AP Euro Art
1/42
Earn XP
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
43 Terms
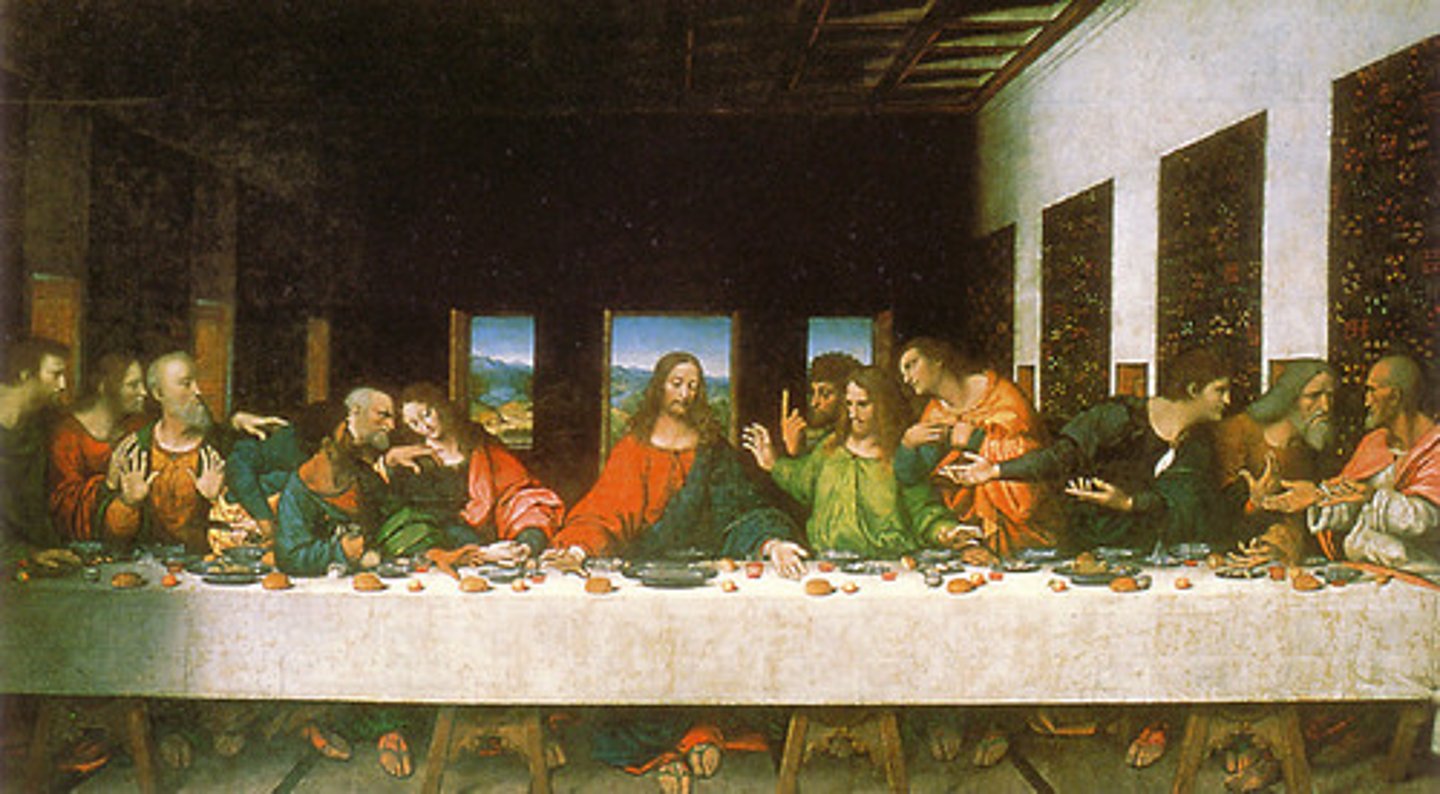
Leonardo da Vinci, 1495-1498, Renaissance
The Last Supper

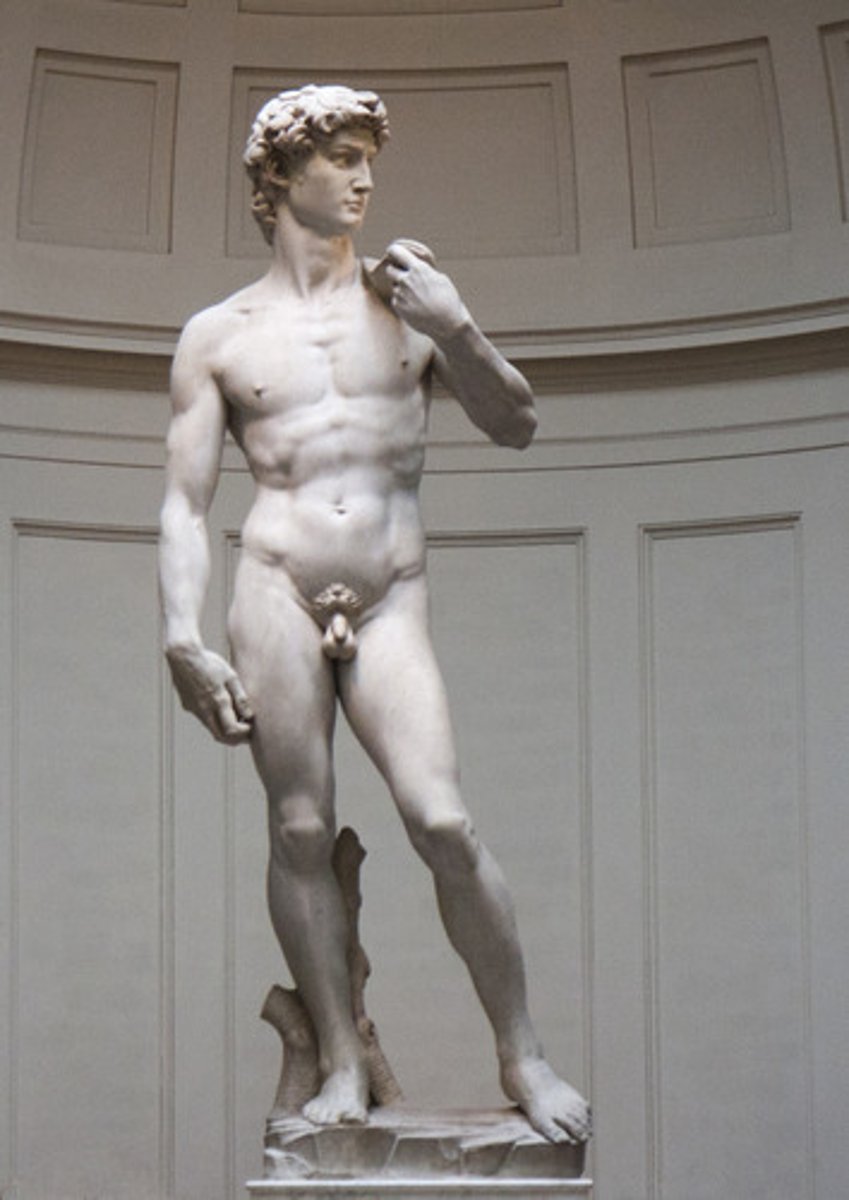
Michelangelo, 1501-1504, Renaissance
David

