BCM. 32 Photorespiration, C4 and CAM
1/20
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
21 Terms
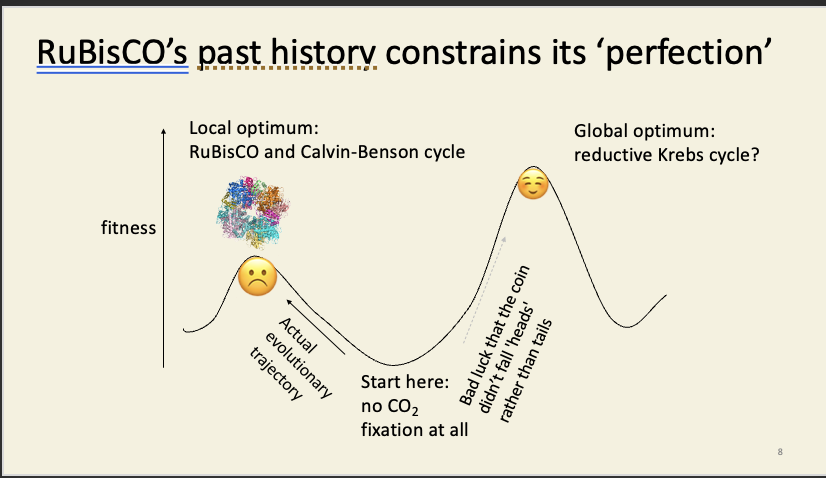
As are your eyes: your retina is wired in ‘backwards’, resulting in a blind spot. Cephalopod eyes are wired in in the logical way.
But there’s no way to get from our misdesigned eyes to the cephalopod-like system, because all intermediate steps (eyes partly wired-in right) would be worse than what we have already, and would therefore be less fit (leave fewer offspring on average).
We are stuck on our local peak unless the landscape shifts significantly, e.g. if – as a species, over a long timeframe – we no longer needed eyes (like a cave fish) and/or relied on some other sense (e.g. sonar), then the trough of despair would be less deep, and might then become traversable should we later come to need eyes again.
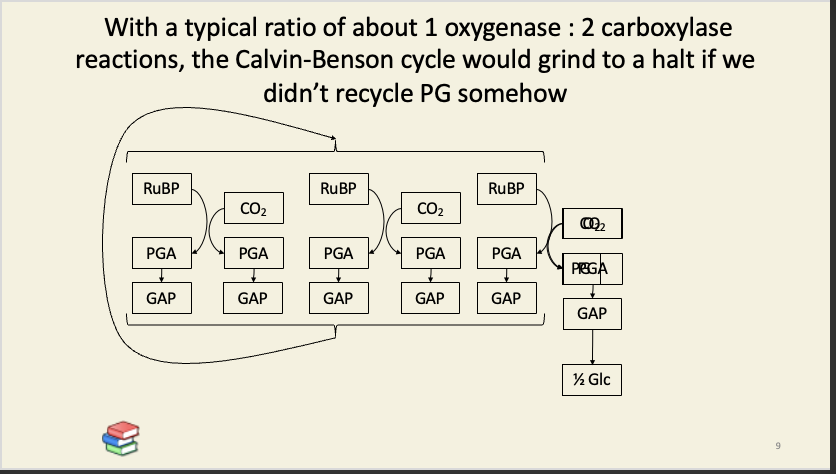
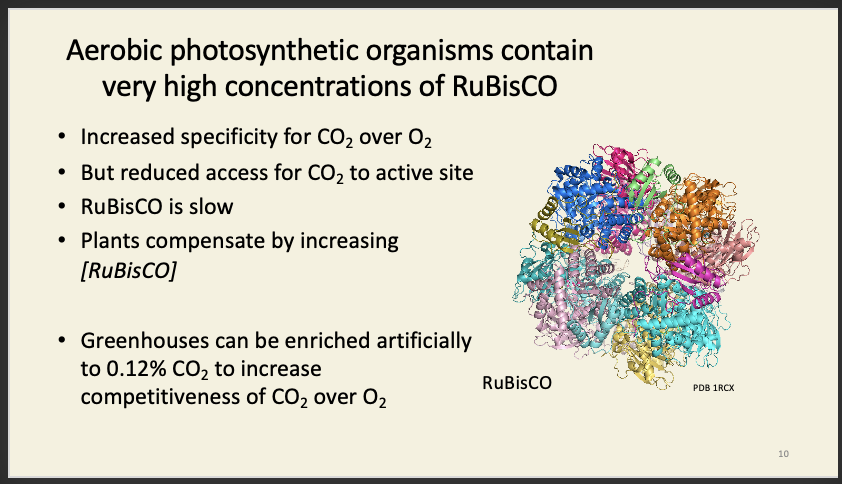
This is like security at an airport: better security (higher specificity) means longer queues (slower reactions) means more security guards (more RuBisCO).
