125 eyes ears mouth tongue cranial nerves
1/91
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
92 Terms
disease of eyes
screen time, sun/UV rays and wildfire smoke and pollution -71% of canadians have had eye symptoms in past two years
common problems w/ eyes
vision changes, itchy eyes, dry eyes, infection, glaucoma, cataracts
eyes general survey
overall impression: eyebrow placement, lashes, eye color -skin: colour, rashes, skin around eye, oozing -anatomy: as expected, symmetry, movement symmetrical -movement symmetrical, behaviour expected
eyes symptom history
ask about concern -LATERSNAPS - know whats normal vs not normal
eye health history
visual difficulty (acuity, blurring, blind spots) -acute or slow progressive problem? -refraction errors -pain -photophobia (light sensitivity) -strabismus -diplopia -redness, discharge -meds -chronic illness -surgical history -allergies -glasses/contacts -self care -eye protection -resources
refraction errors
myopia (near sightedness), hyperopia, presbyopia, astigmatism
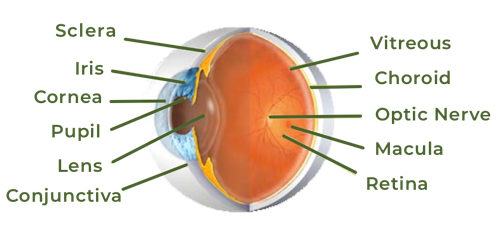
physical assessment eyes
inspection and palpation -need to know and recognize anatomy -brows and lashes
conjunctiva
clear, some small blood vessels -tissues should be pink and well vascularized
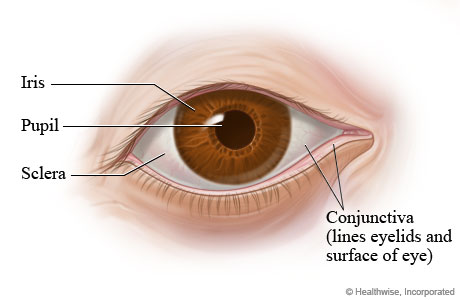
sclera
white, small minor vessels
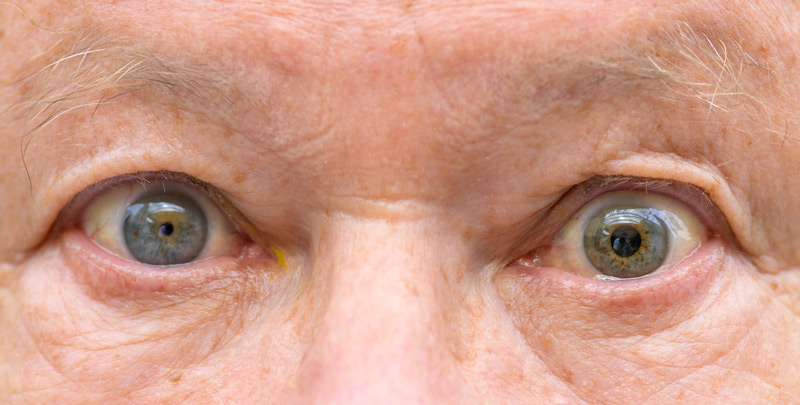
anisocoria
unequal pupil size, harmless if genetic, bad if after trauma
miosis
small or ocnstricted pupil, eyelids asymmetrical, indicates trauma
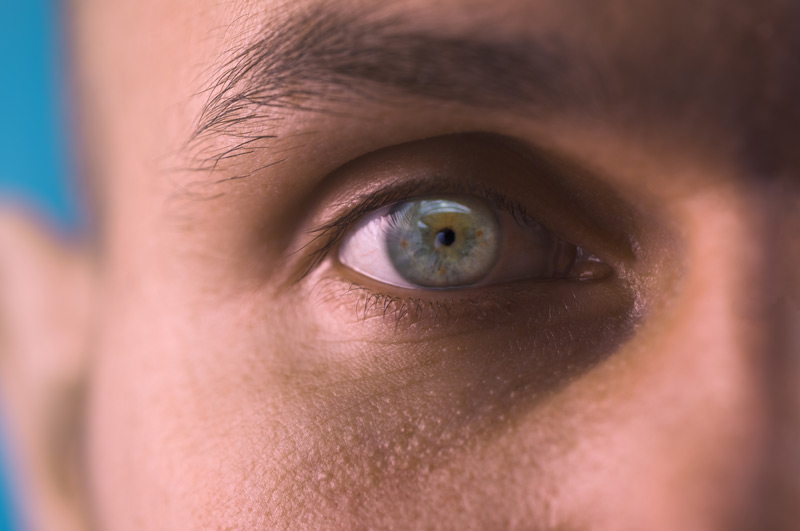

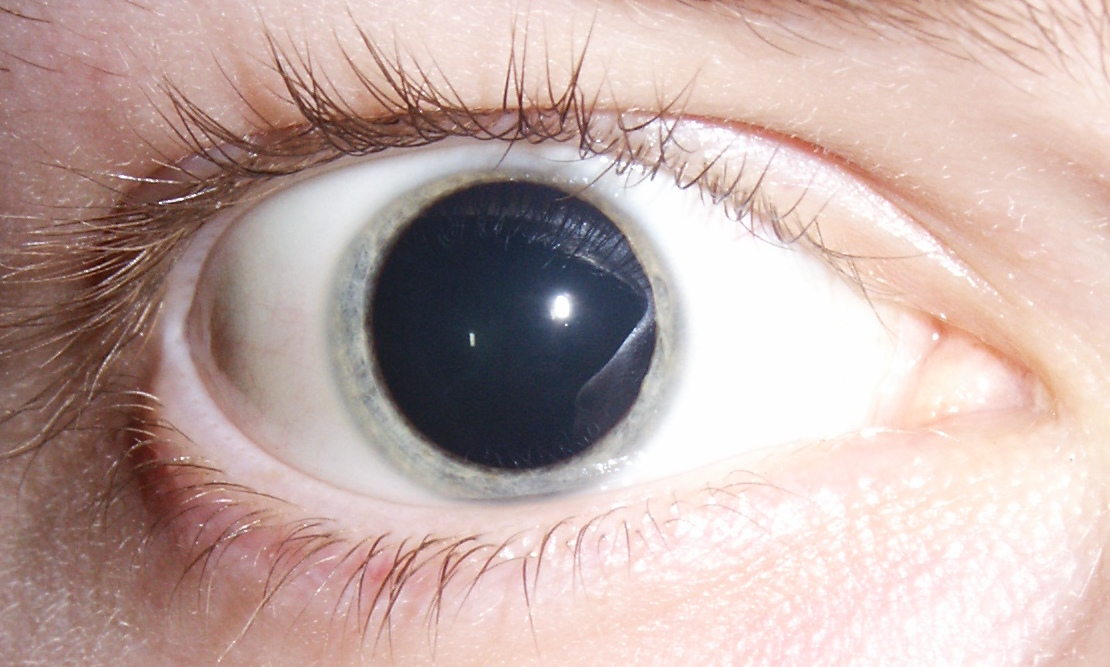
mydriasis
dilated pupils, can happen after eyedrops, but can indicate brain injury
arcu senalis
older adults more common, discoloration around cornea, cholesterol deposits, concerning in younger patients
pupillary light response
respond symmetrically and as expected, direct and consenual response, can indicate normal anatomy and neurological response -also done on newborns
