Embryonic Development and Principles of Heredity
1/22
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
23 Terms
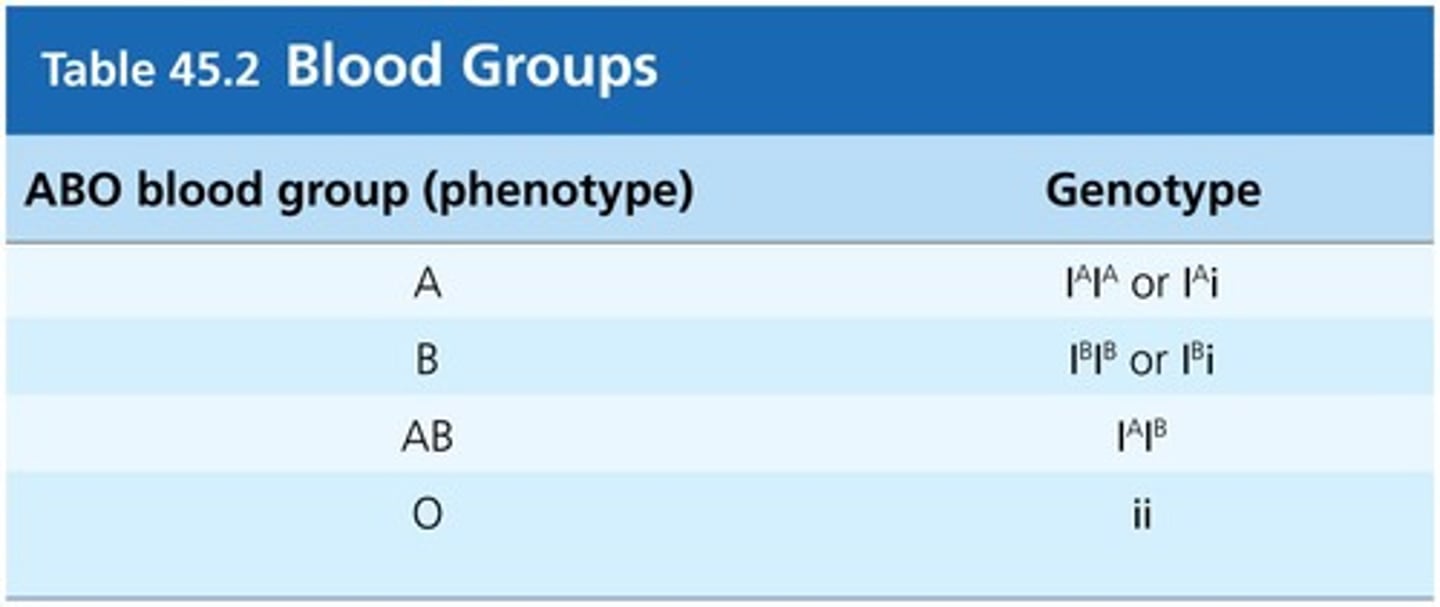
Fertilization
Male and female pronuclei are in the process of fusing - about 24 hours - in fallopian tube.
Zygote
Fertilized egg with one nucleus containing (normally) 46 chromosomes.
Embryo
Weeks 3-8 of development.
Fetus
Week 9 to birth.
Differentiation
Cellular 'decision' to become a particular cell type.
Amnion
Surrounds growing embryo, filled with fluid (amniotic fluid), ruptures at birth.
Allantois
Becomes umbilical cord.
Yolk sac
Provides nutrients very early in development then placenta takes over, creates embryonic blood cells, becomes part of the digestive system.
Embryoblast
Inner cell mass.
Implantation
By the time implantation is complete, gastrulation is also complete.
Chorionic villi
Reach into endometrium into blood-filled sinusoids.
Decidua basalis
Endometrium beneath embryo, will become part of the placenta.
Decidua capsularis
Endometrium on the luminal side of uterus.
Genotype
Genes.
Phenotype
Expression of the gene (what you see).
Allele
Version of the gene (may be dominant or recessive).
Locus
Specific 'address' of the gene on the chromosome (loci - plural).
Dominant
The version of the allele that is expressed (you see this one - the phenotype is seen).
