Chapter 16 (Marieb) The Endocrine System
1/77
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
78 Terms
D) cortisol
Gluconeogenesis occurs in the liver due to the action of ________.
A) aldosterone
B) insulin
C) secretin
D) cortisol
D) thymus gland
Normal development of the immune response is due in part to hormones produced by the ________.
A) adrenal medulla
B) pancreas
C) thyroid gland
D) thymus gland
D) second messengers
Virtually all of the protein or amino acid-based hormones exert their effects through intracellular ________.
A) ions
B) deactivators
C) nucleotides
D) second messengers
A) enzyme
Which of the following is not a category of endocrine gland stimulus?
A) enzyme
B) humoral
C) neural
D) hormonal
D) hormones
Chemical substances secreted by cells into the extracellular fluids and that regulate the metabolic function of other cells in the body are called ________.
A) enzymes
B) antibodies
C) proteins
D) hormones
B) is partly contained within the infundibulum
The hypothalamic-hypophyseal tract ________.
A) connects the hypophysis to the pituitary gland
B) is partly contained within the infundibulum
C) conducts aldosterone to the hypophysis
D) is the site of prolactin synthesis
D) All of these are signs.
Which of the following is not a cardinal sign of diabetes mellitus?
A) polyuria
B) polydipsia
C) polyphagia
D) All of these are signs.
B) type of hormone
Which of the choices below is not a factor required for target cell activation by hormone receptor interaction?
A) blood levels of hormone
B) type of hormone
C) number of receptors for that hormone
D) strength of the bond between the receptor and hormone
A) release is an example of a positive feedback control mechanism
Oxytocin ________.
A) release is an example of a positive feedback control mechanism
B) is an adenohypophyseal secretion
C) exerts its most important effects during menstruation
D) controls milk production
D) is inhibited by alcohol
ADH ________.
A) increases urine production
B) promotes dehydration
C) is produced in the adenohypophysis
D) is inhibited by alcohol
A) entering some cells and binding to intracellular receptors within the nuclei
Thyroid hormone exerts its influence by ________.
A) entering some cells and binding to intracellular receptors within the nuclei
B) exerting only a minor effect on body metabolism
C) causing a reduction in the number of blood vessel adrenergic receptors, and therefore decreasing blood pressure
D) acting to decrease basal metabolic rate
B) production by the adrenal gland is insignificant compared with sex hormone release from the gonads during late puberty
Gonadocorticoid(s) ________.
A) synthesized by the adrenal medulla are primarily androgens
B) production by the adrenal gland is insignificant compared with sex hormone release from the gonads during late puberty
C) secretion inhibition is highly dependent on a negative feedback loop involving ACTH
D) hypersecretion can result in adrenogenital syndrome, also called feminization
C) down-regulation
Sometimes prolonged excessive exposure to high hormone concentrations causes a phenomenon known as ________.
A) diabetes mellitus
B) cellular inhibition
C) down-regulation
D) metabolism of protein kinases
D) direct control of the nervous system
Which of the following is not a change that may be caused by hormonal stimulus?
A) a change in membrane potential
B) the stimulation of a genetic event resulting in protein synthesis
C) an increase in enzymatic activity
D) direct control of the nervous system
C) the presence of the appropriate receptors on the cells of the target tissue or organ
The ability of a specific tissue or organ to respond to the presence of a hormone is dependent on ________.
A) the location of the tissue or organ with respect to the circulatory path
B) the membrane potential of the cells of the target organ
C) the presence of the appropriate receptors on the cells of the target tissue or organ
D) nothingall hormones of the human body are able to stimulate any and all cell types because hormones are powerful and nonspecific
C) hypophyseal portal system
Several hormones are synthesized in the hypothalamus and transported to the anterior pituitary gland. The mechanism of transportation from hypothalamus to anterior pituitary gland is through the ________.
A) hepatic portal system
B) general circulatory system
C) hypophyseal portal system
D) feedback loop
D) it is only a hormone storage area that receives hormones from the hypothalamus for release
The neurohypophysis or posterior lobe of the pituitary gland is not a true endocrine gland because ________.
A) it is strictly a part of the neural system and has little or nothing to do with hormonal release
B) embryonically it was an endocrine tissue, but in the adult human it is no longer functional
C) it is unable to function as an endocrine tissue because it is actually part of the neural system due to its location
D) it is only a hormone storage area that receives hormones from the hypothalamus for release
A) entering the nucleus of a cell and initiating or altering the expression of a gene
Steroid hormones exert their action by ________.
A) entering the nucleus of a cell and initiating or altering the expression of a gene
B) finding an appropriate cell receptor and initiating cAMP activity
C) stimulating the synthesis of a glycogen
D) increasing blood pressure
D) binding to specific receptors and employing the services of G proteins and cAMP
The second-messenger mechanism of hormone action operates by ________.
A) synthesizing more of the hormone than is actually needed
B) increasing the basal metabolic rate in the target organ
C) not responding to a feedback mechanism
D) binding to specific receptors and employing the services of G proteins and cAMP
D) during protein kinase activation, enzymes phosphorylate many other enzymes
Hormones often cause a cell to elicit multiple responses; this is because ________.
A) there are thousands of receptors on the cell membrane
B) the receptors bind to several hormones at the same time
C) the protein kinases are rapidly metabolized
D) during protein kinase activation, enzymes phosphorylate many other enzymes
C) G protein acts as the link between first and second messengers
Cells that respond to peptide hormones usually do so through a sequence of biochemical reactions involving receptor and kinase activation. In order for cells to respond, it is necessary for first and second messengers to communicate. This is possible because ________.
A) peptide hormones always enter the cell membrane and elicit a response without assistance from other messengers
B) hormones alter cellular operations through stimulation of a gene directly
C) G protein acts as the link between first and second messengers
D) the hormone receptor complex moves into the cytoplasm as a unit
B) steroid hormones, because both diffuse easily into target cells
Thyroid hormone (a small iodinated amine) enters target cells in a manner similar to ________.
A) insulin, because insulin is a small peptide
B) steroid hormones, because both diffuse easily into target cells
C) growth hormone, because the thyroid works synergistically with thyroid hormone
D) glucagon, because the structure of glucagon is similar to that of thyroid hormone
B) epinephrine
When it becomes necessary to enlist the fight-or-flight response, a hormone that is released during the alarm phase of the general adaptation syndrome is ________.
