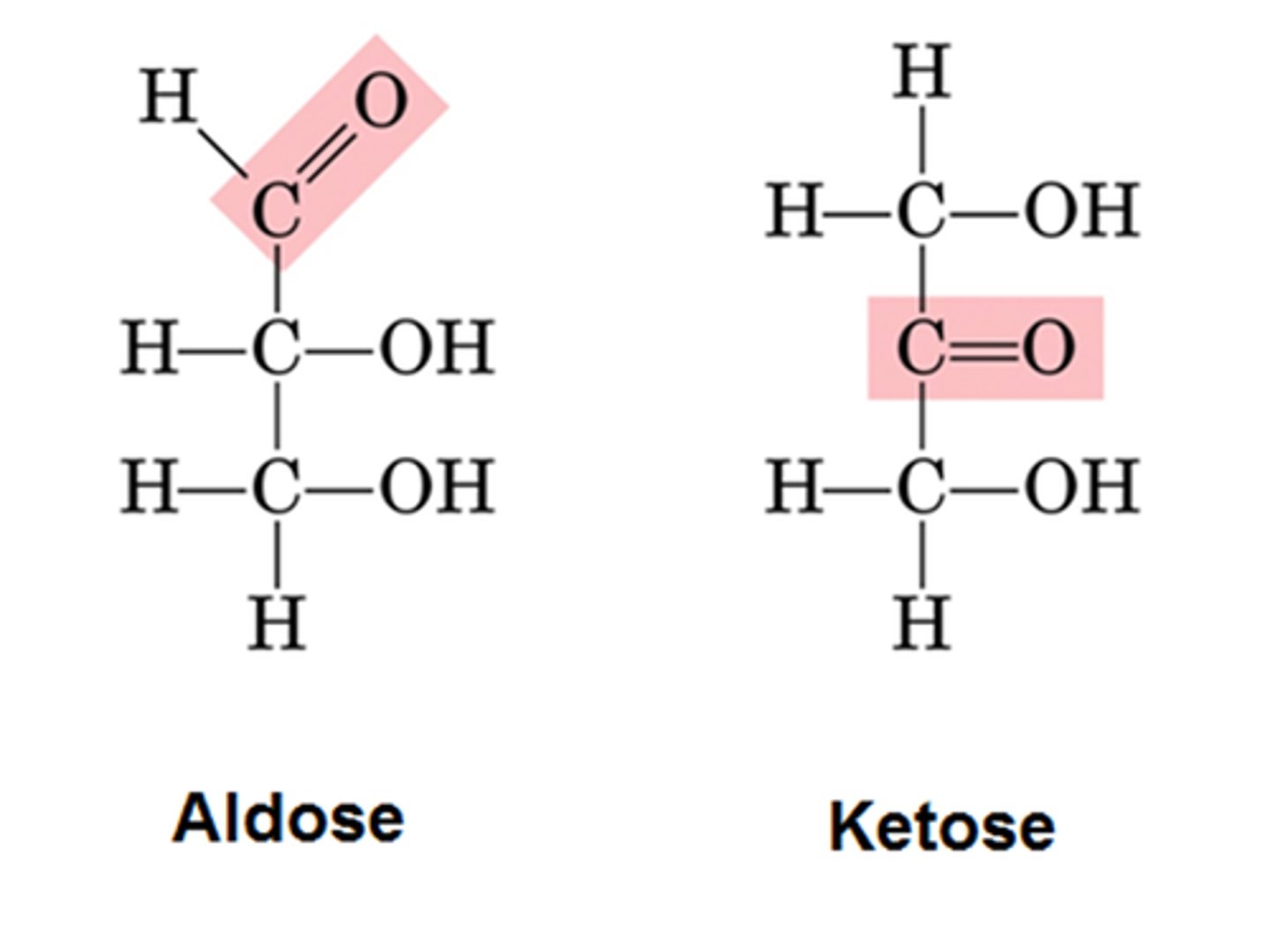
Ketose
ketone + sugar
Complex monnosacharides
are basically polysaccharides-- polymers of covalently linked monosaccharides
Monnosaccharide
are aldehyes or ketones that have two or more hydroxl groups
Carbohydrates can differ in what way?
isomeric forms
Aldehyde + OH
hemiacetal
The open chain form of ribose, glucose, fructose and many other sugars cyclize into what?
Rings
Pre-dominant forms of sugars such as ribose, glucose and fructose in solution are not what?
open chains
Glucose
the form of sugar that circulates in the blood and provides the major source of energy for body tissues. When its level is low, we feel hunger.
