Grade 9 Science exam
1/150
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
151 Terms
observation:
Factual, unbiased characteristic about an object or event that is collected with the senses or with simple experiments and measurements.
accuracy
how close a measurement is to the accepted value
precision
how close a series of measurements are to eachother
controlled variable
Something that stays the same during the experiment to keep the results comparable.
Ex: duration of experiment, location, species
Inference:
Inferences are conclusions or “guesses” that are made based on your observations and prior knowledge.
Is it inference or observation?The water is filled to the 250ml mark with water
observation example
Is it inference or observation? The caterpillar did not eat the moth because it is not carnivore
Inference example
Quantitative observations:
measurable or countable, usually involves numbers
Qualitative observations
describable, not measurable, usually involves adjectives
Ex: The triple beam balance has a metallic, reflective surface and a sliding weight system.
Carbon cycle:
The element carbon is found in seawater, the atmosphere, roots
Carbon moves from different parts of the cycle
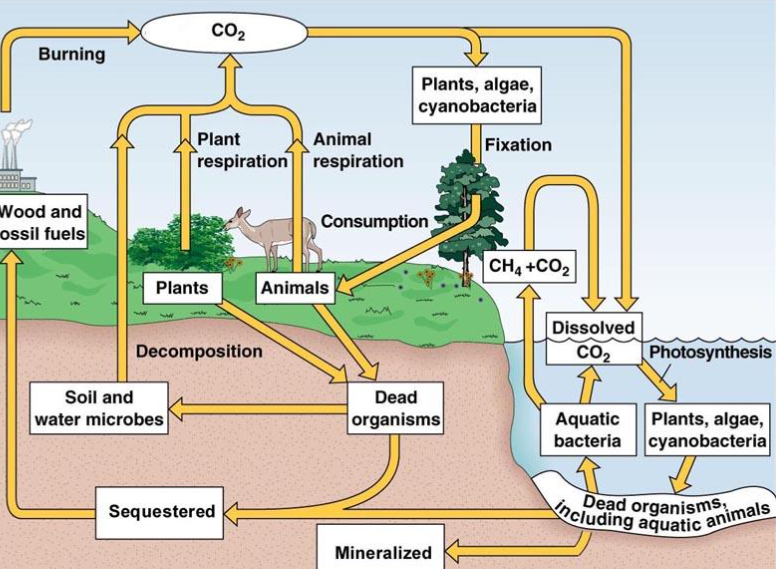
Fixtion (carbon cycle)
photosynthesis by land: taking CO2 into glucose
Consumption (carbon cycle):
Most organisms cannot use CO2 directly
They get it by eating other organisms
Biological molecules are broken down and reused
Cellular respiration (breaking down glucose realeases CO2
Aquatic Ecosystem (carbon cycle) :
CO2 dissolves in water, allowing aquatic producers to photosynthesize
Humain impacts on CO2 (carbon cycle):
Burning fossil fuels (realeasing CO2)
Deforisation
Acid accelerates CO2 realease from limestone ( when acid reacts with limestone it realeases CO2)
CO2 levels are higher over the years
Sequestration (carbon cycle):
when carbon from dead organisms trapped underground as fossil fuels
Decomposition ( carbon cycle):
bacteria, fungi breaks down dead plants and animals and returns carbon back into the atmosphere
Minerilization ( carbon cycle):
Dead organisms are transfferered into mineral form fossil form
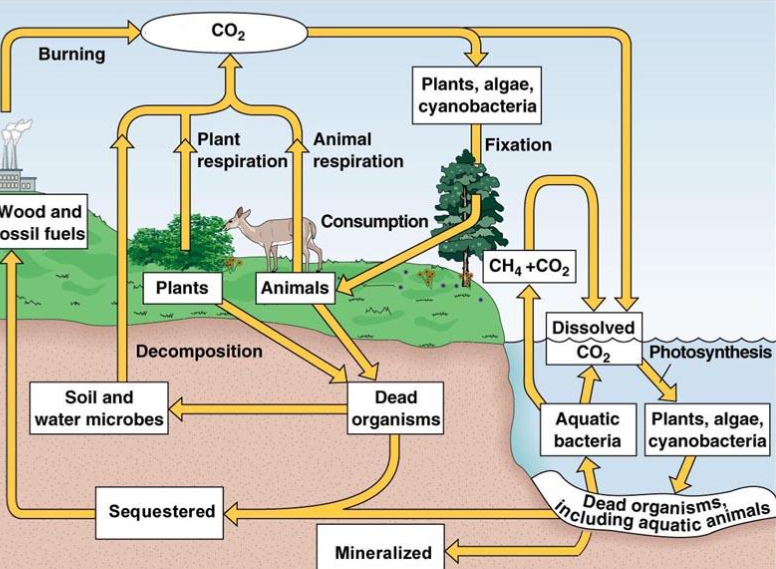
Aquatic carbon cycle:
CO2 dissolves in water (dissoloution)
Biotic Elements in an Ecosystem
plants (trees, grass and seaweed)
animals (frogs, foxes, birds wolves etc.)