Algae and bacteria can concentrate C02 and RuBisCO
some algae have HCO3- ion pumps in cell membrane, and carbonic anhydrase packed into ‘pyrenoids’ in the stroma
some bacteria pack RuBisCO into icosahedral carboxysomes along with carbonic anhydrase

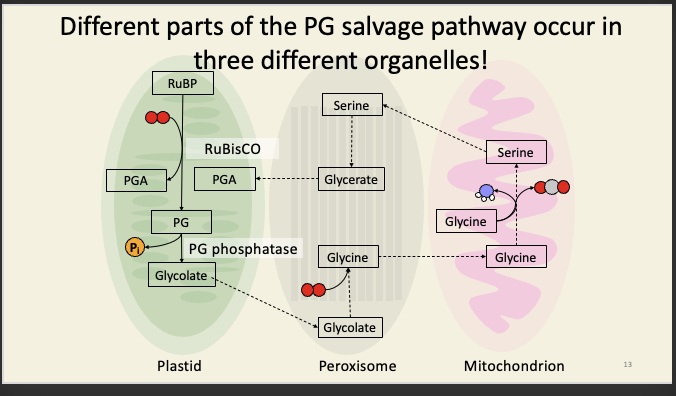
The ammonia is recycled into an amino group in the plastid, using the glutamine synthetase pathway we discussed in BCM. This consumes reducing equivalents. A reducing equivalent is just a cofactor/currency that donates electrons and which could be interchanged with NAD(P)H: e.g. ferredoxin, thiol groups, etc.
C4 metabolism is a neater adaptation against photorespiration found in many sub/tropical plants
C4 plants include maize (Zea mays) and sugarcane (Saccharum officinarum)
but most of our crops are C3, includeing wheat (Triticum aestivum), rice (Orzya sativa), and potato (Solanum tuberosum)
C4 was discovered by Hatch and Slack feeding 14CO2 to sugarcane → first, products were C4 acids, not C3 PGA (Malic acid, Oxaloacetic acid, Aspartic acid)
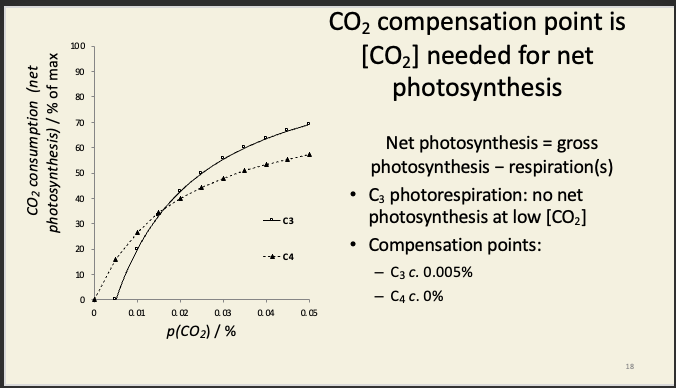
Suppression of photorespiration by C4 allows a plant to withstand stress
Stomata narrow/close during water stress
[CO2] in mesophyll falls to compensation point
this is lower in C4 plants
only half as much water lost
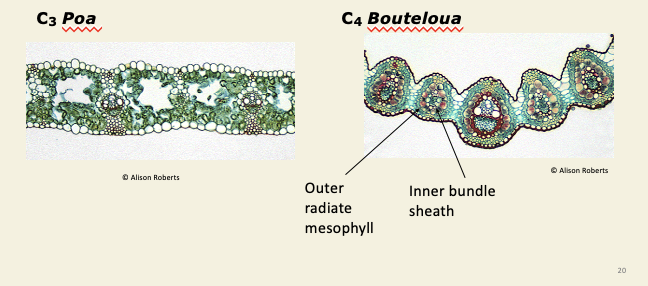
C4 plants show kranz anatomy - photosynthetic tissue is concentrated around veins
