The cell chapter 7
1/31
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
32 Terms
What are the three principles of the cell theory?
1. All living organisms are composed of one or more cells
2. Cells are the basic unit of structure and organization of all living organisms
3. Cells arise only from previously existing cells, with cells passing copies of their genetic material on to their daughter cells
Why is "the cell theory" a theory and not "the cell hypothesis"?
The cell theory is based on facts and observations.
Why aren't viruses considered to be alive?
They do not meet the standards of what biologists consider to be living organisms.
What is the difference between the cell membrane, cytoplasm, and organelles?
1) cell membrane: the membrane surrounding the cytoplasm of a cell.
2) cytoplasm: the fluid inside the cell.
3) organelles: the discrete structures inside the cell.
Geometrically, why are cells so small? Physiologically, why are cells so small?
1) As a cell decreases in size, the surface and volume ratio increases.
2) The smaller the cell, the more efficient the cell can diffuse (the more it can receive the nutrients it needs)
List four differences between a prokaryotic and a eukaryotic cell. Nucleus, shape of DNA, Organelles. Transcription and Translation?
Prokaryotic:
a) no nucleus
b) circular DNA
c) no membrane-bound organelles
d) begins at the same time
Eukaryotic:
a) has a nucleus
b) the DNA is linear
c) many membrane-bound organelles
d) one at a time
Be able to identify: nuclear envelope, nucleolus, nuclear pore, and where the chromatin is.
nuclear envelope: membrane bound nuclear pore
nucleus: dark core
chromatin, middle contains chromosomes
What is the function of the nucleolus?
Produces the ribosomes for the cell.
Where is the chromatin in the nucleus?
In the middle. Is the DNA. Chromosomes
What is a gene? What does it do?
Molecular unit of heredity. Specify the functions we need in order to survive, pass genetic traits to offspring, biochemical processes.
Describe the journey from DNA to protein. Include the following in this order: DNA, gene, mRNA, nuclear pore, Rough Endoplasmic Reticulum, ribosome, protein, transport vesicle, cis-face of the Golgi Body, trans-face of the Golgi Body, lysosome
DNA > Protein DNA > Gene > mRNA Travels outside the > nuclear pore through the > rough ER to a > ribosome that synthesizes the protein through translation > then leaves through transport vesicle > go to CIS face of the golgi body > creates lysosomes
What is the function of the rough ER?
Synthesizes Proteins
What is the function of the smooth ER?
Synthesizes lipids, steroids, metabolizes carbohydrates. No ribosomes. Detoxidies,
If you look at an animal cell was predominately made of smooth ER, what organ did that cell come from?
Liver
What are the functions of the Golgi Body?
Modifies, sorts, and packages molecules for cell secretion. "exocytosis" creation of lysosomes.
What happens at the cis-face of the Gody Body? Trans-face?
Cis recieve vesicles from ER."recieving" Trans "shipping"
What does a lysosome look like?
little black dots in a cell
What functions does a lysosome have?
Digestion of food (phagocytosis), recycle cell materials (autophagy), programmed cell death.
What organelle ensures that you don't have webbed feet?
lysosome
What does a vacuole derive from?
ER/ golgi
What are the functions of a vacuole in a plant? In an animal?
plant: storage of proteins in seeds, disposal site of harmful molecules, colors
animal: expel excess water, contractile vacuoles
What organelle is responsible for giving flowers their color?
vacuole
How many membranes does a mitochondrion have? Why?
double membrane because it makes its own ribosomes and proteins
Why do mitochondria have their own DNA? What can they do with it that most other organelles can't?
So that they can replicate like bacteria through fission. Make ribosomes and some proteins.
What are the functions of the mitochondrion?
site of cellular respiration energy transformer
The structure of the cytoskeleton is made up of what?
interconnected microtubes
What are three functions of the cytoskeleton in various cells?
structural support, change in cell shape, cell movement
How many membranes does a chloroplast have? Why?
2, has its own DNA
Be able to identify from a picture: stroma, grana, thykaloid, inner membrane, outermembrane.
