chem exam 2
1/61
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
62 Terms
Which property is not associated with an acid?
has a bitter taste
The conjugate acid of CO32- is HCO₃⁻
True
The conjugate base of H₂PO₄⁻ is H3PO4
false
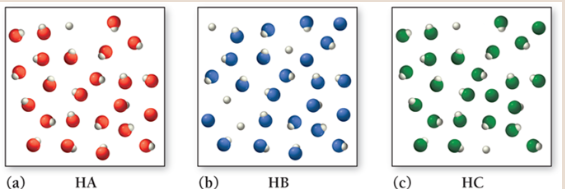
Consider the three generic weak acids HA, HB, and HC. The images shown here represent the ionization of each acid at room temperature. Which acid has the largest Ka?
HB
Consider the following acids and their dissociation constants,
H2SO3(aq) + H2O(l) ⇄ H3O+(aq) + HSO3−(aq) Ka=1.2×10−2
HS−(aq) + H2O(l) ⇄ H3O+(aq) + S2−(aq) Ka=1.3×10−19
Which is the stronger acid, H2SO3 or HS−?
H2SO3
Water is amphoteric because it can act as an acid and a base. True/False?
True
Calculate [OH−] at 25 °C for each solution and determine if the solution is acidic, basic, or neutral.
[H3O+] = 7.5 × 10−5 M
acidic
If a solution has a pH of 3, is it considered acidic, basic, or neutral?
acidic
If a solution has a pOH of 3, is it considered acidic, basic, or neutral?
basic
Find the pH of a 0.0010 M HCl solution.
3
Determine the pH of a 0.025 M sulfuric acid (H2SO4) solution.
1.3
Find the [H3O+] of a 0.100 M HCN solution. Ka of the acid is 4.9 x 10-10
7.0×10−6
Find the pH of a 0.0010 M NaOH solution.
11
Find the pH of a 0.225 M KOH solution.
13.35
Find the pH of a 0.100 M NH3 solution. Kb of the base is 1.76 x 10-5.
11.12
C₅H₅NH⁺
Classify this cation as a weak acid or pH-neutral
weak acid
Determine if the solution formed by below salt is acidic, basic, or neutral:
CH3NH3NO3
acidic
HNO3 has a greater acidity than HNO2. True/False?
true
Which of the following is an Arrhenius base?
KOH
Which of the following is a Br∅nsted-Lowry base?
H2O
What is the conjugate acid of H2PO4⁻?
H3PO4
Which of the following is NOT a conjugate acid-base pair?
NH4+/NH2-
Which of the following species is amphoteric?
HPO42-
Arrhenius acid
produce protons in aqueous solution
Arrhenius base
produce hydroxyl ions in aqueous solution
Bronsted-Lowry acid
proton donor
Bronsted-Lowry base
proton acceptor
Calculate the concentration of H3O⁺ in a solution that contains 2.5 × 10-5 M OH⁻ at 25°C. Identify the solution as acidic, basic or neutral.
4.0 × 10-10 M, basic
Which of the following acids is the strongest? The acid is followed by its Ka value.
HClO2, 1.1 × 10-2
What is the concentration of hydroxide ions in pure water at 30.0∘C, if Kw at this temperature is 1.69 × 10-14?
1.30 × 10-7 M
Give the characteristics of a strong acid.
has a large Ka value
ionizes completely in aqueous solutions
has equilibrium far to the right
has a weaker bond to hydrogen
all of the above
What is the Kw of pure water at 50.0°C, if the pH is 6.630?
5.50 × 10-14
Which of the following is a Br∅nsted-Lowry acid?
NH4+
What is the conjugate base of HPO42⁻ ?
PO43-
Which of the following solutions would have the highest pH? Assume that they are all 0.10 M in acid at 25∘C. The acid is followed by its Ka value.
HC6H5O, 1.3 × 10-10
Identify the products when hydrochloric acid completely ionizes in water.
H3O+ and Cl-
Identify the products that are in equilibrium with NH3 and H2O.
NH4+ and -OH
Which of the following statements is TRUE?
The conjugate base of a very weak acid is stronger than the conjugate base of a strong acid.
What is the pH of pure water at 40.0°C if the Kw at this temperature is 2.92 × 10-14?
6.767
Which of the following is TRUE?
An acidic solution has [H3O⁺] > [OH⁻].
What is the Kw of pure water at 50.0°C, if the pH is 6.630?
5.50 × 10-14
Calculate the hydronium ion concentration in an aqueous solution with a pH of 9.85 at 25°C.
1.4 × 10-10 M
Calculate the concentration of H3O⁺ in a solution that contains 1.8 × 10-5 M OH⁻ at 25°C. Identify the solution as acidic, basic, or neutral.
5.5 × 10-10 M, basic
Calculate the hydroxide ion concentration in an aqueous solution with a pH of 9.85 at 25°C.
7.1 × 10-5 M
Determine the pH of a 0.033 M HNO3 solution
1.48
Calculate the hydroxide ion concentration in an aqueous solution with a pOH of 8.85 at 25°C.
1.4 × 10-9 M
Calculate the pH of a solution that contains 7.8 × 10-6 M OH⁻ at 25°C.
8.89
Calculate the hydronium ion concentration in an aqueous solution with a pOH of 4.33 at 25°C.
2.1 × 10-10 M
Identify the strongest acid.
2.00 M HCl
Determine the [H3O+] concentration for a 0.200 M solution of HCl.
2.00 × 10-1 M
Find the percent ionization of a 0.337 M HF solution. The Ka for HF is 3.5 × 10-4.
3.2%
Determine the pH of a 0.461 M C6H5CO2H M solution if the Ka of C6H5CO2H is 6.5 × 10-5.
2.26
Determine the Ka of an acid whose 0.294 M solution has a pH of 2.80.
8.5 × 10-6
Place the following in order of increasing acid strength.
HBrO HBrO2 HBrO4 HBrO4
HBrO < HBrO2 < HBrO3 < HBrO4
A Lewis base
donates an electron pair
Determine the [H3O⁺] in a 0.265 M HClO solution. The Ka of HClO is 2.9 × 10-8.
8.8 × 10-5 M
Which of the following bases is the weakest? The base is followed by its Kb value.
C5H5N, 1.7 × 10-9
Which one of the following salts, when dissolved in water, produces the solution with the highest pH?
CaO
Which one of the following salts, when 1 mole is dissolved in water, produces the solution with a pH closest to 7.00?
KCl
Which of the following is a Lewis acid?
AlBr3
Which of the following is a Lewis base?
H2S
If the pKa of HCHO2 is 3.74 and the pH of an HCHO2/NaCHO2 solution is 3.00, which of the following is TRUE?
[HCHO2] > [NaCHO2]