A) estrogen
B) epinephrine
C) angiotensinogen
D) renin
D) humoral stimulation
One of the least complicated of the endocrine control systems directly responds to changing blood levels of ions and nutrients. Which of the following describes this mechanism?
A) the rapid oxidation of carbohydrates
B) catabolic inhibition
C) protein synthesis
D) humoral stimulation
D) bones and skeletal muscles
The major targets of growth hormone are ________.
A) the blood vessels
B) the adrenal glands
C) the liver
D) bones and skeletal muscles
B) targeting the bone and activating osteoclasts so that calcium will be released
The parathyroid glands maintain adequate levels of blood calcium. This is accomplished through ________.
A) blocking the action of growth hormone
B) targeting the bone and activating osteoclasts so that calcium will be released
C) antagonizing the synthesis of calcitonin
D) slowing the activity of tissues that require calcium for activity
A) the heart
Which organ is responsible for synthesizing ANP?
A) the heart
B) the kidney
C) the skin
D) the spleen
C) cortisol
Mineralocorticoid is to aldosterone as glucocorticoid is to ________.
A) testosterone
B) estrogen
C) cortisol
D) epinephrine
B) adipocytes
Leptin is secreted by ________.
A) lymphocytes
B) adipocytes
C) goblet cells
D) fibroblasts
B) aldosterone
The most important regulator of electrolyte concentrations in extracellular fluids is ________.
A) insulin
B) aldosterone
C) glucagon
D) cortisol
C) epinephrine
Which of the following is not a steroid-based hormone?
A) estrogen
B) aldosterone
C) epinephrine
D) cortisone
D) a hormone-receptor complex that interacts directly with the cell's DNA
Which of the following would be associated with the action of steroids on cells?
A) extracellular receptors with a specificity for only a single amino acid sequence on the hormone
B) an enzyme that catalyzes the formation of cyclic AMP
C) second-messenger systems
D) a hormone-receptor complex that interacts directly with the cell's DNA
A) possible activation of several different second-messenger systems
Cellular responses to hormones that initiate second-messenger systems include ________.
A) possible activation of several different second-messenger systems
B) cyclic AMP phosphodiesterase formation of an active second messenger
C) formation of a specific protein kinase that acts on a series of extracellular intermediates
D) hormone binding to intracellular receptors
D) first enter into the hypophyseal portal system
Regulating hormones from the hypothalamus ________.
A) enter venous circulation and travel to the heart, which pumps the hormone-containing blood to the pituitary
B) enter the hepatic portal system, which feeds the pituitary
C) travel by arteries to the pituitary
D) first enter into the hypophyseal portal system
B) secretion is regulated by a hypothalamic secretion
ACTH ________.
A) is secreted by the posterior pituitary
B) secretion is regulated by a hypothalamic secretion
C) causes the release of hormones from the adrenal medulla
D) is not a tropic hormone
D) Parathyroid hormone is the single most important regulator of calcium levels in the blood.
Which of the following is true about calcium homeostasis?
A) Increased calcitonin levels will cause increased blood calcium levels.
B) High calcium levels cause bone resorption.
C) Parathyroid hormone causes an increase in osteoblast activity.
D) Parathyroid hormone is the single most important regulator of calcium levels in the blood.
B) functions to increase sodium reabsorption
Aldosterone ________.
A) is secreted by the neurohypophysis
B) functions to increase sodium reabsorption
C) presence increases potassium concentration in the blood
D) production is greatly influenced by ACTH
A) TH
The only amine hormone to act like a steroid is ________.
A) TH
B) ACTH
C) GH
D) ADH
C) liver
Which organ does not have hormone production?
A) heart
B) kidney
C) liver
D) skin
C) up-regulation
In circumstances where the body requires prolonged or increased levels of a hormone, the DNA of target cells will specify the synthesis of more receptors on the surface of the cells of the target organ. This is known as ________.
A) the cell's sensitivity reaction
B) cellular affinity
C) up-regulation
D) a reaction to a stressor
C) hydrocortisones
Eicosanoids do not include ________.
A) paracrines
B) leukotrienes
C) hydrocortisones
D) prostaglandins
C) FSH stimulates sperm production in the testes.
A man has been told that he is not synthesizing enough follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH), and for this reason he may be unable to father a child. Choose the correct statement to explain this problem.
A) FSH stimulates estrogen secretion by ovarian cells; therefore it is not synthesized by males.
B) The physician is wronga hormone made in the adenohypophysis could not influence fertility.
C) FSH stimulates sperm production in the testes.
D) The man must be producing progesterone, which inhibits the synthesis of FSH.
A) liver
Which of the following organs is affected by thyroid hormone in adults?
A) liver
B) spleen
C) thyroid gland
D) brain
B) It does not require a second messenger to effect a response.
Thyroxine is a peptide hormone, but its mechanism is different from other peptide hormones. Which of the following statements is true concerning this difference?
A) It causes positive feedback.
B) It does not require a second messenger to effect a response.
C) It is very specific in the cell type it targets.
D) It is a stimulant of cellular metabolism and targets all cells.
A) by increasing blood glucose, fatty acid, and amino acid levels and enhancing blood pressure
How do glucocorticoids enable the body to deal appropriately with stress?
A) by increasing blood glucose, fatty acid, and amino acid levels and enhancing blood pressure
B) by decreasing the heart rate, thus decreasing blood pressure
C) by stimulating the pancreas to release insulin
D) by blocking the neurotransmitters that prepare the body for the stress response
B) calcium
What ion is sometimes used as a second messenger of amino acidbased hormones?
