Microbiology All Labs (1-6)
1/164
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Microbiology flashcards practice, Goodluck ★ =)
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
165 Terms

Safety Shower

Eyewash station

Eyewash station

Pipette aid
Automatic pipette

Examination gloves (non-sterile)
- Before touching broken skin, mucous membranes, blood or other body fluids, or soiled instruments
- Before touching contaminated waste material
- Before performing invasive procedures
- After each patient appointment, remove gloves and perform hand hygiene.
- Replace with a new pair of gloves before examining the next patient or any time a tear or hole is apparent

Surgical gloves
- Sterile gloves are used during surgical procedures
- the skin remains exclusively in contact with the inner surface of the gloves & never touch the outer surfaces with your skin

Surgical mask
- Examining a patient on droplet isolation i.e., respiratory infection.
- To protect oral & nasal mucosa from splashes of blood or saliva
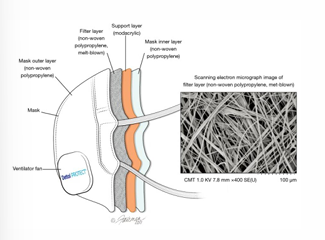
Filtering facepiece (FFP) respirators
Are to be worn to treat patients with severe respiratory infections transmitted by small nuclei and can pass through the surgical mask e.g., COVID19, TB, measles

FFP2= N95 respirator
Aerosol filtration percentage: not less than 94%

FFP3= N99 respirator
Aerosol filtration percentage: not less than 99%
The FFP3 mask is the most filtering of the FFP masks!

what is this equipment called
face shield
face shields are used to avoid splashing of blood and saliva.

Safety goggles
Safety goggles or face shields are used to avoid splashing of blood and saliva.
All protective eyewear must be decontaminated & dried after each use.

Scrub Suit
- Worn to enter patient’s treatment area.
- Changed daily or more often, if visibly soiled.
- Not to be worn outside the clinic area
Surgical Gown
- Must be worn to enter operation theatre or patient’s treatment area.
- Not to be worn outside the clinic area.
Impermeable Surgical Gown
- Waterproof (rubber or plastic).
- When large blood spill is anticipated or in surgical procedures.

Standard Laboratory Practices
Decontamination
(cleaning, disinfection & sterilization)
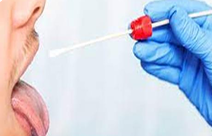
Proper Selection of specimen
- Collect specimens from the actual infection site, during the acute phase of infection
- Collect enough specimen.
- Collect specimen before starting antibiotic therapy, whenever possible

Proper Collection of specimen
- Use sterile collection devices & containers.
- Number of specimens needed for the best chance of recovery of the causative microorganisms (for example, 3 successive morning sputum samples for TB)
- Pus specimen is always superior to a swab
- Label specimens appropriately.
Should be handled with care
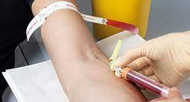
Samples are collected by various methods:
Aspiration
pus, blood for blood culture

Samples are collected by various methods:
Swabbing
throat swab
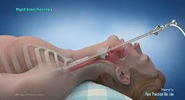
Samples are collected by various methods:
Endoscopic specimen
bronchoalveolar lavage, gastric biopsy
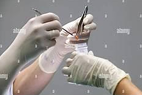
Samples are collected by various methods:
Surgical specimens

Are these suitable for microbiological applications?
Nope, Cotton swab with wood shafts are not suitable for microbiological collection applications

Rayon swabs
Rayon swabs with plastic shafts are preferred in microbiological collection applications

Flocked swabs
suitable in microbiological collection applications, pick up more sample and are designed to release more of the sample during processing

Blood Culture Bottles
Two sets of cultures from 2 separate sites before starting antibiotics are ideal & 3 sets of blood cultures have a 96% sensitivity in detecting bacteremia.