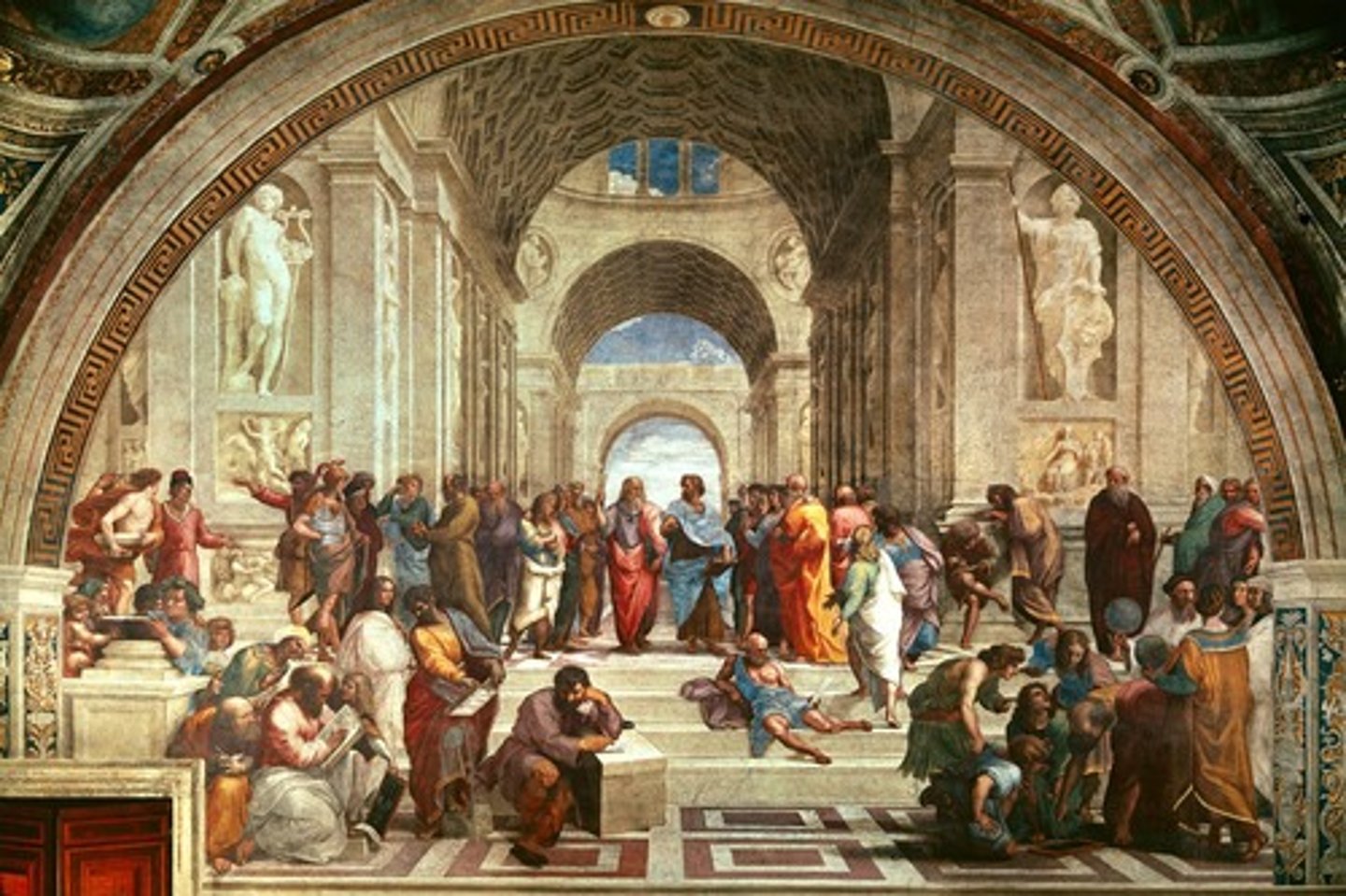
School of Athens, Raphael, 1510, Renaissance
School of Athens

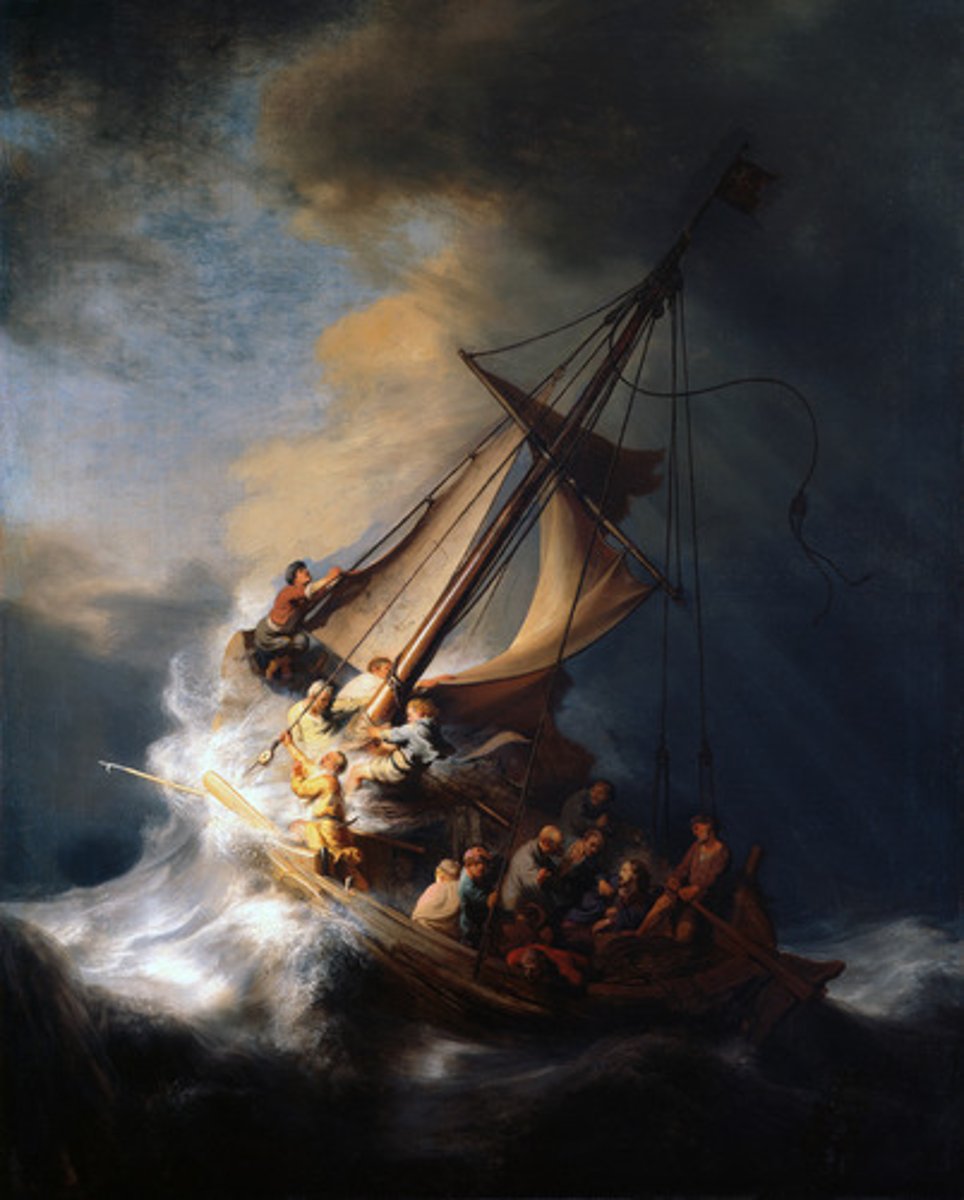
Rembrandt, 1633, Baroque
The Storm on the Sea of Galilee

