PCL Exam 1
1/70
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
71 Terms
Steps to Draft a Presentation
-Define your audience and purpose.
-Outline your main points.
-Develop your content with supporting. details.
-Design your slides for clarity and engagement.
Tips for Effective Presentations (design tips)
-Use bullet points for clarity.
-Include visuals. (charts, images)
-Keep text concise.
-Visual appeal & readability.
Tips for Effective Presentations (delivery tips)
-Practice your presentation
-Engage with your audience.
-Use clear and conf ident speech.
-Appropriate talking speed & seamless transitions.
Visual aid tools considerations
-Ease of use / familiarity.
-System capabilities where presenting.
-Your access.
-Collaboration.
-Features(templates, design tools)
Importance of Reliable Drug Information
-Ensure accurate and safe in formation is presented.
-Learn about something new or stay updated with current guideline.
Drug information key resources
-Online databases (UpToDate, Lexidrug, NatMed, PharmacyLibrary.)
- Primary literature (clinical trials, research articles)
-Drug labeling (FDA , package insert)
-Manufacturer website (healthcare resources, anticipate patient questions)
Steps for utilizing Drug Information
-Identify the information needed.
-Choose the appropriate resource(s).
-Evaluate the credibility of the source.
-Apply the information to your presentation and audience
Importance of Citations
-Avoid plagiarism.
-Give credit to original authors.
-Allow readers to verify sources.
-Enhance the credibility of your work.
There are two options if you are doing a presentation for a Ferris COP class for citations
-Rule 1a: Superscript Numbering Using Handout's Numbering.
-Rule 1b: Placing References at bottom of slide.
Steps to Create Citations
-Identify the source type. (book, article, website, etc.)
-Gather necessary information. (author, title, publication date, etc.)
-Format according to the chosen citation style. (CitingResources Guide)
What is the best drug information resource to learn about an herbal supplement?
NatMed
What resource should be used for citations for presentations done within the College?
College of Pharmacy Citing Resources Guide
Pharmacist Patient Care Process (PPCP)

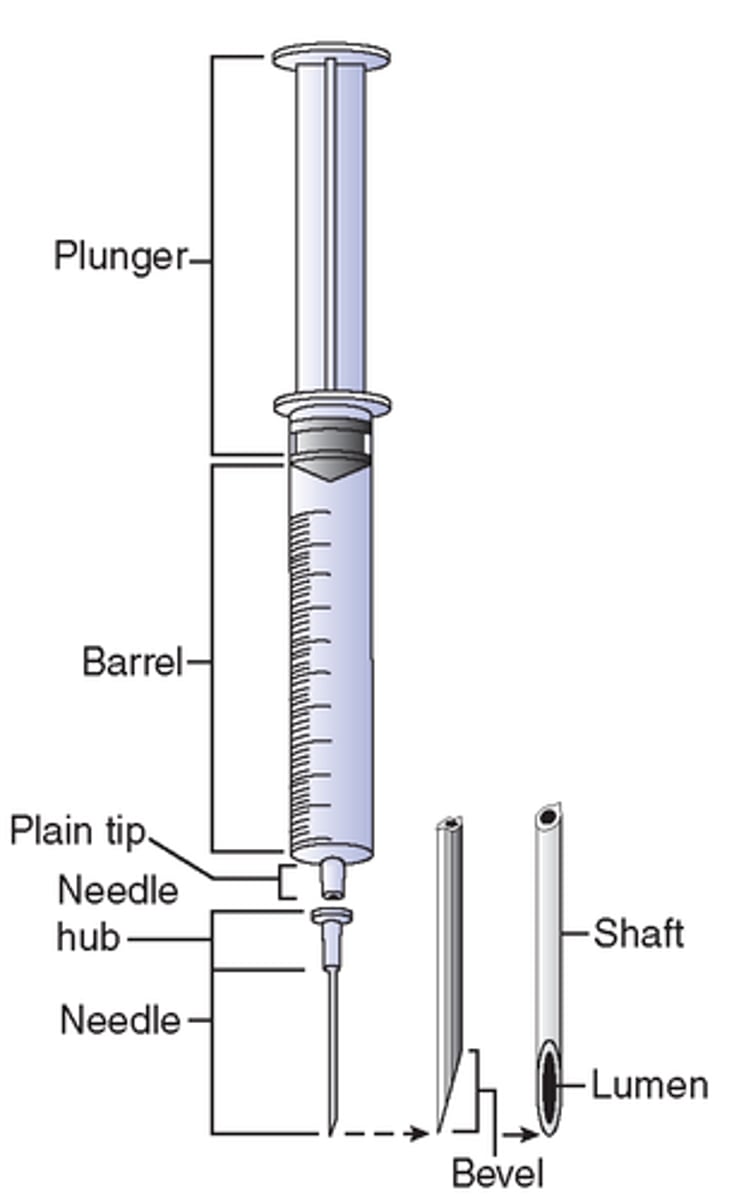
needle parts
Personal Protective Equipment (PPE)
-Shoe covers
-Beard cover
-Hair cover
-Jacket/Gown
-Gloves
--Sterile
--powder-free
If air added exceeds volume of solution withdrawn
positive pressure is created
If amount of air removed exceeds volume of solution is removed
negative pressure within the vial will result.