Blood Culture Bottles
Two sets of cultures from 2 separate sites before starting antibiotics are ideal & 3 sets of blood cultures have a 96% sensitivity in detecting bacteremia.
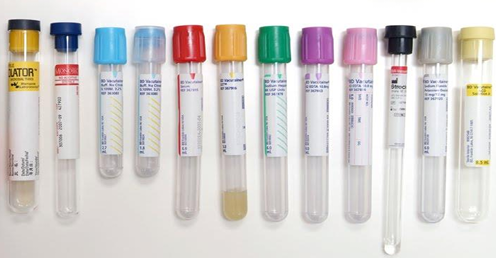
Blood Collection tubes

Microbiology Containers
Containers used for microbiological investigations should be
Sterile, Leak-proof
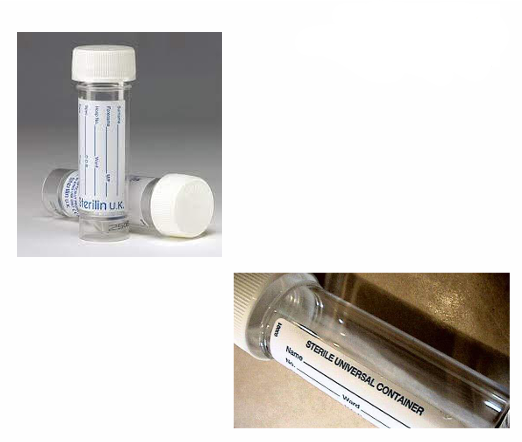

Sterile Universal Container for Specimen Collection

Sample type?
Sputum Sample
(better morning sputum sample: the most concentrated)
Sputum sample is obtained by coughing and is examined in the laboratory
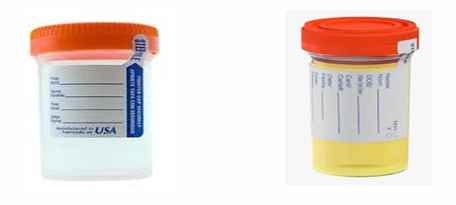
Sample type?
Urine Sample
(better morning urine sample)
the first urine passed by the patient at the beginning of the day should be sent for examination. This specimen is the most concentrated, therefore the most suitable for culture, microscopy, and biochemical analysis.
What method of COLLECTION & TRANSPORT OF URINE is this?
Clean-Catch Midstream Urine
Sterile, dry, wide-necked, leakproof container
Instructions for patients: • Wash hands. • Cleanse the area around the urethral opening with clean water • Dry the area with a sterile gauze pad • Collect the urine (middle of the urine flow

What method of COLLECTION & TRANSPORT OF URINE is this?
Urine Sample from Catheter
Urine is aspirated with a sterile needle& syringe from the aspiration port of the catheter, NOT FROM THE URINE COLLECTION BAG.
What method of COLLECTION & TRANSPORT OF URINE is this?
Sterile Urine Collection Bag (Pediatric Urine Collector)
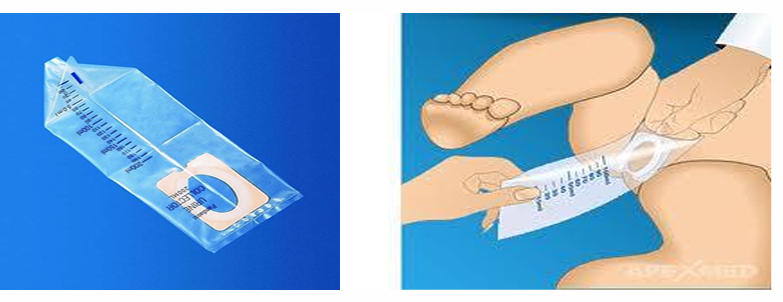
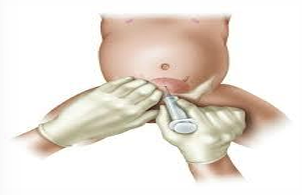
What method of COLLECTION & TRANSPORT OF URINE is this?
Suprapubic aspiration of urine
is a simple technique for obtaining an uncontaminated specimen of urine in children