Ribose
A five-carbon sugar present in RNA
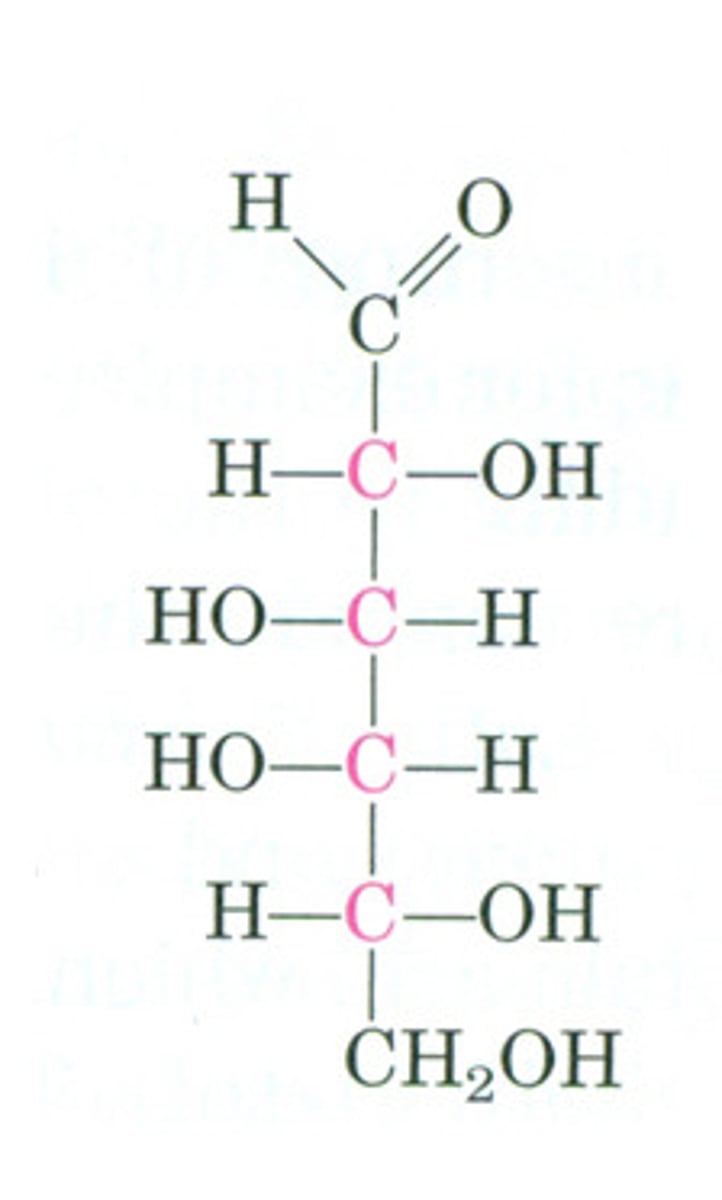
Mannose
C2 epimer of glucose
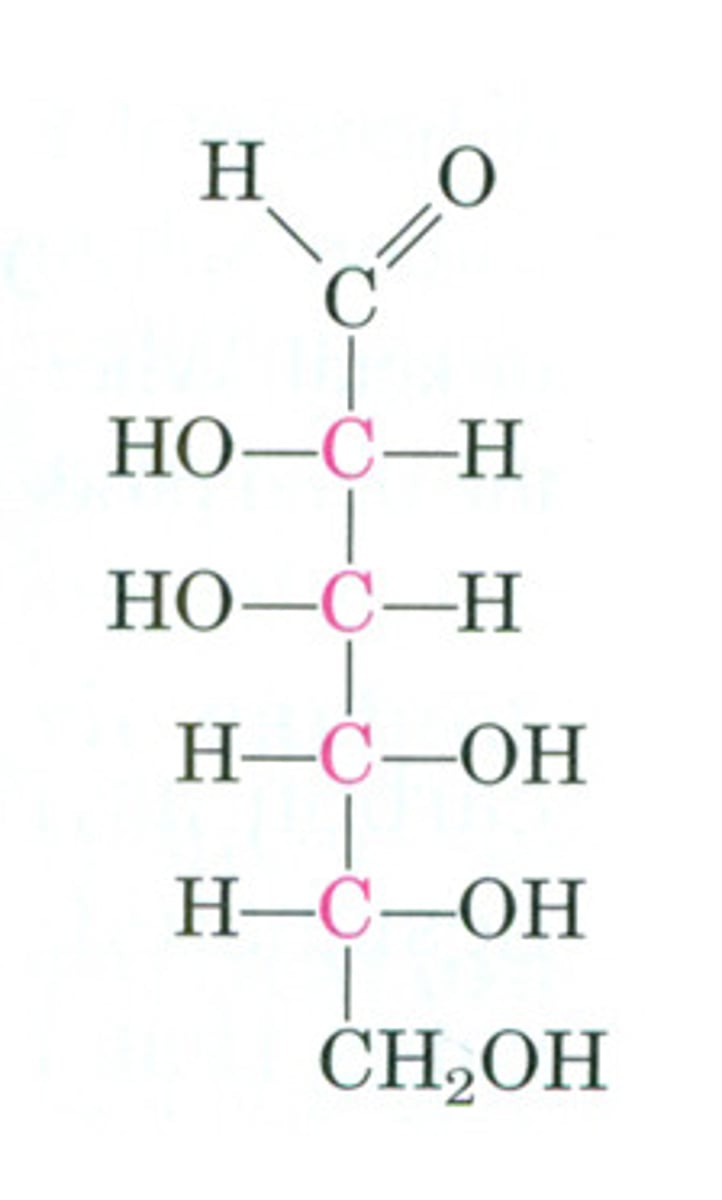
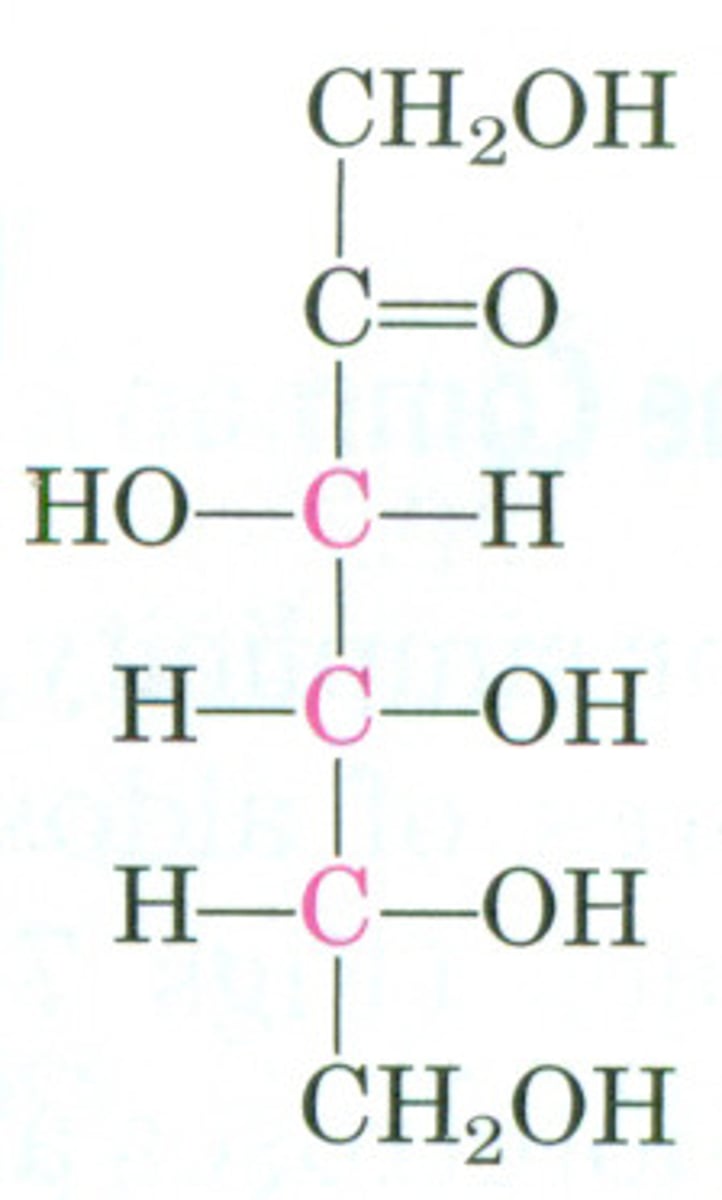
Fructose
a hexose sugar found especially in honey and fruit.
Galactose
milk sugar
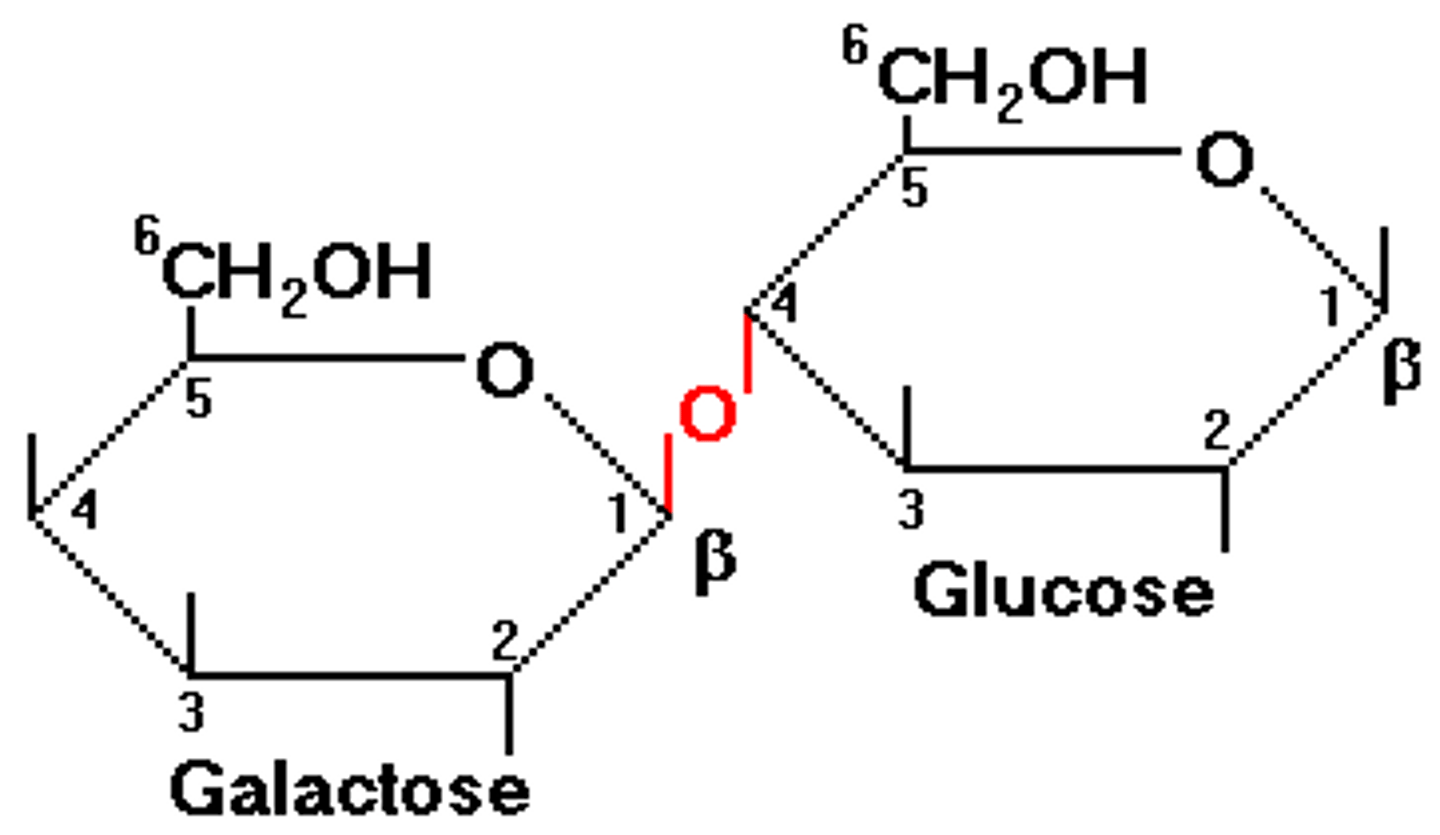
Lactose
glucose + galactose (beta 1,4)
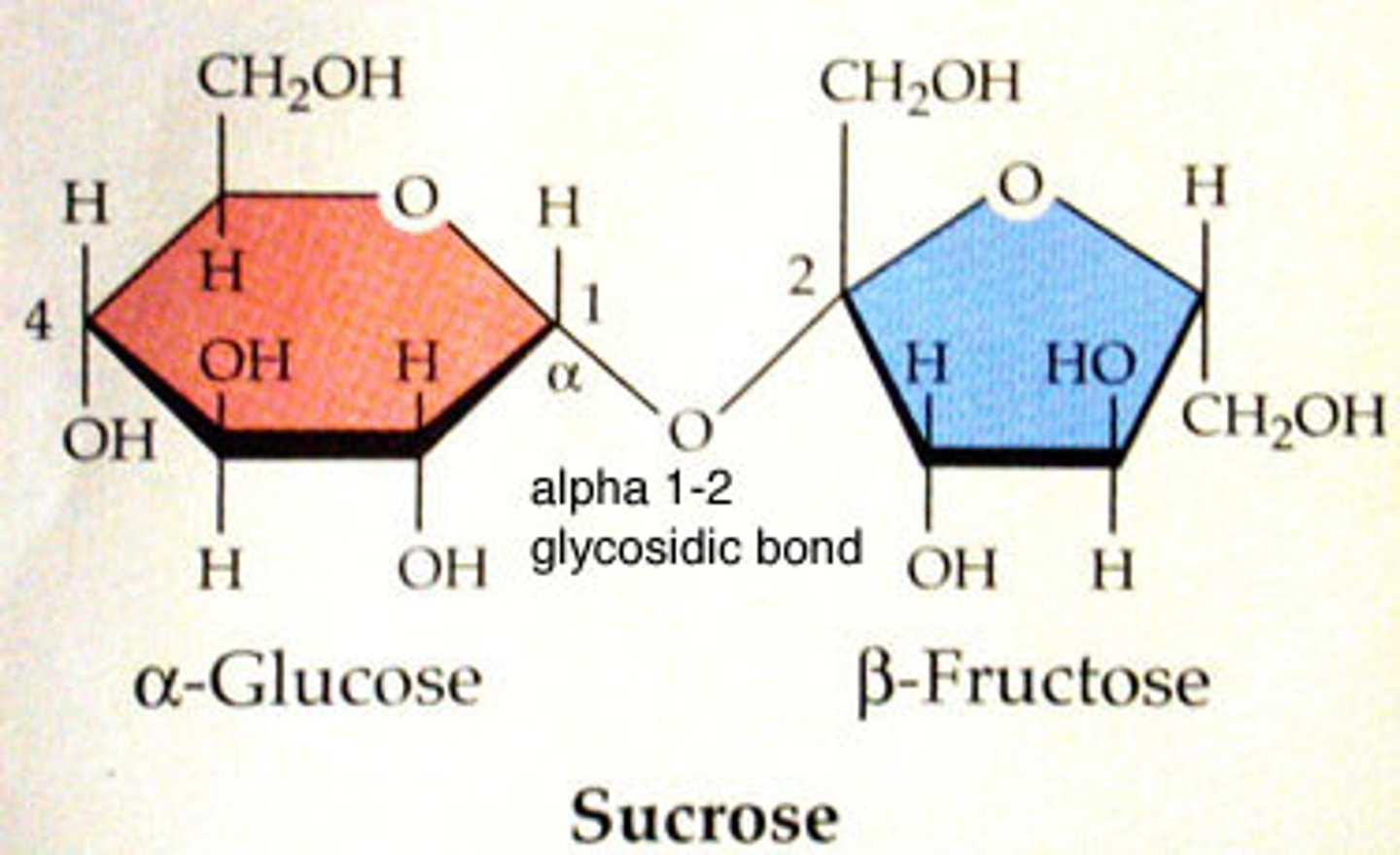
Sucrose
(a)glucose + (b)fructose (alpha 1,2)
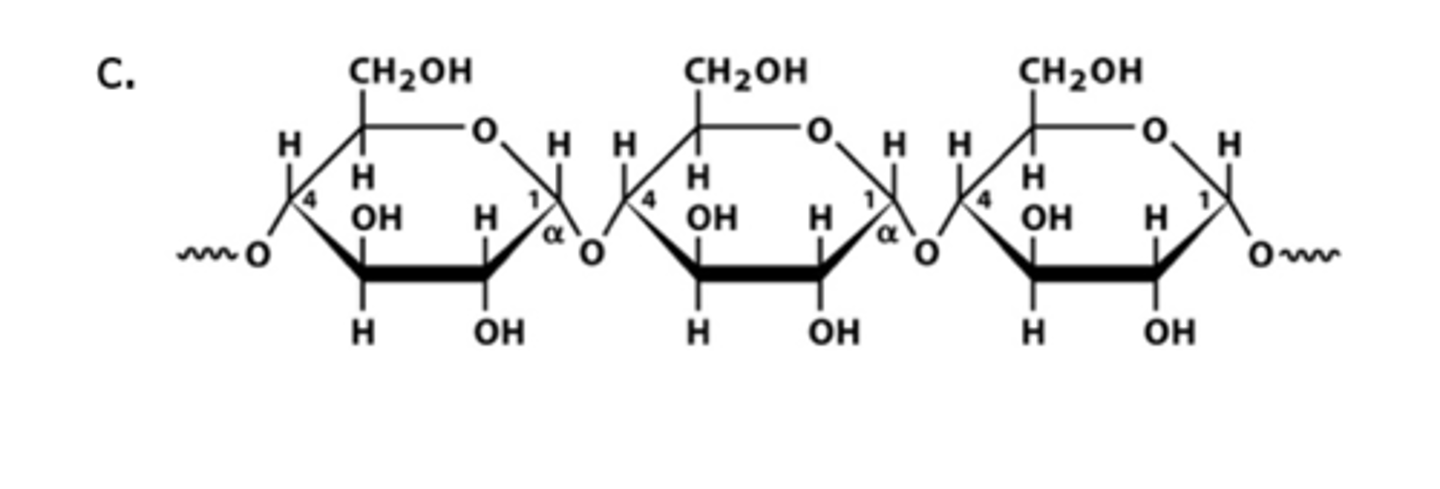
Starch
storage form of glucose in plants; aids the next generation of plants
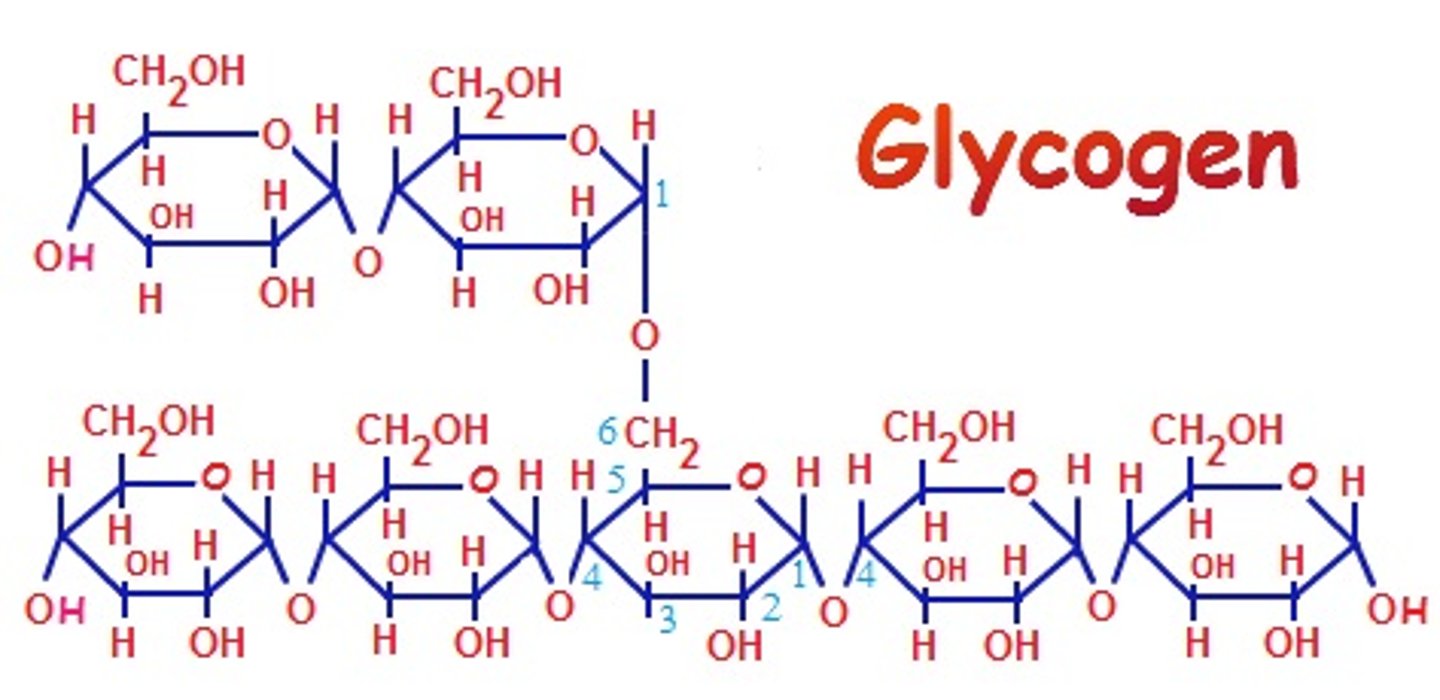
Glyogen
the storage form of glucose in humans and animals, alpha 1,4 and alpha 1-6
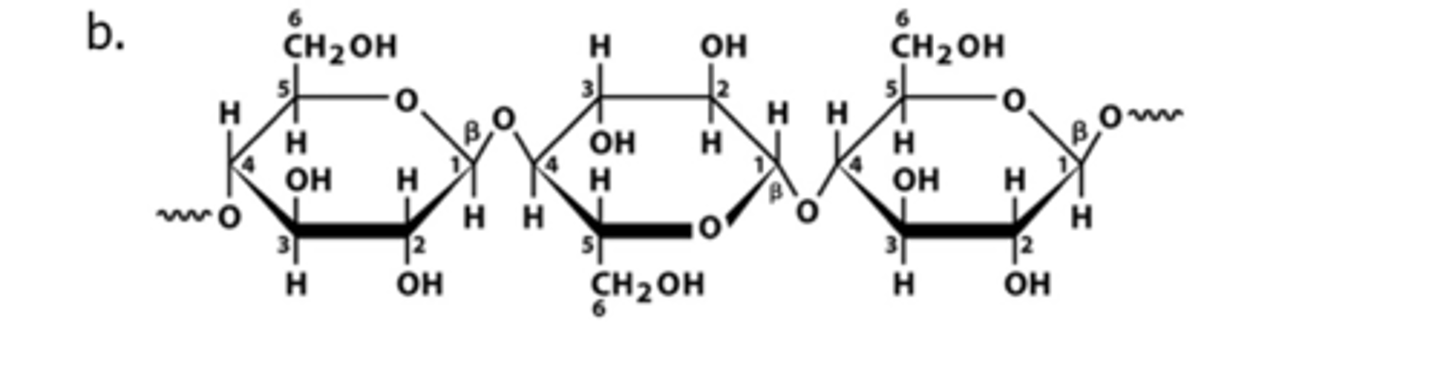
Cellouse
Polysaccharides that provide structural support for plants
Carbohydrates enzyme
alpha-amylase
cellulose enzyme
Cellulate
lactose enzyme
lactase
ATP hydrolysis is
exergonic, spontaneous
Cow can survive by eating only hay, but human can't. Why?