visual acuity
eyes ability to accommodate to see far and near
test of macular fx
macula fives ride to majority of optic nerve fibers
snellens test
distance visual acuity -distance from chart 20 ft away / distance that someone with expected vision would stand from the chart to read that line -20/20 is normal -legal blindness 20/200
jaegar test
near vision -14 inches from eye -read to smallest letter
extraocular muscles and movements
see eys respond to symmetric manner -cardinal directions -corneal reflection -cover test
cover test
examiner covers eye and looks for movement and then uncovers eye and looks for movement
strabismus
altered extra ocular movement -generally same eye will cause problem -unilateral changes -hypotropia, hypertropia, exotropia (eye turns out), esotropia (eye turns in)
lesions and visual field deficits
whats/where causing change? -lesions, alterations, cut, tear, tumor, interruption in neural path
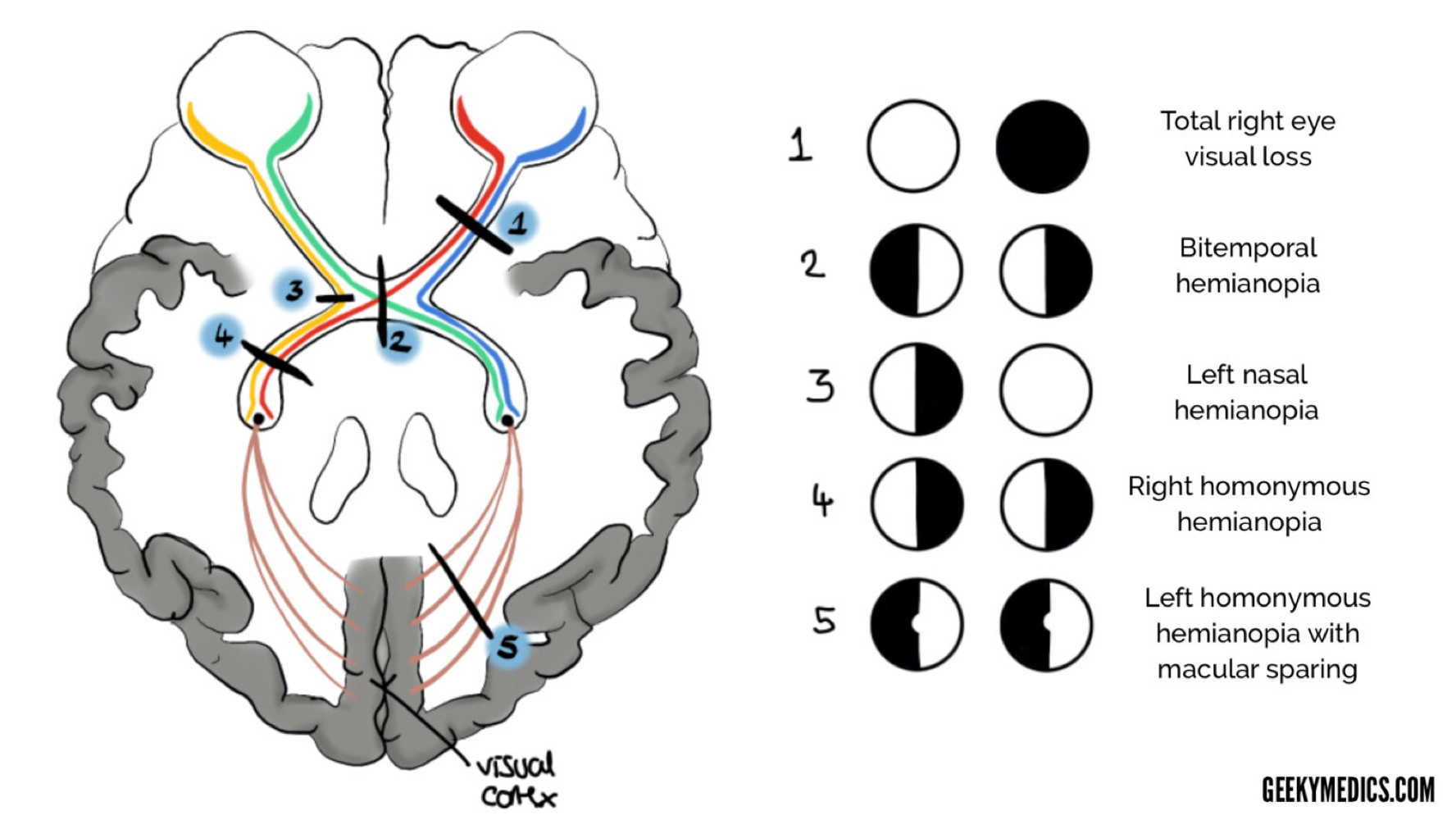
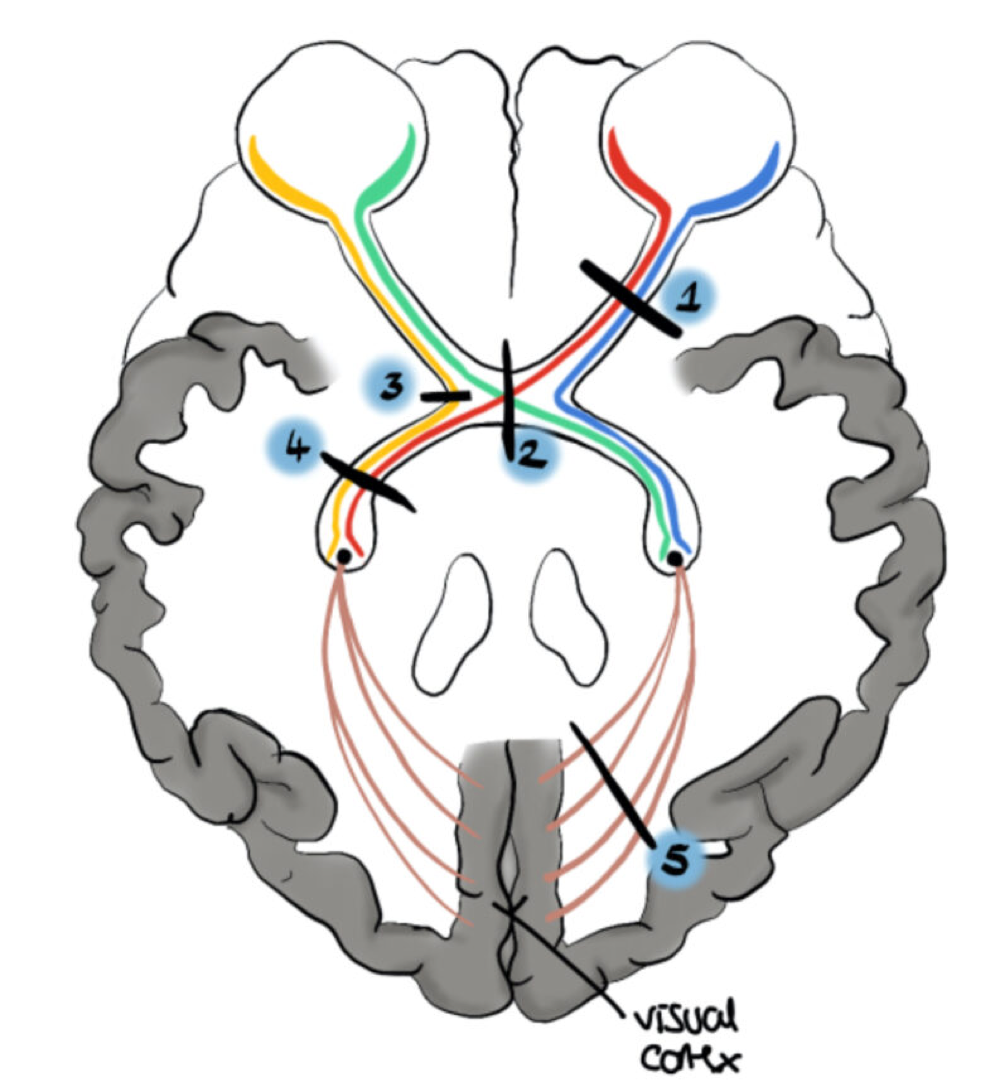
right vision loss
1 -after cross over
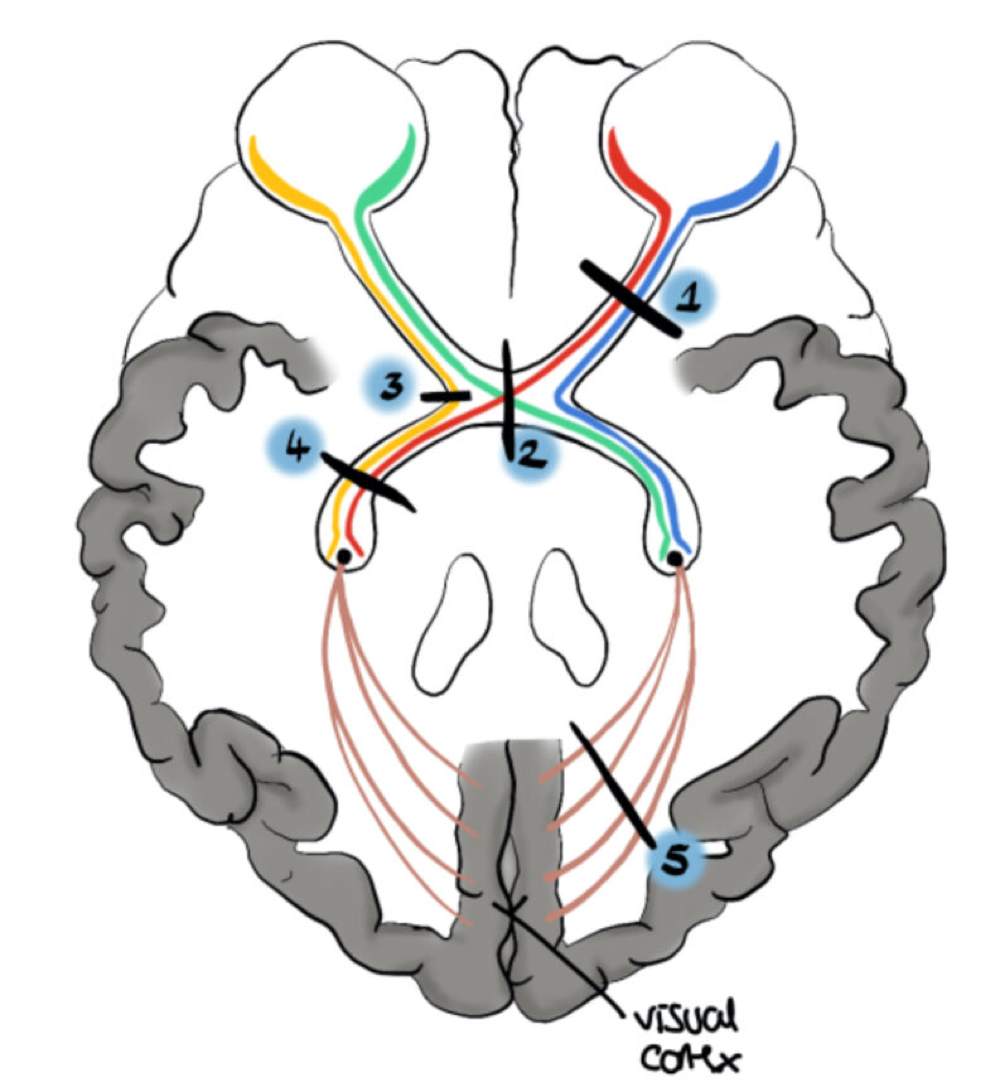
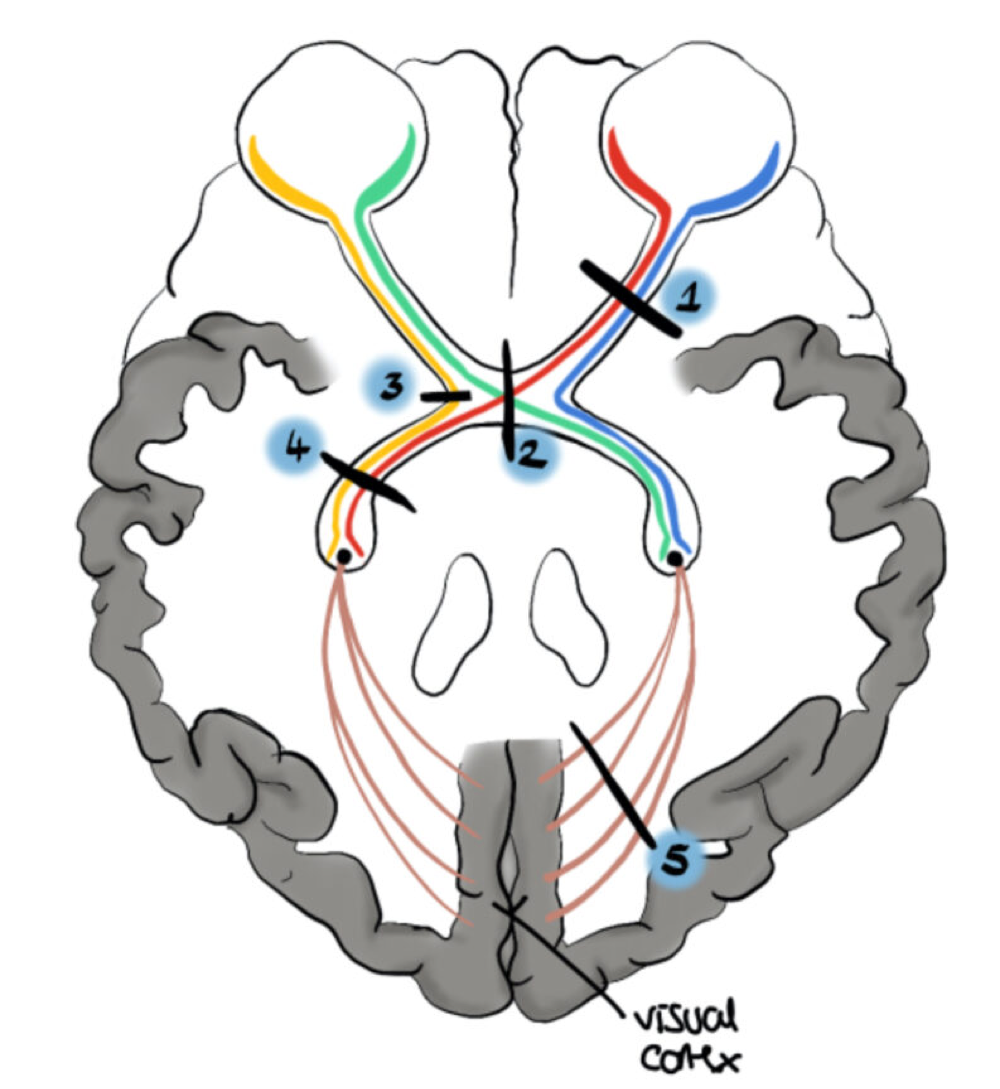
bitemporal hemianopia
loss on outer sides of vision -2 at crossover
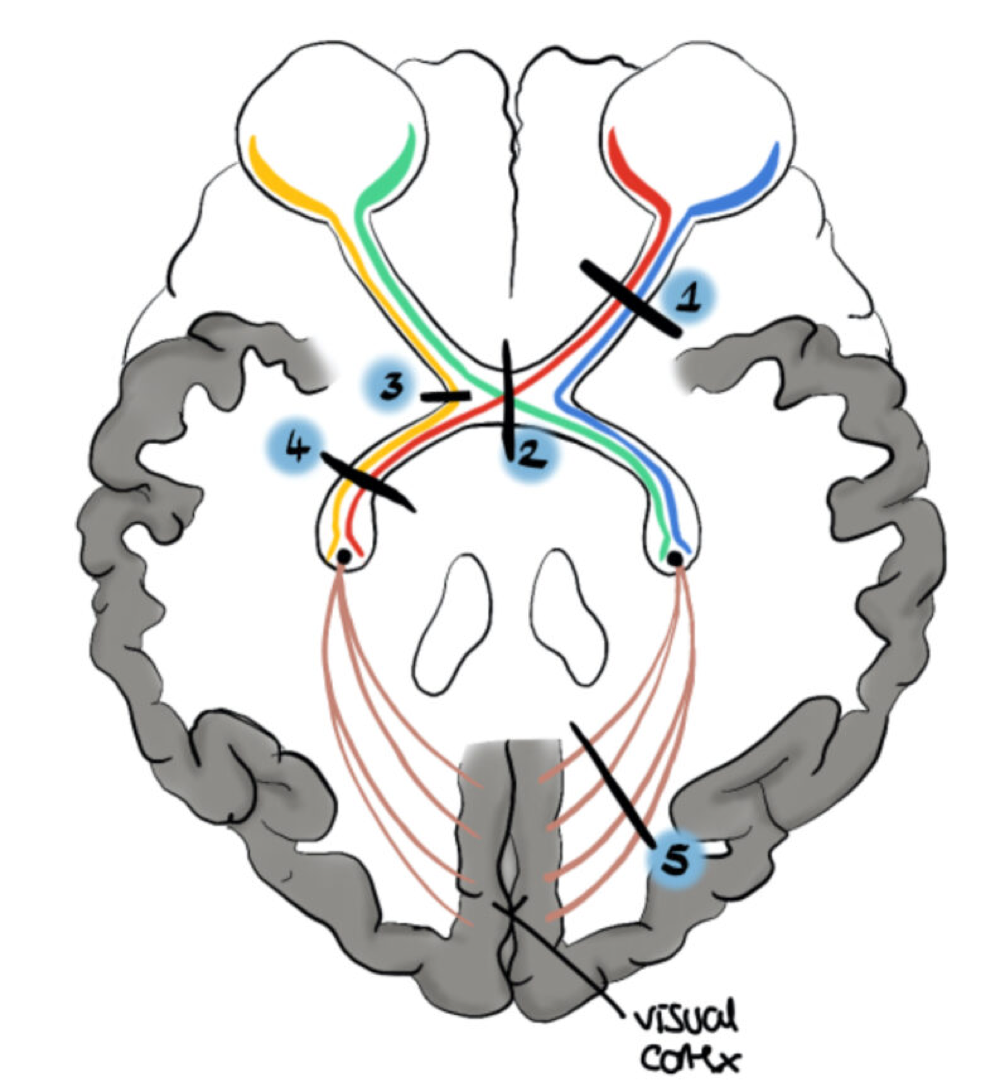
left nasal hemianopia
loss of right side of vision of left eye -3
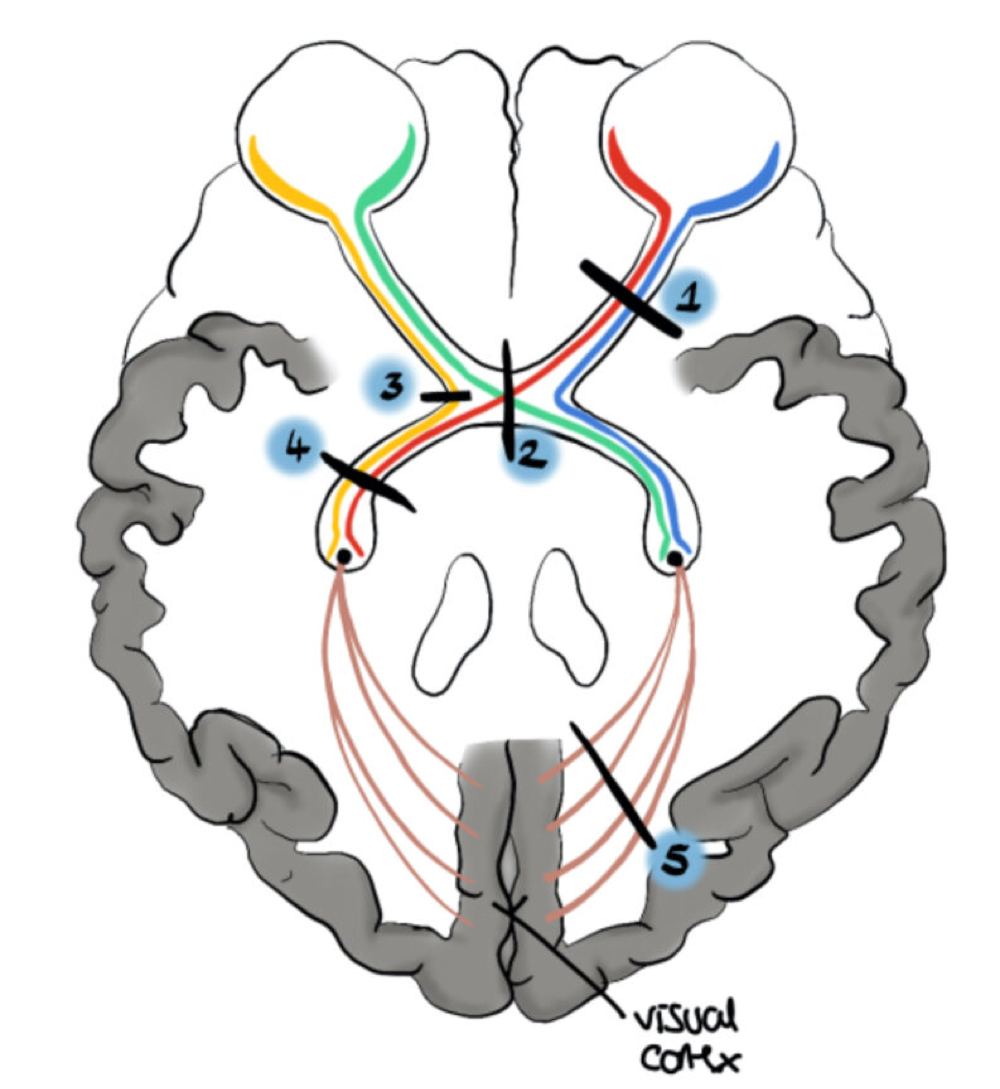
right homonymous hemianopia
loss of vision of right side of both eyes -4
left homonymous hemianopia with macular sparing
vision loss in left half of both eyes but central part still has vision left homonymous hemianopia with macular sparing -5 -caused by lesion in right occipital lobe of brain
static confrontation
test for visual fields -close one eye, test each quadrant
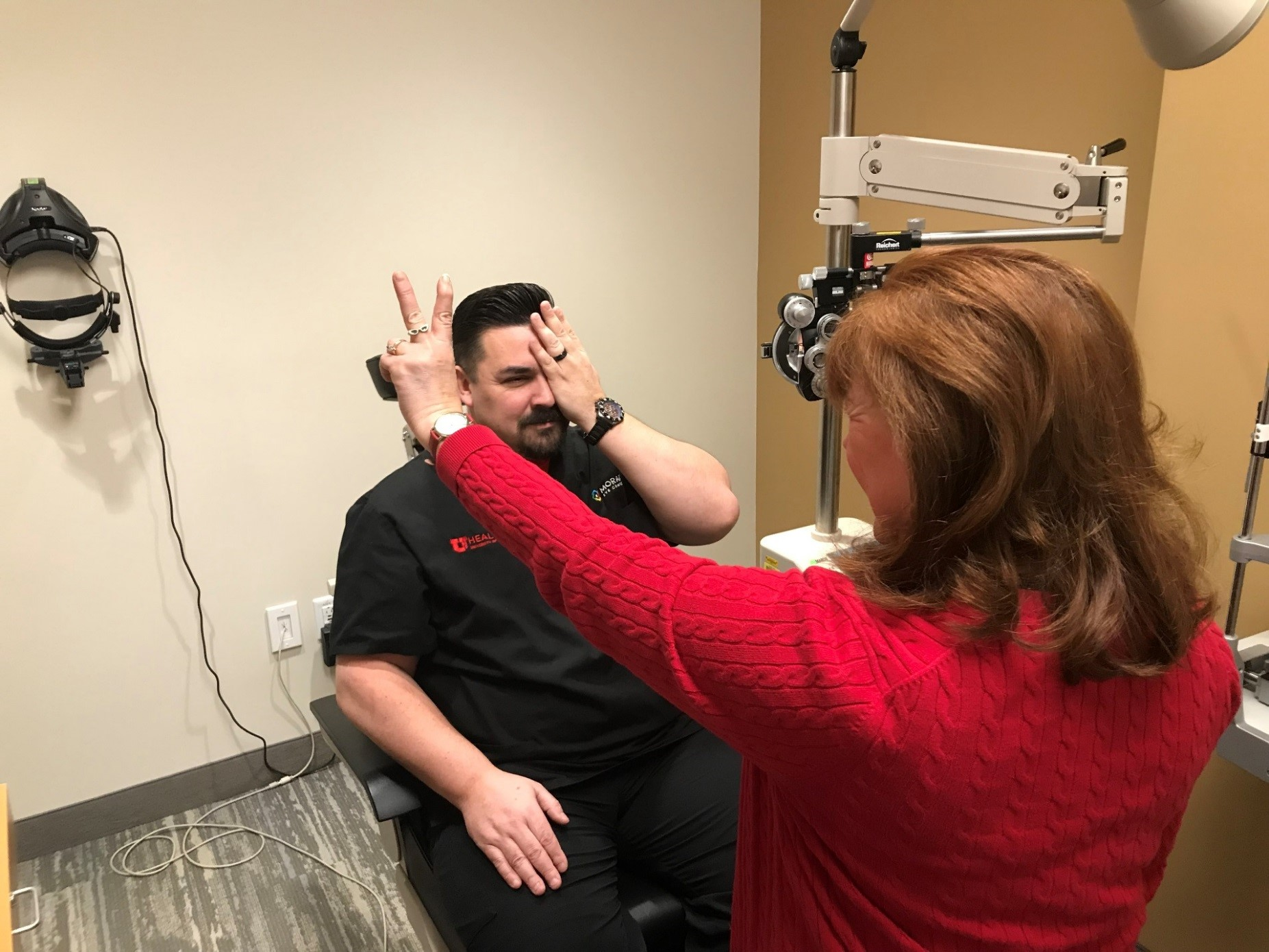
kinetic confrontation
test visual fields -slowly bring fingers in to compare visual fields
internal ocular structures