Container for what?
Stool Sample Container
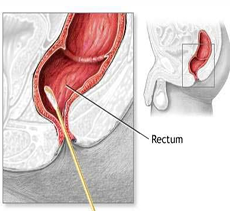
Rectal Swab
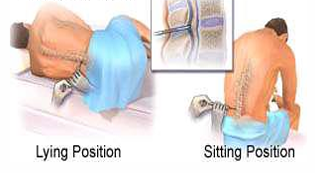
Cerebrospinal Fluid (CSF) Collection by Lumbar Puncture Technique
The collection of CSF is an invasive technique and should be performed by an experienced personnel (Only physician) under strict aseptic conditions
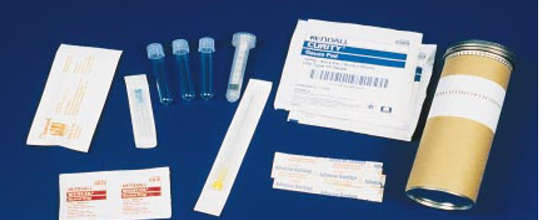
CSF Collection Kit
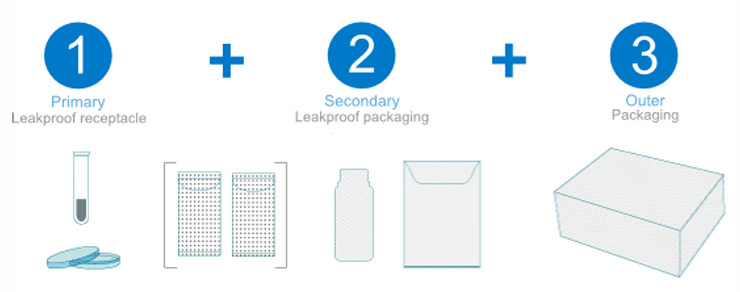
Triple Containment Packaging for Specimen transport
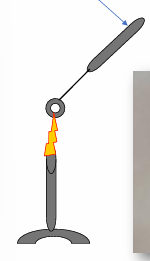
Smear preparation:
Bacterial Loop