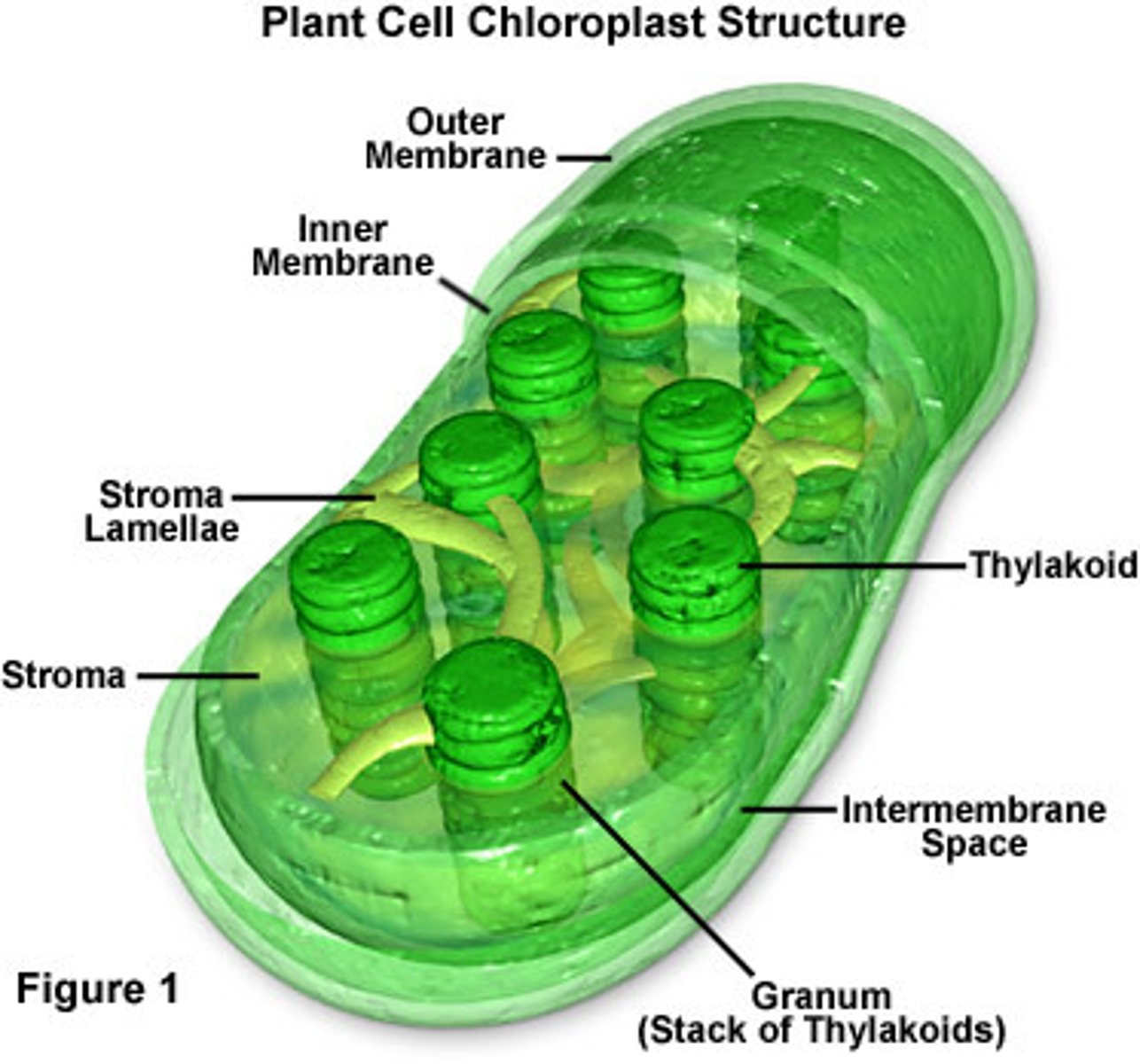
Chlorophyll are attached to which part of the chloroplast?
thykaloid
What is the function of the chloroplast?
the "host" of photosynthesis
List four differences between an animal cell and a plant cell.
plant: cell wall, cytoskeleton, chloroplast, large ventral vacuole
plant cells are rectangular
animal: cell membrane only, rounded cells