Wound Management
1/54
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
55 Terms
Wound
Any sharp injury that damages the dermis of the skin
Classification of Wounds
Clean wound
Contanminated wound
Infected wound
Clean Wound
These types of wounds are not infected, do not exhibit any signs of inflammation, and are typically closed
Cotaminated Wound
these are open traumatic or surgical wounds involving a major break in sterile technique that shows evidence of inflammation
Infected wound
Old, traumatic wounds containnig dead tissue and wounds with evidence of clinical infection.
Types of wounds
Open and closed wounds
Open wounds are classified with what
…the objeect that caused the wounds
Types of Open wound
Incisions or incised wounds
Lacerations
Abrasions (Grazes)
Puncture wounds/Penetration wounds
Gunshot wounds
Incisions or incised wounds
These are wounds caused by a clean sharp object such as a knife
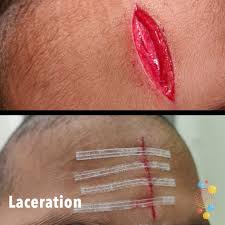
Lacerations
an irregular wound caused by a blunt impact to soft tissue that lies over hard tissue
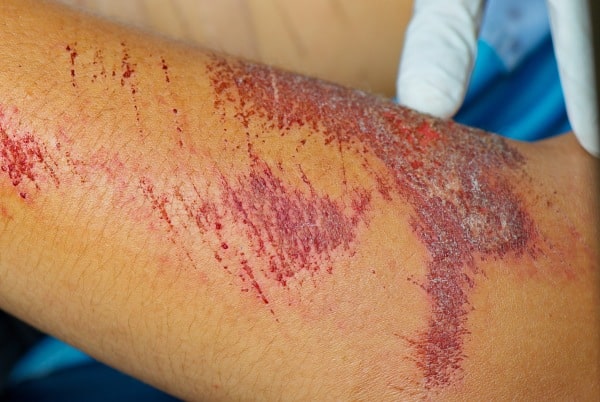
Abrasion (grazes)
A superficial wound in which the topmost layer of the skin (epidermis) is scraped off
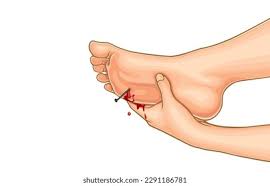
Puncture wounds/ Penetration wounds
this wound is caused by a pointed object entering the body
Gunshot wound
this is the wound caused by a bullet or projectile driving into or through the body
Types of closed wounds
Contrusions (Bruises)
Haematomas (Blood Tumors)
Crushing injuries
Contrusions
This wound is caused by a blunt force that damages the tissue under the skin
Haematomas (Blood Tumors)
This wound is caused by a damage to a blood vessel that causes blood to collect under the skin
Crushing injuries
This wound is caused by a great amount of force applied over a long period of time
Wound Healing
This is a dynamic process that leads to the restoration of a tissue’s integrity and function
Phases of wound healing
Inflammatory Phase
Proliferative Phase
Maturation Phase
Inflammatory Phase
This occurs when damage on the endothelial cells causes a release of cytokines that increase the expression of integrands in circulating lymphocytes
This phase controls bleeding and prevents infection
Function of Histamine, serotonin and kinins
Causes vasoconstriction, decreases blood loss and act as chemotactic factors for neurophils
Neurophils
These are cells that travel to the site of an infection to quickly destroy invading bacteria or pathogens.
They also remove cellular debris
Poliferative Phase
In this phase, fibroblasts migrate into the wound and secrete collagen type III
Angiogenesis occurs by 48 hours.
This lasts for about 3 weeks.
Maturation phase
In this phase, collagen III is converted to collagen I. This stage lasts for 9-12 months
Acute wound
this is a wound that goes thorugh an orderly and timely reparative process that results in the restoration of an anatomic function
Chronic wound
this is a wound that has faile to go through the orderly process of wound healing. The healing process is prolonged and incomplete with a lack of complete restoration of integrity
Factors that affect wound healing (DIDNT HEAL)
Diabetes
Infections
Drugs
Nutritional problems
Tissue necrosis
Hypoxia
excessive tension on wound edges
Another wound
Low temperature
Hypoxia
inadequate tissue oxygenation due to local vasoconstriction
What nutrient deficiencies affect wound healing
Vitamin A, C and Zinc
How does Diabetes affect wound healing
it slows down wound healing because high blood sugar levels damage blood vessels, reducing blood flow to the wound. This means less oxygen and nutrients reach the wound, making it harder for the body to repair itself.
Tissue Necrosis
This is tissue death, and it causes when there is too little of blood to the tissue
Common Chronic Wounds
Diabetic Ulcers
Decubitus Ulcers/ Pressue sore/ bed sore
Ischemia
a condition that results to a reduction in the flow of blood to a part of the body due to blood vessel blockage
The common cause of foot and leg amputation
Diabetic ulcers
Decubitus Ulcers/ Pressue ulcer/ Bed sore
This is a type of wound that results in a prolonged pressue on the skin leading to ischemia
what indicates deep tissue injury
Bruises
Stages of Pressure Ulcer
Non-blanchable erythema
Partial thickness
Full thickness skin loss
Full thickness tissue loss
Full Thickness Skin Loss
Subcutaneous fat may be visible
Tendon and or muscles are not exposed
Slough may be present
Full thickness tissue loss
slough may be present
Bone, tendon or muscle maybe exposed
This stage may go so deeep that it may cause osteomyelitis or osteitis
Bone or muscle may be directly palpable
In what areas can stage 3 of pressure ulcer be shallow
Areas of the body without a lot of adipose tissue like the bridge of the nose.
the tendons and bone are not visible in what stages of pressure ulcer
Stage 1 and stage 2
Inverse pressure Relationship
Low pressure over a very long time is more damaging than high pressure over a short time.
Prevention of Pressure Ulcers
understanding the etiologial factors
Shear
Nutritional Status
Impaired mental status
Diabetes
Wound Management
reduce or eliminate the causative factor
Identify and eliminate infections
Absorb excessive exudate
Protect healing wound
Functions of Blood
Carries oxygen and carbon dioxide to and from and cells
Carries nutrients
carries hormones
Removes wastes
Arteries
Carries blood away from the heart
Veins
Carries blood to the heart
Capillaries
this is where gas, nutrients and waste exchange takes place
Types of Bleeding
Internal bleeding and External bleeding
Signs of Internal Bleeding
Pain and ternderness
Vomiting blood
Broken ribs
Brusies on the neck and chest
Bllod in urine
Types of External Bleeding
Arterial Bleeding
Venous Bleeding
Capillary Bleeding
Ways to control external bleeding
Use of a tourniquet
ELevation
Application of pressure
Pressure points
When not to use the elvation method
when there are possible fractures
Spinal injury
Endothelial Cells
forms a single cell layer on blood vessels that facilitatae the exchange of materials between the bloodstream and the surrounding tissues
Cytokines
These molecules control the activity and growth of the immune system