Smear preparation:
Red Heat
Bacteriological loops, wires & forceps tips are sterilized by holding them in the flame until they are red hot
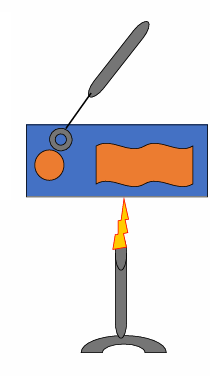
Smear preparation:
Fixation
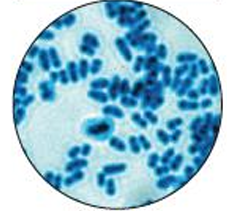
Simple stain:
Methylene blue
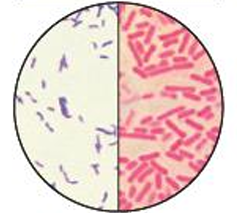
Differential stains:
Gram Stain
purple = gram +ve
pink = gram -ve
Differential stains:
Acid-fast Stain:
Red = Acid-fast
Blue = Non-Acid fast
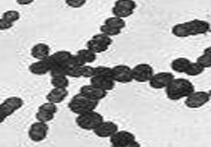
What Bacterial Morphology?
Cocci
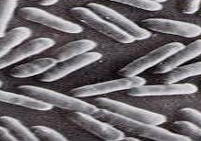
What Bacterial Morphology?
Bacilli
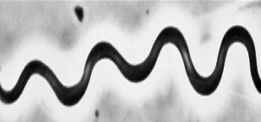
What Bacterial Morphology?
Spiral
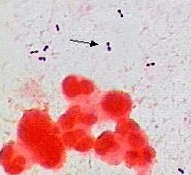
What Bacterial Arrangement?
Cocci Pairs
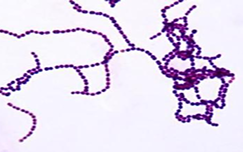
What Bacterial Arrangement?
Cocci Chains
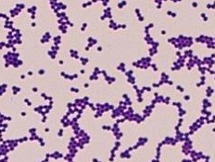
What Bacterial Arrangement?
Cocci Clusters (groups)
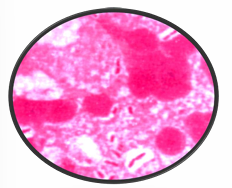
What Bacterial Arrangement?
Bacilli Pairs
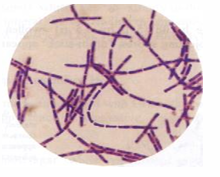
What Bacterial Arrangement?
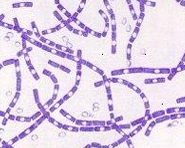
Bacilli Chains
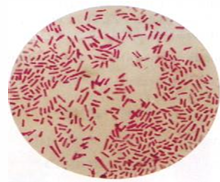
What Bacterial Arrangement?
Bacilli - No special arrangement
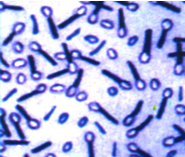
Bacterial Spores that appear unstained by Gram’s stain
Bacterial Spores that appear unstained by Gram’s stain
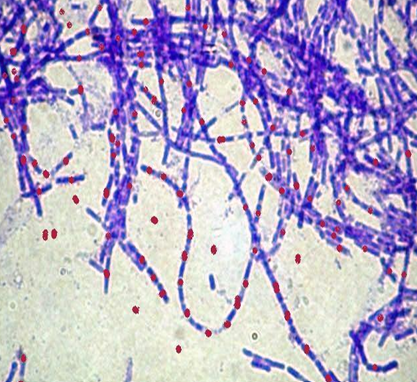
Bacterial Spores that appear stained by Spore Stain
Bacterial Capsule that appear unstained Halo by Gram’s Stain
Bacterial Capsule that appear unstained Halo by Gram’s Stain
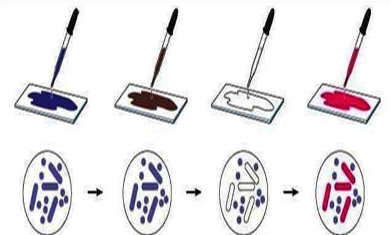
Gram Staining Technique
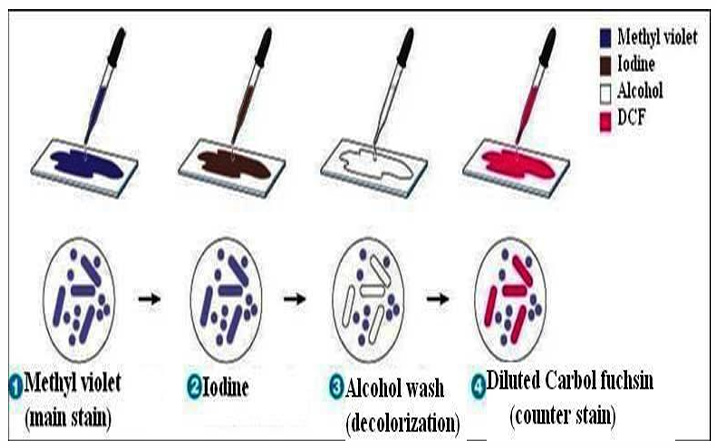
Important:
Differential Staining: What’s Gram’s stain
heating requirement?
In Gram staining, heating is required for fixation, not for staining itself.
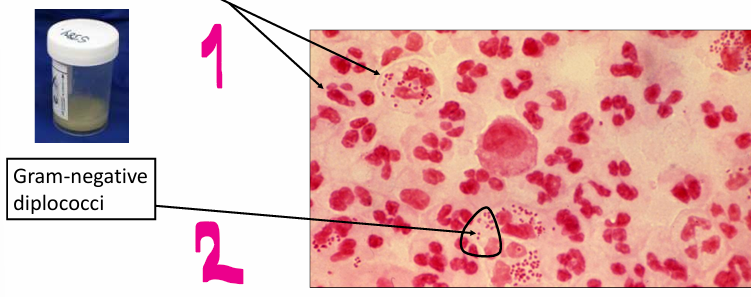
Direct or indirect method of staining?
Direct
from the specimen itself
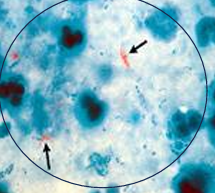
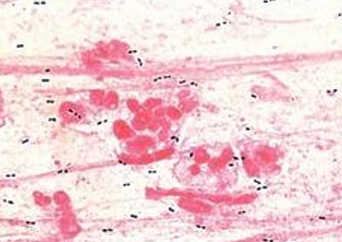
picture note:
1 - Pus cells
2- Gram negative diplococci
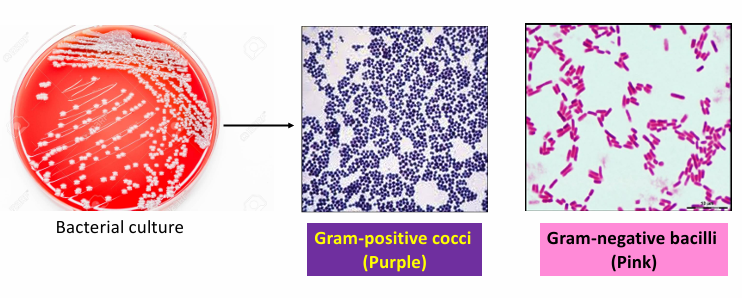
Direct or indirect method of staining?
Indirect
from bacterial Culture
Microscope?
Light source?
Stain?
Microscope: Fluorescent (UV)
Light source: Ultraviolet rays
Stain: Fluorescent stain
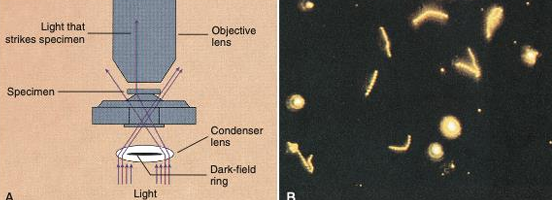
Microscope?
Detects what?
Organism example?
Microscope: Dark Field Micro
Detects what: detection of certain motile organisms directly in patient specimens
Organism example: spirochetes (appear bright, motile with corkscrew movement against a dark background)
Spirochetes cannot be seen by light microscopy because of their thin dimensions & are difficult to grow in culture.