A) iron
B) calcium
C) sodium
D) chlorine
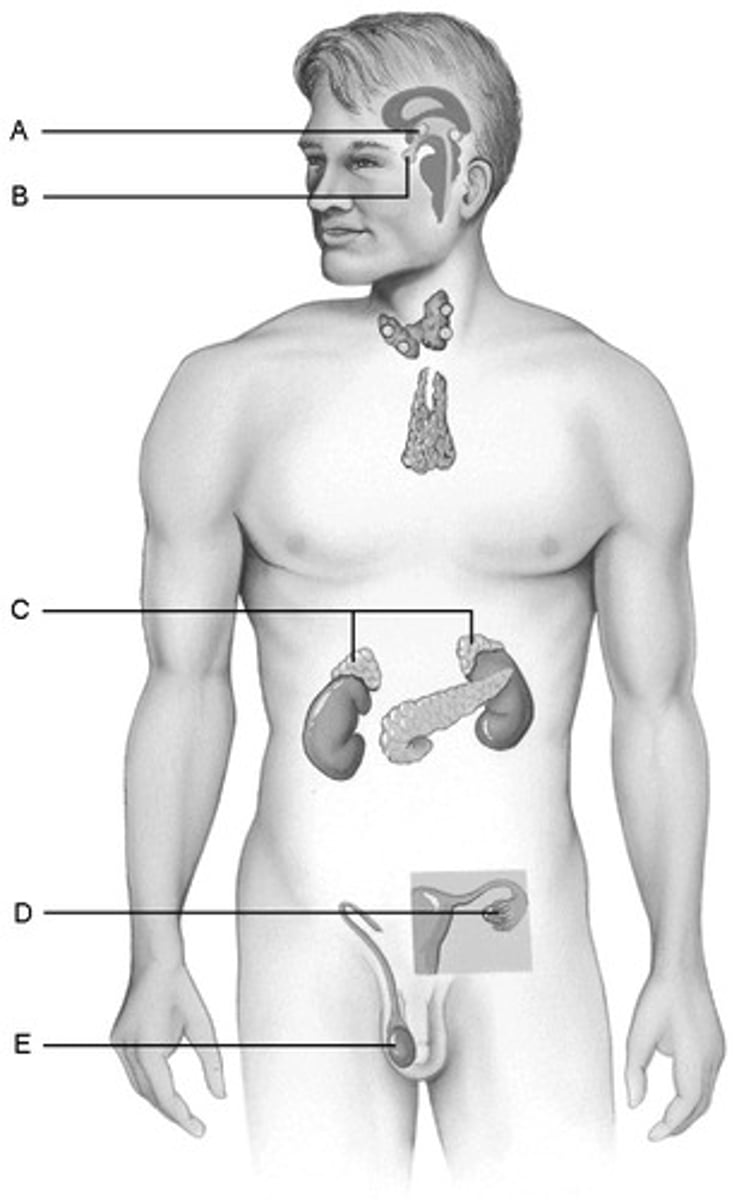
D. Ovaries
Produces hormones that promote the development of the female secondary sexual characteristics at puberty.
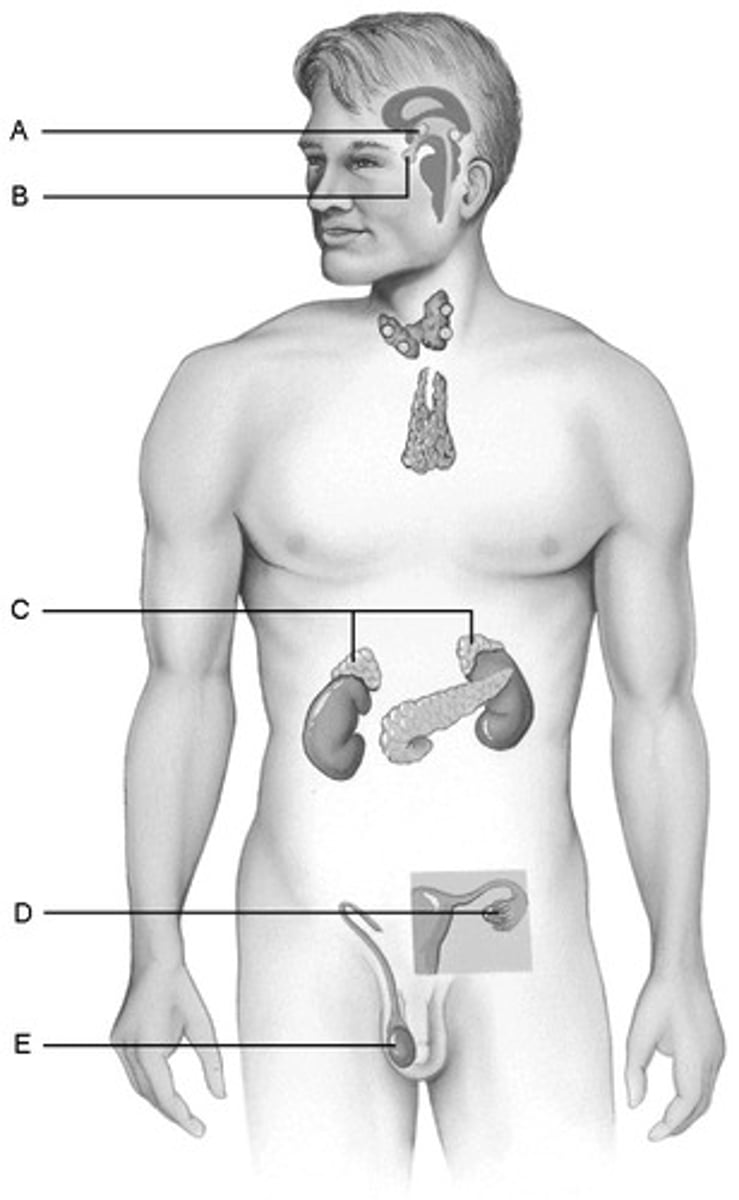
B.Pituitary Gland
Storehouse for the hormones produced by the hypothalamus of the brain