Cows can digest cellulose because of the bacteria in their stomach produces cellulate; humans can't because we don't have that bacteria.
Describe the location and function of the enzyme lactase
Small intestine and its purpose is to breakdown glucose and galactose
How do the products generated by lactase enter intestinal epithelial cells and subsequently enter the blood stream?
Products generated by lactase enter the intestinal epithelial cells by the SGLT1 transporter and enter the bloodstream with the GLUT2 transporter
What happens in the intestines of individuals who are lactose intolerant?
They slowly metabolize galactose and glucose due to deficiency of the enzyme, lactase. If these individuals consume products that contain lactose (milk & cheese); it will cause gastrointestinal problems (major gas and diarrhea), which disturbs the absorption of fats and proteins.
Lactose intolerance can be diagnosed
Lactose Intolerance Test and Hydrogen breath test
Briefly explain catabolism
Catabolism: The breakdown of molecules in your body to obtain energy oxidation; and its products are CO2 and H2O (energetically favorable)
Explain anabolism
The synthesis of compounds in your body using the energy during catabolism reduction and its products are proteins, lips, & nucleic acids (energetically unfavorable)
Explain why The Oxidation of Carbon Fuels Is an Important Source of Cellular Energy
To aid in the formation of ATP
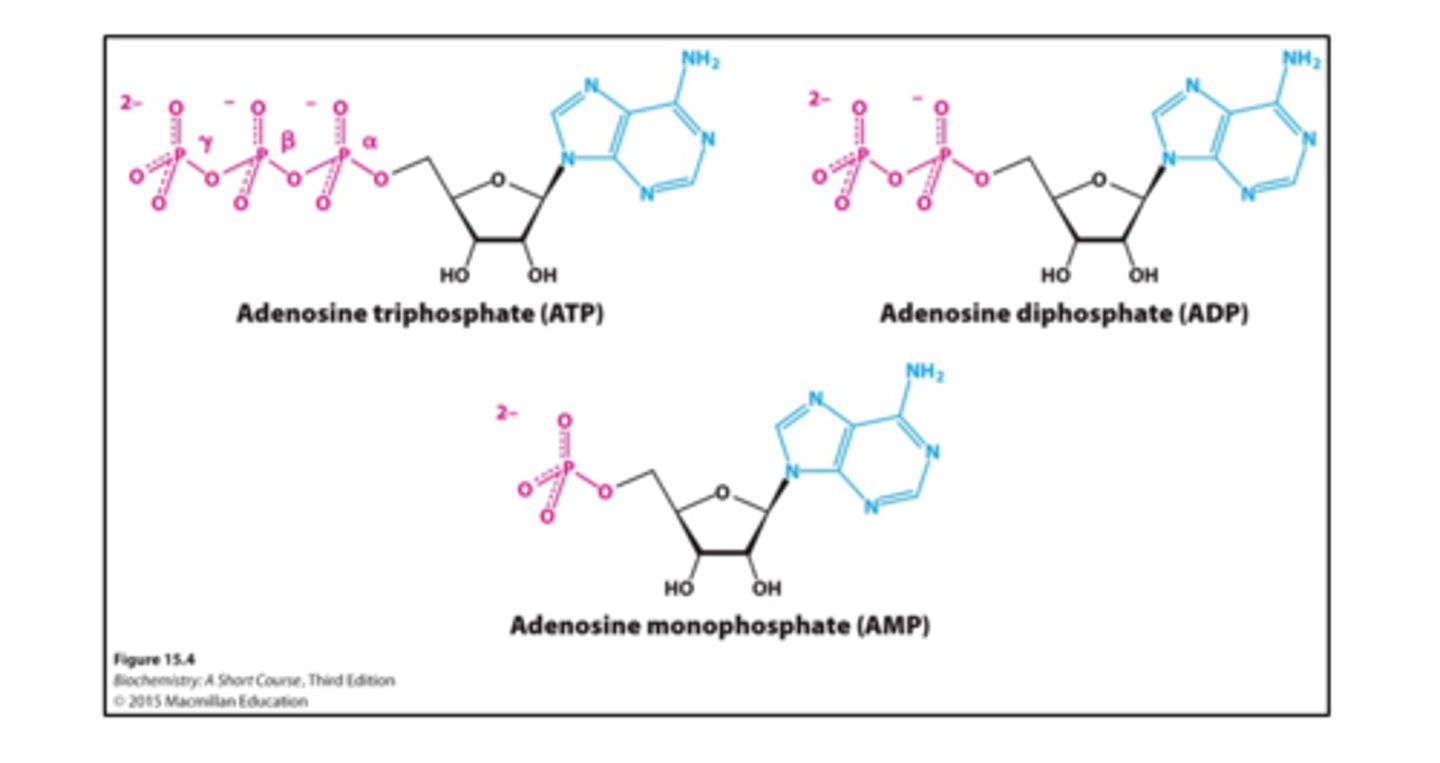
ATP
is the universal energy currency inside most cells
Why does the hydrolysis of ATP have a negative ∆G°’ value? Why doesn’t ATP spontaneously hydrolyze in the cell?
The hydrolysis of ATP has a negative (delta G not) because it gives up/releases the phosphate groups.
ATP doesn’t spontaneously hydrolyze in the cell because it has to overcome the activation energy (Ea) in the cell.