Microscope?
Types of this Microscope?
Magnification power?
Detects what?
Microscope: Electron Microscope
Types of this Microscope: SEM and TEM
Magnification power: more than 100,000X up to 2,000,000X
Detection: of Viruses and intracellular organelles
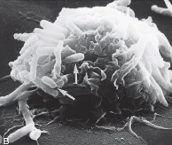
SEM of E. coli interacting with the surface of a human mast cell
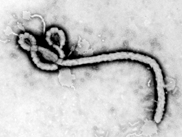
TEM of Ebola virus

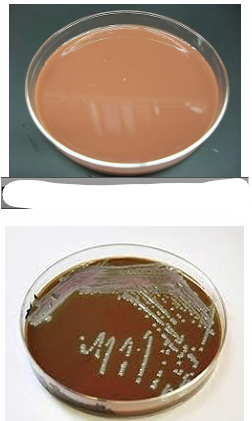
What physical nature of culture media is this? is it Turbid or Clear?
Turbid fluid culture media (= bacterial growth)

What physical nature of culture media is this? is it Turbid or Clear?
Clear fluid culture media (= No bacterial growth)
Disadvantages of Liquid fluid media?
- Cannot be used for bacterial identification.
- Allow growth of bacteria in mixture
Uses for Liquid fluid culture media?
•Bacterial cultivation (Peptone water - Nutrient broth)
•Biochemical reactions (e.g., sugar media)
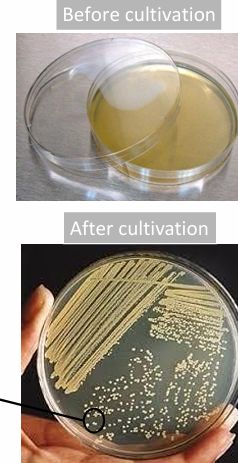
What physical nature of culture media is this?
Solid culture media
Bacterial growth appears in the form of colonies
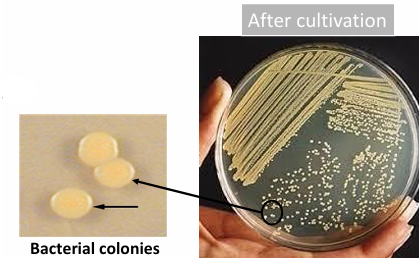
Uses for Solid culture media?
• Isolation and identification of bacteria
• Antimicrobial sensitivity testing

What type of Culture media is this?
What’s it’s name?
Basal (simple) media:
Name: Peptone Water
•Support growth of most non-fastidious organisms (= bacteria which do not have high nutritional requirements).

What type of Culture media is this?
What’s it’s name?
Basal (simple) media:
Name: Nutrient Broth
•Support growth of most non-fastidious organisms (= bacteria which do not have high nutritional requirements).