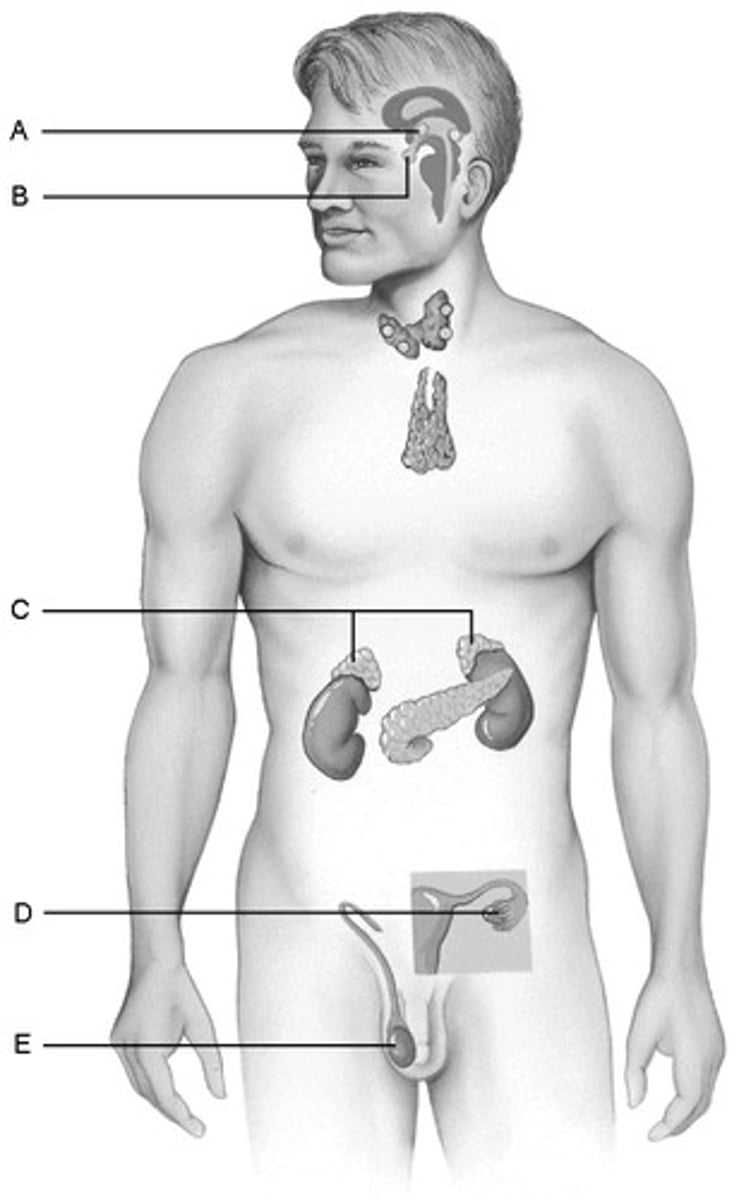
E.Testes
Produce hormones that direct the production of the secondary male sex characteristics
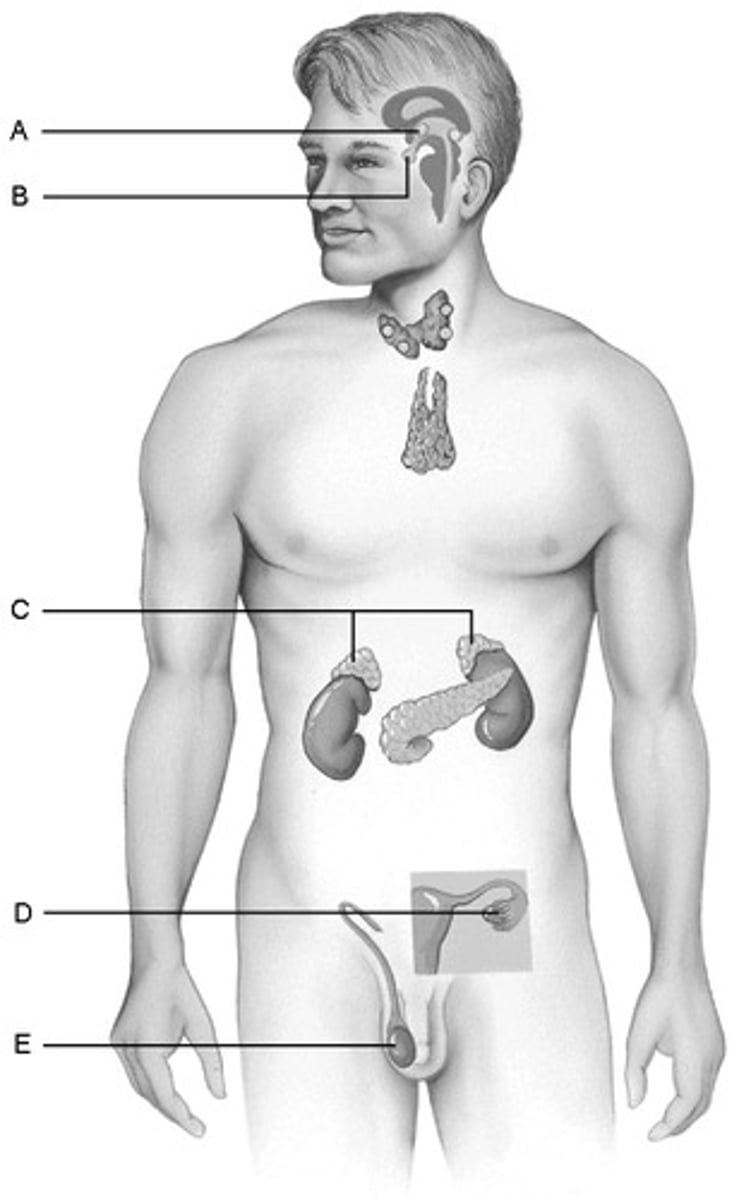
C.Adrenal glands
Produce steroid hormones and glucocorticoids and mineralocorticoids.