When does "Proper Use" start?
When the decision is made to obtain the medication.
When does it end?
When the effects of the medication are no longer felt.
How do we ensure proper use?
-Policies and Procedures, Pharmacy and Therapeutics Committee.
-Tertiary Literature: LexiComp, Micromedex, Sanford Guide, Trissel's,USP 7978, CDC, ACCP, JNC 89, ASHP etc.
-Secondary Literature: PubMed, MedWatch.
-Primary Literature: Clinical Trials.
-Education (patients, nurses, physicians, administrators).
-Technology (drug interaction screener, eMAR, dispensing cabinets, barcodes)
-Document, Document, Document.
-Audits (nurses, physicians, staff)
-Accreditation (Joint Commission, HFAP, CMS)
-Law (FDA, DEA, Federal Law, State Law, State Board of Pharmacy)
what is proper use
-Clinically appropriate.
-Administered correctly.
-cost effective
stored correctly
-sterile
-employee risk is managed
-Emergency Preparedness
What is a medication?
-a compound or preparation used for the treatment or prevention of disease, especially a drug or drugs taken by mouth.
-IV fluids, saline flushes, patient medications brought from home, EMS stock, clinic stock.
State Board of Pharmacy
-Responsible for licensing pharmacies, pharmacists, pharmacy technicians and wholesalers.
-Can perform an unannounced inspection of a pharmacy during normal business hours.
-May work with other governing bodies.
--DEA: in the case of drug diversion
--Joint commission: In the case of sterile compounding
Michigan's state board of Pharmacy consists of...
6 pharmacists
1 pharmacy technician
4 public members
State Law
-Often developed with input from the Board of Pharmacy.
-Allows for criminal prosecution (fines, incarceration)
-Applies to all healthcare professionals
Federal Law
-Allows for criminal prosecution.
-Applies to all healthcare professionals.
-Grants authority to federal governing bodies. (FDA,CMS)
-Can conduct inspections.
Centers for Medicare and MedicaidServices (CMS)
-Responsible for the administration of Medicare and Medicaid. 1 in 3 Americans receive services.
-Hospitals must be compliant with CMS standards or CMS will not recognize themas a provider.
-Establishes increased reimbursement for high performing health systems.
-Uses the Hospital Consumer Assessment of Healthcare Providers and Systems(HCAHPS) surveys for comparisons of health care systems.
-Uses Diagnosis Related Groups (DRGs) for payment.
-Will not pay for a readmission within 30 days
HCAHPS
-Surveys sent to patients to assess the patient's perception of care.
-Data provided by the health systems.
--Rate of post-op infections, rate of all cause mortality, etc.
