COMSCI2101 _OS - M1
1/24
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
25 Terms
Operating System
It is a group of programs that allow a user to control and communicate with a computer.
Operating System
It manages the hardware, software, memory, and processes of the computer.
Operating System
It is the most important software that runs on a computer.
Normally, a number of computer programs operate concurrently, requiring access to the computer's processor (CPU), memory, and storage.
Hardware and Software
Computer System is composed of….
Software
In which part of the computer system is the OS categorized?
Operating System
It manages all hardware and software which controls every file, device, section of main memory and nanosecond of processing time. It is also the central controller in a computer.
• Microsoft Windows
• macOS
• Linux
• Android
• iOS
Commonly used Operating Systems
1. Memory Manager
2. Processor Manager
3. Device Manager
4. File Manager
5. Network Manager
Operating System Managers (5 Essential Managers of OS)
Manager Tasks
• Monitor its resources continuously.
• Enforce the system policies that determines who gets what, when, and how.
• Allocate and Deallocate the resource when appropriate.
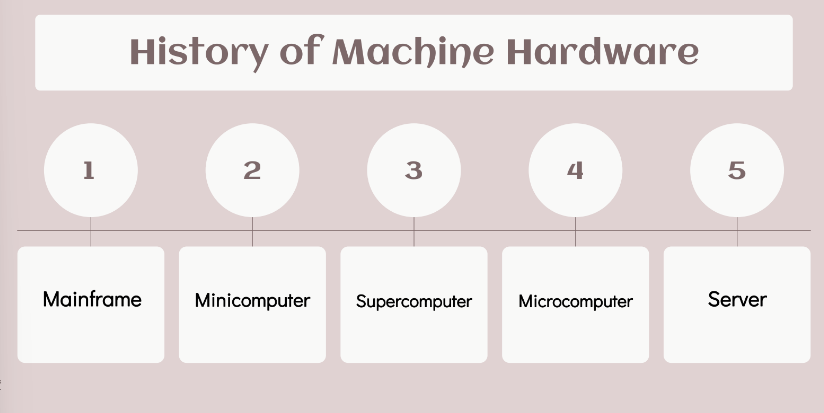
Identify the History of Machine Hardware in order.
Mainframe
• A large machine in size with high internal memory capacity.
IBM 360 (1964)
A classic example of an early mainframe
IBM 360 model 30
• Required an air-conditioned room about 18 feet square.
• The CPU was 5 feet high and 6 feet wide.
• Internal memory of 64k.
• $200,000 in 1964 dollars.
MINI Computer
• Developed to meet the needs of smaller institutions
MINI Computer
Compared to mainframe, it is smaller in size and memory capacity and cheaper.
Minicomputers
a.k.a. midrange computers
SUPER Computer
• Massive machine that handles massive computations
• It was developed primarily for government applications
• For military operations and weather forecasting
SUPER Computer
Cray supercomputer is an example of this computer.
- 6 to 1,000 processors
- Performs up to 2.4 trillion floating-point
operations per second (2.4 teraflops)
Uses:
- Scientific research
- Customer support or product development
MICRO Computer
Developed for single users in the late 1970s.
Physical size was smaller that the mini
Workstations
• Most powerful microcomputers
• Developed for commercial, educational, and government enterprises
• Networked together
Workstations
• Support engineering and technical users
- Massive mathematical computations
- Computer – aided design (CAD)
- Applications
Servers
These powerful computers provide specialized services to other
computers on client/server networks. Such computers perform critical network tasks.
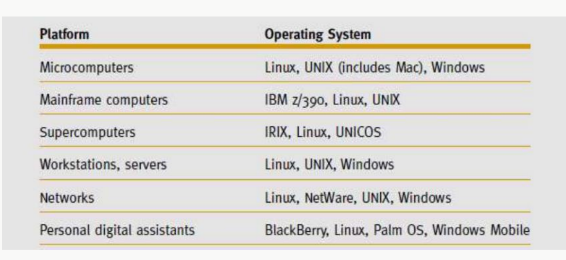
OS in different platforms