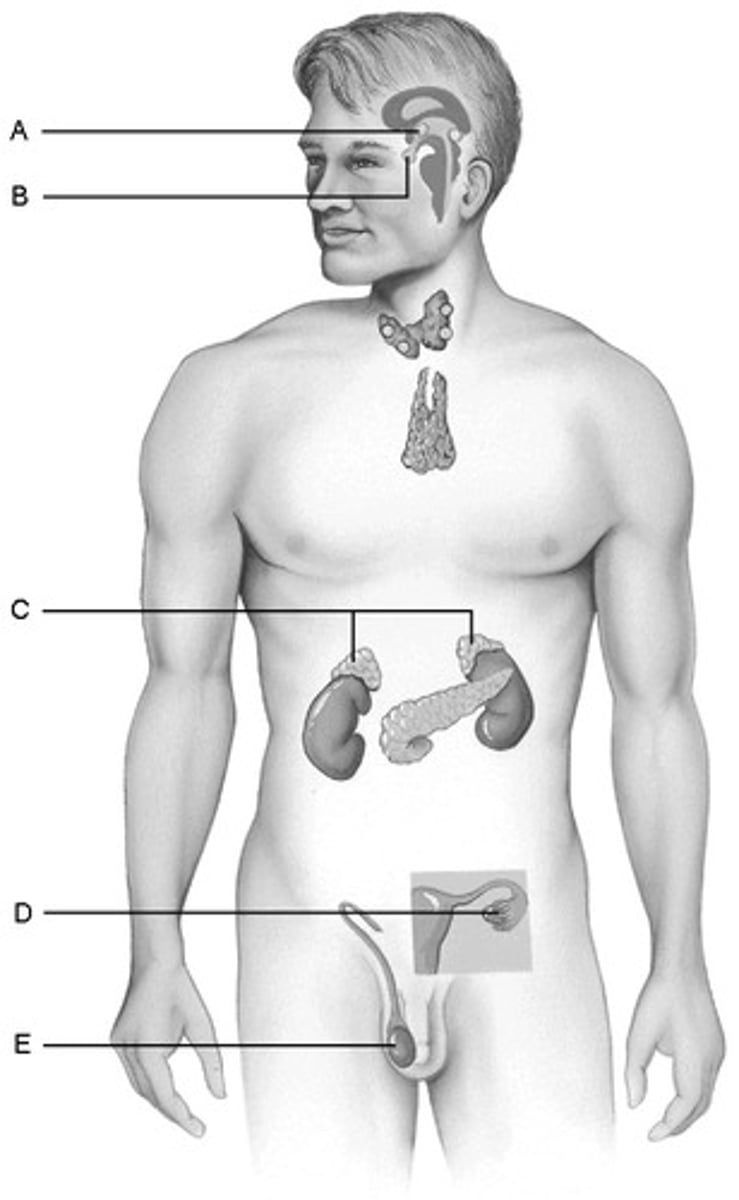
A.hypothalamus
Produces hormones and is considered a neuroendocrine organ
A
Match the following hormone with the target:
Growth Hormone-releasing hormone (GHRH)
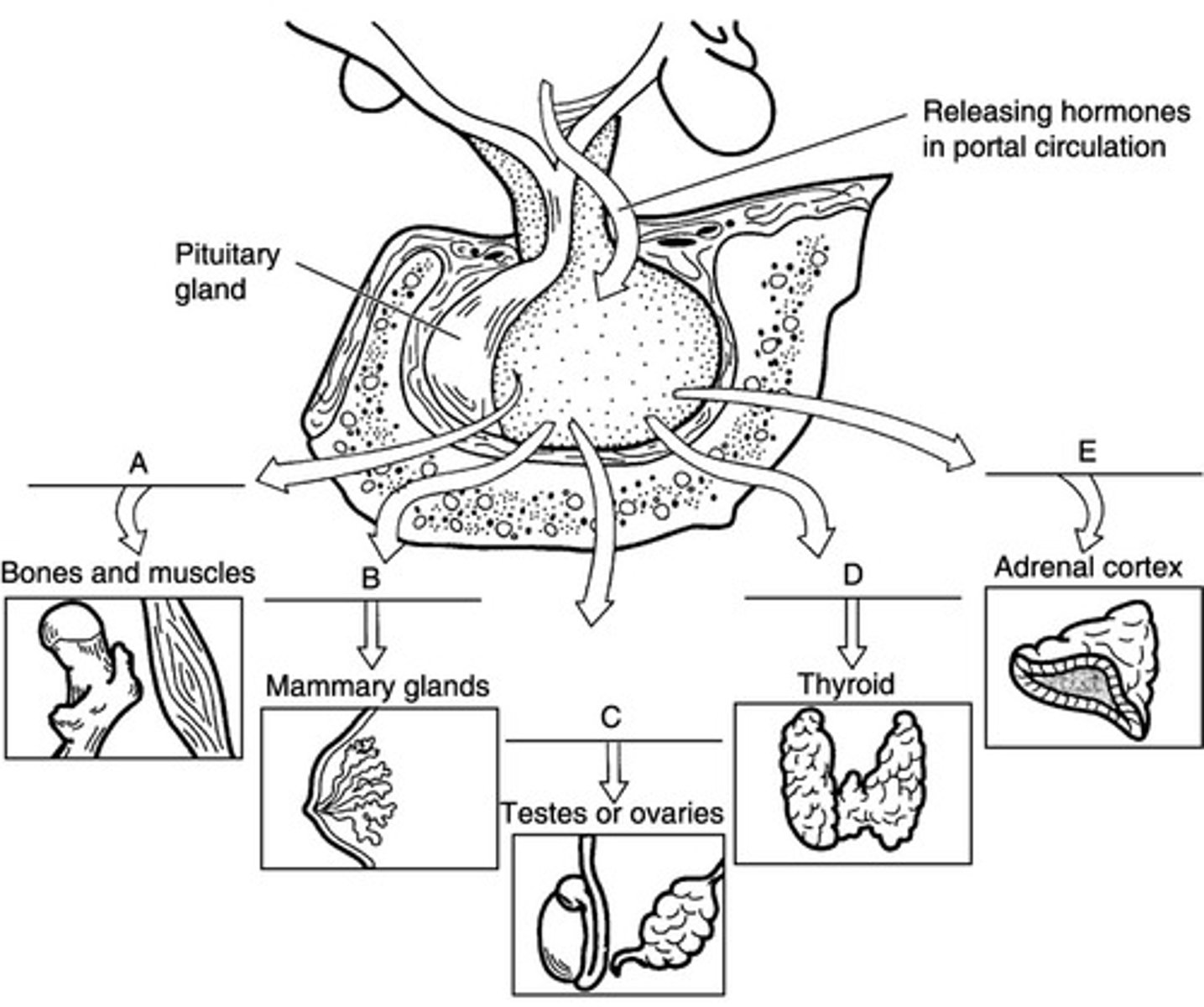
C
Match the following hormone with the target:
gonadotropin-releasing hormone (GnRH)
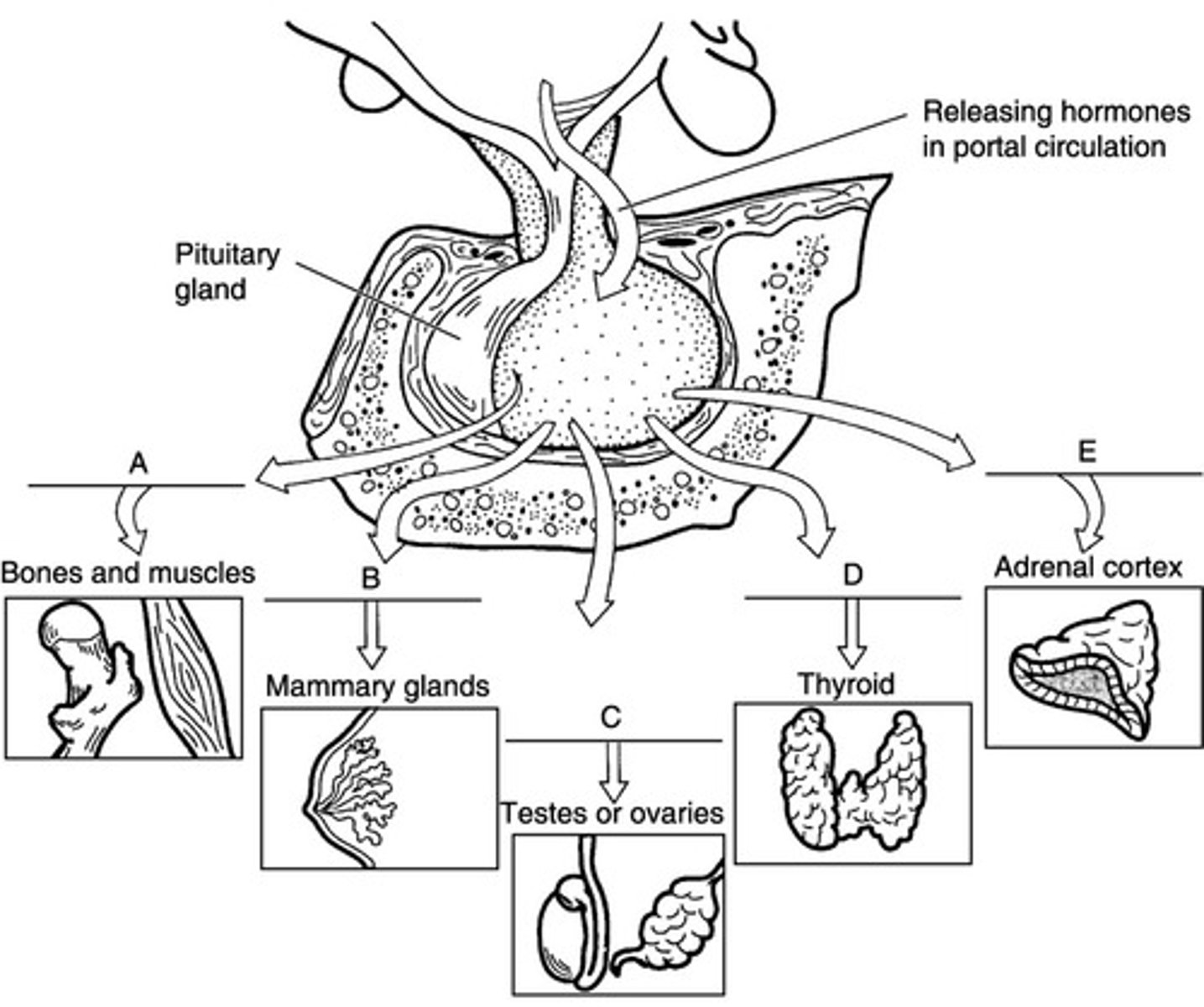
B
Match the following hormone with the target:
Prolactin-releasing hormone (PRH)
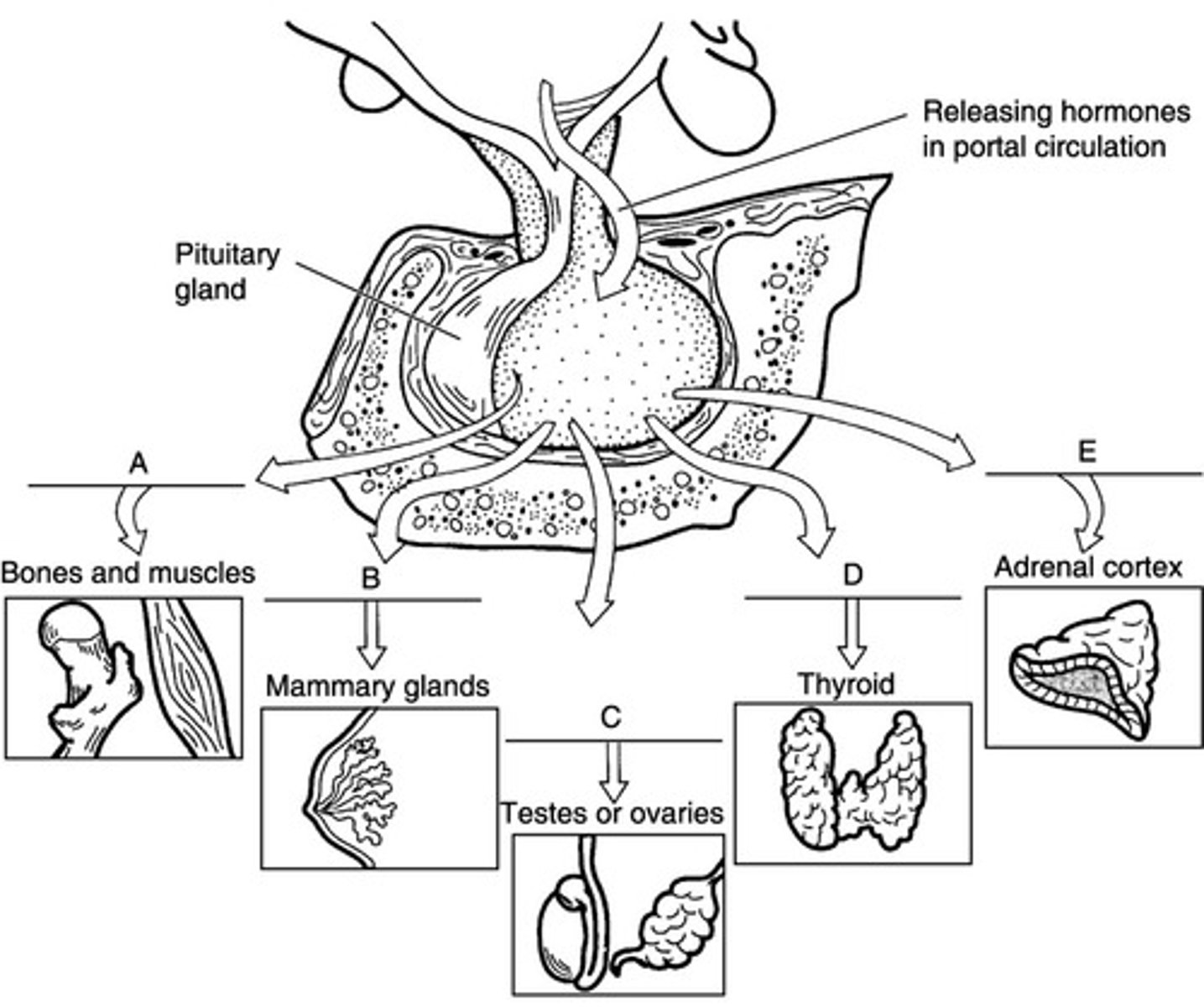
E
Match the following hormone with the target:
Corticotropin-releasing hormone (CRH)
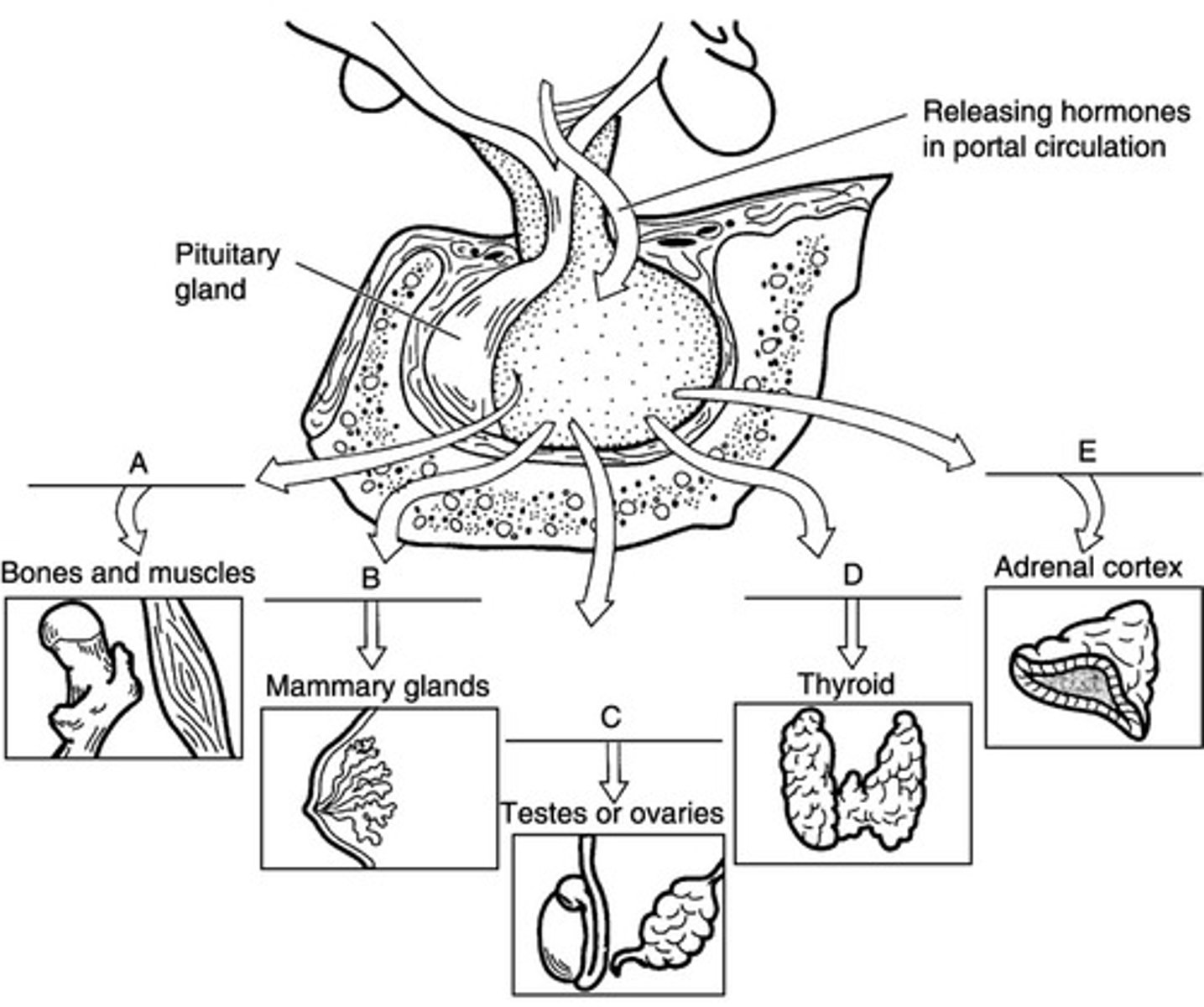
D
Match the following hormone with the target:
Thyrotropin-releasing hormong (TRH)
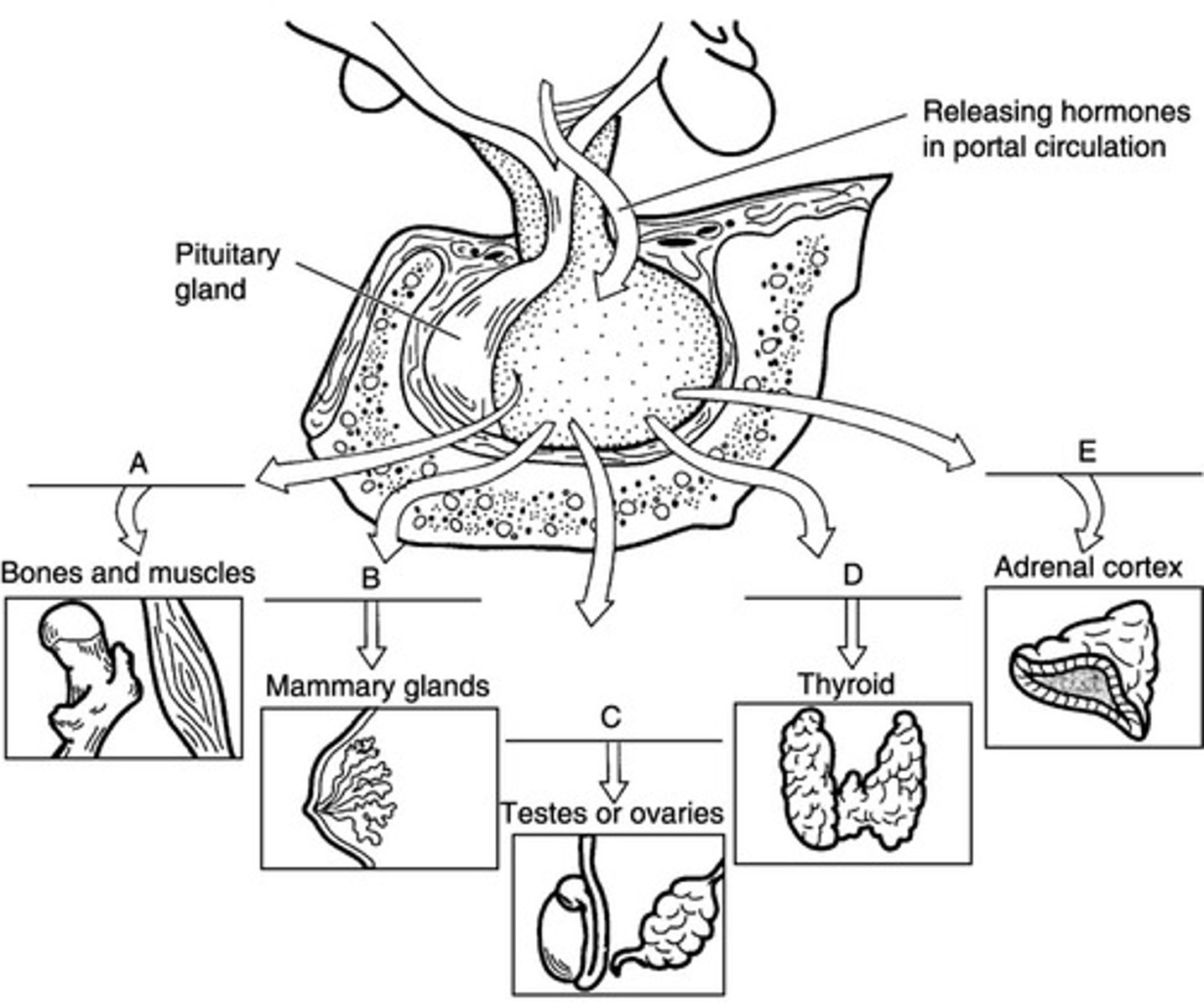
C.Grave's disease
Match the following:
A.Addison's disease
B.Acromegaly
C.Grave's disease
D.Diabetes mellitus
E.Pituitary dwarfism
An autoimmune problem involving the thyroid gland
E.Pituitary dwarfism
Match the following:
A.Addison's disease
B.Acromegaly
C.Grave's disease
D.Diabetes mellitus
E.Pituitary dwarfism
Hyposecretion of growth hormone
D.diabetes mellitus
Match the following:
A.Addison's disease
B.Acromegaly
C.Grave's disease
D.Diabetes mellitus
E.Pituitary dwarfism
hyposecretion of the pancreas
A.Addison's disease
Match the following:
A.Addison's disease
B.Acromegaly
C.Grave's disease
D.Diabetes mellitus
E.Pituitary dwarfism