Recessive
The version that can be 'hidden' by the expression of the dominant gene.
Homozygous
Both alleles are the same (either both dominant or both recessive).
Heterozygous
Alleles are different; one allele is dominant and one is recessive.
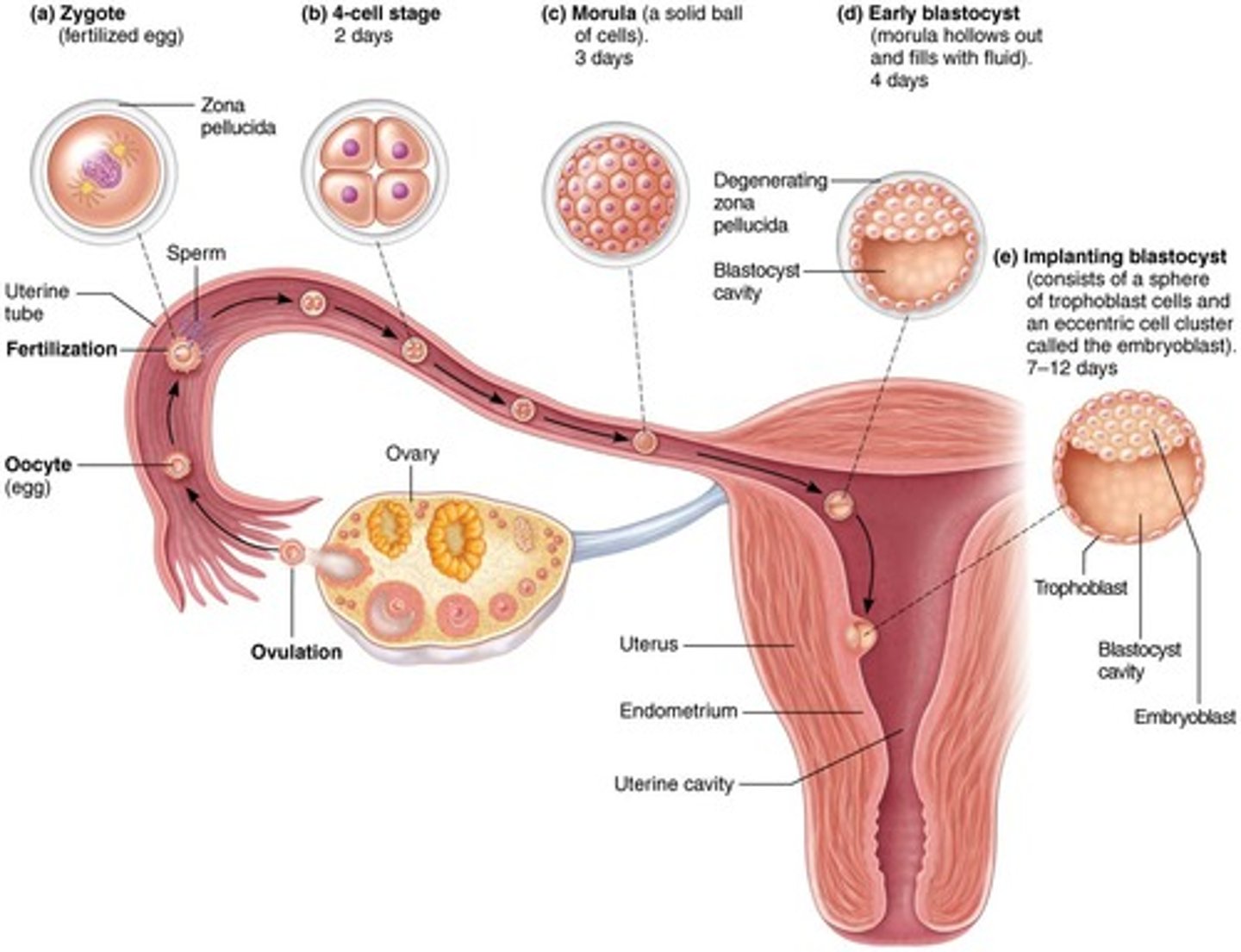
Punnett square
Given genotype of parents, predict percentage of genotype and phenotype of offspring (assuming total dominance).