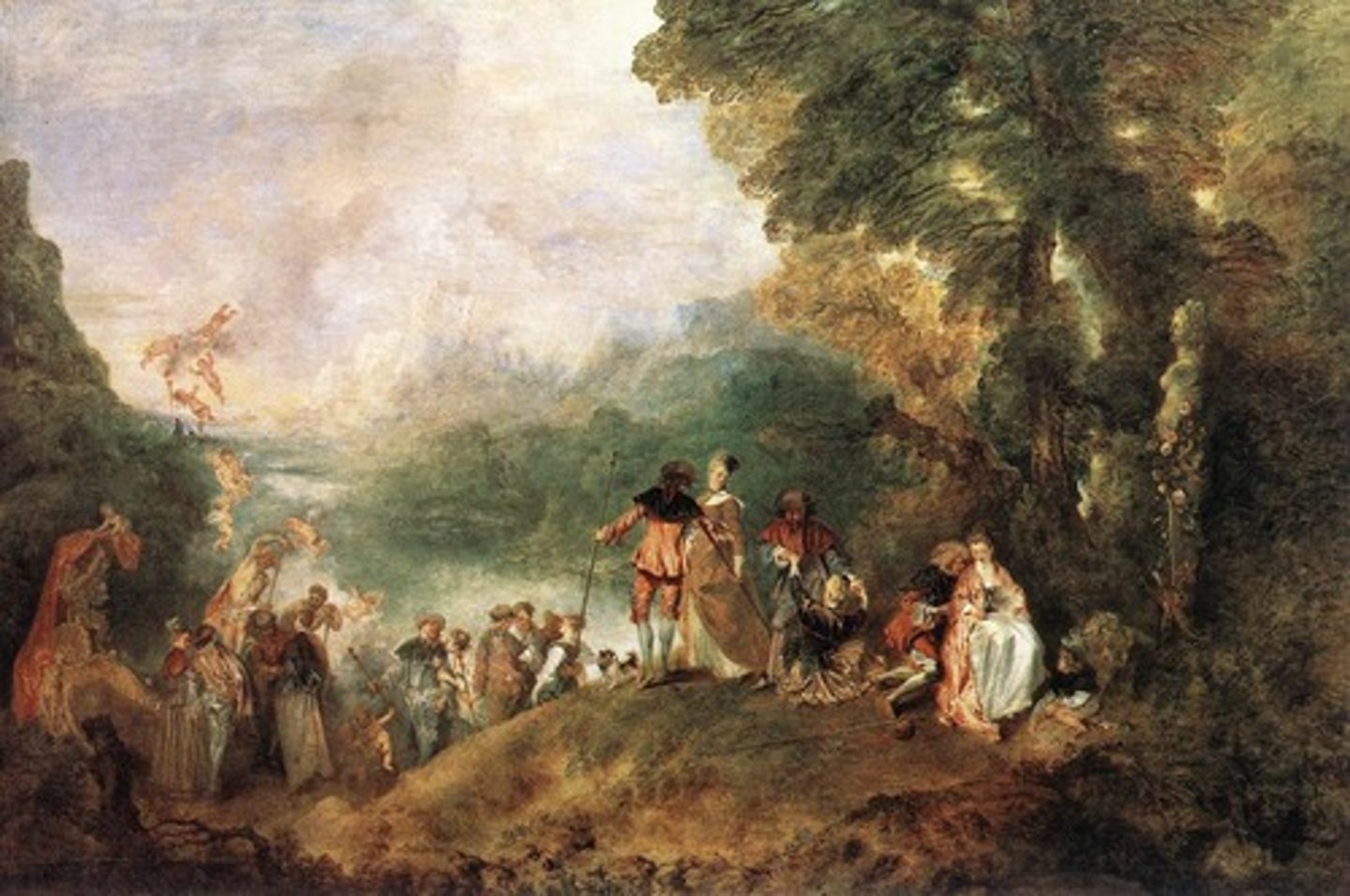
Watteau, 1717, Baroque
Pilgrimage to Cythera

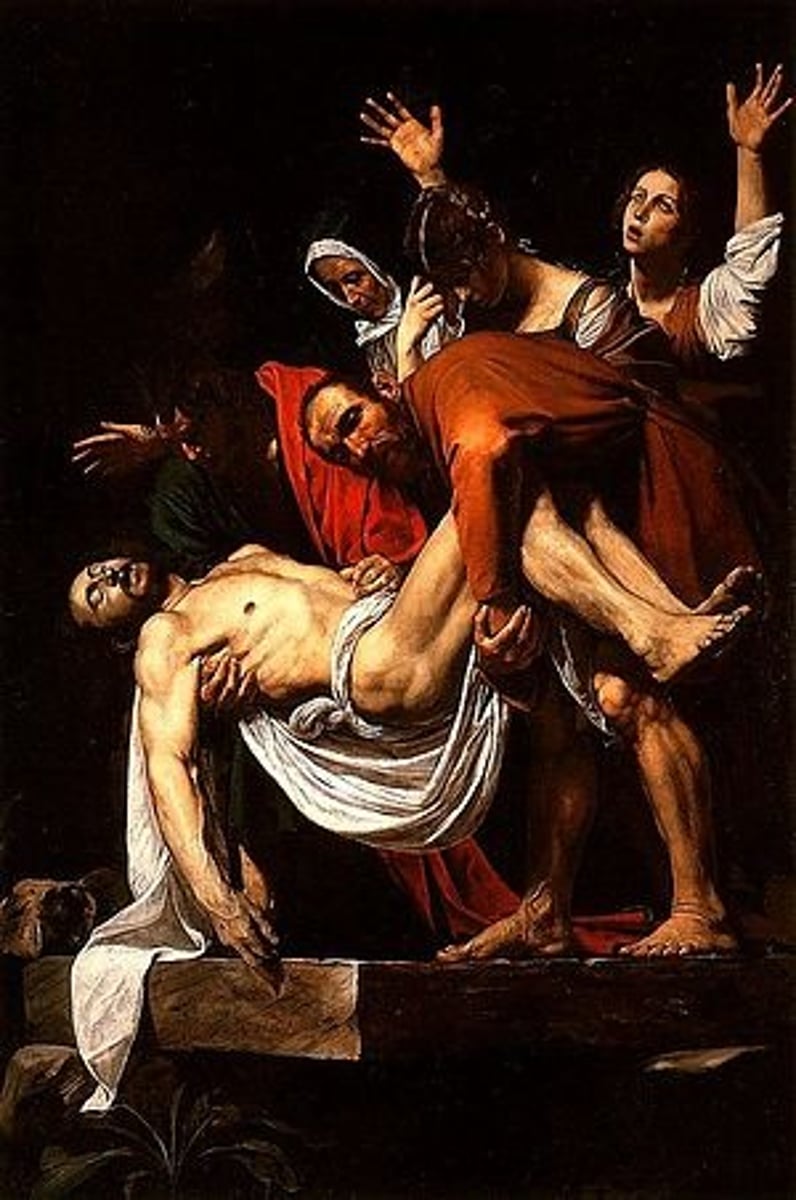
Jacopo da Pontormo, 1525-1528, Rococo
The Entombment of Christ