Hyposecretion of the adrenal cortex
B.acromegaly
Match the following:
A.Addison's disease
B.Acromegaly
C.Grave's disease
D.Diabetes mellitus
E.Pituitary dwarfism
Hypersecretion of growth hormone
A.myxedema
Match the following:
A.Myxedema
B.Cretinism
C.Gigantism
D.Cushing's disease
hyposecretion of the thyroid in adults
D.Cushing's disease
Match the following:
A.Myxedema
B.Cretinism
C.Gigantism
D.Cushing's disease
Hypersecretion of the adrenal cortex
C.gigantism
Match the following:
A.Myxedema
B.Cretinism
C.Gigantism
D.Cushing's disease
Hypersecretion of growth hormone
B.cretinism
Match the following:
A.Myxedema
B.Cretinism
C.Gigantism
D.Cushing's disease
Hyposecretion of the thyroid in infants
C.hypophysis
Match the following:
A.Thyroid
B.Adrenal medulla
C.Hypophysis
D.Parathyroid
E.Pancreas
The size & shape of a pea; produces hormones and stimulates other endocrine glands
B.adrenal medulla
Match the following:
A.Thyroid
B.Adrenal medulla
C.Hypophysis
D.Parathyroid
E.Pancreas
The gland that controls the fight-or-flight reaction
E.pancreas
Match the following:
A.Thyroid
B.Adrenal medulla
C.Hypophysis
D.Parathyroid
E.Pancreas
produces hormones that regulate glucose levels in the body
D.parathyroid
Match the following:
A.Thyroid
B.Adrenal medulla
C.Hypophysis
D.Parathyroid
E.Pancreas
produces a hormone that controls blood levels of calcium and potassium by their removal from bone tissue