--Key markers of quality. (ejection fraction being assessed on CHF patients)
--Data requested change periodically.
Accredits health care systems on behalf of CMS and other third party payers
-The Joint Commission.
-Healthcare Facilities Accreditation Program (HFAP)
-Facilities can choose one or both accrediting bodies.
The Joint Commission
-Accredits about 80% of hospitals nationwide.
-Also accredits other health systems.
-Conducts site surveys every 3 years or more frequently if necessary.
-Considered very stringent.
HFAP
-Accredits the remaining 20% of hospitals.
-Mainly accredits hospitals and surgical centers.
-Conducts site surveys every 3 years or more frequently as necessary.
-Considered less stringent.
Pharmacy and Therapeutics Committee (P&T)
-Manages the formulary of the health system.
-Comprised of pharmacists, physicians, nurses, administrators, quality-improvement managers and other health care staff.
-Is a subgroup of the medical staff and is chaired by a physician.
-Collaborate to
--Implement cost-effective prescribing practices.
--Assess clinical outcomes.
--Provide education
--Create administrative programs to promote evidence-based prescribing.
MEDDRUN
-State owned resource.
-Caches called MedPacks that contain medications and medical supplies.
-Designed to be used in case of exposure to cyanide, nerve agents, pesticides, toxic industrial chemicals, radiation, biological hazards .(anthrax, plague)
CHEMPACK
-federally owned resource
-contains nerve agent antidotes and anticonvulsants
340B
-Government program that requires drug manufactures to provide eligible healthcare organizations medications at a reduced cost.
-Only applies to outpatients
-Eligibility is assessed every 3 months based on income status of patients served.
P&T Functions
-determine formulary.
-decide who can prescribe specific medication.
-approve policies and procedures regarding medication use.
-what to do about drug shortages.
-complete quality assurance activities.
-monitor adverse reaction/medication errors.
-Create education regarding medication. use.
Types of P&T
-Single P&T
--Reasonable for standalone or small institutions.
-System P&T
--Oversight, structure, and manage formulary options.
--Works with local P&Ts to refine and implement formulary.
--Requires alignment, buy in and communication between system and local committees.
-Subcommittees
--Infectious disease, oncology, pediatrics, critical care, surgery, etc.
Pharmacy Benefit Manager (PBM)
-Third party administrator of prescription drug programs for health plans.
-Hired to process and pay prescription drug claims and are responsible for. creating and updating a health plan's formulary.
-Can get the best rebates, prices by negotiating with drug companies and payers.
Pharmacy's role on P&T
-Creating monographs.
-Evaluating medications on formulary for adoption or deletion.
-Quality assurance programs.
-Preparing education for those impacted by P&T decisions.
-Tracking new FDA approvals, dosage forms and shortages.
-Tracking medication usage.
-Accreditation requires annual review of all medications.
Drug Formularies (P&T)
-Most efficacious, safe and cost effective with fewest side effects or drug interactions.
-Consider a variety of dosage forms, strengths, ease of preparation, storage, and cost.
-Typically, 2-3 drugs within a class will be available.
Drug Formularies goal (P&T)
Selection of medication necessary for treatment of all disease states likely to be seen in that institution.
Types of Formulary
-Open: All drugs on market on formulary (think Community Pharmacy)
-Closed: Limited drugs available.
--Positive: Start with blank sheet and add drugs to formulary.
--Negative: Start with stock or current list and remove drugs.
expiration date
-Assigned by the manufacturer
-Determined using extensive analytical testing
beyond use date
-Assigned by a pharmacist.
-Determined based on available scientific evidence or per manufacturer recommendations.
Determining BUD
-Must consider both Sterility and Stability data.
--The lesser of the 2 BUDs above is the BUD assigned.
-USP Chapter <797> provides guidance on determining BUD regarding Sterility.
Chemical Stability BUD is often extrapolated based on
-Direct testing or literature.
-Manufacturer information.
-Theoretical predictions.