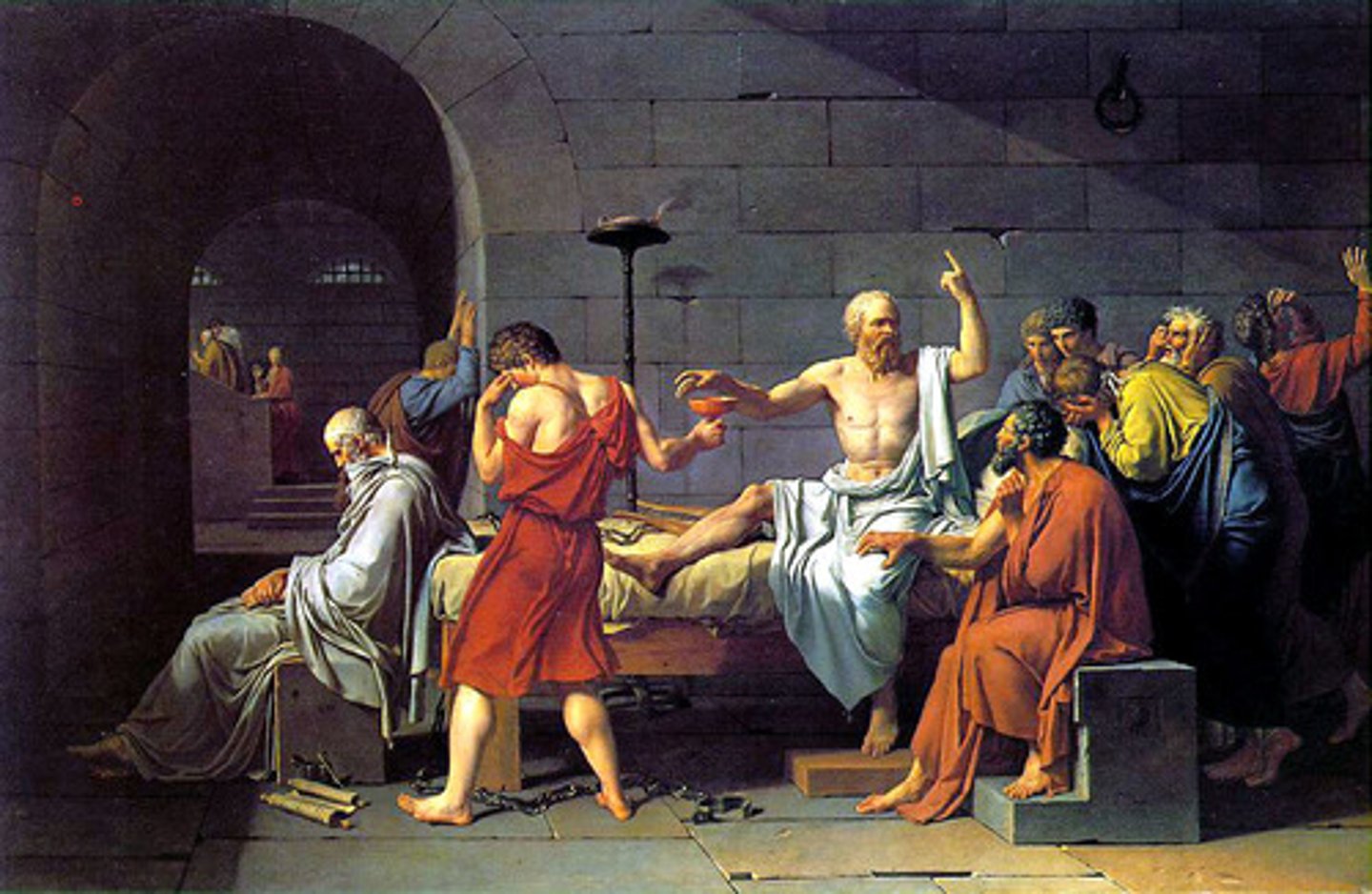
Jacques-Louis David, 1787, Neoclassism
The Death of Socrates

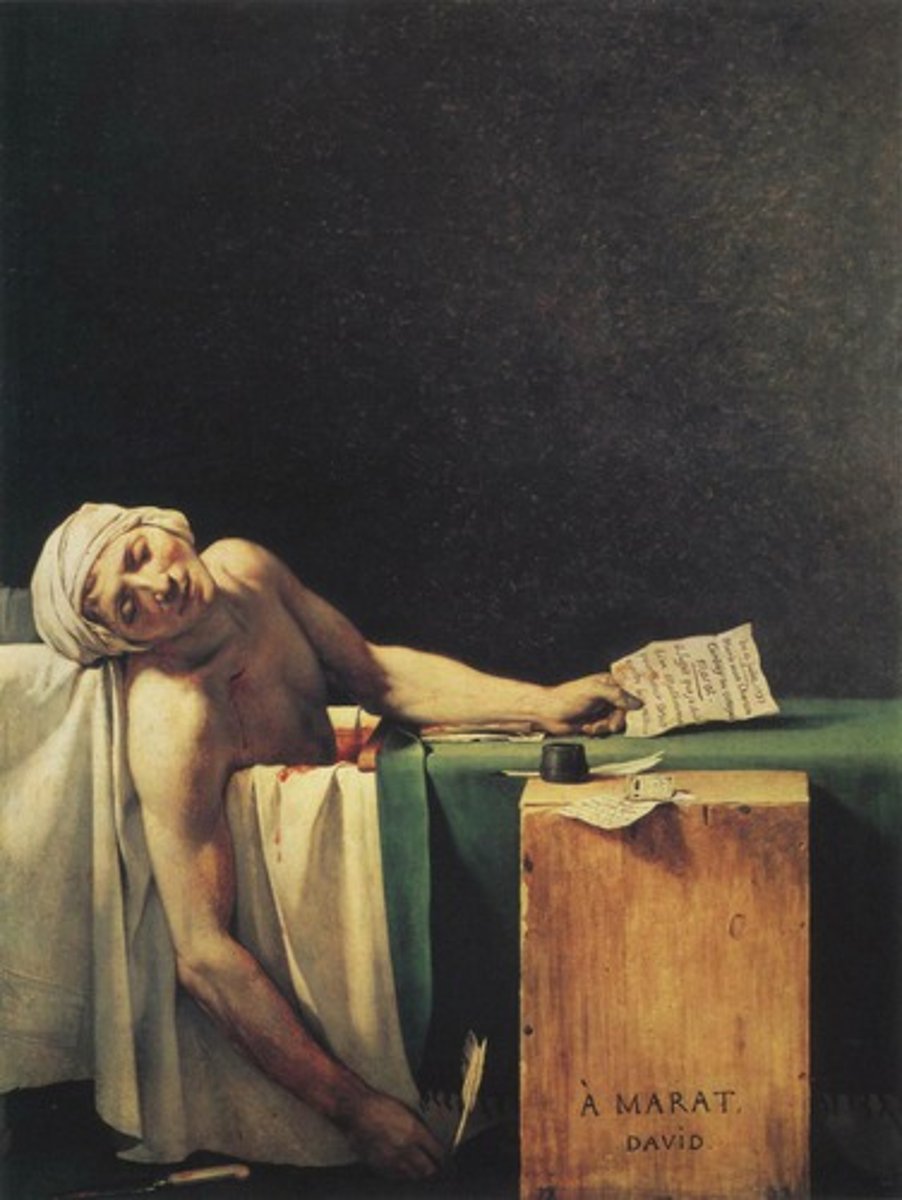
Jacques-Louis David, 1793, Neoclassism
The Death of Marat