Abiotic Elements of an ecosystem
sunlight water soil wind temperature
Community
(ecology) a group of organisms living the same region and interacting with each other
Earths Four Major Spheres
lithosphere (land), Hydrosphere (water), Biosphere (living things) and atmosphere (air)
Lithosphere
contains all the cold hard solid land of the planets surface and the semi solid land underneath the crust
Hydrosphere
contains all the solid liquid and gaseous water of the planet
ranges from 10km to 29km below earths surface
ninety seven percent of the earths water is salty
Biosphere
contains all the planets living things
includes all the microorganisms plants and animals
living things form ecological communities based on the physical surrounding of an area
Atmosphere
contain all the air of the earth
extends 1m below the earths surface and 10,000 km above
creates the weather on the planet
Ecosytems
All the interacting parts of a biological community and it’s environment
carbon+water(+light energy) = glucose and oxygen
photosynthesis
gluscose+oxygen = carbon dioxide+water (+energy)
cellular respiration
Herbivore
animal that wats plants or other producers
Carnivore
animal that eats other animals
Omnivore
animal that eats both plants and animals
scavenger
animal that feeds on the remains of another ecosystem ( eats dead animals)
food web
a community of organisms where there are several interrelated food chains
why is it important for a species to be a part of a complex food web?
a complex food web is thought to be more stable
Primary Producers
organisms that make their own food by sunlight or chemical energy from deep sea vents
Primary Consumers
animals that eat primary producers; also known as herbivores
Secondary Consumers
eat primary consumers; can be carnivores or omnivores
Tertiary Consumers
eat secondary consumers; carnivores
Decomposers
organisms that break down wastes and dead organisms and return raw materials to the environment
After an organism dies...
it is eventually eaten by detrivores and broken down bt decompsers and the exchange of energy continues
Each trophic level has __ % less energy
10%
Most food chain have _____
no more than four or five links
Abiotic features such as ___, ___, ___ can affect an organisms ability to survive
temperature, light and soil
ecosystems require
temperature, light and soil to survive
Biotic factors such as ______ for food light space and mates can affect an organisms ability to survive
competition
Why is Death necessary in Nature?
1. population can grow too big and create compition
2. dead organisms create better soil for plants which creates new life and better food
Biodiversity
refers to the variety of living species found in an ecosystem
more energy and nutrients =
greater biodiversity and population
sustainability
refers to an ecosystems ability to support life and maintain resources for future generations
greater the biodiversity
- greater the oppertunity to find food
- the more stable an ecosystem is
-greater is the oppertunity to find new forms of food + medicine
am autotroph
makes its own food; primary producer
a heterotroph
eats other organisms
Sustainible ecoststen
An ecosystem that is capable of withstanding pressure and giving support to a variety of organisms
Biotic interactions:
Symbiosis:
Any interaction between 2 different species. Ex: bee gets nectar
Predation:
when organism consumes another for food.
The one that is consumed is called prey
the one that eats is called predator
Competition:
Competition between something : ressources…. at the same location and time
Ex: two trees and sunlight.dandelions and grass
Dominant species:
Species that are abudance and has the most total mass of any living organism (biomass)
Removal can cause decrease biodiversity
Keystone species:
Equally important as dominant species
Can affect the population numbers and the health of an ecosystem
Not abundant (large amount)
Plants or animals. Ex: sea otter
Ecosystem engineer:
a species that causes such dramatic change to landscapes that it creates a new ecosystem
sucession in ecosystem:
series of changes in an ecosystem that ocurs over time following a disturbance
What does a food chain show
shows a single path of energy flow, also how different plants and animals in an ecosystem are connected through feeding relationships.