use opthalmascope -vasculature, fovea, optic nerve, smooth vessels (if has thicker portion its a blockage) -compare left to right to see issue
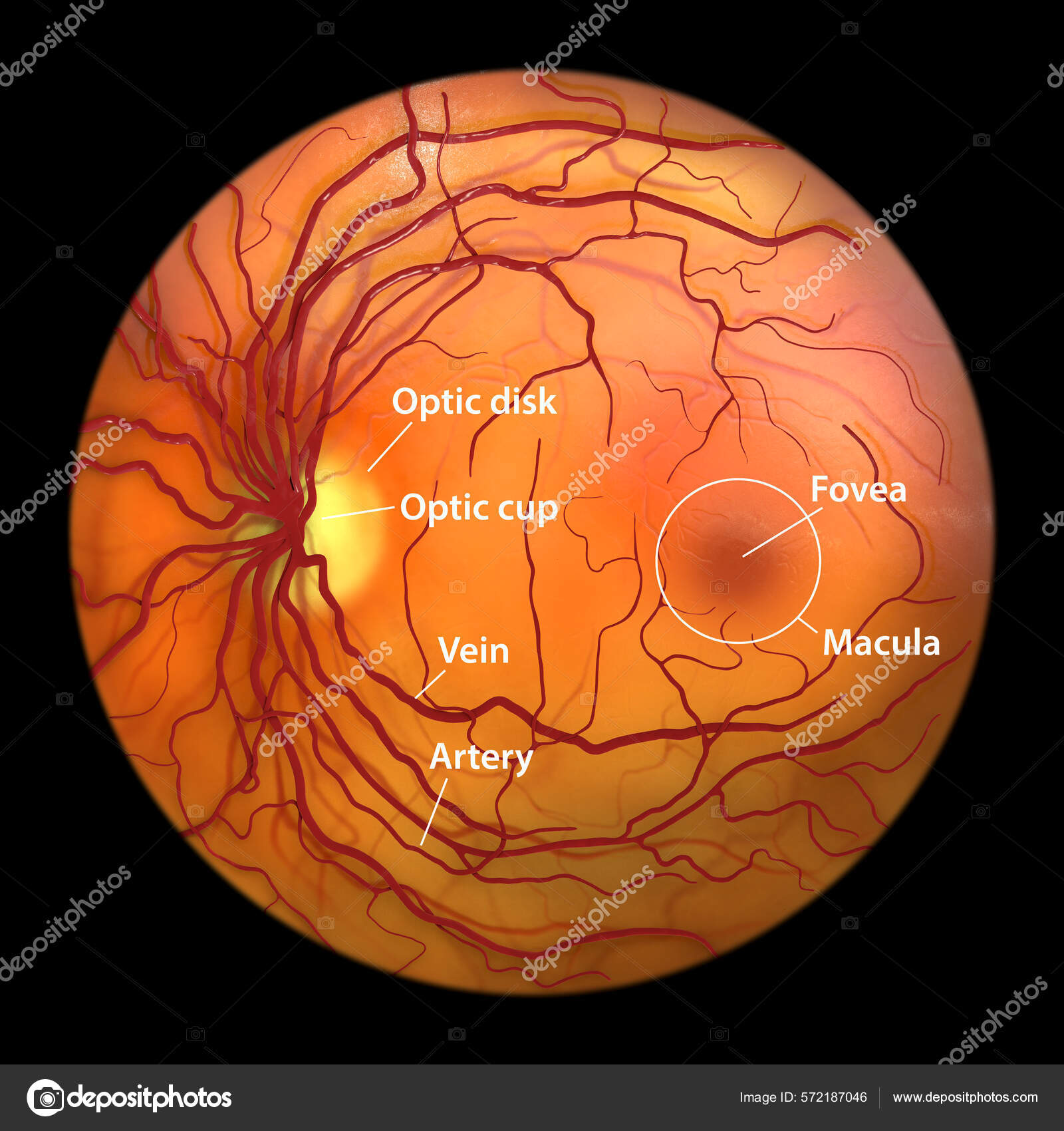
fundoscopy
to see macula, vein width > artery 2:3 or 4:5, see optic disc -arterial or venous changes can mean elevated bp, cholesterol or trauma
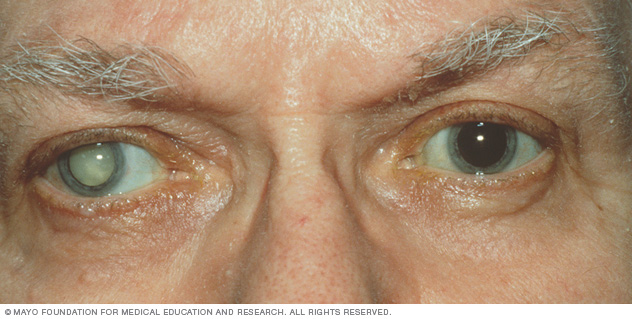
cataracts
in older popn -healthy lens, clear and responsive, fills up with fluid and plaques, gets opaque and effects vision, can go blind
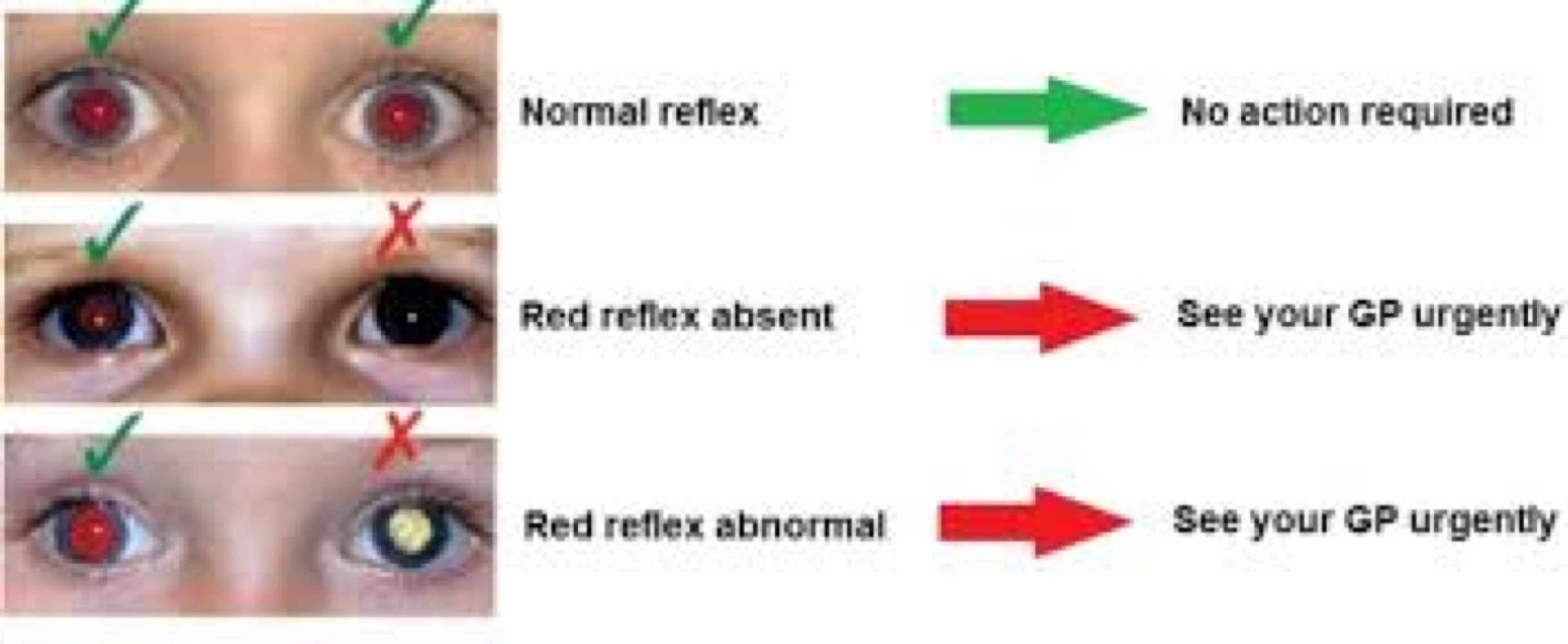
red reflux
important screening tool for kids to check for retinablastoma (eye cancer) -light should be symmetrical
why test pupils when have brain injury
way of testing neural anatomy and neural pathway -brain and eyes intricately involved -can indicate subderal hemotoma or lesion can effect path which effects eyes -pressure from blood on brain can put pressure on nerves and tumours, blood clots etc can do same
disease/disorders of ears