Jan Van Eyck, 1434, Northern Renaissance
Arnolfini Portrait

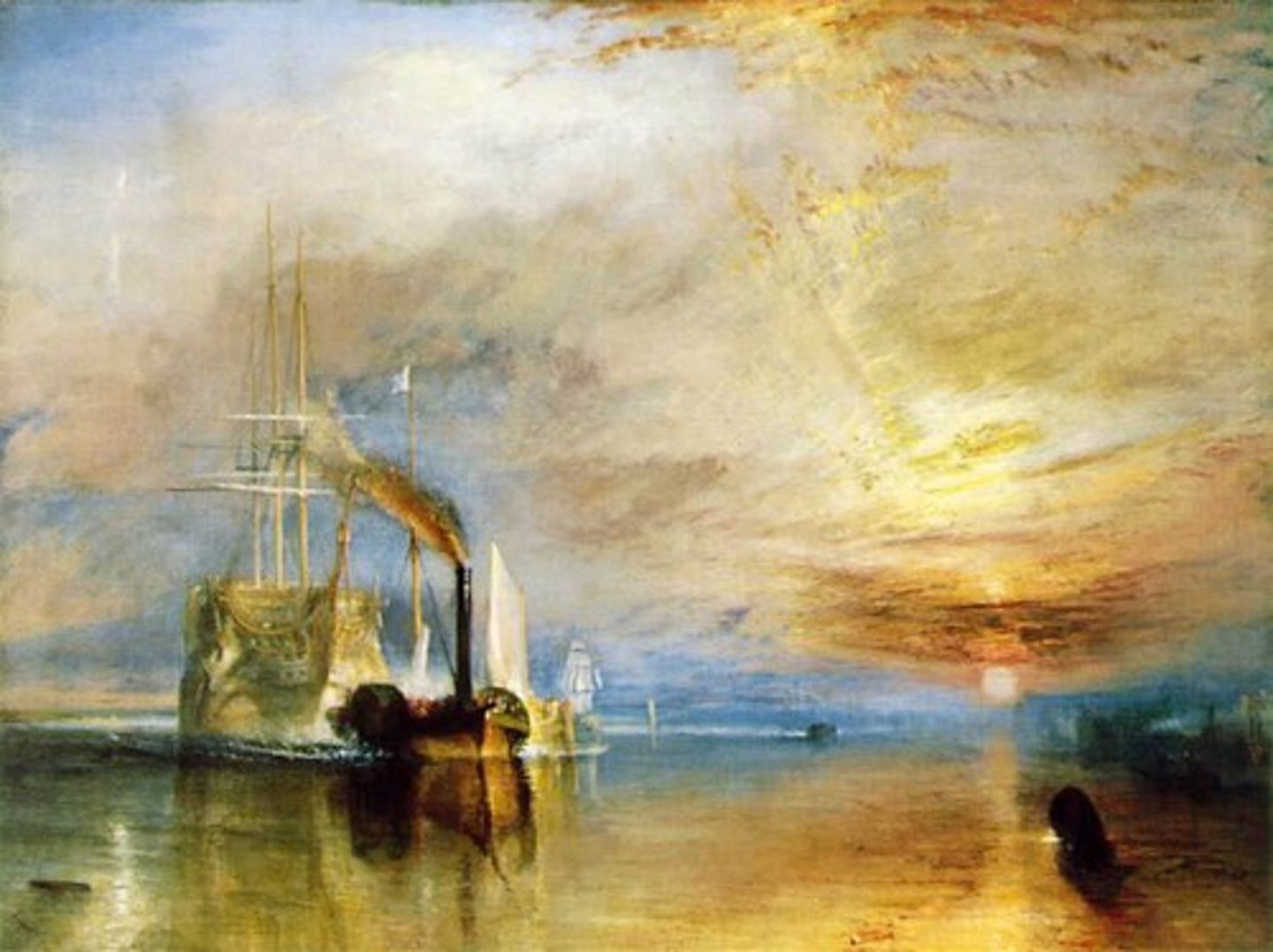
Turner, 1838, Romanticism
The Fighting Temeraire

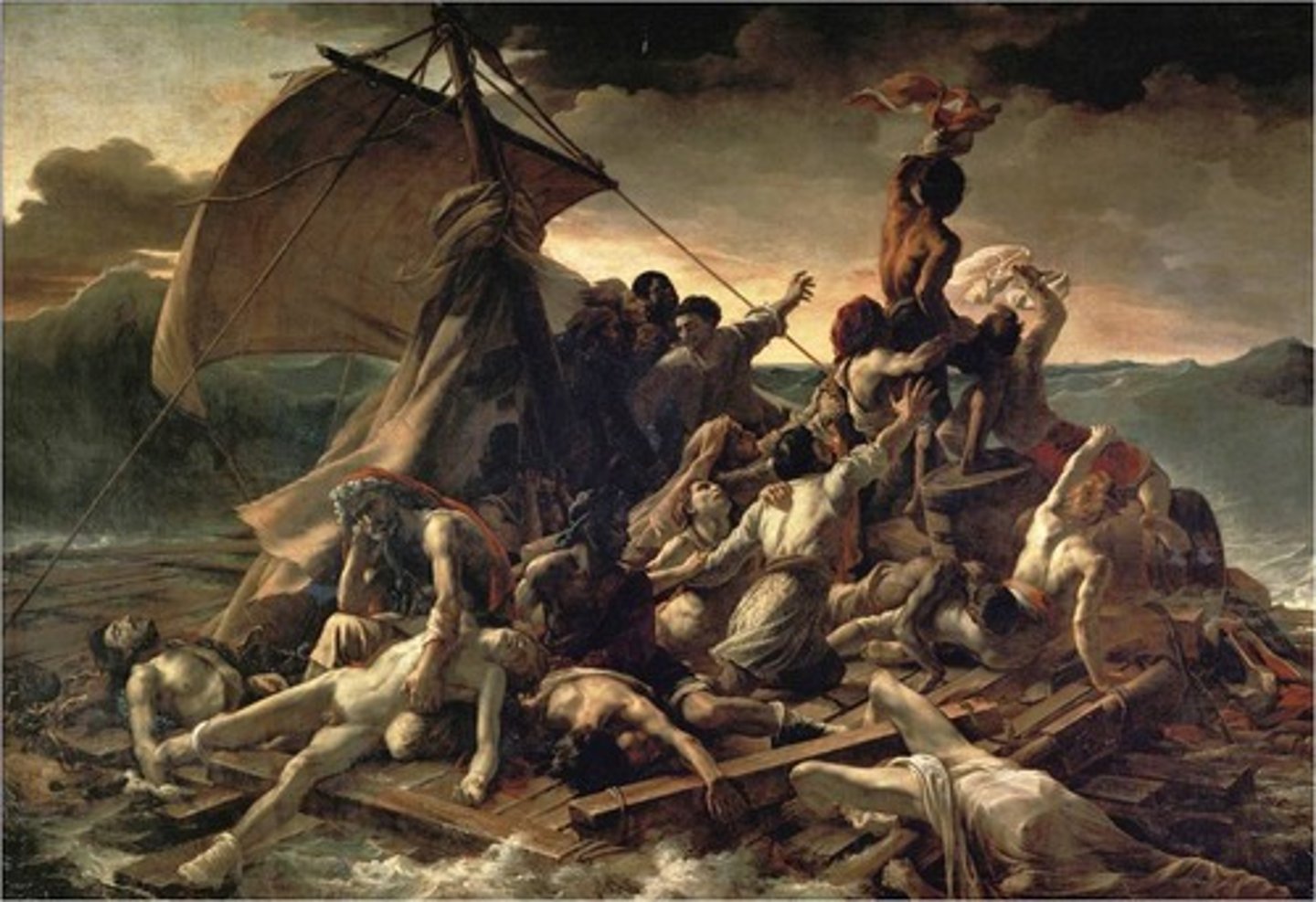
Géricault, 1818-1819, Romanticism
The Raft of the Medusa