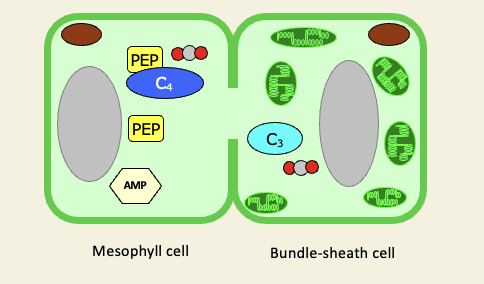
In C4 plants, what is the initial CO2 assimilation done by
assimilation is by PEP carboxylase in mesophyll, not RuBisCO
RuBisCO is still needed, but is separated into bundle sheath
PEP+CO2+H20 → Oxaloacetate + Pi
General anatomy of the C4 biochemical pump
CO2 fixation by PEP carboxylase occurs in the mesophyll resulting in C4 acids translocated into bundle-sheath and decarboxylated
C02 enters Calvin cycle via Rubisco as usual
C3 fragment is returned to the mesophyll and metabolised back to PEP
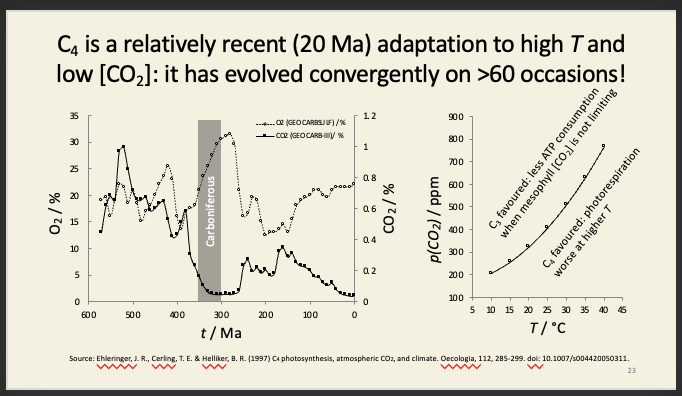
RuBisCO discriminates a little between 13C and 12C, preferentially incorporating the latter into PGA.
PEP carboxylase does not discriminate against 13C nearly so much, so the ratio of 12C to 13C can be used to determine whether fossil plant material (or indeed, a bag of sugar from beet vs. sugar cane) used C3 or C4 photosynthesis.
Crassulacean acid metabolism (CAM) plants is like C4++
mostly succulent xerophytes or epiphytes e.g. cactuses, crassula, pineapple
NADP-ME but no kranz anatomy
has evolved on more than 30 occasions
slow growing, few crops
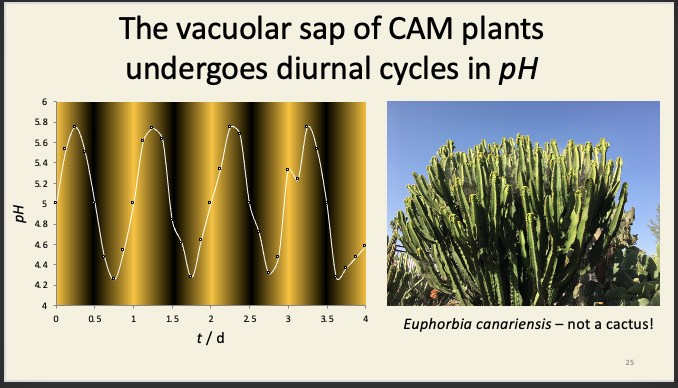
CAM separates PEP carboxylase and rubisco temporarily, whereas C4 metabolism spatially separates them
CAM storage mechanism
Night:
Stomata open
CO2 fixed by PEP carboxylase
Day:
Stomata closed
Stored malate in vacuole
Consumed by Rubisco