between 40-79, 63% of men and 46% of women had measurable hearing loss -much more common
hypertension
this and meds used to tx have been linked to hearing loss and tinnitus
ears general survey
skin colour, rashes, fluid, anatomy as expected, symmetry,
ears symptom history
lots of otitis media in kids -tell me about concern -LATERSNAPS
ears health history
earaches, infections/discharge, hearing loss, environmental noise, tinnitus, meds, vertigo (can be related to inner or middle, self care behaviours (ear protection, cleaning)
otalgia
earaches
otorrhea
infections/discharge
one of biggest risks to hearing
environmental noise
physical inspection ears
inspection, palpation/techniques -know anatomy, notice abnormal things -palpate for lesions, cysts, proper cartilage
middle ear
use otoscope, manubrium and light reflex (right has right side light reflex) -put in safely and brace -pull pinna up and back as adult -pull pinna straight down for kids
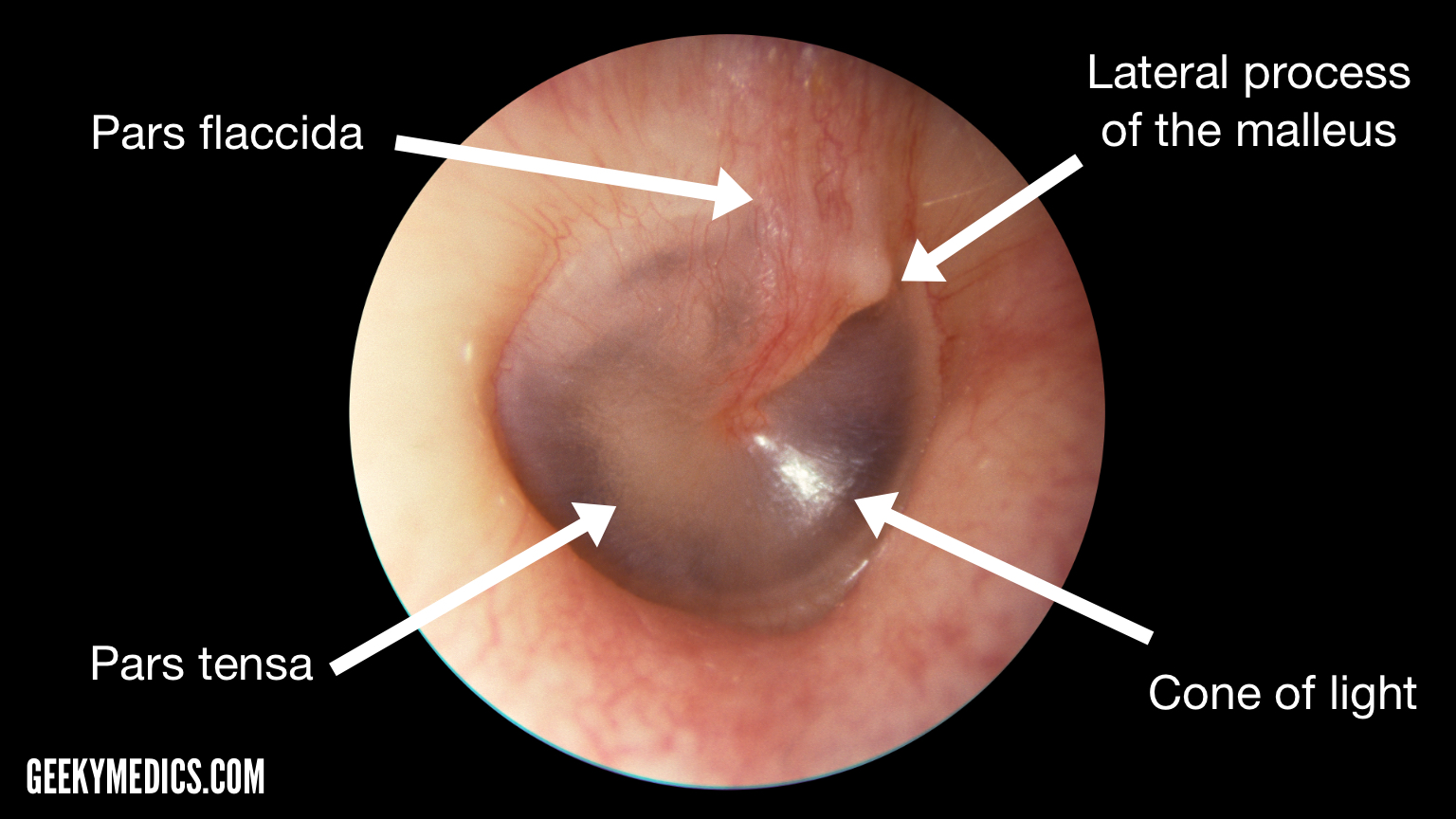