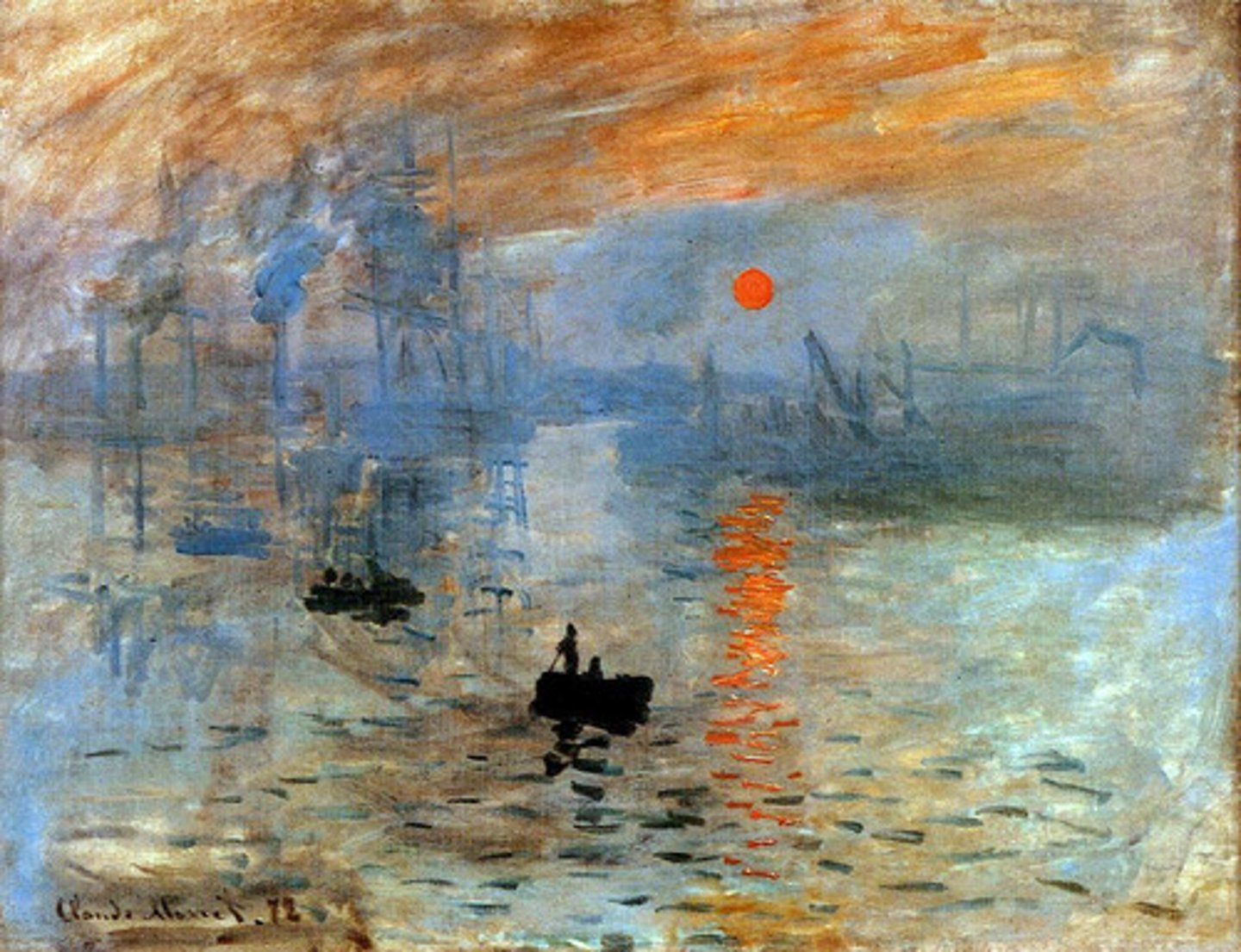
Monet, 1872, Impressionism
Impression, Sunrise
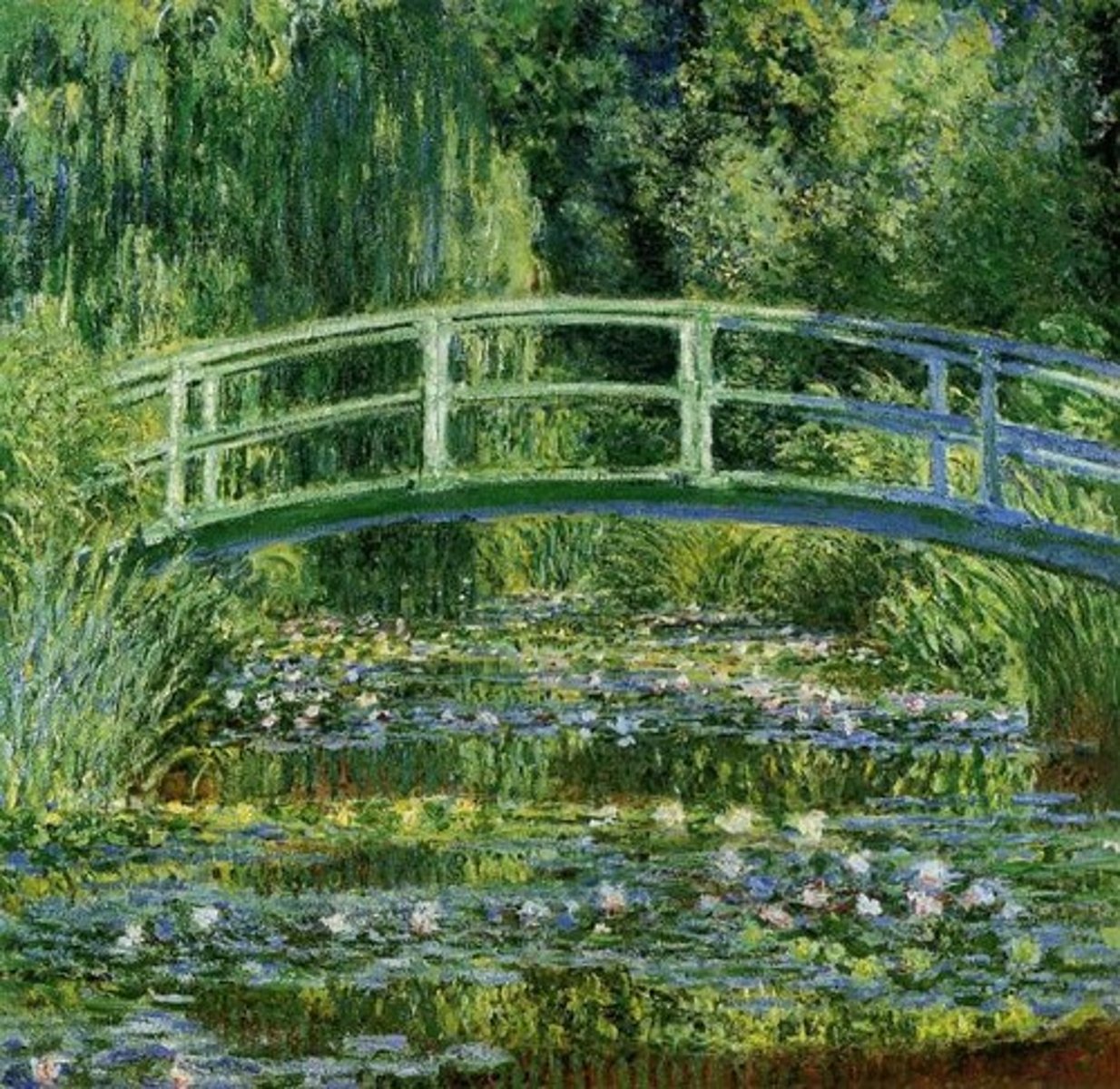
Monet, 1899, Impressionism
The Water-Lily Pond