A.thyroid
Match the following:
A.Thyroid
B.Adrenal medulla
C.Hypophysis
D.Parathyroid
E.Pancreas
Produces the body's major metabolic hormones
D.Excessively high blood iodine concentrations
Factors that inhibit TSH release do NOT include ____
A.presence of ADH
B.rising levels of glucocorticoids
C.somatostatin
D.excessively high blood iodine concentrations
D.first enter into the hypophyseal portal system
Regulating hormones from the hypothalamus ____
A.enter venous circulation and travel to the heart, which pumps the hormone-containing blood to the pituitary
B.enter the hepatic portal system, which feeds the pituitary
C.travel by arteries to the pituitary
D.first enter into the hypophyseal portal system
A.include ACTH and TSH
Tropic Hormones _____
A.include ACTH and TSH
B.do NOT regulate the function of other endocrine glands
C.exert their effects on cells by direct gene activation
D.include GH and PRL
D.promotes long bone growth during the formative years
Growth hormone ______
A. is also called somatostatin
B.is regulated by humoral mechanisms
C.secretion results in a decrease in muscle mass
D.promotes long bone growth during the formative years
C.An amino acid derivative can be a hormone
Select the correct statement about hormonal structure of function
A.Prostaglandins are biologically active peptides
B.Modified cholesterol forms the main structural component of the peptone hormones
C.An amino acid derivative can be a hormone
D.an example of local hormone is testosterone
D.a hormone-receptor complex that interacts directly with cell's DNA
Which of the following would be associated with the action of steroids on cells
A.extracellular receptors with a specificity for only a single amino acid sequence on the hormone
B.an enzyme that catalyzes the formatinpo of cyclic AMP
C.second-messenger systems
D.a hormone-receptor complex that interacts directly with cell's DNA
A.possible activation of several different second-messenger systems
Cellular responses to hormones that initiate second-messenger systems include_____
A.possible activation of several different second-messenger systems
B.cyclic AMP phosphodiesterase formation of an active second messenger
C.formation of a specific protein kinase that acts on a series of extracellular intermediates
hormone binding to intracellular receptors
D.hormone binding to intracellular receptors
C.when the body's glucose level rises
Insuline, a small (51-amino acid) protein, is synthesized by the beta cells of the pancreas. This hormone is released _____
A.in excessive amounts in obese people
B.in response to severe physical stress (i.e. ten mile run)
C.when the body's glucose level rises
D.when the body's gllucose level drops