What properties of ATP make it an especially effective phosphoryl-transfer-potential compound?
The phosphate groups of ATP specifically the partial negative oxygens on the phosphate group, which are repelling each other, making the compound less stable
Which of these molecules is least stable because of electrostatic repulsion? How does this help to explain the high phosphoryl-transfer potential of ATP, i.e., the spontaneity of ATP hydrolysis?
The least stable molecule is ATP.
The more unstable they are, the more they want to give up that phosphate group, hence, the higher gibbs free energy & the high phosphoryl-transfer potential of ATP.
How are proteins digested?
enzymatic activity secreted by the pancreas; proteases
proteases convert proteins into amino acids and peptides
Pepsin optimal activity; 1 to 2 pH, very acidic
How are carbs digested?
the action of salivary amylases
how are lipids (fats) digested?
digestion in the stomach; with grinding and mixing in the stomach--converts lipids into emulsion, which is lipid droplets and water
Lactose tolerant blood glucose levels
should increase after drinking a lactose product
lactose intolerant blood glucose levels
should stay the same or decrease after consuming a lactose product, has trouble digesting and absorbing the product
Hydrogen breath tests for lactose tolerant
hydrogen levels should be less due to the enzyme lactase
Hydrogen breath tests for lactose intolerant
production of hydrogen gas increases due to the lack of the enzyme lactase
UDP-glucose
enhances the energy content of a molecule
activated energy rich molecule
glycotransferases
catalyze the formation of glycosidic bonds
glycosidic bond
A glycosidic bond is a covalent bond in which a carbohydrate to the side of Asparagine (N-Linked) or the side chain of serine or threonine ( O-Linked). THINK OF AST
erythroprotein
has oligosaccharides linked with 3 asparagine residues and one serine
AS
proteoglycans
function as structural components and lubricants
Carbohydrates make up a much larger percentage by weight of the proteoglycan compared with simple glycoproteins
mucoprotein or mucins
key component of mucus, serve as lubricants, reduce friction b/t surfaces and trap molecules
Lectins
carbohydrate binding proteins
lectins on one cell recognize and bind to carbohydrates on another cell with multiple weak interactions.
Emulsification
is enhanced with the aid of bile salts, amphipathic molecules, making the triacylglycerols more readily digested
emulsion
a mixture of lipid droplets and water.
Pyranose formation
The open-chain form of glucose cyclizes when the C-5 hydroxyl group attacks carbon atom C-1 of the aldehyde group to form an intramolecular hemiacetal. Two anomeric forms, designated α and β,can result
D-glucose and L-glucose are enantiomers, meaning that their molecular structures are mirror images of each other.