What type of Culture media is this?
What’s it’s name?
Basal (simple) media:
Name: Nutrient Agar slope
•Support growth of most non-fastidious organisms (= bacteria which do not have high nutritional requirements).

What type of Culture media is this?
What’s it’s name?
Basal (simple) media:
Name: Nutrient Agar plate
•Support growth of most non-fastidious organisms (= bacteria which do not have high nutritional requirements).
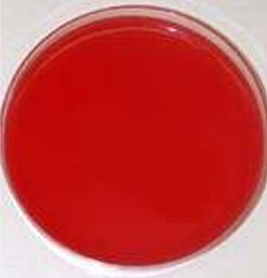
What type of Culture media is this?
What’s it’s name?
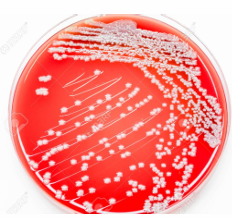
Enriched media:
Name: Blood agar
• Enhance growth of fastidious nutritional requirements). organisms (= bacteria which have high
• In addition to the basal media components, they contain highly nutritive substances as blood, serum or eggs, required for the growth of specific organisms
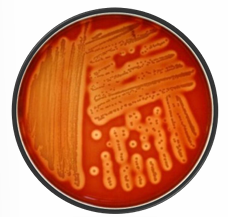
Hemolysis Type?
Beta-Hemolysis
Complete lysis of RBCs producing clear zones around bacterial colonies (due to hemolysin toxin)
Hemolysis Type?
Alpha-Hemolysis
Reduction of RBCs hemoglobin into methemoglobin producing greenish discoloration
Hemolysis Type?
Gamma Hemolysis
no Hemolysis
What type of Culture media is this?
What’s it’s name?
Enriched media
Chocolate agar
Nutrient agar + 5-10% blood but after adding blood heat in water bath to 80ºC for 10 min.
•Uses: Culture of fastidious organisms

What type of Culture media is this?
What’s it’s name?
Enriched media
Loeffler ’s serum
uses: Culture of Corynebacterium diphtheriae

What type of Culture media is this?
What’s it’s name?
Selective media
Contains an inhibitory substance that selects for the growth of certain bacterial genera & inhibits others.
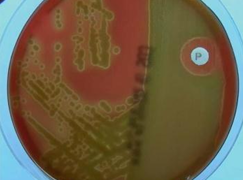
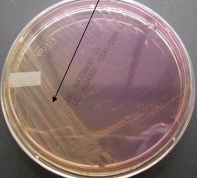
Name: Lowenstein Jensen (L-J) Medium (unioculated)
Composition: Nutrient agar + beaten eggs (to make it enriched) + malachite green (an added dye to make it selective for mycobacteria)
uses: Isolation of mycobacteria (TB)
What type of Culture media is this?
What’s it’s name?
composition?
uses?
Selective media
Contains an inhibitory substance that selects for the growth of certain bacterial genera & inhibits others.
Name: Lowenstein Jensen (L-J) Medium (Inoculated)
Composition: Nutrient agar + beaten eggs (to make it enriched) + malachite green (an added dye to make it selective for mycobacteria)
uses: Isolation of mycobacteria (TB)

What type of Culture media is this?
What’s it’s name?
Composition?
uses?
Differential media
Employ some factor that allows colonies of one bacterial type to exhibit certain metabolic or culture characteristics
Name: MacConkey’s agar
Composition: Peptone water + agar
Selective agent: crystal violet and bile salts inhibit Gram-positive and non-enteric Gram-negative organisms.
Differential agents: lactose + neutral red (pH indicator)
Uses: culture of enteric Gram-negative bacteria
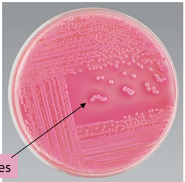
Lactose-fermenter bacteria, what type of media is it being cultivated on?
MacConkey’s agar
Non- Lactose-fermenter bacteria, what type of media is it being cultivated on?
MacConkey’s agar
What type of Culture media is this?
What’s it’s name?
Composition?
uses?
Differential media
Employ some factor that allows colonies of one bacterial type to exhibit certain metabolic or culture characteristics
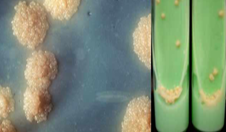
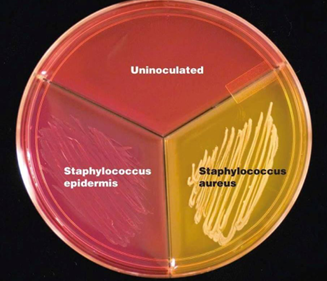
Name: Mannitol Salt Agar
Composition: Peptone water + agar
Selective agent: inhibits most Gram-negative and Gram-positive bacteria. It selects for growth of staphylococci (halotolerant).
Differential agents: mannitol + phenol red (pH indicator)
Uses: isolation of staphylococci (Stapylococcus aureus colonies appear yellow) due to mannitol fermentation
Other staphylococci produce pink colonies)