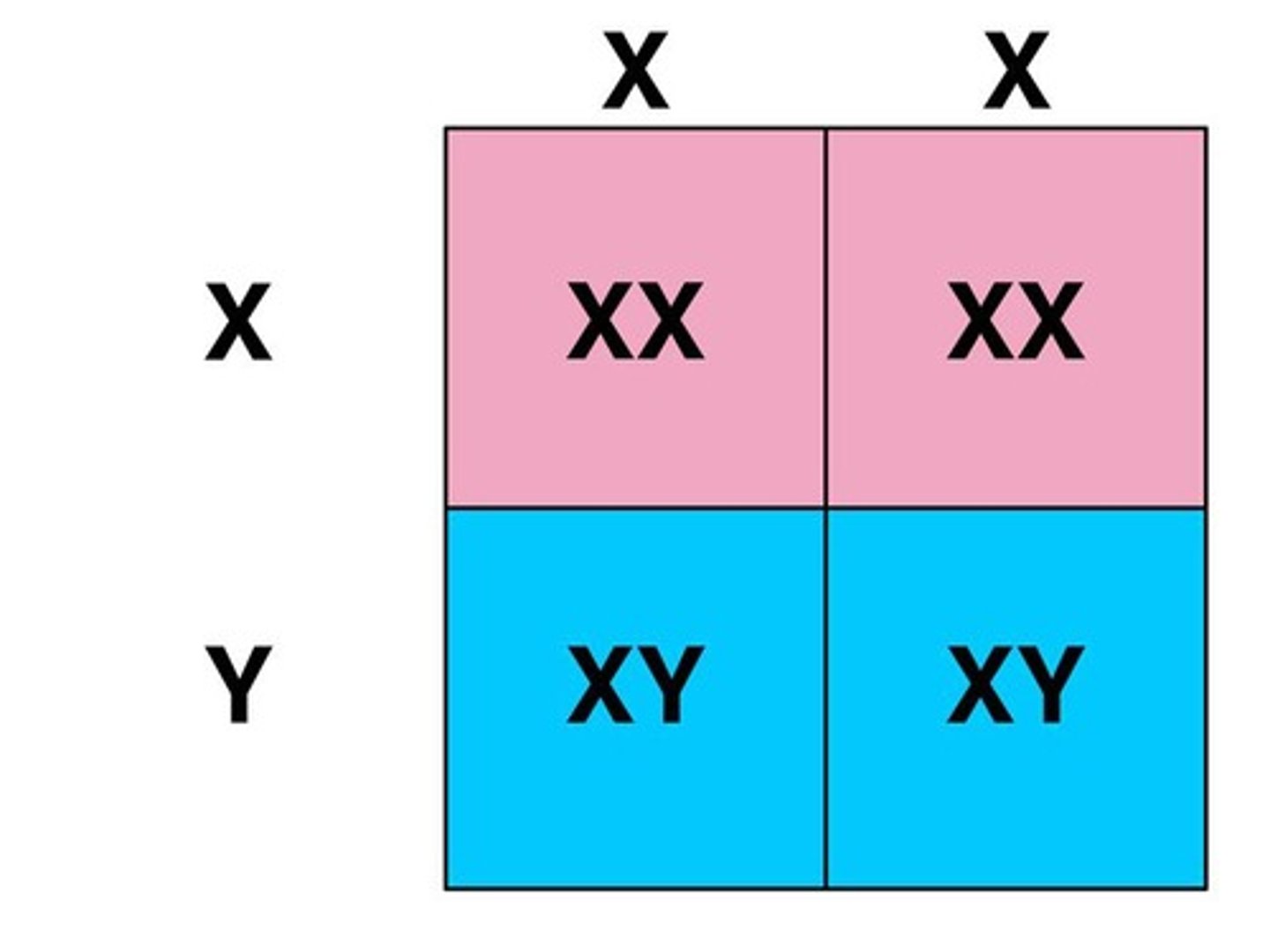
ABO blood group
A case of codominance; Mom - ii (genotype) O (phenotype), Dad - IAi.