Van Gogh, 1889, Post-Impressionism
The Starry Night

Seurat, 1884-1886, Post-Impressionism
A Sunday Afternoon on the Island of La Grande Jatte
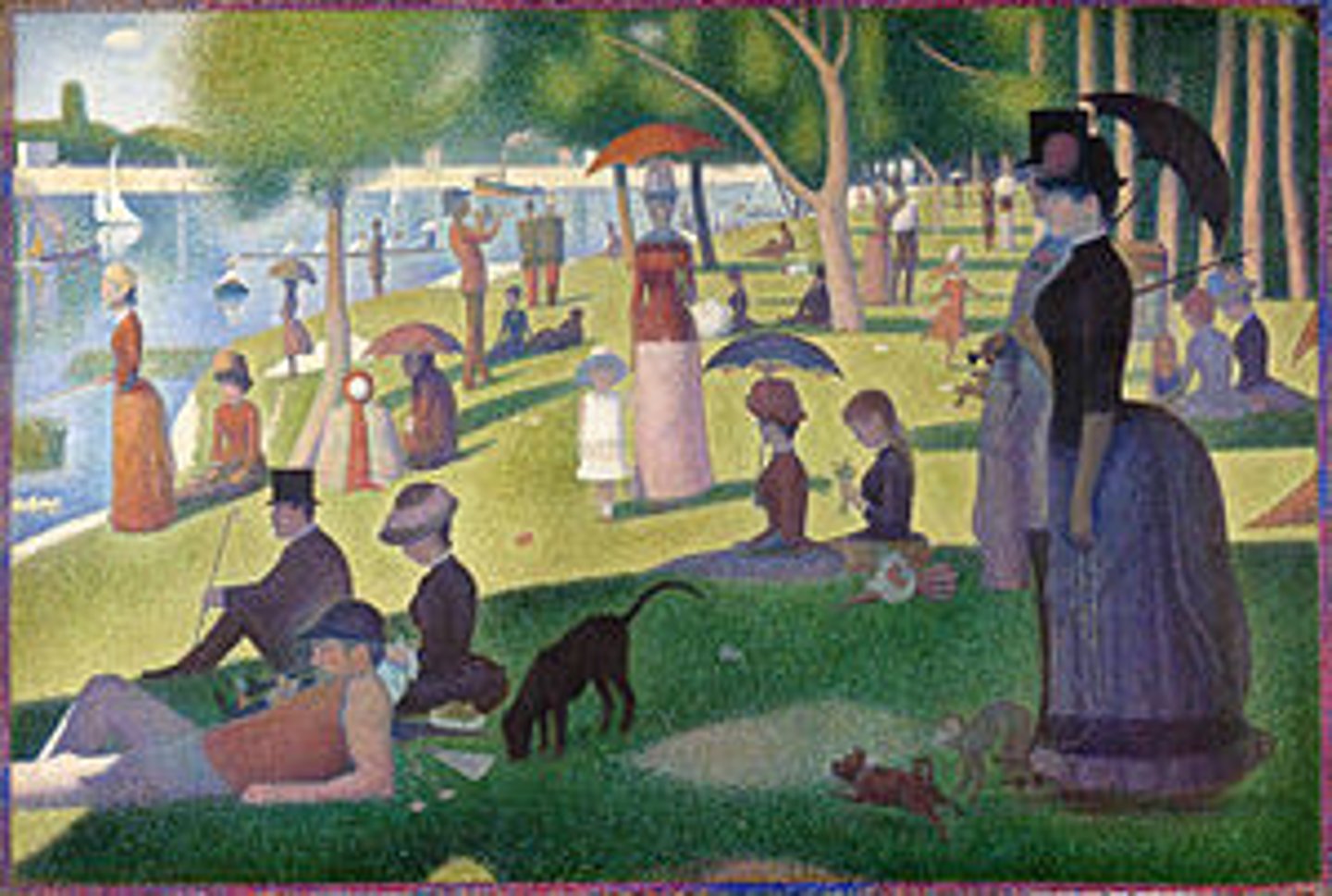
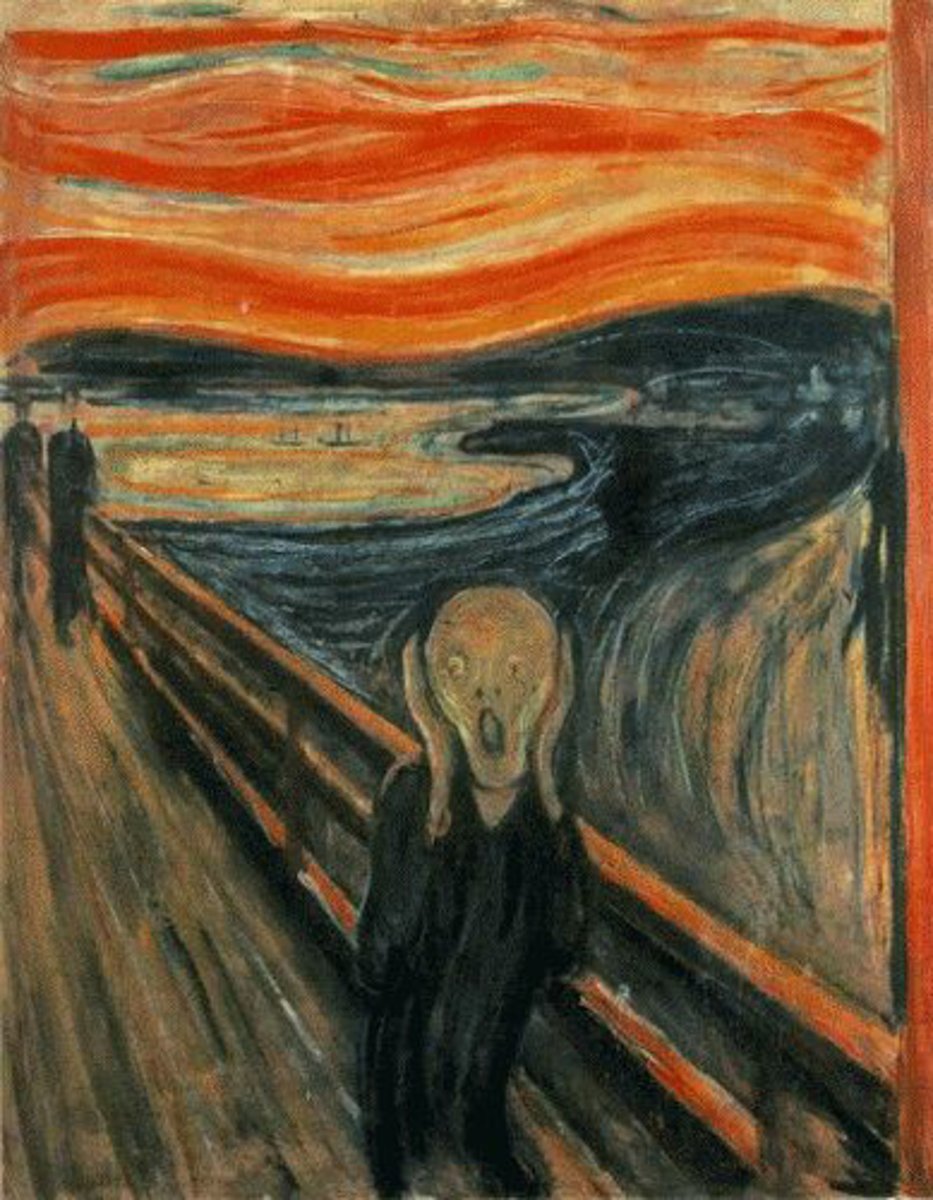
Munch, 1893, Expressionism
The Scream