tympanic membrane
should be vascular colour, almost clear, light grey, umbo is yellowish, manubrium more vascular -no light reflex in otitis media
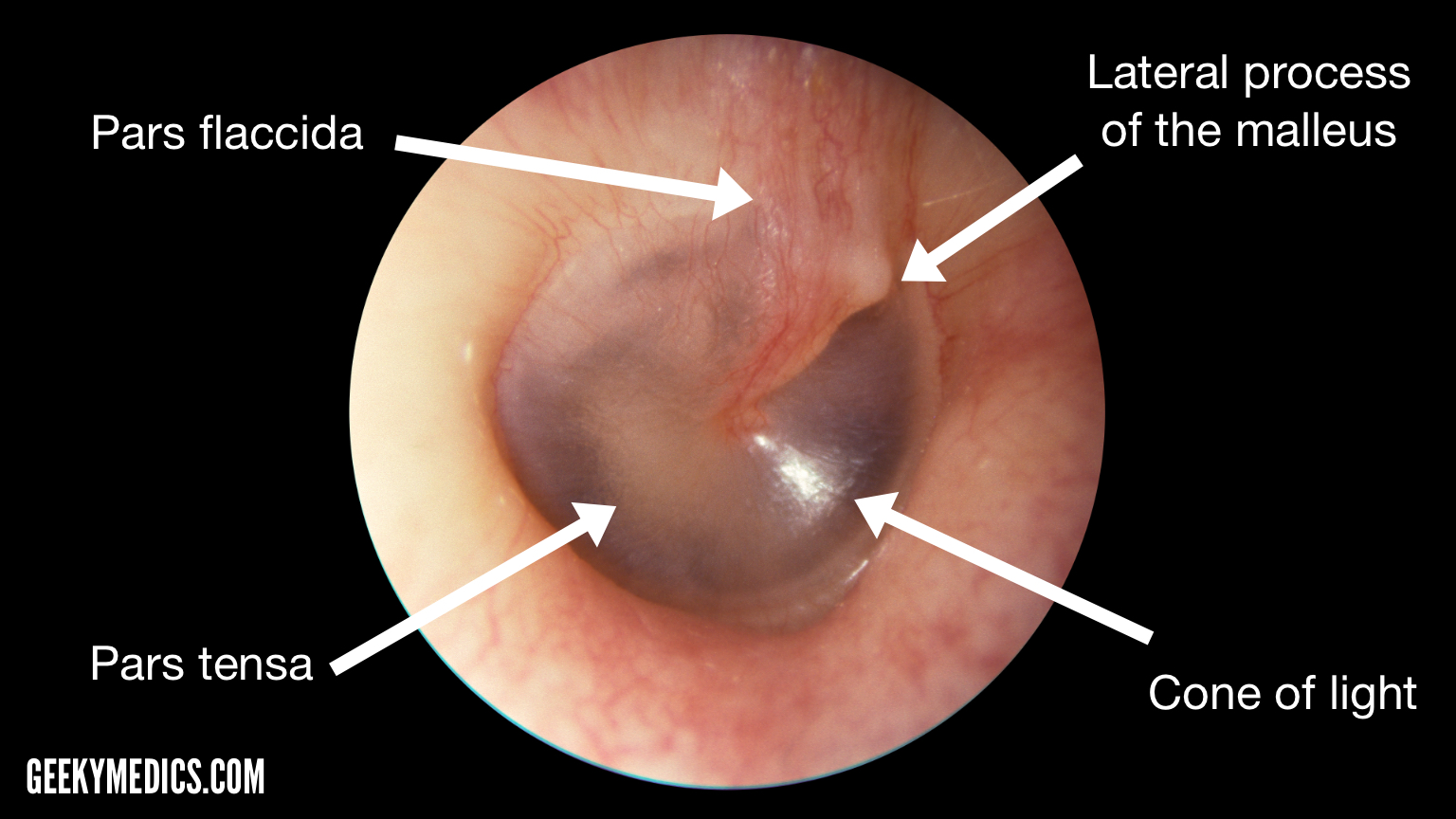
abnormal tympanic membrane
full, very vascular membrane -infected ear pushes membrane out -can put tube in ear to release chronic fluid build up
whisper test
from 60 cm away, one ear covered, should be able to hear whisper -if cant move onto rinne and weber test
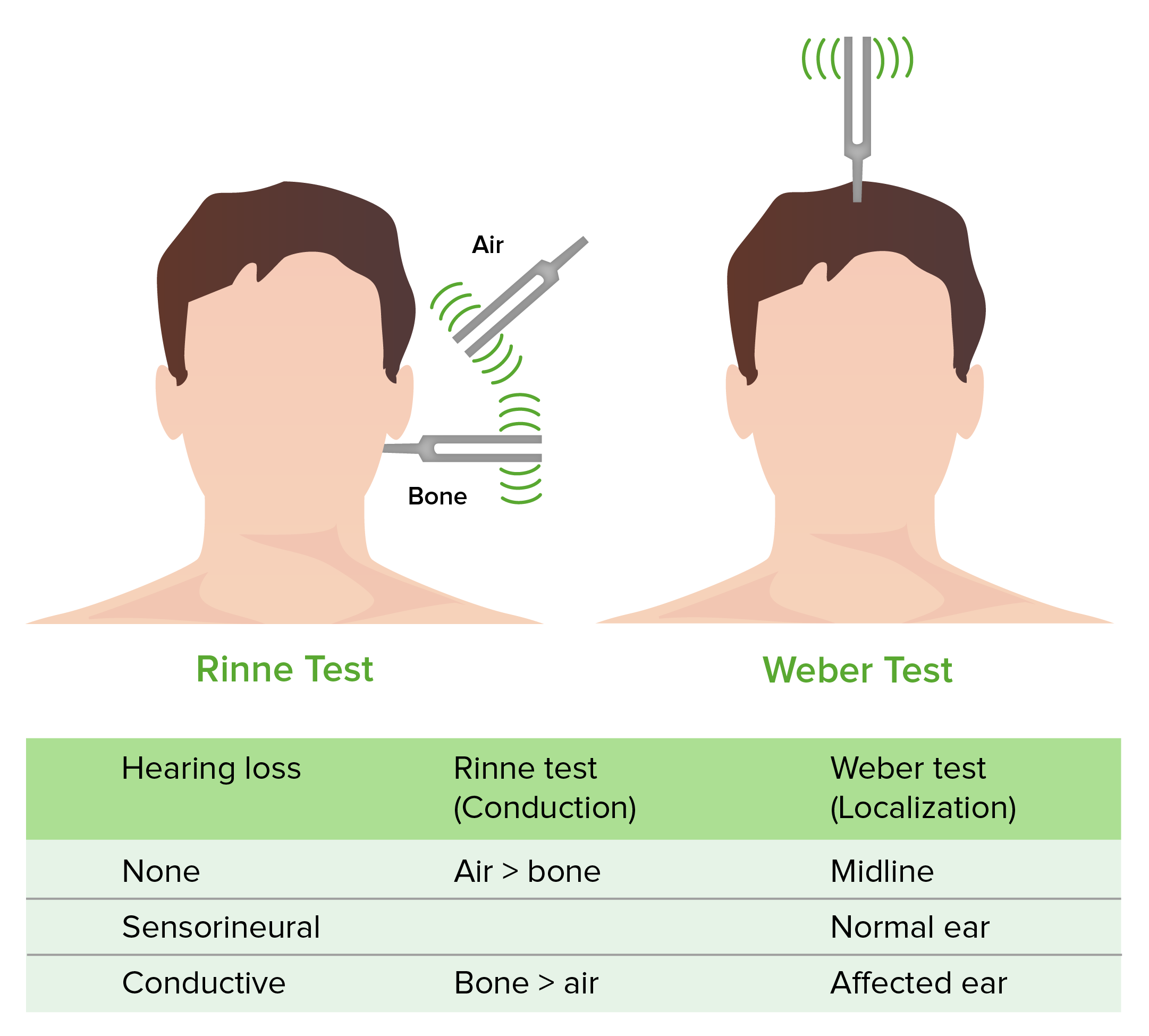
rinne test
should have better air conduction than bone conduction -conductive hearing loss if bone is longer than air
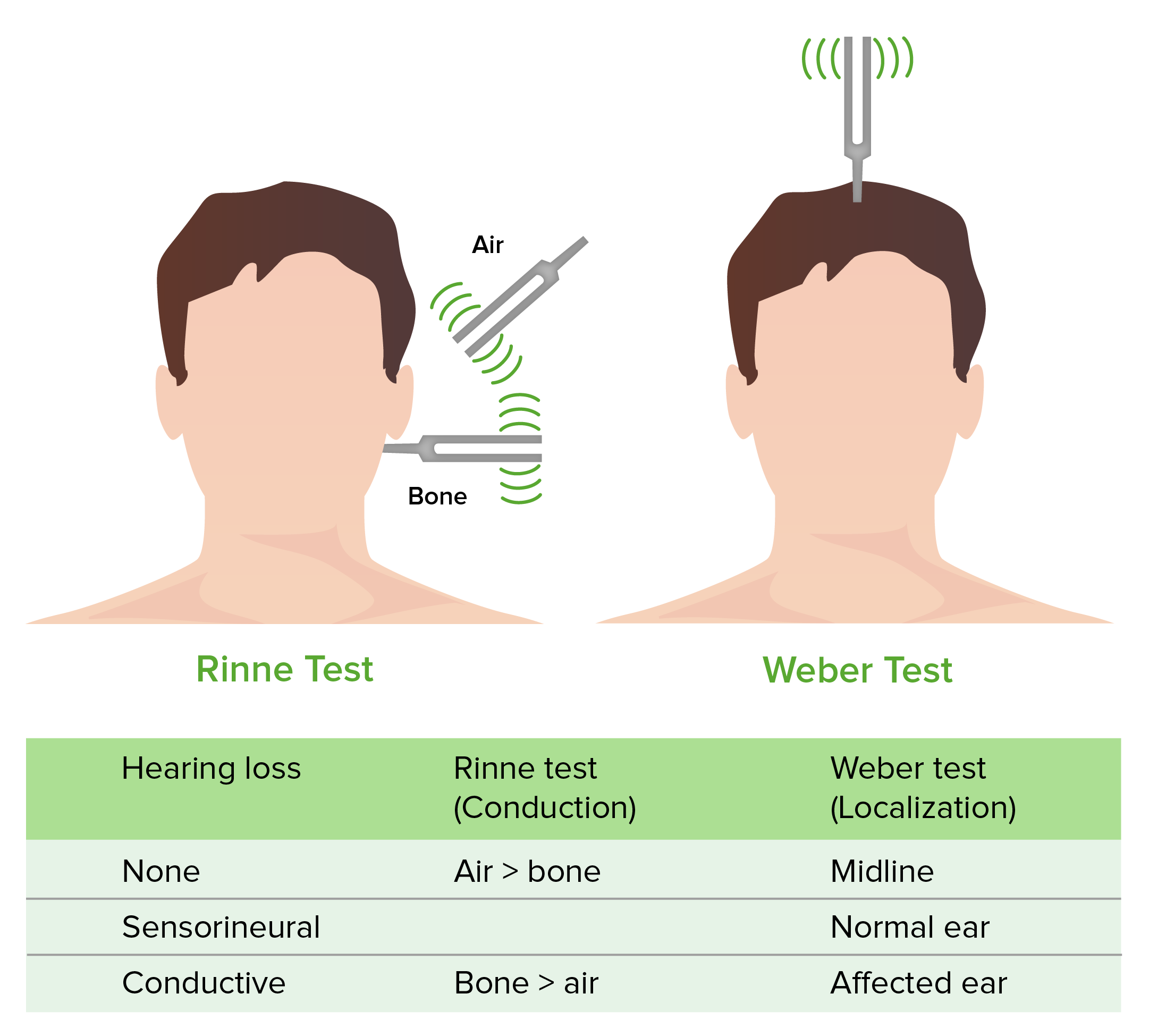
weber test
when fork applied should hear equally on both sides
mouth and tongue disorders
gum disease, gingivitis, cavities, oral cancer, thrush, sore throats, lesions
gum disease
one of the most common dental problems adults face, but can begin at just about any age.
gingivitis
inflammation of the gums.