What type of Culture media is this?
What’s it’s name?
Composition?
uses?
Differential media
Employ some factor that allows colonies of one bacterial type to exhibit certain metabolic or culture characteristics
Name: Triple sugar iron (TSI) agar
Composition: H2S Indicator system; If the organism is hydrogen sulfide (H2S) producer, black color is produced.
Uses: Presumptive identification of Enterobacteriaceae based on fermentation of glucose, lactose, sucrose and the production of gas and H2S
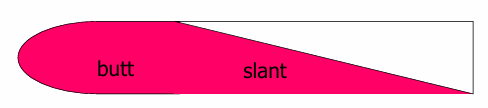

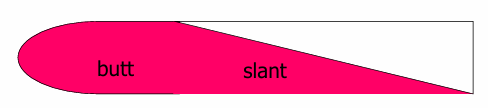
Test Type and Description?
Test type: TSI test (Triple sugar Iron)
Description: Uninoculated TSI or no sugar fermentation
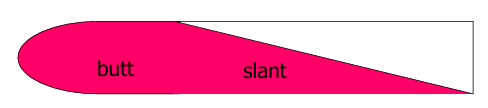
Red slant + Red Butt

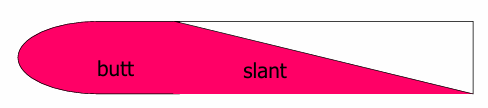
Test Type and Description?
Test type: TSI test (Triple sugar Iron)
Description: Glucose + Lactose/ Sucrose fermentation
Yellow slant + Yellow Butt

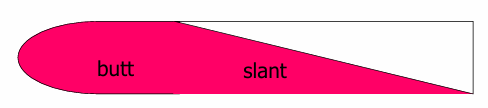
Test Type and Description?
Test type: TSI test (Triple sugar Iron)
Description: Only glucose fermentation
Red slant + Yellow Butt
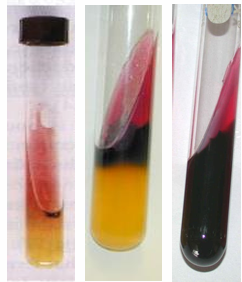
Test Type and Description?
Test type: TSI test (Triple sugar Iron)
Description: Only glucose fermentation + H2S production
Red slant + Yellow Butt + Black color
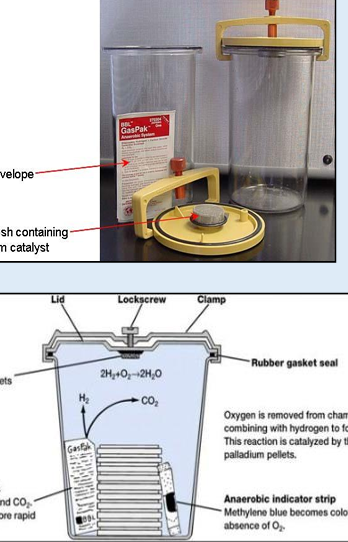
What type of Culture media is this?
What’s it’s name?
uses?
Culture: Anaerobic media
Name: Anaerobic GasPaksystem
Principle: removal of oxygen in the environment.
Uses: culture of strictly anaerobic bacteria
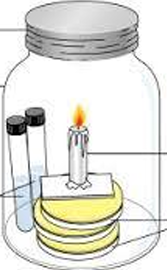
What type of Culture media is this?
What’s it’s name?
uses?
Culture: Anaerobic media
Name: Candle jar
Principle: removal of oxygen in the environment.
Uses: culture of strictly anaerobic bacteria