What do the arrows in the food chain/ web show
it shows energy flow
What is prey
gets hunted
Parasite
lives of host for nutrients
Scanvanger
eats dead animals
Photosynthesis:
Carbon dioxide, hydrogen, oxygen
Happens in chloroplast using chlorophyll
Convertts sunlight into glucose
Stores energy as starch
captive breeding
the breeding of rare or endangered wildlife in a controlled setting to increase the population size (they are trying to bring back a specie sizespecially when it is endangered or close to extinction.)
like zoos
How does monoculture farming affect energy flow?
Monoculture disrupts natural energy flow by reducing biodiversity and relying heavily on artificial energy inputs.
How does agriculture impact the water cycle?
Agriculture alters the water cycle through irrigation, runoff, and pollution of water sources with fertilizers and pesticides.
How does agriculture affect the carbon cycle?
Agriculture increases carbon emissions through fossil fuel use, deforestation, and soil disturbance.
What is monoculture farming?
Monoculture farming is the practice of growing a single crop species over a large area, often repeatedly each season.
What is a watershed?
A watershed collects rain and melted snow and sends it to one main body of water.
What is a biome?
A biome is a large area of the Earth with a certain climate, plants, and animals that are adapted to that environment.
water cycle:
The water cycle is the way water moves through the Earth and atmosphere over and over again.
What is an invasive specie
An invasive species is an organism that is not native to the ecosystem it is found in.
Invasive species threaten native organisms as they compete for resources and often spread aggressively due to the lack of predators
What is sublimation in water cycle?
Ice or snow turns straight into vapor, no liquid change
Condensation in water cycle:
Water vapor turns directly into clouds
Deposition in water cycle:
Opposite of sublimation
Water vapor turns into snow or ice
What is runoff in the water cycle:
Water flows over land into rivers, lakes
What is collection in the water cycle:
Water gathers in oceans, lakes, rivers
What is innfiltiration in water cycle?
Water soaks into the ground
What is precolation in the water cycle?
water moves deeper underground
What is plant uptake in water cycle?
roots take in water from the soil
Cellular respiration
Occurs in the Mitochondria
Converts glucose → ATP energy
realeases stored energy
Abotic CO2:
CO2 in the atmosphere
CO2 in oceans
Carbon in the Earth’s crust
Ways to stop climate change:
Use solar, wind energy, instead of burning gas and coal
Plant trees, protect forests
Use less gas
Save water and energy
Coverments can make laws to protect Earth and people
Monocultural Farming Pros:
Few resources required, low costs
more efficient with machinery
Monocultural Farming cons:
Higher risks of pests or diseases
Depletes soil nutrition faster
Reduces bioderversity, leading to decline of benefitial insects, esp pollinators
5 major biomes:
Grassland, Aquatic, forests, desert, tundra
Which watershed is RHSS located in?
Along the border of the Rouge River watershed and the Don river watershed
What is climate change?
Climate change is the long term shift in temperatures and weather paterns
occurs naturally but increasing by human activities
trap heat in atmosphere by holding the sun’s warmth
ex: CO2, methane, nitrous oxide, ozone
meaning the earth’s getting hotter, weather changes, and storms and droughts are more common
Alternatives of Monocultural farming:
Polyculture:
Grows multiple crop species together
Promotes biodiversity, improves resilence and reduces pest outbreaks
Cover cropping: crops that are grown to shade and protect soil, not to be harvesred
Prevents soil erosian
Ehance soil growth
Transpiration in the water cycle:
Plants realease water vapor into air
Atom
the basic (and smallest) unit of a chemical element. Made up of three parts, proton, electron, neutron.
Chemical Change
usually irreversible chemical reaction involving the rearrangement of the atoms of one or more substances and a change in their chemical properties or composition, resulting in the formation of at least one new substance. The formation of rust on iron is a chemical change.
Density
the mass of stuff that is packed into a certain space of stuff. Density is mass per unit volume.
Formula: D= M/V
Isotope
2 or more forms of an element that have the same number of protons but a different number of neutrons. Each isotope has a unique mass number.
Ion
a charged atom that has either gained or lost an electron to become fulfilled.use "-ide" for simple negative ions, not positive ones
Ide for nonmetal
Lithum ion for metal
Ionic bond
a chemical bond in which one atom loses an electron to form a positive ion and the other atom gains an electron to form a negative ion.
Ionic Compound
a compound made of oppositely charged ions. Formed between metal and non-metal elements
Isotope
2 or more forms of an element that have the same number of protons but a different number of neutrons. Has unique mass number.