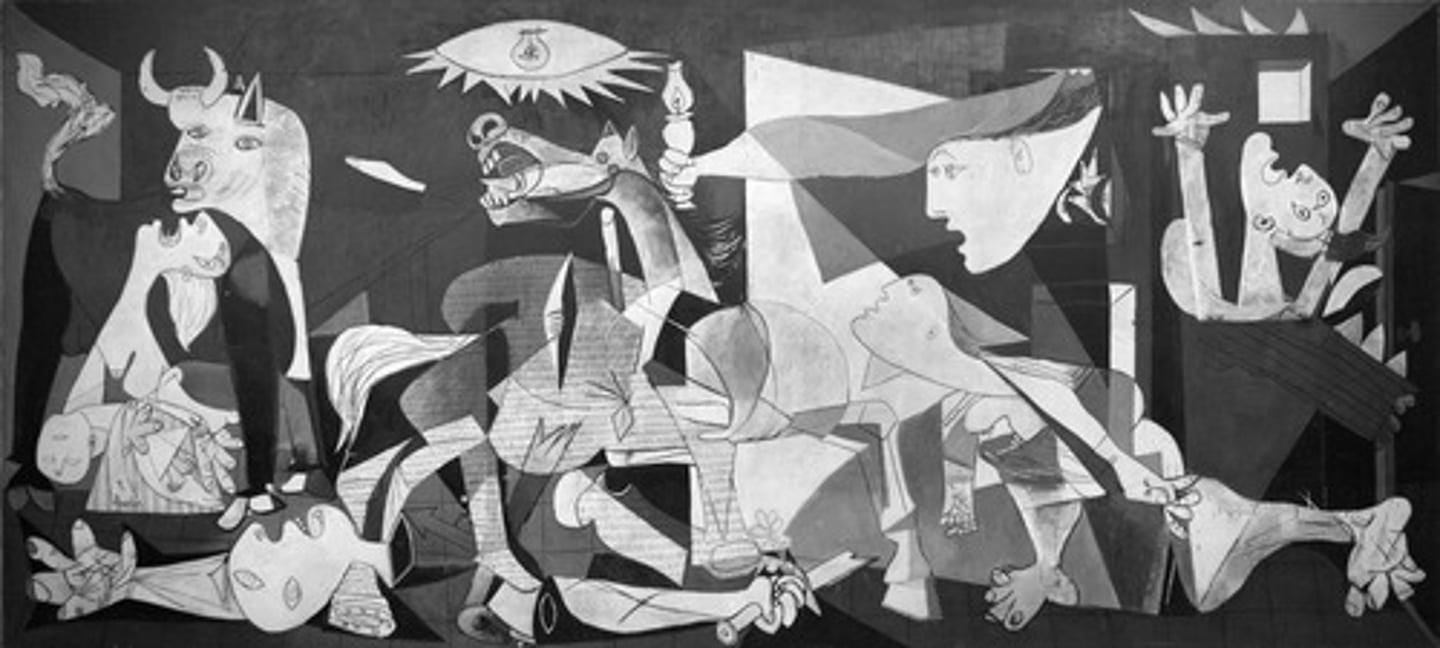
Picasso, 1937, Cubism
Guernica

Focused only on religious themes, unrealistic and 2 dimensional (5th-15th centuries)
Medieval
A revival of classical ideas (greek/roman) that emphasized humanism/realism, moving away from religious themes (1350-1620)
Renaissance
Focused on capturing everyday life and the world in extreme detail, using oil paints (1400-1600)
Northern Renaissance
A reaction against the symmetry of renaissance art incorporating motion/emotion, used by catholic church (1600-1750)
Baroque
An artistic style that replaced baroque, highly secular, emphasizing grace, charm, and gentle action (1720-1760)
Rococo
A reaction to baroque and rococo art, reverting back to renaissance themes of straight, clear, lines and roman/greek ideals (1760-1840/50)
Neoclassism
Appealed to emotion rather than reason, emphasis on nature and a rejection of classism (1780-1850)
Romanticism
Captured fleeting moments and the effect of light/color, focused on ordinary subjects (1860-1880)
Impressionism
Rejected the limitations of Impressionism, distorting forms by emphasizing geometric forms and using unnatural/random colors (1886-1905)
Post-Impressionism
A break from traditional art, moving more towards abstraction and a focus on modern themes of industrialization/war
20th Century Art
Emphasized the artists inner emotions over reality, bold colors, distorted forms (~1905-1920)
Expressionism
Subject matter is portrayed by geometric forms, emphasizing the 2-dimensionality of the canvas (1907-1914)
Cubism
Accepted all open standards of art and behavior and delighted in outrageous conduct (1920-1930)
Dadaism
Italian Renaissance painter known for blending science and art, in his works “Mona Lisa” and “The Last Supper” (1452-1519)
Leonardo da Vinci
Italian Renaissance painter/sculptor/architect known for his representation of High Renaissance artistic styles in the Sistine Chapel or “David” (1475-1564)
Michelangelo
Italian Renaissance painter/architect known for his mastery of the frescoes shown in “The School of Athens” (1483-1520)
Raphael
Flemish Northern Renaissance painter known for his realistic, 3 dimensional works shown in “Arnolfini Portrait” (1390-1441)
Jan Van Eyck
Italian Baroque sculptor known for developing the Baroque style of sculpture shown in “Apollo and Daphne” (1598-1680)
Gian Lorenzo Bernini
French Rococo painter known for spurring a revival of interest in color and movement, shown in “The Embarkation Cythera” (1684-1721)
Jean-Antoine Watteau
French Neoclassical painter known for his works “Oath of the Horatii” and “The Death of Marat” (1748-1825)
Jacques-Louis David
English Romantic painter, known as “the painter of light” because of his interest in color used to portray the “mood” of the artwork, shown in “The Fighting Temeraire” and “The Shipwreck” (1775-1851)
J. M. W. Turner
French Realist painter, known for his paintings of peasant farmers like “The Gleaners” and “The Man with the Hoe” (1814-1875)
Jean-François Millet
French Impressionist painter and leader of the impressionist movement by experimenting with natural light and bright colors, shown in works like “Impression, Sunrise” and “The Water Lily Pond” (1840-1926)
Claude Monet
French Post-Impressionist painter known as the “father of modern art” because of his analytical approach to nature, bridging the gap between Impressionism and 20th Century Art, shown in “The Card Players” and “The Basket of Apples” (1839-1906)
Paul Cézanne
Dutch Post-Impressionist painter known for his vivid colors and expressive brushwork, shown in “The Starry Night” and “Café Terrace at Night” (1853-1890)
Vincent Van Gogh
Spanish 20th Century painter/sculptor known for founding Cubism, shown in “Guernica” (1881-1973)
Pablo Picasso