cavities
small hole that forms on surface of a tooth
oral cancer
disease resulting from abnormal cell growth in the mouth, lips, tongue, or throat
mouth general survey
overall impresion, skin, colour, anatomy as expected, movement symmetrical especially of tongue and while talking
mouth health history
pain, movement concerns, sores/lesions, sore throat, burning, coughing, reflux -prevention:last dental appointment? -self care routine: toothpaste, flossing, bad breath causes
mouth physical exam
know anatomy, teeth amount, colour, texture, lips, mouth, tongue movement, upper and lower palate, uvula, look at vascularization
adult teeth amount
32
kids teeth amount
20
red flags
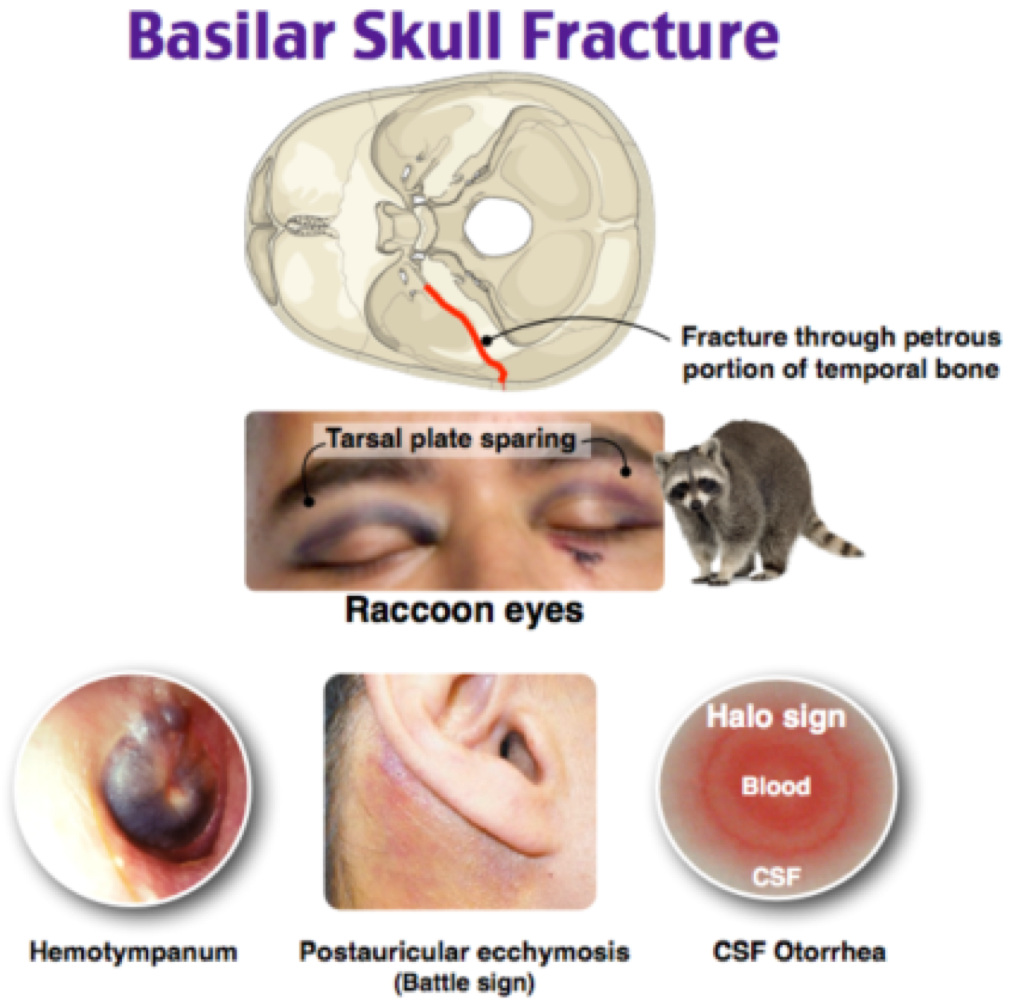
trauma to eyes or ears -sudden changes in vision or hearing -raccoon eye -fluid leaking
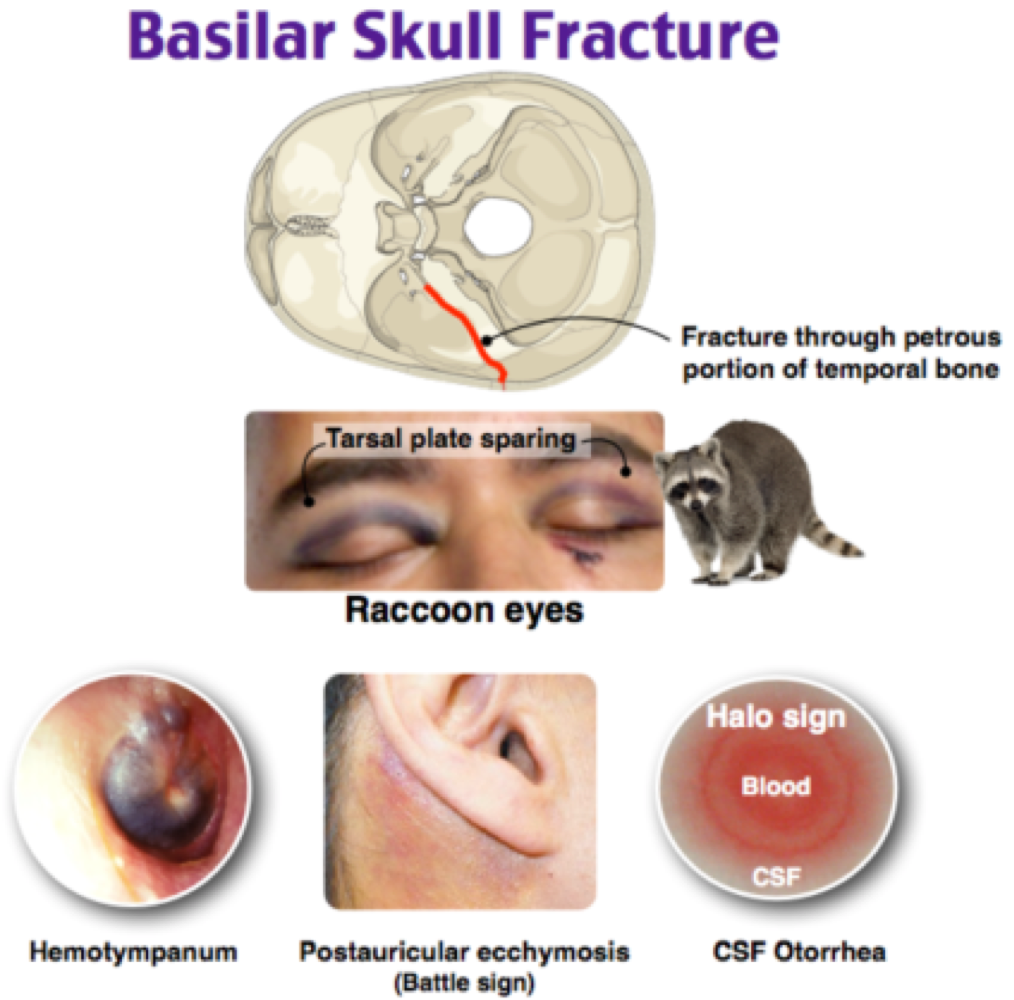
raccoon eyes
take time to develop -need to protect brain
cn 1
olfactory, smell, sensory
cn 2
optic, vision, sensory
cn 3,4,6
oculomotor, trochlear, abducens -move eyes -cn 3 constricts pupil and accomodates, also mixed-others are motor
cn 5
trigeminal -chews, feels the face, front of head -mixed
cn 7
facial -moves the face, tastes, salivates, cries, feels some ear parts -mixed
cn 8
vestibulocochlear -hears, regulates balance -sensory
cn 9
glossopharyngeal -taste, salivate, swallows, monitors carotid body and sinus -mixed
cn 10
vagus -tastes, swallows, lifts palates, talks, communication to and from thoraco-abdominal viscera -mixed
cn 11
accessory -turns head, lifts shoulders -motor
cn 12
hypoglossal -moves tongue -motor
cn 1 test
smell test -head traumas, pressure or changes that puts pressure on nerve can change response
cn 2 test
visual acuity -field of vision -visualization of fundus -pupillary light response
cn 2 and 3 test
PERRLA -symmetry to pupils and cornea
PERRLA
pupils, equal, round, reactive to light, and accommodation
cn 3, 4, 6 test
follow and track hand, convergence test
cn 3 and 7 test
position of eyelid -opening, closing and positioning, symmetry
cn 5 test motor
-for mouth jaw, temporal masseters -ask to open mouth and observe for jaw deviation -palpate masseter and temporalis muscles and ask client to clench -move jaw side to side and examiner try to push midline
cn 5 test sensory
compare sides, pain and temperature -light touch -eyes, tongue, taste
jaw jerk reflex
dont do normally, patient mouth is slightly open with jaw relaxed -examine tap front of patients chin w/ reflex hammer -expected response is masseter and temporalis muscles contract, which causes mouth to close suddenly -indicates normal trigeminal nerve
cn 7 test motor
observe facial movements -symmetrical -facial expression test
cn 7 test sensory and autonomic
taste anterior of tongue -external ear sensation rarely detected -function of stapedius muscles (should contract at loud noise) -lacrimal glands: ask about dry eye -salivary glands: ask abt dry mouth
hyperacusis
over sensitive to sound -possible disfunction of stapedius muscle -cn 7 damage proximal to stapedius muscle
cn 5 and 7 test
corneal reflex: automatic blinking touch cotton ball to eye -conjunctival reflex
cn 8 test
vestibular nerve -observe eyes for nystagmus -romberg test
nystagmus
eyes make rapid, repetitive, uncontrolled movements -romberg test: stand with eyes open then eyes closed and see how balance is (some times not effective) -requires proprioception, vision, and vestibular fx
cn 7 and 8 test
acoustic reflex -respond to sound and vocalization -stapedius with loud noise (7) or own voice (8) -ipsilateral stimulus (on one side) causes bilateral response -tympanometry test -sensorineural hearing loss = diminished reflex
tympanometry
a test that measures how well your eardrum moves in response to air pressure and sound -probe changes air pressure and produces a tone
cn 9 and 10 test
tested together -oropharyngeal muscles kkkk? -mmmm also 7 -lalala also 12 -swallowing -gag reflex -x alone: palatal arches: damaged side can’t work, look for lowered and flattened palatal arch -palates should rise equally and symmetrically
cn 11 test
push head against hand and shoulder up against hands -larger muscles -shoulder should be equal at rest
cn 12 test
cheek and jaw movements

rinne test positive
AC>BC