Risk Levels (Sterility)
-USP 797 2022 defines three risk categories based on probability of contamination
-Category 1, Category 2, and Category 3
Category 1
-located in an unclassified space known as segregated compounding area
-12 hours at room temperature
-24 hours refrigerated
Category 2
-located in an ISO 7 buffer room with an ISO 8 ante room (ante room must be ISO 7 for hazardous meds.
-prepared from sterile ingredients, not terminally sterilized.
-4 days at room temperature.
-10 days in the refrigerator.
-45 days in the freezer
Category 3
-This category has enhanced cleaning, monitoring requirements and preparations must undergo sterility and endotoxin testing
-60 days at room temperature.
-90 days in refrigerator
-120 days in the freezer
BUD exceptions (Sterility)
-Proprietary Bag and VialSystems (addEASE, ADD-Vantage, Mini Bag Plus)
=If CSP is prepared from nonsterile ingredients shorter BUDs must be assigned.
-If end product testing is performed BUD's can be extended.
Types of Stability
chemical, physical, microbiological, therapeutic, toxicological
Factors Influencing Stability
-concentration of medication
-packaging
-exposure to light
-temperature
-medication delivery devices
Elements of the Medical Record
-Consent.
-Orders.
-Notes.
-Nurse Notes.
-Lab.
-Flow Charts.
-Care Plans.
-Consults.
-Discharge.
-Medication Administration Record.
Consent
-Patient's consent to be treated.
-Very little importance to pharmacy except in the case of patients who may refuse certain types of treatment.
Orders
-Very important to pharmacy.
-Everything in the hospital requires an order.
-Arranged in reverse chronological order. (newest orders are first)
-Orders must have appropriate documentation(notes) to support them.
Notes
-Nearly all clinical documentation resides here.
-Used by nearly all providers (except nurses and specialists)
-Provides reasoning to support orders.
-Provides documentation to support billing.
-Physicians use a standard physician note format.
Components of a Physician's Note
-Medical history (H&P)
-Laboratory test results and diagnostic testing results.
-Problem list.
-Plan.
Nurses Notes
-Nurse's area for documentation.
-Very detailed.
-Can contain bedside lab testing (ie blood glucose)
-Great resource for up-to-date vitals.
-Great resource for in-depth information about the patient.
Lab
-Contains all chemistry and culture data.
-Also organized in reverse chronological order.
-Labs and cultures should be reviewed daily by the pharmacist.
Flow Charts
Graphical representation of labs and/or vitals
Care Plans
-Detailed information about nurse's plans to care for patient during and after the hospital stay.
-Resource for understanding heath literacy and barriers to care.
Consults
-Specialist physician's clinical documentation.
-Sometimes specialists will also chart in notes section.
Discharge
-All materials related to discharge.
-All discharge medication lists and instructions should be. constructed or at the very least reviewed by a pharmacist.
Medication Administration Record (MAR)
-Usually resides with the nurse taking care of patient, not in the patient chart.
-Contains documentation regarding doses given or not given.
-Generated daily by the pharmacy department.
Electronic medical record systems
-Computerized Physician Oder entry (CPOE), eMAR (ElectronicMedication Administration Record).
-Electronic filing of data.
-Some data may still be in paper format.
Paper-based records
-Should offer the same data as the electronic medical record.
-May be used in tandem with electronic systems.
Systematic Approach to Data Collection benefits
-Consistency.
-Systematic evaluation of drug-related problems.
-Smooth transition of care between pharmacists.
-Useful resource during patient care rounds.
Developing a Problem List includes
-Disease states
-Drug-related problems
-Preventive measures
Drug-Related Problems (DRPs)
-Events or issues surrounding drug therapy that actually or potentially interfere with a patient's ability to receive an optimal outcome.
-At least 7 DRPs have been described in the published literature.
Seven DRPs
-Indication lacking drug ie. Pt with an infection who is not on an antibiotic
-Indication with incorrect drug.
-Wrong dosage.
-Inappropriately receiving drug.
-Adverse reaction to a drug.
-Drug interaction.
-Drug lacking indication