TRUE
Anomeric Carbon
Before becoming cyclic, it is the carbonyl carbon
After becoming cyclic, it is bonded to the OH that determines anomeric form (alpha or beta)
The cyclic forms of carbohydrates
can exist in two forms, α- and β-based on the position of the substituent at the anomeric center.
Carbohydrates Are Attached to Proteins to Form Glycoproteins
True! as 50% of the proteome consists of glycoproteins
Homeostasis.
Maintaining a constant cellular environment requires complex metabolic regulation that coordinates the use of nutrient pools
OIL RIG stands for
oxidation is loss, reduction is gain (of electrons)
Four factors differentiate the stability of the reactants and products:
1. electrostatic repulsion,
2. resonance stabilization,
3. an increase in entropy,
4. stabilization due to hydration.
Energy charge ranges from 0 (all AMP) to 1(all ATP)
TRUE
ATP, ADP and AMP are
Recycled
ATP + ADP + AMP =
Constant
Chylomicron formation
Free fatty acids and monoacylglycerols are absorbed by intestinal epithelial cells.
Triacylglycerols are resynthesized and packaged with other lipids and proteins to form chylomicrons, which are then released into the lymph system
Lack of Glycosylation Can Result in Pathological Conditions
TRUE because of Hurler's disease
Many of the proteins secreted from cells are glycosylated, or modified by the attachment of carbohydrates, including most proteins present in the serum component of blood
True because of ABO blood type
Blood Groups
Are Based on Protein Glycosylation Patterns on the surfaces of red blood cells
The results of carbohydrate digestion, primarily glucose, galactose, and fructose, are transported into the intestinal cells by specific transport proteins
The carbohydrates also exit the cell with the assistance of transport proteins
SGLT1 and GLUT2 transporters
as carbon becomes oxidized throughout glycolysis or b-oxidation (basically carbon loses electrons by associating with oxygen –energy is released)
The energy is captured to make ATP
An oxidation-reduction reaction
is a reaction in which electrons are transferred.
Why does glucose need a transporter to cross the cell membrane?
It is a large, hydrophilic, polar molecule
GLUT1 location and function
location: all mammalian tissues
function: basal glucose uptake
GLUT2 location and function
location: liver & pancreatic B cells
function: in pancreas, plays role in insulin regulation. in liver, removes excess glucose from blood.
GLUT3 location and function
location: all mammalian tissues
function: basal glucose uptake
GLUT4 location and function
location: muscle and fat cells
function: transport of glucose into muscle + fat, regulated by insulin
GLUT5 location and function
location: small intestine
function: primarily a fructose transporter
Which glucose transporter (GLUT) is responsible for transport of glucose into muscle and fat cells?
GLUT4
What molecule regulates transport of GLUT protein to the cell surface in muscle and fat cells?
insulin
What is the main role of glycolysis?
to generate ATP
WHY are steps 1, 3, and 10 energetically favorable?
irreversible reactions
steps 1 +3 : ATP hydrolysis
step 10: phosphoenolpyruvate has a higher phosphoryl transfer potential than ATP
Regulated enzymes often catalyze __ reactions.
irreversible
function of allosteric enzymes
regulate the flux of biochemicals through metabolic pathways
allosteric enzymes depend on alterations in ___ structure
quarternary
Which form is active form?
R form
Which form is less active form?
T form
When [ATP] is low, describe kM.
How does this effect glycolysis?
low Km.
activates glycolysis
When [ATP] is high, describe kM.
How does this effect glycolysis?
high Km
inhibits glycolysis
What is the glycolysis pathway regulated by?
energy charge
High energy charge ____ glycolysis
inhibits
bc ATP generating pathway is high
Low energy charge ___ glycolysis
stimulates
bc ATP generating pathway is low
How many moles of ATP, NADH, and pyruvate are formed from 1 mole of glucose in glycolysis?
ATP: 2
NADH: 2
pyruvate: 2
When ATP is needed, glycolysis is __.
activated
When ATP levels are sufficient, glycolysis is __.
inhibited
Hexokinase is inhibited by
glucose-6-phosphate
PFK-1 is inhibited by
ATP and citrate
Pyruvate kinase is inhibited by
ATP
Why is oxidation of the aldehyde carbon energetically favorable?
Oxygen is very electronegative. Energy is released when it goes into oxidized form
Referring to Figure 16.3, explain in your own words how glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate dehydrogenase overcomes the energetically unfavorable process of phosphorylation after oxidation.
study
The enzyme aldolase catalyzes the following reaction in the glycolytic pathway:
The ΔG°′ for the reaction is +23.8 kJ mol−1, whereas the ΔG in the cell is −1.3 kJ mol−1. Explain how the reaction can be endergonic under standard conditions and exergonic under intracellular conditions.
Under the standard conditions the reaction is endergonic because it doesn't account for the concentrations of reactants and products. With concentrations accounted for in intracellular conditions, the reaction can be exergonic if the concentration of reactants is greater than concentration of products
Substrate-Level Phosphorylation
The enzyme-catalyzed formation of ATP by direct transfer of a phosphate group to ADP from an intermediate substrate in catabolism.
What is the phosphate donor in substrate level phosphorylation?
a kinase substrate with high phosphoryl transfer potential